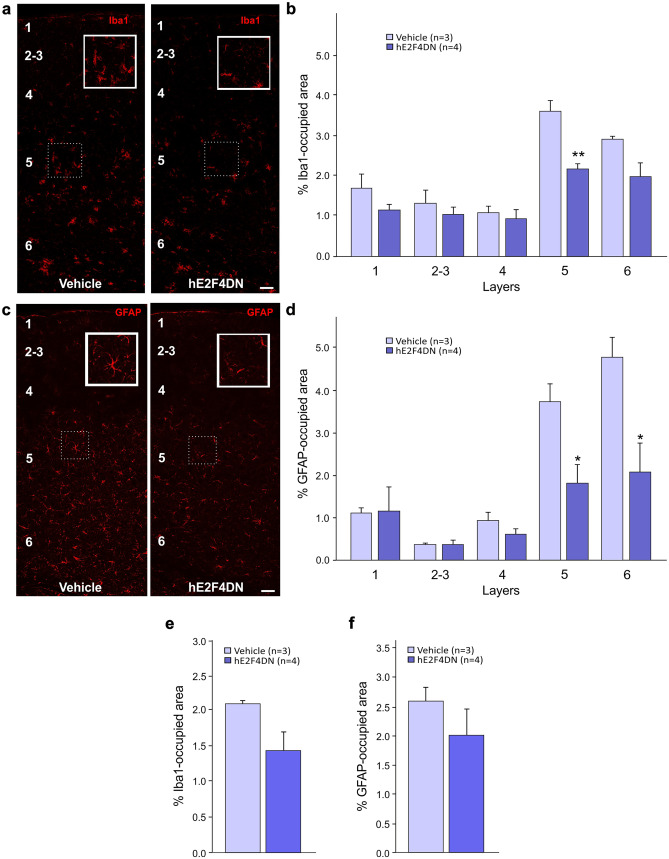
Fig. 4.
Systemic administration of the AAV-hE2F4DN vector attenuates microgliosis and reactive astrocytosis in the cerebral cortex of h5xFAD mice. (a) Representative Iba1 immunostaining in the cerebral cortex of 6.5-month-old h5xFAD mice administered with either vehicle or AAV-hE2F4DN at 1.5 months. Notice the decreased area occupied by Iba1-positive labeling in the cerebral cortex of h5xFAD mice expressing neuronal hE2F4DN. Inserts show Iba1 staining of the indicated dashed boxes. Layers are indicated with Arabic numbers. (b) Percentages of the areas occupied by Iba1 immunostaining in the indicated cortical layers (F(1,25) = 20.1462; p = 0.0001; unbalanced two-way ANOVA). Numbers refer to the different cortical layers. (c) Representative GFAP immunostaining in the cerebral cortex of 6.5-month-old h5xFAD mice administered with either vehicle or AAV-hE2F4DN at 1.5 months. Notice the decreased GFAP-positive labeling and reactivity of astrocytes in the cerebral cortex of h5xFAD mice expressing neuronal hE2F4DN. Inserts show GFAP staining of the indicated dashed boxes. Layers are indicated with Arabic numbers. (d) Percentages of the areas occupied by GFAP immunostaining in the indicated cortical layers (F(1,25) = 13.9501; p = 0.001; unbalanced two-way ANOVA). Numbers refer to the different cortical layers. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; unbalanced two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc two-tailed Student’s t test. Scale bar, 50 μm. (e, f) Systemic administration of the AAV-hE2F4DN vector leads to a tendency for the attenuation of microgliosis and reactive astrocytosis in the hippocampus of h5xFAD mice. Percentage of area occupied by Iba1 immunostaining (e). Percentage of area occupied by GFAP immunostaining (f)