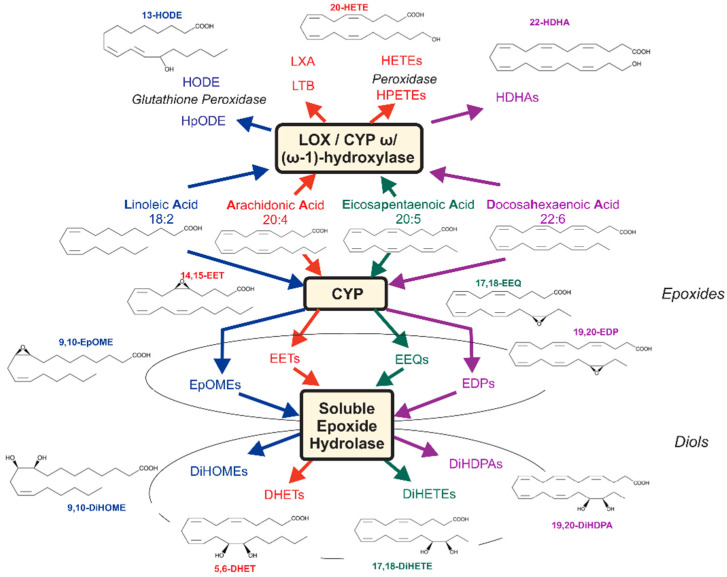
Figure 1.
Assessment of cytochrome P450 epoxygenase (CYP) and 12- and 15-lipoxygenase (LOX)/CYP (omega-1)-hydroxylase pathways in response to hemodialysis treatment. Arachidonic (AA), linoleic (LA), eicosapentaenoic (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acids (DHA) are converted to epoxyoctadecenoic acids (EpOMEs, e.g., 9,10-EpOME), epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EEQs, e.g., 17,18-EEQ), epoxyeicosatrienoic acid (EETs, e.g., 5,6-EET), and epoxydocosapentaenoic acids (EDPs, e.g., 19,20-EDP) by CYP epoxygenase, respectively. EpOMEs, EETs, EEQs, and EDPs are primarily converted to dihydroxyctadecenoic acids (DiHOMEs), dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids (DHETs, e.g., 5,6-DHET), dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (DiHETEs, e.g., 17,18-DiHETE), and dihydroxydocosapentaenoic acids (DiHDPAs, e.g., 19,20-DiHDPA) by the soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH). LA, EPA, AA, and DHA are converted to hydroperoxylinoleic acids (HpODEs), hydroxyoctadecadienoic acids (HODEs), leukotriene B (LTB), lipoxin A (LXA), hydroxydocosahexaenoic acids (HDHAs), hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HPETEs), and hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HETEs) by LOX, CYP omega/(omega-1)-hydroxylase, and peroxidase pathways. The metabolites measured in these metabolic pathways follow the changes observed in LA, AA, EPA, and DHA metabolism, respectively. Modified from [4].