Abstract
Background & Aims
We previously showed that abundance of Candida tropicalis is significantly greater in Crohn’s disease patients compared with first-degree relatives without Crohn’s disease. The aim of this study was to determine the effects and mechanisms of action of C tropicalis infection on intestinal inflammation and injury in mice.
Methods
C57BL/6 mice were inoculated with C tropicalis, and colitis was induced by administration of dextran sodium sulfate in drinking water. Disease severity and intestinal permeability subsequently were evaluated by endoscopy, histology, quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction, as well as 16S ribosomal RNA and NanoString analyses (NanoString Technologies, Seattle, WA).
Results
Infected mice showed more severe colitis, with alterations in gut mucosal helper T cells (Th)1 and Th17 cytokine expression, and an increased frequency of mesenteric lymph node–derived group 2 innate lymphoid cells compared with uninfected controls. Gut microbiome composition, including changes in the mucin-degrading bacteria, Akkermansia muciniphila and Ruminococcus gnavus, was altered significantly, as was expression of several genes affecting intestinal epithelial homeostasis in isolated colonoids, after C tropicalis infection compared with uninfected controls. In line with these findings, fecal microbiome transplantation of germ-free recipient mice using infected vs uninfected donors showed altered expression of several tight-junction proteins and increased susceptibility to dextran sodium sulfate–induced colitis.
Conclusions
C tropicalis induces dysbiosis that involves changes in the presence of mucin-degrading bacteria, leading to altered tight junction protein expression with increased intestinal permeability and followed by induction of robust Th1/Th17 responses, which ultimately lead to an accelerated proinflammatory phenotype in experimental colitic mice.
Keywords: C tropicalis, Colitis, A muciniphila, Mycobiome
Abbreviations used in this paper: B6, C57BL/6; CARD9, caspase-associated recruitment domain adaptor 9; CD, Crohn’s disease; CFU, colony forming unit; Cldn, claudin; CWRU, Case Western Reserve University; DSS, dextran sodium sulfate; FMT, fecal microbiome transplantation; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; GF, germ-free; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; IEBD, intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; ILC, innate lymphoid cell; MLN, mesenteric lymph node; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; qPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction; RFU, relative fluorescence unit; RORγT+, __; rRNA, ribosomal RNA; RT, reverse-transcription; T-bet+, _; Th, helper T cell; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; UC, ulcerative colitis
Graphical abstract
Summary.
In this article, we report that mice infected with Candida tropicalis, and challenged with dextran sodium sulfate, showed increased intestinal permeability and severe colitis compared with uninfected controls, with alterations in cytokine, tight junction protein, and microbiome profiles.
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) are chronic inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract that include 2 major forms: Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). Any part of the gastrointestinal tract can be affected by CD. Patients can experience a variety of symptoms including weight loss, diarrhea, nausea, and multiple surgeries. To date, a complete cure for CD is not available, with the main treatment focused on maintaining patients in a phase of remission using steroids and biological therapies.1 The main problem associated with the use of these immunosuppressive therapies is the occurrence of several side effects, such as opportunistic infections and teratogenicity.2 Hence, novel strategies are needed to treat CD. IBD etiology is multifactorial. In fact, the disease is characterized by a complex interplay between environmental and genetic factors, particularly an inappropriate inflammatory response to commensal microbes in genetically affected subjects.3
Recently, several studies highlighted the importance of the fungal community in the pathophysiology of IBD, especially the role of Candida species in the etiology of CD. Hoarau et al4 found that patients with CD have much higher levels of the fungus Candida tropicalis compared with their first-degree relatives without CD. In addition, levels of C tropicalis present in the intestine were correlated positively with 2 harmful bacteria: Serratia marcescens and Escherichia coli.5 C tropicalis represents part of the human microbiome and it commonly is present on the epidermis, bronchi, gastrointestinal tract, and genital tract.6,7 Furthermore, C tropicalis has been recognized as the most common pathogenic fungus of the non-albicans Candida species.8 Candidiasis caused by C tropicalis has increased worldwide, indicating this fungus may be an emerging pathogenic yeast, especially in neutropenic patients or patients with dysbiosis resulting from antimicrobial use.9
Based on its biological effects, we hypothesized that C tropicalis infection may alter the gut microbiome community and that the resulting dysbiosis may predispose the host to developing IBD. We, therefore, investigated how C tropicalis infection affects the severity of dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis in C57BL/6 (B6) mice. Furthermore, we used 16S ribosomal RNA analysis to characterize the fecal microbiome of the experimental mice before and after C tropicalis challenge to determine whether fungal infection could lead to dysbiosis. We report herein that the bacteria Akkermansia muciniphila and Ruminococcus gnavus were more and less abundant, respectively, in the gut of infected mice. Mechanistically, we showed that germ-free (GF) mice transplanted with fecal material from mice infected with C tropicalis showed altered expression of several tight-junction proteins and increased susceptibility to DSS-induced colitis. Finally, we showed that the expression of several genes affecting intestinal epithelial homeostasis in isolated colonoids was altered after C tropicalis infection compared with uninfected controls.
Results
Oral Inoculation of C tropicalis Confers Enhanced Susceptibility to DSS-Induced Colitis in B6 Mice
We first hypothesized that oral inoculation with C tropicalis would alter susceptibility to experimental colitis in mice. We tested our hypothesis by analyzing the severity of DSS colitis in B6 mice that were pretreated with oral gavage of either C tropicalis inoculum (infected group) or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (control group). Uninfected mice, spared DSS treatment, were used as the negative control.
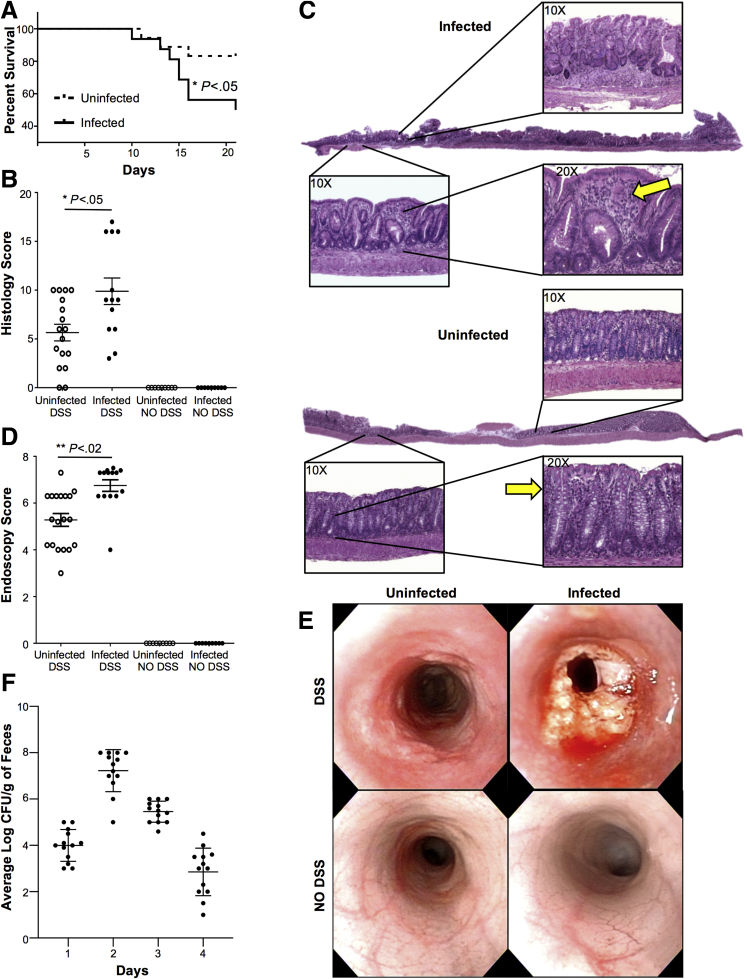
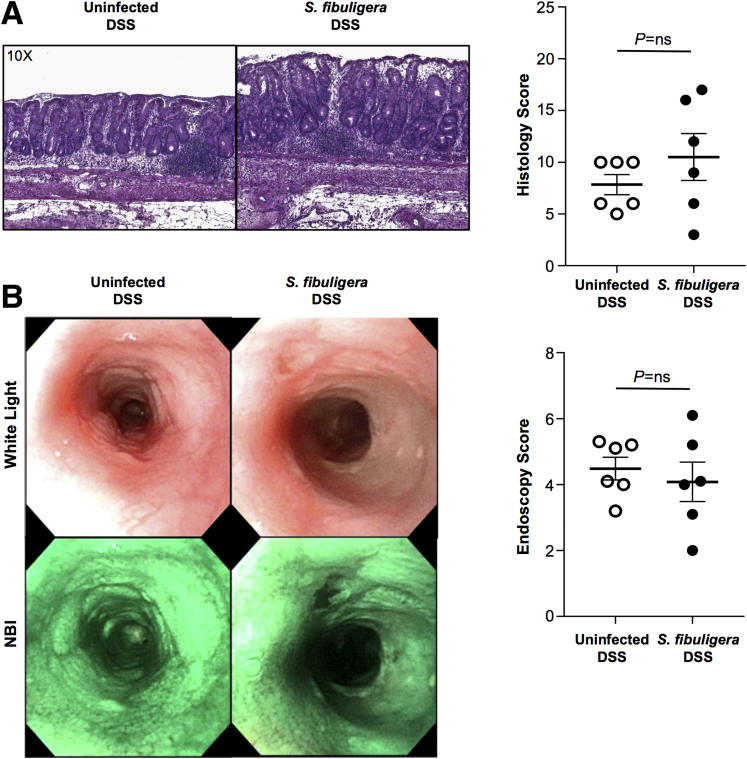
We found that all mice survived during the period of DSS administration. In contrast, during the consequent 2 weeks (recovery phase), mice infected with C tropicalis showed a significantly increased mortality rate compared with uninfected mice (95% CI, 1.038–11.24; P < .05) (Figure 1A). In line with these clinical findings, histologic analysis of mice colons also showed that infected mice had significantly more severe colitis compared with controls (P < .05), as was indicated clearly by increased mucosal damage and cell infiltration in infected mice (Figure 1B and C). Untreated mice with DSS (both uninfected and infected) showed no sign of colitis, mucosal damage, or cell infiltration in the mucosa. Finally, the harmful effect of C tropicalis was corroborated further by our endoscopic study, which showed that infected mice had a significantly increased thickness of colonic mucosa and a higher percentage of intestinal erosions (P < .001, vs uninfected controls). Moreover, untreated mice with DSS (both uninfected and infected) showed no sign of erosion, ulcers, or bleeding, as shown by the presence of visible submucosal blood vessels, a typical sign of normal mucosal thickness (Figure 1D and E). To verify if C tropicalis effectively colonized the gut of the infected mice, the fecal fungal burden was assessed daily after the last day of inoculation. The colony forming units (CFUs) were present in the stool of the infected mice for up to 4 days after the last inoculum (Figure 1F). Mice had no culturable fungus after day 4 (day 5–7 after infection) and before the induction of DSS colitis. To evaluate whether the increased susceptibility to DSS colitis that we observed was a specific effect of C tropicalis, we induced DSS colitis in a separate group of mice that were inoculated with the nonpathogenic yeast Saccharomycopsis fibuligera (serving as a negative control group). Indeed, histologic and endoscopic analysis showed that mice inoculated with S fibuligera did not show significant differences in terms of colitis severity when compared with the control PBS-inoculated group (P = NS for both) (Figure 2).
Figure 1.
Oral inoculation of C tropicalis confers enhanced susceptibility to DSS-induced colitis in B6 mice. (A) Percentage survival of mice after 7 days of 2.5% DSS treatment and 14 days of recovery with drinking water (Gehan–Breslow–Wilcoxon test; hazard ratio for infected mice, 3.415; 95% CI, 1.038–11.24; P < .05). (B) Histologic analysis shows increased colonic inflammation in infected mice compared with uninfected controls (unpaired t test, 9.885 ± 1.357 vs 5.647 ± 0.852; P < .05; N ≥ 13/group). Uninfected mice, spared DSS treatment, were used as the negative control. (C) Representative colonic histopathologic sections of infected mice show active cryptitis, severe ulcers, increased thickness of the intestinal mucosa, and increased inflammatory cells (yellow arrows) in the lamina propria (panel above). Sections form the uninfected mice treated with DSS (uninfected panel) show regenerative mucosa with mild active cryptitis and minimal inflammatory cells compared with the infected littermates. (D) Endoscopic evaluation shows increased colitis in the distal colon of the infected mice compared with the uninfected controls (unpaired t test, 6.75 ± 0.25 vs 5.28 ± 0.28; P < .02; N = 13/group). (E) Endoscopic images of the distal colon show severe inflammation in infected mice (right top panel) compared with the uninfected (left top panel). Control mice without DSS treatment (uninfected: left bottom panel; infected: right bottom panel) show an absence of ulcers, no infiltration of inflammatory cells in the lamina propria, and no damaged epithelium. (F) Fecal fungal burden assessed from day 1 after the last C tropicalis inoculum through day 4 shows that mice infected with C tropicalis had no culturable fungus on day 5 after the last inoculum. Zeiss Axiophot/Axiocam (Jena, Germany) imaging equipment was used. Data are presented as means ± SEM, and are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Figure 2.
S fibuligera inoculation does not increase susceptibility to DSS-induced colitis in mice. (A) Representative histopathologic sections show no significant difference in the mucosa of mice infected with S fibuligera compared with uninfected mice (unpaired t test: 7.82 ± 1.38 vs 10.31 ± 2.67; P = .62). (B) High-resolution endoscopic images obtained with white light and narrow band imaging (NBI) of the distal colon after 7 days of DSS treatment and 14 days of recovery show no significant differences in inflammation in mice infected with S fibuligera compared with uninfected mice (unpaired t test: 4.33 ± 0.86 vs 4.08 ± 1.32; P = .57). Data are presented as means ± SEM; N = 6; P = NS.
C tropicalis Infection Modifies the Colonic Mucosal Immunophenotype During Acute DSS-Induced Colitis
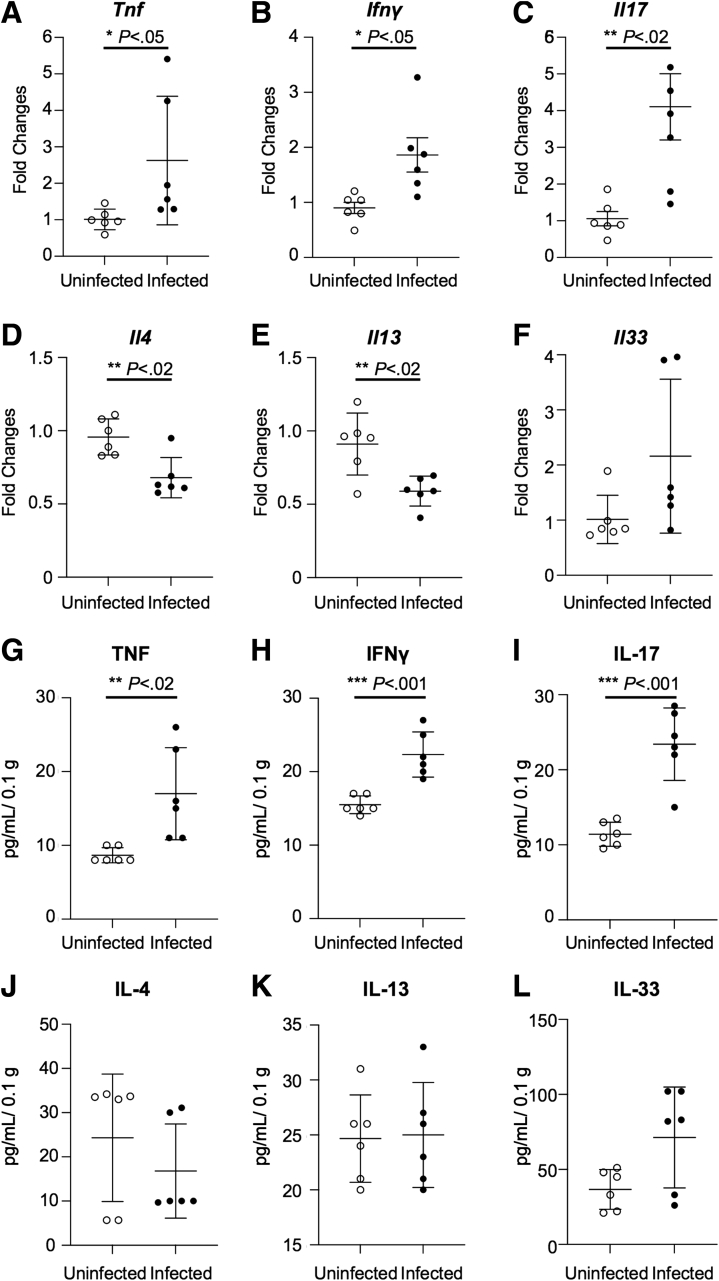
Next, to examine the immunologic basis for the aforementioned proinflammatory effect of C tropicalis infection during acute chemical colitis, we characterized the colonic mucosal immunophenotype from infected and uninfected mice after 14 days of DSS recovery. By measuring cytokine expression in colon samples, we detected a significant increase of tumor necrosis factor (Tnf) (P ≤ .05), interferon (Ifn)-γ (P < .05), and interleukin (Il)17 (P < .02) (Figure 3A–C) in C tropicalis–infected B6 mice (vs uninfected controls). On the other hand, Il4 (P < .02) and Il13 (P < .02) were decreased significantly in the infected mice (Figure 3D and E). In addition, we detected a trend toward increased expression of Il33 in the infected group, although not to a statistically significant level (Figure 3F). Furthermore, when colon samples harvested from infected and uninfected mice were cultured for 24 hours, protein levels of TNF (P < .02), IFNγ (P < .001), and IL17 (P < .001) were increased significantly in the infected mice compared with the controls (Figures 3G–I). Conversely, we did not find any significant difference in protein levels of IL4 and IL13 (Figures 3J and K). Moreover, we detected a trend toward increased production of IL33 in the infected group, although not to a statistically significant level (Figure 3L).
Figure 3.
C tropicalis infection modifies the colonic mucosal immunophenotype during acute DSS-induced colitis. Increased expression of (A) Tnf (unpaired t test: 2.62-fold vs 1.01-fold; P ≤ .05; N = 6), (B) Ifnγ (unpaired t test: 1.86-fold vs 0.90-fold; P < .05), and (C) Il17 (unpaired t test: 3.91-fold vs 0.91-fold; P < .02) in infected mice compared with uninfected controls. Decreased expression of (D) Il4 (unpaired t test: 0.68-fold vs 0.98-fold; P < .02) and (E) Il13 (unpaired t test: 0.59-fold vs 0.91-fold; P < .02) in infected mice compared with uninfected controls. No significant differences were observed in (F) Il33 between the 2 groups (unpaired t test: 1.51-fold vs 0.84-fold; P = NS). Increased protein levels of (G) TNF (unpaired t test: 17.00 ± 6.23 vs 8.67 ± 1.03; P < .02), (H) IFNγ (unpaired t test: 22.33 ± 3.08 vs 15.50 ± 1.23; P < .001), and (I) IL17 (unpaired t test: 46.83 ± 9.66 vs 22.83 ± 3.19; P < .001) in tissue explants from colons of infected vs uninfected mice. No significant differences were observed in (J) Il4 (unpaired t test: 16.80 ± 10.66 vs 24.30 ± 14.41; P = NS), (K) IL13 (unpaired t test: 25.00 ± 4.78 vs 24.67 ± 3.98; P = NS), and (L) IL33 (unpaired t test: 71.33 ± 33.63 vs 36.67 ± 13.25; P = NS). Data are presented as means ± SEM, and are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Taken together, these data strongly suggest that infection with C tropicalis renders B6 mice more susceptible to acute chemical colitis, an effect that is associated with alterations of the mucosal immunologic microenvironment toward Th1/Th17 dominant immunity.
Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells Are Altered in Infected Mice After DSS Treatment
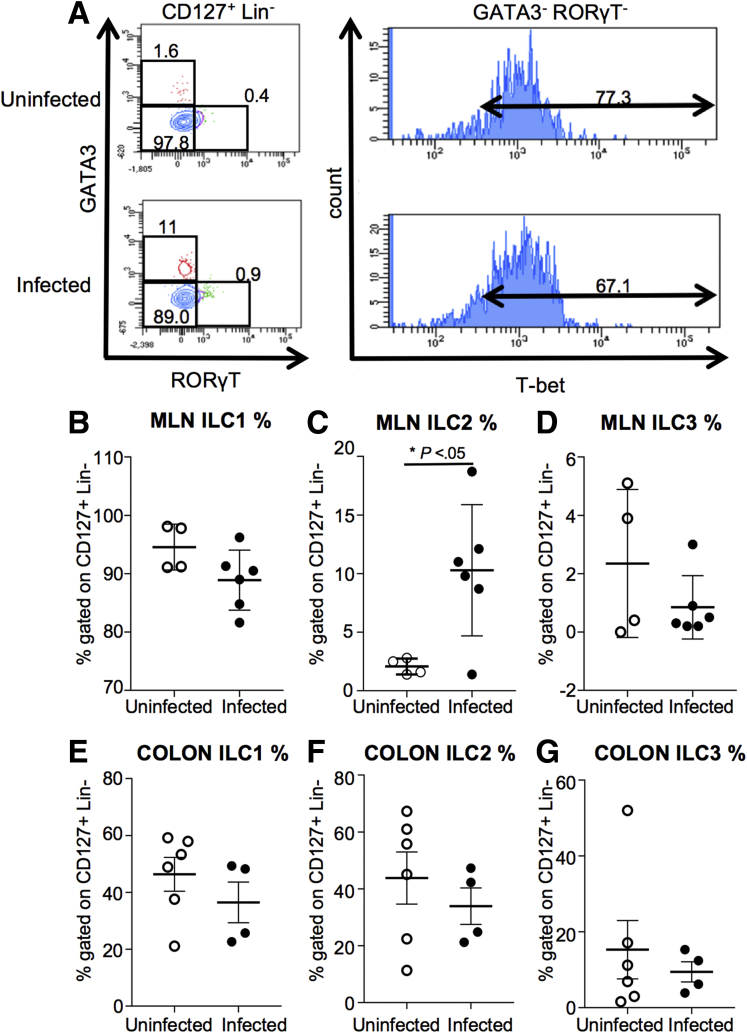
Because innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) have been reported to play a role in immune defense against candidiasis,10,11 we also investigated the effect of infection with C tropicalis on the mucosal populations of ILCs (Figure 4A). Our flow cytometry analysis showed that GATA Binding Protein 3 (GATA3)+ group 2 ILCs (ILC2s) (gated on CD127+ Lin-) were increased significantly in the mesenteric lymph nodes (MLNs) of infected mice as compared with the uninfected group (Figure 4C). In contrast, we did not observe any significant differences in the other major ILC populations, namely T-bet+ ILC1s and Retinoid-related orphan receptor gamma t (RORγT)+ ILC3s in the MLNs (Figure 4B and D). Furthermore, flow cytometry analysis showed that T-bet+ ILC1s, GATA3+ ILC2s, and RORγT+ ILC3s were not significantly different in the colons of the 2 groups (Figures 4E–G).
Figure 4.
ILC2s are altered in infected mice after DSS treatment. (A) Gating strategy for ILCs. ILCs are identified by gating on CD45+ live cells, and then looking for a population positive for CD127 and negative for lineage (Lin) markers CD11c dendritic cells (DCs), CD11b (myeloid cells), Ter-119 (granulocytes), B220 (B cells), Ly-6g, and CD3 (lymphocytes). From the CD127+ Lin- population, we gated on GATA3+ cells (ILC2), RORγT+ cells (ILC3), and cells negative for GATA3 and RORγT that were positive for T-bet (ILC1). Dot plots are representative of ILCs in the mesenteric lymph nodes. (B) T-bet+ ILC1s do not display significant differences between the 2 groups (unpaired t test, 99.55 ± 1.96 vs 88.90 ± 2.10; P = NS; N ≥ 4). (C) GATA3+ ILC2s (gated on CD127+ Lin-) of the infected mice show a significant increase compared with the uninfected group (unpaired t test, 10.28 ± 2.28 vs 2.08 ± 0.34; P < .05). (D) RORγT+ ILC3s show no significant differences between the 2 groups (unpaired t test, 0.85 ± 0.44 vs 2.35 ± 1.27; P = NS). (E) T-bet+ ILC1s do not display significant differences in the colonic mucosa between the 2 groups (unpaired t test, 43.33 ± 5.97 vs 36.45 ± 7.13; P = NS; N ≥ 4). (F) GATA3+ ILC2s do not display significant differences in the colonic mucosa between the 2 groups (unpaired t test, 43.82 ± 9.14 vs 33.90 ± 6.42; P = NS; N ≥ 4). (G) RORγT+ ILC3s show no significant difference in the colonic mucosa between the 2 groups (unpaired t test, 15.30 ± 7.70 vs 9.45 ± 2.65; P = NS). Data are presented as means ± SEM, and are representative of 3 independent experiments.
C tropicalis Infection Leads to Discrete Alterations of the Mouse Microbiome
The increased susceptibility of C tropicalis–infected mice to DSS colitis that was shown earlier may be owing to a direct stimulatory effect of this pathogen on the mouse mucosal immune system. Nevertheless, another possibility is that C tropicalis expansion acts indirectly by affecting the composition of the gut microbiome, which, in turn, may invariably shape mucosal immunologic responses and modify susceptibility to acute chemical injury.
To address the second hypothesis, we performed a comparative analysis of individual mouse fecal microbiomes before and 6 days after inoculation with C tropicalis (or PBS as the control group). Our microbiome characterization using 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) analysis clearly showed that β-diversity was significantly different between the 2 groups on day 6 after gavage treatment (P < 0.001) (Figure 5A, right panel). As expected, no differences were seen between the 2 groups at baseline (ie, before gavage) (Figure 5A, left panel), indicating that the observed diversity by day 6 is the specific effect of C tropicalis administration.
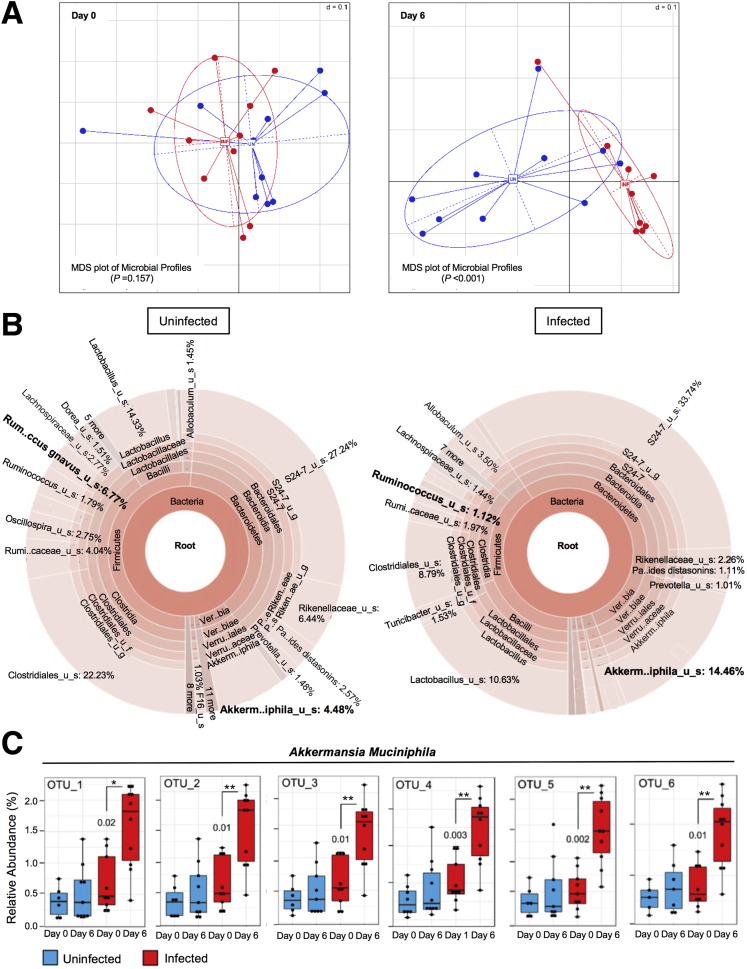
Figure 5.
C tropicalis infection leads to discrete alterations of the mouse microbiome. (A) 16S rRNA analysis. The β-diversity between the 2 groups was not significantly different before the infection (P = NS; N = 10/group), but it became significantly different on day 6 after the C tropicalis infection (P < .001). (B) Analysis of the percentage of bacterial species in the feces of infected vs uninfected mice showed that A muciniphila abundance was increased significantly compared with the control group (unpaired t test, percentage gut microbiome: 14.46 ± 1.97 vs 4.48 ± 2.17; P < .02). R gnavus also was decreased significantly in the infected mice compared with the control group (unpaired t test, percentage gut microbiome: 1.12 ± 0.23 vs 6.77 ± 2.4; P < .05). (C) Six different operational taxonomic units (OTUs) indicated that A muciniphila was significantly more abundant in the infected mice compared with the uninfected littermates (unpaired t test, P < .05). Data are represented as means ± SEM, and are representative of 3 independent experiments. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .02. Minimum Data Set.
Figure 5B shows the microbiome differences between the 2 groups of mice (infected vs uninfected); it is shown that administration of C tropicalis was associated with specific alterations at the genus and species level. In particular, R gnavus was significantly less abundant in infected mice (P < .05). In contrast, A muciniphila was significantly more abundant in infected mice as compared with controls (P < .02). Furthermore, A muciniphila was confirmed to be the bacterial species that was affected the most by C tropicalis administration because it is persistently shown in 6 different operational taxonomic units that were tested (P < .05) (Figure 5C). Finally, bacteria belonging to the genus Lactobacillus showed a trend for decreased abundance in the infected group, although this did not reach statistical significance (P = NS).
Gut Microbiome Alteration Leads to Changes in Mucus Production in the Colonic Epithelium
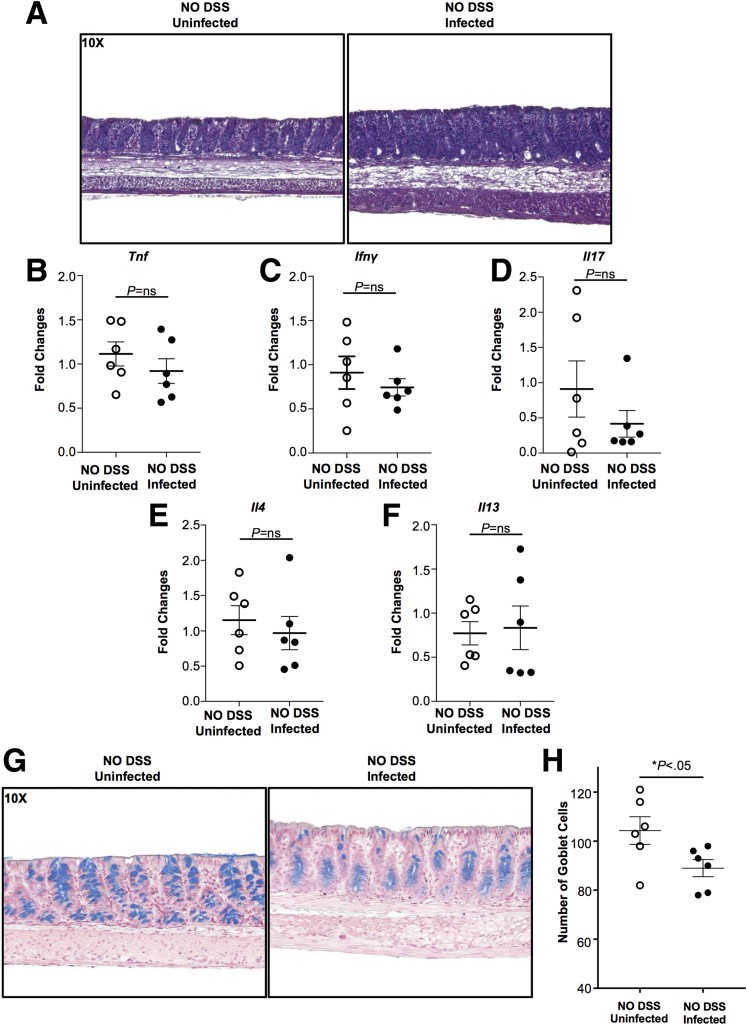
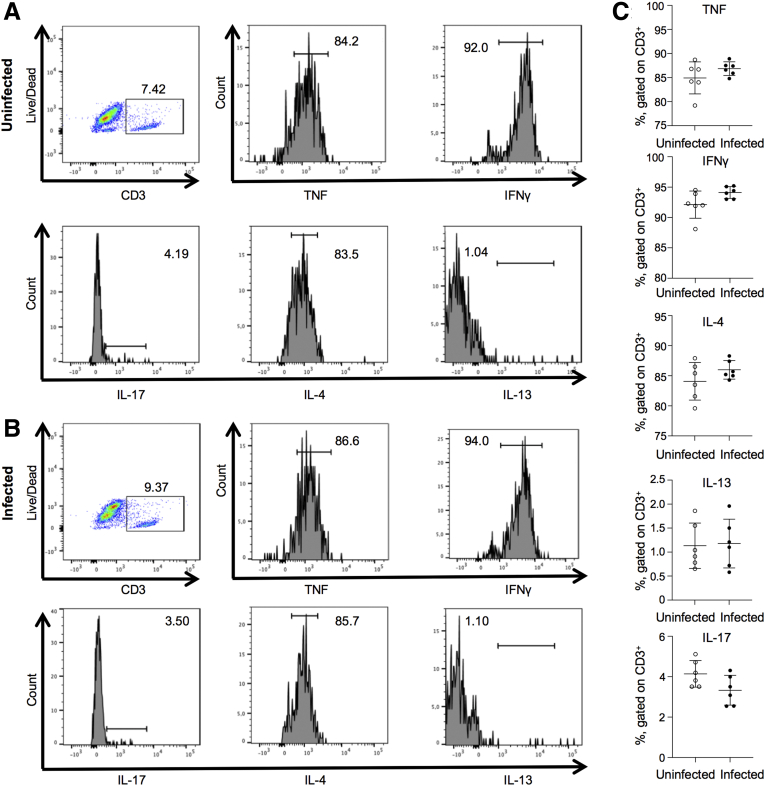
One possibility for the increased susceptibility of C tropicalis–infected mice to DSS colitis could be that infection with this fungal strain creates a proinflammatory environment per se at the intestinal mucosa. To address this hypothesis, we studied B6 mice that were inoculated only with C tropicalis without subsequent DSS treatment. As a negative control, we used B6 mice without C tropicalis inoculation. Histologic analysis showed that neither group developed signs of colonic damage (Figure 6A). Furthermore, we characterized the colonic mucosal immunophenotype of infected and uninfected mice by measuring cytokine expression in colon samples, and did not detect any significant differences in the expression of various helper T cells (Th)1, Th2, and Th17 cytokines compared with uninfected mice (Figure 6B–F). Flow cytometry analysis confirmed the quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) data on lymphocytes isolated from MLNs (Figure 7A–C). A second possibility that was raised by our results could be that the main cause of increased susceptibility to DSS colitis was the shift that was observed in the gut microbiome of C tropicalis–inoculated mice. Because the major changes concerned mucin-degrading bacteria, we explored the possibility that infected mice showed changes in mucus production. To address our second hypothesis, we used Alcian blue stain to quantify the abundance of mucin-producing goblet cells in the colonic epithelium of the 2 groups of mice. Our results clearly showed that goblet cells were decreased significantly in colonic sections of B6 mice after C tropicalis inoculation (P < .05 vs control group) (Figure 6G and H).
Figure 6.
Gut microbiome alteration leads to changes in mucus production in the colonic epithelium. (A) Representative colonic histologic sections of infected mice (right panel) and uninfected mice (left panel) show no signs of colonic inflammation in the 2 groups. No significant differences were found in the expression of (B) Tnf (unpaired t test: 0.92-fold vs 1.11-fold; P = NS; N = 6), (C) Ifnγ (unpaired t test: 0.74-fold vs 0.91-fold; P = NS), (D) Il17 (unpaired t test: 0.42-fold vs 0.91-fold; P = NS), (E) Il4 (unpaired t test: 0.97-fold vs 1.15-fold; P = NS), and (F) Il13 (unpaired t test: 0.83-fold vs 0.77-fold; P = NS). (G and H) Representative colonic sections stained with Alcian blue show that mice gavaged with C tropicalis (right panel) have a significant decrease of goblet cells compared with the control group (left panel) (unpaired t test, 89.0 ± 3.50 vs 104.3 ± 5.65; P < .05; N = 6/group). Zeiss Axiophot/Axiocam (Jena, Germany) imaging equipment was used. Data are presented as means ± SEM, and are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Figure 7.
Lymphocytes are not altered in B6 mice after C tropicalis infection only. (A and B) Gating strategy for lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are identified by gating on CD3+ live cells, and then looking for subsets positive for TNF, IFNγ, IL4, IL13, and IL17. Dot plots are representative of lymphocytes in the MLNs. (C) Lymphocytes did not display significant differences between the (A) uninfected vs (B) infected groups: TNF (unpaired t test: 84.93 ± 3.32 vs 86.85 ± 1.42; P = .22), IFNγ (unpaired t test: 92.12 ± 2.24 vs 94.12 ± 0.97; P = .07), IL4 (unpaired t test: 84.08 ± 3.12 vs 85.98 ± 1.54; P = .21), IL13 (unpaired t test: 1.13 ± 0.47 vs 1.17 ± 0.51; P = .87), and IL17 (unpaired t test: 4.14 ± 0.66 vs 3.33 ± 0.74; P = .07). Data are represented as means ± SEM; N = 6. P = NS.
Taken together, these findings indicate that the critical mechanism for the proinflammatory effect of C tropicalis during DSS colitis is not a direct immunostimulatory effect on local immunocytes, but rather the rearrangement of bacterial microflora and a corresponding deleterious effect on mucus production.
Increased Susceptibility to DSS Colitis and Altered Intestinal Permeability Are Transferable via Transplantation of Fecal Material From Mice Infected With C tropicalis
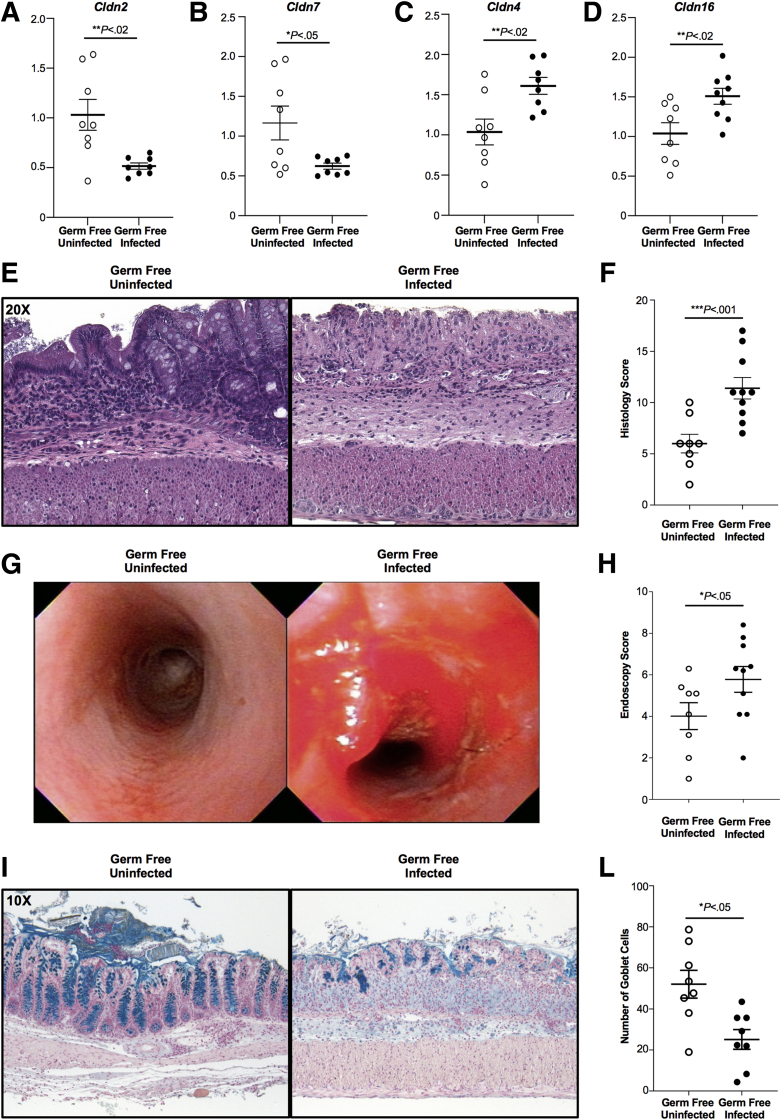
To validate our hypothesis that dysbiosis involving mucin-degrading bacteria including A muciniphila and R gnavus lead to changes in mucus production and consequently altered intestinal permeability, we characterized the colonic epithelial expression of tight junction proteins from GF mice transplanted with fecal material of B6 mice previously inoculated with C tropicalis or PBS (controls). Reverse-transcription (RT)-qPCR analysis showed that colonic epithelial cells from the experimental group were characterized by a significant decrease of Claudin (Cldn)2 (P < .02) and Cldn7 (P < .05) in the experimental group compared with controls (Figure 8A and B). On the other hand, Cldn4 (P < .02) and Cldn16 (P < .02) were increased significantly in the experimental group compared with controls (Figure 8C and D).
Figure 8.
Increased intestinal permeability and susceptibility to DSS colitis is transferable via transplantation of fecal material from mice infected with C tropicalis. Decreased expression of (A) Cldn2 (unpaired t test: 0.50-fold vs 0.93-fold; P < .02; N = 8) and (B) Cldn7 (unpaired t test: 0.61-fold vs 1.07-fold; P < .05) in GF mice gavaged with fecal material of C tropicalis–infected mice compared with uninfected controls. Increased expression of (C) Cldn4 (unpaired t test: 1.62-fold vs 1.03-fold; P < .02) and (D) Cldn16 (unpaired t test: 1.55-fold vs 1.07-fold; P < .02) in GF mice gavaged with fecal material of C tropicalis–infected mice compared with uninfected controls. (E) Representative histopathologic sections of GF mice transplanted with fecal material infected with C tropicalis show an increased percentage of ulcers, increased thickness of the intestinal mucosa, and increased inflammatory cells (right panel) compared with uninfected GF controls (left panel). (F) Histologic analysis shows a significant increase of acute colitis in GF mice transplanted with infected fecal material compared with uninfected GF controls (unpaired t test: 11.23 ± 0.80 vs 6.0 ± 0.91; P < .05; N ≥ 8/group). (G) Endoscopic images of the distal colon show severe inflammation in transplanted GF mice (right panel) compared with the uninfected controls (left panel). (H) Endoscopic analysis shows increased colitis in the distal colon of the transplanted GF mice compared with the uninfected controls (unpaired t test: 6.03 ± 0.55 vs 4.01 ± 0.65; P < .05; N ≥ 8/group). (I–L) Representative colonic sections stained with Alcian blue show that GF mice gavaged with infected fecal material have a significant decrease of goblet cells compared with the control group (unpaired t test: 21.39 ± 5.39 vs 50.28 ± 9.10; P < .05; N = 6/group). Zeiss Axiophot/Axiocam (Jena, Germany) imaging equipment was used. Data are presented as means ± SEM, and are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Furthermore, to mechanistically confirm that C tropicalis exerts its deleterious effects on colitis severity by altering the composition of mouse microbiome, we then tested whether increased susceptibility to DSS colitis could be transferred after fecal microbiome transplantation (FMT). B6 mice were gavaged with C tropicalis or PBS (controls) as fecal donors and GF mice were used as recipients. Because of the high mortality of GF mice after DSS administration, we killed the mice 4 days after the end of DSS treatment, instead of 2 weeks. Histologic analysis showed that GF mice that were gavaged with infected fecal material were more susceptible to DSS colitis compared with those gavaged with uninfected fecal material (P < .001). This was associated with increased muscular hypertrophy and less preservation of mucosal architecture (Figure 8E and F). Similarly, by endoscopic evaluation, GF mice gavaged with infected fecal material showed more intestinal bleeding, more ulcerations, and increased thickness of the colonic mucosa compared with controls (P < .05) (Figures 8G and H). Finally, via Alcian blue stain, we quantified the abundance of mucin-producing goblet cells in the colonic epithelium and found that this was decreased significantly in colonic sections of GF mice gavaged with infected fecal material compared with the control group (P < .05) (Figure 8I and 8L).
Taken together, these data strongly suggest that the microbiome shift promoted by C tropicalis infection leads to changes in the expression of specific tight junction proteins causing altered intestinal permeability and, as a result, the altered microflora is capable of inducing enhanced susceptibility to colitis upon fecal transplantation in GF mice.
C tropicalis Infection Is Associated With Increased Intestinal Permeability
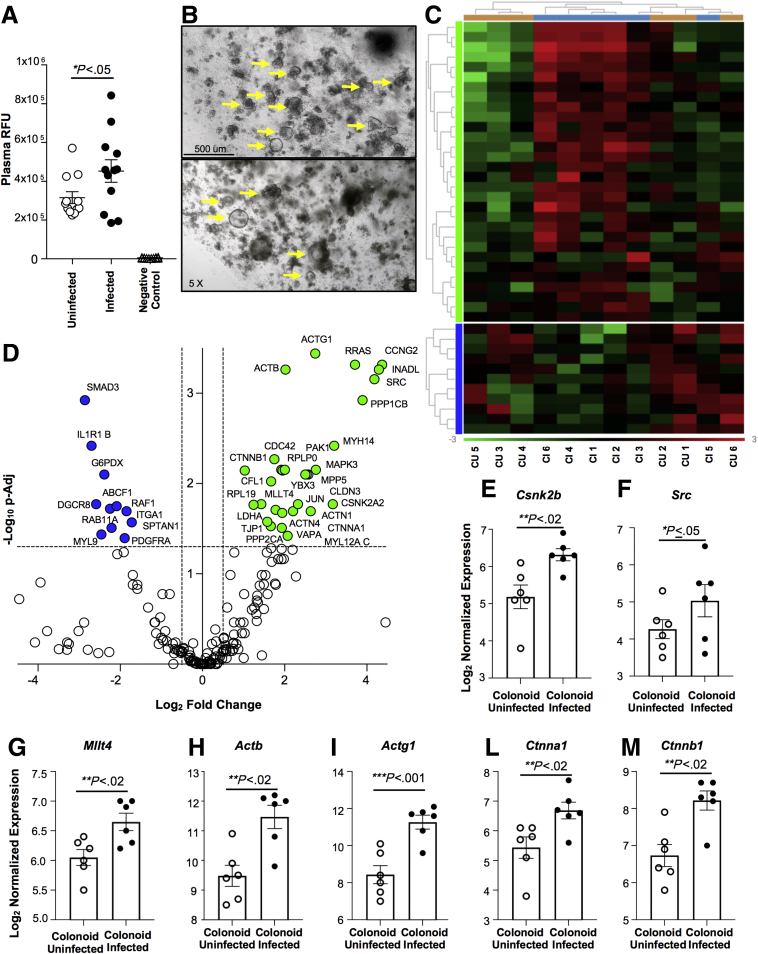
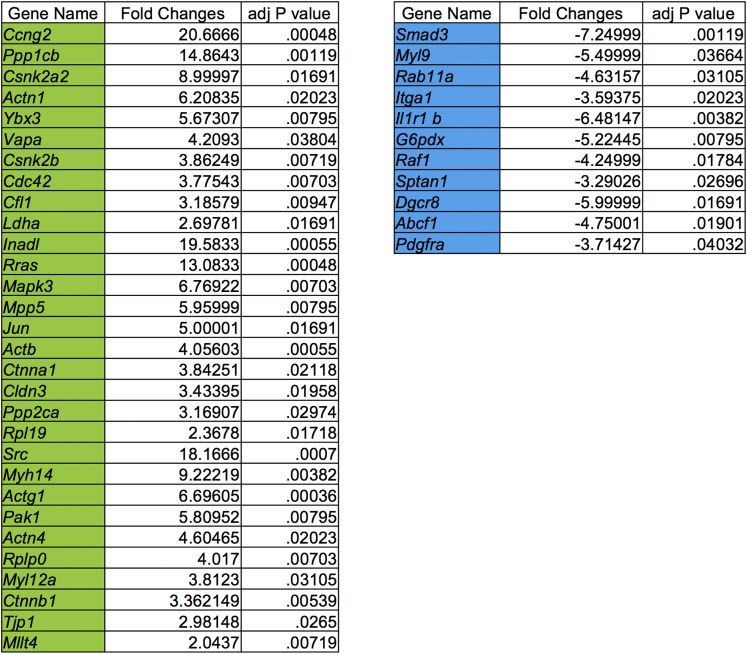
To seek confirmation that the changes in mucus production caused by C tropicalis infection lead to altered intestinal permeability, we performed a fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-dextran (70 kilodaltons) permeability assay. Infected and uninfected B6 mice were gavaged with FITC-dextran. Relative fluorescence unit (RFU) plasma levels were measured 4 hours after the gavage. The negative control group was represented by plasma of uninfected mice that were not gavaged with FITC-dextran. We detected that RFU plasma levels in infected mice were increased significantly compared with uninfected mice (P < .05) (Figure 9A). Furthermore, because intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction (IEBD) is considered an important risk factor for the pathogenesis of CD, we isolated crypts from the colon of the experimental mice and subsequently generated colonoids from the intestinal epithelium of mice infected and uninfected with C tropicalis to highlight the molecular mechanisms induced in the colonic epithelium as a response to C tropicalis infection. Although colons of the 2 groups had normal histologic features, such as normal villi architecture and no acute inflammation, we detected a trend toward a decreased number of developed colonoids in infected mice compared with the uninfected group, albeit this was not statistically significant (Figure 9B). To further clarify the mechanisms that determine altered intestinal permeability and potential epithelial barrier dysfunction in infected mice we used a Mouse NanoString Panel focused on 230 genes affecting intestinal-epithelial barrier function and epithelial homeostasis (NanoString Technologies, Seattle, WA). The data obtained can be visualized in the heatmap showing the clustering of genes significantly increased or decreased compared with the uninfected control group (Figure 9C). We used uninfected mice to define baseline homeostatic expression and observed differences with infected mice for 17.8% of the genes analyzed. Specifically, 30 genes were up-regulated significantly in infected mice and 11 were down-regulated (Figure 9D). Functional classification of the 41 genes that were different between infected and uninfected mice showed that the majority belonged to families of genes involved in the transcription and translation of proteins affecting the functionality of intercellular junctions. In particular, the up-regulated genes were related to the activation of the cadherin signaling pathway (P ≤ .05) and adherens junctions interactions (P < .02), such as Csnk2b, Src, Mllt4, Actb, Actg1, Ctnna, and Ctnnb1 (Figure 9E–M). A complete list of genes with significantly different expression between colonoids cultured from infected vs uninfected mice is shown in Figure 10.
Figure 9.
C tropicalis infection is associated with intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction. (A) (FITC-dextran) permeability assay shows that infected mice have significantly increased plasma levels of RFUs after gavage of FITC-dextran compared with uninfected mice (unpaired t test: 452,737 ± 57,787 vs 315,778 ± 30,446; P < .05; N = 12/group). (B) Representative 5× magnification images of large intestinal colonoids (indicated by yellow arrows) composed of crypts and stem cells obtained from uninfected (top) and infected (bottom) mice after 6 days in culture. (C) Heatmap of normalized data, highlighting associations between genes differently expressed in colonoids cultured from infected and uninfected mice. Data are plotted, providing associations between gene expression (blue, down-regulation; green, up-regulation) and sample treatment. Each row represents a single probe and each column represents a single sample, and plot is scaled with relation to average probe performance across samples to give all genes equal mean and variance. Hierarchical clustering was used to generate dendrograms. (D) Volcano plot expressing NanoString data for 230 genes was obtained with ROSALIND software and showed that colonoids cultured from infected mice have 11 genes down-regulated and 30 genes up-regulated compared with uninfected mice. Increased expression of (E) Csnk2b (unpaired t test: 6.32-fold vs 5.18-fold; P < .02; N = 6), (F) Src (unpaired t test: 5.03-fold vs 4.25-fold; P ≤ .05), (G) Mllt4 (unpaired t test: 6.65-fold vs 6.05-fold; P < .02), (H) Actb (unpaired t test: 11.47-fold vs 9.48-fold; P < .02), (I) Actg1 (unpaired t test: 11.27-fold vs 8.43-fold; P < .001), (L) Ctnna1 (unpaired t test: 6.68-fold vs 5.43-fold; P < .02), and (M) Ctnnb1 (unpaired t test: 8.22-fold vs 6.73-fold; P < .02) in infected mice compared with uninfected controls. Zeiss Axiophot/Axiocam (Jena, Germany) imaging equipment was used. Data are presented as means ± SEM, and are representative of 3 independent experiments.
Figure 10.
List of genes with significantly different expression between colonoids of infected vs uninfected mice. A total of 17.8% of the genes analyzed were different. Thirty genes were up-regulated significantly (highlighted in green) in colonoids generated from infected mice and 11 were down-regulated (highlighted in blue).
Discussion
In the present study, we report that intestinal infection with C tropicalis was associated with increased severity of DSS colitis in B6 mice, which was indicated by enhanced, proinflammatory Th1/Th17 immune responses. We also provide mechanistic evidence for the pathogenic mechanism of this effect by showing that infection with C tropicalis did not induce a proinflammatory mucosal immunophenotype per se in the absence of challenge with DSS. Rather, the worse outcome was mediated through intimate interactions between intestinal bacteria and fungi that take place during acute DSS-induced colitis. Such interactions include specific alterations in fecal microbiome composition that may produce downstream weakening of the mucus barrier and that render the microbiome of C tropicalis–infected mice capable of transferring disease susceptibility to GF mice upon fecal transplantation.
In our study, we used large-scale sequencing and bioinformatics analysis to compare the gut microbiome of mice that were infected with C tropicalis with uninfected controls. Heterogeneity analysis of fecal microbial communities clearly showed diverse microbiome compositions between infected and uninfected mice. We undertook a very meticulous experimental approach to ensure the specificity of the observed microbiome changes because recent research has highlighted a concerning microbiome variability between results from different laboratories.12 To overcome such problems, we collected fresh fecal samples from each mouse and homogenized them; the mixed suspension was gavaged to all experimental mice before the C tropicalis infection. This ensured uniform microbiome composition at baseline because no differences were observed in β-diversity between the 2 groups as shown by our 16S rRNA analysis. In contrast, after C tropicalis infection, there was a critical shift of the microbiome structure in infected mice. These data strongly support the notion that the gut microbiome variation was induced by the yeast infection and represents the major driving force for the increased susceptibility of infected mice to DSS-induced colitis. Further evidence was provided by the fecal transplant experiment to GF mice because recipient mice adopted the phenotype of their donors, with GF mice transplanted with fecal material from infected mice being more susceptible to DSS-induced colitis. Furthermore, the presence of C tropicalis itself was necessary for inducing the microbiome shift but not for the deterioration of colitis, because Candida was undetectable in the fecal samples 3 days after inoculation in GF mice. Our findings agree with those of Iliev et al13 who showed fungal dysbiosis and increased susceptibility to chemically induced colitis in mice deficient for the receptor dectin-1, a protein involved mainly in antifungal immunity. Furthermore, in support of the translational relevance of our work, multiple studies have reported fungal dysbiosis in IBD patients, highlighted by fungal overgrowth at the colonic mucosa in both UC14 and CD.15,16 Further emphasizing the clinical relevance of the findings presented herein, significant increases in the relative abundance of C tropicalis were shown in patients with IBD.17,18 Finally, a recent study by Leonardi et al19 has shown that patients with a clinical response to FMT have a higher abundance of Candida in their pre-FMT stool and a lower Candida abundance and increased microbial diversity after FMT, indicating that Candida may have proinflammatory effects during intestinal inflammation and IBD.
In addition to the aforementioned shifts in β-diversity, we also were able to show significant changes in distinct bacterial taxa between the 2 experimental groups. Among them, microorganisms of the species A muciniphila were increased consistently in fecal samples 6 days after the infection with C tropicalis. These data are in agreement with the work of Seregin et al,20 who showed that increased colonization of A muciniphila was sufficient to induce intestinal inflammation in both specific-pathogen-free and GF Il10-/- mice. Along the same line, it was shown that A muciniphila also was increased in Salmonella Typhimurium-infected gnotobiotic mice with gut inflammation.21 Taken together, our data and those studies point to an association between A muciniphila expansion and gut inflammation, which is, at first, unexpected, given the fact that this microorganism is a common member of the gut microbiome of healthy human subjects. This, however, may be explained by the functional effects of A muciniphila expansion in relation to its mucin-degrading properties via the production of mucolytic enzymes.22,23 We hypothesize, therefore, that its expansion before DSS colitis may result in degradation of the mucus layer followed by defective barrier function, and, eventually, by intestinal inflammation. Our findings support this hypothesis because we observed decreased numbers of mucin-producing goblet cells at the colonic mucosa of infected mice. Such breakdown of mucus integrity may have deleterious effects given its important contribution to mucosal homeostasis. Those include mucus functioning as a nutritional source for bacterial proliferation,24 as a regulator of gut colonization, and as an amplifier of host defense by inhibiting bacterial adhesion and toxin secretion to the mucosal surface.25 On the other hand, we also detected decreased abundance of R gnavus in C tropicalis–infected mice, which also is a mucin-degrading bacterium. This is in contrast to reports of increased R gnavus abundance during flares of CD.26 Such discrepancies may be explained by the fact that a specific effect is not explained solely by changes in bacterial abundance. As an example, Eun et al27 showed that R gnavus lysates were capable of inducing dramatic ex vivo Th1 and Th17 responses in MLNs of gnotobiotic Il10-/- mice, although bacterial abundance was low. Overall, we speculate that the increase of A muciniphila was the critical driver for the mucin degradation observed in the GF mice and the subsequent development of intestinal inflammation in fecal transplant recipients. The importance of mucus protection during intestinal inflammation has been emphasized by studies in mice deficient in mucin 2,28 which develop severe colitis, and experiments in human beings showing structural alterations of the colonic mucus barrier in patients with UC.29
Moreover, multiple studies have reported evidence in support of IEBD preceding the onset of intestinal flares, suggesting a major role for IEBD in disease development.30,31 We examined the expression of genes involved in intestinal barrier homeostasis to determine if there was any difference in GF mice gavaged with fecal material from C tropicalis–infected donors compared with GF mice gavaged with fecal material from uninfected donors (controls). Among the genes analyzed, we detected a significant decrease in Cldn2 and increase in Cldn4 in the experimental group compared with controls. This is very interesting because it has been shown previously that Cldn2 has the capacity to decrease barrier function of Cldn4.32 Hence, a decrease of Cldn2 may lead to increased Cldn4 expression, previously reported to be increased in CD and UC patients during active inflammation.33 A decrease of Cldn7 also was observed in the GF experimental group. This is in agreement with the work of Xing et al,34 showing that the deletion of the tight junction protein Cldn7 in mice leads to mucosal ulceration and severe intestinal epithelial damage. The association between decreased Cldn7 expression and epithelial barrier disruption also was confirmed by Ding et al,35 who showed, using electron microscopy analysis, that Cldn7-/- mice had intercellular gaps below tight junctions and cell matrix loosening, leading to severe intestinal defects such as epithelial cell sloughing, inflammation, and mucosal ulcerations.
We used a colonoid-based model that recapitulates the epithelial cell phenotype of B6 mice after C tropicalis infection to analyze the epithelial molecular responses induced by Candida infection. Several studies have used gastrointestinal organoids previously to study the effects of different bacterial infections, such as Clostridium difficile36 or Salmonella Typhimurium.37 Our study showed that C tropicalis inoculation not only severely affected the abundance of mucin protecting the intestinal epithelium, but it also deeply affected the expression of 41 genes implicated in maintaining intestinal epithelial barrier function and, consequently, epithelial homeostasis. Our data are in line with a recent study by Kinchen et al38 that showed that UC patients present dysregulation of colonic intestinal stem cells leading to intestinal barrier dysfunction. Furthermore, in our study, adherens junctions interactions and the cadherin signaling pathway were the 2 molecular pathways mainly affected by Candida infection. Naturally, this makes sense because adherens junctions are widely present in the epithelial tissue to maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier.39 In addition, the colon is surrounded by a monolayer that encompasses a cadherin-dependent barrier, which is necessary for the homeostasis of the large intestine.40
In the present work, we also defined the immunologic characteristics of the severe colitis that occurred in mice infected with C tropicalis. First, we observed up-regulation of Th-17 immunity in infected mice with significant increases in Il17 expression. This is not surprising given the well-established role of Th17 cells in antifungal immunity. In further relevance to the current study, IL17-dominant responses may play an integral protective role as part of host defense mechanisms against candidiasis.41,42 In particular, impaired IL17 regulation renders mice incapable of controlling mucosal infections or systemic invasion of C tropicalis.43 Second, we also detected increased expression of Tnf in infected mice. This is in agreement with the study by Whibley et al,44 who focused on mice deficient in dectin-1/caspase-associated recruitment domain adaptor 9 (CARD9), a receptor associated with immunity against candidiasis.45 They showed that CARD9-deficient mice showed increased fungal growth and higher mortality rates after C tropicalis infection. In line with our study, this was associated with critically compromised Tnf expression because CARD9-depleted neutrophils and monocytes were unable to produce TNF after infection with C tropicalis, whereas mice lacking TNF were more susceptible to this infection. Finally, after DSS challenge, C tropicalis–infected mice had significantly higher numbers of ILC2s in the MLNs, without any effect on the percentages of ILC1s or ILC3s. Although we were not able to identify the trigger behind this specific expansion of ILC2s, it is noticeable that it was associated with a definitive trend for Il33 increase in the group of infected mice. IL33 is a member of the IL1 cytokine family with many diverse and even opposite functions, depending on the particular immunologic scenario.46 Thus, it is highly relevant to our present findings that IL33 may promote type 2 immune responses via stimulation of ILC2s activity.47,48 ILC2s respond to epithelial cell–derived cytokines such as IL33, IL25, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin, and are known to be critical for immunity against extracellular parasites, allergic inflammation, and restitution of epithelial barrier integrity in the lungs after viral infection. In addition, IL33-induced, ILC2-mediated enhancement of tissue repair mechanisms recently was described.49,50 These data raise the possibility of an IL33–ILC2 axis that participates in the response to environmental insults, which, according to our study, also may include infection with Candida species. Furthermore, ILC2 frequency was not different in the colonic mucosa of the infected mice. This is in agreement with the fact that Th2 cytokines such as Il4 and IL13 were down-regulated at the messenger RNA level in infected mice, but were not significantly different at the protein level in colonic samples.
In conclusion, we provide evidence for a deleterious effect of C tropicalis infection on the severity of DSS colitis in mice and propose a pathogenic model that involves both microbiome shifts and rearrangements of the mucosal immunophenotype. In particular, fungal inoculation does not affect mucosal immunity per se but weakens the function of the defensive mucosal barrier by facilitating expansion of microbiome components with mucin-degrading properties, most prominently A muciniphila species. Eventually, this is followed by induction of dominant mucosal Th1/Th17 responses and expansion of ILC2s, all of which culminate in an accelerated proinflammatory phenotype in C tropicalis–infected mice. Based on our discoveries, we speculate that interkingdom interactions may deeply affect the immune system of IBD patients and may underlie disease flares as a result of generation of a proinflammatory environment. Deeper understanding of such interactions will further elucidate IBD pathogenesis but also may offer unique treatment opportunities for these devastating diseases.
Materials and Methods
Experimental Animals
B6 mice (Mus musculus) were propagated in the Animal Resource Center at Case Western Reserve University (CWRU). All mice used in this study were between 15 and 18 weeks of age and were age- and sex-matched among experimental groups.
Experimental mice were housed in ventilated micro-isolator cages (Allentown, Inc, Allentown, NJ) with cotton nestlets for environmental enrichment (Envigo, Indianapolis, IN) and 1/8-inch corn bedding, and kept on 12-hour light/dark cycles.
All mice had ad libitum access to water and standard laboratory rodent diet P3000 (Harlan Teklad, Indianapolis, IN) throughout the experiments. Harem breeding was set up by co-housing one 8-week-old male with two 8-week-old females. All procedures were approved by the CWRU Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and were in accordance with the Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care guidelines. All experiments were conducted in a blinded manner, without prior knowledge of treatments and mouse groups by the experimenter. Mice were randomized to different interventions using a progressive numeric number. The code for each mouse was known only to the animal caretaker and was revealed at the end of the study.
Homogenization of the Fecal Pellets
To control for cage-to-cage variability that could be attributable to gut microbiome changes, corn bedding from each cage was collected, mixed for 3 minutes, and then an equal amount of pellets was redistributed in each experimental cage a week before the C tropicalis inoculation. At the same time, 20 mg of fecal pellets were collected from each mouse in sterile PBS. All the pellets were homogenized in PBS using glass beads of 0.5-mm diameter (11079105; Biospec Products, Bartlesville, OK) and of 1.0-mm diameter (11079110; Biospec Products). The fecal homogenate then was gavaged (200 μL/mouse, once per day for 3 consecutive days).
Induction of Colitis
Induction of acute colitis was achieved by exposing mice to sterilized 2.5% (wt/vol) DSS (batch DB001-31; TdB Consultancy AB, Uppsala, Sweden) in drinking water for 7 days. Our protocol for induction of DSS colitis includes renewal of the DSS solution every 3 days. B6 mice were allowed ad libitum access to water. Mice returned to normal drinking water after 7 days of DSS and were allowed to recover for 2 weeks. Daily monitoring was performed for body weight, fecal bleeding, and the presence of loose stools.
Yeast Challenge and Determination of CFUs
The clinical C tropicalis strain was isolated from a fecal sample taken from a CD patient and used as the infecting fungus.4,51 C tropicalis was plated on Sabouraud dextrose agar and incubated at 37°C for 2 days. C tropicalis cells were harvested by centrifugation and normal saline (0.85% NaCl) washes. A challenge inoculum of 1 × 109/mL was prepared using a hemocytometer. Each mouse was challenged with 1 × 108 blastospores in 0.1 mL normal saline via oral gavage once per day for 3 consecutive days (n = 3). Animals were considered infected after successful dosing and inoculum confirmation in the stool. This process was performed 4 days before the administration of 2.5% DSS in drinking water. Quantification of fecal fungal burden (CFUs/mL) was determined by plating on Sabouraud dextrose agar. CFUs were calculated as log CFUs per g of feces. As control, we gavaged 2 extra groups of B6 mice with PBS or nonpathogenic yeast S fibuligera.
Endoscopy
Colonoscopy was performed using a flexible digital ureteroscope (URF-V; Olympus America, Center Valley, PA) with an 8.5F (2.8-mm) tapered-tip design and motion range. The endoscope system included a video system center (Olympus America), a xenon light source (Olympus America), and a video recorder (MediCapture, Philadelphia, PA). Endoscopy images were obtained on an Olympus BX41 microscope (magnification, 100× and 200×; objective, 10×; eyepiece, 10×). Colonoscopy was performed on day 21 after DSS administration, and inflammation was evaluated using a previously validated endoscopic scoring system.52 Briefly, the system considers 4 different parameters to evaluate colonic inflammation: perianal findings (diarrhea, bloody feces, or rectal prolapse); wall transparency (based on the ability to see the blood vessels of the colonic mucosa); intestinal bleeding (spontaneous or induced by the endoscope because of the mucosal friability), and focal lesions (edema, erosions, and ulcers). Subscores for each parameter ranging from 0 (normal colonoscopy) to 3 (maximum severity of colonic changes) were used to evaluate colonic inflammation and to assess the potential presence of tumor lesions. The sum of these subscores was used to define colonic health as follows: healthy (0–1), mild colitis (2–4), moderate colitis (5–7), and severe colitis (8–13). Mice were anesthetized by isoflurane, USP (Butler Schein Animal Health, Dublin, OH) before performing endoscopy; no colonoscopy preparations, such as fasting or laxatives, were required.
Histology
Colons from infected and uninfected mice were removed, flushed of fecal contents, opened longitudinally, and placed in Bouin’s fixative. Tissues were embedded in paraffin and stained with H&E. Inflammation was evaluated by a trained pathologist in a blinded fashion using a previously described scoring system.53 Briefly, scores ranging from 0 (normal histology) to 3 (maximum severity of histologic changes) were used to evaluate 4 individual histologic subindices for the following: (1) active inflammation (infiltration with neutrophils); (2) chronic inflammation (lymphocytes, plasma cells, and macrophages in the mucosa and submucosa); (3) percentage of re-epithelialization; and (4) percentage of ulceration.
qRT-PCR
Colon samples from each mouse were collected and subjected to physical homogenization (with 100 mg of 1.4-mm ceramic beads, 4000 rpm), and total RNA was isolated using an RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Reverse transcription was performed using the High Capacity RNA-to-complementary DNA Kit (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA). qPCR amplification of complementary DNA samples was performed using clear 96-well plates (Roche, Branchburg, NJ) and the Roche 480 LightCycler SYBR Green (Roche) run template settings (hot start 95°C for 10 minutes, 40 amplification cycles; 95°C for 15 seconds; 60°C for 30 seconds; and 72°C for 30 seconds); β-actin was used as a housekeeping gene.
Primers for RT-qPCR
The following primers were custom designed and synthesized by Integrated DNA Technology (Coralville, IA). For mouse work, we used the following: β-actin: forward primer, 5’-CAGGGTGTGATGGTGGGAATG-3’; reverse primer, 5’-GTAGAAGGTGTGGTGCCAGATC-3’; Tnfα: forward primer, 5’-GCGGTGCCTATGTCTCAG-3’; reverse primer, 5’-GCCATTTGGGAACTTCTCATC-3’; Ifn-γ: forward primer, 5′-TGAGCTCATTGAATGCTTGG-3′; reverse primer, 5′-ACAGCAAGGCGAAAAAGGAT-3′; Il17: forward primer, 5’-GCTCCAGAAGGCCCTCAGA-3’; reverse primer 5’-CTTTCCCTCCGCATTGACA-3’; Il4: forward primer, 5′-GCTAGTTGTCATCCTGCTCTTC-3′; reverse primer, 5′-GGCGTCCCTTCTCCTGTG-3′; Il13: forward primer, 5’-GGGAGTCTGGTCTTGTGTGATG-3’; reverse primer, 5’-TTGCTTGCCTTGGTGGTCTC-3’; Il33: forward primer, 5′-TCCTTGCTTGGCAGTATCCA-3′; reverse primer, 5’-TGCTCAATGTGTCAACAGACG-3′.
Tissue Culture and Cytokine Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays
Colon samples were collected from both infected and uninfected mice (0.1 g/sample) and cultured in complete RPMI 1640 medium for 24 hours. Supernatants subsequently were collected for TNF, IFNγ, IL4, IL13, IL17, and IL33 analysis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN). All enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were performed according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Flow Cytometry
MLNs were collected and crushed through a 40-μm nylon mesh. To analyze ILCs and lymphocytes, single-cell suspensions of MLNs were incubated, respectively, with live/dead Fixable Violet and live/dead Fixable Blue Dead Cell Stain Kit (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, WA) to determine cell viability, washed with fluorescence-activated cell sorter buffer, followed by incubation with fluorescently conjugated antibodies for 20 minutes at 4°C, and then with fixation/permeabilization buffer (eBioscience, San Diego, CA) for 30 minutes at 4°C in the dark. Cells then were washed with permeabilization buffer and stained with a combination of fluorescently conjugated antibodies for 30 minutes at room temperature, to detect intracellular proteins. The following antibodies were used to detect ILCs: mouse lineage antibody cocktail with antibodies raised against CD3 (clone 145-2C11, 100301; BioLegend, San Diego, CA), Gr-1 (clone RB6-8C5, 108401; BioLegend), CD11b (clone M1/70, 101207; BioLegend), B220 (clone RA3-6B2, 103211; BioLegend), Ter-119 (clone Ter-119, 116207; BioLegend); CD11c (clone N418, 14011482; eBioscience), CD45 (clone 30-F11, 14045182; eBioscience), GATA-3 (clone TWAJ, 1:50, 12996642; eBioscience), IL7Rα (clone A7R34, 135011; BioLegend), RORγT (clone AFKJS-9, 12698882; eBioscience), and T-bet (clone eBio4B10, 12582582; eBioscience). The following antibodies were used to detect lymphocytes expressing cytokines: mouse lineage antibody cocktail with antibodies raised against CD3 (clone 145-2C11, 553067; BD Biosciences, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada), TNF (clone MP6-XT22, 506313; BioLegend), IFNγ (clone XMG1.2, 505842; BioLegend), IL4 (clone 11B11, 3120520; Sony, Bothell, WA), IL17A (clone TC11-18H10.1, 3134610; Sony), and IL13 (clone 13A, NBP1-43239APC; Novus Biologicals, Centennial, CO). Flow-cytometric acquisition was performed on a FACSAria sorter (Mississauga, ON, Canada). Data subsequently were analyzed using FlowJo_V10 software (Tree Star, Ashland, OR) by gating on live cells based on forward vs side-scatter profiles, then gating on singlets using forward scatter area vs height, followed by dead-cell exclusion and then cell subset-specific gating. CountBright absolute counting beads (Thermo Scientific) were used to determine absolute cell number of ILCs by flow cytometry, according to the manufacturer’s instructions. ILCs were characterized by gating on CD45+ live cells, and then looking for a population positive for CD127 and negative for lineage markers CD11b (myeloid cells), Ter-119 (granulocytes), CD11c dendritic cells (DCs), Ly-6g (neutrophils), B220 (B cells), and CD3 (lymphocytes). From the CD127+ lineage- population, we gated on GATA3+ cells (ILC2), RORγT+ cells (ILC3), and cells negative for GATA3 and RORγT that were positive for T-bet (ILC1). Lymphocytes were characterized by gating on CD3+ live cells.
Microbiome Analyses
After 3 days of fecal homogenization, 1 fecal pellet from each mouse was collected and stored at -80ºC. A week after the fecal homogenization, 1 group of B6 mice was infected with C tropicalis through gavage (1 × 106 U/100 uL PBS), and the control group was gavaged with PBS (100 μL). A second sample of fecal pellets from each mouse then was collected 6 days after the infection of the experimental group. Stool samples were analyzed by 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing investigating the gut microbiome. Metagenomic DNA was extracted from fecal aliquots thawed on ice and resuspended in 600 mL DNA stabilization buffer (Stratec Biomedical, Birkenfeld, Germany) and 400 mL phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1 by volume; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO). Cells were mechanically lysed (3 × 6.5 m/s for 40 s) with 500 mg, 0.1-mm glass beads (Roth, Goshen, IN) using a bead-beater (MP Biomedicals, Solon, OH) fitted with a cooling adapter. After heat treatment (95°C, 8 min) and centrifugation (16,000 × g; 5 min; 4°C), 150 mL supernatant was incubated with 15 mL ribonuclease (0.1 mg/mL; Amresco, Cleveland, OH) at 37°C and centrifuged (550 3 × g; 30 min). DNA was purified with the NucleoSpin Genomic deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) Clean-up Kit (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany), following the manufacturer’s instructions. Concentrations and purity were determined with the NanoDrop and Qubit system (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and stored at -20°C. Preparation of amplicon libraries (V3–V4 region) and sequencing were performed as described in detail previously.54 After purification with the AMPure XP system (Brea, CA), sequencing was performed in paired-end mode (275 bp) with pooled samples containing 25% (vol:vol) PhiX standard library in a MiSeq system (Illumina, Inc, San Diego, CA) prepared according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Raw reads were processed with the Integrated Microbial Next Generation Sequencing pipeline (Munich, Germany),55, 56, 57 based on the UPARSE approach.58 In brief, sequences were demultiplexed, trimmed to the first base with a quality score less than 3, and then paired. Sequences with less than 350 and more than 500 nucleotides and paired reads with an expected error greater than 3 were excluded from the analysis. Remaining reads were trimmed by 10 nucleotides on each end to prevent analysis of the regions with distorted base composition observed at the start of sequences. The presence of chimeras was tested with UCHIME (San Francisco, CA).59 Operational taxonomic units were clustered at 97% sequence similarity, and only those with a relative abundance greater than 0.5% in 1 or more samples were kept. Taxonomies were assigned an 80% confidence level using the RDP (East Landsing, MI) classifier,60 the SILVA database (Bremen, Germany) applying SINA (Bremen, Germany),61 and EzBioCloud (Seoul, Republic of Korea).62
Fecal Microbiome Transplantation and Intestinal Inflammation
We used GF B6 mice to assess the effect of the microbiome on DSS-induced colitis severity after FMT using gut microbiome isolated from mice previously inoculated with C tropicalis or PBS. All mice were caged using the GF-grade nested isolation (NesTiso, Rensselaer, NY) caging system63 and maintained on nonedible Aspen bedding (Walton Hills, OH). Mice were fed autoclaved GF-grade 40 to 50 kGy irradiated pellet food (PMI Nutrition International, LLC (St. Louis, MO); Labdiet, Charles River (Garfield Heights, OH); Vac-Pac Rodent 6/5 irradiated (St. Louis, MO), 5% kcal% fat) and water (double-autoclaved) was given ad libitum. Each mouse received daily oral gavages (0.1 mL/10 g of body weight; 107 CFUs/100 μL) for 3 consecutive days. Seven days after the fecal transplant, acute colitis was induced in the 2 groups by administration of 2.5% DSS in drinking water for 7 days. Colitis severity in the fecal microbiome transplanted mice was assessed at the end of experiments using histologic and endoscopic analysis. Protocols on animal handling, housing, and transplant of fecal microbiome into GF mice were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and the Institutional Review Board at CWRU, following the National Research Council Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Measures to control for bedding-dependent microbial bias/overgrowth were implemented in all experiments, as previously described.63
Intestinal Permeability Assay
FITC-dextran (70 kilodaltons) and acid-citrate-dextrose solutions were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Mice were fasted for 6 hours before the test. Then, mice were administered a dose (150 uL/mouse) of FITC-dextran in sterile 1× PBS (80 mg/mL) through gavage technique. After 4 hours, blood was collected in a capillary tube by nicking the tail of the mouse in its proximal region. Acid-citrate-dextrose solution was added 15% vol/vol as an anticoagulant. Then, all blood samples were centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 10 minutes. Plasma was collected in a new 1.5-mL tube and kept in the dark at 4°C. Plasma then was diluted 1:10 in PBS and transferred to a black, opaque-bottom, 96-well plate. A volume of 100 uL was transferred into each well. PBS was used as blank. Readings of RFUs were measured by a SpectraMax i3x (San Jose, CA) spectrophotometer in triplicate and averaged. Fluorescence was determined at 530 nm with excitation at 485 nm.
Intestinal Epithelial Cell Isolation
Mice were killed and colon was collected, cut open, and placed on a Tissue Culture-Treated (TC) dish with a small amount of Hank’s balanced salt solution (GIBCO, Gaithersburg, MD) to keep it moist. The tissue samples then were incubated in a digestive solution containing 3 mL Hank’s balanced salt solution with Ca2+/Mg2+, 150 μL DNase (10 mg/mL; Sigma-Aldrich), 30 μL collagenase (100 mg/mL; Sigma-Aldrich), and 300 μL dispase (STEMCELL Technologies, Vancouver, Canada) for 1 hour at 37ºC at 150 rpm. The cells of each colon sample then were filtered with a 100-μm strainer and collected into a flow cytometry tube. Then, the cells were incubated with 10 μL rat anti-mouse CD16/CD32 antibody (553142; BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ) in 6 mL flow cytometry buffer containing EDTA (0.5 mol/L) and HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich) for 10 minutes on ice. After that, each sample was incubated with 5 μL Allophycocyanin (APC) anti-mouse CD326 epithelial cellular adhesion molecule (Ep-CAM) antibody (118213; BioLegend) on a shaker for 1 hour on ice in the dark. Positive cells then were sorted through BD Biosciences Aria and processed for subsequent qRT-PCR analysis.
Mouse Intestinal Colonoid Isolation, Culture, and Passage
Mice were killed and colon was collected, cut open longitudinally in a Petri dish with cold PBS without Ca2+/Mg2+ (Sigma-Aldrich), vigorously washed using forceps, and cut in 2- to 5-mm pieces. Next, the pieces were collected in a 50-mL Falcon tube filled with 30 mL Dulbecco′s Phosphate Buffered Saline (DPBS) plus 120 μL ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid 0.5 mol/L (Sigma-Aldrich) and incubated for 45 minutes at 4ºC. Subsequently, colon pieces were collected in 4 fractions of 25 mL DPBS. The 4 fractions were inspected under a microscope (10× objective) to identify the fractions enriched in crypts and with low level of debris. The chosen fraction was spun down (450 × g for 10 minutes at 4ºC). The supernatant was removed and the pellet was resuspended in 150 μL Intesticult (STEMCELL Technologies) and 150 μL Matrigel basement membrane matrix (Corning, Inc, Corning, NY). Aliquots of 40 μL of this solution then were plated in a prewarmed 48-well plate (VWR, Radnor, PA) into the center of the well and incubated for 10 minutes at 37ºC, allowing the Matrigel to polymerize. Finally, 350 μL Intesticult was added in each well of the plate. Colonoids were cultured for 10 days and passaged once after 6 days. Total RNA was extracted on day 10 and gene expression was measured by NanoString analysis.
NanoString Gene Expression Analysis
Total RNA was extracted from colonoids of uninfected and infected mice after 10 days of culture. Extracted RNA was incubated with a custom panel of 250 bar-coded probes (NanoString Technologies) specific for genes associated with intestinal-epithelial barrier function and epithelial homeostasis (NanoString Technologies). Genes were selected from Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Pathways for tight junction (map04530), regulation of actin cytoskeleton (map04810), colorectal cancer (map05210), most with significant overlapping membership in adherens junction (map04520), focal adhesion (map04510), Wingless-related integration site (Wnt) (map04310), and other pathways. NanoString technology is characterized by high reproducibility and sensitivity. As criteria of differential expression, we used the following: >2-fold change and P ≤ .05. Six biological replicates per condition were evaluated. Standard NanoString protocols were followed. Reporter probes, hybridization solution, sample, and capture probes were mixed together and hybridized overnight at 65ºC. After hybridization, samples were transferred and processed in the NanoString nCounter Prep Station. The Prep Station washed away excess probes and purified the target/probe complexes using magnetic beads. Briefly, the hybridization solution containing the target-probe complexes is mixed with magnetic beads complementary to sequences on the capture probe. This process is followed by a washing step to remove the excess reporter probes. The target-probe complexes then were hybridized to magnetic beads complementary to sequences on the reporter probe. A final washing step was performed to remove excess capture probes. The purified target/probe complexes were deposited in a cartridge, laid flat, and immobilized for data collection. Data were analyzed by ROSALIND (freely available at https://rosalind.onramp.bio), with a HyperScale architecture developed by OnRamp BioInformatics, Inc (San Diego, CA). Read distribution percentages, violin plots, identity heatmaps, and sample Minimum Data Set plots were generated as part of the QC step. Normalization was performed by dividing counts within a lane by the geometric mean of the normalizer probes from the same lane. The NormqPCR R library64 was used to select normalizer probes using the geNorm algorithm. Fold changes and P values were calculated using criteria provided by Nanostring. Clustering of genes for the final heatmap of differentially expressed genes was performed using the Partitioning Around Medoids method using the Flexible Procedures for Clustering R library,2 which takes into consideration the direction and type of all signals on a pathway; the position, role, and type of every gene; and so forth. Hypergeometric distribution was used to analyze the enrichment of pathways, gene ontology, domain structure, and other ontologies. The topGene Ontology R library (Buffalo, NY)65 was used to determine local similarities and dependencies between GO terms to perform Elim pruning correction. Several database sources were referenced for enrichment analysis, including Interpro (Stoneham, MA),66 NCBI (Bethesda, MD),67 MSigDB (San Diego, CA),68 REACTOME (Toronto, ON, Canada),69 and WikiPathways (Maastricht, Netherlands).70 Enrichment was calculated relative to a set of background genes relevant for the experiment.
Statistical Analysis
Experiments were conducted at a minimum in duplicate. Univariate and multivariate analyses were conducted using the collective data from replicated experiments. When the data fulfilled the assumptions for parametric statistics, comparisons of continuous data across experimental groups were conducted using Student t tests. Alternative nonparametric tests were used for data with unfulfilled distributional assumptions regarding the normality of the data. Data were expressed as SEMs, and 95% CIs were reported when appropriate. An α level of .05 was considered significant. All analyses were conducted with GraphPad software (San Diego, CA).
All authors had access to the study data and reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Study Approval
All experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Case Western Reserve University and conducted following the Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care guidelines.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Core services provided by the Cleveland Digestive Research Core Center, the Genomics Core Facility of the CWRU School of Medicine's Genetics and Genome Sciences Department. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants R01DK055812 (F.C.), R01DK042191, P01DK091222, P30DK097948 (F.C., T.T.P.), R01DK056762 (T.T.P.), and 1 R01 AI145289-01A1 (M.G.).
CRediT Authorship Contributions
Luca Di Martino (Conceptualization: Lead; Formal analysis: Lead; Investigation: Lead)
Carlo De Salvo (Methodology: Equal)
Ludovica Buttò, PhD (Formal analysis: Equal)
Kristine-Ann Buela (Formal analysis: Equal)
Christopher Hager (Methodology: Equal; Resources: Equal)
Mahmoud Ghannoum (Conceptualization: Equal; Resources: Equal; Supervision: Equal)
Abdullah Osme (Formal analysis: Equal)
Giorgos Bamias (Supervision: Equal; Writing – original draft: Equal)
Theresa Pizarro (Writing – original draft: Equal)
Fabio Cominelli, MD, PhD (Funding acquisition: Lead; Supervision: Lead; Writing – original draft: Lead)
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest The authors disclose no conflicts.
Funding This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants DK042191, DK055812, DK091222, and DK097948 (F.C.), DK125526 (L.D.M.), and R01AI145289-01A1 (M.G.).
Data Transparency The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
- 1.Roda G., Chien Ng S., Kotze P.G., Argollo M., Panaccione R., Spinelli A., Kaser A., Peyrin-Biroulet L., Danese S. Crohn's disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020;6:22. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-0156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nguyen N.H., Singh S., Sandborn W.J. Positioning therapies in the management of Crohn's disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18:1268–1279. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.10.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Alhagamhmad M.H., Day A.S., Lemberg D.A., Leach S.T. An overview of the bacterial contribution to Crohn disease pathogenesis. J Med Microbiol. 2016;65:1049–1059. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hoarau G., Mukherjee P.K., Gower-Rousseau C., Hager C., Chandra J., Retuerto M.A., Neut C., Vermeire S., Clemente J., Colombel J.F., Fujioka H., Poulain D., Sendid B., Ghannoum M.A. Bacteriome and mycobiome interactions underscore microbial dysbiosis in familial Crohn's disease. mBio. 2016;7 doi: 10.1128/mBio.01250-16. e01250-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hager C.L., Ghannoum M.A. The mycobiome: role in health and disease, and as a potential probiotic target in gastrointestinal disease. Dig Liver Dis. 2017;49:1171–1176. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2017.08.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Negri M., Martins M., Henriques M., Svidzinski T.I., Azeredo J., Oliveira R. Examination of potential virulence factors of Candida tropicalis clinical isolates from hospitalized patients. Mycopathologia. 2010;169:175–182. doi: 10.1007/s11046-009-9246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Oksuz S., Sahin I., Yildirim M., Gulcan A., Yavuz T., Kaya D., Koc A.N. Phospholipase and proteinase activities in different Candida species isolated from anatomically distinct sites of healthy adults. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2007;60:280–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kothavade R.J., Kura M.M., Valand A.G., Panthaki M.H. Candida tropicalis: its prevalence, pathogenicity and increasing resistance to fluconazole. J Med Microbiol. 2010;59:873–880. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.013227-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Colombo A.L., Nucci M., Park B.J., Nouer S.A., Arthington-Skaggs B., da Matta D.A., Warnock D., Morgan J., Brazilian Network Candidemia Study Epidemiology of candidemia in Brazil: a nationwide sentinel surveillance of candidemia in eleven medical centers. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44:2816–2823. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00773-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gladiator A., Wangler N., Trautwein-Weidner K., LeibundGut-Landmann S. Cutting edge: IL-17-secreting innate lymphoid cells are essential for host defense against fungal infection. J Immunol. 2013;190:521–525. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bernink J.H., Ohne Y., Teunissen M.B.M., Wang J., Wu J., Krabbendam L., Guntermann C., Volckmann R., Koster J., van Tol S., Ramirez I., Shrestha Y., de Rie M.A., Spits H., Romero Ros X., Humbles A.A. c-Kit-positive ILC2s exhibit an ILC3-like signature that may contribute to IL-17-mediated pathologies. Nat Immunol. 2019;20:992–1003. doi: 10.1038/s41590-019-0423-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Costea P.I., Hildebrand F., Arumugam M., Backhed F., Blaser M.J., Bushman F.D., de Vos W.M., Ehrlich S.D., Fraser C.M., Hattori M., Huttenhower C., Jeffery I.B., Knights D., Lewis J.D., Ley R.E., Ochman H., O'Toole P.W., Quince C., Relman D.A., Shanahan F., Sunagawa S., Wang J., Weinstock G.M., Wu G.D., Zeller G., Zhao L., Raes J., Knight R., Bork P. Enterotypes in the landscape of gut microbial community composition. Nat Microbiol. 2018;3:8–16. doi: 10.1038/s41564-017-0072-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Iliev I.D., Funari V.A., Taylor K.D., Nguyen Q., Reyes C.N., Strom S.P., Brown J., Becker C.A., Fleshner P.R., Dubinsky M., Rotter J.I., Wang H.L., McGovern D.P., Brown G.D., Underhill D.M. Interactions between commensal fungi and the C-type lectin receptor dectin-1 influence colitis. Science. 2012;336:1314–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.1221789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ott S.J., Kuhbacher T., Musfeldt M., Rosenstiel P., Hellmig S., Rehman A., Drews O., Weichert W., Timmis K.N., Schreiber S. Fungi and inflammatory bowel diseases: alterations of composition and diversity. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2008;43:831–841. doi: 10.1080/00365520801935434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Liguori G., Lamas B., Richard M.L., Brandi G., da Costa G., Hoffmann T.W., Di Simone M.P., Calabrese C., Poggioli G., Langella P., Campieri M., Sokol H. Fungal dysbiosis in mucosa-associated microbiota of Crohn's disease patients. J Crohns Colitis. 2016;10:296–305. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjv209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lewis J.D., Chen E.Z., Baldassano R.N., Otley A.R., Griffiths A.M., Lee D., Bittinger K., Bailey A., Friedman E.S., Hoffmann C., Albenberg L., Sinha R., Compher C., Gilroy E., Nessel L., Grant A., Chehoud C., Li H., Wu G.D., Bushman F.D. Inflammation, antibiotics, and diet as environmental stressors of the gut microbiome in pediatric Crohn's disease. Cell Host Microbe. 2015;18:489–500. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.09.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stamatiades G.A., Ioannou P., Petrikkos G., Tsioutis C. Fungal infections in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review. Mycoses. 2018;61:366–376. doi: 10.1111/myc.12753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zuo T., Ng S.C. The gut microbiota in the pathogenesis and therapeutics of inflammatory bowel disease. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:2247. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Leonardi I., Paramsothy S., Doron I., Semon A., Kaakoush N.O., Clemente J.C., Faith J.J., Borody T.J., Mitchell H.M., Colombel J.F., Kamm M.A., Iliev I.D. Fungal trans-kingdom dynamics linked to responsiveness to fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) therapy in ulcerative colitis. Cell Host Microbe. 2020;27:823–829.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.03.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Seregin S.S., Golovchenko N., Schaf B., Chen J., Pudlo N.A., Mitchell J., Baxter N.T., Zhao L., Schloss P.D., Martens E.C., Eaton K.A., Chen G.Y. NLRP6 protects Il10(-/-) mice from colitis by limiting colonization of Akkermansia muciniphila. Cell Rep. 2017;19:2174. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ganesh B.P., Klopfleisch R., Loh G., Blaut M. Commensal Akkermansia muciniphila exacerbates gut inflammation in Salmonella Typhimurium-infected gnotobiotic mice. PLoS One. 2013;8 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chia L.W., Hornung B.V.H., Aalvink S., Schaap P.J., de Vos W.M., Knol J., Belzer C. Deciphering the trophic interaction between Akkermansia muciniphila and the butyrogenic gut commensal Anaerostipes caccae using a metatranscriptomic approach. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2018;111:859–873. doi: 10.1007/s10482-018-1040-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Collado M.C., Derrien M., Isolauri E., de Vos W.M., Salminen S. Intestinal integrity and Akkermansia muciniphila, a mucin-degrading member of the intestinal microbiota present in infants, adults, and the elderly. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007;73:7767–7770. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01477-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Derrien M., Vaughan E.E., Plugge C.M., de Vos W.M. Akkermansia muciniphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a human intestinal mucin-degrading bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2004;54:1469–1476. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.02873-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lievin-Le Moal V., Servin A.L. The front line of enteric host defense against unwelcome intrusion of harmful microorganisms: mucins, antimicrobial peptides, and microbiota. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006;19:315–337. doi: 10.1128/CMR.19.2.315-337.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Png C.W., Linden S.K., Gilshenan K.S., Zoetendal E.G., McSweeney C.S., Sly L.I., McGuckin M.A., Florin T.H. Mucolytic bacteria with increased prevalence in IBD mucosa augment in vitro utilization of mucin by other bacteria. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:2420–2428. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Eun C.S., Mishima Y., Wohlgemuth S., Liu B., Bower M., Carroll I.M., Sartor R.B. Induction of bacterial antigen-specific colitis by a simplified human microbiota consortium in gnotobiotic interleukin-10-/- mice. Infect Immun. 2014;82:2239–2246. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01513-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Velcich A., Yang W., Heyer J., Fragale A., Nicholas C., Viani S., Kucherlapati R., Lipkin M., Yang K., Augenlicht L. Colorectal cancer in mice genetically deficient in the mucin Muc2. Science. 2002;295:1726–1729. doi: 10.1126/science.1069094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.van der Post S., Jabbar K.S., Birchenough G., Arike L., Akhtar N., Sjovall H., Johansson M.E.V., Hansson G.C. Structural weakening of the colonic mucus barrier is an early event in ulcerative colitis pathogenesis. Gut. 2019;68:2142–2151. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Madsen K., Cornish A., Soper P., McKaigney C., Jijon H., Yachimec C., Doyle J., Jewell L., De Simone C. Probiotic bacteria enhance murine and human intestinal epithelial barrier function. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:580–591. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.27224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Resta-Lenert S., Smitham J., Barrett K.E. Epithelial dysfunction associated with the development of colitis in conventionally housed mdr1a-/- mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005;289:G153–G162. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00395.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Turksen K., Troy T.C. Barriers built on claudins. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:2435–2447. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Weber C.R., Nalle S.C., Tretiakova M., Rubin D.T., Turner J.R. Claudin-1 and claudin-2 expression is elevated in inflammatory bowel disease and may contribute to early neoplastic transformation. Lab Invest. 2008;88:1110–1120. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2008.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Xing T., Benderman L.J., Sabu S., Parker J., Yang J., Lu Q., Ding L., Chen Y.H. Tight junction protein claudin-7 is essential for intestinal epithelial stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;9:641–659. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2019.12.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ding L., Lu Z., Foreman O., Tatum R., Lu Q., Renegar R., Cao J., Chen Y.H. Inflammation and disruption of the mucosal architecture in claudin-7-deficient mice. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:305–315. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.10.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Leslie J.L., Huang S., Opp J.S., Nagy M.S., Kobayashi M., Young V.B., Spence J.R. Persistence and toxin production by Clostridium difficile within human intestinal organoids result in disruption of epithelial paracellular barrier function. Infect Immun. 2015;83:138–145. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02561-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhang Y.G., Wu S., Xia Y., Sun J. Salmonella-infected crypt-derived intestinal organoid culture system for host-bacterial interactions. Physiol Rep. 2014;2:e12147. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kinchen J., Chen H.H., Parikh K., Antanaviciute A., Jagielowicz M., Fawkner-Corbett D., Ashley N., Cubitt L., Mellado-Gomez E., Attar M., Sharma E., Wills Q., Bowden R., Richter F.C., Ahern D., Puri K.D., Henault J., Gervais F., Koohy H., Simmons A. Structural remodeling of the human colonic mesenchyme in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell. 2018;175:372–386 e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.08.067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chelakkot C., Ghim J., Ryu S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50:103. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0126-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Daulagala A.C., Bridges M.C., Kourtidis A. E-cadherin beyond structure: a signaling hub in colon homeostasis and disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:2756. doi: 10.3390/ijms20112756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.LeibundGut-Landmann S., Wuthrich M., Hohl T.M. Immunity to fungi. Curr Opin Immunol. 2012;24:449–458. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2012.04.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hernandez-Santos N., Gaffen S.L. Th17 cells in immunity to Candida albicans. Cell Host Microbe. 2012;11:425–435. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.04.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Mengesha B.G., Conti H.R. The role of IL-17 in protection against mucosal Candida infections. J Fungi (Basel) 2017;3:52. doi: 10.3390/jof3040052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Whibley N., Jaycox J.R., Reid D., Garg A.V., Taylor J.A., Clancy C.J., Nguyen M.H., Biswas P.S., McGeachy M.J., Brown G.D., Gaffen S.L. Delinking CARD9 and IL-17: CARD9 protects against Candida tropicalis infection through a TNF-alpha-dependent, IL-17-independent mechanism. J Immunol. 2015;195:3781–3792. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Drummond R.A., Collar A.L., Swamydas M., Rodriguez C.A., Lim J.K., Mendez L.M., Fink D.L., Hsu A.P., Zhai B., Karauzum H., Mikelis C.M., Rose S.R., Ferre E.M., Yockey L., Lemberg K., Kuehn H.S., Rosenzweig S.D., Lin X., Chittiboina P., Datta S.K., Belhorn T.H., Weimer E.T., Hernandez M.L., Hohl T.M., Kuhns D.B., Lionakis M.S. CARD9-dependent neutrophil recruitment protects against fungal invasion of the central nervous system. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11 doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Schmitz J., Owyang A., Oldham E., Song Y., Murphy E., McClanahan T.K., Zurawski G., Moshrefi M., Qin J., Li X., Gorman D.M., Bazan J.F., Kastelein R.A. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity. 2005;23:479–490. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sonnenberg G.F., Artis D. Innate lymphoid cells in the initiation, regulation and resolution of inflammation. Nat Med. 2015;21:698–708. doi: 10.1038/nm.3892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chang Y.J., Kim H.Y., Albacker L.A., Baumgarth N., McKenzie A.N., Smith D.E., Dekruyff R.H., Umetsu D.T. Innate lymphoid cells mediate influenza-induced airway hyper-reactivity independently of adaptive immunity. Nat Immunol. 2011;12:631–638. doi: 10.1038/ni.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yin H., Li X., Hu S., Liu T., Yuan B., Gu H., Ni Q., Zhang X., Zheng F. IL-33 accelerates cutaneous wound healing involved in upregulation of alternatively activated macrophages. Mol Immunol. 2013;56:347–353. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.05.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rak G.D., Osborne L.C., Siracusa M.C., Kim B.S., Wang K., Bayat A., Artis D., Volk S.W. IL-33-dependent group 2 innate lymphoid cells promote cutaneous wound healing. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136:487–496. doi: 10.1038/JID.2015.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hager C.L., Isham N., Schrom K.P., Chandra J., McCormick T., Miyagi M., Ghannoum M.A. Effects of a novel probiotic combination on pathogenic bacterial-fungal polymicrobial biofilms. mBio. 2019;10 doi: 10.1128/mBio.00338-19. e00338-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kodani T., Rodriguez-Palacios A., Corridoni D., Lopetuso L., Di Martino L., Marks B., Pizarro J., Pizarro T., Chak A., Cominelli F. Flexible colonoscopy in mice to evaluate the severity of colitis and colorectal tumors using a validated endoscopic scoring system. J Vis Exp. 2013;80 doi: 10.3791/50843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Corridoni D., Kodani T., Rodriguez-Palacios A., Pizarro T.T., Xin W., Nickerson K.P., McDonald C., Ley K.F., Abbott D.W., Cominelli F. Dysregulated NOD2 predisposes SAMP1/YitFc mice to chronic intestinal inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:16999–17004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1311657110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Lagkouvardos I., Kläring K., Heinzmann S.S., Platz S., Scholz B., Engel K.H., Schmitt-Kopplin P., Haller D., Rohn S., Skurk T. Gut metabolites and bacterial community networks during a pilot intervention study with flaxseeds in healthy adult men. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015;59:1614–1628. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201500125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bazanella M., Maier T.V., Clavel T., Lagkouvardos I., Lucio M., Maldonado-Gomez M.X., Autran C., Walter J., Bode L., Schmitt-Kopplin P., Haller D. Randomized controlled trial on the impact of early-life intervention with bifidobacteria on the healthy infant fecal microbiota and metabolome. Am J Clin Nutr. 2017;106:1274–1286. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.117.157529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lagkouvardos I., Fischer S., Kumar N., Clavel T. Rhea: a transparent and modular R pipeline for microbial profiling based on 16S rRNA gene amplicons. PeerJ. 2017;5 doi: 10.7717/peerj.2836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lagkouvardos I., Joseph D., Kapfhammer M., Giritli S., Horn M., Haller D., Clavel T. IMNGS: A comprehensive open resource of processed 16S rRNA microbial profiles for ecology and diversity studies. Sci Rep. 2016;6:33721. doi: 10.1038/srep33721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Edgar R.C. UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods. 2013;10:996–998. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Edgar R.C., Haas B.J., Clemente J.C., Quince C., Knight R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:2194–2200. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Wang Q., Garrity G.M., Tiedje J.M., Cole J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007;73:5261–5267. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00062-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Pruesse E., Peplies J., Glöckner F.O. SINA: accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:1823–1829. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yoon S.-H., Ha S.-M., Kwon S., Lim J., Kim Y., Seo H., Chun J. Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2017;67:1613–1617. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Rodriguez-Palacios A., Aladyshkina N., Ezeji J.C., Erkkila H.L., Conger M., Ward J., Webster J., Cominelli F. Cyclical bias' in microbiome research revealed by a portable germ-free housing system using nested isolation. Sci Rep. 2018;8:3801. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20742-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Perkins J.R., Dawes J.M., McMahon S.B., Bennett D.L., Orengo C., Kohl M. ReadqPCR and NormqPCR: R packages for the reading, quality checking and normalisation of RT-qPCR quantification cycle (Cq) data. BMC Genomics. 2012;13:296. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Alexa A., Rahnenfuhrer J., Lengauer T. Improved scoring of functional groups from gene expression data by decorrelating GO graph structure. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:1600–1607. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Mitchell A.L., Attwood T.K., Babbitt P.C., Blum M., Bork P., Bridge A., Brown S.D., Chang H.Y., El-Gebali S., Fraser M.I., Gough J., Haft D.R., Huang H., Letunic I., Lopez R., Luciani A., Madeira F., Marchler-Bauer A., Mi H., Natale D.A., Necci M., Nuka G., Orengo C., Pandurangan A.P., Paysan-Lafosse T., Pesseat S., Potter S.C., Qureshi M.A., Rawlings N.D., Redaschi N., Richardson L.J., Rivoire C., Salazar G.A., Sangrador-Vegas A., Sigrist C.J.A., Sillitoe I., Sutton G.G., Thanki N., Thomas P.D., Tosatto S.C.E., Yong S.Y., Finn R.D. InterPro in 2019: improving coverage, classification and access to protein sequence annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:D351–D360. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Geer L.Y., Marchler-Bauer A., Geer R.C., Han L., He J., He S., Liu C., Shi W., Bryant S.H. The NCBI BioSystems database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:D492–D496. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Subramanian A., Tamayo P., Mootha V.K., Mukherjee S., Ebert B.L., Gillette M.A., Paulovich A., Pomeroy S.L., Golub T.R., Lander E.S., Mesirov J.P. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:15545–15550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506580102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Fabregat A., Jupe S., Matthews L., Sidiropoulos K., Gillespie M., Garapati P., Haw R., Jassal B., Korninger F., May B., Milacic M., Roca C.D., Rothfels K., Sevilla C., Shamovsky V., Shorser S., Varusai T., Viteri G., Weiser J., Wu G., Stein L., Hermjakob H., D'Eustachio P. The reactome pathway knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:D649–D655. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Slenter D.N., Kutmon M., Hanspers K., Riutta A., Windsor J., Nunes N., Melius J., Cirillo E., Coort S.L., Digles D., Ehrhart F., Giesbertz P., Kalafati M., Martens M., Miller R., Nishida K., Rieswijk L., Waagmeester A., Eijssen L.M.T., Evelo C.T., Pico A.R., Willighagen E.L. WikiPathways: a multifaceted pathway database bridging metabolomics to other omics research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:D661–D667. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]