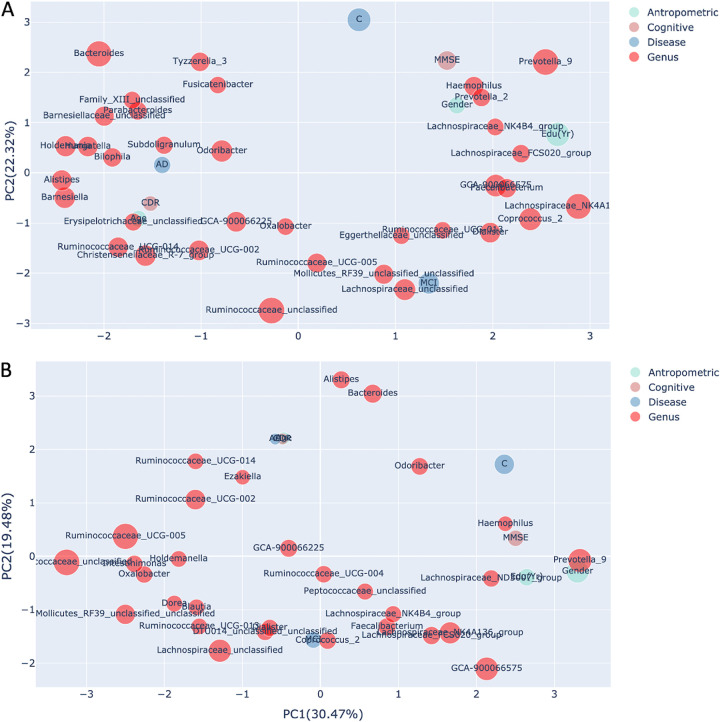
FIG 8.
Principal-component analysis of SAFE scores of taxa and clinical variables shows the overall pattern of the association. (A) Principal-component analysis of the SAFE scores and clinical metadata based on Bray-Curtis distance showing the associations of taxa (red [only the top 30 are shown]) with the clinical variable category (blue, brown, or green). Marker size is scaled with respect to taxon SAFE scores. Samples from the control group are shown to be associated with the taxa Prevotella_9, species of Lachnospiraceae, and GCA90006675 and the clinical variables, gender, MMSE, and education, while AD samples were more closely associated with taxa such as Subdoligranulum, Odoribacter, Bilophila, Alistipes, and Bacteroides and CDR and age. The MCI group was coenriched with Ruminocoaceae_unclassified, some members of the Lachnospiraceae family, Faecalibacterium, Ruminocoaceae_UCG_005, and Lachnospiraceae_unclassified. (B) Principal-component analysis of the SAFE scores of taxa (red [only the top 30 are shown]) and clinical variable category based on Jensen-Shannon distance. The associations of taxa and clinical variables with the cohort groups are largely coherent with the PCA based on Bray-Curtis distance.