The 4-methoxyphenyl group is disposed on one side of the bicyclic core and the oxygen atoms of the hydroxyl and acetyl groups are disposed on the other. The unsaturated portion of the core adopts an envelope conformation. In the crystal, O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds form chains extending along the a-axis direction. These are linked into layers parallel to the ac plane by additional C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯π(ring) interactions.
Keywords: crystal structure, tetrahydroisoquinoline, ethyl ester, hydrogen bond, C—H⋯π(ring)
Abstract
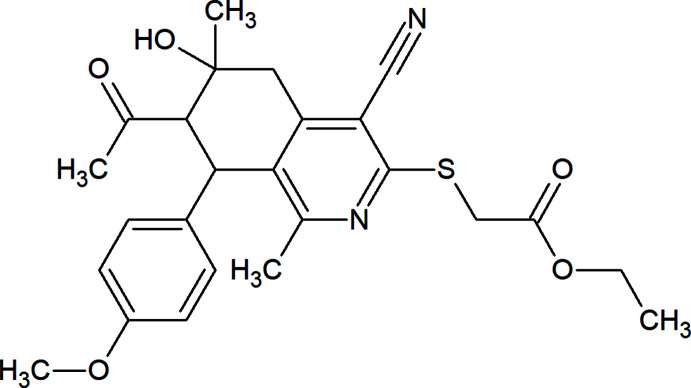
In the title molecule, C25H28N2O5S, (alternative name ethyl 2-{[7-acetyl-4-cyano-6-hydroxy-8-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydroisoquinolin-3-yl]sulfanyl}acetate) the 4-methoxyphenyl group is disposed on one side of the bicyclic core and the oxygen atoms of the hydroxyl and acetyl groups are disposed on the other side. In the crystal, a layered structure parallel to the ac plane is generated by O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds plus C—H⋯π(ring) interactions.
Chemical context
Some tetrahydroisoquinoline (THISQ) based compounds are of medicinal and biological importance, being used as antitumoral (Pingaew et al., 2014 ▸; Castillo et al., 2018 ▸), antifungal (Scott et al., 2002 ▸) and anti-inflammatory agents (Siegfried et al., 1989 ▸). Other tetrahydroisoquinolines were used as inhibitors including B-rafV600E or p38 kinase inhibitors (Lu et al., 2016 ▸; Rosales et al., 2007 ▸). The THISQ core can easily be functionalized to build other heterocyclic rings on the carbocyclic ring (Xu et al., 2002 ▸; Carroll et al., 2007 ▸; Demers et al., 2008 ▸, Marae et al., 2021a
▸). Recently, we have used some compounds related to THISQ as durable fluorescent dyes for cotton (Marae et al., 2021b
▸). The widespread importance of these compounds motivated us to further study the THISQ core. Here we report the synthesis and crystal structure determination of the title compound.
Structural commentary
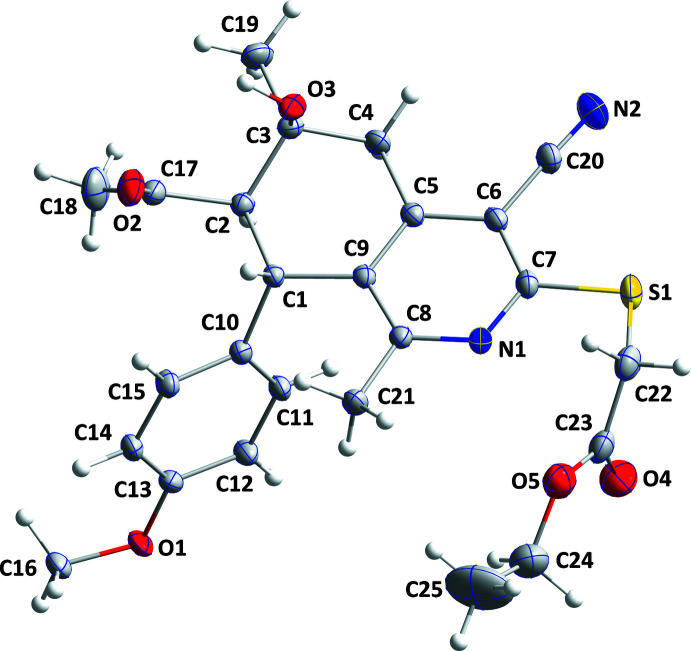
The ethyl sulfanylacetate, acetyl and cyano groups and both methyl groups (C19 and C21) are in equatorial positions with respect to the bicyclic core, while the hydroxyl and anisole groups on the cyclohexane ring occupy an axial and bisectional position, respectively (Fig. 1 ▸). The C10–C15 benzene ring is inclined to the N1/C5–C9 pyridine ring by 82.57 (6)°. The C1–C5/C9 cyclohexane ring is in an envelope conformation, with atom C3 at the flap position [deviation from best plane = 0.367 (1) Å] and puckering parameters (Cremer & Pople, 1975 ▸) Q T = 0.5180 (12) Å, θ = 53.85 (13)° and φ = 109.07 (17)°.
Figure 1.
The title molecule with labelling scheme and 50% probability ellipsoids.
Supramolecular features
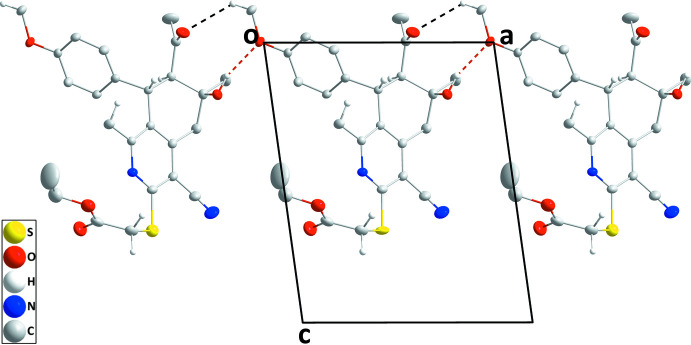
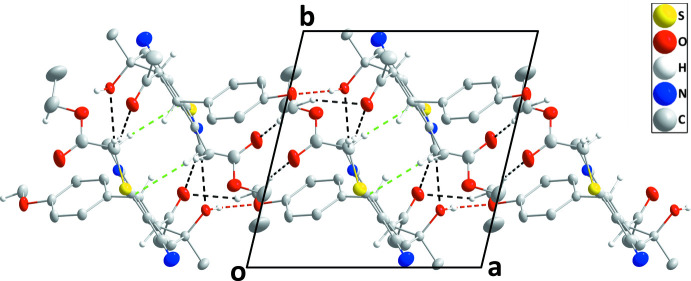
In the crystal of the title compound, chains of molecules extending along the a-axis direction are formed by O3—H3⋯O1 and C16—H16C⋯O2 hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 2 ▸). These are connected into layers parallel to the ac plane by C21—H21A⋯O2, C22—H22A⋯O3 and C24—H24B⋯O4 hydrogen bonds as well as C22—H22B⋯Cg1 interactions (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 3 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of the N1/C5–C9 pyridine ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3—H3⋯O1i | 0.90 (2) | 2.05 (2) | 2.9283 (12) | 164 (2) |
| C16—H16C⋯O2ii | 0.98 | 2.47 | 3.1566 (15) | 127 |
| C21—H21A⋯O2iii | 0.98 | 2.51 | 3.3956 (15) | 150 |
| C22—H22A⋯O3iv | 0.99 | 2.44 | 3.1815 (15) | 131 |
| C22—H22B⋯Cg1iv | 0.99 | 2.58 | 3.4559 (15) | 147 |
| C24—H24B⋯O4v | 0.99 | 2.52 | 3.442 (2) | 154 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y, z; (ii) x-1, y, z; (iii) -x+1, -y+1, -z; (iv) -x+1, -y+1, -z+1; (v) -x, -y+1, -z+1.
Figure 2.
A portion of one chain viewed along the b-axis direction. O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are depicted by red and black dashed lines, respectively.
Figure 3.
Packing viewed along the c-axis direction giving an elevation view of one layer. Hydrogen bonds are depicted as in Fig. 2 ▸ while C—H⋯π(ring) interactions are indicated by green dashed lines.
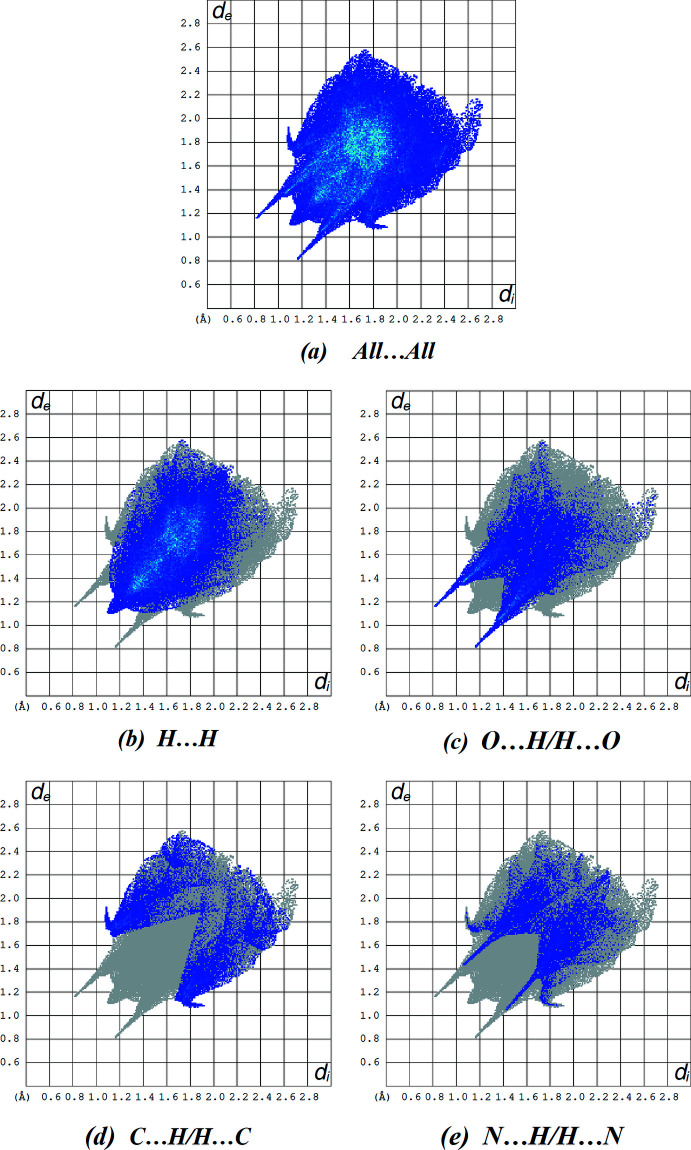
Hirshfeld surface analysis
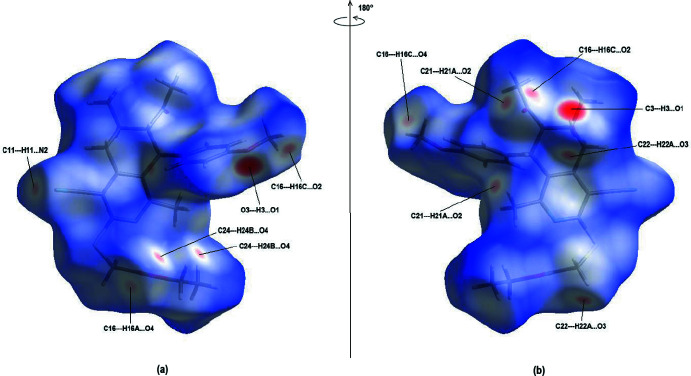
Hirshfeld surface analysis (Spackman & Jayatilaka, 2009 ▸) was carried out using CrystalExplorer17.5 (Turner et al., 2017 ▸). The Hirshfeld surface and their associated two-dimensional fingerprint plots were used to quantify the various intermolecular interactions in the title compound. In the Hirshfeld surface plotted over d norm in the range −0.4903 (red) to +1.6396 (blue) a.u. (Fig. 4 ▸), the white areas indicate contacts with distances equal to the sum of van der Waals radii, and the red and blue areas indicate distances shorter (in close contact) or longer (distinct contact) than the van der Waals radii, respectively (Venkatesan et al., 2016 ▸). The bright-red spots indicate their roles as the respective donors and/or acceptors.
Figure 4.
(a) Front and (b) back sides of the three-dimensional Hirshfeld surface of the title compound mapped over d norm, with a fixed colour scale of −0.4903 (red) to +1.6396 (blue) a.u.
Fingerprint plots (Fig. 5 ▸ b–e; Table 2 ▸) reveal that H⋯H (47.6%), O⋯H/H⋯O (19.7%), C⋯H/H⋯C (12.5%) and N⋯H/H⋯N (11.6%) interactions make the greatest contributions to the surface contacts. S⋯H/H⋯S (6.4%), N⋯C/C⋯N (0.7%), O⋯C/C⋯O (0.5%), O⋯O (0.5%) and C⋯C (0.4%) contacts also contribute to the overall crystal packing of the title compound. The Hirshfeld surface analysis confirms the importance of H-atom contacts in establishing the packing. The large number of H⋯H, O⋯H, C⋯H and N⋯H interactions suggest that van der Waals interactions and hydrogen bonding play the major roles in the crystal packing (Hathwar et al., 2015 ▸).
Figure 5.
Two-dimensional fingerprint plots for the title compound, showing (a) all interactions, and delineated into (b) H⋯H, (c) O⋯H/H⋯O, (d) C⋯H/H⋯C and (e) N⋯H/H⋯N interactions. The d i and d e values are the closest internal and external distances (in Å) from given points on the Hirshfeld surface.
Table 2. Summary of short interatomic contacts (Å) in the title compound.
| Contact | Distance | Symmetry operation |
|---|---|---|
| O1⋯H3 | 2.051 (16) | −1 + x, y, z |
| H21A⋯O2 | 2.51 | 1 − x, 1 − y, −z |
| H22A⋯O3 | 2.44 | 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z |
| O4⋯H16A | 2.60 | x, y, 1 + z |
| H24B⋯H24B | 2.44 | −x, 1 − y, 1 − z |
| H11⋯N2 | 2.61 | 1 − x, − y, 1 − z |
| H18B⋯H2 | 2.49 | 1 − x, − y, −z |
| H21C⋯H16B | 2.51 | −x, 1 − y, −z |
| H25B⋯H25B | 2.34 | −x, 2 − y, 1 − z |
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD version 5.42, updated September 2021; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for tetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives gave nine compounds very similar to the title compound. In the crystal of NAQRIJ (Mague et al., 2017 ▸), dimers form through complementary sets of inversion-related O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. These are connected into zigzag chains along the c-axis direction by pairwise C—H⋯N interactions that also form inversion dimers. In KUGLIK (Langenohl et al., 2020 ▸), the heterocyclic amines are alternately connected to the hydrogen-bonding system along the c axis, which leads to the formation of syndiotactic polymer chains in this direction. In the crystal of DUSVIZ (Selvaraj et al., 2020 ▸), molecules are linked via C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. In AKIVUO (Al-Taifi et al., 2021 ▸), a layered structure with layers parallel to (10
 ) is generated by O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. In ULUTAZ (Naghiyev et al., 2021 ▸), molecules are linked via N—H⋯O and C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional network, and the crystal packing is dominated by C—H⋯π bonds. In CARCOQ (Lehmann et al., 2017 ▸), molecules are linked by O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming chains propagating along the a-axis direction. The chains are linked by C—H⋯F hydrogen bonds, forming layers lying parallel to the ab plane. In POPYEB (Ben Ali et al., 2019 ▸), molecules are packed in a herringbone manner parallel to (103) and (10
) is generated by O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. In ULUTAZ (Naghiyev et al., 2021 ▸), molecules are linked via N—H⋯O and C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional network, and the crystal packing is dominated by C—H⋯π bonds. In CARCOQ (Lehmann et al., 2017 ▸), molecules are linked by O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming chains propagating along the a-axis direction. The chains are linked by C—H⋯F hydrogen bonds, forming layers lying parallel to the ab plane. In POPYEB (Ben Ali et al., 2019 ▸), molecules are packed in a herringbone manner parallel to (103) and (10
 ) via weak C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π(ring) interactions. In ENOCIU (Naicker et al., 2011 ▸) various C—H⋯π and C—H⋯O bonds link the molecules together. In NIWPAL (Bouasla et al., 2008 ▸), the molecules are linked by N—H⋯O intermolecular hydrogen bonds involving the sulfonamide function to form an infinite two-dimensional network parallel to the (001) plane.
) via weak C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π(ring) interactions. In ENOCIU (Naicker et al., 2011 ▸) various C—H⋯π and C—H⋯O bonds link the molecules together. In NIWPAL (Bouasla et al., 2008 ▸), the molecules are linked by N—H⋯O intermolecular hydrogen bonds involving the sulfonamide function to form an infinite two-dimensional network parallel to the (001) plane.
Synthesis and crystallization
7-Acetyl-4-cyano-1,6-dimethyl-6-hydroxy-8-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-isoquinoline-3(2H)-thione (5 mmol, 1.91 g) and sodium acetate trihydrate (1.36 g, 10 mmol) were suspended in 50 ml of absolute ethanol, then 0.55 ml of ethyl chloroacetate (5.3 mmol) were added and the mixture was refluxed for one h. During reflux, the yellow colour disappeared gradually over time to afford a colourless reaction mixture. The reaction mixture was then left to cool at room temperature and the formed precipitate was collected by fiitration, washed with water, dried in air and recystallized from ethanol to give the title compound as cubic crystals, yield 2.11 g (94%); m.p. 453–455 K. IR (cm−1): 3454 (O—H); 3048 (C—H aromatic); 2970, 2913 (C—H aliphatic); 2215 (C≡N); 1743 (C=O, ester); 1697 (C=O, acetyl). 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz) δ: 6.80–6.86 (dd, J = 8 Hz, 4H, ArH), 4.24–4.26 (d, J = 8 Hz, 1H, C8H), 4.12–4.15 (q, J = 6 Hz, 2H, OCH2), 3.89–3.92 (dd, 2H, SCH2), 3.78 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.38 (s, 1H, OH), 3.09–3.12 (d, J = 12 Hz, 1H, C5H), 3.03–3.05 (d, J = 8 Hz, 1H, C7H), 2.89–2.92 (d, J = 12 Hz, 1H, C5H), 1. 90 (s, 3H, CH3 at C-1), 1.80 (s, 3H, COCH3), 1.34 (s, 3H, CH3 at C-6), 1.18–1.21 (t, J = 6 Hz, 3H, CH3 of ester group).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. All C-bound H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions (C—H = 0.95–1.00 Å) while the hydrogen atom attached to O3 was found from a difference map, and was subsequently refined isotropically [O3—H3 = 0.903 (17) Å] with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(O). All C-bound H atoms were included as riding contributions with isotropic displacement parameters 1.2 times those of the parent atoms (1.5 for methyl groups).
Table 3. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C25H28N2O5S |
| M r | 468.55 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P\overline{1} |
| Temperature (K) | 150 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 10.0643 (6), 10.3592 (7), 12.0685 (8) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 83.296 (1), 80.770 (1), 75.638 (1) |
| V (Å3) | 1199.23 (13) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.17 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.35 × 0.29 × 0.27 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker SMART APEX CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.82, 0.96 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 22695, 6509, 5177 |
| R int | 0.023 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.695 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.045, 0.133, 1.11 |
| No. of reflections | 6509 |
| No. of parameters | 305 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.71, −0.22 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022000378/vm2259sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022000378/vm2259Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022000378/vm2259Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2141278
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
JTM thanks Tulane University for support of the Tulane Crystallography Laboratory. Author contributions are as follows: synthesis and organic chemistry parts preparation, EAA, YAE, ISM; conceptualization and study guide, EAB, SKM; financial support, EAA; crystal data production and validation, JTM; paper preparation and Hirshfeld study, MA.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C25H28N2O5S | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 468.55 | F(000) = 496 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.298 Mg m−3 |
| a = 10.0643 (6) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 10.3592 (7) Å | Cell parameters from 9995 reflections |
| c = 12.0685 (8) Å | θ = 2.5–29.5° |
| α = 83.296 (1)° | µ = 0.17 mm−1 |
| β = 80.770 (1)° | T = 150 K |
| γ = 75.638 (1)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1199.23 (13) Å3 | 0.35 × 0.29 × 0.27 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 6509 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 5177 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.023 |
| Detector resolution: 8.3333 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 29.6°, θmin = 1.7° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −13→13 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | k = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.82, Tmax = 0.96 | l = −16→16 |
| 22695 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: dual |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.045 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.133 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.11 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0848P)2 + 0.0389P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 6509 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 305 parameters | Δρmax = 0.71 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. The diffraction data were obtained from 3 sets of 400 frames, each of width 0.5° in ω, colllected at φ = 0.00, 90.00 and 180.00° and 2 sets of 800 frames, each of width 0.45° in φ, collected at ω = –30.00 and 210.00°. The scan time was 10 sec/frame. |
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. H-atoms attached to carbon were placed in calculated positions (C—H = 0.95 - 1.00 Å) while that attached to oxygen was placed in a location derived from a difference map and its coordinates adjusted to give O—H = 0.87 %A. All were included as riding contributions with isotropic displacement parameters 1.2 - 1.5 times those of the attached atoms. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.40179 (4) | 0.33194 (3) | 0.67126 (2) | 0.02919 (11) | |
| O1 | −0.01601 (8) | 0.26808 (9) | −0.00282 (7) | 0.0261 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.65454 (10) | 0.31103 (10) | −0.03628 (7) | 0.0325 (2) | |
| O3 | 0.76674 (8) | 0.24179 (8) | 0.18545 (7) | 0.02199 (18) | |
| H3 | 0.8202 (16) | 0.2524 (10) | 0.1190 (13) | 0.033* | |
| O4 | 0.08897 (11) | 0.46076 (12) | 0.66388 (9) | 0.0455 (3) | |
| O5 | 0.13749 (11) | 0.65264 (10) | 0.58156 (8) | 0.0357 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.35085 (10) | 0.41231 (10) | 0.46279 (8) | 0.0208 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.67128 (14) | 0.03469 (14) | 0.60676 (11) | 0.0424 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.46954 (11) | 0.29768 (11) | 0.16884 (9) | 0.0159 (2) | |
| H1 | 0.500590 | 0.379658 | 0.134272 | 0.019* | |
| C2 | 0.57706 (11) | 0.17513 (11) | 0.12120 (9) | 0.0173 (2) | |
| H2 | 0.531350 | 0.098468 | 0.129582 | 0.021* | |
| C3 | 0.70498 (11) | 0.13262 (11) | 0.18391 (9) | 0.0193 (2) | |
| C4 | 0.65493 (12) | 0.09343 (12) | 0.30675 (10) | 0.0223 (2) | |
| H4A | 0.620266 | 0.011333 | 0.310543 | 0.027* | |
| H4B | 0.734138 | 0.072924 | 0.350225 | 0.027* | |
| C5 | 0.54209 (11) | 0.20148 (11) | 0.35998 (9) | 0.0179 (2) | |
| C6 | 0.52467 (11) | 0.20985 (12) | 0.47729 (9) | 0.0199 (2) | |
| C7 | 0.42631 (12) | 0.31658 (12) | 0.52466 (9) | 0.0205 (2) | |
| C8 | 0.36570 (11) | 0.40524 (11) | 0.35083 (9) | 0.0177 (2) | |
| C9 | 0.45724 (11) | 0.29873 (11) | 0.29599 (9) | 0.0166 (2) | |
| C10 | 0.33305 (11) | 0.30117 (11) | 0.12715 (9) | 0.0176 (2) | |
| C11 | 0.24375 (12) | 0.22431 (12) | 0.18378 (9) | 0.0206 (2) | |
| H11 | 0.263234 | 0.176107 | 0.253526 | 0.025* | |
| C12 | 0.12671 (12) | 0.21705 (12) | 0.13990 (10) | 0.0227 (2) | |
| H12 | 0.065702 | 0.165748 | 0.180301 | 0.027* | |
| C13 | 0.09882 (11) | 0.28515 (12) | 0.03646 (9) | 0.0200 (2) | |
| C14 | 0.18526 (12) | 0.36397 (12) | −0.02017 (9) | 0.0225 (2) | |
| H14 | 0.165733 | 0.412138 | −0.089914 | 0.027* | |
| C15 | 0.30109 (12) | 0.37198 (12) | 0.02605 (9) | 0.0212 (2) | |
| H15 | 0.359409 | 0.427055 | −0.012431 | 0.025* | |
| C16 | −0.03346 (13) | 0.32073 (14) | −0.11635 (10) | 0.0267 (3) | |
| H16A | 0.052176 | 0.288044 | −0.166573 | 0.040* | |
| H16B | −0.054905 | 0.418620 | −0.120457 | 0.040* | |
| H16C | −0.109566 | 0.291484 | −0.139534 | 0.040* | |
| C17 | 0.61828 (12) | 0.20825 (12) | −0.00420 (10) | 0.0227 (2) | |
| C18 | 0.60948 (18) | 0.11357 (16) | −0.08583 (12) | 0.0404 (4) | |
| H18A | 0.654485 | 0.138974 | −0.160555 | 0.061* | |
| H18B | 0.512060 | 0.117187 | −0.089559 | 0.061* | |
| H18C | 0.656149 | 0.022519 | −0.060849 | 0.061* | |
| C19 | 0.81182 (13) | 0.01430 (13) | 0.13312 (11) | 0.0280 (3) | |
| H19A | 0.849094 | 0.041750 | 0.056329 | 0.042* | |
| H19B | 0.767456 | −0.059489 | 0.131300 | 0.042* | |
| H19C | 0.887278 | −0.015108 | 0.179227 | 0.042* | |
| C20 | 0.60828 (13) | 0.11221 (13) | 0.54794 (10) | 0.0258 (3) | |
| C21 | 0.27853 (12) | 0.52205 (12) | 0.29046 (10) | 0.0236 (2) | |
| H21A | 0.327912 | 0.540938 | 0.215809 | 0.035* | |
| H21B | 0.259623 | 0.600477 | 0.333793 | 0.035* | |
| H21C | 0.190956 | 0.501257 | 0.282226 | 0.035* | |
| C22 | 0.31143 (14) | 0.50489 (13) | 0.67068 (10) | 0.0286 (3) | |
| H22A | 0.305095 | 0.534976 | 0.746654 | 0.034* | |
| H22B | 0.366449 | 0.558138 | 0.617296 | 0.034* | |
| C23 | 0.16744 (14) | 0.53363 (14) | 0.63858 (10) | 0.0303 (3) | |
| C24 | 0.00183 (17) | 0.68891 (18) | 0.54348 (14) | 0.0490 (4) | |
| H24A | −0.072036 | 0.696185 | 0.608938 | 0.059* | |
| H24B | −0.007797 | 0.619864 | 0.497063 | 0.059* | |
| C25 | −0.0099 (3) | 0.8197 (2) | 0.4757 (3) | 0.0934 (9) | |
| H25A | 0.062343 | 0.810824 | 0.410224 | 0.140* | |
| H25B | 0.001445 | 0.886882 | 0.522048 | 0.140* | |
| H25C | −0.101112 | 0.847711 | 0.450117 | 0.140* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0375 (2) | 0.03615 (19) | 0.01391 (15) | −0.00874 (14) | −0.00410 (13) | −0.00088 (12) |
| O1 | 0.0185 (4) | 0.0418 (5) | 0.0196 (4) | −0.0100 (4) | −0.0083 (3) | 0.0052 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0360 (5) | 0.0411 (6) | 0.0226 (5) | −0.0181 (4) | 0.0007 (4) | 0.0018 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0192 (4) | 0.0271 (4) | 0.0219 (4) | −0.0090 (3) | −0.0012 (3) | −0.0056 (3) |
| O4 | 0.0337 (6) | 0.0612 (7) | 0.0426 (6) | −0.0229 (5) | −0.0002 (5) | 0.0106 (5) |
| O5 | 0.0392 (5) | 0.0333 (5) | 0.0325 (5) | −0.0047 (4) | −0.0021 (4) | −0.0057 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0213 (5) | 0.0254 (5) | 0.0155 (4) | −0.0052 (4) | −0.0023 (4) | −0.0012 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0461 (7) | 0.0444 (7) | 0.0312 (6) | −0.0021 (6) | −0.0128 (6) | 0.0117 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0158 (5) | 0.0182 (5) | 0.0142 (5) | −0.0049 (4) | −0.0033 (4) | 0.0001 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0163 (5) | 0.0195 (5) | 0.0168 (5) | −0.0050 (4) | −0.0017 (4) | −0.0027 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0171 (5) | 0.0204 (5) | 0.0206 (5) | −0.0041 (4) | −0.0022 (4) | −0.0033 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0207 (5) | 0.0217 (6) | 0.0214 (6) | −0.0006 (4) | −0.0038 (4) | 0.0020 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0174 (5) | 0.0193 (5) | 0.0177 (5) | −0.0061 (4) | −0.0037 (4) | 0.0013 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0188 (5) | 0.0237 (6) | 0.0171 (5) | −0.0059 (4) | −0.0049 (4) | 0.0034 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0230 (5) | 0.0254 (6) | 0.0145 (5) | −0.0091 (5) | −0.0029 (4) | 0.0008 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0158 (5) | 0.0223 (5) | 0.0154 (5) | −0.0053 (4) | −0.0023 (4) | −0.0012 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0154 (5) | 0.0203 (5) | 0.0153 (5) | −0.0064 (4) | −0.0030 (4) | −0.0002 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0168 (5) | 0.0206 (5) | 0.0151 (5) | −0.0031 (4) | −0.0032 (4) | −0.0018 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0194 (5) | 0.0267 (6) | 0.0156 (5) | −0.0060 (4) | −0.0050 (4) | 0.0033 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0183 (5) | 0.0314 (6) | 0.0193 (5) | −0.0099 (5) | −0.0038 (4) | 0.0048 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0152 (5) | 0.0271 (6) | 0.0175 (5) | −0.0030 (4) | −0.0040 (4) | −0.0020 (4) |
| C14 | 0.0216 (5) | 0.0291 (6) | 0.0157 (5) | −0.0045 (5) | −0.0054 (4) | 0.0031 (4) |
| C15 | 0.0218 (5) | 0.0250 (6) | 0.0175 (5) | −0.0086 (4) | −0.0036 (4) | 0.0034 (4) |
| C16 | 0.0222 (6) | 0.0387 (7) | 0.0197 (6) | −0.0058 (5) | −0.0095 (5) | 0.0020 (5) |
| C17 | 0.0189 (5) | 0.0308 (6) | 0.0182 (5) | −0.0050 (5) | −0.0016 (4) | −0.0040 (5) |
| C18 | 0.0571 (10) | 0.0423 (8) | 0.0242 (7) | −0.0115 (7) | −0.0059 (6) | −0.0121 (6) |
| C19 | 0.0229 (6) | 0.0268 (6) | 0.0309 (7) | 0.0021 (5) | −0.0023 (5) | −0.0085 (5) |
| C20 | 0.0283 (6) | 0.0292 (6) | 0.0191 (6) | −0.0073 (5) | −0.0042 (5) | 0.0043 (5) |
| C21 | 0.0238 (6) | 0.0243 (6) | 0.0194 (5) | 0.0011 (5) | −0.0040 (5) | −0.0011 (4) |
| C22 | 0.0335 (7) | 0.0344 (7) | 0.0209 (6) | −0.0127 (5) | −0.0005 (5) | −0.0081 (5) |
| C23 | 0.0315 (7) | 0.0387 (7) | 0.0197 (6) | −0.0099 (6) | 0.0045 (5) | −0.0059 (5) |
| C24 | 0.0383 (8) | 0.0555 (10) | 0.0449 (9) | 0.0022 (7) | −0.0026 (7) | −0.0031 (8) |
| C25 | 0.0751 (16) | 0.0498 (12) | 0.139 (3) | 0.0112 (11) | −0.0281 (16) | 0.0228 (14) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C7 | 1.7672 (11) | C10—C11 | 1.3927 (15) |
| S1—C22 | 1.7966 (14) | C11—C12 | 1.3882 (16) |
| O1—C13 | 1.3742 (14) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| O1—C16 | 1.4355 (14) | C12—C13 | 1.3940 (15) |
| O2—C17 | 1.2116 (15) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| O3—C3 | 1.4223 (14) | C13—C14 | 1.3863 (16) |
| O3—H3 | 0.903 (17) | C14—C15 | 1.3944 (16) |
| O4—C23 | 1.2046 (17) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| O5—C23 | 1.3298 (17) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| O5—C24 | 1.457 (2) | C16—H16A | 0.9800 |
| N1—C7 | 1.3240 (15) | C16—H16B | 0.9800 |
| N1—C8 | 1.3439 (14) | C16—H16C | 0.9800 |
| N2—C20 | 1.1443 (17) | C17—C18 | 1.4956 (18) |
| C1—C9 | 1.5206 (14) | C18—H18A | 0.9800 |
| C1—C10 | 1.5278 (15) | C18—H18B | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.5501 (15) | C18—H18C | 0.9800 |
| C1—H1 | 1.0000 | C19—H19A | 0.9800 |
| C2—C17 | 1.5258 (15) | C19—H19B | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.5421 (15) | C19—H19C | 0.9800 |
| C2—H2 | 1.0000 | C21—H21A | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.5290 (16) | C21—H21B | 0.9800 |
| C3—C19 | 1.5311 (15) | C21—H21C | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.5028 (16) | C22—C23 | 1.5093 (19) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9900 | C22—H22A | 0.9900 |
| C4—H4B | 0.9900 | C22—H22B | 0.9900 |
| C5—C9 | 1.3941 (15) | C24—C25 | 1.488 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.4087 (15) | C24—H24A | 0.9900 |
| C6—C7 | 1.3972 (16) | C24—H24B | 0.9900 |
| C6—C20 | 1.4369 (16) | C25—H25A | 0.9800 |
| C8—C9 | 1.4053 (15) | C25—H25B | 0.9800 |
| C8—C21 | 1.4957 (15) | C25—H25C | 0.9800 |
| C10—C15 | 1.3893 (15) | ||
| C7—S1—C22 | 98.39 (6) | C13—C14—C15 | 119.48 (10) |
| C13—O1—C16 | 116.26 (9) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.3 |
| C3—O3—H3 | 109.5 | C15—C14—H14 | 120.3 |
| C23—O5—C24 | 115.10 (12) | C10—C15—C14 | 121.43 (11) |
| C7—N1—C8 | 119.27 (10) | C10—C15—H15 | 119.3 |
| C9—C1—C10 | 113.57 (9) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.3 |
| C9—C1—C2 | 113.46 (9) | O1—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C10—C1—C2 | 106.92 (8) | O1—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C9—C1—H1 | 107.5 | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C10—C1—H1 | 107.5 | O1—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 107.5 | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C17—C2—C3 | 111.24 (9) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C17—C2—C1 | 108.37 (9) | O2—C17—C18 | 121.16 (12) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 112.73 (9) | O2—C17—C2 | 120.04 (11) |
| C17—C2—H2 | 108.1 | C18—C17—C2 | 118.78 (11) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 108.1 | C17—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 108.1 | C17—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| O3—C3—C4 | 106.22 (9) | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| O3—C3—C19 | 110.37 (9) | C17—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C19 | 109.61 (10) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| O3—C3—C2 | 111.05 (9) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 107.54 (9) | C3—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C19—C3—C2 | 111.84 (9) | C3—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 112.68 (9) | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 109.1 | C3—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 109.1 | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4B | 109.1 | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4B | 109.1 | N2—C20—C6 | 177.83 (14) |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 107.8 | C8—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C9—C5—C6 | 118.33 (10) | C8—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C9—C5—C4 | 121.92 (10) | H21A—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.67 (10) | C8—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 119.09 (10) | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C20 | 119.89 (10) | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C20 | 121.00 (11) | C23—C22—S1 | 114.39 (9) |
| N1—C7—C6 | 122.29 (10) | C23—C22—H22A | 108.7 |
| N1—C7—S1 | 116.98 (9) | S1—C22—H22A | 108.7 |
| C6—C7—S1 | 120.69 (9) | C23—C22—H22B | 108.7 |
| N1—C8—C9 | 122.66 (10) | S1—C22—H22B | 108.7 |
| N1—C8—C21 | 113.87 (10) | H22A—C22—H22B | 107.6 |
| C9—C8—C21 | 123.45 (10) | O4—C23—O5 | 124.65 (13) |
| C5—C9—C8 | 118.17 (10) | O4—C23—C22 | 124.79 (13) |
| C5—C9—C1 | 121.80 (10) | O5—C23—C22 | 110.53 (11) |
| C8—C9—C1 | 119.86 (9) | O5—C24—C25 | 107.60 (17) |
| C15—C10—C11 | 118.27 (10) | O5—C24—H24A | 110.2 |
| C15—C10—C1 | 120.46 (10) | C25—C24—H24A | 110.2 |
| C11—C10—C1 | 121.02 (9) | O5—C24—H24B | 110.2 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 121.02 (10) | C25—C24—H24B | 110.2 |
| C12—C11—H11 | 119.5 | H24A—C24—H24B | 108.5 |
| C10—C11—H11 | 119.5 | C24—C25—H25A | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 119.91 (10) | C24—C25—H25B | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—H12 | 120.0 | H25A—C25—H25B | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 120.0 | C24—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| O1—C13—C14 | 124.12 (10) | H25A—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| O1—C13—C12 | 116.04 (10) | H25B—C25—H25C | 109.5 |
| C14—C13—C12 | 119.84 (10) | ||
| C9—C1—C2—C17 | −159.86 (9) | C21—C8—C9—C5 | 174.35 (10) |
| C10—C1—C2—C17 | 74.15 (10) | N1—C8—C9—C1 | −179.57 (10) |
| C9—C1—C2—C3 | −36.30 (12) | C21—C8—C9—C1 | −0.96 (16) |
| C10—C1—C2—C3 | −162.29 (9) | C10—C1—C9—C5 | 125.98 (11) |
| C17—C2—C3—O3 | 67.55 (12) | C2—C1—C9—C5 | 3.61 (14) |
| C1—C2—C3—O3 | −54.40 (12) | C10—C1—C9—C8 | −58.88 (13) |
| C17—C2—C3—C4 | −176.63 (9) | C2—C1—C9—C8 | 178.74 (9) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 61.42 (12) | C9—C1—C10—C15 | 143.67 (11) |
| C17—C2—C3—C19 | −56.24 (13) | C2—C1—C10—C15 | −90.40 (12) |
| C1—C2—C3—C19 | −178.19 (9) | C9—C1—C10—C11 | −42.15 (14) |
| O3—C3—C4—C5 | 64.88 (12) | C2—C1—C10—C11 | 83.77 (12) |
| C19—C3—C4—C5 | −175.88 (10) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | 0.81 (17) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −54.09 (12) | C1—C10—C11—C12 | −173.49 (10) |
| C3—C4—C5—C9 | 23.77 (15) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 1.36 (18) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −153.08 (10) | C16—O1—C13—C14 | 9.11 (16) |
| C9—C5—C6—C7 | −1.73 (16) | C16—O1—C13—C12 | −170.76 (10) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 175.24 (10) | C11—C12—C13—O1 | 177.43 (10) |
| C9—C5—C6—C20 | 179.59 (11) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −2.44 (18) |
| C4—C5—C6—C20 | −3.44 (17) | O1—C13—C14—C15 | −178.52 (11) |
| C8—N1—C7—C6 | 2.08 (18) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 1.34 (18) |
| C8—N1—C7—S1 | 179.98 (8) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | −1.94 (17) |
| C5—C6—C7—N1 | −1.67 (18) | C1—C10—C15—C14 | 172.40 (10) |
| C20—C6—C7—N1 | 177.03 (11) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | 0.87 (18) |
| C5—C6—C7—S1 | −179.50 (8) | C3—C2—C17—O2 | −73.61 (14) |
| C20—C6—C7—S1 | −0.80 (16) | C1—C2—C17—O2 | 50.84 (14) |
| C22—S1—C7—N1 | −15.41 (11) | C3—C2—C17—C18 | 107.90 (13) |
| C22—S1—C7—C6 | 162.54 (10) | C1—C2—C17—C18 | −127.65 (12) |
| C7—N1—C8—C9 | 0.94 (17) | C7—S1—C22—C23 | 69.08 (10) |
| C7—N1—C8—C21 | −177.79 (10) | C24—O5—C23—O4 | −3.71 (19) |
| C6—C5—C9—C8 | 4.47 (16) | C24—O5—C23—C22 | 178.31 (11) |
| C4—C5—C9—C8 | −172.42 (10) | S1—C22—C23—O4 | 36.21 (17) |
| C6—C5—C9—C1 | 179.69 (10) | S1—C22—C23—O5 | −145.80 (9) |
| C4—C5—C9—C1 | 2.79 (16) | C23—O5—C24—C25 | −176.43 (17) |
| N1—C8—C9—C5 | −4.26 (16) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the N1/C5–C9 pyridine ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O3—H3···O1i | 0.90 (2) | 2.05 (2) | 2.9283 (12) | 164 (2) |
| C16—H16C···O2ii | 0.98 | 2.47 | 3.1566 (15) | 127 |
| C21—H21A···O2iii | 0.98 | 2.51 | 3.3956 (15) | 150 |
| C22—H22A···O3iv | 0.99 | 2.44 | 3.1815 (15) | 131 |
| C22—H22B···Cg1iv | 0.99 | 2.58 | 3.4559 (15) | 147 |
| C24—H24B···O4v | 0.99 | 2.52 | 3.442 (2) | 154 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y, z; (ii) x−1, y, z; (iii) −x+1, −y+1, −z; (iv) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (v) −x, −y+1, −z+1.
References
- Al-Taifi, E. A., Maraei, I. S., Bakhite, E. A., Demirtas, G., Mague, J. T., Mohamed, S. K. & Ramli, Y. (2021). Acta Cryst. E77, 121–125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ben Ali, K. & Retailleau, P. (2019). Acta Cryst. E75, 1399–1402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bouasla, R., Berredjem, M., Aouf, N.-E. & Barbey, C. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Brandenburg, K. & Putz, H. (2012). DIAMOND, Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2016). APEX3, SADABS and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Carroll, F. I., Robinson, T. P., Brieaddy, L. E., Atkinson, R. N., Mascarella, S. W., Damaj, M. I., Martin, B. R. & Navarro, H. A. (2007). J. Med. Chem. 50, 6383–6391. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Castillo, J.-C., Jiménez, E., Portilla, J., Insuasty, B., Quiroga, J., Moreno-Fuquen, R., Kennedy, A. R. & Abonia, R. (2018). Tetrahedron, 74, 932–947.
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
- Demers, S., Stevenson, H., Candler, J., Bashore, C. G., Arnold, E. P., O’Neill, B. T. & Coe, J. W. (2008). Tetrahedron Lett. 49, 3368–3371.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hathwar, V. R., Sist, M., Jørgensen, M. R. V., Mamakhel, A. H., Wang, X., Hoffmann, C. M., Sugimoto, K., Overgaard, J. & Iversen, B. B. (2015). IUCrJ, 2, 563–574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Krause, L., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sheldrick, G. M. & Stalke, D. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 3–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Langenohl, F., Otte, F. & Strohmann, C. (2020). Acta Cryst. E76, 298–302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, A., Lechner, L., Radacki, K., Braunschweig, H. & Holzgrabe, U. (2017). Acta Cryst. E73, 867–870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lu, B., Cao, H., Cao, J., Huang, S., Hu, Q., Liu, D., Shen, R., Shen, X., Tao, W., Wan, H., Wang, D., Yan, Y., Yang, L., Zhang, J., Zhang, L., Zhang, L. & Zhang, M. (2016). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 26, 819–823. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mague, J. T., Mohamed, S. K., Akkurt, M., Bakhite, E. A. & Albayati, M. R. (2017). IUCrData, 2, x170390.
- Marae, I. S., Bakhite, E. A., Moustafa, O. S., Abbady, M. S., Mohamed, S. K. & Mague, J. T. (2021a). ACS Omega, 6, 8706–8716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Marae, I. S., Sharmoukh, W., Bakhite, E. A., Moustafa, O. S., Abbady, M. S. & Emam, H. (2021b). Cellulose, 28, 5937–5956.
- Naghiyev, F. N., Grishina, M. M., Khrustalev, V. N., Khalilov, A. N., Akkurt, M., Akobirshoeva, A. A. & Mamedov, İ. G. (2021). Acta Cryst. E77, 195–199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Naicker, T., Govender, T., Kruger, H. G. & Maguire, G. E. M. (2011). Acta Cryst. C67, o100–o103. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Pingaew, R., Mandi, P., Nantasenamat, C., Prachayasittikul, S., Ruchirawat, S. & Prachayasittikul, V. (2014). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 81, 192–203. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rosales, A. & Bernado, V. (2007). Pyrazoloisoquinoline Derivatives. WIPO Patent WO2007/060198A12007.
- Scott, J. D. & Williams, R. (2002). Chem. Rev. 102, 1669–1730. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Selvaraj, J. P., Mary, S., Dhruba, J. B., Huidrom, B. S., Panneerselvam, Y. & Piskala Subburaman, K. (2020). Acta Cryst. E76, 1548–1550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Siegfried, L., Helmut, V., Guenther, W., Thomas, S., Eckart, S., Dieter, L., Gunter, L. & Ger East, D. D. (1989). Chem. Abstr. 110, 75554g.
- Spackman, M. A. & Jayatilaka, D. (2009). CrystEngComm, 11, 19–32.
- Turner, M. J., McKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Spackman, M. A., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2017). Crystal Explorer. University of Western Australia.
- Venkatesan, P., Thamotharan, S., Ilangovan, A., Liang, H. & Sundius, T. (2016). Spectrochim. Acta A, 153, 625–636. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xu, R., Dwoskin, L. P., Grinevich, V., Sumithran, S. P. & Crooks, P. A. (2002). Drug Dev. Res. 55, 173–186.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022000378/vm2259sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022000378/vm2259Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022000378/vm2259Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2141278
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report