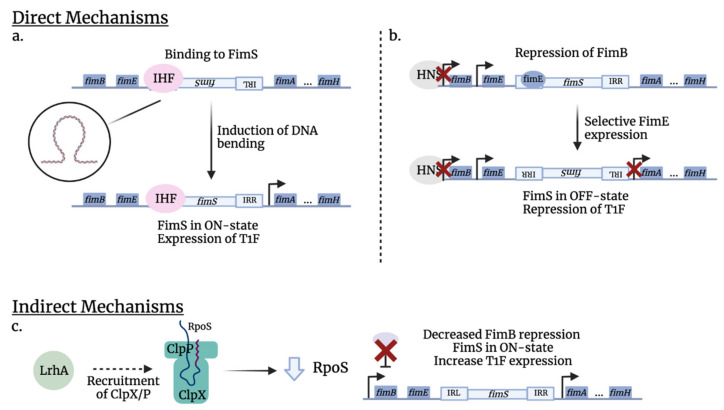
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of action of stress regulators on type 1 fimbriae expression. (a) Regulators can bind directly to fimS to influence phase variation. For example, IHF binds to regions of fimS to induce a sharp DNA bend that facilitates the recombination of the fim switch. In nutrient-deprived environments, such as when bacteria enter the stationary phase, IHF expression will be induced, increasing phase variation, and influencing type 1 fimbriae expression. (b) Regulators can block recombinase expression to influence fimS phase variation. In the case of H-NS, the regulator can bind to the FimB promoter to block its expression, resulting in more FimE production. Since FimE facilitates phase variation of fimS in the OFF-state, type 1 fimbriae will be repressed. This is a simplified model of regulation by H-NS as the latter binds to both FimB and FimE promoters. (c) Other regulators may be indirectly linked to stress by influencing direct stress regulators. Although LrhA can act directly on type 1 fimbriae and flagellar gene expression, it is indirectly linked to stress via the RpoS network. LrhA recruits ClpX/P protease complex through an unknown mechanism (dotted arrow), leading to reduced RpoS production. As a result, FimB repression decreases and more fimS is found in the ON-state, which increases type 1 fimbriae expression.