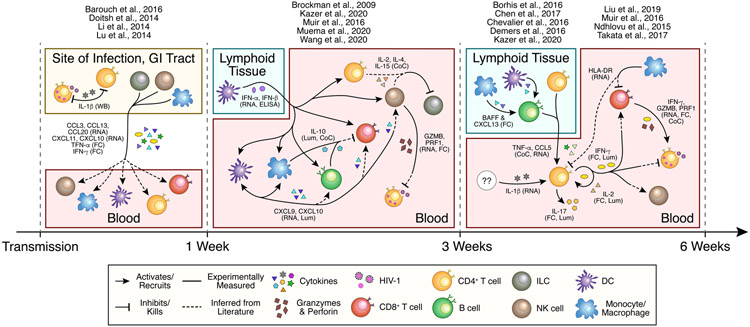
Figure 2. Known and inferred immune cell signaling during untreated acute HIV infection.
Understanding the interplay between distinct immune subsets in acute HIV infection is essential to disentangle the effects of key cytokines (e.g. Type I and II interferons, IL-10, IL-17, etc.) on each cell type. Moreover, realizing the compartment specific responses and their effects will allow for more targeted treatment. Experimentally measured interactions are depicted with solid arrows. Interactions for which only the signaler or receiver has been measured are shown by arrows with hybrid solid and dashed lines, which are inferred from literature on chronic infection or other models. The supporting assay for each interaction is listed with each cytokine or factor. GZMB = granzyme B; PRF1 = perforin; WB = Western Blot; RNA = RNA-sequencing; FC = Flow Cytometry; ELISA = Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay; Lum = Luminex Multiplex Assay; CoC = in vitro coculture.