In this issue of Blood, Herishanu et al report on the antibody response to a third dose of BNT162b2 messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) who fail to respond with a measurable humoral response after 2 doses of the vaccine.1 This approach is recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for those with moderate to severely compromised immune systems, with the rationale that immunocompromised patients are especially vulnerable to severe COVID-19 infections and may not build the same level of immunity to 2-dose vaccine series compared with healthy controls. Importantly, the results of this study show that around one-fourth (23.8%) of patients with CLL formed antibodies following the third dose of the vaccine after failing to respond to standard 2-dose vaccination regimen.
Patients with CLL are predisposed to infections, both bacterial and viral, because of the inherent immune defects due both to therapy and to the intrinsic immunosuppressive nature of CLL.2 Not surprisingly, patients with CLL have an increased risk for severe COVID-19 disease and mortality.3
Herishanu et al previously reported the reduced efficacy of the standard 2-dose regimen of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in patients with CLL.4 Antibody response against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was detected in only 39% of the patients with CLL, confirming previously published data on low serological response rates in general to vaccines in patients with CLL.5 A larger registry study performed by the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society confirmed relatively low rates of antibody response in patients with CLL, with 36% seronegative after completion of the vaccine series.6
To study the effect of a third dose of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in seronegative patients with CLL/SLL, Herishanu et al included 172 patients in their prospective study conducted under the framework of the Israeli CLL Study Group. This is the first report of the efficacy of the third vaccine dose in patients with CLL/SLL and answers a question many of our patients are asking. With a median interval of 179 days (>5 months) between second and third doses, antibody response following the third dose was seen in 23.8% of patients (41/172). In contrast, administration of a third dose of the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 vaccine 2 months after the second dose induced seropositivity in 49% of kidney transplant recipients who did not respond after 2 vaccine doses.7 The difference may be due to the inherent immune deficit seen in CLL/SLL, differences in immune suppressive treatments used in these 2 conditions, with B-cell–directed therapies used predominantly in CLL/SLL compared with T-cell immunosuppression in organ transplant recipients, or differences owing to the interval between the second and third doses.
Like previous reports, this analysis showed that treatment significantly affects antibody response. Treatment-naive and previously treated patients had a response rate approaching 40% compared with only 12% in those receiving active treatment. For example, in patients receiving Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor or venetoclax plus anti-CD20 antibody, the antibody response rates after 2 doses were 15.3% and 7.7%, respectively. Exposure to anti-CD20 antibody within the last 12 months significantly reduced the rate of response to the third dose of vaccine (1/28 patients responded). Breakthrough COVID-19 infection developed in 4 patients: 2 patients were on active treatment with ibrutinib; 1 patient was treatment naive; and 1 patient had completed treatment with obinituzumab monotherapy. Three patients recovered, and 1 patient died of COVID-19. Three of these patients were seronegative, and 1 patient was seropositive with a low antibody titer.
This paper confirms the benefits of an additional dose of vaccination for this vulnerable group of patients with CLL/SLL; however, ∼37% of patients with CLL/SLL continue to be seronegative and vulnerable to severe morbidity and mortality from COVID-19. Additional means and methods need to be devised and tested to extend the benefit of vaccination to more patients with CLL/SLL.
With multiple reports now showing that the antibody-mediated response is markedly impaired during active treatment and after recent exposure to anti-CD20 antibody, every attempt to vaccinate patients before starting therapy should be made. For the same reason, given very low seroconversion rates when anti-CD20 antibodies are part of the therapy, postponing initiation of such therapy until after vaccination could be considered. For patients who are already on active treatment, it is currently unknown if holding treatment will affect vaccine response, and if so, for how long treatment needs to be held, although this strategy may be considered for individual patients with disease under good control. Recent reports have suggested that heterologous prime booster vaccination (mix and match) may facilitate a stronger response, and this strategy may provide additional benefit to these patients.8 Although humoral responses parallel cellular response, the effect of additional vaccine dose on T-cell responses in patients with CLL needs to be studied as well, to better understand the protection offered by T-cell response, especially in patients who fail to generate a humoral response.9
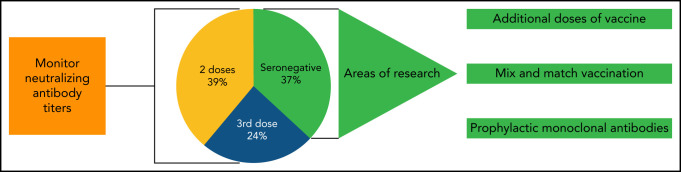
Finally, as the pandemic progresses, research continues to advance treatments and other strategies to fight the deadly virus. With better treatments available, recent reports have reflected improved mortality in patients with CLL/SLL compared with last year.10 However, vaccines are still considered the best strategy to control a highly communicable disease. Results from this prospective clinical trial will help guide development of strategies to increase the possibility of seroconversion in an immune-compromised host, utility of monitoring anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, and the possibility of using targeted anti–SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies as a preventative/prophylactic treatment in seronegative patients with CLL/SLL (see figure).
Potential strategies to improve vaccination efficacy in CLL. Even following 3 doses of mRNA vaccine, up to 37% of patients remain seronegative. Current areas of research include adding additional “booster” doses of vaccine and “mix and match” of different vaccine types. As well, long-acting monoclonal antibodies are a potential strategy for those who are unable to mount a vaccine response.
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: S.A.B. consulted for Pharmacyclics, Janssen, Beigene, and AstraZeneca, received honorarium for OncLive, and a travel grant from Arqule. J.A.W. receives research funding from Pharmacyclics, Janssen, Karyopharm, Morphosys, and Schrodinger and consults for Janssen, Pharmacyclics, Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Arqule, Beigene, Loxo, and Newave.
REFERENCES
- 1.Herishanu Y, Rahav G, Levi S, et al. Efficacy of a third BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine dose in patients with CLL who failed standard 2-dose vaccination. Blood. 2022; 139(5):678-685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tadmor T, Welslau M, Hus I. A review of the infection pathogenesis and prophylaxis recommendations in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia [published correction appears in Expert Rev Hematol. 2018;11(1):ix]. Expert Rev Hematol. 2018; 11(1):57-70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mato AR, Roeker LE, Lamanna N, et al. Outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with CLL: a multicenter international experience. Blood. 2020;136(10):1134-1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Herishanu Y, Avivi I, Aharon A, et al. Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2021;137(23):3165-3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mauro FR, Giannarelli D, Galluzzo CM, et al. Response to the conjugate pneumococcal vaccine (PCV13) in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Leukemia. 2021;35(3):737-746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Greenberger LM, Saltzman LA, Senefeld JW, Johnson PW, DeGennaro LJ, Nichols GL. Antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in patients with hematologic malignancies. Cancer Cell. 2021;39(8): 1031-1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Benotmane I, Gautier G, Perrin P, et al. Antibody response after a third dose of the MRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients with minimal serologic response to 2 doses. JAMA. 2021;326(11):1063-1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Schmidt T, Klemis V, Schub D, et al. Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of heterologous ChAdOx1 nCoV-19/mRNA vaccination. Nat Med. 2021;27(9): 1530-1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Malard F, Gaugler B, Gozlan J, et al. Weak immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with hematologic malignancies. Blood Cancer J. 2021;11(8):142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Roeker LE, Eyre TA, Thompson MC, et al. COVID-19 in patients with CLL: improved survival outcomes and update on management strategies. Blood. 2021; 138(18):1768-1773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.