Abstract
Bismuth vanadate (BiVO4) has been widely investigated as a photocatalyst or photoanode for solar water splitting, but its activity is hindered by inefficient cocatalysts and limited understanding of the underlying mechanism. Here we demonstrate significantly enhanced water oxidation on the particulate BiVO4 photocatalyst via in situ facet-selective photodeposition of dual-cocatalysts that exist separately as metallic Ir nanoparticles and nanocomposite of FeOOH and CoOOH (denoted as FeCoOx), as revealed by advanced techniques. The mechanism of water oxidation promoted by the dual-cocatalysts is experimentally and theoretically unraveled, and mainly ascribed to the synergistic effect of the spatially separated dual-cocatalysts (Ir, FeCoOx) on both interface charge separation and surface catalysis. Combined with the H2-evolving photocatalysts, we finally construct a Z-scheme overall water splitting system using [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− as the redox mediator, whose apparent quantum efficiency at 420 nm and solar-to-hydrogen conversion efficiency are optimized to be 12.3% and 0.6%, respectively.
Subject terms: Photocatalysis, Artificial photosynthesis, Nanoscale materials
Artificial photosynthesis offers an integrated means to convert light to fuel, but efficiencies are often low. Here, authors report a Z-scheme system utilizing Ir and FeCoOx co-catalysts to enhance charge separation on BiVO4 facets that achieves high quantum efficiencies for overall water splitting.
Introduction
Particulate photocatalytic overall water splitting (OWS) based on inorganic semiconductor materials with relative good photostability has been demonstrated as one of the most promising ways of realizing scalable and economically viable solar hydrogen production to address energy- and environment-related issues1–12. To achieve high solar-to-hydrogen (STH) energy conversion efficiency, it is necessary to increase the quantum efficiency of photocatalytic OWS over a wide range of wavelengths, particularly the use of visible light11,12. However, extended visible light utilization is generally accompanied by a decreased driving force of the photogenerated carriers to make charge separation extremely difficult. Furthermore, the construction of OWS systems faces serious challenges originating from the sluggish kinetics of water oxidation involving uphill energy barrier and multiple electron transfer13. Consequently, visible-light-driven photocatalytic OWS systems are not only limited in number, but also show lower efficiency than those driven by ultraviolet light14–19. Accordingly, it is highly desirable to precisely design and modify photocatalysts with efficient visible light utilization for promotion of water oxidation.
N-type monoclinic bismuth vanadate (BiVO4) has emerged as one of the most promising visible-light-responsive photocatalysts and photoanodes for water oxidation since Kudo’s report in 199820–28. Owing to its advantages, such as efficient light absorption in the visible light region, good carrier mobility, controllable exposed facets, and non-toxic properties, BiVO4 semiconductor has been widely and successfully employed as the water oxidation photocatalyst for the assembly of Z-scheme OWS systems using solid conductor (i.e., Au, reduced graphene oxide) or redox couple (i.e., Fe3+/2+, [Fe(CN)6]3−/4−) as electron mediator15,16,29–31. Specifically, our previous work revealed that the spatial separation of photogenerated electrons and holes can be achieved on the anisotropic facets of BiVO432, based on which reduction and oxidation cocatalysts are selectively deposited on different facets to remarkably promote its water oxidation and the efficiency of OWS under visible light16. Although the BiVO4 photocatalyst has been widely investigated for the assembly of artificial Z-scheme OWS systems, the apparent quantum efficiency (AQE) and STH conversion efficiency achieved so far are still considerably below what is expected. This is mainly due to the shortage of effective cocatalyst regulation and the lack of in-depth understanding of the microscopic mechanisms behind it33,34. Notably, for the assembly of the redox couple-mediated Z-scheme OWS system shown in Fig. 1, the loading of effective cocatalysts is extremely important not only for the acceleration of interfacial electron transfer between the H2-evolving photocatalyst (HEP) and the O2-evolving photocatalyst (OEP), but also for the promotion of surface reaction kinetics of water splitting35–38. Therefore, it is a long-term task to develop innovative cocatalysts and unravel their structures as well as influence mechanism on water splitting.
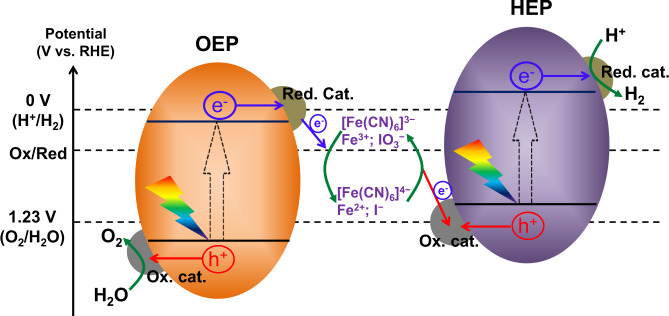
Fig. 1. The energy diagram for a two-step photoexcitation (also called Z-scheme) system with an aqueous redox mediator for overall water splitting.
Red. cat.: reduction cocatalyst; Ox. cat.: oxidation cocatalyst; RHE: reversible hydrogen electrode; HEP: H2-evolving photocatalyst; OEP: O2-evolving photocatalyst.
In this study, we address the sluggish water oxidation of BiVO4 via in situ photodeposition of dual innovative cocatalysts, with emphasis on elucidating the local structures of the cocatalysts and the mechanism of promotion of water oxidation. We demonstrate that the nanocomposite of FeOOH and CoOOH (denoted as FeCoOx) in situ formed on the {110} facet of BiVO4 not only lowers Gibbs free energy barrier of water oxidation, but also makes a better promotion on the electron transfer as well as charge separation compared with the commonly used CoOx cocatalyst. Furthermore, the Ir cocatalyst in situ deposited on the {010} facet of BiVO4 was found to exhibit superior reduction ability of [Fe(CN)6]3− ions to our previously reported Au. Based on the facet-selective loading of the innovative dual-cocatalysts, the evolution rate of O2 on the BiVO4 was significantly enhanced, and a particulate Z-scheme OWS system with an AQE of 12.3% at 420 nm and a STH of 0.6%, was finally fabricated using [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− as a redox mediator and ZrO2/TaON or MgTa2O6−xNy/TaON as the HEP. Our results demonstrate the importance and effectiveness of developing suitable cocatalysts for enhancing interfacial charge separation and surface water oxidation kinetics in promoting solar energy conversion.
Results
Structural characterizations of cocatalysts photodeposited
The anisotropic BiVO4 with exposed {010} and {110} facets was prepared according to our previous study39. The Ir nanoparticles and FeCoOx nanocomposite were in situ photodeposited on the surface of BiVO4 from an aqueous solution containing the precursors K2IrCl6, CoSO4, and redox [Fe(CN)6]3− ions. The as-obtained sample is hereafter denoted as Ir-FeCoOx/BiVO4. As expected from our previous findings on the spatial separation of photogenerated electrons and holes on the anisotropic BiVO432, the Ir nanoparticles, and FeCoOx nanocomposite were clearly observed to be selectively deposited on the {010} and {110} facets of BiVO4, respectively (Fig. 2a, b). For comparison, the in situ photodeposition of single Ir or CoOx particles on BiVO4 was similarly obtained (denoted as Ir/BiVO4 and CoOx/BiVO4), and the sample was characterized by field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) to further confirm the facet-selective deposition (Supplementary Fig. 1). It should be noted that the morphology of the cocatalysts located on the {110} facet of Ir-FeCoOx/BiVO4 (Fig. 2b) is clearly different from that of the CoOx/BiVO4 sample (Supplementary Fig. 1b), demonstrating the possible interaction between Fe and Co-based compounds. And the change in the long wavelength range of UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra (DRS) can confirm the successful deposition of the dual-cocatalysts (Supplementary Fig. 2). The deposited Ir species were verified to exist as metallic Ir nanoparticles by means of X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy (Supplementary Fig. 3) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy image (Supplementary Fig. 4).
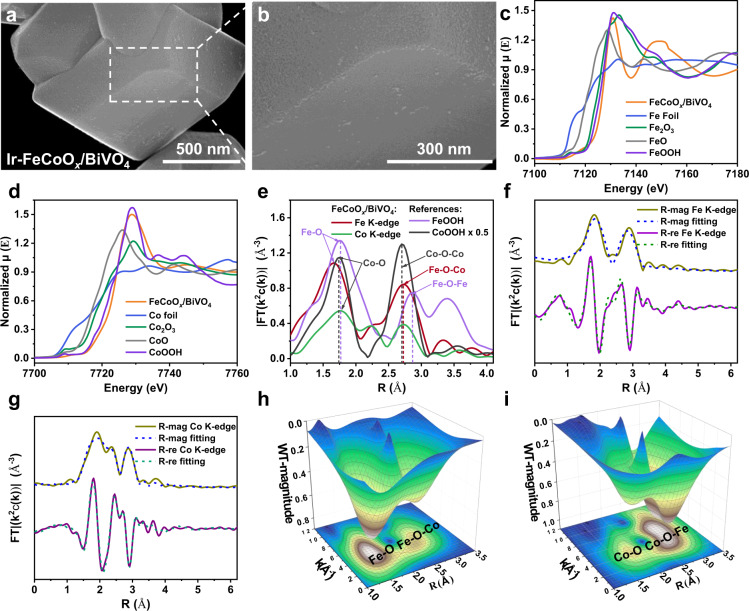
Fig. 2. Morphology and structural characterizations of typical samples.
a, b FESEM images of the Ir-FeCoOx/BiVO4 with different magnification times. c–i Structural characterizations of the FeCoOx/BiVO4 sample together with references: c Normalized Fe K-edge XANES μ(E) spectra. d Normalized Co K-edge XANES μ(E) spectra. e Fe K-edge and Co K-edge radial distance χ(R) space spectra. f Fourier-transformed (FT)-Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) fitting curves at R space of Fe K-edge. g FT-EXAFS fitting curves at R space of Co K-edge. h Fe K-edge 3D contour wavelet transform. i Co K-edge 3D contour wavelet transform.
To unravel the formation of the FeCoOx nanocomposite on the {110} facets of BiVO4, the existing state and dispersion of both Fe and Co elements on FeCoOx/BiVO4 (free of Ir nanoparticles to rule out its possible interference during characterization) were first analyzed. According to the elemental mapping results shown in Supplementary Fig. 5, both Fe and Co species are similarly located and dispersed, accompanied by the existence of O, which further demonstrates that Co and Fe combine together in the form of oxidation state during the photo-oxidation process. The deposition of Fe should result from redox ions in the reaction solution. The coexistence of both Fe and Co can be further revealed by electron energy loss spectroscopy analysis (Supplementary Fig. 6). And their oxidation states can be confirmed to be Fe3+ and Co3+ by the Fe and Co K-edge XANES measurements through comparing with the reference materials (Fig. 2c, d, respectively).
Second, the radial distance space spectra χ(R) of Fe and Co in FeCoOx/BiVO4 and their corresponding references were analyzed, which provides more convincing support for the formation of nanocomposite. As shown in Fig. 2e and Supplementary Fig. 7, the peaks located at approximately 2.72 Å assigned to the Fe–O–Co bond are consistently observed in both the Fe and Co K-edge of the FeCoOx/BiVO4 sample, but no scattering path signals attributing to the Co–Co bond (2.41 Å) from Co foil, Fe–Fe bond (2.47 Å) from Fe foil, Co–O–Co bond (2.69 Å) from CoOOH, or Fe–O–Fe bond (2.86 Å) from FeOOH can be observed. This clearly reveals that the formation of nanocomposite is a homogeneous phase of bimetallic hydroxide, instead of single-phase Fe or Co hydroxides. It should be pointed out that the possible nanocomposite of Fe2O3 and Co2O3 can be ruled out by comparing the fingerprint feature pattern of normalized XANES μ(E) spectra (Fig. 2c, d and Supplementary Fig. 8a, b) and the first derivative of the normalized XANES μ(E) spectra (Supplementary Fig. 8c, d). In particular, as shown in Supplementary Fig. 8c, d, the peak positions of FeCoOx/BiVO4 are closer to the FeOOH and CoOOH references. Based on these results, the phase species of the FeCoOx on the surface of BiVO4 sample can be deduced to be more similar to FeOOH/CoOOH with respect to Fe2O3/Co2O3. In addition, compared with the corresponding single-phase hydroxides FeOOH and CoOOH, Fe/BiVO4 sample exhibits much shorter Fe–O bond and longer Co–O bond, and the length of Co–O–Fe bond is between Co–O–Co and Fe–O–Fe (Fig. 2e). This demonstrates the existence of electron transfer and a strong interaction between Fe and Co in the FeCoOx/BiVO4 sample, providing further proof about the formation of the nanocomposite.
Third, the formation of the nanocomposite can be further verified by the results of quantitative χ(R) space spectra fitting and wavelet transform of χ(k). As seen in Supplementary Table 1, Fe–O–Co bond with similar coordination numbers (Fe–O–Co: 2 at ca. 2.745 Å in Fe K-edge; Co–O–Fe: 2 at ca. 2.761 Å in Co K-edge) can be confirmed. The good fitting results of χ(R) and χ(k) space spectra (Fig. 2f, g and Supplementary Fig. 9) with reasonable R-factors and the obtained fitting parameters (Supplementary Table 1) provide a quantitative illustration of the existence of Fe–O–Co bond originating from the nanocomposite structure. As similarly revealed in Fig. 2h, i, the Fe–O–Co bond located at [χ(k), χ(R)] of [4.2, 2.74] or Co–O–Fe bond ([6.4, 2.76]) as well as the Fe–O bond ([4.8, 1.64]) or Co–O bond ([4.2, 1.88]) with two scattering path signal can be observed for both Fe and Co K-edge wavelet transform of χ(k) spectra of FeCoOx/BiVO4, but the characteristic scattering path signal of Fe–Fe bond ([8.4, 2.52]), Co–Co bond ([7.8, 2.42]), Fe–O–Fe bond ([5.6 2.82]) or Co–O–Co bond ([6.8, 2.78]) is not observed as similarly as the reference sample (Supplementary Fig. 10).
Effect of reduction and oxidation cocatalysts
As shown in Fig. 1, the water oxidation process of OEP is strongly dependent on both the reduction and oxidation cocatalysts. Therefore, understanding the effect of deposited Ir and FeCoOx cocatalysts is highly desirable. As depicted in Fig. 3a, the ability of the deposited metallic Ir to reduce [Fe(CN)6]3− ions was evaluated and found to exhibit a much higher cathode current than that of our previously reported Au nanoparticles on BiVO416, indicating its superior performance in activating and reducing the [Fe(CN)6]3− ions. In addition, the deposition of Ir or Au cocatalyst on the surface of BiVO4 can significantly decrease the charge-transfer resistance (Rct) across the semiconductor/electrolyte interface (Fig. 3b), further revealing the effectiveness of the deposited cocatalysts in accelerating the electron transfer from BiVO4 to the [Fe(CN)6]3− ions (values of Rs and Rct listed in Supplementary Table 2). Meanwhile, the promotion effect of Ir is better than that of Au.
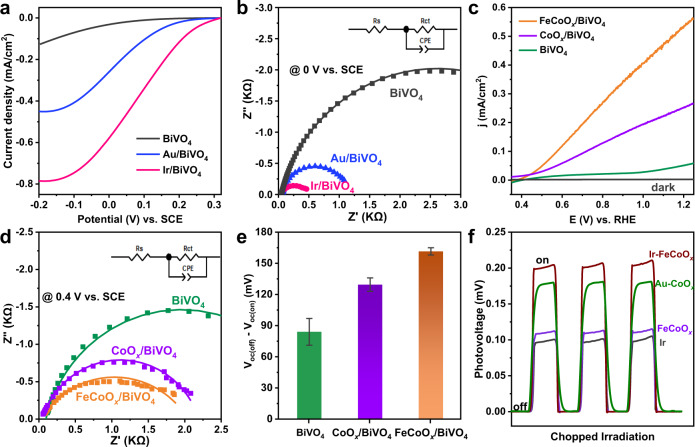
Fig. 3. Electrochemical measurements and characterizations of typical samples.
a Linear sweep voltammetry curves of typical samples in the 100 mM sodium phosphate buffer solution (pH 6.0) containing 5 mM K3[Fe(CN)6]. b EIS spectra of typical samples in a 100 mM sodium phosphate buffer solution (pH 6.0) containing 5 mM K3[Fe(CN)6]. SCE, saturated calomel electrode. c Photocurrent density-potential curves of BiVO4, CoOx/BiVO4, and FeCoOx/BiVO4. d EIS spectra of BiVO4, CoOx/BiVO4, and FeCoOx/BiVO4 in a 100 mM sodium phosphate buffer solution (pH 6.0). e Comparison of difference of OCPs on the BiVO4, CoOx/BiVO4, and FeCoOx/BiVO4 under dark and illumination conditions. Measurements were taken at least three times for separate samples and average values are presented with the standard deviation as the error bar. f Comparison of promotion effect of cocatalysts on the SPV values of the BiVO4 photocatalyst under chopped visible light irradiation.
To determine the effect of the FeCoOx nanocomposite, the efficiencies of charge separation and injection (denoted as ηsep and ηinj, respectively) on the FeCoOx/BiVO4 photoanode (CoOx/BiVO4 and BiVO4 as references) were evaluated by referring to a previous photoelectrochemical analysis22. Figure 3c and Supplementary Fig. 11a show that the current of the BiVO4 photoanode can be remarkably promoted after the deposition of FeCoOx and CoOx in both cases, with and without the use of a hole scavenger, among which FeCoOx exhibits a much better promotion effect than CoOx. On this basis, both ηsep and ηinj on the FeCoOx/BiVO4 photoanode were calculated to be higher than that of the CoOx/BiVO4 photoanode (Supplementary Fig. 11c, d), demonstrating the better promotion effect of the FeCoOx nanocomposite on both the separation of photogenerated carriers and the injection of holes into the reaction solution (i.e., surface reaction) with respect to CoOx. The excellent promotion of FeCoOx on the surface reaction can be further supported by the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) results given in Fig. 3d and Supplementary Table 3, based on which the Rct resistance on the FeCoOx/BiVO4 electrode is the smallest among the three electrodes investigated. On the other hand, the superior promotion effect of FeCoOx on the charge separation can also be evidenced by its larger open-circuit potential (OCP) on the FeCoOx/BiVO4 compared with CoOx/BiVO4 (Fig. 3e). Based on the previous result that a larger difference of OCPs under dark and illumination conditions corresponds to more intense band bending40, therefore the FeCoOx/BiVO4 sample can be deduced to own a more intense band bending than the CoOx/BiVO4 sample, leading to a significantly improved ηsep and the more intense band bending should result from the p-n heterojunction between FeCoOx and BiVO441.
Encouraged by the understanding of the functionalities of both reduction and oxidation cocatalysts (i.e., Ir and FeCoOx), the synergistic effect of dual-cocatalysts on the charge separation was examined using the surface photovoltage (SPV) spectrum. As shown in Fig. 3f, the sample with both Ir and FeCoOx deposited exhibits a greater SPV amplitude with respect to the sample with single Ir or FeCoOx loaded. It should be mentioned that a much better promotion effect is also observed for the sample with facet-selective deposition of Ir and FeCoOx compared to that with facet-selective deposition of Au and CoOx. These results reveal the importance of both facet-selective deposition of dual-cocatalysts and the development of innovative cocatalysts for maximizing the promotion effect.
Density functional theory calculations on the O2-evolving reaction
Density functional theory (DFT) calculations were performed to further elucidate the microscopic mechanism of the promotion effect of the FeCoOx cocatalyst on the O2-evolving reaction (OER) from the viewpoint of both surface catalysis and interfacial charge transfer. As shown in Fig. 4a–c, the CoOx–FeOx–CoOx–FeOx and CoOx–CoOx–CoOx–CoOx clusters were simply extracted and placed on the {110} facets of BiVO4 to simulate the FeCoOx/BiVO4 and CoOx/BiVO4 interfaces, respectively, which origin from the structure of EXAFS measurement. And the schematic of the whole OER mechanism on the FeCoOx/BiVO4 and CoOx/BiVO4 is given in Supplementary Fig. 12 and illustrated in detail in supporting information. Fig. 4d and e presents the Gibbs free energy change diagram of the four elementary steps of OER on the surface of FeCoOx/BiVO4 and CoOx/BiVO4, during which the Co and Fe sites on FeCoOx/BiVO4 were mainly considered as the active sites, respectively. It was demonstrated that the rate-determining step of FeCoOx/BiVO4 (Co or Fe site) and CoOx/BiVO4 is the adsorption of one OH− to form OOH∗ from O∗. The largest decrease of the Gibbs free energy barrier was observed for FeCoOx/BiVO4 (Co site), whereas the OER performance of FeCoOx/BiVO4 (Fe site) is much weaker than that of the corresponding Co site, suggesting that the Co site acts as the main OER site.
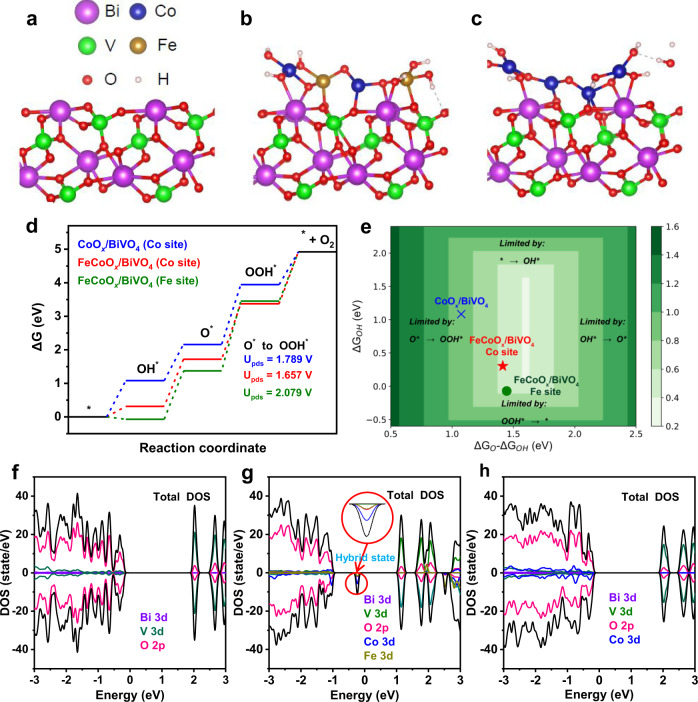
Fig. 4. Theoretical understanding of the promotion effect of the FeCoOx cocatalyst.
Visual representation of structures of BiVO4 {110} surface (a) FeCoOx/BiVO4 {110} interface (b) and CoOx/BiVO4 {110} interface (c) for the DFT calculations. d Free energy diagram for OER process on FeCoOx/BiVO4 and CoOx/BiVO4 {110} interfaces. The surface structures with various reaction intermediates are shown alongside the free energy diagram. Upds, equilibrium potential for the potential determining step. e Theoretical overpotential plot with O∗ and OH∗ binding energies as descriptors. Calculated densities of state for the BiVO4 {110} surface (f), FeCoOx/BiVO4 {110} interface (g), and CoOx/BiVO4 {110} interface (h).
Next, we plotted the calculated densities of states (DOS) of the BiVO4 {110} surface, CoOx/BiVO4 {110} interface, and FeCoOx/BiVO4 {110} interface (Fig. 4f, g, h and Supplementary Fig. 13). Both CoOx and FeCoOx are set to be located at the {110} facets of BiVO4. For the bare BiVO4 {110} surface, there is a direct bandgap about 2.1 eV between the valence band and conduction band (Fig. 4f). However, when the CoOx–FeOx–CoOx–FeOx cluster is settled on the {110} surface of BiVO4, a mixed band mainly composed of Co 3d, Fe 3d, and O 2p states emerges between the valence band and conduction band (Fig. 4g). It has been demonstrated that the localization of photoexcited holes, as well as subsequent charge separation can be promoted through the formation of mixed bands42. In addition, the DOS of the CoOx/BiVO4 {110} interface (Fig. 4h) has no similar result as that of the FeCoOx/BiVO4 {110} interface (Fig. 4g, bandgap = 2.0 eV), implying that the loading of FeCoOx on BiVO4 should have better charge separation. In order to microscopically understand the better electron transfer on the FeCoOx with respect to the CoOx, their bader charges were calculated and compared. As given in Supplementary Table 4, the changing trend of bader charge on the Co active site after introduction of Fe (increase from 1.2 a.u. in CoOx/BiVO4 to 1.3 a.u. in FeCoOx/BiVO4) is in line with the changing one of experimental valence state (Supplementary Fig. 14). Compared to the CoOx/BiVO4, the higher bader charge on the Co active site in FeCoOx/BiVO4 indicates its stronger oxidation capacity as well as more beneficial electron transfer43. In addition, as shown in Supplementary Fig. 15, the d-band center (Ed) value of Co active sites in FeCoOx/BiVO4 was calculated as −1.63 eV, which is sharply increased with respect to the CoOx/BiVO4 (−2.56 eV). This demonstrates that the electronic structure of Co active sites can be well modulated and optimized in the FeCoOx/BiVO4 due to the introduction of Fe atoms to get much stronger adsorption properties to the OER intermediates according to the d-band center theory44,45. According to previous experimental and theoretical demonstration, the Fe site is relatively inactive during the OER process46,47. So we deduce that the role of Fe is to assist in modifying the geometric and electronic structure of Co in the OER together with our results that very limited contributions of Fe 3d states are observed for the mixed band (Fig. 4g). These conclusions from DFT calculation well match with the aforementioned experimental results.
Photocatalytic performances of Z-scheme OWS
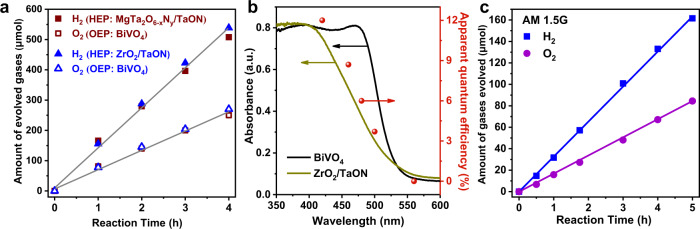
The modified BiVO4 was employed as an OEP for the assembly of efficient Z-scheme OWS systems together with ZrO2/TaON or MgTa2O6−xNy/TaON as a HEP under visible light irradiation. The HEPs were prepared and modified with cocatalysts according to previously reported procedures16,48,49, and the diffraction structure and morphology features were coarsely revealed by their powder X-ray diffraction patterns and FESEM images (Supplementary Figs. 16, 17). The contents of deposited Ir and Co on BiVO4 were optimized to be 0.8 and 0.2 wt%, respectively, via the photocatalytic O2 evolution reaction (Supplementary Figs. 18, 19). As seen in Fig. 5a, stable evolution curves of H2 and O2 with the stoichiometric molar ratio of 2:1 can be observed at the experimental region using the optimized photocatalysts, indicating the successful achievement of the OWS process. Moreover, regardless of using ZrO2/TaON or MgTa2O6−xNy/TaON as the HEP, similar OWS activities with the initial rates of H2 and O2 evolution (ca. 160 and 80 μmol/h, respectively) were separately observed, implying that the O2 evolution on BiVO4 is the rate-determining step, as similarly observed in our previous study16. It should be pointed out that when the Ir-CoOx(Imp.)/BiVO4 with Ir and Co randomly impregnated is employed as the OEP, the OWS will not be achieved owing to the significantly decreased O2-evolving activity (Supplementary Fig. 20). This indicates the importance of facet-selective deposition of dual-cocatalysts in promoting the O2-evolving activity and fabricating a successful OWS system. The multiple cycles of time-course curves shown in Supplementary Figs. 21 and 22 demonstrate the good photostability of the system constructed in this study. The AQE value of OWS as a function of absorption wavelength was found to be in good accordance with the UV-Vis DRS of the OEP and HEP, indicating that the Z-scheme OWS system is driven by visible light excitation (Fig. 5b and Supplementary Fig. 23). The optimal AQE value of OWS at 420 ± 10 nm is 12.3%, and the AQE value at the 500 ± 10 nm is about 3%, demonstrating the wide visible light utilization. According to the activity measurements under the irradiation of AM 1.5 G (Fig. 5c), the STH energy conversion efficiency was calculated to be 0.6%. To the best of our knowledge, both the AQE and STH values should be the highest among the suspending particulate photocatalytic OWS systems using inorganic semiconductor materials with visible light utilization, regardless of one-step or two-step (i.e., Z-scheme) systems.
Fig. 5. Photocatalytic activity of Z-scheme OWS.
a Time course of Z-scheme OWS on the optimized conditions under visible light irradiation. b Dependence curve of AQE value as a function of irradiation wavelength, and UV-Vis DRS of the HEP and OEP. c Time curve of Z-scheme OWS under illumination of the standard solar simulator (AM 1.5 G, 100 mW cm−2). Reaction conditions: a 50 mg OEP, 50 mg HEP (ZrO2/TaON, 1.0 wt% Rh, 1.5 wt% Cr) or 50 mg OEP, 100 mg HEP (MgTa2O6-xNy/TaON, 2.5 wt% Rh, 3.75 wt% Cr), 100 mL 25 mM sodium phosphate buffer solution (pH 6.0) containing K4[Fe(CN)6] (10 mM), 300 W xenon lamp (λ ≥ 420 nm), temperature: 288 K, Pyrex top-irradiation type. b 75 mg OEP, 75 mg HEP (ZrO2/TaON, 1.0 wt% Rh, 1.5 wt% Cr), 150 mL 25 mM sodium phosphate buffer solution (pH 6.0) containing K4[Fe(CN)6] (10 mM), 300 W xenon lamp, temperature: 298 K, Pyrex top-irradiation type. (c) 50 mg OEP, 50 mg HEP (ZrO2/TaON, 1.0 wt% Rh, 1.5 wt% Cr), 100 mL 25 mM sodium phosphate buffer solution (pH 6.0) containing K4[Fe(CN)6] (10 mM), temperature: 288 K, Pyrex top-irradiation type.
Discussion
Here, we show a highly efficient Z-scheme OWS system with benchmarked AQE and STH value over particulate inorganic semiconductor photocatalysts with visible light utilization. The success is mainly ascribed to the in situ facet-selective photodeposition of innovative dual-cocatalysts (Ir nanoparticles and FeCoOx nanocomposite), based on which the sluggish water oxidation on BiVO4 can be largely overcome. Besides the finding and structural unraveling of efficient cocatalysts, the microscopic work mechanism of both reduction and oxidation cocatalysts on the interfacial charge transfer and surface catalysis has been well elucidated respectively. These results should be encouraging and enlightening to the design and assembly of OWS systems for more efficient solar-to-chemical energy conversion.
Methods
Synthesis of modified-TaON and BiVO4
ZrO2-modified TaON (Zr/Ta = 0.1) sample and MgTa2O6−xNy/TaON (Mg/Ta = 0.15) composite were used as the HEPs. The ZrO2-modified sample was synthesized by nitridation of the ZrO2/Ta2O5 composite and the MgTa2O6−xNy/TaON was prepared by nitridation of the MgTa2O6/Ta2O5 composite under an ammonia flow (20 mL min–1) at 1123 K for 15 h by referring to the previous works48,49. BiVO4 was chosen as the OEP, which was similarly synthesized according to our previous hydrothermal process39. Typically, 10 mmol NH4VO3 and 10 mmol Bi(NO3)3·5H2O were dissolved in 2.0 M nitric acid solution, whose pH value was then adjusted to be about 0.5 with ammonia solution (25–28 wt%). The mixed solution was strongly stirred until the observation of a light yellow precipitate that was further aged for about 2 h and then transferred to a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave for 10 h hydrothermal treatment at 473 K.
Preparation of Ir/BiVO4 and CoOx/BiVO4
The deposition of Ir or CoOx on the surface of BiVO4 was carried out by the photodeposition method. Typically, 0.2 g BiVO4 powder was dispersed in deionized water containing a calculated amount of K2IrCl6 (2.0 wt%) or CoSO4 (2.0 wt%), and hole (CH3OH) or electron (NaIO3) scavenger, separately. The well-mixed solution was then irradiated by 300 W xenon lamp free of any cut-off filter for 2 h. The as-obtained powders after filtration and washing are correspondingly denoted as Ir/BiVO4 and CoOx/BiVO4, which were used for further characterizations and tests.
Preparation of FeCoOx/BiVO4 and Ir-FeCoOx/BiVO4
Both of the samples were similarly prepared by the in situ photodeposition. Meanwhile, 25 mM phosphate buffer solution (PBS, pH = 6, 50 mL) containing a calculated amount of CoSO4 and [Fe(CN)6]3− ions was prepared for the synthesis of FeCoOx/BiVO4, while 25 mM phosphate buffer solution (PBS, pH = 6, 50 mL) containing a calculated amount of K2IrCl6, CoSO4 and [Fe(CN)6]3− ions was prepared for synthesis of Ir-FeCoOx/BiVO4.
Preparation of HEP
The deposition of nanoparticulate rhodium-chromium mixed oxides (denoted as RhyCr2−yO3) as a cocatalyst was carried out by the photodeposition method. 0.2 g ZrO2-modified TaON or MgTa2O6−xNy/TaON was dispersed in 20 v% 150 mL methanol solution. A certain amount of Na3RhCl6 and K2CrO4 (1.0 wt% Rh and 1.5 wt% Cr vs. photocatalyst for ZrO2/TaON and 2.0 wt% Rh and 3.75 wt% Cr vs. photocatalyst for MgTa2O6-xNy/TaON) were added as the precursors. The deposition was carried out under the full-spectral irradiation of 300 W xenon lamp for 6 h. Whereafter, the irradiated solution was centrifuged and washed with distilled water, and then dried at 353 K for overnight to get powder for use.
Preparation of BiVO4 electrodes
The BiVO4 photoanode was prepared according to the previous work50. First of all, Bi(NO3)3·5H2O, NH4VO3, and polyvinyl alcohol were dissolved in 60% HNO3 to prepare the precursor solution. Then the precursor solution was spin-coated on the FTO followed by heat treatment at 623 K for 2 h in air to form the BiVO4 seed layer. Second, the treated FTO was immersed in 2.0 M HNO3 aqueous solution containing Bi(NO3)3·5H2O and NH4VO3, whose pH was adjusted to be 0.9 by adding NH3·H2O drop by drop. The formed BiVO4 precursor film solution was transferred to a Teflon-lined autoclave with the as-prepared substrate for hydrothermal treatment at 473 K for 12 h. The BiVO4 photoanode film was finally calcined at 773 K for 4 h.
As for the selective deposition of Ir and FeCoOx cocatalysts on the BiVO4 photoanode, similar in situ photodeposition method as the powder was adopted. Specifically, the photoanode was immersed in 25 mM phosphate buffer solution (PBS, pH = 6, 50 mL) containing the K2IrCl6 or/and CoSO4 (K2IrCl6: 40 μL; CoSO4: 10 μL, the concentration of solution: 1 mg/mL) and K3[Fe(CN)6] (0.5 mM) and irradiated for 3 h. Similarly, CoOx was photodeposited on the surface of BiVO4 to prepare the CoOx/BiVO4 photoanode.
Measurements of AQE and STH conversion efficiency
The AQE was measured using a Pyrex top-irradiation-type reaction vessel and a 300 W xenon lamp fitted with band-pass filters (ZBPA420, Asahi Spectra Co., FWHM: 10 nm). The number of photons reaching the solution was measured using a calibrated Si photodiode (LS-100, EKO Instruments Co., LTD.), and the AQE (ϕ) was calculated using the following Eq. (1):
| 1 |
where A, R, and I are coefficients, A represents a coefficient (4 for H2 evolution; 8 for O2 evolution) and R represents the evolution rate of H2 or O2. As measured and calculated, the total number of incident photons at the wavelength of 420, 460, 480, 500, and 560 nm are 8.4 × 1020, 6.5 × 1020, 7.1 × 1020, 4.8 × 1020, and 6.9 × 1020 photons h−1, respectively. The evolution rates of H2 on the system containing RhyCr2–yO3-ZrO2/TaON and Ir-FeCoOx/BiVO4 photocatalysts under the wavelength of 420, 460, 480, 500, and 560 nm were tested to be 41.6, 23.0, 17.5, 7.4, and 0 μmol h−1, respectively. The evolution rates of H2 on the system containing RhyCr2–yO3-MgTa2O6–xNy/TaON and Ir-FeCoOx/BiVO4 photocatalysts under the wavelength of 420, 460, 480, and 560 nm were tested to be 42.4, 19.0, 9.0, and 0 μmol h−1, respectively.
The STH energy conversion efficiency (η) was calculated according to the following Eq. (2):
| 2 |
where RH, ΔG°, P, and S denote the rate of H2 evolution (mol s−1) in photocatalytic water splitting, standard Gibbs energy of water (237.13 × 103 J mol−1), intensity of simulated sunlight (0.1 W cm−2), and irradiation area (4.0 cm2), respectively. The light source was an AM 1.5 G solar simulator (XES-40S2-CE, San-Ei Electric), and a top-irradiation reaction vessel was used. The initial rates of H2 and O2 evolution are about 36 and 18 μmol/h, separately.
Photoelectrochemical tests
As for the tests of linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) and EIS, a platinum plate was used as a counter electrode and the saturated calomel electrode (SCE) as the reference electrode. The phosphate buffer solution (pH = 6, 0.1 M) with 5 mM K3[Fe(CN)6] aqueous solution and phosphate buffer solution (pH = 6, 0.1 M) were used as the electrolyte. The potential of the working electrode was controlled by a potentiostat (CHI 660E) for the LSV test and potentiostat (Solartron analytic AMETEK) for the EIS test. Before the measurement, the solution was purged with argon gas. The Nyquist plots calculated from EIS were performed from 100,000 to 0.1 Hz. Data were fitted using Zview software.
Current–voltage (J–V) curves under irradiation and darkness were recorded on an electrochemical workstation (CHI 660E). The OCP of photoanode were recorded under illumination and darkness using electrochemical workstation (Solartron analytic AMETEK). A 300 W xenon lamp was used as the light source and the irradiation intensity was high enough to produce a flat band condition of the photoanodes. The electrolyte for J–V curves and OCP was 1 M KBi (pH = 9). 0.2 M Na2SO3 was added to the electrolyte as a hole scavenger if necessary.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21902156, 21925206, 21633009), the National Key R&D Program of China (2020YFA0406102, 2017YFA0204904), the DICP Foundation of Innovative Research (DICP I201927), and the Dalian Science and Technology Innovation Fund (2020JJ26GX032). We gratefully acknowledge the BL14W1 beamline of the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF), Shanghai, China, and the 1W1B beamline of the Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility (BSRF), Beijing, China for providing the beam time. The numerical calculations in this paper have been done on the supercomputing system in the Supercomputing Center of University of Science and Technology of China.
Source data
Author contributions
F.Z. conceived and designed the experiments. Y.Q. carried out most of the preparations, activity test, catalyst characterizations, and wrote the first draft. J.Z. carried out the XAFS measurements and analysis. Y.K. conducted DFT calculation. Y.Z. assisted the synthesis of BiVO4 photocatalyst. S.C. assisted the synthesis of MgTa2O6-xNy/TaON heterostructure photocatalyst. D.L. assisted the synthesis of BiVO4 photoanode. W.L. conducted the HRTEM and EELS measurements. Y.C. and T.X. conducted the SPV characterizations. F.Z. and C.L. directed the work and revised the manuscript. J.C. gave corrections about DFT calculation part. K.D. instructed synthesis of H2-evolving photocatalysts and provided useful suggestions and discussion on the EXAFS results. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the manuscript.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks Krishnan Rajeshwar and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the source data. Source data are provided with this paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Yu Qi, Jiangwei Zhang, Yuan Kong.
Contributor Information
Can Li, Email: canli@dicp.ac.cn.
Fuxiang Zhang, Email: fxzhang@dicp.ac.cn.
Supplementary information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41467-022-28146-6.
References
- 1.Fujishima A, Honda K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature. 1972;238:37–38. doi: 10.1038/238037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lewis NS. Toward cost-effective solar energy use. Science. 2007;315:798–801. doi: 10.1126/science.1137014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kudo A, Miseki Y. Heterogeneous photocatalyst materials for water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009;38:253–278. doi: 10.1039/b800489g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chen X, et al. Semiconductor-based photocatalytic hydrogen generation. Chem. Rev. 2010;110:6503–6570. doi: 10.1021/cr1001645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Linic S, Christopher P, Ingram DB. Plasmonic-metal nanostructures for efficient conversion of solar to chemical energy. Nat. Mater. 2011;10:911–921. doi: 10.1038/nmat3151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pinaud BA, et al. Technical and economic feasibility of centralized facilities for solar hydrogen production via photocatalysis and photoelectrochemistry. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013;6:1983–2002. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Li X, Tung C, Wu L. Semiconducting quantum dots for artificial photosynthesis. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018;2:160–173. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hisatomi T, Domen K. Reaction systems for solar hydrogen production via water splitting with particulate semiconductor photocatalysts. Nat. Catal. 2019;2:387–399. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cestellos-Blanco S, et al. Photosynthetic semiconductor biohybrids for solar-driven biocatalysis. Nat. Catal. 2020;3:245–255. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kornienko N, et al. Interfacing nature’s catalytic machinery with synthetic materials for semi-artificial photosynthesis. Nature Nanotech. 2018;13:890–899. doi: 10.1038/s41565-018-0251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang Q, Domen K. Particulate photocatalysts for light-driven water splitting: mechanisms, challenges, and design strategies. Chem. Rev. 2020;120:919–985. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kong D, et al. Recent advances in visible light-driven water oxidation and reduction in suspension systems. Mater. Today. 2018;21:897–924. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bard AJ, Fox MA. Artificial photosynthesis: solar splitting of water to hydrogen and oxygen. Acc. Chem. Res. 1995;28:141–145. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fabian DM, et al. Particle suspension reactors and materials for solar-driven water splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015;8:2825–2850. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wang Q, et al. Scalable water splitting on particulate photocatalyst sheets with a solar-to-hydrogen energy conversion efficiency exceeding 1% Nat. Mater. 2016;15:611–615. doi: 10.1038/nmat4589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Qi Y, et al. Redox-based visible-light-driven Z-scheme overall water splitting with apparent quantum efficiency exceeding 10% Joule. 2018;2:2393–2402. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Maeda K, et al. Photocatalyst releasing hydrogen from water. Nature. 2006;440:295. doi: 10.1038/440295a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chen S, Takata T, Domen K. Particulate photocatalysts for overall water splitting. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017;2:17050. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Takata T, et al. Photocatalytic water splitting with a quantum efficiency of almost unity. Nature. 2020;581:411–414. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2278-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kudo A, et al. Photocatalytic O2 evolution under visible light irradiation on BiVO4 in aqueous AgNO3 solution. Catal. Lett. 1998;53:229–230. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kudo A, Omori K, Kato H. A first aqueous process for preparation of crystal form-controlled and highly crystalline BiVO4 powder from layered vanadates at room temperature and its photocatalytic and photophysical properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999;121:11459–11467. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kim TW, Choi KS. Nanoporous BiVO4 photoanodes with dual-layer oxygen evolution catalysts for solar water splitting. Science. 2014;343:990–994. doi: 10.1126/science.1246913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kim JH, Lee JS. Elaborately modified BiVO4 photoanodes for solar water splitting. Adv. Mater. 2019;31:1806938. doi: 10.1002/adma.201806938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Luo W, et al. Solar hydrogen generation from seawater with a modified BiVO4 photoanode. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011;4:4046–4051. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Abdi FF, et al. Efficient solar water splitting by enhanced charge separation in a bismuth vanadate-silicon tandem photoelectrode. Nat. Commun. 2013;4:2195. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chen YS, Manser JS, Kamat PV. All solution-processed lead halide perovskite-BiVO4 tandem assembly for photolytic solar fuels production. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015;137:974–981. doi: 10.1021/ja511739y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Resasco J, et al. TiO2/BiVO4 nanowire heterostructure photoanodes based on Type II band alignment. ACS Cent. Sci. 2016;2:80–88. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.5b00402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wang Q, et al. Molecularly engineered photocatalyst sheet for scalable solar formate production from carbon dioxide and water. Nat. Energy. 2020;5:703–710. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kato H, et al. Construction of Z-scheme type heterogeneous photocatalysis systems for water splitting into H2 and O2 under visible light irradiation. Chem. Lett. 2004;33:1348–1349. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Iwase A, et al. Reduced graphene oxide as a solid-state electron mediator in Z-scheme photocatalytic water splitting under visible light. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011;133:11054–11057. doi: 10.1021/ja203296z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pan L, et al. Boosting the performance of Cu2O photocathodes for unassisted solar water splitting devices. Nat. Catal. 2018;1:412–420. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Li R, et al. Spatial separation of photogenerated electrons and holes among {010} and {110} crystal facets of BiVO4. Nat. Commun. 2013;4:1432. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yang J, et al. Roles of cocatalysts in photocatalysis and photoelectrocatalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013;46:1900–1909. doi: 10.1021/ar300227e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wang Y, et al. Mimicking natural photosynthesis: solar to renewable H2 fuel synthesis by Z-scheme water splitting systems. Chem. Rev. 2018;118:5201–5241. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sasaki Y, et al. The effect of co-catalyst for Z-scheme photocatalysis systems with an Fe3+/Fe2+ electron mediator on overall water splitting under visible light irradiation. J. Catal. 2008;259:133–137. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Maeda K, Abe R, Domen K. Role and function of ruthenium species as promoters with TaON-based photocatalysts for oxygen evolution in two-step water splitting under visible light. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2011;115:3057–3064. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tabata M, et al. Modified Ta3N5 powder as a photocatalyst for O2 evolution in a two-step water splitting system with an iodate/iodide shuttle redox mediator under visible light. Langmuir. 2010;26:9161–9165. doi: 10.1021/la100722w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ma SSK, et al. Visible-light-driven nonsacrificial water oxidation over tungsten trioxide powder modified with two different cocatalysts. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012;5:8390–8397. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhao Y, et al. A hydrogen farm strategy for scalable solar hydrogen production with particulate photocatalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020;59:9653–9658. doi: 10.1002/anie.202001438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Li D, et al. Crystallographic-orientation-dependent charge separation of BiVO4 for solar water oxidation. ACS Energy Lett. 2019;4:825–831. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wang S, et al. New iron-cobalt oxide catalysts promoting BiVO4 films for photoelectrochemical water splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018;28:1802685. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Chu C, et al. Spatially separating redox centers on 2D carbon nitride with cobalt single atom for photocatalytic H2O2 production. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2020;117:6376–6382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1913403117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhang B, et al. High-valence metals improve oxygen evolution reaction performance by modulating 3d metal oxidation cycle energetics. Nat. Catal. 2020;3:985–992. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Norsköv JK. Chemisorption on metal-surfaces. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1990;53:1253–1295. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Norsköv JK. Electronic factors in catalysis. Prog. Surf. Sci. 1991;38:103–144. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zhang B, et al. Homogeneously dispersed multimetal oxygen-evolving catalysts. Science. 2016;352:333–337. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf1525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Cheng W, et al. Lattice-strained metal-organic-framework arrays for bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysis. Nat. Energy. 2019;4:115–122. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chen S, et al. Efficient visible-light-driven Z-scheme overall water splitting using a MgTa2O6−xNy/TaON heterostructure photocatalyst for H2 evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015;54:8498–8501. doi: 10.1002/anie.201502686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Maeda K, et al. Efficient nonsacrificial water splitting through two-step photoexcitation by visible light using a modified oxynitride as a hydrogen evolution photocatalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010;132:5858–5868. doi: 10.1021/ja1009025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kim C, et al. (040)-Crystal facet engineering of BiVO4 plate photoanodes for solar fuel production. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016;6:1501754. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the source data. Source data are provided with this paper.