Correction to: Scientific Reports 10.1038/s41598-021-93861-x, published online 15 July 2021
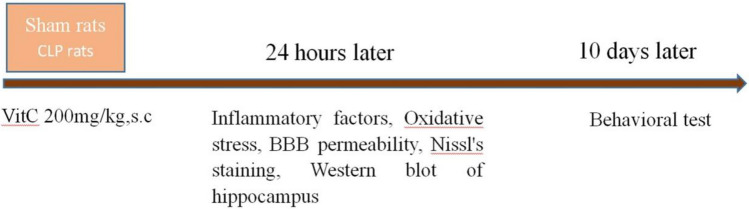
The original version of this Article contained an error in Figure 6, as the method of VitC administration was incorrectly described as a subcutaneous injection, rather than intraperitoneal.
The original Figure 6 and accompanying legend appear below.
Figure 6.
Experimental design. Twenty-four hours after CLP-induced sepsis model was established, inflammatory factors, oxidative stress of serum and hippocampus, BBB permeability, Nissl’s staining of hippocampus, and Western blot of hippocampus were evaluated. Ten days after CLP-induced sepsis model, behavioral tests of rats were performed.
The original Article has been corrected.