Abstract
Translating progress in neuroscience into clinical benefits for patients with psychiatric disorders is challenging because it involves the brain as the most complex organ and its interaction with a complex environment and condition. Dealing with such complexity requires powerful techniques. Computational neuroscience approach to psychiatry integrates multiple levels and types of simulation, analysis and computation according to the different types of computational models to enhance comprehending, prediction and treatment of psychiatric disorder. This approach comprises two approaches: theory-driven and data-driven. In this review, we focus on recent advances in theory-driven approaches that mathematically and mechanistically examine the relationships between disorder-related changes and behavior at different level of brain organization. We discuss recent progresses in computational neuroscience models that relate to psychiatry and show how principles of neural computational modeling can be employed to explain psychopathology.
Keywords: Neuroscience, Theoretical models, Psychiatry, Mathematical computing
INTRODUCTION
Research in the field of psychiatry has experienced a stagnation due to the slow translation of neuroscience advances to definitive measures for the recovery of patients with mental disorders. The large complexity of the human brain and the problems in recognizing and explaining the biological, contextual and environmental underpinnings of mental functions astonish the study of the pathophysiology and etiology of mental disorders, and make an explanatory gap between neuroscience and biological psychiatry at intermediate levels of description that must bind ideas and hypotheses at the molecular level to those manifested at the level of clinical entities, such as depression and schizophrenia. On the other hand, the correspondence between these levels is not one to one. In other words, different biological dysfunctions may generate similar behavioral disturbances and, conversely, one biological dysfunction may affect different apparently unrelated psychological functions [1-3]. Generally, incomplete understanding of human cognitive phenotypes has led to the lack of a concrete bridge between the phenomenological and the molecular events. As a result, we see frequent concerns and questions about the classification of psychiatric disorders, and as a clear example, the ongoing revisions of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) of the American Psychiatric Association [4-6]. It is very difficult to deal with these challenges without theoretical models, conceptual frameworks and powerful computational tools. Although experimental studies yield valuable and useful information to understand the cognitive processes and biological disturbances in mental illness [7-11], they are usually limited by practical, economic or ethical factors. In recent years, computational neuroscience has shown great promise in the field of psychiatry research and computational psychiatry by establishing a connection between pathophysiological and phenomenological aspects of mental illness, thereby reshaping current nosology in more biologically dimensions. Computational psychiatry is an emerging field in expansion at the junction between psychiatry and computational neuroscience [12-14].
Computational neuroscience is a subfield of neuroscience which utilizes theoretical analysis, mathematical models and abstractions of the brain to perceive the principles that control development, structure, physiology, emotional and cognitive processes of the nervous system [15]. The goal of mathematical models in computational neuroscience is to capture the main properties of a biological system at multiple spatiotemporal scales, from membrane potentials, neurotransmitter function and topographic architecture to a psychological faculty like behavior or learning [16,17]. These computational models frame ideas that can be directly examined by psychological or biological experiments. While psychiatric disorders are described essentially by high-level symptoms, computational models can help frame symptoms and hypotheses to fill the gap between psychiatry and neuro-biology. For instance, Maia and Frank showed how modeling using an abductive or deductive approach can result in different predictions for psychiatry [18]. Using the abductive approach researchers start from the proposition of a model of normal function and change the model in different ways to produce new hypotheses of brain and biological dysfunction. Then, these models are fitted to the behavior of patients to determine which hypothesis can explain the patients’ performance. The top hypothesis can then be revised in a try to illustrate the deficits at lower levels, or used to plan new experimental tests that will examine the dysfunction proposed by the hypothesis. On the other hand, the deductive approach starts from the proposition of known neurobiological deficits reported in mental illness, and implement these deficiencies in a computational model. Then, the performance of patients is compared to those of the model. If the model can explain the performance and function deficits reported in patients, it provides a reasonable mechanistic platform that link biology and neurobiology to behavior. Therefore, computational neuroscience and computational psychiatry are important to the future of psychiatry research and will probably play a main role in the logical development of nosologies, preventive and treatment strategies.
On the other hand, there are two very common approaches in computational psychiatry that can be the bridge between neuroscience and psychiatry: theory- driven approaches that look for mechanistically explainable relationships between variables (including observable variables or hypothetical ones), and data-driven approaches that utilize various statistical models and machine learning techniques for the analysis of empirical and experimental data to provide a suitable solution for the issues in the classification, forecasting and treatment of diseases. Data-driven approaches apply machine learning techniques to high dimensional data to improve diseases classification, predict the outcomes of treatment and improve treatment selection. Data-driven approaches are often used to develop clinically useful applications, while theory-driven approaches are often used to enhance our insights into disorders and diseases. Several recent studies have thoroughly reviewed data-driven approaches in detail and examined various aspects of these models [12,14,19-21]. However, much less attention has been paid to theory-driven approaches, which can be an appropriate complement to data-driven methods. Therefore, in this review, we focus on recent advances in theory-driven approaches that mathematically and mechanistically examine the relationships between disorder- related changes and behavior at different level of brain organization.
COMPUTATIONAL MODELING
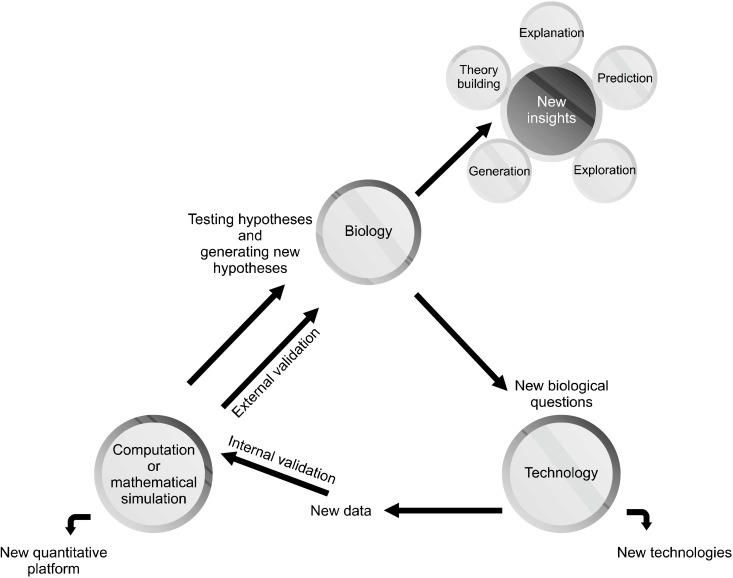
Mathematical or biophysical models provide a quantitative expression for biological phenomena. These synthetic models are built based on physical and mathematical rules, computer-aided tools and biological data from different sources related to the system of interest (e.g., a neural system) and investigate the interaction between components through simulations and mathematical analysis [16]. Figure 1 shows the research process involved in computational modeling to study different biological systems. Based on goal, methodology, simulation level and the capacity to imitate mental illness, three types of models can be identified in computational neuroscience and psychiatry: the phenotypic model, the neurobiological model, and the intermediate model. Scientists choose one of these types of models depending on how nearly and in what sense they want to imitate the target to achieve an appropriate simulated object. In fact, the main difference between these models is the gap between the low level biological function with a high level phenomenological manifestation, i.e., apparent thought, emotion and behavior.
Fig. 1.
Computational modeling re-search process to simulate and study biological systems. There may be direct flows from biology to compu-tational simulation, but in this process we do need powerful hardware and software resources, robotics and other technology-related resources. There-fore, considering the role of tech-nology in this process and flow dia-gram seems logical.
Psychiatric disorders are definitively correlated with brain pathologies, but, as mentioned above, they are currently characterized and categorized by the DSM based on their phenotype manifestations. These disorders involve a broad spectrum of expressions and causes, ranging from largely ambiguous biological and environmental bases to observable behavior and subjective experience [21]. Each of those three models focuses on a particular aspect of psychiatric disorders, based on explicit or implicit, theoretical or practical assumptions that will be explored below.
THE PHENOTYPIC MODELS
This types of models attempts to imitate clinical phenotypes or high level manifestations of the disorder. Turing’s approach to brain simulation is consistent with this view. The focus on mental disorder simulation here is the behavioral phenotype. An ideal phenotypic model should go beyond a black box and be able to simulate a real life system with the ability to provide somatic responses and duplicate verbal and physiological like characteristics of psychiatric disorders. Phenotypic models differ in the degree to which they represent a brain like activity. Thus, there is a range of this type of model from machine learning and artificial intelligence systems that focus merely on the simulation of psychiatric symptoms to a more biologically cognitive system that can produce useful activities in coarsely brain like ways based on high level architecture of the brain.
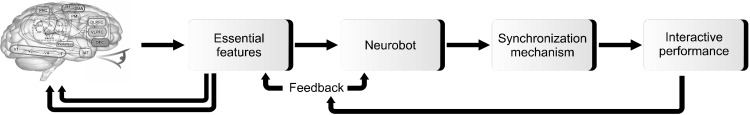
Computer simulations of psychiatric disorders in the form of phenotypic models may help us to better understand the characteristic verbal and emotional responses of a patient who suffers from a specific mental illness and provide a simulator to investigate potential reactions to various stimuli [22]. It may even be possible to understand the fundamental relationship between specific symptoms and the underlying neurobiological function that correlates with or even causes these symptoms. For example, Akbari and Zhuiykov [23] recently developed a bioinspired optoelectronically engineered neurorobotics model with sensorimotor functionalities. The neural engineering framework captures a high level illustration of a cognitive theory and integrates it with related neurophysiological and anatomical constraints, generating a detailed mechanistic model of how numerous interacting neurons can produce the desired behavior efficiently. In [24], a neurorobotics platform is introduced that connects artificial brain neural networks with robots in a comprehensive simulation model. This platform can behave similarly to humans in response to sensorimotor stimuli (Fig. 2). Semantic pointer architecture unified network (Spaun) is a neuron model of the brain that produces motor functions by a mechanistically modeled arm in response to visual stimuli [25]. In a more clinical framework, some studies introduced interactive robots to recognize impulsive or inattentive behaviors in patients with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and autism and provide immediate feedback to them [26,27]. As a result, a phenotypic model of mental illness may imitate and recognize the cognitive processes, perception and reactions involved in a specific disorder. However, the question that arises in the mind is whether the computer can realistically mimic the real life behavior of a patient suffering from a mental illness. In fact, this type of simulation could not be realistically linked to the functioning of the brain or even biological structures. Therefore, the phenotypic type of the model provides no new information about the potential role of biological factors in the pathogenesis of mental illness, nor about the therapeutic effect of certain biological interventions.
Fig. 2.
Simplified phenotypic modeling process of the neurorobotics platform. The user can develop a neurorobotic experiment through a brain model linked to a robotic body or neurobot that interacts in the dynamic environment. Then, the experiment is triggered using a synchronized neural physics simulation. Finally, the performance can be displayed and evaluated in an interactive manner. The brain picture was reused from the article of Eliasmith et al. (Science 2012;338:1202-1205) [25] with original copyright holder’s permission under license number 5084650890717.
THE NEUROBIOLOGICAL MODELS
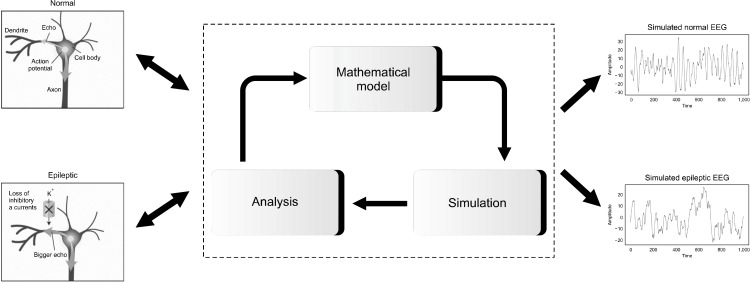
This type of models attempts to imitate low level brain function through the real molecular, synaptic, connec-tivity and neuronal characteristics of the brain in mental illness. The underlying hypothesis in neurobiological models is that high level phenomena are caused by low level neurobiological activity. In fact, these models follow a bottom-up approach to explain a potential disease mechanism in biology [28]. These neurobiological models would help us to recategorize disorders based on biological factors rather than looking at diseases merely as sets of symptoms. The scope of this view would lead us to design and develop therapies to selectively target the underlying abnormal mechanisms. In fact, we can embed a specific mutation into the neurobiological model and then study how that change affects any part of the biological processes [29]. These types of models are suitable for testing hypotheses. They can test possible pathological mechanisms at different low levels. In addition, these models can be used to investigate the effects of various drugs and therapies on synapses and neurotransmitters and other low-level biological processes. However, some researchers have raised doubts regarding the capability of such modeling approach to generate intelligent actions like a human brain. Among the various practical and conceptual concerns, the most serious one in the context of psychiatric disorders relates to the controversial capacity of this approach to reliably simulate psychiatric symptoms. In addition, most of these models relate low-level neurobiological processes to higher-level neurobiological processes in a mental illness rather than behavioral manifestations of that disease. For instance, Tsoutsouras et al. [30] presented a modeling approach based on cellular automata for the loss of neurons and active synapses in limbic brain areas (epileptogenic focus) that causes epileptic seizures by propagating the pathological dynamics from the focal to healthy brain regions. Eventually, they were able to simulate the electrical activity or electroencephalogram of epileptic brain (Fig. 3). In addition, a recent study reviewed neurobiological models of psychotherapy and explained the important role of neuroplasticity models as the neurobiological basis of psychotherapy in mechanistic understanding of underlying neural mechanisms involved in this therapeutic approach [31]. Zilcha-Mano et al. [32] explained the neurobiological underpinnings of therapeutic expectancy and alliance and underlined the importance of neurobiological models to understand these effects. Iglesias et al. [33] explained how neurobiological models can be used to study the effects of neuromodulatory approaches in computational psychiatry.
Fig. 3.
A simple example of the neurobiological modeling process of epilepsy that ultimately results in the simulation of epileptic EEG signal compared to normal EEG signal. EEG, electroencephalogram.
THE INTERMEDIATE MODELS
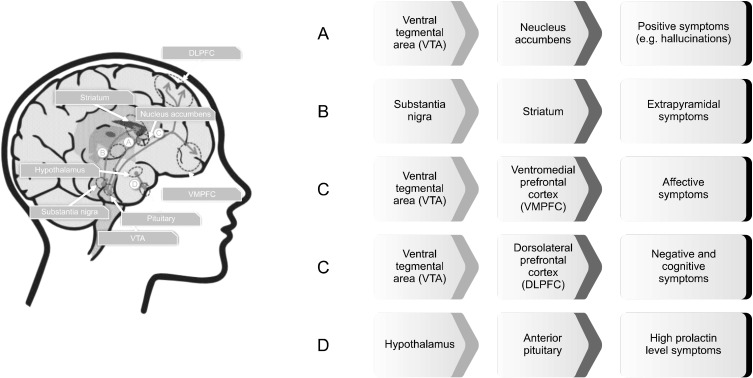
These types of models have received the most attention in the field of computational psychiatry. The intermediate models stand in between the neurobiological and the phenotypic models. These types of models attempt to establish a logical relationship between high-level psychiatric symptoms and low-level biological dysfunction. They differ from both the neurobiological and the phenotypic models, because they neither try to mimic symptoms realistically nor biological structures. Rather, these models would provide means and frameworks for improved theoretical comprehending of mental disorders. Figure 4 shows an example of the intermediate model for conceptualization and understanding of schizophrenia based on the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Various models have been introduced using this approach that can be categorized into three subtypes: synthetic, algorithmic and Bayesian models.
Fig. 4.
An example of the intermediate model for conceptualization and understanding of schizophrenia based on the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. According to this model, schizophrenia is best conceived as a complex disorder which involves multiple dopaminergic pathways.
Synthetic models usually connect different levels of analysis and simulation, and can be used abductively to infer the possible causes for a known outcome (for instance, what kind of perturbation in the release of some neurotransmitters could result in neurodynamics or behavioral disturbances) or deductively to infer the possible consequences of suspected or known causes (for instance, what effects a variation in the concentration of a certain neurotransmitter would have on neural-circuit or behavior dynamics). Previous studies have been used various synthetic biophysical models to connect neurobiological abnormalities in mental illness to its neurodynamical and behavioral consequences [34]. Cortical pyramidal neurons and GABAergic interneurons form an important class of these models that has provided valuable insights in psychiatry. Reducing NMDAR density within inhibitory interneurons suggested that working memory in schizophrenia must be sensitive to distractors similar to the objects held in working memory [35]. Different integrative models have been presented to discover the relationship between NMDAR density and BOLD signals. They suggested that ketamine causes psychosis symptoms and destroys the negative relation between task-related modes and the resting-state default mode [36,37]. Furthermore, dysfunction in the posterior regions of the brain may cause impairments in attentional orientation on different mental arithmetic tasks in ADHD [7]. In another study, a neural network model explored the effect of serotonergic and glutamatergic disturbances in obsessive-compulsive disorder, and suggested that both increased glutamate and decreased serotonin can be a likely neural substrate for obsession [1]. Similar connections from synaptic activities to high-level functions have been achieved through biophysically realistic detailed models of the cortico-striata-thalamic circuits [38,39]. These models explained different aspects of schizophrenia, Tourette’s syndrome, addiction and Parkinson’s disease [18,40]. In summary, synthetic models provide an analytical tool to bridge biological details to symptoms through understanding causally complex relationships between levels of analysis. However, it should be noted that due to the simplifications considered in these models, conclusions are limited to the levels of analysis involved in the model.
Algorithmic reinforcement learning (RL) models provide a quantitative explanation of the mechanisms underlying disturbances of executive function, emotion, decision-making and other functions. These powerful frameworks have formed many aspects and details of systems neuroscience over the last decade. They provide a normative model of choice behavior with neural substrates and neurobiological correlates [41]. Although they differ from synthetic models, they can characterize different aspects of neural activity and subsequent behavior [42,43]. Perhaps the most popular correlate is the relationship between phasic dopaminergic activity in the basal ganglia and reward-seeking/punishment-avoiding behaviors in the presence of reward and punishment as reinforces [44]. Such behaviors are related to subject’s survival and shape the main concern of neural circuits. According to the role of dopamine in modulating NMDAR plasticity and the importance of prediction errors for associative learning, it has suggested that phasic dopamine release under prediction error encoding may serve as a reference to adjust synaptic connections and functions in task-relevant circuits, and that abnormal dopaminergic activities may cause maladaptive learning [33]. However, many studies have suggested that dopamine also encodes uncertainty or precision [45-47]. The field of RL has drawn two different approaches in which past experience and prior beliefs are utilized to predict future reward and punishment: model-based and model-free cognition (a detailed description of these approaches is beyond the scope of the review) [48]. These notions have guided concepts and researches on various mental disorders. Previous studies have linked multiple aspects of RL to a wide variety range of symptoms of psychiatric diseases, including: positive symptoms in schizophrenia (e.g., hallucinations and delusions) with atypical reward prediction errors [49,50], abnormal activity in the limbic motivational systems in response to neural stimuli [51], and aberrant levels of incentive salience because of abnormally increased levels of dopaminergic neurotransmission in prefrontal cortex and ventral striatum [52,53]; negative symptoms of schizophrenia with aberrant effort-cost computations and inability for representing the expected value of rewards [54-57]; relapse prediction in alcohol-dependence with conditioned stimulus-related activation in the nucleus accumbens [58]; impulsivity in ADHD with reduced delay aversion due to over-discounting of delayed rewards [59,60]; anhedonia in depression related to a deficit in reward sensitivity in a different way from that in dopaminergic transmission affecting learning [61].
An important advantage of characterizing reward functions in terms of prior beliefs or past experiences is that the beliefs, that are responsible for individual behavior, can be defined, enabling computational and quantitative phenotyping in terms of attitudes and beliefs [62,63]. This approach shapes the principle of many current computational psychiatry innovations, and even has been extended to game-theoretic models of interpersonal exchange that involves strategic cooperation, competition and social fairness [64,65]. Stag-hunt game and multi-round trust game are two prominent examples of these models that have revealed disorder-specific play styles in many psychiatric disorders, including autism, ADHD, schizophrenia, depression and borderline personality disorders [64,66]. These Bayesian models can be employed to better understand the nature of problem and its solution. One important property of Bayesian models is their emphasis on the use and representation of uncertainty [67]. Accordingly, it has been shown that the statistics of aversive experience play an important role in several processes, from learned helplessness and depression to familiarity in fear conditioning [68-70]. Bayesian models can also be utilized to explore a possible relationship between a certain symptom and suboptimal inference. For instance, subjects with high trait anxiety cannot update optimally how volatile an aversive situation is, while low anxiety controls present close to Bayes-optimum behavior [71]. Generally, these extensions and other approaches derived from behavioral economics could provide a unique opportunity to describe different psychopathies and their genetic or neural correlates.
DISCUSSION
In this brief overview, we have reviewed theory-driven approaches in computational neuroscience and their applications in the computational psychiatry. Our goal here was not to focus on psychiatric disorders such as depression, autism, ADHD, anxiety and others, but rather on computational modeling approaches in neuroscience to characterize and measure the pathobiological mechanisms involved in psychiatric symptoms. Discussion of mental illness modeling should involve the important question of the purposes of doing so. Actually, there is a critical need for new clinical tests that identify the main abnormality that probably underlies the symptoms of a patient such that targeted treatment and medication would be selected as well as spectrum diseases would be split into more distinct subgroups mechanistically. This is where we need to look for answers. In other words, the long-term objective of neuroscience-based computational modeling in psychiatry should be to address this critical need, i.e., better understanding of the pathophysiological processes causing mental disorders, and ultimately diagnosing and treating these pathologies more effectively. The success of most scientific attempts depends on the accuracy and preciseness with which phenomena can be mechanistically modeled. In psychiatry, models are usually developed by prose according to a synthesis and fusion of available experimental findings [72]. An important point in computational modeling is that these models should not be formulated to test certain hypotheses about brain function and dysfunction. Instead, it is much better that they view as mathematical observatories to examine and validate different candidate hypotheses. Thus, a computational model is a powerful tool, not only a hypothesis, and can be linked to clinical tools for patient evaluation. To this end, we need to take advantages of each of above computational models and minimize their limitations and complexities to achieve a comprehensive applicable model. In fact, the complexity of mental disorders and the current biological-pheno-menological gap can benefit from a multi-level method that merges multiple modes of simulation and modeling: a top-down high-level phenotypically symptom oriented mode and a bottom-up low-level biologically oriented mode. Successful modeling of mental illness should include these two modes that correlate with the bottommost and uppermost layers of brain functioning. The phenotypically symptom oriented modeling can benefit from the artificial intelligence, whereas neurobiological modeling can benefit from the different methodologies of computational neuroscience. In computational neuroscience, researcher must learn to compute and analyze without knowing all the parameters. In other words, the model parameters characterizing brain networks are uncertain, numerous and can change over time or situation. The effects of the uncertain parameters of the model and the uncertainty in model predictions can be studied through repeated evaluations of the model, which is often computationally demanding [73].
With the development of numerical algorithms and computational and computer hardware, we will probably include more phenotypic and even neurobiological models in clinical practice in the future. However, according to the characteristics, properties, advantages and limitations of each category of above models, it seems that the intermediate models are now more usable for better understanding of mental illness and clinical setting in general. Regarding the subtypes of intermediate models, it should be noted that the distinction between synthetic, algorithmic and Bayesian models can be vague. For instance, a biophysically detailed model of the basal ganglia can include an algorithmic-like RL module to estimate prediction errors. Moreover, the different types of model may beneficially be used in a joint fashion. This approach enables us to refine and improve the details of one level of characterization limited by the other. For instance, biophysically detailed models of basal ganglia discern between opponent indirect and direct pathways that distinctively process dopaminergic reinforcement signals [74]. The integration of this feature in more abstract algorithmic models makes it possible to computationally analyze its consequences for various behaviors across a broad range of parameters. Furthermore, it also should be noted that Bayesian approaches can be applied to all three subtypes of models for fitting, description, validation and other purposes.
Although theory-driven modeling approaches have yielded important insights into the processes and mechanisms underlying specific disorders at many levels of analysis, they have to be applied yet to clinical problems for the most part. Furthermore, these computational tools have some limitations. Most obvious limitation is that they require considerable expertise and are often opaque and confusing for the non-expert. Hence, how to exchange useful information between clinicians, trialists, experi-mentalists and theorists is challenging for the field. This can be supported by a more focus on establishing utility through the active application of computational appro-aches in clinical trials. Combining theory- and data-driven approaches can be an appropriate way [14,75-79]. Combining theory- and data-driven approaches can be very helpful from an applied point of view [80]. Theory- driven approaches provide an estimation of certain features relevant to a specific disorder, if the prior knowledge and mechanistic understanding of the condition is sufficiently accurate. As a result, they substantially reduce the data dimensionality by limiting the data set to the subspace of a few relevant features and parameters. Then, data-driven approaches can apply machine learning approaches to this lower dimensional data set with higher reliability and efficiency. Such an approach has already been used in a few studies to investigate Huntington’s [81] and schizophrenia [82], and has led to considerable improvements in the classification of behaviors and subtypes of these diseases.
CONCLUSION
In the present review, we have outlined how computational neuroscience can use formal models in different levels to present a mechanistic and functional outlook and interpretation on psychopathology and its underlying pathophysiology. We focused on theory-driven appro-aches and introduced a new category for these computational models, which require substantial skills from cellular and molecular neuroscience, network neuroscience, cognitive neuroscience, computational neuroscience, psychiatry and psychology, computer science, mathematics and engineering to empower the important interdisciplinary field of computational psychiatry. Ongoing progress in computational neuroscience offers remarkable opportunities to design and conduct mechanistic preclinical studies by focusing on different brain circuits models, especially in neurodevelopmental disorders such as schizophrenia, ADHD and autism. These mechanistic studies may be administered at the level of high level manifestations of mental illness using phenotypic models and neurorobotics platform, at the level of low level brain functioning using neurobiological models, or at the intermediary level by establishing interrelationships between the low level and the high level models using different types of intermediate models. It is our belief that some challenges in psychiatry and mental health in general cannot be overcome without the help of theoretical frameworks and computational modeling. However, the practical applications of computational models are still in their infancy, and there is a long way to go to reach the ultimate goal of guiding the design and development of new pharmacological or even cognitive therapeutic strategies through the mechanistic interpretability of computational models.
Acknowledgements
Conceptualization, writing draft, reviewing and editing final manuscript: Ali Khaleghi, Mohammad Reza Mohammadi, Kian Shahi and Ali Motie Nasrabadi.
Footnotes
Funding
None.
Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
- 1.Maia TV, Cano-Colino M. The role of serotonin in orbitofrontal function and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Clin Psychol Sci. 2015;3:460–482. doi: 10.1177/2167702614566809. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Stephan KE, Bach DR, Fletcher PC, Flint J, Frank MJ, Friston KJ, et al. Charting the landscape of priority problems in psychiatry, part 1: classification and diagnosis. Lancet Psychiatry. 2016;3:77–83. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(15)00361-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Talepasand S, Mohammadi MR, Alavi SS, Khaleghi A, Sajedi Z, Akbari P, et al. Psychiatric disorders in children and adolescents: prevalence and sociodemographic correlates in Semnan Province in Iran. Asian J Psychiatr. 2019;40:9–14. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2019.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Khaleghi A, Mohammadi MR, Zandifar A, Ahmadi N, Alavi SS, Ahmadi A, et al. Epidemiology of psychiatric disorders in children and adolescents; in Tehran, 2017. Asian J Psychiatr. 2017;37:146–153. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2018.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mohammadi MR, Ahmadi N, Khaleghi A, Mostafavi SA, Kamali K, Rahgozar M, et al. Prevalence and correlates of psychiatric disorders in a national survey of Iranian children and adolescents. Iran J Psychiatry. 2019;14:1–15. doi: 10.18502/ijps.v14i1.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mohammadi MR, Ahmadi N, Khaleghi A, Zarafshan H, Mostafavi SA, Kamali K, et al. Prevalence of autism and its comorbidities and the relationship with maternal psychopathology: a national population-based study. Arch Iran Med. 2019;22:546–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zarafshan H, Khaleghi A, Mohammadi MR, Moeini M, Malmir N. Electroencephalogram complexity analysis in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder during a visual cognitive task. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2016;38:361–369. doi: 10.1080/13803395.2015.1119252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Khaleghi A, Zarafshan H, Mohammadi MR. Visual and auditory steady-state responses in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019;269:645–655. doi: 10.1007/s00406-018-0902-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mostafavi SA, Khaleghi A, Mohammadi MR. Noninvasive brain stimulation in alcohol craving: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020;101:109938. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.109938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Khaleghi A, Pirzad Jahromi G, Zarafshan H, Mostafavi SA, Mohammadi MR. Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation of prefrontal cortex on risk-taking behavior. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2020;74:455–465. doi: 10.1111/pcn.13025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Khaleghi A, Zarafshan H, Vand SR, Mohammadi MR. Effects of non-invasive neurostimulation on autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2020;18:527–552. doi: 10.9758/cpn.2020.18.4.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wang XJ, Krystal JH. Computational psychiatry. Neuron. 2014;84:638–654. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.10.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Friston KJ, Stephan KE, Montague R, Dolan RJ. Computational psychiatry: the brain as a phantastic organ. Lancet Psychiatry. 2014;1:148–158. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(14)70275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Huys QJ, Maia TV, Frank MJ. Computational psychiatry as a bridge from neuroscience to clinical applications. Nat Neurosci. 2016;19:404–413. doi: 10.1038/nn.4238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jaeger D, Jung R. Encyclopedia of computational neuroscience. Springer; New York: 2015. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dayan P, Abbott LF. Book review: Theoretical neuroscience: computational and mathematical modeling of neural systems. J Cognit Neurosci. 2003;15:154–155. doi: 10.1162/089892903321107891. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kriegeskorte N, Douglas PK. Cognitive computational neuro-science. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21:1148–1160. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0210-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Maia TV, Frank MJ. From reinforcement learning models to psychiatric and neurological disorders. Nat Neurosci. 2011;14:154–162. doi: 10.1038/nn.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Deserno L, Heinz A, Schlagenhauf F. Computational approaches to schizophrenia: a perspective on negative symptoms. Schizophr Res. 2017;186:46–54. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2016.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Valton V, Romaniuk L, Douglas Steele J, Lawrie S, Seriès P. Comprehensive review: computational modelling of schizo-phrenia. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017;83:631–646. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.08.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yahata N, Kasai K, Kawato M. Computational neuroscience approach to biomarkers and treatments for mental disorders. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017;71:215–237. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gold A, Dudai Y. Simulation of mental disorders: II. Computer models, purposes and future directions. Isr J Psychiatry Relat Sci. 2016;53:73–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Karbalaei Akbari M, Zhuiykov S. A bioinspired optoelectronically engineered artificial neurorobotics device with sensorimotor functionalities. Nat Commun. 2019;10:3873. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11823-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Falotico E, Vannucci L, Ambrosano A, Albanese U, Ulbrich S, Vasquez Tieck JC, et al. Connecting artificial brains to robots in a comprehensive simulation framework: the neurorobotics platform. Front Neurorobot. 2017;11:2. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2017.00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Eliasmith C, Stewart TC, Choo X, Bekolay T, DeWolf T, Tang Y, et al. A large-scale model of the functioning brain. Science. 2012;338:1202–1205. doi: 10.1126/science.1225266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zuckerman O, Hoffman G, Kopelman-Rubin D, Klomek AB, Shitrit N, Amsalem Y, et al. In: TEI '16: Tenth Inter-national Conference on Tangible, Embedded, and Embodied Interaction. Eindhoven; Netherlands: 2016. Feb 14-17, KIP3: robotic companion as an external cue to students with ADHD; pp. 621–626. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rakhymbayeva N, Seitkazina N, Turabayev D, Pak A, Sandygulova A. In: HRI '20: Companion of the 2020 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction. Cambridge; UK: 2020. Mar 23-26, A long-term study of robot-assisted therapy for children with severe autism and ADHD; pp. 401–402. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.O'Reilly RC. Biologically based computational models of high-level cognition. Science. 2006;314:91–94. doi: 10.1126/science.1127242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Markram H. The human brain project. Sci Am. 2012;306:50–55. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0612-50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tsoutsouras V, Sirakoulis GC, Pavlos GP, Iliopoulos AC. Simulation of healthy and epileptiform brain activity using cellular automata. Int J Bifurc Chaos. 2012;22:1250229. doi: 10.1142/S021812741250229X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Javanbakht A, Alberini CM. Editorial: Neurobiological models of psychotherapy. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019;13:144. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zilcha-Mano S, Roose SP, Brown PJ, Rutherford BR. Not just nonspecific factors: the roles of alliance and expectancy in treatment, and their neurobiological underpinnings. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019;12:293. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Iglesias S, Tomiello S, Schneebeli M, Stephan KE. Models of neuromodulation for computational psychiatry. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci. 2017;8:e1420. doi: 10.1002/wcs.1420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Murray JD, Anticevic A, Gancsos M, Ichinose M, Corlett PR, Krystal JH, et al. Linking microcircuit dysfunction to cognitive impairment: effects of disinhibition associated with schizophrenia in a cortical working memory model. Cereb Cortex. 2014;24:859–872. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhs370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lisman JE, Coyle JT, Green RW, Javitt DC, Benes FM, Heckers S, et al. Circuit-based framework for understanding neurotransmitter and risk gene interactions in schizophrenia. Trends Neurosci. 2008;31:234–242. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2008.02.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Krystal JH, Karper LP, Seibyl JP, Freeman GK, Delaney R, Bremner JD, et al. Subanesthetic effects of the noncompetitive NMDA antagonist, ketamine, in humans. Psychotomimetic, perceptual, cognitive, and neuroendocrine responses. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994;51:199–214. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1994.03950030035004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Anticevic A, Gancsos M, Murray JD, Repovs G, Driesen NR, Ennis DJ, et al. NMDA receptor function in large-scale anticorrelated neural systems with implications for cognition and schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:16720–16725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1208494109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Frank MJ. Dynamic dopamine modulation in the basal ganglia: a neurocomputational account of cognitive deficits in medicated and nonmedicated Parkinsonism. J Cogn Neurosci. 2005;17:51–72. doi: 10.1162/0898929052880093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gurney KN, Humphries MD, Redgrave P. A new framework for cortico-striatal plasticity: behavioural theory meets in vitro data at the reinforcement-action interface. PLoS Biol. 2015;13:e1002034. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Frank MJ. Linking across levels of computation in model-based cognitive neuroscience. In: Forstmann B, Wagenmakers EJ, editors. An introduction to model-based cognitive neuroscience. Springer; Forstmann B, Wagenmakers EJ, editors. An introduction to model-based cognitive neuroscience. New York: 2015. pp. 159–177. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chen C, Takahashi T, Nakagawa S, Inoue T, Kusumi I. Reinforcement learning in depression: a review of computational research. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015;55:247–267. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Deserno L, Boehme R, Heinz A, Schlagenhauf F. Reinforce-ment learning and dopamine in schizophrenia: dimensions of symptoms or specific features of a disease group? Front Psychiatry. 2013;4:172. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Maia TV. Reinforcement learning, conditioning, and the brain: successes and challenges. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2009;9:343–364. doi: 10.3758/CABN.9.4.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Eshel N, Bukwich M, Rao V, Hemmelder V, Tian J, Uchida N. Arithmetic and local circuitry underlying dopamine prediction errors. Nature. 2015;525:243–246. doi: 10.1038/nature14855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Montague PR, Hyman SE, Cohen JD. Computational roles for dopamine in behavioural control. Nature. 2004;431:760–767. doi: 10.1038/nature03015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Moustafa AA, Sherman SJ, Frank MJ. A dopaminergic basis for working memory, learning and attentional shifting in Parkinsonism. Neuropsychologia. 2008;46:3144–3156. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Schultz W, Preuschoff K, Camerer C, Hsu M, Fiorillo CD, Tobler PN, et al. Explicit neural signals reflecting reward uncertainty. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2008;363:3801–3811. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Adams RA, Huys QJ, Roiser JP. Computational psychiatry: towards a mathematically informed understanding of mental illness. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2016;87:53–63. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2015-310737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Murray GK, Corlett PR, Clark L, Pessiglione M, Blackwell AD, Honey G, et al. Substantia nigra/ventral tegmental reward prediction error disruption in psychosis. Mol Psychiatry. 2008;13:239, 267–276. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4002058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Corlett PR, Murray GK, Honey GD, Aitken MR, Shanks DR, Robbins TW, et al. Disrupted prediction-error signal in psychosis: evidence for an associative account of delusions. Brain. 2007;130(Pt 9):2387–2400. doi: 10.1093/brain/awm173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Romaniuk L, Honey GD, King JR, Whalley HC, McIntosh AM, Levita L, et al. Midbrain activation during Pavlovian conditioning and delusional symptoms in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67:1246–1254. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Schlagenhauf F, Sterzer P, Schmack K, Ballmaier M, Rapp M, Wrase J, et al. Reward feedback alterations in unmedicated schizophrenia patients: relevance for delusions. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;65:1032–1039. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.12.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kapur S. Psychosis as a state of aberrant salience: a framework linking biology, phenomenology, and pharmacology in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160:13–23. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.160.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Waltz JA, Schweitzer JB, Gold JM, Kurup PK, Ross TJ, Salmeron BJ, et al. Patients with schizophrenia have a reduced neural response to both unpredictable and predictable primary reinforcers. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009;34:1567–1577. doi: 10.1038/npp.2008.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Gradin VB, Kumar P, Waiter G, Ahearn T, Stickle C, Milders M, et al. Expected value and prediction error abnormalities in depression and schizophrenia. Brain. 2011;134(Pt 6):1751–1764. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Gold JM, Waltz JA, Matveeva TM, Kasanova Z, Strauss GP, Herbener ES, et al. Negative symptoms and the failure to represent the expected reward value of actions: behavioral and computational modeling evidence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69:129–138. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Gold JM, Strauss GP, Waltz JA, Robinson BM, Brown JK, Frank MJ. Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are associated with abnormal effort-cost computations. Biol Psychiatry. 2013;74:130–136. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.12.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Garbusow M, Schad DJ, Sebold M, Friedel E, Bernhardt N, Koch SP, et al. Pavlovian-to-instrumental transfer effects in the nucleus accumbens relate to relapse in alcohol dependence. Addict Biol. 2016;21:719–731. doi: 10.1111/adb.12243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sonuga-Barke EJ. The dual pathway model of AD/HD: an elaboration of neuro-developmental characteristics. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2003;27:593–604. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2003.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Smith AJ, Becker S, Kapur S. A computational model of the functional role of the ventral-striatal D2 receptor in the expression of previously acquired behaviors. Neural Comput. 2005;17:361–395. doi: 10.1162/0899766053011546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Huys QJ, Pizzagalli DA, Bogdan R, Dayan P. Mapping anhedonia onto reinforcement learning: a behavioural meta- analysis. Biol Mood Anxiety Disord. 2013;3:12. doi: 10.1186/2045-5380-3-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yoshida W, Dziobek I, Kliemann D, Heekeren HR, Friston KJ, Dolan RJ. Cooperation and heterogeneity of the autistic mind. J Neurosci. 2010;30:8815–8818. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0400-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Kishida KT, Montague PR. Imaging models of valuation during social interaction in humans. Biol Psychiatry. 2012;72:93–100. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.02.037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Kishida KT, King-Casas B, Montague PR. Neuroeconomic approaches to mental disorders. Neuron. 2010;67:543–554. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.07.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Sanfey AG. Social decision-making: insights from game theory and neuroscience. Science. 2007;318:598–602. doi: 10.1126/science.1142996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Yoshida W, Seymour B, Friston KJ, Dolan RJ. Neural mechanisms of belief inference during cooperative games. J Neurosci. 2010;30:10744–10751. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5895-09.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Moutoussis M, Fearon P, El-Deredy W, Dolan RJ, Friston KJ. Bayesian inferences about the self (and others): a review. Conscious Cogn. 2014;25:67–76. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2014.01.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Mokhtari Hashtjini M, Pirzad Jahromi G, Sadr SS, Khaleghi A, Hatef B, Meftahi GH. Comparison of the effects of deep brain stimulation of the prelimbic cortex and basolateral amygdala for facilitation of extinction process of conditioned fear. Arch Neurosci. 2020;7 doi: 10.5812/ans.101743. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Huys QJM, Dayan P. A Bayesian formulation of behavioral control. Cognition. 2009;113:314–328. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2009.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Maia TV. Fear conditioning and social groups: statistics, not genetics. Cogn Sci. 2009;33:1232–1251. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-6709.2009.01054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Browning M, Behrens TE, Jocham G, O'Reilly JX, Bishop SJ. Anxious individuals have difficulty learning the causal statistics of aversive environments. Nat Neurosci. 2015;18:590–596. doi: 10.1038/nn.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Fornito A, Zalesky A. Computational approaches to understanding mental dysfunction: progress, challenges, and new frontiers. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2018;3:728–730. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2018.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Einevoll GT, Destexhe A, Diesmann M, Grün S, Jirsa V, de Kamps M, et al. The scientific case for brain simulations. Neuron. 2019;102:735–744. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.03.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Collins AG, Frank MJ. Opponent actor learning (OpAL): modeling interactive effects of striatal dopamine on reinforcement learning and choice incentive. Psychol Rev. 2014;121:337–366. doi: 10.1037/a0037015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Mohammadi MR, Khaleghi A, Nasrabadi AM, Rafieivand S, Begol M, Zarafshan H. EEG classification of ADHD and normal children using non-linear features and neural network. Biomed Eng Lett. 2016;6:66–73. doi: 10.1007/s13534-016-0218-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Khaleghi A, Sheikhani A, Mohammadi MR, Nasrabadi AM, Vand SR, Zarafshan H, et al. EEG classification of adolescents with type I and type II of bipolar disorder. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2015;38:551–559. doi: 10.1007/s13246-015-0375-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Mostafavi SA, Khaleghi A, Mohammadi MR, Akhondzadeh S. Is transcranial direct current stimulation an effective modality in reducing food craving? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr Neurosci. 2020;23:55–67. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2018.1470371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Moeini M, Khaleghi A, Mohammadi MR. Characteristics of alpha band frequency in adolescents with bipolar II disorder: a resting-state QEEG study. Iran J Psychiatry. 2015;10:8–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Khaleghi A, Birgani PM, Fooladi MF, Mohammadi MR. Applicable features of electroencephalogram for ADHD diagnosis. Res Biomed Eng. 2020;36:1–11. doi: 10.1007/s42600-019-00036-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Mohammadi MR, Khaleghi A. Transsexualism: a different viewpoint to brain changes. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2018;16:136–143. doi: 10.9758/cpn.2018.16.2.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Wiecki TV, Antoniades CA, Stevenson A, Kennard C, Borowsky B, Owen G, et al. Computational cognitive biomarker for early-stage Huntington's disease. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0148409. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Brodersen KH, Deserno L, Schlagenhauf F, Lin Z, Penny WD, Buhmann JM, et al. Dissecting psychiatric spectrum disorders by generative embedding. Neuroimage Clin. 2013;4:98–111. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2013.11.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]