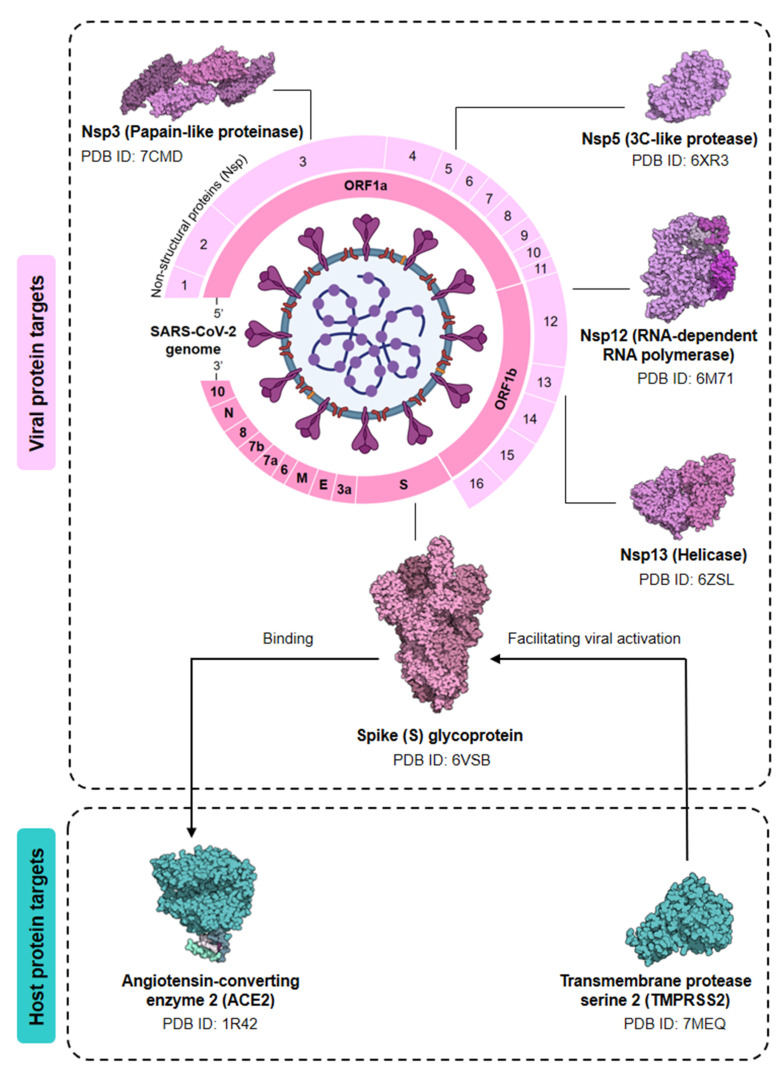
Figure 3.
The structures of possible viral and host protein targets could be inhibited by probiotic metabolites to prevent SARS-CoV-2. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), which locates on host cells, is the primary cell entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2 [174]; transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2), which facilitate viral activation, is a cell surface protein expressed in the respiratory and GI tract [175]. SARS-CoV-2 requires both ACE2 and TMPRSS2 for entry into cells [176]. Spike (S) protein involves mainly in the receptor recognition and viral entry of SARS-CoV-2 [177]; Papain-like proteinase (PLpro) has an essential role in viral polyprotein cleavage and maturation [178]; 3C-like main protease (3CLpro) plays a key role in control viral replication [179]; RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), a viral enzyme, involves in viral RNA replication in host cells [180]; Nsp13 is a helicase requiring adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to translocate and unwind SARS-CoV-2 RNA [181].