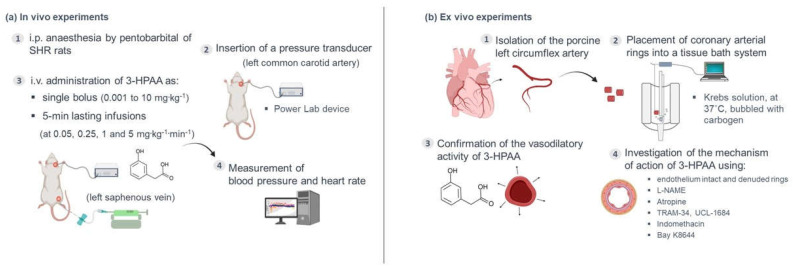
Figure 2.
Graphical scheme of the performed experiments. The first panel (a) depicts the in vivo experiments performed: (1) spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) were anesthetized i.p. by pentobarbital (50 mg·kg−1); (2) a pressure transducer was linked to the left common carotid artery; (3) in one set of experiments, 3-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (3-HPAA) was administered as a single bolus, whereas in another set, it was given as four subsequent 5 min lasting infusions; (4) arterial blood pressure and heart rate were recorded (see Section 2 for details). The second panel (b) depicts the ex vivo experiments performed: (1) the left circumflex porcine coronary artery was isolated and cut into small arterial rings; (2) the rings were placed into an isolated tissue bath of modular type and kept in the Krebs solution at 37 °C, under adequate oxygenation (carbogen 95% O2/5% CO2); (3) the rings were precontracted with KCl and the vasodilatory activity of 3-HPAA was confirmed by measuring changes in isometric tension developed by 3-HPAA (0.1, 0.5 and 1 mM); (4) in a separate set of experiments, the mechanism of action of 3-HPAA was explored by using intact endothelium and denuded rings and a series of inhibitors/antagonists/activators (L-NAME, TRAM-34, UCL-1684, indomethacin, atropine, Bay K8644).