Abstract
Freshwater mussels cannot spread through oceanic barriers and represent a suitable model to test the continental drift patterns. Here, we reconstruct the diversification of Oriental freshwater mussels (Unionidae) and revise their taxonomy. We show that the Indian Subcontinent harbors a rather taxonomically poor fauna, containing 25 freshwater mussel species from one subfamily (Parreysiinae). This subfamily most likely originated in East Gondwana in the Jurassic and its representatives arrived to Asia on two Gondwanan fragments (Indian Plate and Burma Terrane). We propose that the Burma Terrane was connected with the Indian Plate through the Greater India up to the terminal Cretaceous. Later on, during the entire Paleogene epoch, these blocks have served as isolated evolutionary hotspots for freshwater mussels. The Burma Terrane collided with mainland Asia in the Late Eocene, leading to the origin of the Mekong’s Indochinellini radiation. Our findings indicate that the Burma Terrane had played a major role as a Gondwanan “biotic ferry” alongside with the Indian Plate.
Subject terms: Biodiversity, Taxonomy, Biogeography
Introduction
Freshwater mussels (order Unionida) are a diverse and widespread group of large aquatic invertebrates1,2, providing a variety of ecosystem services3,4. These animals are highly sensitive to human impacts and climate changes5–9, revealing dramatically high rates of global decline and regional extinctions10,11. Natural dispersal of freshwater mussels mostly occurs at the larval stage together with their fish hosts, and usually requires direct connections between freshwater basins, because they are unable to cross oceanic barriers2,12–15. Hence, freshwater mussels are considered to be among the best model organisms for biogeographic and paleogeographic reconstructions16–21. Most freshwater mussel species are endemic to a certain faunal region, and multiple single-basin and intra-basin endemics do occur, especially in species-rich faunas such as those of Southeast Asia22–28, North America and Mesoamerica17,29,30, and tropical Africa31. Furthermore, even widespread species share some kind of phylogeographic structure throughout their continuous ranges, e.g. Anodonta anatina (Linnaeus, 1758) in Eurasia32,33 and Megalonaias nervosa (Rafinesque, 1820) in North America34.
Recently, freshwater mussels were used as a model group to perform an updated freshwater biogeographic division of South and Southeast Asia19,23,35. Based on the Unionidae phylogeny and endemism patterns, this area could be delineated to the Oriental, Sundaland, and East Asian freshwater biogeographic regions23. The Oriental Region contains two subregions, i.e. the Indian (Indian Subcontinent from the Indus Basin in Pakistan through Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, and Sri Lanka to the coastal basins of the Rakhine State of Myanmar) and Western Indochina (Myanmar from the Irrawaddy [Ayeyarwady] Basin to the Salween [Thanlwin], Tavoy [Dawei], and the Great Tenasserim [Tanintharyi] rivers) subregions23. A significant geographic barrier associated with the Indo-Burma Ranges in Western Myanmar and Northeastern India (Naga Hills, Chin Hills, and Rakhine Mountains) separates these entities23. The Sundaland Region covers the Mekong, Chao Phraya, and Mae Klong rivers, the drainages of the Thai-Malay Peninsula, and the Greater Sunda Islands23,28,35,36. Finally, the massive East Asian Region expands from coastal basins of Vietnam through eastern China, Korea, and Japan to the Russian Far East20,35,37.
At first glance, the freshwater biogeographic division, outlined above, corresponds well to the boundaries of tectonic blocks such as the Indian Plate (Indian Subregion), Burma Terrane or West Burma Block (Western Indochina Subregion), and the Sunda Plate, containing the Indochina Block and Sibumasu Terrane (Sundaland Region)38–41 (Fig. 1). Dramatic tectonic movements during the Mesozoic and Cenozoic shaped the modern configuration of these blocks42,43. The Indian Plate was a part of East Gondwana and drifted northward as an insular landmass carrying Gondwanan biota39,44,45. Furthermore, the body of modern geological, tectonic, paleomagnetic, and paleontological research indicates that the Burma Terrane most likely represents a Gondwanan fragment that rafted to Asia together with the Indian Plate or as a part of a Trans-Tethyan island arc38,40,41,46–50. However, it is still unclear whether the continental drift could explain the biogeographic patterns in freshwater mussel distribution throughout the Oriental and Afrotropical regions and whether the disjunctive range of several Unionidae clades could reflect Mesozoic tectonic events19,31,51,52. While our knowledge on the taxonomy and evolutionary biogeography of freshwater mussels from tropical Africa, Western Indochina, and Sundaland has largely been improved during the last decade2,19,22–28,31,35,51,53–56, the Unionidae fauna of the Indian Subcontinent57,58 is still waiting for an integrative taxonomic research and thorough biogeographic modeling.
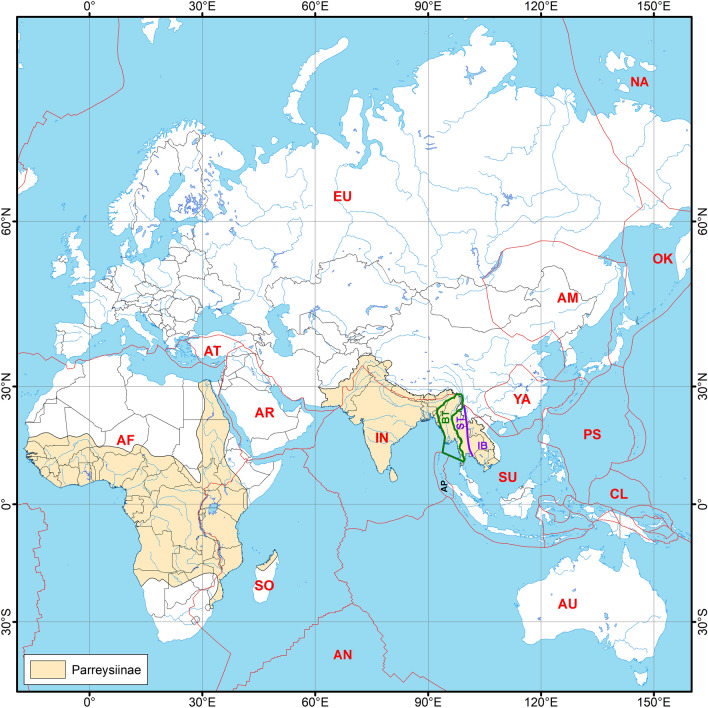
Figure 1.
Global distribution of the subfamily Parreysiinae and tectonic plate boundaries. The subfamily range based on available published sources23,239 and our own data. The red lines indicate tectonic plate boundaries240. The red abbreviations indicate the names of larger tectonic plates: AF African; AM Amurian; AN Antarctic; AR Arabian; AT Anatolian; AU Australian; CL Caroline; IN Indian; NA North American; OK Okinawa; PS Philippine Sea Plate; SO Somalia; SU Sunda (with Indochina Block and Sibumasu Terrane); YA Yangtze. The boundaries of the Burma Terrane (BT), Sibumasu Terrane (ST), Indochina Block (IB), and the Andaman Platelet (AP) are given based on a series of modern tectonic works38–40. The Mogok–Mandalay–Mergui Belt40 is placed here within the boundary of the Burma Terrane. The map was created using ESRI ArcGIS 10 software (https://www.esri.com/arcgis). The topographic base of the map was created with Natural Earth Free Vector and Raster Map Data (https://www.naturalearthdata.com) and Global Self-consistent Hierarchical High-resolution Geography (https://www.soest.hawaii.edu/wessel/gshhg). (Map: Mikhail Yu. Gofarov).
This study (1) presents a taxonomic review of freshwater mussels from the Indian Subcontinent based on the most comprehensive morphological and DNA sequence datasets sampled to date; (2) reconstructs the origins, macroevolution patterns, and diversification of the Parreysiinae based on a multi-locus time-calibrated phylogeny; and (3) postulates a novel hypothesis on a possible role of the Burma Terrane as a separate “biotic ferry” carrying a derivative of the Gondwanan biota to Asia through continental drift processes. Furthermore, we present a complete reappraisal of Mesozoic freshwater mussel species that were described from the Deccan Intertrappean Beds (Upper Cretaceous) on the Indian Subcontinent and an overview of a few doubtful and uncertain recent taxa that were linked to India.
Results
Freshwater mussel fauna of the Indian Subcontinent
Here, we present the most comprehensive phylogenetic and distribution datasets on freshwater mussels (Unionidae) from the Indian Subcontinent sampled to date with supplement of related taxa from Indochina and Africa (Fig. 2 and Supplementary Fig. 1). The phylogeny was reconstructed using partial sequences of the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI), small ribosomal RNA (16S rRNA), and the nuclear large ribosomal RNA (28S rRNA) genes (Dataset 1). Based on the multi-locus phylogeny, DNA-based species delimitation procedures (Supplementary Fig. 2), and morphological data, we show that the Unionidae fauna of the Indian Subcontinent contains members of one subfamily, the Parreysiinae (Table 1). The total species richness of freshwater mussels on the Indian Subcontinent is rather uncertain due to the lack of DNA sequence data for multiple nominal taxa (Table 1). In summary, we propose a list of 25 valid species, almost all of which seem to be endemic to the subcontinent, though only 17 (68.0%) of those taxa were checked by means of a DNA-based approach. The 25 species recorded from the Indian Subcontinent belong to three tribes: Indochinellini (genus Indonaia Prashad, 1918: 8 species), Lamellidentini (genera Lamellidens Simpson, 1900 and Arcidopsis Simpson, 1900: 9 and 1 species, respectively), and Parreysiini (genus Parreysia Conrad, 1853: 6 species) (Figs. 3, 4 and 5)). One more genus, the monotypic Balwantia Prashad, 1919 (Fig. 5h), is considered here as Parreysiinae incertae sedis. The genera Arcidopsis, Balwantia, and Parreysia are endemic to the Indian Subcontinent, while each of the Indonaia and Lamellidens also contains three species from Western Indochina. Furthermore, there is one cementing bivalve species, Pseudomulleria dalyi (Smith, 1898) (Etheriidae), known to occur in India whose systematic assignment is still unclear (see “Discussion”).
Figure 2.
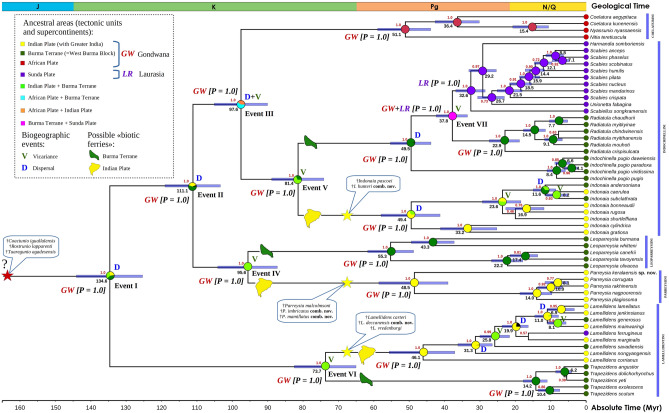
Time-calibrated phylogeny of the Parreysiinae based on the complete data set of mitochondrial and nuclear sequences (five partitions: three codons of COI + 16S rRNA + 28S rRNA). Events I-VII indicate a series of key biogeographic events, shaping the recent distribution of the subfamily (see “Results”). Nodal circle charts indicate the probabilities of certain ancestral areas based on the combined “tectonic plates” scenario (S-DIVA + DIVALIKE). The Sunda Plate contains the Indochina Block and Sibumasu Terrane39. Black color indicates an unexplained origin. Color symbols GW (Gondwana) and LR (Laurasia) indicate the results of the combined “supercontinents” scenario (S-DIVA + DIVALIKE) with the probabilities (P) of each ancestral area being given in square brackets. Stars at branches indicate reliable fossil record of the Mesozoic Parreysiinae in Africa (red) and India (yellow) with available fossil taxa being listed in the corresponding callouts. Taxonomic information on the Mesozoic fossil species from the Indian Subcontinent is given in Table 2. Red numbers near nodes are Bayesian posterior probability (BPP) values of BEAST v. 2.6.3. Black numbers near nodes are the mean node ages. Node bars are 95% HPD of divergence time. Time and biogeographic reconstructions for weakly supported nodes (BPP < 0.70) are not shown. Outgroup taxa are omitted. Stratigraphic chart according to the International Commission on Stratigraphy, 2021 (https://stratigraphy.org/chart).
Table 1.
Taxonomic review of the recent Unionidae (Parreysiinae) from the Indian Subcontinent with supplement of congeneric species from Western Indochina (see Supplementary Note 1 for detail and complete synonymies).
| Taxa with new synonyms | Type locality | Distribution | Tectonic block |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tribe Indochinellini Bolotov, Pfeiffer, Vikhrev & Konopleva, 2018 | |||
| Genus Indonaia Prashad, 1918 | |||
| The caerulea-group | |||
| **Indonaia andersoniana (Nevill, 1877) | Myadoung, Burma [Irrawaddy River near Mya Taung village, 23.7310° N, 96.1486° E, Myanmar]210 | Irrawaddy to Salween Basin, Myanmar211 | Burma Terrane |
| Indonaia bonneaudii (Eydoux, 1838) comb. rev. [= Unio leioma Benson, 1862 syn. nov.] | Les rivières de la presqu'ile de l'Inde [rivers of the Indian Peninsula]212 | Karli River, Western Ghats, India | Indian Plate |
| Indonaia caerulea (Lea, 1831) [= Lampsilis argyratus Rafinesque, 1831 syn. nov.; = Unio nuttallianus Lea, 1856 syn. nov.; = U. pachysoma Benson, 1862 syn. nov.; = Trapezoideus dhanushori Annandale & Prashad, 1921 syn. nov.] | Bengal, India213 | Ganges Basin in India, Nepal, and Bhutan, Brahmaputra and Krishna basins in India; Surma River in Bangladesh; Indus Basin in Pakistan57,61,63,214 | Indian Plate |
| Indonaia rugosa (Gmelin, 1791) comb. nov. [= Diplasma striata Rafinesque, 1831 syn. nov.; = Unio scobina Hanley, 1856 syn. nov.; = Nodularia (Radiatula) lima Simpson, 1900 syn. nov.] | Coromandel fluviis [rivers of the Coromandel Coast of India]215 | Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Krishna basins, India | Indian Plate |
| Indonaia shurtleffiana (Lea, 1856) [= I. khadakvaslaensis Ray, 1966 syn. nov.] | Sina River, < … > Ahmednugger, India [upper reaches of the Sina River near Ahmednager, approx. 19.0835° N, 74.7281° E, Krishna Basin, Maharashtra, India]216 | Krishna and Godavari basins, India | Indian Plate |
| **Indonaia subclathrata (Martens, 1899) | Chindwinfluss bei Kalewa und bei Matu < … > ; einige Stücke auch im Irawaddi selbst bei Yenangyoung [Chindwin River near Kalewa and Matu, approx. 23.1991° N, 94.3071° E, several specimens also from Irrawaddy River near Yenangyaung, approx. 20.4347° N, 94.8720° E, Myanmar]217 | Lower Manipur River and a corresponding section of the Chindwin River, Myanmar53,211 | Burma Terrane |
| *, **Indonaia theobaldi (Preston, 1912) | Manipur, Assam218 | Upper Manipur Valley (including Logtak Lake), India219 | Burma Terrane |
| The cylindrica-group | |||
| Indonaia cylindrica (Annandale & Prashad, 1919) comb. nov. | Yenna River, Upper Kistna watershed, at Medha [Venna River at Medha (now Kanher Reservoir), 17.7887° N, 73.8254° E, Krishna Basin, Maharashtra, India]220 | Endemic to the Upper Krishna Basin, India220 | Indian Plate |
| Indonaia gratiosa (Philippi, 1843) comb. nov. [= Unio corbis Hanley, 1856 syn. nov.; = U. occatus Lea, 1860 syn. nov.; = U. siliguriensis Preston, 1908 syn. nov.] | Nova Hollandia [erroneous; it was collected somewhere in India]221 | Ganges and Brahmaputra basins, India and Nepal | Indian Plate |
| The involuta-group | |||
| *Indonaia involuta (Hanley, 1856) | Assam222 | Upper Brahmaputra Basin in India and Surma River in Bangladesh | Indian Plate |
| *Indonaia olivaria (Lea, 1831) | Bengal213 | Ganges Basin, India61 | Indian Plate |
| Tribe Lamellidentini Modell, 1942 | |||
| Genus Arcidopsis Simpson, 1900 | |||
| *Arcidopsis footei (Theobald, 1876) | Kistna flumine prope ‘Gutparba Falls’ [Gokak Falls, Ghataprabha River, 16.1929° N, 74.7827° E, Krishna Basin, southwestern India]223 | Upper part of the Krishna Basin in Western Ghats, India71,72,124 | Indian Plate |
| Genus Lamellidens Simpson, 1900 [= Velunio Haas, 1919 syn. nov.] | |||
| The corrianus-group | |||
| Lamellidens corrianus (Lea, 1834) [= Unio theca Benson, 1862 syn. nov.] | Calcutta, India224 | Ganges and Krishna basins, India | Indian Plate |
| Lamellidens nongyangensis Preston, 1912 stat. rev. [= L. narainporensis Preston, 1912 syn. nov.; our first reviser action on the precedence of simultaneous synonyms] | Nongyang Lake, South of Patkai [Lake of No Return, 27.2192° N, 96.1439° E, Irrawaddy Basin, Myanmar]218 | Ganges Basin in India, with an isolated population in Lake of No Return, Irrawaddy Basin, Myanmar | Indian Plate, with one isolated population on Burma Terrane |
| **Lamellidens savadiensis (Nevill, 1877) | At Sawady in the Thengleng Stream [Sawadi village, 24.1510° N, 97.1502° E, Myanmar], also at Bhamo [Irrawaddy River near Bhamo city, 24.2594° N, 97.2202° E, Myanmar] and at Shuaygoomyo [Irrawaddy River near Shwegu town, 24.2291° N, 96.7910° E, Myanmar]; four young specimens found at Myadoung [Irrawaddy River near Mya Taung village, 23.7310° N, 96.1486° E, Myanmar] probably also belong to this form210 | Middle Irrawaddy (including Lake Indawgyi) and Sittaung basins, Myanmar56 | Burma Terrane |
| *Lamellidens unioides Nesemann & Sharma in Nesemann et al., 2007 | Mamu Bhanja Pokhra at Hajipur, Muzaffarpur District, Bihar, India [pond, 25.6758° N, 85.2250° E, Mamu Bhanja, Hajipur, Ganges Basin, Muzaffarpur District, Bihar, India]61 | Ganges Basin in India61 | Indian Plate |
| The marginalis-group | |||
| *Lamellidens candaharicus (Hutton, 1849) [= L. rhadinaeus Annandale & Prashad, 1919 syn. nov.] | Canals at Candahar [Kandahar, 31.6148° N, 65.7198° E, Sistan/Helmand Basin, Afghanistan]225 | Endorheic Sistan/Helmand Basin, eastern Iran and Afghanistan78,225 | Indian Plate |
| **Lamellidens ferrugineus (Annandale, 1918) stat. rev. [= Physunio micropteroides Annandale, 1918 syn. nov.; our first reviser action on the precedence of simultaneous synonyms] | The semi-liquid mud at the bottom of the central region of the Inle Lake in water from 7 to 12 feet deep [central part of Lake Inle, 20.5903° N, 96.9025° E, Salween Basin, Myanmar]226 | Lake Inle and streams around, Salween Basin, Myanmar | Connection of Burma Terrane with Sunda Plate |
| *Lamellidens friersoni (Simpson, 1914) comb. nov. | Assam, India74,79 | Upper Brahmaputra Basin, Assam, India74,79 | Indian Plate |
| **Lamellidens generosus (Gould, 1847) [= Unio consobrinus Lea, 1860 syn. nov.; = L. brandti Bolotov, Konopleva & Vikhrev, 2017 syn. nov.] | Newville, Tavoy, British Burmah [Hlaingbwe River near the former Newville village, 16.9834° N, 97.9043° E, Myanmar]227 | Irrawaddy to Lower Salween Basin (including Haungthayaw, Hlaingbwe, and Ataran) in Myanmar; southwestern Yunnan in China | Burma Terrane but reaches the western margin of the Sunda Plate |
| Lamellidens jenkinsianus (Benson, 1862) | Fluvio Assamensi Berhampooter dicto [Brahmaputra River, Assam, India]228 | Ganges, Meghna, Brahmaputra, Godavari, Krishna, and Ambā basins, India and Bangladesh; a few occurrences from Bhutan63 | Indian Plate |
| Lamellidens lamellatus (Lea, 1838) | Ganges River, India229 | Ganges, Krishna, and Mahanadi basins, India | Indian Plate |
| Lamellidens mainwaringi Preston, 1912 [= L. phenchooganjensis Preston, 1912 syn. nov.; our first reviser action on the precedence of simultaneous synonyms] | Siliguri [Siliguri, Ganges Basin, West Bengal, India]218 | Ganges, Karli, Kalni, and Kaladan rivers, India, Bangladesh, and western Myanmar | Indian Plate |
| Lamellidens marginalis (Lamarck, 1819) | Bengale, dans les rizières [rice fields, Bengal, India]230 | Ganges and Krishna basins, India and Nepal; Sri Lanka; Indus Basin in Pakistan57,61 | Indian Plate |
| Tribe Parreysiini Henderson, 1935 | |||
| Genus Parreysia Conrad, 1853 | |||
| The keralaensis-group | |||
| Parreysia keralaensis Bolotov, Pasupuleti & Subba Rao sp. nov. | Periyar River, 10.11° N, 76.37° E, Aluva, Kerala, India | Endemic to Periyar and Pampa basins, India | Indian Plate |
| The corrugata-group | |||
| Parreysia corrugata (Müller, 1774) [= Unio sikkimensis Lea, 1859 syn. nov.; = U. favidens Benson, 1862 syn. nov.; = U. favidens var. chrysis Benson, 1862 syn. nov.; = U. favidens var. deltae Benson, 1862 syn. nov.; = U. favidens var. densa Benson, 1862 syn. nov.; = U. favidens var. trigona Benson, 1862 syn. nov.; = U. favidens var. marcens Benson, 1862 syn. nov.; = U. favidens var. viridula Benson, 1862 syn. nov.; = U. laevirostris Benson, 1862 syn. nov.; = U. smaragdites Benson, 1862 syn. nov.; = U. tripartitus Lea, 1863 syn. nov.; = U. gowhattensis Theobald, 1873 syn. nov.; = U. feddeni Theobald, 1873 syn. nov.; = Parreysia (P.) annandalei Preston, 1912 syn. nov.; = P. favidens var. assamensis Preston, 1912 syn. nov.] | In fluviis littoris Coromandel [rivers of the Coromandel Coast of India]231 | Ganges Basin in India and Nepal; Brahmaputra, Krishna, and Godavari basins in India; Surma River in Bangladesh; Sri Lanka; Indus Basin in Pakistan | Indian Plate |
| Parreysia plagiosoma (Benson, 1862) stat. rev. [= Unio tennentii Hanley & Theobald, 1872 syn. nov.] | Bengal228 | Ganges and Vaghotan basins, India | Indian Plate |
| Parreysia rakhinensis Bolotov et al., 2020 | Kyeintali Stream upstream of Ohtein village, 17.9193° N, 94.5946° E, Rakhine State, Myanmar23 | Rakhine Coast, western Myanmar23 | Indian Plate |
| Parreysia nagpoorensis (Lea, 1860) stat. rev. [= Unio merodabensis Küster, 1861 syn. nov.; = U. triembolus Benson, 1862 syn. nov.; = U. trirostris Musgrave, 1863 syn. nov.; = U. pinax Benson, 1862 syn. nov.] | Ambijiri Tanks, Nagpoor, Bengal, India [Ambazari Pond in Nagpur, 21.1278° N, 79.0439° E, Godavari Basin, Maharashtra, India]232 | Ganges, Krishna, Godavari, and Karli (Pithdhaval) basins, India | Indian Plate |
| The rajahensis-group | |||
| *Parreysia rajahensis (Lea, 1841) | Rajah’s Tank, Calcutta, India [most likely inaccurate; the type shell was probably collected somewhere in the Narmada River basin, e.g. from Maharaja’s Tank in Jabalpur]97,233 | Upstream section of the Narmada River, India97 | Indian Plate |
| Parreysiinae incertae sedis | |||
| Genus Balwantia Prashad, 1919 | |||
| *Balwantia soleniformis (Benson, 1836) | The hills on the N.E. Frontier of Bengal (Silhet) [Sylhet Division, Upper Meghna Basin, northeastern Bangladesh]234 | Upper Brahmaputra, Upper Barak (Dhaleswari), and Upper Meghna basins, India and Bangladesh89–91 | Indian Plate |
*Species whose DNA sequences are not available. All of the other species were studied by means of a molecular approach. **Taxa endemic to the Western Indochina Subregion (Burma Terrane) that are lacking in the fauna of Indian Subcontinent.
Figure 3.
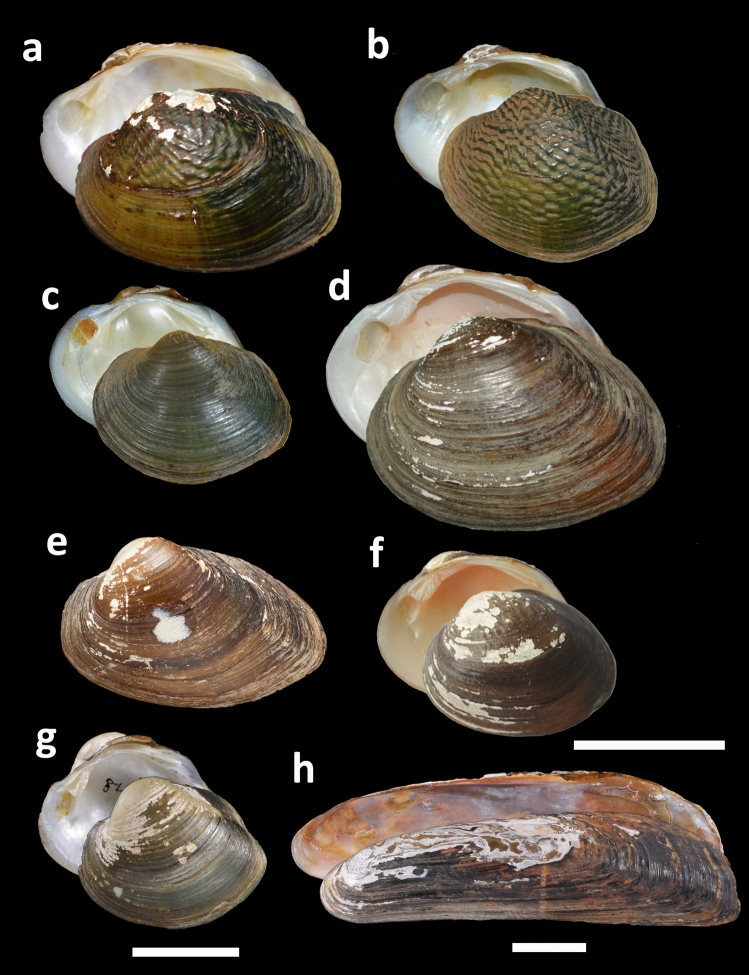
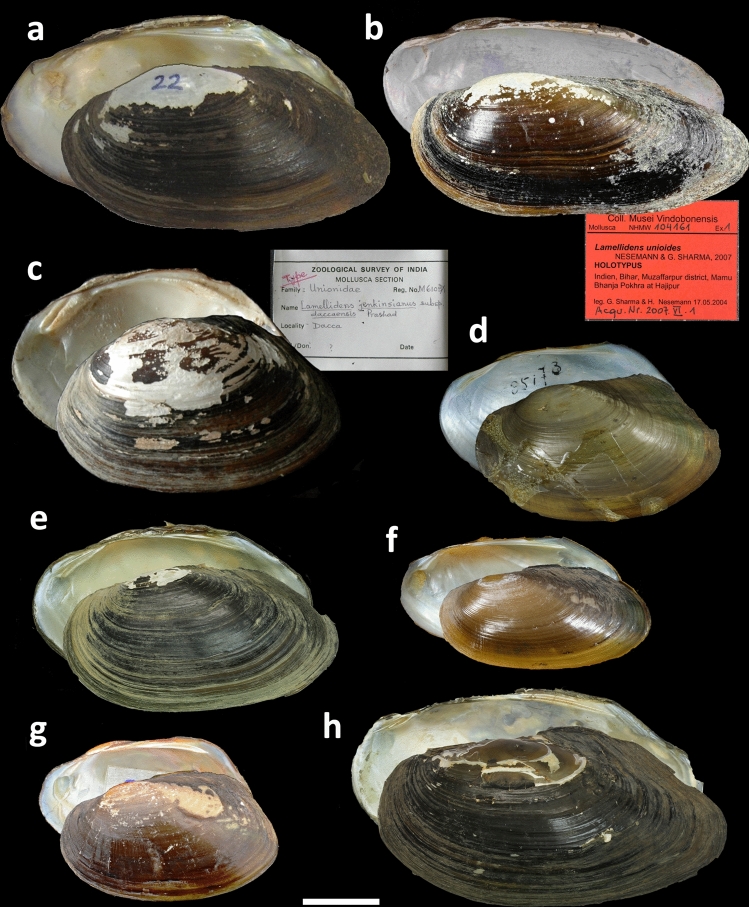
Shell examples of Lamellidens species from the Indian Subcontinent. (a) L. corrianus (Lea, 1834), Gokak, Gatprabha River, Krishna River basin, Western Ghats, Karnataka, India. (b) L. unioides Nesemann & Sharma in Nesemann et al., 2007, Bihar, Muzaffarpur District, Mamu Bhanja Pokhra at Hajipur, India (holotype NHMW 104161). (c) L. jenkinsianus (Benson, 1862), Dacca, Bangladesh (= Parreysia (s. str.) daccaensis Preston, 1912; holotype ZSI M6105/1). (d) L. lamellatus (Lea, 1838), Ganges River, India (holotype NMNH 85173). (e) L. mainwaringi Preston, 1912, Kaladan River, Myanmar (specimen RMBH biv153). (f) L. marginalis (Lamarck, 1819), brook at fish ponds, Hetauda, Ganges Basin, Narayani Zone, Central Region, Nepal (specimen SMF 348831/16.01). (g) L. marginalis (Lamarck, 1819), Krishna River, Nagarjuna Sagar, Telangana, India (museum lot FBRC ZSI 1227; specimen RLm3). (h) L. nongyangensis Preston, 1912 stat. rev., Lake of No Return [= Nongyang Lake], Irrawaddy Basin, Myanmar (topotype RMBH biv893/1). Scale bar = 20 mm. Photos: H. Singh, College of Fisheries, Ratnagiri, BOLD Systems BFB021-12, under a CC BY 3.0 license [a], N. V. Subba Rao and R. Pasupuleti [c, f, g], NMNH collection database under a CC0 1.0 license [d], A. Eschner [b], S. Hof [f], and E. S. Konopleva [e, h].
Figure 4.
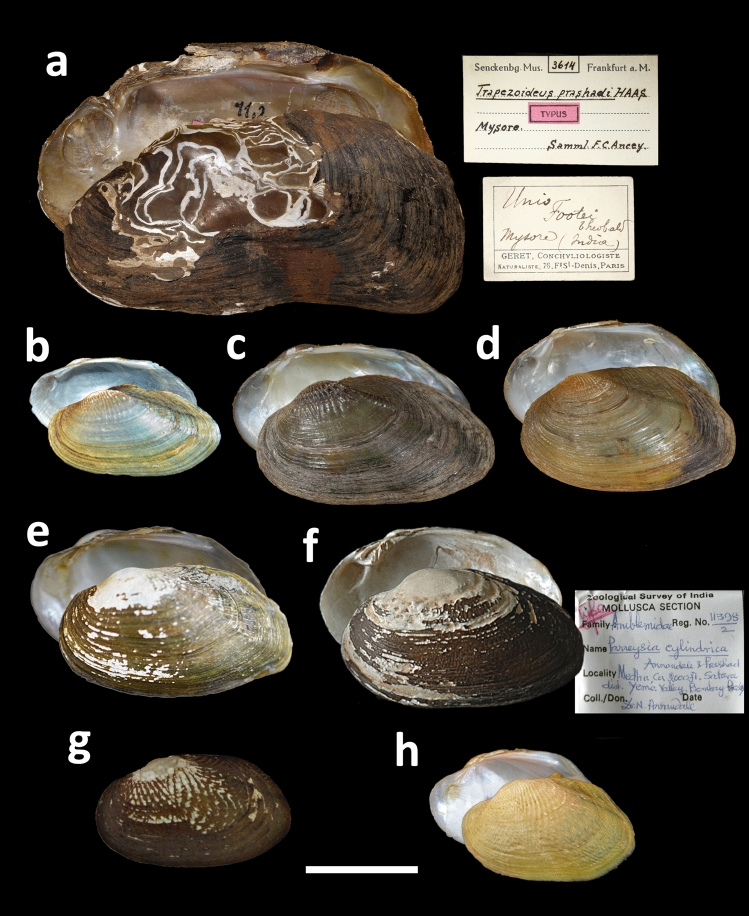
Shell examples of Arcidopsis and Indonaia species from the Indian Subcontinent. (a) A. footei (Theobald, 1876), Kistna flumine prope ‘Gutparba falls’ [Gokak Falls, Ghataprabna River, Krishna Basin, India] (= Trapezoideus prashadi Haas, 1922; holotype SMF 3614). (b) I. caerulea (Lea, 1831), fish pond, Krishna River basin, Uppalapadu, Andhra Pradesh, India (museum lot FBRC ZSI 1229; specimen RRc1). (c) I. caerulea (Lea, 1831), Jhajh nadi, Ganges basin, Narayani Zone, Central Region, Nepal (specimen SMF 348835/17.05). (d) I. gratiosa (Philippi, 1843) comb. nov., Jhajh nadi, Ganges Basin, Narayani Zone, Central Region, Nepal (specimen SMF 348834/17.15). (e) I. shurtleffiana (Lea, 1856), Godavari River, Nashik, Maharashtra, India (museum lot FBRC ZSI 1230; specimen RR3). (f) I. cylindrica (Annandale & Prashad, 1919) comb. nov., Yenna River, Upper Kistna watershed, at Medha, Krishna Basin, Maharashtra, India (syntype ZSI 11398/2). (g) I. cylindrica (Annandale & Prashad, 1919) comb. nov., Yenna River, Upper Kistna watershed, at Medha, Krishna Basin, Maharashtra, India (syntype ZSI 11398/2). (h) I. rugosa (Gmelin, 1791) comb. nov., Krishna River, Nagarjuna Sagar, Telangana, India (FBRC ZSI 1222; specimen RRl1). Scale bar = 20 mm. Photos: S. Hof [a, c-d], and N. V. Subba Rao and R. Pasupuleti [b, e, f, g, h].
Figure 5.
Shells of Parreysia and Balwantia species from the Indian Subcontinent. (a) P. keralaensis sp. nov., Periyar River, Aluva, Kerala, India (holotype FBRC ZSI 1007-a/RCB2). (b) P. keralaensis sp. nov., the type locality (museum lot FBRC ZSI 1007; paratype RCB3). (c) P. corrugata (Müller, 1774), brook at fish ponds, Hetauda, Ganges Basin, Narayani Zone, Central Region, Nepal (specimen SMF 348829/16.02). (d) P. corrugata (Müller, 1774). Krishna River, Nagarjuna Sagar, Telangana, India (museum lot FBRC ZSI 1224; specimen RPf1). (e) P. nagpoorensis (Lea, 1860), Ramganga River near Moradabad, Ganges Basin, Uttar Pradesh, India (= Unio pinax Benson, 1862: syntype UMZC I.105035.B241). (f) P. nagpoorensis (Lea, 1860), Krishna River, Nagarjuna Sagar, Telangana, India (museum lot FBRC ZSI 1224; specimen RPf2). (g) P. rajahensis (Lea, 1841). Rajah’s Tank, India (holotype NMNH 84638). (h) B. soleniformis (Benson, 1836). Brahmaputra River, India (specimen NMNH 127246). Scale bar = 20 mm [a-e, g]; scale bar = 25 mm [f]; scale bar = 30 mm [h]. Photos: N. V. Subba Rao and R. Pasupuleti [a, b, d, f], S. Hof [c], K. Webb [e], and NMNH collection database under a CC0 1.0 license [g, h].
Macroevolution and evolutionary biogeography of the Parreysiinae
Our combined supercontinent-based biogeographic modeling (S-DIVA + DIVALIKE) reveals that this subfamily most likely originated and diversified on Gondwana and its fragments (probability = 1.00), with a secondary radiation of the so-called Mekong’s Indochinellini (sensu Pfeiffer et al., 2018)51, a compact but diverse monophyletic subclade, in the Sundaland Subregion (probability = 1.00) (Fig. 2). The earliest split within the subfamily was associated with the separation of the Lamellidentini from other taxa by a dispersal event (probability = 1.00) and did occur in the Early Cretaceous (mean age = 135 Myr, 95% HPD = 125–144 Myr) (Fig. 2: Event I). Our combined tectonic plate-based ancestral area reconstruction (S-DIVA + DIVALIKE) suggests that this split occurred on the Burma Terrane, Indian Plate or on both of these blocks with equal probability (Fig. 2). The Parreysiini + Leoparreysiini clade most likely separated from the Coelaturini + Indochinellini clade by a dispersal event (probability = 1.00) in the mid-Cretaceous (mean age = 111 Myr, 95% HPD = 103–119 Myr) (Fig. 2: Event II). The Burma Terrane and Indian Plate are returned as the most probable ancestral areas during this event by our combined model (Fig. 2).
A series of vicariance events occurred in the Late Cretaceous: Coelaturini vs. Indochinellini (mean age = 98 Myr, 95% HPD = 90–105 Myr) (Fig. 2: Event III); Parreysiini vs. Leoparreysiini (mean age = 96 Myr, 95% HPD = 87–104 Myr) (Fig. 2: Event IV); Indonaia vs. the rest of the Indochinellini (mean age = 81 Myr, 95% HPD = 74–89 Myr) (Fig. 2: Event V); and Lamellidens vs. Trapezidens (mean age = 74 Myr, 95% HPD = 65–83 Myr) (Fig. 2: Event VI). The first vicariance event was preceded by a dispersal event and most likely corresponded to a split between Africa and Burma Terrane (probability = 0.60) or between Africa and Indian Plate (probability = 0.40). The other events in this series could be linked to repeated splits and reconnections between the Indian Plate and Burma Terrane (probability = 1.00).
The Mekong’s Indochinellini did separate from the Radiatula clade near the terminal Eocene (mean age = 38 Myr, 95% HPD = 34–42 Myr) (Fig. 2: Event VII). Our ancestral area reconstruction suggests that this vicariance event could be linked to a direct connection between Burma Terrane and mainland Asia (probability = 1.00). Exchanges between freshwater mussel faunas of the Indian Plate and Burma Terrane, which traced well in Indonaia and Lamellidens radiations, started in the Late Oligocene (mean age = 24–26 Myr, 95% HPD = 18–30 Myr) and continued in the Late Miocene (mean age = 8 Myr, 95% HPD = 6–11 Myr) (Fig. 2). These vicariance events reflect direct connections (river captures) between freshwater systems of these terranes based on our combined biogeographic reconstruction (probability = 1.00 in almost all cases).
Taxonomy of freshwater mussels from the Indian Subcontinent
This taxonomic section is largely based on our novel phylogenetic and morphological research (Fig. 2 and Supplementary Note 1). A brief overview of the fauna is presented in Table 1, while the taxonomic account and explanatory comments for each species are given in the Supplementary Note 1. Additionally, one new species of the genus Parreysia from Southwestern India is described herein.
Family Unionidae Rafinesque, 1820.
Subfamily Parreysiinae Henderson, 1935.
Tribe Indochinellini Bolotov, Pfeiffer, Vikhrev & Konopleva, 2018.
Genus Indonaia Prashad, 1918.
Type species: Unio caeruleus Lea, 1831 (by original designation)59.
Distribution: Indian and Western Indochina subregions: from Indus River in Pakistan60 through India57,61, Bangladesh, Nepal61,62, and Bhutan63 to the Salween River in Myanmar56.
Comments: This genus contains not less than 11 recent species, eight of which occur on the Indian Subcontinent and three in the Western Indochina (Table 1 and Fig. 4b–h). Here, we tentatively delineate these taxa to three informal species groups (Fig. 2 and Table 1). The caerulea-group contains eight Radiatula-like species having an ovate or elongated shell of moderate thickness. The cylindrica-group joins two Parreysia-like species with a thicker, ovate shell. Finally, the involuta-group combines two peculiar species, sharing a thin, fragile shell. The pseudocardinal teeth in the latter group are lamellar, quite similar to those in Lamellidens taxa. The caerulea- and cylindrica-groups are largely supported by our phylogeny. The involuta-group was separated by means of a morphological approach alone, because the DNA sequences of both Indonaia involuta (Hanley, 1856) and I. olivaria (Lea, 1831) are not available. Based on the phylogenetic data, we transfer the nominal species Parreysia cylindrica Annandale & Prashad, 1919 to the genus Indonaia and propose I. cylindrica comb. nov. (Fig. 2, Fig. 4f–g, and Supplementary Figs. 1–2). Additionally, we revise the synonymy for nominal taxa in this genus (Table 1 and Supplementary Note 1). We chose not to discuss the nominal taxon Indonaia substriata (Lea, 1856) [= Nodularia (s. str.) pecten Preston, 1912]2 from Thailand here, because its generic placement and range are unclear and require future research efforts.
Two Late Cretaceous fossil species from the Intertrappean Beds of the Deccan Plateau in India are considered here as the earliest members of the Indonaia crown group, i.e. †I. hunteri (Hislop, 1860) comb. nov. and †I. pascoei Prashad, 1928 (Table 2 and Supplementary Note 2). Several younger fossil species in this genus were described from Miocene to Pliocene deposits (mostly the Siwalik Group64) in India, Pakistan, Nepal, and Myanmar65–69.
Table 2.
Taxonomic review of the fossil Unionidae (Parreysiinae) from the Maastrichtian Intertrappean Beds of the Deccan Plateau, Indian Plate (see Supplementary Note 2 for detail).
| Taxon | Original combination and synonyms | Type locality | Type specimen** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tribe Indochinellini Bolotov, Pfeiffer, Vikhrev & Konopleva, 2018 | |||
| Genus Indonaia Prashad, 1918 | |||
| †Indonaia hunteri (Hislop, 1860) comb. nov. | †Unio hunteri Hislop (1860)235: p. 174, pl. 6, Fig. 25; †Parreysia hunteri (Hislop, 1860): Modell (1969)67: p. 11 | Karuni, 100 miles S.S.W. of Nagpur city, Hyderabad Territory, British India [near Karanji Village, 19.8567° N, 78.3141° E, Deccan Plateau, Telangana, India]235 | Lectotype PIMB 948 [designated by Hartman et al., 2008]145 |
| †Indonaia pascoei Prashad, 1928 | †Indonaia pascoei Prashad (1928)66: p. 311, pl. 25, Figs. 4–5; †Palindonaia pascoei (Prashad, 1928): Modell (1969)67: p. 9 | “…at a point situated 2 furlongs S. 10° W. of Nawapet (17°43′30" 78°23′45"), Hyderabad State (Deccan)” [ca. 400 m SSW of Nawabpet Village, 17.7177° N, 78.3933° E, Telangana, India]66 | Holotype [based on original designation; not traced but it is probably in the collection of Geological Survey of India]66 |
| Tribe Lamellidentini Modell, 1942 | |||
| Genus Lamellidens Simpson, 1900 | |||
| †Lamellidens carteri (Hislop, 1860) | †Unio carteri Hislop (1860)235: p. 175, pl. 7, Fig. 28; †Lamellidens carteri (Hislop, 1860): Modell (1969)67: p. 11 | Karuni, 100 miles S.S.W. of Nagpur city, Hyderabad Territory, British India [near Karanji Village, 19.8567° N, 78.3141° E, Deccan Plateau, Telangana, India]235 | Lectotype PIMB 949 [designated by Hartman et al., 2008]145 |
| †Lamellidens deccanensis (J. Sowerby in Malcolmson, 1840) comb. nov. | †Unio deccanensis J. Sowerby in Malcolmson (1840)236: pl. 47, Figs. 4–10; †Hyriopsis deccanensis (J. Sowerby, 1827) [erroneous publication year]: Modell (1969)67: p. 12 | Munnoor236 [near Muthnur Village, 19.5192° N, 78.4657° E, Nirmal Hills, Telangana, India]237 | Lectotype PIMB 947 (of rather poor quality) [designated by Hartman et al., 2008]145 |
| †Lamellidens vredenburgi Prashad, 1921 | †Lamellidens vredenburgi Prashad (1921)238: p. 368, pl. 12, Figs. 1–2 | Goraha, Narbada [probably Gora Village, 1.8608° N, 73.6830° E, Narmada District, Gujarat, India]238 | Holotype [based on original designation; not traced but it is probably in the collection of Geological Survey of India]238 |
| Tribe Parreysiini Henderson, 1935 | |||
| Genus Parreysia Conrad, 1853 | |||
| †Parreysia imbricatus (Hislop, 1860) comb. nov. | †Unio imbricatus Hislop (1860)235: p. 175, pl. 7, Fig. 27a-c; †Schistodesmus imbricatus (Hislop, 1860): Modell (1969)67: p. 10 | Mekalgandi Ghat, 150 miles S.S.W. of Nagpur city, Hyderabad Territory, British India235,236 [near Muthnur Village, 19.5192° N, 78.4657° E, Nirmal Hills, Telangana, India]237 | Lectotype PIMB 950 [designated by Hartman et al., 2008]145 |
| †Parreysia malcolmsoni (Hislop, 1860) | †Unio tumida J. Sowerby in Malcolmson (1840): pl. 47, Figs. 11–12 [unavailable as a primary homonym]236; †U. malcolmsoni Hislop (1860): p. 174 [new name for †U. tumida Sowerby in Malcolmson, 1840]235; †Parreysia malcolmensis Modell (1969): p. 11 [error for †U. malcolmsoni Hislop, 1860]67 | Mekalgandi Ghat, 150 miles S.S.W. of Nagpur city, Hyderabad Territory, British India235,236 [near Muthnur Village, 19.5192° N, 78.4657° E, Nirmal Hills, Telangana, India]237 | Lectotype PIMB 953 (complete shell) [designated by Hartman et al., 2008]145 |
| †Parreysia mamillatus (Hislop, 1860) comb. nov. | †Unio mamillatus Hislop (1860)235: p. 175, pl. 7, Fig. 26; †Schistodesmus mamillatus (Hislop, 1860): Modell (1969)67: p. 10 | Karuni, 100 miles S.S.W. of Nagpur city, Hyderabad Territory, British India [near Karanji Village, 19.8567° N, 78.3141° E, Deccan Plateau, Telangana, India]235 | Lectotype PIMB 946 [designated by Hartman et al., 2008]145 |
Tribe Lamellidentini Modell, 1942.
Genus Arcidopsis Simpson, 1900.
Type species: Unio footei Theobald, 1876 (by original designation)70.
Distribution: Endemic to the upper section of the Krishna Basin in Western Ghats, India53,71. At first glance, historical records from “Mysore”72,73 could be linked to the Upper Kaveri Basin near the city of Mysuru53 but are more likely to be attributed to the former State of Mysore, which also covered part of the Upper Krishna Basin.
Comments: This monotypic genus with its single species, A. footei (Table 1 and and Fig. 4a), was placed within the Unionidae incertae sedis1,53 but later it was transferred to the Lamellidentini2. The DNA sequences of this taxon are yet to be generated, and its fossil records are unknown.
Genus Lamellidens Simpson, 1900 [= Velunio Haas, 1919 syn. nov.; type species: Unio velaris Sowerby, 1868 (by monotypy)74,75].
Type species: Unio marginalis Lamarck, 1819 (by original designation)70.
Distribution: Indian and Western Indochina subregions: widespread from Indus River in Pakistan60 through India, Sri Lanka57,61,76, Nepal61,62, Bhutan77, and Bangladesh57 to Salween River in Myanmar56 and southwestern Yunnan in China. Lamellidens candaharicus (Hutton, 1849) [= L. rhadinaeus Annandale & Prashad, 1919 syn. nov.], the westernmost species of this genus, was discovered from the endorheic Sistan/Helmand River drainage in eastern Iran and Afghanistan78.
Comments: This genus contains 12 recent species, nine of which occur on the Indian Subcontinent and three in the Western Indochina (Table 1 and Fig. 3a–h). In this study, we provisionally delineate these species to two informal groups, which are largely supported by our phylogenies (Supplementary Figs. 1–2, Fig. 2 and Table 1). The corrianus-group contains four species usually having a more or less elongated shell, while the marginalis-group joins species with somewhat ovate or rounded shell. Conversely, the shell outline itself cannot be used for diagnostic purposes even between the two species groups, as the shell shape of taxa in this genus is extremely variable, and multiple intermediate forms do occur, e.g. those in Lamellidens marginalis (Fig. 3f–g).
A new formal synonymy is proposed here for several nominal taxa (Table 1). Based on morphological and biogeographic data, we transfer the nominal taxon Physunio friersoni Simpson, 1914 [new name for Unio velaris Sowerby, 1868]79 to Lamellidens and propose L. friersoni (Simpson, 1914) comb. nov. Hence, Velunio Haas, 1919 syn. nov., a monotypic subgenus (section)75 of the genus Physunio Simpson, 1900, established for this taxon, should be considered a synonym of Lamellidens.
The nominal species Unio groenlandicus Mörch, 1868 was introduced based on a description and figure of Schröter80,81. This taxon cannot be attributed to Schröter81, because this author named it as “die breite Mahler-Muschel aus Grönland”, which is not a binomial name. Mörch stated that it “is Unio testudinarius, Spgl. (U. marginalis, Lam.), a common shell from Tranquebar and other places in British East Indies”80. However, we cannot link Schröter’s figure (pl. 9, Fig. 1)81 to a Lamellidens species due to the lack of pseudocardinal teeth. Hence, Unio groenlandicus is here considered a nomen dubium.
There are two older available names belonging to Lamellidens, i.e. Unio testudinarius Spengler, 1793 and U. truncatus Spengler, 1793 that were described from Tranquebar [Tharangambadi, 11.0292° N, 79.8494° E, Kaveri Basin, Tamil Nadu, India]82. Later, Haas redescribed these nominal taxa and illustrated the holotypes83. Based upon morphological examination, Haas considered Lamellidens testudinarius as the oldest available name for L. marginalis, and placed L. truncatus as a synonym of this species83,84. Furthermore, Haas synonymized the majority of nominal Lamellidens taxa under the name L. testudinarius84. However, this concept was largely ignored by subsequent researchers1,2,57. The assigment of these nominal taxa to certain species is not straghtforward. Morphologically, the holotype of Lamellidens testudinarius is an ovate shell83 that could be something from the marginalis-group, e.g. L. marginalis, L. mainwaringi or L. jenkinsianus. In its turn, the holotype of Lamellidens truncatus represents a narrower, elongated shell83 that looks either like L. corrianus or even the recently described L. unioides. Here, we prefer to consider these nominal species as taxa inquirenda but their identity will be clarified in the future based on molecular analyses of topotype samples from Tamil Nadu.
The three earliest fossil members of this genus were described from the Late Cretaceous Intertrappean Beds of the Deccan Plateau in India, i.e. †Lamellidens carteri (Hislop, 1860), †L. deccanensis (J. Sowerby in Malcolmson, 1840) comb. nov., and †L. vredenburgi Prashad, 1921 (Table 2 and Supplementary Note 2). There are several fossil species of Lamellidens from Miocene to Pliocene deposits (mostly the Siwalik Group64) in India, Pakistan, Nepal, and Myanmar66–68,85.
Tribe Parreysiini Henderson, 1935.
Genus Parreysia Conrad, 1853.
Type species: Unio multidentatus Philippi, 1847 (by original designation)86.
Distribution: Indian Subregion: from Indus River in Pakistan60 through India, Sri Lanka57,61,76, Nepal61,62, and Bangladesh57 to coastal drainages of the Rakhine State of Myanmar23.
Comments: This genus contains six recent species endemic to the Indian Subcontinent (Table 1 and Fig. 5a–g). Here, we delineate these species to three informal groups (Fig. 2 and Table 1). The keralaensis-group contains Parreysia keralaensis sp. nov. only (Fig. 5a,b). This new species represents the most distant phylogenetic lineage within the genus (Fig. 2). The corrugata-group comprises four species that are phylogenetically and morphologically close to each other, representing a species complex (Table 1 and Fig. 5c–f). Our time-calibrated phylogeny indicates that the radiation within this group occurred during the Miocene (Fig. 2). Finally, the rajahensis-group contains a single species, Parreysia rajahensis (Lea, 1841). Although the DNA sequences of this species are not available, it probably represents a distant phylogenetic lineage due to a number of specific conchological features such as very thick, triangular shell and massive hinge plate (Fig. 5g).
The synonymy of Parreysia taxa is revised here (Table 1 and Supplementary Note 1). The nominal taxon Parreysia robsoni Frierson, 1927 [holotype NHMUK 1965150; type locality: Black River, North Carolina]87,88 cannot be linked to the Indian fauna, and it is considered here as a junior subjective synonym of Fusconaia masoni (Conrad, 1834) (Ambleminae) based on morphological features.
The three earliest fossil species belonging to this genus were discovered from the Late Cretaceous Intertrappean Beds of the Deccan Plateau in India, i.e. †Parreysia imbricatus (Hislop, 1860) comb. nov., †P. malcolmsoni (Hislop, 1860), and †P. mamillatus (Hislop, 1860) comb. nov. (Table 2 and Supplementary Note 2). There are several fossil species in this genus that were described from Miocene to Pliocene deposits (mostly the Siwalik Group64) in India, Pakistan, Nepal, and Myanmar65–69.
Parreysia keralaensis Bolotov, Pasupuleti & Subba Rao sp. nov.
Figure 5a,b, Supplementary Figs. 3–6, Supplementary Table 2.
LSID: http://zoobank.org/urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:627CB4BE-CD22-495A-8FDD-55F45D971CCD.
Type material: Holotype No. FBRC ZSI 1007-a (RCB2) [shell length 50.0 mm, shell height 33.5 mm, shell width 23.8 mm; reference COI sequence acc. no. KJ872811], Periyar River (downstream), 10.11° N, 76.37° E, Aluva, Kerala, India, 17.01.2014, R. Pasupuleti leg. Paratypes: Six specimens [museum lot No. FBRC ZSI 1007; specimen codes RCB3, RCB4, RCB5, RCB8, RCB9, and RCB12] from the type locality, 17.01.2014, R. Pasupuleti leg.; two specimens [museum lot No. FBRC ZSI 1006; specimen codes RNB1 and RNB2] from Periyar River (upstream), 10.06° N, 76.78° E, Neriamangalam, Kerala, India, 01.12.2014, R. Pasupuleti leg.; one specimen [museum lot No. FBRC ZSI 1223; specimen code RPC10] from Achankovil River, 9.25° N, 76.83° E, Pampa River basin, Kizhavalloor, Kerala, India, 03.09.2014, R. Pasupuleti leg. Reference COI sequences and shell measurements of the type series are given in Supplementary Table 2. The type series is deposited in FBRC ZSI (Hyderabad, Telangana, India).
Etymology: The new species name is dedicated to the Kerala State of India, in which it was collected.
Diagnosis: The new species can be distinguished from other Parreysia taxa by having a prominent, massive, rounded umbo and a specific wave-like sculpture over the umbo or through the entire shell surface (Fig. 5a,b and Supplementary Fig. 3). Additionally, it represents the most distant phylogenetic lineage within the genus (Fig. 2).
Description: Medium-sized mussel: shell length 34.8–59.1 mm, shell height 23.7–38.2 mm, shell width 15.1–28.8 mm (N = 10; Supplementary Table 2). Shell thick, of triangular or rounded shape, slightly inequilateral; ventral margin slightly convex; dorsal, anterior, and posterior margins rounded. Umbo massive, prominent, elevated. Shell sculpture well developed, with specific wave-like ridges, covering the umbonal region or the entire shell. Most specimens share weak corrugate plications posteriorly. Periostracum brown to dark orange with green tinge. Nacre white, with yellowish or pinkish tinge, shining. Hinge plate rather narrow. Left valve with two curved lateral teeth and two strongly indented pseudocardinal teeth. Right valve with one curved lateral tooth and one massive, indented pseudocardinal tooth with a small auxiliary tooth. Anterior adductor scar rounded and deep, posterior adductor scar rounded and very shallow. Umbonal cavity very deep.
Distribution: Periyar and Pampa basins, Kerala, Southwestern India.
Parreysiinae incertae sedis.
Genus Balwantia Prashad, 1919.
Type species: Anodonta soleniformis Benson, 1836 (by original designation)89.
Distribution: Upper Brahmaputra and Upper Barak (Dhaleswari) basins, India89–91.
Comments: This monotypic genus (Table 1 and Fig. 5h) was long thought to be a synonym of Solenaia Conrad, 1869 based on a similar ultra-elongated shell shape1,57. The latter genus was recently revised with separation of several genera such as Solenaia s. str.27,92, Parvasolenaia Huang & Wu, 201993, Koreosolenaia Lee et al., 202037, and Sinosolenaia Bolotov et al., 202194. The first genus is a member of the tribe Contradentini27,92, while the others belong to the Gonideini37,93,94. Bolotov et al. restored Balwantia and placed B. soleniformis within the Contradentini together with two recently described species from Myanmar, having an ultra-elongated shell shape23. However, B. soleniformis shares unhooked glochidia and carries larvae in all the four gills (tetragenous brooding)89, and, hence, cannot be placed in the Contradentini27,95. Pfeiffer et al. considered it a monotypic genus, which may belong to the Parreysiinae27. Here, we place Balwantia as Parreysiinae incertae sedis because of the lack of available DNA sequences. Fossil records of this genus are not available.
Doubtful and uncertain freshwater mussel taxa linked to India
In this section, we present a morphology-based overview of several nominal taxa, which were described by Constantine S. Rafinesque96. Subsequent researchers largely ignored these taxa as “indeterminate Unionidae” and even as “the worthless fabrications of Rafinesque” because of very poor and incomplete descriptions97,98. In the body of available literature on the types of Unionidae described by Rafinesque99–103, any mention of the type series for his Indian taxa is absent. Furthermore, we were unable to locate the current whereabouts of these types neither in European museums nor in those in the USA (including the ANSP Malacology Collection database; http://clade.ansp.org/malacology/collections). Perhaps, the type lots have been sold to a private collector(s), because in the introduction of that paper Rafinesque offered for sale all the type shells described there96. Hence, the types are probably lost. Therefore, our decisions and comments are based exclusively on the original descriptions. Taxa, the protologues of which lack diagnostic features for reliable taxonomic identification, are considered here as nomina dubia.
A complete reappraisal of Rafinesque’s nominal taxa linked to India96 is given in Supplementary Note 3, while a brief summary of our taxonomic decisions is presented here. Diplasma marginata Rafinesque, 1831 is considered a nomen dubium, because its type locality is uncertain (River Tennessee or Hindostan) and the identity is unclear. Three more nominal species cannot be identified with certainty based on the original descriptions and are also considered nomina dubia: Diplasma similis Rafinesque, 1831 (type locality: River Ganges); Diplasma (Hemisolasma) vitrea Rafinesque, 1831 (type locality: River Jellinghy in Bengal [approx. 23.4356° N, 88.4905° E, Jalangi River, West Bengal, India]); and Lampsilis fulgens Rafinesque, 1831 (type locality: River Ganges)96. Hence, the associated genus- and family-group names such as Diplasma Rafinesque, 1831 (type species: Diplasma marginata98), Hemisolasma Rafinesque, 1831 (type species: Diplasma (Hemisolasma) vitrea101,104), Diplasminae Modell, 1942105, and Hemisolasminae Starobogatov, 1970106 also become nomina dubia.
Based on the original descriptions96, Lampsilis argyratus Rafinesque, 1831 (type locality: River Ganges) and Diplasma (Hemisolasma) striata Rafinesque, 1831 (type locality: River Jellinghy in Bengal [approx. 23.4356° N, 88.4905° E, Jalangi River, West Bengal, India]) are considered here as junior synonyms of Indonaia caerulea (Lea, 1831) and I. rugosa (Gmelin, 1791) comb. nov., respectively (Table 1). Furthermore, the diagnostic features, mentioned in the protologue96, clearly indicate that the monotypic genus Loncosilla Rafinesque, 1831 with its type species Loncosilla solenoides Rafinesque, 1831 is not a unionid mussel but a freshwater clam of the family Pharidae. A more in-depth comparative analysis using available taxonomic works on freshwater Pharidae107,108 allowed us to propose the formal synonymy as follows: Novaculina Benson, 1830 [= Loncosilla Rafinesque, 1831 syn. nov.] and Novaculina gangetica Benson, 1830 [= Loncosilla solenoides Rafinesque, 1831 syn. nov.] (Pharidae: Pharellinae).
Additionally, we would note on the enigmatic nominal taxon Unio digitiformis Sowerby, 1868 [holotype NHMUK 1965199; type locality: India] that shares an ultra-elongated shell with pointed posterior margin. Different authors placed it within different genera such as Nodularia Conrad, 1853, Lanceolaria Conrad, 1853, and Indochinella Bolotov et al., 201835,84,109,110. Haas stated that this species is certainly not a member of the Indian fauna84. Based upon a morphological examination of the holotype, we found that it conchologically corresponds to Diplodon parallelopipedon (Lea, 1834) (Hyriidae: Hyriinae), a South American species, which is known to occur in the Paraná Basin and coastal drainages of Uruguay1,2. Hence, its type locality was given in error. The formal synonymy is proposed here as follows: Diplodon parallelopipedon [= Unio digitiformis Sowerby, 1868 syn. nov.].
Discussion
Taxonomic richness and endemism of Oriental freshwater mussels
The Indian Subcontinent houses a rather taxonomically poor fauna of the Unionidae, which contains 25 species belonging to three Gondwanan tribes (Indochinellini, Lamellidentini, and Parreysiini) and one subfamily, the Parreysiinae. All these species are endemic to the region, except for Lamellidens nongyangensis Preston, 1912, a local population of which was recorded in Lake of No Return (Nongyang Lake) near the boundary between India and Myanmar. Our novel results confirm the conclusion of Bolotov et al.19 that the Unionidae faunas of the Indian and Western Indochina subregions share almost 100% level of endemism at the species level and that multiple records of Indian species in Myanmar57,110–113 were based on erroneous identifications. Furthermore, the tribe Parreysiini and the genera Arcidopsis, Balwantia, and Parreysia are unknown beyond the Indian Subregion.
The taxonomic richness of the Unionidae fauna in Western Indochina is 2.5 times higher compared with that on the Indian Subcontinent, with more than 60 species, but it represents an amalgam of the original Gondwanan taxa (Indochinellini, Lamellidentini, and Leoparreysiini), and the Paleogene immigrants from the Sundaland (Contradentini and Pseudodontini)19,22,23,35,56. The genera Indochinella Bolotov et al., 2018, Pseudodon Gould, 1844, Radiatula Simpson, 1900, Trapezidens Bolotov, Vikhrev & Konopleva, 2017, and Yaukthwa Konopleva et al., 2019 are endemic to the Western Indochina Subregion22,23,35,53,56,114. Though Leoparreysia Vikhrev, Bolotov & Kondakov, 2017 was also considered among these endemic clades23,35,56, morphology-based surveys indicate that it may contain at least two species east of the Salween – Mekong drainage divide. First, Leoparreysia subcircularis (Brandt, 1974) [type locality: Mekong River between Takek and Nakon Panom, Laos]115 was recently transferred from Contradentini to Leoparreysiini27. Second, Leoparreysia superstes (Neumayr, 1899) comb. nov. [type locality: Erhai Lake, Upper Mekong Basin, Yunnan, China]116 conchologically corresponds to the Leoparreysiini and is moved from Rhombuniopsis Haas, 1920 (Unioninae: Unionini) to Leoparreysia here. However, the generic placement of both species, mentioned above, is yet to be confirmed by means of the DNA-based approach.
The Indian cementing bivalve Pseudomulleria dalyi (Smith, 1898) was considered a possible Gondwanan relict117. Traditionally, this enigmatic “freshwater oyster” was placed in the Etheriidae based on morphological criteria57,84,110,118,119 but phylogenetic reconstructions using a single available COI sequence of this taxon (acc. No. AF231750) repeatedly indicated that it is a unionid species belonging to the Parreysiinae120–122. Its close affinities with the Unionidae were previously assumed based on anatomical surveys118,123. Conversely, Graf & Cummings considered this COI sequence as potentially problematic due to the discordance of its phylogenetic position with morphological data104 and returned Pseudomulleria dalyi to the Etheriidae1. The latter concept of Pseudomulleria is accepted in the most recent global checklist of freshwater mussel taxa2. Although the COI sequence under discussion seems to be correct, we did not include this taxon to the current list of the Indian Parreysiinae, because a final solution on its family-level placement requires an expanded set of DNA sequences and needs further research efforts2.
We show that several highland areas of the Indian Subcontinent harbor endemic taxa of freshwater mussels with restricted ranges (Table 1). As it was expected117, rivers flowing from the Western Ghats share the highest proportion of regional endemic species such as Arcidopsis footei (Tunga, Ghataprabha, and Koyna rivers, Upper Krishna Basin71,124), Indonaia bonneaudii (Karli River), I. cylindrica comb. nov. (Upper Krishna Basin), Parreysia keralaensis sp. nov. (Periyar and Pampa basins), and Pseudomulleria dalyi (Tunga and Bhadra rivers, Upper Krishna Basin124,125). Further, rivers in Assam and northeastern Bangladesh house at least three narrowly endemic taxa, i.e. Balwantia soleniformis (Upper Brahmaputra and Upper Barak basins), Indonaia involuta (Upper Brahmaputra and Surma basins), and Lamellidens friersoni comb. nov. (Upper Brahmaputra Basin). Finally, Parreysia rajahensis seems to be endemic to the Narmada River97. Hence, these freshwater systems should be considered of highest priority areas for freshwater mussel conservation at the national and global levels.
It was assumed that the Western Ghats could have served as a refugium for the autochthonous Gondwanan fauna during the Deccan eruptions126. At first glance, our data on the taxonomic diversity and endemism of freshwater mussels agree with this hypothesis. This mountain range represents a major evolutionary hotspot for a plethora of taxa with possible Gondwanan affinities such as scorpions126, freshwater gastropods127, freshwater fish128,129, frogs130–133, and evergreen trees134.
The Andaman and Nicobar archipelagoes, being a union territory of India, are located on a separate tectonic platelet, which is confined to the western margin of the Sunda Plate38. These islands may therefore harbor a specific freshwater mussel assemblage that should be different from those on the Indian Subcontinent and Burma Terrane. A single nominal taxon, Alasmodonta nicobarica Mörch, 1872, was described on the basis of one shell from the Nicobar Islands135. Based upon the original description135, this shell is irregularly oval, convex, with irregular growth lines; dorsal margin slightly arched, anterior margin narrowed and rounded, ventral margin slightly concave, posterior margin narrowed and slightly prominent; shell color is olive, with darker bandages and numerous dark green rays; umbo is not prominent, eroded; pseudocardinal teeth are almost completely absent, lateral teeth are lamellar. Simpson placed this nominal taxon in the genus Pseudodon sensu lato70 based on Mörch’s comments in the protologue135 but later transferred it to Pletholophus Simpson, 1900 with respect to the expert opinion of Haas, who has examined the holotype of Alasmodonta nicobarica79. Currently, it is considered a synonym of Pletholophus tenuis (Griffith & Pidgeon, 1833) (Unioninae: Cristariini), an East Asian species2. However, if its type locality is stated correctly, it cannot be assigned to Pletholophus tenuis from a biogeographical point of view35. At first glance, it may be a member of the genus Monodontina Conrad, 1853 (Gonideinae: Pseudodontini). This genus can be distinguished from other taxa by having an ovate or rounded shell and weakly developed pseudocardinal teeth36, which aligns with the original description of Alasmodonta nicobarica. The Monodontina taxa sometimes share green rays through the periostracum. The genus Monodontina is known to occur in southern Myanmar (Lenya River), southern Thailand, Chao Phraya and Mekong basins, and throughout Malaysia and the Greater Sunda Islands23, and, hence, could theoretically be found on the Nicobar Islands. Here, we propose Monodontina nicobarica (Mörch, 1872) comb. nov. as a preliminary taxonomic hypothesis that needs to be checked by means of a DNA-based approach. The Great Nicobar Island with its numerous rivers and streams flowing through primary tropical forests could indeed house some interesting freshwater mussel taxa and must be a focus of future collecting efforts.
Gondwanaland origin and diversification of the Parreysiinae
Our earlier biogeographic scenario on the origin and diversification of the Unionidae19 suggested that the MRCA of Parreysiinae has originated in Western Indochina in the Late Jurassic (ca. 150 Myr), with subsequent dispersal of descendants into Africa in the mid-Cretaceous (ca. 95 Myr) and into India in the Paleocene (ca. 60 Myr). At that time, we did not consider the Burma Terrane as a Gondwanan fragment and used a very restricted set of Indian taxa. Hence, our scenario predicted a Laurasian origin of the Parreysiinae and their westward expansion to East Gondwana starting more than 100 Myr ago that, as Pfeiffer et al. noted51, weakly corresponds to modern paleogeographic reconstructions. The latter authors proposed an alternative hypothesis on the origin of the Parreysiinae51. Their scenario predicted that this subfamily clade originated in Western Eurasia, with subsequent expansions south to Africa, and east to India, Myanmar, and mainland Southeast Asia. Pfeiffer et al. placed these events in the Cenozoic51, after final contact of the Indian Subcontinent with the Eurasian Plate (i.e. since the mid-Eocene42,45), based on multiple Miocene fossils of three Parreysiinae lineages (Coelaturini, Parreysia, and Lamellidens) on Gondwanan fragments. Using these fossils as time calibrations, Ortiz-Sepulveda et al. proposed an additional scenario on African taxa that predicted the Early Miocene origin of the Coelaturini in Eurasia followed by their Early to Middle Miocene expansion into Africa, roughly coinciding with the closure of the Tethys Sea31. Anyway, all the scenarios, outlined above, do not consider modern plate tectonic reconstructions and, though substantially differ by timeframe, support the so-called “Out-of-Asia” model136.
Here, we present an updated reconstruction of the origin and diversification of the Parreysiinae based on our novel biogeographic modeling, expanded paleontological data set, and the newest tectonic and paleomagnetic reconstructions39–42,48,50,137. Our new “Out-of-India-&-Burma” scenario indicates that this subfamily originated in East Gondwana in the Late Jurassic. While Late Triassic or Early Jurassic African Unionidae are unknown, the Mid- to Late Jurassic deposits (age from 170 to 145 Myr) house a species-rich freshwater mussel assemblage, which contains a number of Unionidae and Margaritiferidae taxa138. The ancestors of these groups most likely arrived to East Gondwana from Laurasia through the joined African Plate and Arabia. Several fossil freshwater mussel taxa from the Irhazer Group deposits (Mid- to Late Jurassic) of Niger resemble modern Unionidae in the hinge structure, e.g. the monotypic genera †Coactunio Van Damme & Bogan, 2015, †Rostrunio Van Damme & Bogan, 2015, and †Tuaregunio Van Damme & Bogan, 2015138. These taxa were considered the earliest members of the modern crown-group of the Unionidae in Jurassic Africa138. In our opinion, these rare fossils could be linked to the MRCA or a steam group of the Parreysiinae based on the hinge structure. The initial breakup of East Gondwana from West Gondwana started approximately 160 Myr, separating the Indian Plate together with its proposed satellites from continental Africa45,139. Hence, the Parreysiinae MRCA most likely colonized India earlier (Fig. 6).
Figure 6.
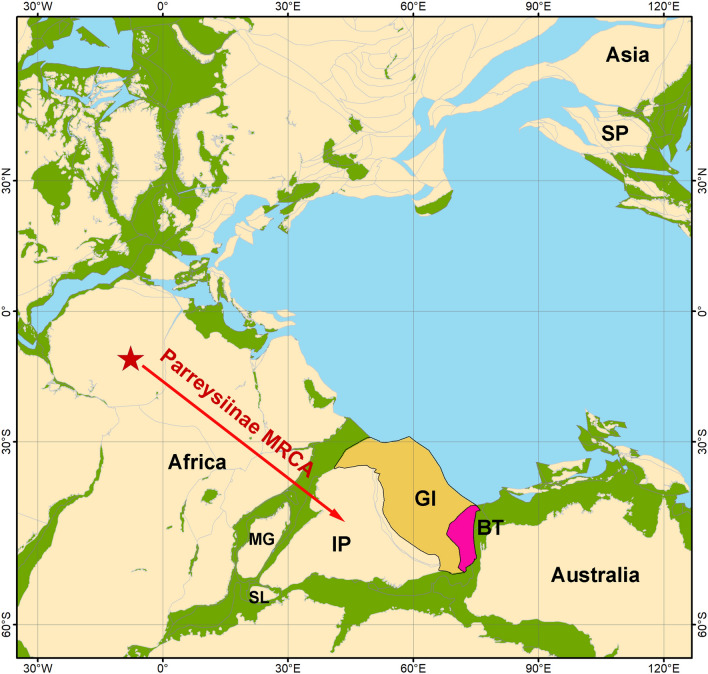
Proposed scenario of the trans-Gondwanan expansion of the Parreysiinae MRCA (red arrow) in the Middle Jurassic (170–165 Myr). We assume that the MRCA of this subfamily migrated through freshwater systems of the African Plate and/or Arabia to an ancient landmass, containing the Indian Plate (with Greater India) and Burma Terrane. Red star indicates fossil records of the earliest African crown-group unionid mussels from Mid- to Late Jurassic deposits in Niger, i.e. †Coactunio iguallalensis, †Rostrunio lapparenti, and †Tuaregunio agadesensis138. IP Indian Plate, BT Burma Terrane, GI Greater India, SP Sunda Plate (with the Indochina Block and Sibumasu Terrane), SL Sri Lanka, MG Madagascar. Color filling is as follows: Burma Terrane (pink), Greater India (light orange), modern land (light yellow), proposed ancient land (light green), and ocean surface (light blue). The paleo-map was reconstructed using GPlates v. 2.3 (https://www.gplates.org)205 and corresponding data sets206–209. Reconstruction of the Greater India in Gondwana follows published works47,139 with additional modifications according to our biogeographic reconstructions. (Maps: Mikhail Yu. Gofarov and Ivan N. Bolotov).
Our scenario further suggests that the earliest diversification in the subfamily occurred on an ancient landmass, containing the Indian Plate and Burma Terrane, which were joined through the Greater India, in the Early Cretaceous47,139 (Fig. 7a). During that period, two large clades, i.e. Lamellidentini (Fig. 2: Event I) and Parreysiini + Leoparreysiini (Fig. 2: Event II) were separated. The splits, outlined above, coincided with a complete disappearance of unionids and margaritiferids in the Early Cretaceous deposits of continental Africa, probably reflecting a major extinction event138. Though it roughly coincides with the global Tithonian extinction event138, the post-Jurassic disappearance of naiads in Africa could also be linked to active development of a large system of rifts, leading to intercontinental marine transgressions140–142. Thereby we could assume that an ancient landmass, which consisted of the modern Indian Plate, Greater India, and Burma Terrane39,40,42,48,137, played a significant role as a refugium for freshwater mussels in the Early Cretaceous. Perhaps some geographic barriers on this landmass such as mountain ranges drove the early macroevolution of the Parreysiinae, as it was suggested for the diversification patterns in the Hyriidae18.
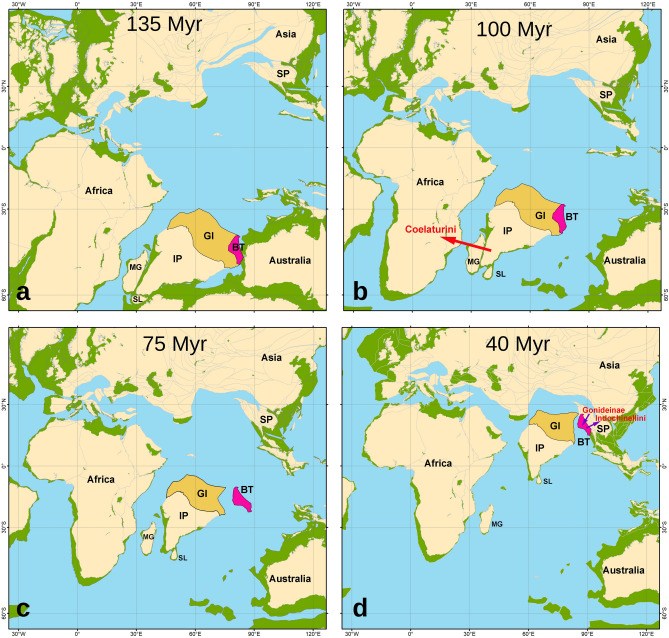
Figure 7.
Proposed scenarios of tectonic evolution of the Indian Plate and Burma Terrane with respect to our time-calibrated phylogenetic reconstruction and statistical biogeographic models for the freshwater mussel subfamily Parreysiinae (see Fig. 2 for detail). The paleo-maps are as follows: (a) Early Cretaceous (135 Myr): unionid mussels have gone extinct in continental Africa but survived on an East Gondwanan fragment containing the Indian Plate (with Greater India) and Burma Terrane, where the first split in the Parreysiinae did occur, i.e. the separation of the Lamellidentini; (b) mid-Cretaceous (100 Myr): colonization event of the Coelaturini MRCA (red arrow) to continental Africa, suggesting direct contact between the Indian Subcontinent and African Plate, probably through Madagascar; the Indian Plate and Burma Terrane are still connected through the Greater India; (c) Late Cretaceous (75 Myr): final separation of the Burma Terrane from the Indian Plate, probably by a partial submergence of the Greater India; both the landmasses served as insular “biotic ferries”, carrying Gondwanan biota to Asia; and (d) Late Eocene (40 Myr): Burma Terrane—Asia collision, leading to the expansion of the Mekong’s Indochinellini MRCA to the Sundaland Subregion and a colonization event of the Pseudodon and Yaukthwa MRCAs (Gonideinae: Pseudodontini and Contradentini)23 to the Burma Terrane (purple arrows). IP Indian Plate, BT Burma Terrane, GI Greater India, SP Sunda Plate (with the Indochina Block and Sibumasu Terrane), SL Sri Lanka, MG Madagascar. Color filling is as follows: Burma Terrane (pink), Greater India (light orange), modern land (light yellow), proposed ancient land (light green), and ocean surface (light blue). The paleo-maps were created using GPlates v. 2.3 (https://www.gplates.org)205 and corresponding data sets206–209, with additional modifications according to a set of novel tectonic and paleomagnetic models39–42,48,137,139 and our biogeographic reconstructions. (Maps: Mikhail Yu. Gofarov and Ivan N. Bolotov).
Our modeling reveals that a re-colonization event of the Parreysiinae from the Indo-Burma refugium into Africa most likely occurred in the mid-Cretaceous (Fig. 7b). This dispersal was followed by a vicariance event (mean age = 98 Myr) that lead to the origin of the African tribe Coelaturini (Fig. 2: Event III). A similar mean age was obtained for the split between the African Parachanna and Oriental Channa clades of snakehead fishes (Channidae) using a set of crown fossil calibrations129. The sister family Aenigmachannidae, a unique subterranean lineage from Western Ghats, separated from the Channidae approximately 110 Myr ago129. The pattern, outlined above, predicts a hypothetical land bridge between the Indian Plate and Africa nearly 100–110 Myr ago, probably through Madagascar45,143. Conversely, India could have reestablished biotic connections with Africa during its collision with the Kohistan–Ladakh Arc along the Indus Suture in the Late Cretaceous (ca. 85 Ma)45, although this geological event postdates our divergence age for the Coelaturini. Briggs assumed that India always remained close to Africa and Madagascar during its northward motion144. Our results, however, suggest that the Indian Plate was linked to Africa sometime in the mid-Cretaceous but this connection was lost afterwards.
Three subsequent splits in the subfamily Parreysiinae reflect the segregation of the Indian Plate and Burma Terrane during the Late Cretaceous (mean age interval 96 to 74 Myr; Fig. 2: Events IV, V, VI). There is no evidence of any connection between these landmasses during a nearly 50-Myr period (74 to 26 Myr), starting near the Campanian—Maastrichtian boundary and covering the entire Paleogene epoch (Fig. 7c). Our review of available fossils from the Deccan Intertrappean Beds reveals that members of Indonaia, Lamellidens, and Parreysia were presented on the Indian Plate145 right before the Cretaceous – Paleogene (K-Pg) boundary146 (Table 2 and Supplementary Note 2). These paleontological findings support our ancestral area reconstruction indicating the Indian origin of these genera. Van Damme et al. noted that Deccan fossils could also belong to the Hyriidae because they often share a crenate or wavy ventral margin138. However, such “plicate” forms could independently evolve in different unionoid families, e.g. the Margaritiferidae (Margaritifera marrianae Johnson, 1983147 and Pseudunio flabellatus (Goldfuss, 1837)148) and Unionidae (genera Amblema Rafinesque, 1820149, Tritogonia Agassiz, 1852150, and others).
The Burma Terrane collided with the Sunda Plate in the Late Eocene (mean age = 38 Myr) that is reflected by the dispersal event of the Mekong’s Indochinellini from the terrane to mainland Asia (Figs. 7d, 2: Event VII). During the same period, members of the tribes Contradentini and Pseudodontini, belonging to the subfamily Gonideinae, colonized the Burma Terrane from Asia (Sunda Plate) that leads to the endemic Pseudodon and Yaukthwa radiations in Western Indochina23. The Sundaland itself most likely represents an ancient evolutionary hotspot for the Gonideinae, because two endemic, deeply divergent tribes were recently discovered from Borneo, i.e. the Ctenodesmini Pfeiffer, Zieritz, Rahim & Lopes-Lima, 2021 and Schepmaniini Lopes-Lima, Pfeiffer & Zieritz, 202128. Though these Bornean clades are yet to be involved into any time-calibrated phylogeny, their phylogenetic position (sister to the Contradentini + Rectidentini and to Pseudodontini, respectively) undoubtedly indicates a Late Mesozoic separation28.
A few species-level splits discovered in the genera Indonaia and Lamellidens indicate that the first re-connection of the Indian Plate and Burma Terrane did occur at the Oligocene – Miocene boundary (mean ages 26 to 24 Myr). Several additional faunal exchanges between these landmasses during the Miocene (mean ages 12 to 8 Myr), most likely reflecting river (stream) capture events, were also uncovered by our phylogeny. These range expansions could be traced in multiple fossil records of Indonaia, Lamellidens, and Parreysia species from Miocene deposits throughout Pakistan, India, Nepal, and Myanmar65–69. Perhaps, the exchanges between freshwater mussel faunas of the Indian Subcontinent and surrounding landmasses during the Miocene were triggered by humid and warm climatic episodes, as it was shown for freshwater gastropods127,151 and amphibians152.
Interestingly, none of the unionid mussels seems to follow the so-called “Into India” scenario, though this pattern frequently occurs in Indian freshwater gastropods127,153,154, frogs155,156, and other animals. In contrast, our biogeographic models trace multiple “Into Burma” expansion events from India and Sundaland, starting since the Burma Terrane – Asia collision in the Late Eocene.
Burma Terrane as a second “biotic ferry” from Gondwana to Asia
There are multiple evidences that the Indian Plate has served as a “biotic ferry”, transferring a derivative of the aboriginal Gondwanan biota to Asia44,157–159. The iconic examples of taxa that are thought to have arrived to Asia by this way were discovered among caecilians160,161, frogs132, freshwater fishes129,162, freshwater crabs163, centipedes164, scorpions126, tarantulas165, and various plants166,167. Our study reveals that unionid mussels, a primarily freshwater group, the dispersal of which requires direct links between landmasses, should surely be added to the list of “passengers” that have travelled through the Tethys Ocean on this tectonic block. Furthermore, we show that the Burma Terrane could be considered a separate “biotic ferry” that also carried members of Gondwanan biota to Asia (Fig. 7a–d). The high degree of endemism discovered in freshwater mussels on the Burma Terrane (and on the Indian Subcontinent as well) reveals that the Gondwanan “biotic ferries” have served as insular evolutionary hotspots, at least during the entire Paleogene (Fig. 7c). Our results support the hypothesis on insular endemism patterns (the so-called “endemic insularity syndrome”) discovered in the paleo-biota from the mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber168–170.
Earlier, it was suggested that several non-Indian Gondwanaland fragments such as the Burma and Lhasa terranes might have transferred Gondwanan lineages into Asia but any direct biogeographic evidence supporting this idea was not available127. The body of literature on this issue is still very limited, and a few available reports are based exclusively on paleontological data. First, a review of biogeographic affinities of numerous plant and animal taxa discovered in the mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber (ca. 100 Myr; near the Albian—Cenomanian boundary) reveals that this biota represents a selection of Gondwanan organisms and that the Burma Terrane could not have separated from East Gondwana before the Early Cretaceous49. From this perspective, ancestors of several secondary freshwater/estuarine and terrestrial groups of Mollusca discovered in Burmese amber such as †Palaeolignopholas piddocks (Pholadidae)171 and some land snail taxa (Diplommatinidae and Pupinidae)172,173 may have also arrived to Asia with the Burma Terrane. The discovery of a freshwater pond snail (Lymnaeidae) in this amber, however, could be linked to a long‐distance dispersal event174. Perhaps it was not a transoceanic dispersal as such but an expansion from the nearby Indian Subcontinent, because the Deccan Trap sedimentary sequence harbors a diverse and species-rich assemblage of fossil freshwater snails, containing the Lymnaeidae, Planorbidae, Pomatiopsidae, Succinidae, Thiaridae, Valvatidae, and Viviparidae taxa175. Second, on the basis of a comprehensive survey on the Eocene flora of Myanmar, the Burma Terrane was considered a Gondwanan fragment that collided with Asia in the Late Eocene (ca. 41 Myr) and facilitated floristic exchange between the terrane, Indian Plate, and Asian mainland176. The dating of the Burma Terrane—Asia collision recovered in this research aligns with our estimate of 38 Myr inferred from the time-calibrated phylogeny of the Parreysiinae.
Conclusion
Our research presents the first DNA-based evidence that the Burma Terrane transferred an ancient derivative of Gondwanan biota to Asia, as India did. These results agree with a growing body of modern paleontological, tectonic, paleomagnetic, and geological research, supporting a Gondwanan origin of the Burma Terrane and its northward rafting through the Tethys Ocean39–41,48,49,176. Based on biogeographic patterns that were discovered in freshwater mussels (Unionidae: Parreysiinae), we propose that this terrane was a part of an ancient landmass, also containing the Indian Plate and Greater India, from the Middle Jurassic (ca. 160 Myr) to the terminal Cretaceous (ca. 75 Myr). Later on, during the Paleogene, the Burma Terrane was an isolated island that has collided with mainland Asia (Sunda Plate) in the Late Eocene (ca. 40 Myr). The biogeographic reconstruction presented here could be used as supplement to modern plate tectonic models, repeatedly indicating northward drifting of the Burma Terrane alongside the Indian Plate40,177. In general, our scenario of tectonic evolution of the region differs from other available scenarios40 by the position of the Burma Terrane in relation to that of the Indian Plate and Greater India.
From this perspective, mainland Southeast Asia represents a Late Eocene collision zone of two tectonic blocks (Burma Terrane and Sunda Plate), initially housing completely different biotas176. These blocks could roughly be delineated via the Sagaing Fault and along the northern part of the Tenasserim Range through the Three Pagodas and Ranong faults178. This unique pattern was largely overlooked until recently which sometimes lead to incorrect conclusions on the origin and diversification of certain taxa, e.g. onychophorans179. To avoid possible reconstruction failures, Western Indochina should be coded as a separate, Gondwana-derived ancestral area in statistical biogeographic and paleontological models. Furthermore, the origin and role of several geographic barriers linked to the collision zone such as the Isthmus of Kra23 and the Salween – Mekong drainage divide35 must be re-considered based on these new findings.
Methods
Data collection
Freshwater mussel samples were collected from various localities in India, Nepal, and Myanmar from 2012 to 2020. A small foot or mantle tissue snip from each specimen from Myanmar and Nepal was fixed with 96% ethanol immediately after collection19,22,23. For the Indian samples, hemolymph was preferred as the source of genomic DNA. The hemolymph samples (0.2 ml per one specimen) were collected using a standard approach180, and genomic DNA was isolated from 0.1 ml of fresh hemolymph using the NucleoSpin® Tissue Kit (Macherey–Nagel GmbH & Co. KG, Germany), following the manufacturer protocol. The partial sequences of the mitochondrial COI, 16S rRNA, and the nuclear 28S rRNA genes were generated using standard protocols described in our earlier works19,53,56. The COI sequences of samples from Nepal were generated using the LCO1490 and COIschneck primers pair181, while those from Indian samples were obtained with the standard Folmer’s primers182. Additional DNA sequences of Indian and African taxa were obtained from NCBI’s GenBank (Datasets 1 and 2).
The dry shell vouchers and ethanol-preserved complete specimens collected by us were deposited in the following collections: FBRC ZSI—Freshwater Biology Regional Centre, Zoological Survey of India, Hyderabad, India (samples from India); SMF—Senckenberg Museum, Frankfurt, Germany (samples from Nepal); and RMBH—Russian Museum of Biodiversity Hotspots, Federal Center for Integrated Arctic Research of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Arkhangelsk, Russia (samples from Myanmar). Additionally, we examined historical shell lots in NMNH—National Museum of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC, United States of America; MCZ—Museum of Comparative Zoology, Cambridge, USA; NHMUK—British Museum of Natural History, London, United Kingdom; MNHN—Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle, Paris, France; MSNG—Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Genova, Genoa, Italy. Furthermore, the MUSSEL Project (MUSSELp) Database (http://mussel-project.uwsp.edu) was used as a reliable source of taxonomic, bibliographic, and morphological information on nominal taxa of freshwater mussels1,2,183.
Phylogenetic analyses
To reconstruct multi-locus phylogeny of the Parreysiinae (3 codons of COI + 16S rRNA + 28S rRNA), we compiled an alignment with 61 unique species-level haplotypes, including four outgroup taxa, that were selected from 203 sequenced specimens (Datasets 1 and 2). The maximum likelihood and Bayesian phylogenies were calculated using IQ-TREE v. 1.6.12184 and MrBayes v. 3.2.7a185, respectively. The IQ-TREE184 analysis was run using an automatic identification of the best evolutionary models for each partition186 and an ultrafast bootstrap algorithm187 via an online server (http://iqtree.cibiv.univie.ac.at)188. The Bayesian analysis was performed through the CIPRES Science Gateway189. We assigned the best-fit evolutionary models to each partition based on the second-order Akaike information criterion (AICc) of MEGA7190 as follows: GTR + G (1st codon of COI); TN93 + G + I (2nd codon of COI); HKY (3rd codon of COI); GTR + G + I (16S rRNA); and GTR + G (28S rRNA). The MrBayes settings were as follows: two runs (each with 50,000,000 generations), four MCMC chains (three cold and one heated; temp = 0.1), sampling every 1000th generation, and a 15% burn-in.
Species delimitation
Two species delimitation approaches were applied through available web-services, that is, the Poisson Tree Process (PTP) modeling (http://mptp.h-its.org)191 and ASAP (assemble species by automatic partitioning; https://bioinfo.mnhn.fr/abi/public/asap)192. As an input tree, we used the maximum likelihood COI phylogeny of the Parreysiinae inferred from IQ-TREE v. 1.6.12184. An initial alignment with 196 in-group COI sequences was compiled (Dataset 1). This alignment was converted to 173 unique haplotypes using an online sequence toolbox, FaBox v. 1.5 (https://birc.au.dk/~palle/php/fabox)193. Four Pseudodontini haplotypes were used as outgroup (Dataset 1). The IQ-TREE analysis was run through an online server (http://iqtree.cibiv.univie.ac.at)184 with settings as described above. Each species-level Molecular Operational Taxonomic Unit (MOTU), probably corresponding to a biological species, was checked with morphological criteria such as the shell shape, shell sculpture, umbo position, structure of pseudocardinal and lateral teeth, and shape of muscle attachment scars56. To link each MOTU to certain nominal species, the conchological features of available specimens were compared with the original taxonomic descriptions23.
Divergence time estimation
Divergence ages were estimated using BEAST v. 2.6.3194,195. The time-calibrated phylogeny was reconstructed based on an external COI evolutionary rate (1.5E-9 substitutions per site per year)196. This rate was obtained using a comprehensive set of mitochondrial genome sequences and several reliable fossil calibrations for Unionidae taxa196 and largely agrees with earlier estimates of the COI molecular clock rate in freshwater mussels147,197. For BEAST runs, we used the same multi-locus dataset as for the IQ-TREE and MrBayes phylogenetic analyses (3 codons of COI + 16S rRNA + 28S rRNA). The molecular clock rate was assigned to the COI partition only. The HKY + G model was applied for each gene partition based on our earlier considerations19. We applied a strict clock algorithm with the Yule speciation process as the tree prior198. The BEAST runs were performed through the CIPRES Science Gateway189. Three independent BEAST runs were performed, each with 150,000,000 generations and tree sampling every 1000th cycle. The resulting log files were checked visually with Tracer v. 1.7.2199. The Effective Sample Size (ESS) values of all the parameters in the combined runs were found to be > 300 after a 50% burn-in. The final tree set was generated using LogCombiner v. 2.6.6194,194 with an additional re-sampling every 5,000th generation and an appropriate burn-in. The consensus tree was found with TreeAnnotator v. 2.6.6194,194.
Ancestral area reconstruction
First, we reconstructed possible ancestral areas using data on the distribution of Parreysiinae species throughout tectonic plates as follows: African Plate (A); Burma Terrane [= West Burma Block]: a separate tectonic block between the Naga Hills, Chin Hills, and Rakhine Hills mountain ranges and the Sagaing, Three Pagodas, and Ranong faults38–40,178; the Mogok–Mandalay–Mergui Belt40 is placed here as a marginal part of the Burma Terrane (B); Indian Plate (C); and Sunda Plate with the Indochina Block and Sibumasu Terrane (D). Second, we tested the role of former supercontinents in the origin of the Parreysiinae clades as follows: Gondwana and its fragments [African Plate + Indian Plate + Burma Terrane]40,177 (A); and Laurasia [Sunda Plate]39 (B).
Ancestral areas were reconstructed with BioGeoBEARS packages200,201 implemented in RASP v. 4.2202. As input files, we used the set of trees and the consensus phylogeny obtained from BEAST runs (see above). The branch length of the trees was converted from years to Myr using a “Scaling Branch Length” option of RASP v. 4.2202 with an appropriate scaling coefficient (1.0E-6). The four outgroup taxa were removed from the trees using a “Remove Selected Groups” option of RASP v. 4.2202. The biogeographic analyses were run with default settings (max areas = 2) but without a set of + J models checking for founder-event speciation200, because these models appear to be rather doubtful from a statistical and conceptual point of view203.
To find the most appropriate biogeographic models, we conducted a comparative analysis of the relative probability of BioGeoBEARS models (DEC, DIVALIKE, and BAYAREALIKE) using the log-likelihood (LnL), AICc, and model weight according to ΔAICc (AICc wt)200–202. For the “supercontinents” reconstruction, the DIVALIKE model shared higher relative probability compared with others with respect to the AICc wt value (Supplementary Table 1). In its turn, the DEC model could be chosen according to that criterion among those reconstructing ancestral areas on the basis of tectonic plates (Supplementary Table 1). However, we selected the DIVALIKE model, sharing similar LnL and AICc values to the DEC model, as the preferred model, because the DEC model did not return well-resolved reconstructions on several nodes. In both (supercontinents and tectonic plates) cases, we additionally calculated S-DIVA model with RASP v. 4.2202 and combined DIVALIKE and S-DIVA204 models using the “Combine Results” option of the software202. These combined models were used in subsequent biogeographic analyses and reconstructions.
Tectonic plate modeling
The tectonic plate reconstructions for selected time intervals were calculated using GPlates 2.3 software (https://www.gplates.org)205 and a corresponding set of digital layers on topological plate model206–209. Additional settings were obtained from a set of novel tectonic and paleomagnetic reconstructions39–42,48,137,139. The paleogeographic positions of the Burma Terrane and Greater India at 165–170, 135, 100, 75, and 40 Myr were modified manually on the basis of our time-calibrated phylogenetic reconstruction and statistical biogeographic models (see above).
Nomenclatural acts
The electronic edition of this article conforms to the requirements of the amended International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), and hence the new name and combinations contained herein are available under that Code from the electronic edition of this article. This published work and the nomenclatural acts it contains have been registered in ZooBank (http://zoobank.org), the online registration system for the ICZN. The LSID for this publication is: http://zoobank.org/urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:FABE4C0F-313E-4AB8-803F-3523595D9A39. The electronic edition of this paper was published in a journal with an ISSN, and has been archived and is available from PubMed Central.
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Maxim Vinarski and the three anonymous reviewers for their constructive and useful comments on earlier versions of this paper. This study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (grant No. 21-17-00126 to I.N.B., A.A.L., and E.S.K.). The Ministry of Science and Higher Education of Russia supported M.Y.G. and I.V.V. (project No. FUUW-2022-0056) and A.V.K. (project No. 0793-2020-0005). We are grateful to Prof. Dr. Subodh Sharma (Kathmandu University, Nepal), Mr. Michael Pfeiffer (March-Hugstetten, Germany), Dr. Kevin Cummings (Prairie Research Institute, Illinois Natural History Survey, Champaign, USA), Dr. Nathan V. Whelan (Southeast Conservation Genetics Lab, Warm Springs Fish Technology Center, US Fish and Wildlife Service, Auburn, Alabama, USA), the late Dr. Tony Whitten (Fauna & Flora International – Asia-Pacific, UK), Mr. Frank Momberg (Director for Program Development and Asia-Pacific Program Director of Fauna & Flora International, UK), Mr. Mark Grindley (Country Director of Fauna & Flora International – Myanmar Program, Myanmar), and the staff of the Department of Fisheries of the Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Irrigation of Myanmar for their great help during this study. Special thanks goes to Dr. Arthur E. Bogan (North Carolina Museum of Natural Sciences, Raleigh, USA) for his useful comments on the type series of Rafinesque’s taxa described from India. We thank Dr. Deepa Jaiswal (Scientist-in-Charge, Freshwater Biology Regional Centre, Zoological Survey of India, Hyderabad, India) for the permission to work in their laboratory and her colleagues Dr. M. Karuthapandi and Ms. R. Sulatana for assisting in photographing the specimens. Furthermore, we are thankful to Dr. Anita Eschner (NHMW Mollusca Collection, Naturhistorisches Museum Wien, Austria), Sigrid Hof (SMF – Senckenberg Museum, Frankfurt, Germany), and Kevin Webb (NHMUK Photographic Unit, Natural History Museum, London, United Kingdom) for providing images of shells from museum collections. Our research in Myanmar was performed under the survey permission No. 5/6000/LFR(210/2018) dated on 23 January 2018 issued by the Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Irrigation of Myanmar and the export permission No. NWCD/CITES/9/5666/2018 dated on 28 June 2018 issued by the Forest Department of the Ministry of Environmental Conservation and Forestry of Myanmar. The sampling of freshwater mussels in Nepal was carried out as a part of scientific collaboration between one of the co-authors (H.F.N.) and the Aquatic Ecology Centre (AEC) at Kathmandu University. No special permission required for our materials and dataset from India, because these samples were collected by native researchers (R.P. and S.K.U.), and were analysed and deposited in India.
Author contributions
I.N.B. and K.-O.N. developed the concept of the study. A.A.L., H.F.N., I.N.B., I.V.V., K.-O.N., N.C., R.P., S.K.U., T.W., and Z.L. collected data. A.V.K., A.A.T., B.F., and S.S.D. processed DNA analyses of samples from Myanmar and Nepal. R.P. and S.K.U. collected freshwater mussel samples and generated DNA sequences in India. I.N.B. performed phylogenetic and biogeographic modeling and prepared a taxonomic overview of the recent and fossil Unionidae. M.Y.G. and I.N.B. created the paleo-maps. E.S.K., N.V.S.R., and R.P. prepared shell images. I.N.B. wrote the paper, with input from K.-O.N., B.F., M.P., E.S.K., N.V.S.R., and R.P. All authors acknowledged the final version of the manuscript.
Data availability
The voucher specimens of freshwater mussels from the Oriental Region are available in SMF— Senckenberg Museum, Frankfurt, Germany; RMBH—Russian Museum of Biodiversity Hotspots, Federal Center for Integrated Arctic Research of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Arkhangelsk, Russia; ZSI—Zoological Survey of India, Kolkata, India; and FBRC ZSI—Freshwater Biology Regional Centre, Zoological Survey of India, Hyderabad, India. The DNA sequences generated in this study could be downloaded from NCBI’s GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank). The DNA sequence accession numbers and collecting locality data for every sample are presented in Datasets 1 and 2.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Nalluri V. Subba Rao is retired.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41598-022-05257-0.
References
- 1.Graf DL, Cummings KS. Review of the systematics and global diversity of freshwater mussel species (Bivalvia: Unionoida) J. Molluscan Stud. 2007;73:291–314. doi: 10.1093/mollus/eym029. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Graf DL, Cummings KS. A 'big data' approach to global freshwater mussel diversity (Bivalvia: Unionoida), with an updated checklist of genera and species. J. Molluscan Stud. 2021;87:034. doi: 10.1093/mollus/eyaa034. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vaughn CC. Ecosystem services provided by freshwater mussels. Hydrobiologia. 2018;810:15–27. doi: 10.1007/s10750-017-3139-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ożgo M, et al. Lake-stream transition zones support hotspots of freshwater ecosystem services: Evidence from a 35-year study on unionid mussels. Sci. Total Environ. 2021;774:145114. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lopes-Lima M, et al. Conservation of freshwater bivalves at the global scale: Diversity, threats and research needs. Hydrobiologia. 2018;810:1–14. doi: 10.1007/s10750-017-3486-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bolotov IN, et al. Climate warming as a possible trigger of keystone mussel population decline in oligotrophic rivers at the continental scale. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:35. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18873-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ferreira-Rodríguez N, et al. Research priorities for freshwater mussel conservation assessment. Biol. Conserv. 2019;231:77–87. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2019.01.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lundquist SP, Worthington TA, Aldridge DC. Freshwater mussels as a tool for reconstructing climate history. Ecol. Ind. 2019;101:11–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.12.048. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sousa R, et al. The role of anthropogenic habitats in freshwater mussel conservation. Glob. Change Biol. 2021;27:2298–2314. doi: 10.1111/gcb.15549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bogan AE. Freshwater bivalve extinctions (Mollusca: Unionoida): A search for causes. Integr. Comp. Biol. 1993;33:599–609. doi: 10.1093/icb/33.6.599. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lydeard C, et al. The global decline of nonmarine mollusks. Bioscience. 2004;54:321–330. doi: 10.1641/0006-3568(2004)054[0321:TGDONM]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hughes J, et al. Past and present patterns of connectivity among populations of four cryptic species of freshwater mussels Velesunio spp (Hyriidae) in central Australia. Mol. Ecol. 2004;13:3197–3212. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2004.02305.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Martel AL, et al. Freshwater mussels (Bivalvia: Margaritiferidae, Unionidae) of the Atlantic Maritime Ecozone. In: McAlpine DF, Smith IM, et al., editors. Assessment of Species Diversity in the Atlantic Maritime Ecozone. NRC Research Press; 2010. pp. 551–598. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Haag WR. North American Freshwater Mussels: Natural History, Ecology, and Conservation. Cambridge University Press; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Smith CH, Pfeiffer JM, Johnson NA. Comparative phylogenomics reveal complex evolution of life history strategies in a clade of bivalves with parasitic larvae (Bivalvia: Unionoida: Ambleminae) Cladistics. 2020;36:505–520. doi: 10.1111/cla.12423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sepkoski JJ, Jr, Rex MA. Distribution of freshwater mussels: Coastal rivers as biogeographic islands. Syst. Biol. 1974;23:165–188. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/23.2.165. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Haag WR. A hierarchical classification of freshwater mussel diversity in North America. J. Biogeogr. 2010;37:12–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2699.2009.02191.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Graf DL, Jones H, Geneva AJ, Pfeiffer JM, III, Klunzinger MW. Molecular phylogenetic analysis supports a Gondwanan origin of the Hyriidae (Mollusca: Bivalvia: Unionida) and the paraphyly of Australasian taxa. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015;85:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2015.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bolotov IN, et al. Ancient river inference explains exceptional Oriental freshwater mussel radiations. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:2135. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02312-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bolotov IN, et al. Integrative taxonomy, biogeography and conservation of freshwater mussels (Unionidae) in Russia. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:3072. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59867-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lopes-Lima M, et al. Diversity, biogeography, evolutionary relationships, and conservation of Eastern Mediterranean freshwater mussels (Bivalvia: Unionidae) Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2021;163:107261. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2021.107261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bolotov IN, et al. Eight new freshwater mussels (Unionidae) from tropical Asia. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:12053. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48528-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bolotov IN, et al. New freshwater mussel taxa discoveries clarify biogeographic division of Southeast Asia. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:6616. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63612-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jeratthitikul E, Paphatmethin S, Zieritz A, Lopes-Lima M, Bun P. Hyriopsis panhai, a new species of freshwater mussel from Thailand (Bivalvia: Unionidae) Raffles Bull. Zool. 2021;69:124–136. doi: 10.26107/RBZ-2021-0011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jeratthitikul E, Sucharit C, Prasankok P. Molecular phylogeny of the Indochinese freshwater mussel genus Scabies Haas, 1911 (Bivalvia: Unionidae) Trop. Nat. Hist. 2019;19:21–36. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jeratthitikul E, Sutcharit C, Ngor PB, Prasankok P. Molecular phylogeny reveals a new genus of freshwater mussels from the Mekong River Basin (Bivalvia: Unionidae) Eur. J. Taxon. 2021;775:119–142. doi: 10.5852/ejt.2021.775.1553. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Pfeiffer JM, Graf DL, Cummings KS, Page LM. Taxonomic revision of a radiation of South-East Asian freshwater mussels (Unionidae: Gonideinae: Contradentini+ Rectidentini) Invertebr. Syst. 2021;35:394–470. doi: 10.1071/IS20044. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zieritz A, et al. A new genus and two new, rare freshwater mussel (Bivalvia: Unionidae) species endemic to Borneo are threatened by ongoing habitat destruction. Aquat. Conserv. 2021 doi: 10.1002/aqc.3695. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Smith CH, Johnson NA, Pfeiffer JM, Gangloff MM. Molecular and morphological data reveal non-monophyly and speciation in imperiled freshwater mussels (Anodontoides and Strophitus) Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018;119:50–62. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2017.10.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Inoue K, et al. A new species of freshwater mussel in the genus Popenaias Frierson, 1927, from Gulf coastal rivers of central Mexico (Bivalvia: Unionida: Unionidae) with comments on the genus. Zootaxa. 2020;4816:457–490. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.4816.4.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ortiz-Sepulveda CM, et al. Diversification dynamics of freshwater bivalves (Unionidae: Parreysiinae: Coelaturini) indicate historic hydrographic connections throughout the East African Rift System. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020;148:106816. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2020.106816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tomilova AA, et al. An endemic freshwater mussel species from the Orontes River basin in Turkey and Syria represents duck mussel’s intraspecific lineage: Implications for conservation. Limnologica. 2020;84:125811. doi: 10.1016/j.limno.2020.125811. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tomilova AA, et al. Evidence for plio-pleistocene duck mussel refugia in the Azov Sea river basins. Diversity. 2020;12:118. doi: 10.3390/d12030118. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pfeiffer JM, Sharpe AE, Johnson NA, Emery KF, Page LM. Molecular phylogeny of the Nearctic and Mesoamerican freshwater mussel genus Megalonaias. Hydrobiologia. 2018;811:139–151. doi: 10.1007/s10750-017-3441-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bolotov IN, et al. A new genus and tribe of freshwater mussel (Unionidae) from Southeast Asia. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:10030. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28385-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Konopleva ES, et al. New freshwater mussels from two Southeast Asian genera Bineurus and Thaiconcha (Pseudodontini, Gonideinae, Unionidae) Sci. Rep. 2021;11:8244. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87633-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lopes-Lima M, et al. Freshwater mussels (Bivalvia: Unionidae) from the Rising Sun (Far East Asia): Phylogeny, systematics, and distribution. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020;146:106755. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2020.106755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rangin C. Active and recent tectonics of the Burma Platelet in Myanmar. Geol. Soc. Lond. Mem. 2017;48:53–64. doi: 10.1144/M48.3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Licht A, et al. Magmatic history of central Myanmar and implications for the evolution of the Burma Terrane. Gondwana Res. 2020;87:303–319. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2020.06.016. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Westerweel J, et al. Burma Terrane part of the Trans-Tethyan arc during collision with India according to palaeomagnetic data. Nat. Geosci. 2019;12:863–868. doi: 10.1038/s41561-019-0443-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Morley CK, Chantraprasert S, Kongchum J, Chenoll K. The West Burma Terrane, a review of recent paleo-latitude data, its geological implications and constraints. Earth Sci. Rev. 2021;220:103722. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103722. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Martin CR, et al. Paleocene latitude of the Kohistan-Ladakh arc indicates multistage India-Eurasia collision. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2020;117:29487–29494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2009039117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Frisch W, Meschede M, Blakey RC. Plate Tectonics: Continental Drift and Mountain Building. Springer Science & Business Media; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ali JR, Aitchison JC. Gondwana to Asia: Plate tectonics, paleogeography and the biological connectivity of the Indian sub-continent from the Middle Jurassic through latest Eocene (166–35 Ma) Earth Sci. Rev. 2008;88:145–166. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2008.01.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chatterjee S, Goswami A, Scotese CR. The longest voyage: Tectonic, magmatic, and paleoclimatic evolution of the Indian plate during its northward flight from Gondwana to Asia. Gondwana Res. 2013;23:238–267. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.07.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.van Hinsbergen D, et al. Greater India Basin hypothesis and a two-stage Cenozoic collision between India and Asia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2012;109:7659–7664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1117262109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.van Hinsbergen DJ, et al. Reconstructing Greater India: Paleogeographic, kinematic, and geodynamic perspectives. Tectonophysics. 2019;760:69–94. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2018.04.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Morley CK, Naing TT, Searle M, Robinson SA. Structural and tectonic development of the Indo-Burma ranges. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020;200:102992. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102992. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Poinar G., Jr Burmese amber: Evidence of Gondwanan origin and Cretaceous dispersion. Hist. Biol. 2019;31:1304–1309. doi: 10.1080/08912963.2018.1446531. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zhang X, et al. Tracing Argoland in eastern Tethys and implications for India-Asia convergence. GSA Bull. 2021;133:1712–1722. doi: 10.1130/B35772.1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Pfeiffer JM, Graf DL, Cummings KS, Page LM. Molecular phylogeny and taxonomic revision of two enigmatic freshwater mussel genera (Bivalvia: Unionidae incertae sedis: Harmandia and Unionetta) reveals a diverse clade of Southeast Asian Parreysiinae. J. Molluscan Stud. 2018;84:404–416. doi: 10.1093/mollus/eyy028. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Whelan NV, Geneva AJ, Graf DL. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of tropical freshwater mussels (Mollusca: Bivalvia: Unionoida) resolves the position of Coelatura and supports a monophyletic Unionidae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2011;61:504–514. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2011.07.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Konopleva ES, et al. A new genus and two new species of freshwater mussels (Unionidae) from Western Indochina. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:4106. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39365-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Muanta S, Jeratthitikul E, Panha S, Prasankok P. Phylogeography of the freshwater bivalve genus Ensidens (Unionidae) in Thailand. J. Molluscan Stud. 2019;85:224–231. doi: 10.1093/mollus/eyz013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zieritz A, et al. Factors driving changes in freshwater mussel (Bivalvia, Unionida) diversity and distribution in Peninsular Malaysia. Sci. Total Environ. 2016;571:1069–1078. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Bolotov IN, et al. New taxa of freshwater mussels (Unionidae) from a species-rich but overlooked evolutionary hotspot in Southeast Asia. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:11573. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11957-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Subba Rao, N. V. Handbook. Freshwater Molluscs of India (Zoological Survey of India, 1989).
- 58.Ramakrishna & Dey, A. Handbook on Indian Freshwater Molluscs (Zoological Survey of India, 2007).
- 59.Prashad B. The marsupium and glochidium of some Unionidae and on the Indian species hitherto assigned to the genus Nodularia. Rec. Indian Mus. 1918;15:143–148. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Burdi GH, Baloch WA, Begum F, Soomro AN, Khuhawar MY. Ecological studies on freshwater bivalve mussels (Pelecypoda) of Indus River and its canals at Kotri Barrage Sindh, Pakistan. Sindh Univ. Res. J. 2009;41:31–36. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Nesemann, H. et al. Aquatic Invertebrates of the Ganga River System: Volume 1—Mollusca, Annelida, Crustacea (in part) (Hasko Nesemann and Chandi Press, 2007).
- 62.Budha PB. A Field Guide to Freshwater Molluscs of Kailali, Far Western Nepal. Central Department of Zoology, Tribhuvan University; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Gittenberger E, Leda P, Gyeltshen C, Sherub S. Distributional patterns of molluscan taxa in Bhutan (Mollusca) Biodiversität Naturausstattung Himalaya. 2018;4:143–151. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Nanda AC, Sehgal RK, Chauhan PR. Siwalik-age faunas from the Himalayan foreland Basin of South Asia. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018;162:54–68. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.10.035. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Vredenburg E, Prashad B. Unionidae from the Miocene of Burma. Rec. Geol. Surv. India. 1921;51:371–374. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Prashad B. On some Fossil Indian Unionidae. Rec. Geol. Surv. India. 1928;60:308–312. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Modell, H. Paläontologische und geologische Untersuchungen im Tertiär von Pakistan. 4. Die tertiären Najaden des Punjab und Vorderindiens. Abhandlungen der Bayerischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, Mathematisch-naturwissenschaftliche Klasse, neue Folge135, 1–49 (1969).
- 68.Takayasu K, Gurung DD, Matsuoka K. Some new species of freshwater bivalves from the Mio-Pliocene Churia Group, west-central Nepal. Trans. Proc. Paleontol. Soc. Jpn. New Ser. 1995;179:157–168. doi: 10.14825/prpsj1951.1995.179_157. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Gurung D. Freshwater molluscs from the Late Neogene Siwalik Group, Surai Khola, western Nepal. J. Nepal Geol. Soc. 1998;17:7–28. doi: 10.3126/jngs.v17i0.32095. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Simpson CT. Synopsis of the naiades, or pearly fresh-water mussels. Proc. U.S. Natl. Mus. 1900;22:501–1044. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Madhyastha NA, Mumbrekar KD. Two endemic genera of bivalves in the Tunga River of the Western Ghats, Karnataka, India. Tentacle. 2006;14:23–24. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Prashad B. Notes on lamellibranchs in the Indian Museum. Rec. Indian Mus. 1920;19:165–173. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Haas F. Eine neude indische Najade, Trapezoideus prashadi. Senckenbergiana. 1922;4:101–102. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Sowerby, G. B. Genus Unio. Conchologica Iconica16, pls. 1, 61–96 (1868).
- 75.Haas, F. Die Unioniden. H.C. Küster, Systematisches Conchylien-Cabinet von Martini und Chemnitz9, 257–288 (1919).
- 76.Hadl G. Results of the Austrian-Ceylonese Hydrobiological Mission 1970 of the 1st Zoological Institute of the University of Vienna (Austria) and the Department of Zoology of the Vidyalankara University of Ceylon, Kelaniya. Part XVIII: Freshwater Mussels Bivalvia. Bull. Fish. Res. Stn. Sri Lanka (Ceylon) 1974;25:183–188. [Google Scholar]
- 77.Gittenberger et al. A Field Guide to the Common Molluscs of Bhutan (National Biodiversity Centre (NBC), Ministry of Agriculture and Forests, 2017).
- 78.Annandale N, Prashad B. The Mollusca of the inland waters of Baluchistan and of Seistan. Rec. Indian Mus. 1919;18:17–62. [Google Scholar]
- 79.Simpson CT. A Descriptive Catalogue of the Naiades, or Pearly Fresh-Water Mussels. Parts I-III. Bryant Walker; 1914. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Mörch OAL. On the land and fresh-water Mollusca of Greenland. Am. J. Conchol. 1868;4:25–40. [Google Scholar]
- 81.Schröter, J. S. Die Geschichte der Flussconchylien: Mit vorzüglicher Rücksicht auf Diejenigen Welche in den Thüringischen Wassern Leben (Halle, bey Johann Jacob Gebauer, 1779).
- 82.Spengler L. Om Slaegterne Chaena Mya og Unio. Skrivter Naturhistorie-Selskabet. 1993;3:16–69. [Google Scholar]
- 83.Haas F. Bemerkungen über Spenglers Unionen. Videnskabelige Meddelelser fra Dansk naturhistorisk Forening i Kjøbenhav. 1913;65:51–66. [Google Scholar]
- 84.Haas F. Superfamilia Unionacea. Das Tierreich. 1969;88:1–663. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Prashad B. On some undescribed freshwater Molluscs from various parts of India and Burma. Rec. Geol. Surv. India. 1930;62:428–433. [Google Scholar]
- 86.Conrad TA. A synopsis of the family of Naïades of North America, with notes, and a table of some of the genera and sub-genera of the family, according to their geographical distribution, and descriptions of genera and sub-genera. Proc. Acad. Natl. Sci. Phila. 1853;6:243–269. [Google Scholar]
- 87.Sowerby GB. Genus Unio. Conchol. Iconica. 1866;16:31–54. [Google Scholar]
- 88.Frierson LS. A Classified and Annotated Check List of the North American Naiades. Baylor University Press; 1927. [Google Scholar]
- 89.Prashad B. Studies on the anatomy of Indian Mollusca. The soft parts of some Indian Unionidae. Rec. Indian Mus. 1919;16:289–296. [Google Scholar]
- 90.Annandale N. Further note on the burrows of Solenaia soleniformis. Rec. Indian Mus. 1919;16:205–206. [Google Scholar]
- 91.Godwin-Austen HH. Description of a new species of Margaritanopsis (Unionidae) from the Southern Shan States, with notes on Solenaia soleniformis. Rec. Indian Mus. 1919;16:203–205. [Google Scholar]
- 92.Pfeiffer JM, Breinholt JW, Page LM. Unioverse: A phylogenetic resource for reconstructing the evolution of freshwater mussels (Bivalvia, Unionoida) Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019;137:114–126. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2019.02.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Huang X-C, et al. Towards a global phylogeny of freshwater mussels (Bivalivia: Unionida): Species delimitation of Chinese taxa, mitochondrial phylogenomics, and diversification patterns. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019;130:45–59. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2018.09.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Bolotov IN, Kondakov AV, Konopleva ES, Vikhrev IV. A new genus of ultra-elongate freshwater mussels from Vietnam and eastern China (Bivalvia: Unionidae) Ecol. Montenegrina. 2021;39:1–6. doi: 10.37828/em.2021.39.1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Pfeiffer JM, Graf DL. Evolution of bilaterally asymmetrical larvae in freshwater mussels (Bivalvia: Unionoida: Unionidae) Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2015;175:307–318. doi: 10.1111/zoj.12282. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Rafinesque, C. S. Continuation of a Monograph of the Bivalve Shells of the River Ohio and Other Rivers of the Western States. By Prof. C.S. Rafinesque. (Published at Brussels, September, 1820). Containing 46 species, from No. 76 to no. 121. Including an Appendix on Some Bivalve Shells of the Rivers of Hindostan, with a Supplement on the Fossil Bivalves of the Western States, and the Tulosites, A New Genus of Fossils (1831).
- 97.Blanford WT. Contributions to Indian Malacology no VII. List of species of Unio and Anodonta described as occurring in India, Ceylon and Burma. J. Asiat. Soc. Bengal. 1866;35:134–155. [Google Scholar]
- 98.Frierson LS. Remarks on classification of the Unionidae. Nautilus. 1914;28:6–8. [Google Scholar]
- 99.Johnson RI. The types of Unionidae (Mollusca: Bivalvia) described by C. S. Rafinesque in the Museum national d’Histoire naturelle, Paris. J. Conchyliol. 1973;110:35–37. [Google Scholar]
- 100.Vanatta EG. Rafinesque’s types of Unio. Proc. Acad. Natl. Sci. Phila. 1915;67:549–559. [Google Scholar]
- 101.Baker HB. Some of Rafinesque’s unionid names. The Nautilus. 1964;77:140–142. [Google Scholar]
- 102.Williams JD, Bogan AE, Garner JT. Freshwater mussels of Alabama and the Mobile Basin in Georgia, Mississippi and Tennessee. University of Alabama Press; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 103.Bogan AE. A resolution of the nomenclatural confusion surrounding Plagiola Rafinesque, Epioblasma Rafinesque, and Dysnomia Agassiz (Mollusca: Bivalvia: Unionidae) Malacol. Rev. 1997;30:77–86. [Google Scholar]
- 104.Graf DL, Cummings KS. Palaeoheterodont diversity (Mollusca: Trigonioida+ Unionoida): What we know and what we wish we knew about freshwater mussel evolution. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2006;148:343–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1096-3642.2006.00259.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Modell H. Das natlirliche System der Najaden. Arch. Molluskenkunde. 1942;74:161–191. [Google Scholar]
- 106.Starobogatov YI. Fauna of Molluscs and Zoogeographic Division of Continental Waterbodies of the Globe. Nauka; 1970. [Google Scholar]
- 107.Bolotov IN, et al. Discovery of Novaculina myanmarensis sp. nov. (Bivalvia: Pharidae: Pharellinae) closes the freshwater razor clams range disjunction in Southeast Asia. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:16325. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34491-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Than W, et al. Phylogeography and distribution of the freshwater razor clams Novaculina myanmarensis and N. gangetica in Myanmar, with notes on two doubtful nominal taxa described as Novaculina members (Bivalvia: Pharidae) Ecol. Montenegrina. 2021;40:59–67. doi: 10.37828/em.2021.40.4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Haas F. Beiträge zu einer Monographie der asiatischen Unioniden. Abhandlungen der Senckenbergischen Naturforschenden Gesellschaft. 1924;38:129–203. [Google Scholar]
- 110.Preston HB. Mollusca (Freshwater Gastropoda & Pelecypoda). Fauna of British India, including Ceylon and Burma. Taylor and Francis; 1915. [Google Scholar]
- 111.Prashad B. A revision of the Burmese Unionidae. Rec. Indian Mus. 1922;24:91–111. [Google Scholar]
- 112.Theobald W. Catalogue of the Recent Shells in the Museum of the Asiatic Society. Bengal Military Orphan Press; 1860. [Google Scholar]
- 113.Zieritz A, et al. Diversity, biogeography and conservation of freshwater mussels (Bivalvia: Unionida) in East and Southeast Asia. Hydrobiologia. 2018;810:29–44. doi: 10.1007/s10750-017-3104-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Konopleva ES, et al. A taxonomic review of Trapezidens (Bivalvia: Unionidae: Lamellidentini), a freshwater mussel genus endemic to Myanmar, with a description of a new species. Ecol. Montenegrina. 2020;27:45–57. doi: 10.37828/em.2020.27.6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Brandt RAM. The non-marine aquatic mollusca of Thailand. Arch. Mollusckenkunde. 1974;105:1–423. [Google Scholar]
- 116.Neumayr M. Süsswasser-Mollusken. Die wissenschaftlichen ergebnisse der reise des grafen Béla Széchenyi in Ostasien. 1899;1877–1880(2):637–662. [Google Scholar]
- 117.Tripathy B, Mukhopadhayay A. Freshwater molluscs of India: An insight of into their diversity, distribution and conservation. In: Rawat M, Dookia S, Sivaperuman C, editors. Aquatic Ecosystem: Biodiversity, Ecology and Conservation. Springer; 2015. pp. 163–195. [Google Scholar]
- 118.Prashad B. VIII—Some Noteworthy Examples of Parallel Evolution in the Molluscan Faunas of South-eastern Asia and South America. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. 1932;51:42–53. doi: 10.1017/s0370164600022987. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Smith EA. Description of Mulleria dalyi, n. sp., from India. Proc. Malacol. Soc. Lond. 1898;3:14–16. [Google Scholar]
- 120.Bogan AE, Hoeh WR. On becoming cemented: Evolutionary relationships among the genera in the freshwater bivalve family Etheriidae (Bivalvia: Unionoida) Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2000;177:159–168. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2000.177.01.09. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Bogan AE, Roe KJ. Freshwater bivalve (Unioniformes) diversity, systematics, and evolution: Status and future directions. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2008;27:349–369. doi: 10.1899/07-069.1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Hoeh WR, Bogan AE, Heard WH, Chapman EG. Palaeoheterodont phylogeny, character evolution, diversity and phylogenetic classification: A reflection on methods of analysis. Malacologia. 2009;51:307–317. doi: 10.4002/040.051.0206. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Woodward MF. On the anatomy of Mulleria dalyi, Smth. J. Molluscan Stud. 1898;3:87–91. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.mollus.a065152. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Aravind NA, et al. The status and distribution of freshwater molluscs of the Western Ghats. In: Molur S, Smith KG, Daniel BA, Darwall WRT, et al., editors. The Status and Distribution of Freshwater Biodiversity in the Western Ghats, India. IUCN and Zoo Outreach Organisation; 2011. pp. 21–42. [Google Scholar]
- 125.Madhyastha NA. Pseudomulleria dalyi (Acostea dalyi): A rare cemented bivalve of Western Ghats. Zoos’ Print J. 2001;16:573. [Google Scholar]
- 126.Loria SF, Prendini L. Out of India, thrice: Diversification of Asian forest scorpions reveals three colonizations of Southeast Asia. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:22301. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78183-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Köhler F, Glaubrecht M. Out of Asia and into India: On the molecular phylogeny and biogeography of the endemic freshwater gastropod Paracrostoma Cossmann, 1900 (Caenogastropoda: Pachychilidae) Biol. J. Lin. Soc. 2007;91:627–651. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8312.2007.00866.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Dahanukar N, Raut R, Bhat A. Distribution, endemism and threat status of freshwater fishes in the Western Ghats of India. J. Biogeogr. 2004;31:123–136. doi: 10.1046/j.0305-0270.2003.01016.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Britz R, et al. Aenigmachannidae, a new family of snakehead fishes (Teleostei: Channoidei) from subterranean waters of South India. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:16081. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73129-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Hedges SB. The coelacanth of frogs. Nature. 2003;425:669–670. doi: 10.1038/425669a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Dutta SK, Vasudevan K, Chaitra MS, Shanker K, Aggarwal RK. Jurassic frogs and the evolution of amphibian endemism in the Western Ghats. Curr. Sci. 2004;86:211–216. [Google Scholar]
- 132.Roelants K, Jiang J, Bossuyt F. Endemic ranid (Amphibia: Anura) genera in southern mountain ranges of the Indian subcontinent represent ancient frog lineages: Evidence from molecular data. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2004;31:730–740. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2003.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Van Bocxlaer I, et al. Mountain-associated clade endemism in an ancient frog family (Nyctibatrachidae) on the Indian subcontinent. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012;62:839–847. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2011.11.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Krishnan RM, Ramesh BR. Endemism and sexual systems in the evergreen tree flora of the Western Ghats, India. Divers. Distrib. 2005;11:559–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1366-9516.2005.00190.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Mörch OAL. Catalogue des Mollusques terrestres et fluviatiles des anciennes colonies du golfe du Bengale. J. Conchyliol. 1872;20:303–345. [Google Scholar]
- 136.Graf DL, Cummings KS. Freshwater mussel (Mollusca: Bivalvia: Unionoida) richness and endemism in the ecoregions of Africa and Madagascar based on comprehensive museum sampling. Hydrobiologia. 2011;678:17–36. doi: 10.1007/s10750-011-0810-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Li Z, et al. Kinematic evolution of the West Burma block during and after India-Asia collision revealed by paleomagnetism. J. Geodyn. 2020;134:101690. doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2019.101690. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Van Damme D, Bogan AE, Dierick M. A revision of the Mesozoic naiads (Unionoida) of Africa and the biogeographic implications. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015;147:141–200. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.04.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Hall R. Late Jurassic-Cenozoic reconstructions of the Indonesian region and the Indian Ocean. Tectonophysics. 2012;570:1–41. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.04.021. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Bosworth W. Mesozoic and early Tertiary rift tectonics in East Africa. Tectonophysics. 1992;209:115–137. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(92)90014-W. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Guiraud R, Bosworth W, Thierry J, Delplanque A. Phanerozoic geological evolution of Northern and Central Africa: An overview. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2005;43:83–143. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2005.07.017. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Wilson M, Guiraud R. Magmatism and rifting in Western and Central Africa, from Late Jurassic to Recent times. Tectonophysics. 1992;213:203–225. [Google Scholar]
- 143.Chatterjee, S., Scotese, C. R. & Bajpai, S. Indian Plate and Its Epic Voyage from Gondwana to Asia: Its Tectonic, Paleoclimatic, and Paleobiogeographic Evolution (Special Paper 529, The Geological Society of America, 2017).
- 144.Briggs JC. The biogeographic and tectonic history of India. J. Biogeogr. 2003;30:381–388. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2699.2003.00809.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Hartman JH, Erickson DN, Bakken A. Stephen Hislop and his 1860 Cretaceous continental molluscan new species descriptions in Latin from the Deccan Plateau, India. Palaeontology. 2008;51:1225–1252. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-4983.2008.00807.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Vandamme D, Courtillot V, Besse J, Montigny R. Paleomagnetism and age determinations of the Deccan Traps (India): Results of a Nagpur-Bombay Traverse and review of earlier work. Rev. Geophys. 1991;29:159–190. doi: 10.1029/91RG00218. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Bolotov IN, et al. Multi-locus fossil-calibrated phylogeny, biogeography and a subgeneric revision of the Margaritiferidae (Mollusca: Bivalvia: Unionoida) Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016;103:104–121. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2016.07.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Lyubas AA, et al. A taxonomic revision of fossil freshwater pearl mussels (Bivalvia: Unionoida: Margaritiferidae) from Pliocene and Pleistocene deposits of Southeastern Europe. Ecol. Montenegrina. 2019;21:1–16. doi: 10.37828/em.2019.21.1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Campbell DC, et al. Phylogeny of North American amblemines (Bivalvia, Unionoida): Prodigious polyphyly proves pervasive across genera. Invertebr. Biol. 2005;124:131–164. [Google Scholar]
- 150.Lopes-Lima M, et al. Revisiting the North American freshwater mussel genus Quadrula sensu lato (Bivalvia: Unionidae): Phylogeny, taxonomy and species delineation. Zool. Scr. 2019;48:313–336. doi: 10.1111/zsc.12344. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Aksenova OV, et al. Species richness, molecular taxonomy and biogeography of the radicine pond snails (Gastropoda: Lymnaeidae) in the Old World. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:11199. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29451-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Kosuch J, Vences M, Dubois A, Ohler A, Böhme W. Out of Asia: Mitochondrial DNA evidence for an oriental origin of tiger frogs, genus Hoplobatrachus. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2001;21:398–407. doi: 10.1006/mpev.2001.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Sil M, Aravind NA, Karanth KP. Into-India or out-of-India? Historical biogeography of the freshwater gastropod genus Pila (Caenogastropoda: Ampullariidae) Biol. J. Lin. Soc. 2020;129:752–764. doi: 10.1093/biolinnean/blz171. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Sil M, Aravind NA, Karanth KP. Role of geography and climatic oscillations in governing into-India dispersal of freshwater snails of the family: Viviparidae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019;138:174–181. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2019.05.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Garg S, Biju SD. New microhylid frog genus from Peninsular India with Southeast Asian affinity suggests multiple Cenozoic biotic exchanges between India and Eurasia. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:1906. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38133-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Gorin VA, et al. A little frog leaps a long way: Compounded colonizations of the Indian Subcontinent discovered in the tiny Oriental frog genus Microhyla (Amphibia: Microhylidae) PeerJ. 2020;8:e9411. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Karanth KP. An island called India: Phylogenetic patterns across multiple taxonomic groups reveal endemic radiations. Curr. Sci. 2015;108:1847–1851. [Google Scholar]
- 158.Karanth KP. Out-of-India Gondwanan origin of some tropical Asian biota. Curr. Sci. 2006;90:789–792. [Google Scholar]
- 159.Datta-Roy A, Karanth KP. The Out-of-India hypothesis: What do molecules suggest? J. Biosci. 2009;34:687–697. doi: 10.1007/s12038-009-0057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Gower DJ, et al. A molecular phylogeny of ichthyophiid caecilians (Amphibia: Gymnophiona: Ichthyophiidae): Out of India or out of South East Asia? Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 2002;269:1563–1569. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2002.2050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Kamei RG, et al. Discovery of a new family of amphibians from northeast India with ancient links to Africa. Proc. R. Soc. B. 2012;279:2396–2401. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2012.0150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Yamahira K, et al. Mesozoic origin and ‘out-of-India’radiation of ricefishes (Adrianichthyidae) Biol. Let. 2021;17:20210212. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2021.0212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Klaus S, Schubart CD, Streit B, Pfenninger M. When Indian crabs were not yet Asian-biogeographic evidence for Eocene proximity of India and Southeast Asia. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010;10:287. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-10-287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Joshi J, Karanth PK, Edgecombe GD. The out-of-India hypothesis: Evidence from an ancient centipede genus, Rhysida (Chilopoda: Scolopendromorpha) from the Oriental Region, and systematics of Indian species. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2020;189:828–861. doi: 10.1093/zoolinnean/zlz138. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Foley S, Krehenwinkel H, Cheng DQ, Piel WH. Phylogenomic analyses reveal a Gondwanan origin and repeated out of India colonizations into Asia by tarantulas (Araneae: Theraphosidae) PeerJ. 2021;9:e11162. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Dayanandan S, Ashton PS, Williams SM, Primack RB. Phylogeny of the tropical tree family Dipterocarpaceae based on nucleotide sequences of the chloroplast rbcL gene. Am. J. Bot. 1999;86:1182–1190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Conti E, Eriksson T, Schönenberger J, Sytsma KJ, Baum DA. Early Tertiary out-of-India dispersal of Crypteroniaceae: Evidence from phylogeny and molecular dating. Evolution. 2002;56:1931–1942. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2002.tb00119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Chen J, et al. Eurypterogerron kachinensis gen et sp nov, a remarkable minlagerrontid (Hemiptera, Cicadomorpha) in mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber. Cretaceous Res. 2020;110:104418. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2020.104418. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Rasnitsyn AP, Öhm-Kühnle C. Three new female Aptenoperissus from mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber (Hymenoptera, Stephanoidea, Aptenoperissidae): Unexpected diversity of paradoxical wasps suggests insular features of source biome. Cretac. Res. 2018;91:168–175. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2018.06.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Zhang Q, Rasnitsyn AP, Wang B, Zhang H. Hymenoptera (wasps, bees and ants) in mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber: A review of the fauna. Proc. Geol. Assoc. 2018;129:736–747. doi: 10.1016/j.pgeola.2018.06.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Bolotov IN, et al. A new fossil piddock (Bivalvia: Pholadidae) may indicate estuarine to freshwater environments near Cretaceous amber-producing forests in Myanmar. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:6646. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86241-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Balashov IA, Perkovsky EE, Vasilenko DV. A mid-Cretaceous land snail Burminella artiukhini gen. et. sp. nov. from Burmese amber: A “missing link” between Pupinidae and other Cyclophoroidea? (Caenogastropoda) Cretaceous Res. 2021;118:104941. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2021.104941. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Balashov I. An inventory of molluscs recorded from mid-Cretaceous Burmese amber, with the description of a land snail, Euthema annae sp. nov. (Caenogastropoda, Cyclophoroidea, Diplommatinidae) Cretaceous Res. 2021;118:104676. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2020.104676. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Yu T, Neubauer TA, Jochum A. First freshwater gastropod preserved in amber suggests long-distance dispersal during the Cretaceous Period. Geol. Mag. 2021;58:1327–1334. doi: 10.1017/S0016756821000285. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Bingle-Davis, M. J. Systematics, diversity, and origins of Upper Cretaceous continental molluscan fauna in the infra- and intertrappean strata of the Deccan Plateau, central India (PhD Dissertation) (University of North Dakota, 2012).
- 176.Huang H, et al. At a crossroads: The late Eocene flora of central Myanmar owes its composition to plate collision and tropical climate. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2021;291:104441. doi: 10.1016/j.revpalbo.2021.104441. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Westerweel J, et al. Burma Terrane collision and northward indentation in the Eastern Himalayas recorded in the Eocene-Miocene Chindwin Basin (Myanmar) Tectonics. 2020;39:e2020TC006413. doi: 10.1029/2020TC006413. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Soe TT, Watkinson IM. The Sagaing Fault Myanmar. Geol. Soc. 2017;48:413–441. doi: 10.1144/M48.19. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 179.de Sena Oliveira I, et al. Earliest onychophoran in amber reveals Gondwanan migration patterns. Curr. Biol. 2016;26:2594–2601. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.07.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Gustafson LL, et al. Evaluation of a nonlethal technique for hemolymph collection in Elliptio complanata, a freshwater bivalve (Mollusca: Unionidae) Dis. Aquat. Org. 2005;65:159–165. doi: 10.3354/dao065159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Jaksch K, Eschner A, Rintelen TV, Haring E. DNA analysis of molluscs from a museum wet collection: A comparison of different extraction methods. BMC. Res. Notes. 2016;9:348. doi: 10.1186/s13104-016-2147-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994;3:294–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Graf DL. Patterns of freshwater bivalve global diversity and the state of phylogenetic studies on the Unionoida, Sphaeriidae, and Cyrenidae. Am. Malacol. Bull. 2013;31:135–153. doi: 10.4003/006.031.0106. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Nguyen L-T, Schmidt HA, Haeseler VA, Minh BQ. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015;32:268–274. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Ronquist F, et al. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012;61:539–542. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/sys029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Kalyaanamoorthy S, Minh BQ, Wong TKF, von Haeseler A, Jermiin LS. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods. 2017;14:587–589. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Hoang DT, Chernomor O, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ, Vinh LS. UFBoot2: Improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017;35:518–522. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msx281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Trifinopoulos J, Nguyen LT, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:W232–W235. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Miller, M., Pfeiffer, W. & Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE) 1–8 (IEEE, 2010).
- 190.Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016;33:1870–1874. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Kapli P, et al. Multi-rate Poisson tree processes for single-locus species delimitation under maximum likelihood and Markov chain Monte Carlo. Bioinformatics. 2017;33:1630–1638. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Puillandre N, Brouillet S, Achaz G. ASAP: Assemble species by automatic partitioning. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021;21:609–620. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Villesen P. FaBox: An online toolbox for fasta sequences. Mol. Ecol. Notes. 2007;7:965–968. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.01821.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Bouckaert R, et al. BEAST 2.5: An advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019;15:1–28. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Bouckaert R, et al. BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014;10:e1003537. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Zieritz A, et al. Mitogenomic phylogeny and fossil-calibrated mutation rates for all F-and M-type mtDNA genes of the largest freshwater mussel family, the Unionidae (Bivalvia) Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2020;193:1088–1107. doi: 10.1093/zoolinnean/zlaa153. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Froufe E, et al. Who lives where? Molecular and morphometric analyses clarify which Unio species (Unionida, Mollusca) inhabit the southwestern Palearctic. Org. Divers. Evol. 2016;16:597–611. doi: 10.1007/s13127-016-0262-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Drummond AJ, Suchard MA, Xie D, Rambaut A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012;29:1969–1973. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mss075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Rambaut A, et al. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018;67:901–904. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syy032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Matzke NJ. Model selection in historical biogeography reveals that founder-event speciation is a crucial process in island clades. Syst. Biol. 2014;63:951–970. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syu056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Matzke NJ. Probabilistic historical biogeography: New models for founder-event speciation, imperfect detection, and fossils allow improved accuracy and model-testing. Front. Biogeogr. 2013;5:242–248. doi: 10.21425/F5FBG19694. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Yu Y, Blair C, He XJ. RASP 4: Ancestral state reconstruction tool for multiple genes and characters. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020;37:604–606. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msz257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Ree RH, Sanmartín I. Conceptual and statistical problems with the DEC+ J model of founder-event speciation and its comparison with DEC via model selection. J. Biogeogr. 2018;45:741–749. doi: 10.1111/jbi.13173. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Yu Y, Harris AJ, He X. S-DIVA (Statistical Dispersal-Vicariance Analysis): A tool for inferring biogeographic histories. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010;56:848–850. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2010.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Müller RD, et al. GPlates: Building a virtual Earth through deep time. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2018;19:2243–2261. doi: 10.1029/2018GC007584. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Müller RD, et al. A global plate model including lithospheric deformation along major rifts and orogens since the Triassic. Tectonics. 2019;38:1884–1907. doi: 10.1029/2018TC005462. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Cao X, et al. A deforming plate tectonic model of the South China Block since the Jurassic. Gondwana Res. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2020.11.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Young A, et al. Global kinematics of tectonic plates and subduction zones since the late Paleozoic Era. Geosci. Front. 2019;10:989–1013. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2018.05.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Torsvik TH, et al. Pacific-Panthalassic reconstructions: Overview, errata and the way forward. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2019;20:3659–3689. doi: 10.1029/2019GC008402. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Nevill G. List of the Mollusca brought back by Dr. J. Anderson from Yunnan and Upper Burma, with descriptions of new species. J. Asiatic Soc. Bengal. 1877;46:14–41. [Google Scholar]
- 211.Bolotov IN, et al. Indonaia rectangularis (Tapparone-Canefri, 1889), comb. nov., a forgotten freshwater mussel species from Myanmar. ZooKeys. 2019;852:23–30. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.852.33898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Eydoux F. Mollusques. Magasin Zool. 1838;8:181–192. [Google Scholar]
- 213.Lea I. Observations on the Naïades, and descriptions of new species of that and other families. Trans. Am. Philos. Soc. 1831;4:63–121. [Google Scholar]
- 214.Nesemann HA, Sharma SU, Sharma GO, Sinha RK. Illustrated checklist of large freshwater bivalves of the Ganga River system (Mollusca: Bivalvia: Solecurtidae, Unionidae, Amblemidae) Nachrichchtenblatt Ersten Vorarlberger Malakologischen Gesellschaft. 2005;13:1–51. [Google Scholar]
- 215.Gmelin JF. Systema Naturae per Regna Tria Naturae, Secundum Classes, Ordines, Genera, Species, cum Characteribus, Differentiis, Synonymis, locis. Curt. 1791;1(6):3021–3909. [Google Scholar]
- 216.Lea I. Description of twenty-five new species of exotic uniones. Proc. Acad. Natl. Sci. Phila. 1856;8:92–95. [Google Scholar]
- 217.Martens EV. Binnen-Conchylien aus Ober-Birma. Arch. Nat. 1899;65:30–48. [Google Scholar]
- 218.Preston HB. A catalogue of the Asiatic naiades in the collection of the Indian Museum, Calcutta, with descriptions of new species. Rec. Indian Mus. 1912;7:279–308. [Google Scholar]
- 219.Annandale N, Prashad B. XXVIII. The aquatic and amphibious Mollusca of Manipur. Rec. Indian Mus. 1921;22:529–631. [Google Scholar]
- 220.Annandale N, Prashad B. Some freshwater molluscs from the Bombay Presidency. Rec. Indian Mus. 1919;16:139–152. [Google Scholar]
- 221.Philippi, R. A. Unio. Tab. I. Abbildungen und Beschreibungen neuer oder wenig gekannter Conchylien1, 19–20 (1843).
- 222.Hanley S. An Illustrated and Descriptive Catalogue of Recent Bivalve Shells. Williams and Norgate; 1856. Appendix, containing descriptions of the shells delineated in the plates, yet not described in the text; with a systematic list of the engravings, etc; pp. 335–389. [Google Scholar]
- 223.Theobald W. Descriptions of some new land and freshwater shells from India and Burmah. J. Asiatic Soc. Bengal. 1876;45:184–189. [Google Scholar]
- 224.Lea I. Observations on the Naïades; and descriptions of new species of that and other families. Trans. Am. Philos. Soc. 1834;5:23–119. [Google Scholar]
- 225.Hutton T. Notices of some land and fresh water shells occurring in Afghanistan. J. Asiatic Soc. Bengal. 1849;18:649–661. [Google Scholar]
- 226.Annandale N. Aquatic molluscs of the Inlé Lake and connected waters. Rec. Indian Mus. 1918;14:103–182. [Google Scholar]
- 227.Gould AAD. Gould described new shells, received from Rev Mr Mason, of Burmah. Proc. Boston Soc. Nat. Hist. 1847;2:218–221. [Google Scholar]
- 228.Benson WH. Descriptions of Indian and Burmese species of the genus Unio, Retz. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1862;10:184–195. [Google Scholar]
- 229.Lea I. Description of new freshwater and land shells. Trans. Am. Philos. Soc. 1838;6:1–154. [Google Scholar]
- 230.Lamarck, J.-B. Histoire naturelle des animaux sans vertèbres. Vol. 6 (Chez l'Auteur, 1819).
- 231.Müller OF. Vermivm Terrestrium et Fluviatilium, Seu Animalium Infusoriorum, Helminthicorum et Testaceorum, non Marinorum, Succincta Historia. Havniae Lisiae. 1774;2:1–214. [Google Scholar]
- 232.Lea I. Descriptions of three new species of exotic uniones. Proc. Acad. Natl. Sci. Phila. 1860;11:331. [Google Scholar]
- 233.Lea I. Continuation of paper on fresh water and land shells. Proc. Am. Philos. Soc. 1841;2:30–34. [Google Scholar]
- 234.Benson WH. Descriptive catalogue of a collection of land and fresh-water shells, chiefly contained in the museum of the Asiatic Society. J. Asiatic Soc. Bengal. 1836;5:741–750. [Google Scholar]
- 235.Hislop S. Description of fossil shells, from the above-described deposits. Q. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 1860;16:166–181. [Google Scholar]
- 236.Malcolmson JG. XXXVIII: On the Fossils of the Eastern portion of the Great Basaltic District of India. Trans. Geol. Soc. Lond. 1840;5:537–575. [Google Scholar]
- 237.Newbold C. Summary of the Geology of Southern India. Part V. Fresh-water Limestones and Cherts. J. R. Asiatic Soc. Great Br. Irel. 1846;8:219–227. [Google Scholar]
- 238.Prashad B. On a new fossil unionid from the intertrappean beds of Peninsular India. Rec. Geol. Surv. India. 1921;51:368–370. [Google Scholar]
- 239.Lopes-Lima M, et al. Phylogeny of the most species-rich freshwater bivalve family (Bivalvia: Unionida: Unionidae): Defining modern subfamilies and tribes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017;106:174–191. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2016.08.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Bird P. An updated digital model of plate boundaries. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2003;4:1–52. doi: 10.1029/2001GC000252. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 241.Preece RC, et al. William Benson and the Golden Age of Malacology in British India. Trop. Nat. Hist. 2022;22:1–612. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The voucher specimens of freshwater mussels from the Oriental Region are available in SMF— Senckenberg Museum, Frankfurt, Germany; RMBH—Russian Museum of Biodiversity Hotspots, Federal Center for Integrated Arctic Research of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Arkhangelsk, Russia; ZSI—Zoological Survey of India, Kolkata, India; and FBRC ZSI—Freshwater Biology Regional Centre, Zoological Survey of India, Hyderabad, India. The DNA sequences generated in this study could be downloaded from NCBI’s GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank). The DNA sequence accession numbers and collecting locality data for every sample are presented in Datasets 1 and 2.