Abstract
Patients with relapsed/refractory early T-cell precursor lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (ETP-ALL/LBL) respond poorly to traditional therapy and have dismal prognosis. CD7 is a promising therapeutic targets for chimeric antigen receptor modified T cell therapy (CART) due to its widely expression in almost all T-cell malignancies. Here we present the anti-CD7 CART therapy in a 11-year-old male with TP53 mutated relapsed/refractory ETP-ALL/LBL. The patient suffered second relapse after haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, showing resistance to 4 lines salvage therapies including venetoclax. Nanobody derived CD7-CART cells were manufactured by co-transducing CAR-T cells with a CD7 protein expression blocker. 70.5% of blasts (CD7 expression: 92.6%) and extensive extramedullary disease (mediastinal mass, enlarged lymph nodes and spleen) were observed prior to CD7-CART-cell therapy. A total of 5 × 106/kg donor-derived CD7-CART-cells were infused. Hematological and extramedullary remission were both achieved, with persistence of CD7-CART-cells be detected until the last followup at 96th days after the infusion. Reversible adverse effects including grade 3 cytokine release syndrome and macrophage activation syndrome were observed. This case demonstrated that CD7-CART was a potent and safe salvage therapy in relapsed/refractory ETP-ALL/LBL patient with high tumor burden.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials. gov, NCT04785833, Registered on March 8, 2021, prospectively registered.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s40364-022-00352-w.
Keywords: Chimeric antigen receptor T-cells, CD7, Early T-cell precursor lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma, Relapsed / refractory
To the editor:
Early T cell precursor lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (ETP-ALL/LBL) shows higher remission failure/relapse rates and worse outcomes compared with other T-ALL subtypes [1, 2]. CAR T-cell therapy is a promising salvage strategy in T-ALL, however, it has not been independently reported in ETP-ALL/LBL patients. Manufacturing difficulty resulted from shared expression of antigens between normal and malignant T-cells poses the main challenge [3]. We constructed the first CD7 CAR-modified NK cell lines based on anti-CD7 nanobody sequences [4] and demonstrated its robust anti-tumor activity against malignant T cells in vitro. Base on this, we developed non gene-editing CD7 CAR-T cells which overcome the fratricide of CD7 CAR-T cells through preventing expression of CD7 in the cell membrane with a protein expression blocker [5] (Fig. 1a, Supplementary Fig. 1–2). Here, we report the successful application of this anti-CD7 CAR-T cell product in a relapsed/refractory ETP-ALL/LBL patient.
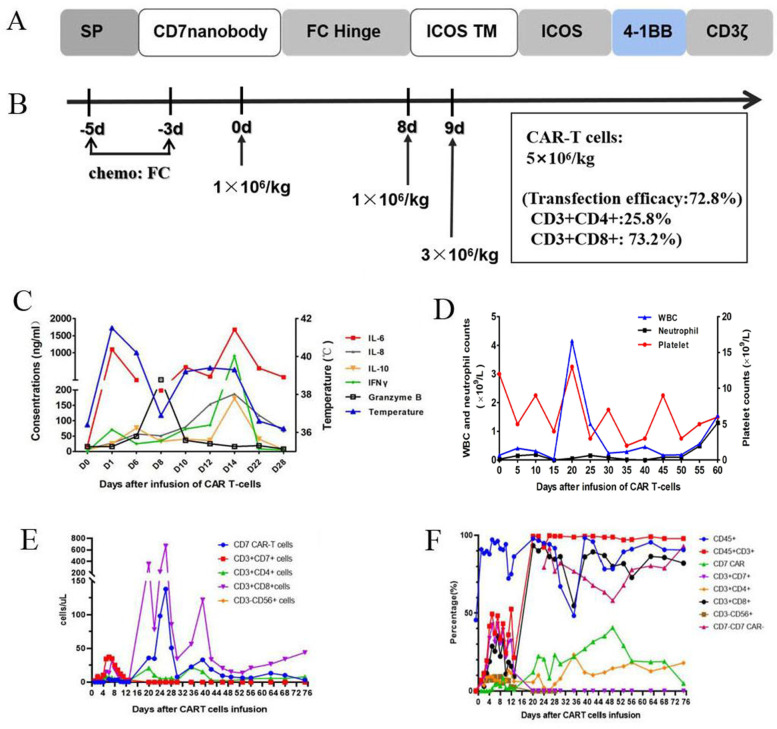
Fig. 1.
Characteristics of CD7 CAR T-cells (a, b) and change of cytokines and amplification of CAR T-cells (c-f). a, Schematic structure of the CD7 CAR T-cells; b, CAR-T cells were infused at a total of 5 × 106/kg for 3 days; c Change of cytokines and temperature in the first month after CD7 CAR T-cells infusion. d Change of blood cell counts after CD7 CAR T-cells infusion. e, f Flowcytometry analysis of absolute (e) and relative CAR T-cell copies and the fraction of T-cells (f) in the peripheral blood samples after CAR T-cells infusion
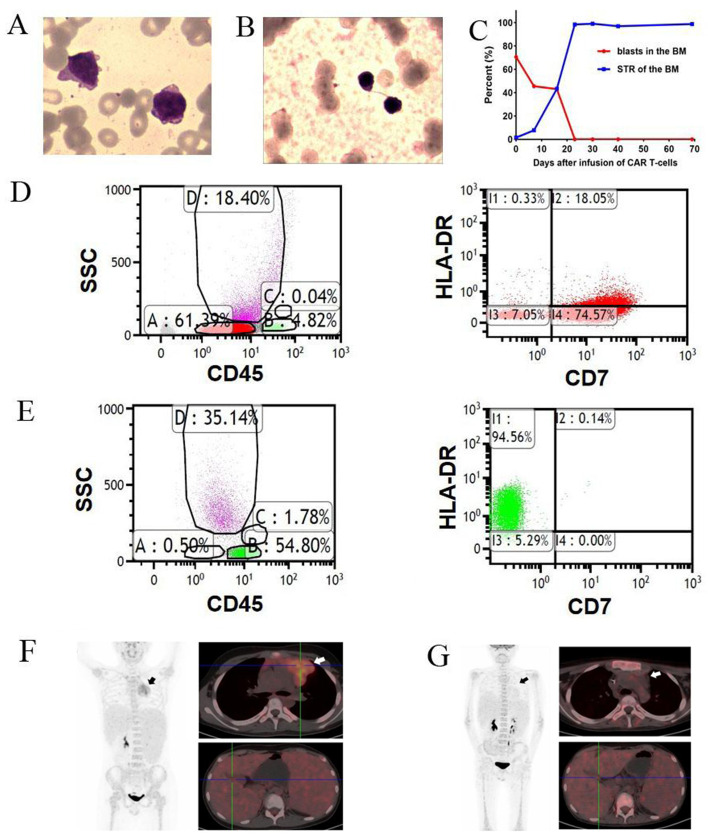
An 11-year-old male was diagnosed with ETP-ALL/LBL in February 2016. He underwent haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation at CR2 in January 2019. The disease relapsed again in January 2021. After failure of 4 lines of salvage therapies (venetoclax with decitabine, high-dose cytarabine-based chemotherapy, chidamide and donor-derived CD38 CAR-T cell therapy), he was enrolled in an anti-CD7 CAR-T clinical trial (NCT04785833). Before infusion of anti-CD7 CAR-T cells, bone marrow (BM) showed 70.5% of blasts (Fig. 2a). A complex karyotype with ETV6, NOTCH1 and TP53 mutations were detected. Only 1.5% of donor cells were detected in the BM (Fig. 2c). Flow cytometry revealed 58.5% of blasts (positive for cCD3/CD7/CD15/CD33/CD34; weakly positive for CD5 and negative for CD1a/CD8). 92.6% of blasts were positive for CD7 (Fig. 2d) (Supplementary Table 1). PET-CT scan revealed extensive extramedullary involvement, including a mediastinal mass (5.0 cm × 5.7 cm × 4.7 cm) and high FDG metabolism in the spleen and nasopharyngeal, cervical, mediastinal, abdominal, and inguinal lymph nodes (Fig. 2f). Chemotherapy (fludarabine 30 mg/m2 and cyclophosphamide 300 mg/m2) was administered 5, 4, and 3 days before the first infusion of HSCT donor-derived CAR-T cells (April 15, 2021), followed by two once-daily infusions at 8 and 9 days after the first infusion. The effective anti-CD7 CAR-T cells totaled 5 × 106 cells/kg (Fig. 1b).
Fig. 2.
BM analysis and PET-CT scan of the patient before and after CD7 CAR T-cells infusion. a, BM morphology before infusion of CD7 CAR T-cells; b, BM morphology after infusion of CD7 CAR T-cells; c, Change of percentage of BM blasts and donor chimerism (STR) before and after CD7 CAR T-cells infusion; d, e, Flow cytometry analysis before (d) and after (e) CD7 CAR Tcells infusion. f, g PET-CT scan before (f) and after (g) CD7 CAR T-cells infusion
The patient developed a high fever (39.6 °C, peaked at 41.1 °C the next day and lasted for 15 days) and tachycardia approximately 24 h after the first infusion (Fig. 1c). The peaks of serum IL-6 (93 times higher than baseline) and IFNγ were detected on the 14th day postinfusion (Fig. 1c). Pancytopenia, hypotension and pleural effusion were observed, with no signs of organ toxicity or immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome. Low fibrinogen, elevated ferritin, NK cell deficiency and elevated soluble CD25 were observed. Grade 3 cytokine release syndrome and macrophage activation syndrome were considered as described [6, 7] and were relieved with tocilizumab, dexamethasone, plasma exchange and supportive care. White blood cells and neutrophils returned to normal on the 57th day, and independence of red blood cell infusion was achieved on the 50th day after infusion (Fig. 1d). Platelets were still dependent on transfusion at the last follow-up. No activation of CMV or EBV and no signs of GVHD were observed.
The BM aspirates showed hypoplasia with no blasts according to morphology and flow cytometry, with full donor chimerism 30 days after CAR T-cells infusion (Fig. 2b, c, e). BM aspirates were normocellular with no blasts, 4.4 × 10− 4 of blasts by flow cytometry, showed normal karyotype and full donor chimerism and were TP53 mutation-negative on day 91 (Supplementary Table 1). PET-CT scan at day 100 showed disappearance of the mediastinal mass and enlarged lymph nodes with no hypermetabolic lesions in other lymph nodes or the spleen (Fig. 2g). The CAR-T cells remained detectable, with no CD7-positive T cells and CD7-negative T cells as the predominant CD3-positive population (62–92%) in the PB at the last follow-up (Fig. 1e-f, Supplementary Fig. 3–4).
ALL/LBL exhibits universal overexpression of T-cell markers such as CD4, CD5 and CD7 [8]. CD4- and CD5-CAR-T cells were only evaluated in preclinical studies [9, 10]. Autologous CD7 CAR-T cell therapy was reported in a relapsed pediatric T-ALL [11]. HSCT donor-derived CD7 CAR-T cell therapy was reported in 12 T-ALL cases [12]. Compared with those patients, this is the first ETP-ALL/LBL case, who had a significantly higher tumor burden (70.5% of blasts in the BM and extensive extramedullary infiltration) before CAR-T cells infusion. Our patient achieved deep remission after the CD7 CAR-T cell therapy though he had unfavorable genetics and was resistant to all the available salvage treatments. This encouraging results not only confirmed our in vitro assays (Supplementary Fig. 2), but also also implied that this nanobody-based CD7 CAR-T cells could be a promising strategy for relapsed/refractory ETP-ALL/LBL.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1 : Supplementary Figure 1. Flow cytometry analysis on the anti-CD7 CAR T-cells. Supplementary Figure 2. Cytotoxicity analysis of the anti-CD7 CAR T-cells. Supplementary Figure 3. Timeline of treatments and responses. Supplementary Figure 4. T-cell fractions in the PB post CAR T-cells infusion. Supplementary Table 1. Baseline clinical characteristics of the patient. Supplementary Table 2. A panel of 222 genes detected by next generation sequencing.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all members of the study team, the patient and their family, and Suzhou PersonGen BioTherapeutics (Suzhou) Co., Ltd.
Abbreviations
- BM
Bone marrow
- CAR
Chimeric antigen receptor
- CR
Complete remission
- CRS
Cytokine release syndrome
- ETP-ALL/LBL
Early T-cell precursor lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma
- HSCT
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Authors’ contributions
HpD conducted the study, provided patient care, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper. WC, HmM analyzed the data and was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. QyC, WjZ provided patient care and analyzed the data. MqZ performed flow cytometry. HmM participated in the generation of clinical cell products and analyzed the data. XmZ participated in the clinical care. LY designed the clinical CART vector, supervised the production of CAR T-cell product, and reviewed the manuscript. DpW and XwT conceived of the study, participated in the clinical care, supervised the research, analyzed the data, and reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
The authors thank all members of the study team, the patient, and their family. This work was supported by research grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81873443, 81900175), Major Natural Science Research Projects in institutions of higher education of Jiangsu Province (19KJA210002), The Key Science Research Project of Jiangsu Commission of Health (K2019022), Translational Research Grant of NCRCH (2020ZKZC04) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20190181, BK20201169, BK20170360), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the conclusions are included within this article.
Declarations
Ethics approval consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University (2021018) and was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The parents of this patient provided written informed consent about the publication of the clinical details.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient and his parents.
Competing interests
The author reports no conflicts of interest in this work.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Hai-ping Dai, Wei Cui, Lin Yang, De-pei Wu and Xiao-wen Tang contributed equally to this work.
Contributor Information
Lin Yang, Email: yanglin@suda.edu.cn.
De-pei Wu, Email: drwudepei@163.com.
Xiao-wen Tang, Email: xwtang1020@163.com.
References
- 1.Coustan-Smith E, Mullighan CG, Onciu M, Behm FG, Raimondi SC, Pei D, et al. Early T-cell precursor leukaemia: a subtype of very high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(2):147–156. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70314-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Inukai T, Kiyokawa N, Campana D, Coustan-Smith E, Kikuchi A, Kobayashi M, et al. Clinical significance of early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: results of the Tokyo Children's Cancer Study Group Study L99-15. Br J Haematol. 2012;156(3):358–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2011.08955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cooper ML, Choi J, Staser K, Ritchey JK, Devenport JM, Eckardt K, et al. An “off-the-shelf” fratricide-resistant CAR-T for the treatment of T cell hematologic malignancies. Leukemia. 2018;32(9):1970–1983. doi: 10.1038/s41375-018-0065-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.You F, Wang Y, Jiang L, Zhu X, Chen D, Yuan L, et al. A novel CD7 chimeric antigen receptor-modified NK-92MI cell line targeting T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am J Cancer Res. 2019;9(1):64–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Png YT, Vinanica N, Kamiya T, Shimasaki N, Coustan-Smith E, Campana D. Blockade of CD7 expression in T cells for effective chimeric antigen receptor targeting of T-cell malignancies. Blood Adv. 2017;1(25):2348–2360. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2017009928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lee DW, Santomasso BD, Locke FL, Ghobadi A, Turtle CJ, Brudno JN, et al. ASTCT consensus grading for cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicity associated with immune effector cells. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25(4):625–638. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.12.758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, et al. HLH-2004: diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007;48(2):124–131. doi: 10.1002/pbc.21039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Peipp M, Küpers H, Saul D, Schlierf B, Greil J, Zunino SJ, et al. A recombinant CD7-specific single-chain immunotoxin is a potent inducer of apoptosis in acute leukemic T cells. Cancer Res. 2002;62(10):2848–2855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pinz K, Liu H, Golightly M, Jares A, Lan F, Zieve GW, et al. Preclinical targeting of human T-cell malignancies using CD4-specific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-engineered T cells. Leukemia. 2016;30(3):701–707. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mamonkin M, Rouce RH, Tashiro H, Brenner MK. A T-cell-directed chimeric antigen receptor for the selective treatment of T-cell malignancies. Blood. 2015;126(8):983–992. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-02-629527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Xie L, Ma L, Liu S, Chang L, Wen F. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells targeting CD7 in a child with high-risk T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;96:107731. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pan J, Tan Y, Wang G, Deng B, Ling Z, Song W, et al. Donor-derived CD7 chimeric antigen receptor T cells for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: first-in-human, phase I trial. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(30):3340–3351. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.00389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1 : Supplementary Figure 1. Flow cytometry analysis on the anti-CD7 CAR T-cells. Supplementary Figure 2. Cytotoxicity analysis of the anti-CD7 CAR T-cells. Supplementary Figure 3. Timeline of treatments and responses. Supplementary Figure 4. T-cell fractions in the PB post CAR T-cells infusion. Supplementary Table 1. Baseline clinical characteristics of the patient. Supplementary Table 2. A panel of 222 genes detected by next generation sequencing.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets supporting the conclusions are included within this article.