To the Editor:
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) are an integral component of the evaluation of patients with pulmonary diseases.1 Due to concerns for virus transmission, multiple respiratory societies recommend to postpone or limit PFTs during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic.2, 3, 4, 5, 6 Repeated forced breathing maneuvers during PFTs may generate bioaerosol by airway opening7 , 8 or inducing cough.1 , 7 However, the concentrations of particles that are generated and change over time during and after PFTs are unknown, leading to the current recommendation to close PFT laboratories for 20 minutes to 3 hours between tests.2, 3, 4 Thus, we investigated aerosol particle generation and clearance during and after PFTs.
Methods
This prospective observational study was conducted in three PFT laboratories located at Rush University Medical Center (room size, 3 × 3 × 2.8 m), Rush Oak Park Hospital (room size, 3.6 × 4.6 × 2.8 m), and an outpatient clinic (room size, 3.4 × 4.6 × 2.8 m) with air exchange frequencies of five, three, and nine times/h, respectively. Adult patients whose condition required PFTs were enrolled after screening negative for coronavirus disease 2019. The study was approved, and informed consent was waived by the ethics committee at Rush University.
In all three facilities, PFTs were performed with a VMAX ENCORE PFT machine (Vyaire Medical, Mettawa, IL). During PFTs, patients sat upright and breathed through the mouthpiece connected to a filter (MicroGard II PFT Filter, Vyaire Medical). PFT technologists wore N95 masks with face shield or powered air purification respirators during the entire test. A calibrated optical particle sizer (Model 3889; Kanomax USA, Inc, Andover, NJ), which was used in all three laboratories, was placed at a lateral position 60 cm away from patient’s face; particle concentrations were monitored. Once testing was completed, the patient left the room; the PFT technologist discarded the single-use mouthpiece and filter, exited the room, and closed the door. Particle concentrations were measured continuously for 30 to 60 minutes after the test was completed. No entry into the room was permitted during this period.
Scatterplots were drawn at various time intervals; particle concentrations of different sizes and fit curves were drawn with mean and range of 95% CIs with the use of an exponential decay model with OriginPro software (OriginPro 2019, Northampton, MA). The clearance time was calculated from the equation in the exponential decay model. The interval from test completion to when the particle concentrations returned to the lowest concentrations was also recorded for each laboratory. The average of particle concentrations of different sizes during the entire PFT test was taken from each individual, and the peak concentration was compared with the lowest concentration at different laboratories and overall with the use of the Wilcoxon Sign Rank test and paired t-test, respectively. Comparisons were conducted with the use of SPSS software (version 26.0; SPSS, Chicago, IL); P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
We enrolled 28 patients (13 men; mean age [± SD], 56.7 ± 14.0 years; mean height, 169.7 ± 10.0 cm, and median [interquartile range] weight, 91.2 kg [80.2-103.0 kg]). Complete PFTs (including spirometry or slow vital capacity, lung volumes, and diffusion testing) in 19 patients; five complete PFTs with bronchodilator test via metered-dose inhaler and spacer and four spirometry tests were performed. Average time for completing PFTs was 35 ± 10 minutes. Patients’ demographics, pulmonary functions, and PFT types in three laboratories were similar.
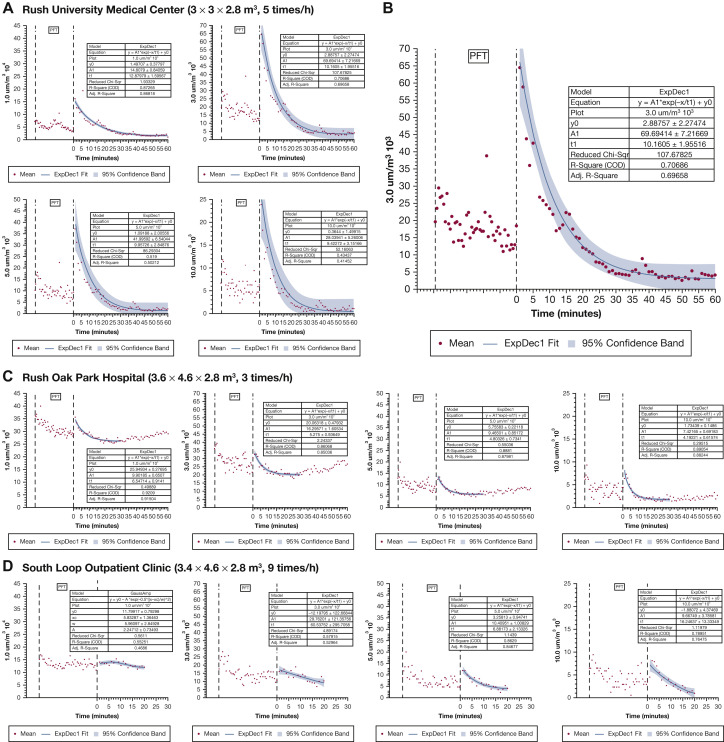
For particles ≤0.5μm in size, there was relatively high ambient level before and after PFTs, with a small increment during testing and decrease after the test with return to pretest level (ambient) after 25 to 30 minutes. Larger particles increased with testing, peaked at the end of testing, then decreased after the test to reach their lowest concentration (Fig 1 ). In the PFT laboratory (Rush Oak Park Hospital) that had low air exchange frequency (three per hour) and larger room size, with one additional window air conditioner, the particle concentrations had a high ambient level at the beginning of testing, decreased to their lowest level after the test was completed, followed by an increase towards pretest levels.
Figure 1.
A-D, The changes of concentrations of aerosol particles at different sizes (1-10 μm) during and after pulmonary function testing. A, In the PFT laboratory located at Rush University Medical Center, with room size of 3 × 3 × 2.8 m3 and air exchange frequency of five times per hour, the concentrations of large particles (≥1 μm) were high during PFTs and peaked at the end of the test. Particle concentrations took 25-30 minutes to return to a stable baseline level. B, Graph shows the changes of concentrations of aerosol particles of 3 μm. C, In the PFT laboratory located at Rush Oak Park Hospital, with room size of 3.6 × 4.6 × 2.8 m3 and air exchange frequency of three times per hour and one additional air conditioner, the concentrations of aerosol particles of all sizes decreased as PFTs were performed then slightly increased at the end of the test. Particle concentrations continued to decrease to their lowest level within 15-20 minutes then began to increase towards pretest levels. Fit curve was drawn with the use of the data that were acquired in the first 30 minutes. D, In the PFT laboratory located at the South Loop Outpatient Clinic, with room size of 3.4 × 4.6 × 2.8 m3 and air exchange frequency of nine times per hour, the concentrations of particles with sizes ≥3 μm were high during PFTs then decreased to baseline level within 15-20 minutes of the conclusion of testing. Particles with sizes ≤1 μm were unchanged during and after PFTs. A1 = amplitude; Adj = adjusted; COD = coefficient of determination; ExpDec1 = single exponential fitting; PFT = pulmonary function testing; sqr = square; t1 = time constant; y0 = offset.
Compared with baseline, concentrations of aerosol particles with sizes ≥1 μm were higher when PFTs were performed (Table 1 ). After PFTs were completed, the process took approximately 20 minutes for particle concentrations to return to the lowest baseline level for the two larger laboratories. In the smaller PFT laboratory with air exchange frequency of five per hour, the process took 30 to 50 minutes for particle concentrations to return to the lowest baseline level, which was similar to the results from the fit curve.
Table 1.
Particle Concentrations With Different Sizes During and After Pulmonary Function Testing, the Interval to Return to Lowest Level, Clearance Time in Each Hospital, and Overall Results
| Hospital | Particle Size (μm), Concentrations/m3 | Particle Concentrations at Different Times |
Peak vs Lowest P Value | Time to Return to Lowest Level (min) | Particle Clearance Time Constant in the Fit Curvea | Clearance Time Constantb ×4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average During PFT | Peak During PFT | Lowest After PFT | ||||||
| Overall (N = 28) | 0.3, 105/m3 | 502.0 ± 396.5 | 533.4 ± 441.2 | 490.6 ± 371.6 | .291 | 16.3 ± 7.4 | … | … |
| 0.5, 104/m3 | 293.0 ± 274.1 | 327.5 ± 339.3 | 264.3 ± 231.9 | .021 | 27.0 ± 111.4 | … | … | |
| 1.0, 103/m3 | 153.3 ± 100.3 | 202.7 ± 142.4 | 124.1 ± 108.2 | <.001 | 27.3 ± 16.2 | … | … | |
| 3.0, 103/m3 | 19.1 ± 7.6 | 32.6 ± 16.8 | 9.7 ± 7.9 | <.001 | 31.3 ± 18.6 | … | … | |
| 5.0, 103/m3 | 8.5 ± 4.4 | 15.2 ± 10.9 | 3.0 ± 2.1 | <.001 | 23.0 ± 6.6 | … | … | |
| 10.0, 102/m3 | 42.5 ± 31.8 | 95.2 ± 62.5 | 9.3 ± 9.6 | <.001 | 23.0 ± 4.4 | … | … | |
| Rush University Medical Centerc (n = 9) | 0.3, 105/m3 | 51.2 ± 8.1 | 57.3 ±17.0 | 49.4 ± 10.4 | .262 | 8 | NA | NA |
| 0.5, 104/m3 | 25.4 ± 4..8 | 34.2 ± 17.1 | 17.3 ± 7.0 | .005 | 40 | NA | NA | |
| 1.0, 103/m3 | 56.6 ± 18.7 | 79.3 ± 68.2 | 16.7 ± 6.5 | .008 | 46 | 12.9 ± 1.6 | 51.6 ± 17.6 | |
| 3.0, 103/m3 | 18.4 ± 9.5 | 29.4 ± 12.2 | 3.0 ± 2.3 | <.001 | 52 | 10.2 ± 2.0 | 40.8 ± 32.0 | |
| 5.0, 103/m3 | 10.1 ± 6.2 | 18.1 ± 13.7 | 1.7 ± 1.1 | .010 | 30 | 10.0 ± 2.8 | 40.0 ± 11.2 | |
| 10.0, 102/m3 | 60.7 ± 39.0 | 117.7 ± 66.1 | 5.2 ± 6.2 | .001 | 28 | 9.4 ± 3.2 | 37.6 ± 24.0 | |
| Rush Oak Park Hospitald (n = 8) | 0.3, 105/m3 | 872.2 ± 247.2 | 940.7 ± 343.0 | 815.1 ± 196.9 | .102 | 22 | NA | NA |
| 0.5, 104/m3 | 574.8 ±217.0 | 656.3 ± 351.6 | 491.4 ± 150.4 | .068 | 22 | NA | NA | |
| 1.0, 103/m3 | 312.3 ± 49.7 | 366.8 ± 73.6 | 253.5 ± 46.2 | .003 | 19 | 6.5 ± 0.9 | 26.0 ± 3.6 | |
| 3.0, 103/m3 | 28.5 ±8.2 | 39.3 ± 22.3 | 17.8 ± 6.7 | .015 | 26 | 5.3 ± 0.9 | 21.2 ± 3.6 | |
| 5.0, 103/m3 | 10.0 ± 3.1 | 13.2 ± 9.0 | 4.9 ± 2.1 | .028 | 22 | 4.8 ± 0.7 | 19.2 ± 2.8 | |
| 10.0, 102/m3 | 40.8 ±10.9 | 70.6 ± 59.7 | 13.2 ± 9.2 | .027 | 21 | 4.2 ± 0.6 | 16.8 ± 2.4 | |
| South Loop Outpatient Clinice (n = 11) | 0.3, 105/m3 | 609.4 ± 118.6 | 625.1 ± 119.4 | 646.3 ± 128.2 | .372 | 19 | NA | NA |
| 0.5, 104/m3 | 318.5 ± 82.4 | 329.1 ± 71.3 | 331.9 ± 83.4 | .867 | 19 | NA | NA | |
| 1.0, 103/m3 | 134.2 ± 43.3 | 168.9 ± 48.1 | 112.8 ± 26.3 | .014 | 17 | NA | NA | |
| 3.0, 103/m3 | 15.1 ± 9.7 | 28.3 ± 14.1 | 9.0 ± 3.7 | .024 | 16 | NA | NA | |
| 5.0, 103/m3 | 7.9 ± 62 | 13.5 ± 9.3 | 2.4 ± 1.6 | .022 | 17 | 6.9 ± 2.1 | 27.6 ± 8.4 | |
| 10.0, 102/m3 | 45.1 ± 44.8 | 94.2 ± 57.7 | 10.0 ± 13.2 | .025 | 20 | 16.2 ± 1.3 | 64.8 ± 53.2 | |
NA = not available; PFT = pulmonary function testing.
The clearance time constant was calculated from the equation with the use of exponential decay model with the fit curve y = A1∗exp (-x/t1) + y0, where t1 was the time constant.
Defined as 98% of aerosol particles can be cleared in this time frame.
Room size, 3×3×2.8 m3; air exchange frequency, five times per hour.
Room size, 3.6×4.6×2.8 m3; air exchange frequency, three times per hour, with an additional air conditioner.
Room size, 3.4×4.6×2.8 m3; air exchange frequency, nine time per hour.
Discussion
Our clinical study, with the largest sample size in three PFT laboratories, confirms the widely held view, which previously was investigated in five healthy volunteers, that PFTs generate aerosol particles even when a breathing filter is used.9 More importantly, we assessed the interval between PFTs that allowed for particle clearance after completing the test.
Particles in the respirable range (0.5-5 μm) may carry virus and remain suspended in room air for an extended period.10 A larger room size and more frequent air exchanges could reduce particle concentration by dilution and faster clearance.7 Use of a filter that traps exhaled particles could explain the absence of a peak particulate concentration during testing. Particle concentrations would probably be higher if such a breathing filter was not used. Instead, we noted the peak in particle concentration at the end of the testing, when the patients removed their mouthpiece and started talking or breathing without wearing a facemask. This finding agrees with the previous study in healthy volunteers.9 We did not record whether the patients coughed during and after PFT. Regardless, placement of a facemask immediately after removing the mouthpiece from a patient could mitigate aerosol particle production.
This study was performed in PFT laboratories with different room sizes and ventilation systems. The patterns with particles <0.3 μm may be related to the sensitivity limits of the particle sizes for that range. Future studies that will investigate more laboratories with different settings can help to explore various factors that influence aerosol generation and clearance in PFT laboratories.
Although performing PFTs in negative-pressure rooms may be preferred, our data suggest that reductions of ambient particles can be achieved in rooms with less aggressive ventilation exchanges and that exposure to staff members during and after PFT procedures is, to some extent, independent of the particle clearance time. To avoid transmission of infection, PFT technologists should take high-level personal protective equipment precautions during testing of any patient during this pandemic. Alternative methods that include portable electronic spirometry and self-monitoring technologies might be considered.11
Acknoweldgments
Other contributions: We thank Rongshou Zheng, MPH, for his help with the statistical analysis. This study was approved by the institutional review board in Rush University Medical Center (approval No. 20032402-IRB01).
Footnotes
FUNDING/SUPPORT: The authors have reported to CHEST that no funding was received for this study.
FINANCIAL/NONFINANCIAL DISCLOSURES: The authors have reported to CHEST the following: J. L. discloses research support from Fisher & Paykel Healthcare and Rice Foundation and lecture honorarium from AARC and Fisher & Paykel Healthcare Ltd outside the submitted work. D. V. provides consulting to Ohio medical and has research support from Teleflex Medical, INC. J. F. is Chief Science Officer for Aerogen Pharma Corp, San Mateo, CA, USA. R. D. reports remuneration from GSK Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bayer, Mylan, Teva, and Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, as well as research support from Mylan outside the submitted work. None declared (E. M., R. K., R. M., G. J., J. P.).
CLINICALTRIAL REGISTRATION: NCT 04353531
References
- 1.Hull J.H., Lloyd J.K., Cooper B.G. Lung function testing in the COVID-19 endemic. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(7):666–667. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30246-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.British Thoracic Society, Association for Respiratory Technology & Physiology Respiratory function testing during endemic COVID-19. https://www.artp.org.uk/write/MediaUploads/Standards/COVID19/Respiratory_Function_Testing_During_Endemic_COVID_V1.5.pdf
- 3.Lung function testing during COVID-19 pandemic and beyond - Recommendation from ERS Group 9.1 (Respiratory function technologists /Scientists). European Respiratory Society Groups 9.1 and 4.1. https://ers.app.box.com/s/zs1uu88wy51monr0ewd990itoz4tsn2h
- 4.Thoracic Society of Australia & New Zealand, Australian and New Zealand Society of Respiratory Science Peak respiratory bodies recommend suspension of lung function testing. https://www.thoracic.org.au/documents/item/1864
- 5.Gemicioğlu B., Börekçi Ş., Dilektaşlı A.G., Ulubay G., Azap Ö., Saryal S. Turkish Thoracic Society experts consensus report: Recommendations for pulmonary function tests during and after COVID 19 pandemic. Turk Thorac J. 2020;21(3):193–200. doi: 10.5152/TurkThoracJ.2020.20107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wilson K.C., Kaminsky D.A., Michaud G., et al. Restoring pulmonary and sleep services as the COVID-19 pandemic lessens: from an association of pulmonary, critical care, and sleep division directors and American Thoracic Society coordinated task force. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020;17(11):1343–1351. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202005-514ST. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dhand R., Li J. Coughs and sneezes: Their role in transmission of respiratory viral infections, including SARS-CoV-2. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;202(5):651–659. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202004-1263PP. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Almstrand A.C., Bake B., Ljungström E., et al. Effect of airway opening on production of exhaled particles. J Appl Physiol. 2010;108(3):584–588. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00873.2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Helgeson S.A., Lim K.G., Lee A.S., Niven A.S., Patel N.M. Aerosol generation during spirometry. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020;17(12):1637–1639. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202005-569RL. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Liu Y., Ning Z., Chen Y., et al. Aerodynamic characteristics and RNA concentration of SARS-CoV-2 aerosol in Wuhan hospitals during COVID-19 outbreak. Nature. 2020;582:557–560. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2271-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kouri A., Gupta S., Yadollahi A., et al. Addressing reduced laboratory-based pulmonary function testing during a pandemic. Chest. 2020;158(6):2502–2510. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]