Fig. 3. Timeline of mecC-MRSA CC130, CC425 and CC1943 evolution in Europe.
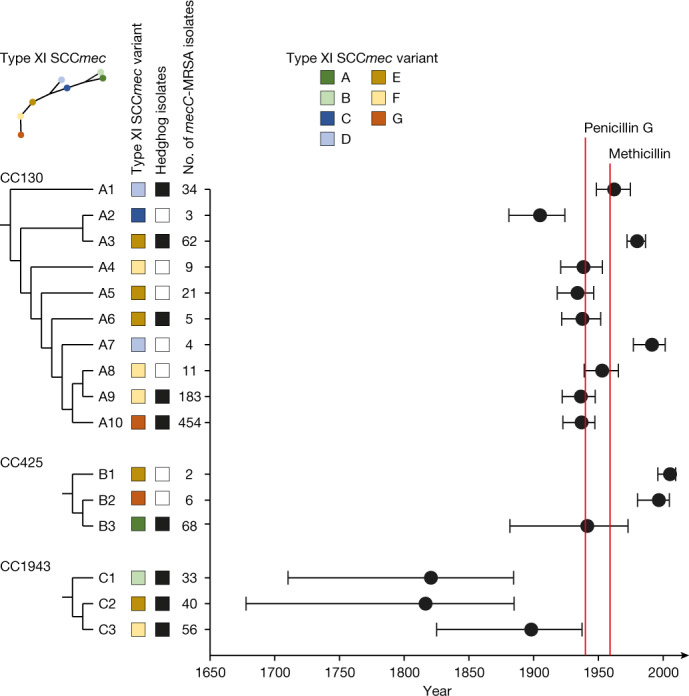
Manual mapping of the tips on the type XI SCCmec phylogeny onto the CC130, CC425 and CC1943 phylogenies, and vice versa, enabled us to assign the mecC-MRSA isolates to 16 monophyletic lineages containing orthologous type XI SCCmec elements (A–G). The trees are redrawn from Supplementary Figs. 2–5 to illustrate the branching order of the different type XI SCCmec variants and mecC-MRSA lineages. Branch lengths are not drawn to scale. The presence and absence of hedgehog isolates in a given lineage are shown as black and white boxes, respectively. A detailed description of the geographical distribution and host range of major mecC-MRSA CC130, CC425 and CC1943 lineages is provided in Extended Data Fig. 7. The estimated date of the most recent common ancestor and 95% confidence interval of each mecC-MRSA lineage are illustrated by filled circles and horizontal lines, respectively. The introduction of penicillin G and methicillin as therapeutic options is indicated by red lines.
