Abstract
During the race for the development of a vaccine against COVID-19, even before its commercialization, part of the population has already shown a growing fear of its application. We designed an analytical cross-sectional study using an anonymous survey in the 25 departments of Peru. We surveyed whether the participants were planning on getting vaccinated, as well as other characteristics that were cross-checked in a uni-, bi- and multivariate manner. Of the 1776 respondents, 70% (1251) stated that they were planning to be vaccinated, 20% (346) did not know yet or doubted it, and 10% (179) did not want to be vaccinated. We observed that those who did not get infected with COVID-19 exhibited a higher frequency to not wanting or were uncertain about getting vaccinated (aPR: 1.40; 95% CI: 1.09–1.81; p-value = 0.008). In contrast, there was a lower frequency of vaccine refusal among university students (aPR: 0.75; 95% CI: 0.61–0.92; p-value = 0.005) and healthcare workers (aPR: 0.59; 95% CI: 0.44–0.80; p-value = 0.001); adjusted by place of residence. There is still an important percentage of respondents who do not want to be vaccinated or are hesitant to do it, which was associated with educational level, being a healthcare worker and if they were previously infected with COVID-19. Our results could offer useful information about COVID-19 vaccination campaigns.
Keywords: COVID-19, Peru, vaccine, vaccination, coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, vaccines, pandemic
1. Introduction
Since December 2019, the world changed by the COVID-19 pandemic with over 258 million confirmed cases, over 5.1 million deaths and over 7.4 billion vaccine doses administered worldwide as of 23 November 2021 [1]. This disease is characterized by progressive and severe pneumonia, with characteristic symptoms such as fever, dyspnea, dry cough, fatigue, headache, anosmia and ageusia [2,3,4]. The first confirmed case in Peru was reported on 8 March 2020 [5], and the number of cases rapidly increased despite the measures established by the Peruvian government [6,7]. Multiple publications have illustrated the fragmented healthcare system in Peru [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16], which has not been the most effective during the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in a high number of physicians’ deaths [17], limited public policies [18] and detrimental effects to the mental status of the population [19,20,21] and the increase in technostress in university students [22]. Furthermore, Peru has reported discrepancies in the official reports of COVID-19 deaths nationwide [23], poor execution of SARS-CoV-2 testing and reporting [24] and an increased number of COVID-19 cases in children and adolescents [6,25].
Physical isolation was the main preventive measure implemented worldwide to avoid contagion [6,26,27], which caused multiple lifestyle changes in people. Many people have experienced fear of being infected while experiencing the death of family members and friends [28], which has resulted in anxiety and mental distress [29,30]. The widespread disinformation [5,31], fake news [7] and anti-vaccine comments [32,33] have caused fear in the population who seek solutions to prevent or alleviate the symptoms of the disease, since they feel the only resource available is to self-help, self-care and self-medicate [34]. Therefore, it has been reported that some people resort to self-medication [35,36] and others to the use of medicinal plants [37,38] as potential but unproven methods to ameliorate and/or prevent symptoms related to COVID-19. Many have urged that the general state of disinformation be addressed by governmental institutions [39,40,41].
The Peruvian government implemented various regulations to control the purchases of vaccines from different pharmaceutical companies. For instance, the Ministry of Health in Peru made the first publication regarding a vaccine against COVID-19 in September 2020 in the resolution No. 686-2020 to establish guidelines regulations on vaccine research as a result of the COVID-19 outbreak [42]. Then, the first legal standard related to the COVID-19 vaccine was published in October 2020, through ministerial resolution No. 848-2020 with the objective of implementing safe vaccination as a preventive measure against COVID-19 in the country, through the provision of safe and quality vaccines, their administration and proper management [43]. Additionally, this resolution introduced the different Vaccination Phases I, II and III, where the target populations and other measures were indicated to be able to implement the plan [43]. Phase I had the objective of protecting the integrity of the healthcare system by vaccinating the healthcare personnel working in the public and private sector, personnel from the armed forces and police, firefighters, Red Cross, security personnel, brigade members and cleaning personnel and students of health-related careers first [43]. This was followed by Phase II, with the objective of reducing severe morbidity and mortality in the population at greatest risk, which included adults over 60 years, people with comorbidities, the population of native or indigenous communities and personnel working at the National Penitentiary Institute and incarcerated people [43]. Finally, Phase III had the objective of reducing the transmission of infection in continuity and generating herd immunity, which included people between 18 and 59 years of age [43]. An official schedule detailing the projection to vaccinate 27.4 million Peruvians with the two doses was announced, including children between ages 12 to 18 [44]. Furthermore, starting on 26 November 2021 a third vaccine dose can be administered to adults over 18 years who received the second dose at least 5 months before [45].
The National Center for Supply of Strategic Health Resources (CENARES) was assigned to execute the purchase agreement with the company Sinopharm to purchase the first approved vaccine in Peru on January 2021 [46], followed by AstraZeneca on the same month [47], Pfizer on February 2021 [48] and additional Pfizer and AstraZeneca vaccine doses through COVAX facility on March 2021 [49]. Peru has approved, through its regulatory agency DIGEMID, four out of the eight vaccines approved for emergency use around the world [50]. The first vaccine against COVID-19 to receive the conditional sanitary registration by DIGEMID in Peru was Pfizer, which occurred on February 2021, allowing for its import and use in vaccination campaigns [51]. On April 2021, the AstraZeneca vaccine obtained permission from DIGEMID for the active immunization of Peruvians over 18 years of age [52]. On July 2021, Johnson & Johnson’s Jannsen vaccine was approved by DIGEMID [53]. The last of the vaccines to obtain conditional health registration in Peru was Sinopharm’s COVID-19 vaccine on August 2021 [54]. Regardless of its late approval, this was the first vaccine to be applied in Peru after it received exceptional use to import of one million doses [54].
With all the purchases going as planned to cover the vaccination of population of Peru, some changes were made to the National Vaccination Plan against COVID-19 in Peru, adding that Phase I must include healthcare workers [55]. Then a high-level consultative team was formed to recommend the criteria and ethical considerations in decision-making regarding the prioritization of groups to be vaccinated during the execution of the National Vaccination Plan against COVID-19 [56]. With the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in Peru, it was decided to regulate the framework of clinical trials by implementing rapid ethical review and supervision processes through the creation of the Transitional National Research Ethics Committee for evaluation and supervision of COVID-19 Clinical Trials (CNTEI-COVID-19) [57]. However, these ethical measures were violated with the political scandal called Vacunagate that involved 470 people inoculated outside the clinical trial with the Sinopharm vaccine before it was approved and was available for emergency use in Peru [58,59]. The list of those secretly vaccinated included the President of the Peru and his wife, senior officials from the Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, authorities from the two universities where the trial was conducted (Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia and Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos), the team of study researchers, teachers and researchers from both universities and even a representative of the Catholic Church [58,59]. This event gave rise to public protests and anger among the Peruvian population because the clinical malpractice and the evident preference for the political elite regardless of the critical situation the country as suffering with a high number of deaths and the economic impact in Peru, exposing again the corruption in the country [58,59,60,61,62]. The alarming and unethical actions of the inoculated professionals caused distrust of the clinical trial that was carried out, the educational institutions involved and the need for vaccination by the population [62]. As an immediate action, the National Institute of Health ensured future protection by forming a National Bioethics Commission to create norms and establish sanctions to avoid further breaches of medical ethics and improve training in ethics and scientific integrity for researchers [63].
Since the beginning of the pandemic, possible vaccines have been developed by different laboratories. Thus, in December 2020, the first vaccine, Pfizer/BioNTech, was approved in the United Kingdom, initiating the vaccination of front-line healthcare personnel and at-risk populations such as the elderly, a process that was followed by different countries [64]. However, during the race for the development of a vaccine against COVID-19, even before its commercialization, part of the population already showed a growing fear of receiving it. This fear was justified by the lack of knowledge of the adverse effects and complications, the lack of confidence in the process, due to the reduced research time and some myths such as the insertion of chips, among others [65,66,67,68]. Despite the fact that Peru was in the first place with the most deaths from COVID-19 during 2020, a rejection attitude towards vaccines against the disease was observed. This reduced acceptance of vaccination was due to the high prevalence of fear of adverse effects that the country was facing, reaching 90.5% [69]. A survey carried out in January 2021 showed us that since August of the previous year, there was an increase in people who did not plan to be vaccinated against COVID-19, going from 22 to 48%, justified by distrust of the countries that manufacture the vaccines, fear of adverse effects and even a preference for being treated with ivermectin [70]. However, thanks to political corruption scandals due to clandestine vaccination in the Vacunagate, a loss of this prevalence of fear of adverse effects has been achieved [58,69]. The importance of this issue is reflected in the vaccination process itself, especially after knowing that some sectors of the population refuse to get vaccinated in countries where the process has already begun [71]. In Peru, vaccination is already underway for people over 12 years old and a third vaccine dose is been administered to adults over 18 years who received the second dose at least 5 months before. As of 26 November 2021, 17.8 million people in Peru have received both doses of the COVID-19 vaccine, constituting about 65% of the intended 27.4 million people to be vaccinated [50]. Therefore, it is necessary to determine the factors associated for people in Peru not wanting to be vaccinated. The general objective of our study was to determine the sociodemographic predictors associated with the willingness of getting vaccinated against COVID-19 in Peru.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Population
An analytical cross-sectional study was carried out in the 25 departments of Peru. A self-administered virtual survey was conducted as shown in Appendix A. The survey was initially evaluated by 10 expert judges using Aiken’s V [72]. After including the experts’ observations, a pilot study was performed in the second week of November 2020 in the 25 departments of Peru. The pilot data were used to calculate the minimal sample size necessary for the actual study. We utilized non-probability snowball sampling [73]. The necessary sample size was calculated using the determinants related to the acceptance of the COVID-19 vaccine in the United States and Southeast Asia by extracting the percentage of vaccine acceptance and the confidence interval [74,75]. For Peru, it was determined that the minimum sample size was 385 individuals, with a prevalence of vaccine acceptance of 50%, a 95% confidence interval and a margin of error of 5%. This was calculated with Epidat software (V.4.2.). To this end, personal data, education, work situation, comorbidities, exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus, knowledge about COVID-19, perception of risk about the new COVID-19, sources of information and preventive measures were taken into account.
2.2. Variables
The primary variable was whether they would agree to receive the COVID-19 vaccine. We utilized a previously published instrument [75], which was adapted and translated to Spanish. In addition, the instrument was culturally validated through a report that evaluated each question from the survey on three criteria: relevance, coherence and clarity. The report was filled by a specialist in Social Sciences and then the survey was sent to the population. The survey consisted of 2 groups of questions: demographic questions and knowledge about COVID-19.
For the covariables, we considered the sociodemographic variables (age, gender, education, marital status, department of residence, having a chronic disease, household size, work situation) and knowledge about coronavirus (being sick with COVID-19, the reason for getting vaccinated against COVID-19, knowledge about the COVID-19 pandemic and level of knowledge about COVID-19).
2.3. Procedures
The actual survey used for the study was adapted virtually, in order to reach as many participants as possible in the different departments, due to the Peruvian state of health emergency. The survey was shared between the second week of December 2020 and the third week of January 2021 through social networks (WhatsApp, Facebook and Instagram) with the objective of reaching the population over 18 years old of the 25 departments of Peru. According to the National Institute of Statistics and Informatics (INEI), the last census conducted in 2017 showed that five departments comprised more than half of the country’s population [76]. These were Lima, Piura, La Libertad, Arequipa and Cajamarca; it was prioritized to take more surveys in these regions. In order to do this, the researchers contacted healthcare personnel to ask for collaboration and dissemination of the survey, providing informed consent where the confidentiality of the information is assured. The survey was available to the participants who accepted the informed consent, voluntarily participated in the study and authorized the use of their data for the present study.
2.4. Data Analysis
Each survey was entered into a database in Microsoft Excel 2013, where quality control was performed by reviewing the complete and correct completion of the surveys. This was carried out with Stata v.14 statistical software. Then, a descriptive analysis of the categorical variables was made, obtaining frequencies and percentages; for the quantitative variable, the normality of the data was analyzed and described with central tendency and dispersion measures. A figure was also prepared to show the percentages of each of the categories of the three dependent variables.
Subsequently, a bivariate analysis was generated, where the dependent variables was crossed with each independent variable, for which the p-values were obtained in each case. Then, for the multivariate statistics, the variables that were statistically significant in the bivariate model were crossed in each case. For this analysis the generalized linear models were used (with the Poisson family, the log function, models for robust variances and adjusted by each respondent site). The adjusted prevalence ratios, the 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) and the p-values were obtained. In each one of the crossings, the p-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
2.5. Ethical Aspects
The project followed the guidelines for ethical aspects. The research protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas (approval code PI 393-20). The participants were selected to answer the scientific questions, respecting their ideology, identity, judgment, prejudices and other relevant events of the interviewee. The individuals participated in the research in an informed, anonymous and voluntary manner. In addition, in order to conduct the survey, an informed consent was requested. Finally, in order for this study to be solely for research purposes, no participant data were disclosed.
3. Results
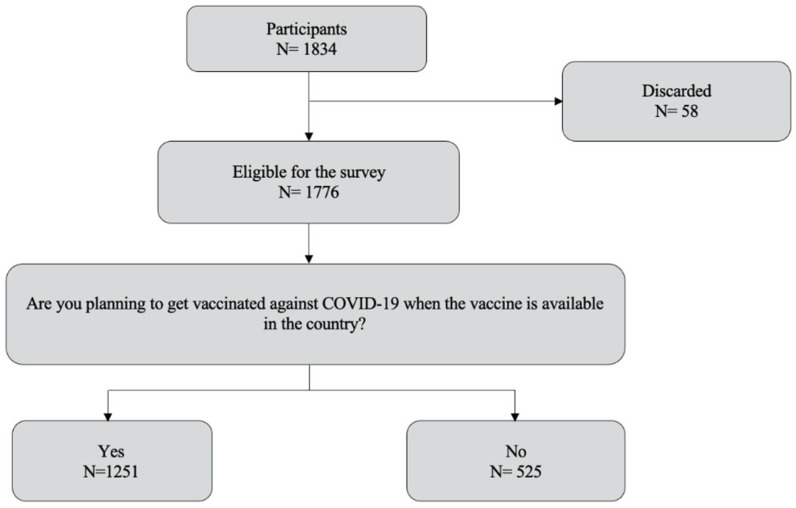
A total of 1834 people, residents of the 25 departments of Peru, were invited to participate in the survey, of which 1776 were eligible for the survey. Fifty-eight participants were not taken into account because they were repeated or the provided data lacked coherence. Those eligible for the survey were 18 years or older, had internet access and accepted the informed consent prior to the administration of the survey (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the survey respondents.
Table 1 shows that, out of the 1776 respondents, 57.9% (1028) were female, the median age was 24 (interquartile range: 20–28 years), the majority had university education (67.5%), had no chronic diseases (80.4%), were not healthcare workers (89.5%), had a median of 4 people at home (interquartile range: 3–5 people), had not yet been infected with COVID-19 (61.1%), nor had their family members (45.3%) and they were planning to be vaccinated (70.4%).
Table 1.
Sociodemographic characteristics of respondents.
| Variable | Frequency | Percentage/Interquartile Range |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Male | 748 | 42.1% |
| Female | 1028 | 57.9% |
| Age (years of age) a | 24 | 20–28 |
| Level of education | ||
| High school or lower | 145 | 8.2% |
| Technical | 241 | 13.6% |
| University | 1199 | 67.5% |
| Postgraduate | 191 | 10.8% |
| Household size a | 4 | 3–5 |
| Healthcare worker | ||
| No | 1589 | 89.5% |
| Yes | 187 | 10.5% |
| With a chronic disease | ||
| No | 1428 | 80.4% |
| Yes | 348 | 19.6% |
| Got infected with COVID-19? | ||
| No | 1085 | 61.1% |
| Yes (confirmed with a test) | 244 | 13.7% |
| Yes (without a test) | 112 | 6.3% |
| I don’t know/it is possible | 335 | 18.9% |
| Family or friends got infected with COVID-19? | ||
| No | 805 | 45.3% |
| Yes (confirmed with a test) | 657 | 37.0% |
| Yes (without a test) | 156 | 8.8% |
| I don’t know/it is possible | 158 | 8.9% |
| Will you get vaccinated against COVID-19? | ||
| No | 179 | 10.1% |
| Yes | 1251 | 70.4% |
| I don’t know yet. | 346 | 19.5% |
a Median and interquartile range are shown.
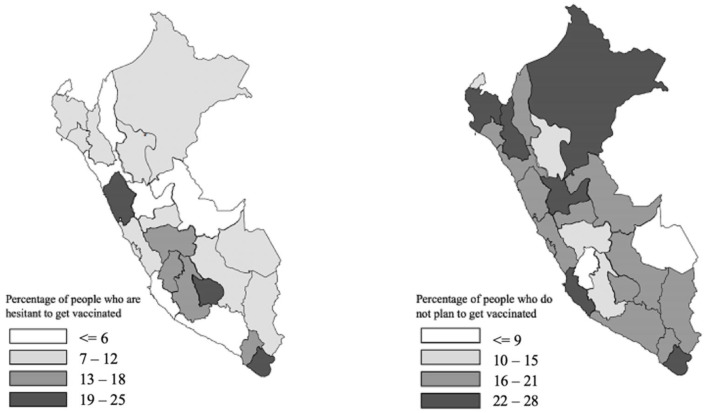
The collected data indicated significant differences in the acceptance of the COVID-19 vaccine in the different departments of Peru. Departments in the central and south highlands of the country had the highest percentages of people who did not plan to be vaccinated or were hesitant to be vaccinated (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Geographical distribution of people that are hesitant or do not plant to get vaccinated in Peru.
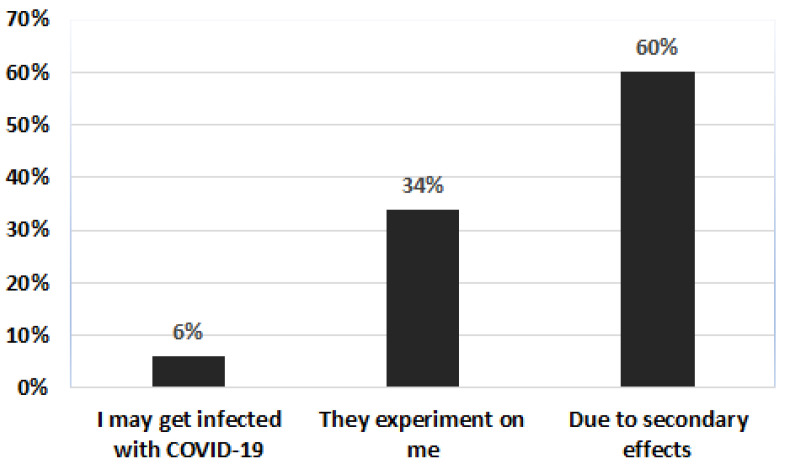
Among the reasons indicated by respondents who did not plan to be vaccinated by a possible COVID-19 vaccine, the most frequent was the fear of side effects (60%), followed by believing that “they are experimenting on me” (34%) and to a lesser extent “I may get sick with COVID-19” (6%) (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Reasons why people do not plan to be vaccinated against COVID-19 in Peru.
As shown on Table 2, the bivariate analysis between the sociodemographic characteristics and the intent to get vaccinated, differences were found in regard to age (p = 0.021), educational level (p < 0.001), being a healthcare worker (p < 0.001), having been sick with COVID-19 (p < 0.001) or if their family or friends got sick (p = 0.003).
Table 2.
Bivariate analysis of sociodemographic characteristics and the intent to get vaccinated against COVID-19 in Peru.
| Variable | Will You Get Vaccinated? | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | I Don’t Know | ||
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 72 (9.6%) | 539 (72.1%) | 137 (18.3%) | 0.439 |
| Female | 107 (10.4%) | 712 (69.3%) | 209 (20.3%) | |
| Age (years of age) a | 29 (21–42) | 24 (20–37) | 23 (20–39) | 0.021 |
| Level of education | ||||
| High school or lower | 16 (11.0%) | 89 (61.4%) | 40 (27.6%) | <0.001 |
| Technical | 20 (8.3%) | 175 (72.6%) | 46 (19.1%) | |
| University | 107 (8.9%) | 856 (71.4%) | 236 (19.7%) | |
| Postgraduate | 36 (18.9%) | 131 (68.6%) | 24 (12.5%) | |
| Household size a | 4 (3–5) | 4 (3–5) | 4 (3–5) | 0.456 |
| Healthcare worker | ||||
| No | 167 (10.5%) | 1096 (69.0%) | 326 (20.5%) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 12 (6.4%) | 155 (82.9%) | 20 (10.7%) | |
| With a chronic disease | ||||
| No | 152 (10.6%) | 988 (69.2%) | 288 (20.2%) | 0.058 |
| Yes | 27 (7.8%) | 263 (75.6%) | 58 (16.6%) | |
| Got infected with COVID-19? | ||||
| No | 113 (10.4%) | 798 (73.6%) | 174 (16.0%) | <0.001 |
| Yes (confirmed with a test) | 17 (7.0%) | 169 (69.3%) | 58 (23.7%) | |
| Yes (without a test) | 12 (10.7%) | 85 (75.9%) | 15 (13.4%) | |
| I don’t know/it is possible | 37 (11.0%) | 199 (59.4%) | 99 (29.6%) | |
| Family or friends got infected with COVID-19? | ||||
| No | 81 (10.1%) | 588 (73.0%) | 136 (16.9%) | 0.003 |
| Yes (confirmed with a test) | 66 (10.0%) | 457 (69.6%) | 134 (20.4%) | |
| Yes (without a test) | 17 (10.9%) | 113 (72.4%) | 26 (16.7%) | |
| I don’t know/it is possible | 15 (9.5%) | 93 (58.9%) | 50 (31.6%) | |
a Median and interquartile range are shown, p-values were calculated through the Kruskall–Wallis test. The other p-values were calculated with the Chi-squared test.
As shown on Table 3, when multivariate analysis (adjusted by department of residence) was performed, it was found that those who had a higher frequency of not wanting or not knowing if they were going to be vaccinated were those who did not know if they had been infected with COVID-19 (aPR: 1.40; 95% CI: 1.09–1.81; p-value = 0.008). In contrast, there was a lower frequency of refusal to the vaccine among university students (aPR: 0.75; 95% CI: 0.61–0.92; p-value = 0.005) and healthcare workers (aPR: 0.59; 95% CI: 0.44–0.80; p-value = 0.001).
Table 3.
Bivariate and multivariate analysis of sociodemographic characteristics and the intent to get vaccinated against COVID-19 in Peru.
| Variable | aPR (95% Confidence Internal) p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Bivariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |
| Female | 1.10 (0.95–1.27) 0.186 | Did not use the model |
| Age (years of age) | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) 0.459 | Did not use the model |
| Level of education | ||
| High school or lower | Ref. | Ref. |
| Technical | 0.71 (0.49–1.01) 0.062 | 0.72 (0.49–1.04) 0.077 |
| University | 0.74 (0.60–0.92) 0.007 | 0.75 (0.61–0.92) 0.005 |
| Postgraduate | 0.81 (0.55–1.21) 0.312 | 0.93 (0.63–1.37) 0.724 |
| Household size | 1.00 (0.96–1.05) 0.965 | Did not use the model |
| Healthcare worker | 0.55 (0.41–0.74) <0.001 | 0.59 (0.44–0.80) 0.001 |
| With a chronic disease | 0.79 (0.58–1.09) 0.148 | Did not use the model |
| Got infected with COVID-19? | ||
| No | Ref. | Ref. |
| Yes (confirmed with a test) | 1.16 (0.93–1.45) 0.179 | 1.15 (0.89–1.49) 0.289 |
| Yes (without a test) | 0.91 (0.62–1.34) 0.640 | 0.88 (0.56–1.39) 0.595 |
| I don’t know/it is possible | 1.53 (1.23–1.91) <0.001 | 1.40 (1.09–1.81) 0.008 |
| Family or friends got infected with COVID-19? | ||
| No | Ref. | Ref. |
| Yes (confirmed with a test) | 1.13 (0.92–1.39) 0.256 | 1.04 (0.82–1.32) 0.744 |
| Yes (without a test) | 1.02 (0.72–1.46) 0.902 | 0.96 (0.65–1.41) 0.827 |
| I don’t know/it is possible | 1.53 (1.09–2.15) 0.015 | 1.22 (0.83–1.78) 0.310 |
4. Discussion
Evidence suggests that the next global challenge, after successfully developing a vaccine against COVID-19, will be to persuade a sufficient proportion of the inhabitants to accept vaccination, and thus mitigate the impact of the virus around the world [77,78]. It has been reported that the willingness to get vaccinated against COVID-19 in Kuwait was positively influenced by younger age, being male, having a higher education level, having been previously vaccinated against seasonal influenza, being a healthcare worker and working in the private sector [79]. Similar results were observed in a study that assessed the COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among Ethiopian healthcare workers [80], among undergraduate students from central and southern Italy [81] and among the Chinese population [82]. In the latter study it was observed that the COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy was modest in China [82]. A study that evaluated the willingness to get vaccinated against COVID-19 in Burkina Faso, Ethiopia, Malawi, Mali, Nigeria and Uganda reported that four in five people were willing to get vaccinated, except in Ethiopia [83]. It was found that the main reason for this discrepancy in Ethiopia was because of the potential side effects of the vaccine [83]. This was also observed in a study performed in Saudi Arabia where the vaccine refusers indicated that their safety concerns would only be dissipated with more reported clinical studies [84]. These concerns have been related to belief in conspiracy theories [85] and the wait-and-see approach to assess possible long-term health risks [86].
According to previously published studies related to the intention, associated predictors and attitude towards vaccination against COVID-19 in Peru, it was found that adults and older adults are the most willing to accept the vaccine [87]. However, other factors were also found to be associated with vaccination against COVID-19. For example, in the study by Herrera et al., a higher prevalence of intention to vaccinate was found in people with COVID-19 symptoms, economic insecurity, fear that they or a family member would get sick and those who received recommendations from family members, friends, health workers, the World Health Organization (WHO) or government officials [88]. On the other hand, in a study carried out in Arequipa where 120 people who went to a popular market were surveyed, it was found that people over 25 years of age and with a higher level of education had higher intention to get vaccinated [89]. In the Caycho et al. study, the results indicated that the most important predictor for getting vaccinated against COVID-19 was confidence in vaccines [90]. In addition, being over 65 years old, residing in Lima, being afraid of getting sick, spreading or dying from COVID-19, perceiving a greater probability or severity of contracting the disease, thinking of or receiving information about COVID-19, suffering from anxiety and having postponed a previous vaccination was associated with a greater intention to get vaccinated [90]. Moreover, in the study by Serpa et al., adults and the elderly who were well informed about vaccination and had a higher level of education, especially educators, healthcare personnel and education students, were identified with a favorable attitude towards vaccination against COVID-19 [91].
Through this study in Peru, we found that seven out of ten respondents are willing to be vaccinated against COVID-19. That is, three out of ten respondents were unwilling or hesitant to be vaccinated. These results is similar to the current 65% of people vaccinated with both doses in Peru [50]. We also identified multiple independent variables associated with vaccine acceptance, such as a level of education, which was previously reported in the United States [75,78]. This could be a possible explanation for the high acceptance rate compared to the United Kingdom, Australia, the United States, Qatar and China, which are also within the herd immunity threshold, estimated to be between 55 and 82% to stop infection [75,77,78,92,93,94,95]. This finding is consistent with the results of previous studies in the United States, where it was found that having more years of education implied an increased acceptance of the COVID-19 vaccine [75,78,95,96]. That could be explained by the fact that these individuals have greater accessibility to information related to the vaccine, where the group with postgraduate education had a 75% willingness to vaccinate compared to those with a lower level of education [75]. Our results show that healthcare workers were the ones who most wanted to be vaccinated, as they were less likely to refuse the vaccine. It has been reported that healthcare workers see the possibility that being immunized would prevent the severe form of disease caused by COVID-19 [78,92,95,96,97]. Educating the population about the importance of COVID-19 vaccination, especially vulnerable populations, will require the effort of the government in conjunction with healthcare workers [75,98]. Therefore, hesitancy and resistance to vaccination should be addressed as early as possible by health science professionals [77,78,96,99].
Other determinants affecting vaccine acceptance were self-exposure to SARS-CoV-2 virus by those who did not know or doubted that they had been infected; thus, they were less interested in being vaccinated. In our study, we identified considerable differences in the desire to get vaccinated in several departments in the central highlands and some in the northern part of the country, who did not want to be vaccinated, which could be due to the inequality gap existing in the different regions of Peru. The differences between departments require differentiated responses from a territorial approach by the authorities [75,95,100]. Supporting this, a World Bank study indicated that inequality factors such as educational level, stable salary jobs, access to Internet and gender have contributed to the existing gap. This could be an explanation for the different opinions obtained in the study and the great impact of the pandemic in such places [75,78,95]. It is important to highlight that there is a small part of the population who are skeptical in regard of vaccination in general and not only of a new vaccine against COVID-19 [97]. This poses a risk to individuals and their community, since exposure to a contagious disease puts people at risk due to its rapid ability to spread if a significant portion of the population is not vaccinated [75,77,78,96,101]. For these reasons, a state approach to regions with lower vaccine acceptance rates would be appropriate, through different strategies, such as promoting access to basic health and education services, since a large part of the population is not in a position to comply with the provisions recommended by the country [77,78,95]. Even though 70% of the Peruvian population has received both COVID-19 vaccines, multiple regions of Peru reported lower vaccination rates, especially in the central highlands and northern part of the country [102], which matches with our results. Because of this sociodemographic discrepancies in COVID-19 vaccination in Peru, the government of announced that since 10 December 2021 it is mandatory for adults older than 18 years old to present a vaccination record with both COVID-19 vaccines doses to access all closed public spaces, excluding pharmacies and hospitals [103]. Furthermore, since the implementation of this measure a high number of non-vaccinated and incomplete vaccinated people filled vaccination centers across multiple regions in Peru, which could allow the country to reach the target 80% of its population to be vaccinated before the end of 2021 [104].
Limitations
Regarding limitations, the fidelity and veracity of the data were considered since this is a study with a very important subjective component. We depend on the willingness of the population to collaborate. In addition, as this is a cross-sectional observational study, we do not have the capacity to make a prospective and retrospective analysis of the situation. On the other hand, we do not know if past experiences can influence people’s decision on the acceptance of the vaccine, since different phases of the pandemic lead to different responses to the situation [94,97]. This was the case in Italy, where it was found that as the perception of risk increased, more people were open to the possibility of being vaccinated against COVID-19 [75,78,94,97]. Additionally, our study focused on a sample of the population; this sample is representative of the general adult population and does not include members of the public who are institutionalized (e.g., incarcerated), or difficult to reach such as homeless people or those without internet access. The inability to reach these sectors limits the generalizability of our results. Finally, vulnerable groups such as children and the elderly were not taken into account [77]. We recommend considering these sectors for future studies. Another limitation is bias that occurred as a result of the cross-sectional study design to determine definitive cause and effect associations. Similarly, the responders performed a self-reported assessment in an online data collection platform, which could lead to under- or over-reporting, and the data collector does not have the ability to verify or validate.
It should be considered that the intention to receive the vaccine in this study does not necessarily translate into the actual number of people who will accept or decline a vaccination. For this reason, it is advisable to continue with health promotion in the different departments of Peru [78,104]. Despite these limitations, our findings provide important evidence regarding the level of acceptance and resistance to COVID-19 vaccination in a general population sample. Our study highlights the importance of understanding the various social, economic, political and psychological factors that contribute to hesitancy and resistance to COVID-19 vaccination, and how they can be used to maximize the positive public health effect. We would like to encourage more researchers to conduct similar studies using this population in order to better understand vaccine acceptance.
5. Conclusions
Acceptance of the COVID-19 vaccine in Peru is influenced by the level of education. This acceptance is relatively high in people with university education but decreases in people with high school or a lower level of education. If the educational level is an important factor, the government should provide greater accessibility to information and education about vaccines. In addition, given that healthcare workers are the sector that most want to be vaccinated, it is also important that they work together with governments to educate the population about the importance of vaccination.
Acknowledgments
Gustavo Alba Figueroa and José Manuel Pizarro García are thanked for their support and motivation to initiate the investigation, their valuable contribution is appreciated.
Appendix A
Annex 1. Sociodemographic characteristics and the intent to get vaccinated against COVID-19 in Peru.
Demographics
-
1. Gender:
-
□Male
-
□Female
-
□
-
2.
Age: _____ years
-
3. Education:
-
□Primary school
-
□High school
-
□Technical degree
-
□University degree
-
□Postgraduate
-
□
-
4. Civil status:
-
□Single
-
□Married
-
□Divorced
-
□Other, specify: _____
-
□
-
5. Department you live in Peru:
-
□Amazonas
-
□Ancash
-
□Apurimac
-
□Arequipa
-
□Ayacucho
-
□Cajamarca
-
□Callao
-
□Cusco
-
□Huancavelica
-
□Huanuco
-
□Ica
-
□Junin
-
□La Libertad
-
□Lambayeque
-
□Lima
-
□Loreto
-
□Madre de Dios
-
□Moquegua
-
□Pasco
-
□Piura
-
□Puno
-
□San Martin
-
□Tacna
-
□Tumbes
-
□Ucayali
-
□
-
6. Do you work in healthcare?
-
□Yes
-
□No
-
□
-
7. Do you have a chronic illness (diabetes, hypertension, asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, cancer)?
-
□Yes
-
□No
-
□
-
8.
How many people live in your home? _____
-
9. Have you been sick with COVID-19?
-
□Yes, confirmed
-
□Yes, but not yet confirmed
-
□No
-
□Don’t know
-
□
-
10. Family or friends got infected with COVID-19?
-
□Yes, confirmed
-
□Yes, but not yet confirmed
-
□No
-
□Don’t know
-
□
-
11. What is your current work situation?
-
□Employed (questions below appear if this option is selected)
-
I. Are you working from home?
-
□Yes
-
□No
-
□
-
II. Have your work hours been reduced due to the current COVID-19 pandemic?
-
□Yes
-
□No
-
□
-
III. Are you worried about losing your job in the next 6 months due to the COVID-19 pandemic?
-
□Yes
-
□No
-
□
-
I.
-
□Unemployed (the next question appears if this option is selected)
-
I. Is your unemployment a result of the COVID-19 pandemic?
-
□Yes
-
□No
-
□
-
I.
-
□Retired
-
□Student
-
□
-
12. Have you been vaccinated against the flu virus (influenza or pneumococcus) in the last few months?
-
□Yes
-
□No
-
□Don’t know
-
□
-
13. Do you plan to get vaccinated against the flu?
-
□Yes
-
□No
-
□Don’t know
-
□
-
14. Do you plan to get vaccinated against COVID-19?
-
□Yes (questions below appear if this option is selected)
-
I. What is the main reason to get vaccinated?
-
□Protect my health
-
□Protect my family members
-
□
-
II. If you had to choose the country of origin of the vaccine, which one would you select?
-
□China
-
□Germany
-
□England
-
□United States
-
□Switzerland
-
□India
-
□Peru
-
□Other: _____
-
□
-
I.
-
□No
-
□Don’t know
-
□
-
15. Do you have any fear of receiving the COVID-19 vaccine?
-
□Yes (question below appears if this option is selected)
-
I. Why?
-
□It can cause me some damage (secondary effect)
-
□I can get sick from COVID-19
-
□They are experimenting with me
-
□
-
I.
-
□No
-
□Don’t knowKnowledge about COVID-19
-
□
-
16. Are you aware of the novel coronavirus/COVID-19 pandemic?
-
□Yes
-
□No → (this explanation pops up if this option is selected) There is a pandemic of respiratory disease caused by a novel (new) coronavirus. The disease has been named “coronavirus disease 2019” or COVID-19. Although the virus was first identified in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China, it has now spread across the globe with millions of infections and deaths.
-
□Don’t know → (this explanation pops up if this option is selected) There is a pandemic of respiratory disease caused by a novel (new) coronavirus. The disease has been named “coronavirus disease 2019” or COVID-19. Although the virus was first identified in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China, it has now spread across the globe with millions of infections and deaths.
-
□
-
17. How did you learn about the novel coronavirus/COVID-19 pandemic?
-
□Television
-
□Newspapers/magazines
-
□Websites
-
□Family/friends
-
□Healthcare professionals (For example: doctors, nurses, pharmacists or other health professionals)
-
□Health officials (For example: Ministry of Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Institute of Health)
-
□Social media
-
□
-
18. How would you rate your knowledge level on novel coronavirus/COVID-19?
-
□Very poor
-
□Poor
-
□Average
-
□Good
-
□Very good
-
□
-
19. Which of the following statements is correct about the definition of novel coronavirus/COVID-19?
-
□The novel coronavirus/COVID-19 is a respiratory disease caused by a viral infection.
-
□Displayed symptoms usually include respiratory symptoms accompanied by fever, but novel coronavirus/COVID-19 is not contagious
-
□The novel coronavirus/COVID-19 can progress to a severe illness but never leads to death
-
□Don’t know
-
□
-
20. Which of the following statements is correct about transmission route of novel coronavirus/COVID-19?
-
□Novel coronavirus/COVID-19 is transmitted through coughing or sneezing.
-
□Novel coronavirus/COVID-19 is not transmitted by close contact with people.
-
□Don’t know
-
□
-
21.
Which of the following are effective preventative measures for yourself and/or others against the novel coronavirus/COVID-19?
| Yes | No | Don’t Know | |
| Hand-washing | |||
| Avoiding touching your eyes, nose and mouth with unwashed hands | |||
| Using disinfectants | |||
| Staying home when you are sick | |||
| Taking herbal supplements | |||
| Covering your cough or sneeze | |||
| Eating a balanced diet | |||
| Avoiding close contact with someone who is sick | |||
| Using vitamin supplements | |||
| Using caution when opening mail | |||
| Avoiding eating meat | |||
| Exercising regularly | |||
| Wearing a face mask | |||
| Using hand sanitizer | |||
| Using drugs | |||
| Social/physical distancing | |||
| Using homeopathic remedies |
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: D.V., L.F.S., A.N.-V., K.P.D. and C.R.M.; methodology: D.V., L.F.S., A.N.-V., K.P.D., A.A.-R., J.A.Y. and C.R.M.; validation: D.V., L.F.S., A.N.-V., K.P.D. and C.R.M.; formal analysis: D.V., L.F.S., A.N.-V. and K.P.D.; investigation: D.V., L.F.S., A.N.-V., K.P.D., A.A.-R., J.A.Y. and C.R.M.; data curation: A.A.-R., J.A.Y. and C.R.M.; writing—original draft preparation: D.V., L.F.S., A.N.-V., K.P.D. and C.R.M.; writing—review and editing: A.A.-R., J.A.Y. and C.R.M.; visualization: D.V., L.F.S., A.N.-V., K.P.D., A.A.-R., J.A.Y. and C.R.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Universidad Norbert Wiener, Grant N° 124-2021-R-UPNW.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study because it does not involve any risk to the participant’s life or health. No substance has been tested on the participants or put them in danger at any time.
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived because it would not be part of any medical intervention and no drug substance was to be tested.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval & Informed Consent
The research protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas (approval code PI 393-20). All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Dong E., Du H., Gardner L. An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020;20:533–534. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30120-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.González-Bustamante B. Evolution and early government responses to COVID-19 in South America. World Dev. 2021;137:105180. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2020.105180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yang W., Cao Q., Qin L., Wang X., Cheng Z., Pan A., Dai J., Sun Q., Zhao F., Qu J., et al. Clinical characteristics and imaging manifestations of the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A multi-center study in Wenzhou city, Zhejiang, China. J. Infect. 2020;80:388–393. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.02.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gavriatopoulou M., Korompoki E., Fotiou D., Ntanasis-Stathopoulos I., Psaltopoulou T., Kastritis E., Terpos E., Dimopoulos M.A. Organ-specific manifestations of COVID-19 infection. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020;20:493–506. doi: 10.1007/s10238-020-00648-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rojas Román B., Moscoso S., Chung S.A., Limpias Terceros B., Álvarez-Risco A., Yáñez J.A. Tratamiento de la COVID-19 en Perú y Bolivia y los riesgos de la automedicación. Rev. Cuba. Farm. 2020;53:1–20. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yáñez J.A., Alvarez-Risco A., Delgado-Zegarra J. Covid-19 in Peru: From supervised walks for children to the first case of Kawasaki-like syndrome. BMJ. 2020;369:m2418. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m2418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Alvarez-Risco A., Mejia C.R., Delgado-Zegarra J., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S., Arce-Esquivel A.A., Valladares-Garrido M.J., Rosas del Portal M., Villegas L.F., Curioso W.H., Sekar M.C., et al. The Peru Approach against the COVID-19 Infodemic: Insights and Strategies. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020;103:583–586. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.20-0536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Álvarez-Risco A., Arellano E.Z., Valerio E.M., Acosta N.M., Tarazona Z.S. Pharmaceutical care campaign as a strategy for implementation of pharmaceutical services: Experience Peru. Pharm. Care Esp. 2013;15:35–37. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Alvarez-Risco A., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S. Prescription errors as a barrier to pharmaceutical care in public health facilities: Experience Peru. Pharm. Care Esp. 2015;17:725–731. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Alvarez-Risco A., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S., Diaz-Risco S. Pharmacovigilance as a tool for sustainable development of healthcare in Peru. Pharmacovigil. Rev. 2018;10:4–6. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Alvarez-Risco A., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S., Rosen M.A., García-Ibarra V., Maycotte-Felkel S., Martínez-Toro G.M. Expectations and interests of university students in covid-19 times about sustainable development goals: Evidence from Colombia, Ecuador, Mexico, and Peru. Sustainability. 2021;13:3306. doi: 10.3390/su13063306. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Alvarez-Risco A., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S., Stevenson J.G. Pharmacists and mass communication for implementing pharmaceutical care. Am. J. Pharm. Benefits. 2015;7:e125–e126. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Alvarez-Risco A., Quiroz-Delgado D., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S. Pharmaceutical care in hypertension patients in a peruvian hospital. Indian J. Public Health Res. Dev. 2016;7:183–188. doi: 10.5958/0976-5506.2016.00153.4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Alvarez-Risco A., Turpo-Cama A., Ortiz-Palomino L., Gongora-Amaut N., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S. Barriers to the implementation of pharmaceutical care in pharmacies in Cusco, Peru. Pharm. Care Esp. 2016;18:194–205. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Enciso-Zarate A., Guzmán-Oviedo J., Sánchez-Cardona F., Martínez-Rohenes D., Rodríguez-Palomino J.C., Alvarez-Risco A., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S., Diaz-Risco S. Evaluation of contamination by cytotoxic agents in Colombian hospitals. Pharm. Care Esp. 2016;18:241–250. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mejía-Acosta N., Alvarez-Risco A., Solís-Tarazona Z., Matos-Valerio E., Zegarra-Arellano E., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S. Adverse drug reactions reported as a result of the implementation of pharmaceutical care in the Institutional Pharmacy DIGEMID-Ministry of Health. Pharm. Care Esp. 2016;18:67–74. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gonzales-Tamayo L., Arevalo-Oropeza M., Yáñez J.A. COVID-19 Physician Deaths in Peru: A Result of an Underfunded and Fragmented Healthcare System. [(accessed on 1 November 2021)]. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3676849.
- 18.Mejia C.R., Ticona D., Rodriguez-Alarcon J.F., Campos-Urbina A.M., Garayar-Peceros H., Catay-Medina J.B., Porta-Quinto T., Garay-Rios L., Ignacio-Quinte C., Guevara-Sosa S. Percepción de las medidas de salud pública en Perú para frenar el avance de la COVID-19. Rev. Cuba Investig. Bioméd. 2021;40:e737. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yáñez J.A., Afshar Jahanshahi A., Alvarez-Risco A., Li J., Zhang S.X. Anxiety, Distress, and Turnover Intention of Healthcare Workers in Peru by Their Distance to the Epicenter during the COVID-19 Crisis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020;103:1614–1620. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.20-0800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yan J., Kim S., Zhang S.X., Foo M.-D., Alvarez-Risco A., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S., Yáñez J.A. Hospitality Workers’ COVID-19 Risk Perception and Depression: A Contingent Model Based on Transactional Theory of Stress Model. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2021;95:102935. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2021.102935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Alvarez-Risco A., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S., Yanez J.A. Opportunity for eHealth due to COVID-19 Outbreak: Case of Peru. [(accessed on 1 November 2021)];Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020 doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3741715. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3741715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Alvarez-Risco A., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S., Yáñez J.A., Rosen M.A., Mejia C.R. Influence of Technostress on Academic Performance of University Medicine Students in Peru during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability. 2021;13:8949. doi: 10.3390/su13168949. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yáñez J.A., Chung S.A., Inga-Berrospi F., Mejia C.R. Demographic and Geographic COVID-19 Death Risk Factors in Peru. A Nationwide Analysis. [(accessed on 1 November 2021)];EClinicalMedicine. 2020 doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3648543. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3648543. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yáñez J.A., Alvarez-Risco A., Delgado-Zegarra J. Rapid Response: Does Peru Really Have That High Number of COVID-19 Confirmed Cases? The Deception of Combining RT-PCR and Rapid Test Results. [(accessed on 1 July 2020)]. Available online: https://www.bmj.com/content/369/bmj.m2518/rr-4.
- 25.Yáñez J.A., Alvarez-Risco A., Delgado-Zegarra J. Rapid Response: Clearing the Path for COVID-19 in Peru? The Decision of Supervised Walks for Children and Adolescents. [(accessed on 3 June 2020)]. Available online: https://www.bmj.com/content/369/bmj.m1918/rr-9.
- 26.Salathé M., Althaus C.L., Neher R., Stringhini S., Hodcroft E., Fellay J., Zwahlen M., Senti G., Battegay M., Wilder-Smith A., et al. COVID-19 epidemic in Switzerland: On the importance of testing, contact tracing and isolation. Swiss Med Wkly. 2020;150:1112. doi: 10.4414/smw.2020.20225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.MacIntyre C.R. Case isolation, contact tracing, and physical distancing are pillars of COVID-19 pandemic control, not optional choices. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020;20:1105–1106. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30512-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.VanderWeele T.J. Challenges Estimating Total Lives Lost in COVID-19 Decisions: Consideration of Mortality Related to Unemployment, Social Isolation, and Depression. JAMA. 2020;324:445–446. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhang S.X., Chen J., Afshar Jahanshahi A., Alvarez-Risco A., Dai H., Li J., Patty-Tito R.M. Succumbing to the COVID-19 Pandemic—Healthcare Workers Not Satisfied and Intend to Leave Their Jobs. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2021;7:1–10. doi: 10.1007/s11469-020-00418-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chen X., Zhang S.X., Jahanshahi A.A., Alvarez-Risco A., Dai H., Li J., Ibarra V.G. Belief in a COVID-19 conspiracy theory as a predictor of mental health and well-being of health care workers in Ecuador: Cross-sectional survey study. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020;6:e20737. doi: 10.2196/20737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bernard R., Bowsher G., Sullivan R., Gibson-Fall F. Disinformation and Epidemics: Anticipating the Next Phase of Biowarfare. Health Secur. 2020;19:3–12. doi: 10.1089/hs.2020.0038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Stolle L.B., Nalamasu R., Pergolizzi J.V., Varrassi G., Magnusson P., LeQuang J., Breve F. Fact vs. Fallacy: The Anti-Vaccine Discussion Reloaded. Adv. Ther. 2020;37:4481–4490. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01502-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Burki T. The online anti-vaccine movement in the age of COVID-19. Lancet Digit. Health. 2020;2:e504–e505. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30227-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Matias T., Dominski F.H., Marks D.F. Human needs in COVID-19 isolation. J. Health Psychol. 2020;25:871–882. doi: 10.1177/1359105320925149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Quispe-Cañari J.F., Fidel-Rosales E., Manrique D., Mascaro-Zan J., Huamán-Castillón K.M., Chamorro-Espinoza S.E., Garayar-Peceros H., Ponce-López V.L., Sifuentes-Rosales J., Alvarez-Risco A., et al. Self-medication practices during the COVID-19 pandemic among the adult population in Peru: A cross-sectional survey. Saudi Pharm. J. 2021;29:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2020.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yáñez J.A., Chung S.A., Román B.R., Hernández-Yépez P.J., Garcia-Solorzano F.O., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S., Inga-Berrospi F., Mejia C.R., Alvarez-Risco A. Chapter 14-Prescription, over-the-counter (OTC), herbal, and other treatments and preventive uses for COVID-19. In: Hadi Dehghani M., Karri R.R., Roy S., editors. Environmental and Health Management of Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Academic Press; London, UK: 2021. pp. 379–416. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lim X.Y., Teh B.P., Tan T.Y.C. Medicinal Plants in COVID-19: Potential and Limitations. Front. Pharmacol. 2021;12:611408. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.611408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Villena-Tejada M., Vera-Ferchau I., Cardona-Rivero A., Zamalloa-Cornejo R., Quispe-Florez M., Frisancho-Triveño Z., Abarca-Meléndez R.C., Alvarez-Sucari S.G., Mejia C.R., Yañez J.A. Use of medicinal plants for COVID-19 prevention and respiratory symptom treatment during the pandemic in Cusco, Peru: A cross-sectional survey. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0257165. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Pomeranz J.L., Schwid A.R. Governmental actions to address COVID-19 misinformation. J. Public Health Policy. 2021;42:201–210. doi: 10.1057/s41271-020-00270-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kolluri N.L., Murthy D. CoVerifi: A COVID-19 news verification system. Online Soc. Netw. Media. 2021;22:100123. doi: 10.1016/j.osnem.2021.100123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Alvarez-Risco A., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S., Yanez J.A. Telemedicine in Peru as a Result of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Perspective from a Country with Limited Internet Access. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021;105:6–11. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.21-0255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.MINSA . Resolución Ministerial N° 686-2020-MINSA-Norma Técnica de Salud para la Investigación y Desarrollo de Vacunas contra Enfermedades Infecciosas. Ministerio de Salud; Lima, Peru: 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 43.MINSA . Resolución Ministerial N° 848-2020-MINSA-Plan Nacional de Vacunación contra la COVID-19. Ministerio de Salud; Lima, Peru: 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 44.MINSA Covid-19: Conoce Aquí el Cronograma de Vacunación para Personas de 12 Años a Más. [(accessed on 25 November 2021)]. Available online: https://elperuano.pe/noticia/124671-covid-19-conoce-aqui-el-cronograma-de-vacunacion-para-personas-de-12-anos-a-mas/
- 45.PCM Campaña Nacional de Vacunación contra la COVID-19. [(accessed on 25 November 2021)]. Available online: https://www.gob.pe/institucion/pcm/campa%C3%B1as/3451-campana-nacional-de-vacunacion-contra-la-covid-19.
- 46.MINSA . Resolución Ministerial N° 023-2021-MINSA-CENARES se Encargue de Ejecutar el Acuerdo de Compraventa con la Empresa Sinopharm. Ministerio de Salud; Lima, Peru: 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 47.MINSA . Resolución Ministerial N° 078-2021-MINSA-CENARES Gestionar, Implementar y Ejecutar el Contrato de Compraventa con la Empresa Astrazeneca. Ministerio de Salud; Lima, Peru: 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 48.MINSA . Resolución Ministerial N° 209-2021-MINSA-Ejecutar el Acuerdo de Fabricación y Suministro Suscrito con la Empresa Pfizer S.A. Ministerio de Salud; Lima, Peru: 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 49.MINSA . Resolución Ministerial N° 443-2021-MINSA-Encargar a CENARES en el Marco de Acuerdo de Compromisos Gestione Autorización Sanitaria. Ministerio de Salud; Lima, Peru: 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 50.MINSA Coronavirus: Vacunas contra la COVID-19 en el Perú. [(accessed on 23 November 2021)]. Available online: https://www.gob.pe/11571-coronavirus-vacunas-contra-la-covid-19-en-el-peru.
- 51.RPP Digemid Otorga Registro Sanitario Condicional a Vacuna de Pfizer Contra la COVID-19. [(accessed on 23 November 2021)]. Available online: https://rpp.pe/peru/actualidad/coronavirus-en-peru-digemid-otorga-registro-sanitario-condicional-a-vacuna-de-pfizer-contra-la-covid-19-noticia-1318775?ref=rpp.
- 52.CenadIM La DIGEMID Otorga Autorización Excepcional para la Importación y Uso de la Vacuna COVID 19 AstraZeneca (ChAdOx1-S [recombinant]) [(accessed on 23 November 2021)]. Available online: https://bvcenadim.digemid.minsa.gob.pe/noticias/422-la-digemid-otorga-autorizacion-excepcional-para-la-importacion-y-uso-de-la-vacuna-covid-19-astrazeneca-chadox1-s-recombinant.
- 53.DIGEMID Ministerio de Salud Autorizó el Registro Sanitario Condicional de la Vacuna contra la COVID-19 de la Farmacéutica Johnson & Johnson. [(accessed on 23 November 2021)]. Available online: https://www.digemid.minsa.gob.pe/noticias/2021/07/ID=1912/ministerio-de-salud-autorizo-el-registro-sanitario-condicional-de-la-vacuna-contra-la-covid-19-de-la-farmaceutica-johnson-johnson.
- 54.DIGEMID Digemid del Ministerio de Salud Otorga Registro Sanitario Condicional a la Vacuna contra la COVID-19 de Sinopharm. [(accessed on 23 November 2021)]. Available online: https://www.digemid.minsa.gob.pe/noticias/2021/08/ID=2478/digemid-otorga-registro-sanitario-condicional-a-la-vacuna-contra-la-covid-19-de-sinopharm.
- 55.MINSA . Resolución Ministerial N° 161-2021-MINSA-Modificar el Rubro “Fases de Vacunación” del Plan Nacional de Vacunación contra la COVID-19. Ministerio de Salud; Lima, Peru: 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 56.MINSA . Resolución Ministerial N° 139-2021-MINSA-Conformación de un Equipo Consultivo de Alto Nivel. Ministerio de Salud; Lima, Peru: 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lope P.C., Carracedo S., Romani F. The regulation of COVID-19 clinical trials in Peru. Rev. Peru Med. Exp. Salud Publica. 2021;38:171–177. doi: 10.17843/rpmesp.2021.381.6627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kenyon G. Vacuna-gate escalates in Peru. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021;21:463. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00157-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Mayta-Tristán P., Aparco J.P. Use of experimental vaccine outside of clinical trial: The “Vacunagate” case. Rev. Peru Med. Exp. Salud Publica. 2021;38:203–205. doi: 10.17843/rpmesp.2021.382.8694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Mayta-Tovalino F., Munive-Degregori A., Mendoza R., Alvitez-Temoche D. Vacunagate scandal and its possible impact on the vaccination against COVID-19 of health professionals in Peru. J. Int. Oral Health. 2021;13:310–311. doi: 10.4103/jioh.jioh_49_21. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Chauvin L. Peruvian COVID-19 vaccine scandal spreads. Lancet. 2021;397:783. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00508-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Collave Garcia Y. ‘Vacunagate’ ¿Cómo Afecta a la Ciencia Peruana el Escándalo de las Vacunas Extra de Sinopharm? [(accessed on 24 November 2021)]. Available online: https://elcomercio.pe/tecnologia/ciencias/vacunagate-como-afecta-el-escandalo-de-las-vacunas-extra-de-sinopharm-a-la-ciencia-peruana-noticia/
- 63.Cabezas-Sanchez C., Hurtado-Roca Y., Suárez-Moreno V. Peru to punish bending of clinical-trial rules. Nature. 2021;595:650. doi: 10.1038/d41586-021-02056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ritchie H., Mathieu E., Rodes-Guirao L., Appel C., Giattino C., Ortiz-Ospina E., Hasell J., Macdonald B., Baltekian D., Roser M. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Vaccinations. [(accessed on 1 November 2021)]. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinations.
- 65.Institute of Global Health Innovation Covid-19: Global Attitudes towards a COVID-19 Vaccine; Covid Data Hub. [(accessed on 1 November 2021)]. Available online: https://www.imperial.ac.uk/media/imperial-college/institute-of-global-health-innolvation/GlobalVaccineInsights_ICL-YouGov-Covid-19-Behaviour-Tracker_20210520_v2.pdf.
- 66.OCU Encuesta OCU: Los Españoles y la Vacuna. [(accessed on 1 November 2021)]. Available online: https://www.ocu.org/salud/medicamentos/noticias/encuesta-vacuna-covid.
- 67.Faasse K., Newby J. Public Perceptions of COVID-19 in Australia: Perceived Risk, Knowledge, Health-Protective Behaviors, and Vaccine Intentions. Front. Psychol. 2020;11:551004. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.551004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Volkman J.E., Hokeness K.L., Morse C.R., Viens A., Dickie A. Information source’s influence on vaccine perceptions: An exploration into perceptions of knowledge, risk and safety. J. Commun. Healthc. 2021;14:50–60. doi: 10.1080/17538068.2020.1793288. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Urrunaga-Pastor D., Bendezu-Quispe G., Herrera-Añazco P., Uyen-Cateriano A., Toro-Huamanchumo C.J., Rodriguez-Morales A.J., Hernandez A.V., Benites-Zapata V.A. Cross-sectional analysis of COVID-19 vaccine intention, perceptions and hesitancy across Latin America and the Caribbean. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2021;41:102059. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2021.102059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Gutiérrez-Zevallos J.D., Espíritu-Martínez L.B. COVID-19: Vaccination in a developing country. J. Public Health. 2021;43:e362–e363. doi: 10.1093/pubmed/fdab072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Sallam M. COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy Worldwide: A Concise Systematic Review of Vaccine Acceptance Rates. Vaccines. 2021;9:160. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9020160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Aiken L.R. Three Coefficients for Analyzing the Reliability and Validity of Ratings. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1985;45:131–142. doi: 10.1177/0013164485451012. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Naderifar M., Goli H., Ghaljaei F. Snowball Sampling: A Purposeful Method of Sampling in Qualitative Research. Strides Dev. Med. Educ. 2017;14:e67670. doi: 10.5812/sdme.67670. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Harapan H., Wagner A.L., Yufika A., Winardi W., Anwar S., Gan A.K., Setiawan A.M., Rajamoorthy Y., Sofyan H., Mudatsir M. Acceptance of a COVID-19 Vaccine in Southeast Asia: A Cross-Sectional Study in Indonesia. Front. Public Health. 2020;8:381. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Malik A.A., McFadden S.M., Elharake J., Omer S.B. Determinants of COVID-19 vaccine acceptance in the US. EClinicalMedicine. 2020;26:100495. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Costa Aponte F. Resultados Definitivos de los Censos Nacionales 2017. INEI; Lima, Peru: 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 77.Murphy J., Vallières F., Bentall R.P., Shevlin M., McBride O., Hartman T.K., McKay R., Bennett K., Mason L., Gibson-Miller J., et al. Psychological characteristics associated with COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy and resistance in Ireland and the United Kingdom. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:29. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20226-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Seale H., Heywood A.E., Leask J., Sheel M., Durrheim D.N., Bolsewicz K., Kaur R. Examining Australian public perceptions and behaviors towards a future COVID-19 vaccine. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021;21:120. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-05833-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Al-Ayyadhi N., Ramadan M.M., Al-Tayar E., Al-Mathkouri R., Al-Awadhi S. Determinants of Hesitancy Towards COVID-19 Vaccines in State of Kuwait: An Exploratory Internet-Based Survey. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy. 2021;14:4967–4981. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S338520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Mohammed R., Nguse T.M., Habte B.M., Fentie A.M., Gebretekle G.B. COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among Ethiopian healthcare workers. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0261125. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Gallè F., Sabella E.A., Roma P., De Giglio O., Caggiano G., Tafuri S., Da Molin G., Ferracuti S., Montagna M.T., Liguori G., et al. Knowledge and Acceptance of COVID-19 Vaccination among Undergraduate Students from Central and Southern Italy. Vaccines. 2021;9:638. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9060638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Wu J., Li Q., Silver Tarimo C., Wang M., Gu J., Wei W., Ma M., Zhao L., Mu Z., Miao Y. COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy Among Chinese Population: A Large-Scale National Study. Front. Immunol. 2021;12:781161. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.781161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Kanyanda S., Markhof Y., Wollburg P., Zezza A. Acceptance of COVID-19 vaccines in sub-Saharan Africa: Evidence from six national phone surveys. BMJ Open. 2021;11:e055159. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-055159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Altulahi N., AlNujaim S., Alabdulqader A., Alkharashi A., AlMalki A., AlSiari F., Bashawri Y., Alsubaie S., AlShahrani D., AlGoraini Y. Willingness, beliefs, and barriers regarding the COVID-19 vaccine in Saudi Arabia: A multiregional cross-sectional study. BMC Fam. Pract. 2021;22:247. doi: 10.1186/s12875-021-01606-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Bronstein M.V., Kummerfeld E., MacDonald A., III, Vinogradov S. Willingness to vaccinate against SARS-CoV-2: The role of reasoning biases and conspiracist ideation. Vaccine. 2021 doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.11.079. in press . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Zein S., Abdallah S.B., Al-Smadi A., Gammoh O., Al-Awaida W.J., Al-Zein H.J. Factors associated with the unwillingness of Jordanians, Palestinians and Syrians to be vaccinated against COVID-19. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021;15:e0009957. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Caycho-Rodríguez T., Carbajal-León C., Vivanco-Vidal A., Saroli-Araníbar D. Intention to vaccinate against COVID-19 in Peruvian older adults. Rev. Esp. Geriatr. Gerontol. 2021;56:245–246. doi: 10.1016/j.regg.2021.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Herrera-Añazco P., Uyen-Cateriano A., Urrunaga-Pastor D., Bendezu-Quispe G., Toro-Huamanchumo C.J., Rodríguez-Morales A.J., Hernández A.V., Benites-Zapata V.A. Prevalencia y factores asociados a la intención de vacunarse contra la COVID-19 en el Perú. Rev. Peru. Med. Exp. Salud Publica. 2021;38:381–390. doi: 10.17843/rpmesp.2021.383.7446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Corrales C., Alberto J.M. Percepciones de la Aceptación de la Vacuna contra el COVID-19 en Personas Que Acuden a un Mercado Popular en Arequipa 2021. Universidad Nacional de San Agustín de Arequipa; Arequipa, Peru: 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 90.Caycho-Rodríguez T., Tomás J.M., Carbajal-León C., Vilca L.W., Reyes-Bossio M., Intimayta-Escalante C., Vivanco-Vidal A., Saroli-Araníbar D., Esteban R.F.C., White M. Sociodemographic and Psychological Predictors of Intention to Receive a COVID-19 Vaccine in Elderly Peruvians. Trends Psychol. 2021;21:1–18. doi: 10.1007/s43076-021-00099-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Serpa Barrientos A., Tito-Huamani P.L., Soria Qui Jaite J.J., Pena Tomas B.G., Geraldo Campos L.A. Attitude towards COVID-19 Vaccination in the Peruvian Population. J. Res. Med. Dent. Sci. 2021;9:1–10. [Google Scholar]
- 92.Alabdulla M., Reagu S.M., Al-Khal A., Elzain M., Jones R.M. COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy and attitudes in Qatar: A national cross-sectional survey of a migrant-majority population. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses. 2021;15:361–370. doi: 10.1111/irv.12847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Sanche S., Lin Y.T., Xu C., Romero-Severson E., Hengartner N., Ke R. High Contagiousness and Rapid Spread of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26:1470–1477. doi: 10.3201/eid2607.200282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Wang J., Jing R., Lai X., Zhang H., Lyu Y., Knoll M.D., Fang H. Acceptance of COVID-19 Vaccination during the COVID-19 Pandemic in China. Vaccines. 2020;8:482. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8030482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Ditekemena J.D., Nkamba D.M., Mutwadi A., Mavoko H.M., Siewe Fodjo J.N., Luhata C., Obimpeh M., Van Hees S., Nachega J.B., Colebunders R. COVID-19 Vaccine Acceptance in the Democratic Republic of Congo: A Cross-Sectional Survey. Vaccines. 2021;9:153. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9020153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Kuter B.J., Browne S., Momplaisir F.M., Feemster K.A., Shen A.K., Green-McKenzie J., Faig W., Offit P.A. Perspectives on the receipt of a COVID-19 vaccine: A survey of employees in two large hospitals in Philadelphia. Vaccine. 2021;39:1693–1700. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.02.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Caserotti M., Girardi P., Rubaltelli E., Tasso A., Lotto L., Gavaruzzi T. Associations of COVID-19 risk perception with vaccine hesitancy over time for Italian residents. Soc. Sci. Med. 2021;272:113688. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.113688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Coustasse A., Kimble C., Maxik K. COVID-19 and Vaccine Hesitancy: A Challenge the United States Must Overcome. J. Ambul. Care Manag. 2021;44:71–75. doi: 10.1097/JAC.0000000000000360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Verger P., Scronias D., Dauby N., Adedzi K.A., Gobert C., Bergeat M., Gagneur A., Dubé E. Attitudes of healthcare workers towards COVID-19 vaccination: A survey in France and French-speaking parts of Belgium and Canada, 2020. Eurosurveillance. 2021;26:2002047. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.3.2002047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Casapia J.P. Crisis por el Coronavirus Aumentó las Desigualdades en el Perú, Banco Mundial. 2021. [(accessed on 1 November 2021)]. Available online: https://www.bancomundial.org/es/news/press-release/2020/09/08/crisis-por-el-coronavirus-aumento-las-desigualdades-en-el-peru.
- 101.Phadke V.K., Bednarczyk R.A., Salmon D.A., Omer S.B. Association Between Vaccine Refusal and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases in the United States: A Review of Measles and Pertussis. JAMA. 2016;315:1149–1158. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.MINSA Vacunación COVID-19-Perú. [(accessed on 21 December 2021)]. Available online: https://www.minsa.gob.pe/reunis/data/vacunas-covid19.asp.
- 103.MINSA Covid-19: Desde Este Viernes 10 de Diciembre Será Obligatorio el Carné de Vacunación. [(accessed on 21 December 2021)]. Available online: https://elperuano.pe/noticia/135041-covid-19-desde-este-viernes-10-de-diciembre-sera-obligatorio-el-carnet-de-vacunacion.
- 104.Gestión COVID: ¿Se Llegará al 80% de Cobertura de Población Vacunada Antes de Culminar el 2021? [(accessed on 21 December 2021)]. Available online: https://gestion.pe/peru/resumen-del-ano-2021-covid-19-peru-llegara-al-80-de-la-cobertura-poblacion-vacunada-antes-de-culminar-el-2021-minsa-nndc-noticia/
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.