Visual Abstract
Keywords: acute kidney injury, mortality, epidemiology and outcomes, veterans, cohort studies
Abstract
Background and objectives
AKI, a frequent complication among hospitalized patients, confers excess short- and long-term mortality. We sought to determine trends in in-hospital and 1-year mortality associated with AKI as defined by Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes consensus criteria.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements
This retrospective cohort study used data from the national Veterans Health Administration on all patients hospitalized from October 1, 2008 to September 31, 2017. AKI was defined by Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes serum creatinine criteria. In-hospital and 1-year mortality trends were analyzed in patients with and without AKI using Cox regression with year as a continuous variable.
Results
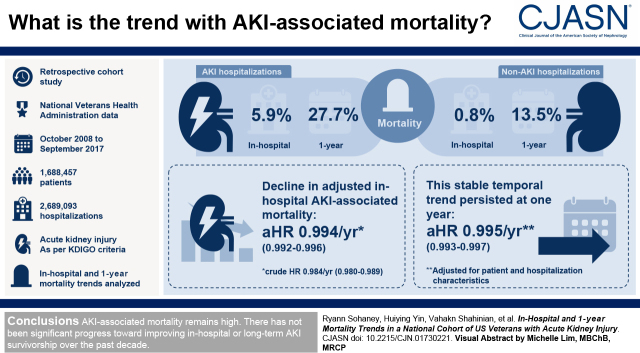
We identified 1,688,457 patients and 2,689,093 hospitalizations across the study period. Among patients with AKI, 6% died in hospital, and 28% died within 1 year. In contrast, in-hospital and 1-year mortality rates were 0.8% and 14%, respectively, among non-AKI hospitalizations. During the study period, there was a slight decline in crude in-hospital AKI-associated mortality (hazard ratio, 0.98 per year; 95% confidence interval, 0.98 to 0.99) that was attenuated after accounting for patient demographics, comorbid conditions, and acute hospitalization characteristics (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.99 per year; 95% confidence interval, 0.99 to 1.00). This stable temporal trend in mortality persisted at 1 year (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.00 per year; 95% confidence interval, 0.99 to 1.00).
Conclusions
AKI associated mortality remains high, as greater than one in four patients with AKI died within 1 year of hospitalization. Over the past decade, there seems to have been no significant progress toward improving in-hospital or long-term AKI survivorship.
Introduction
AKI, an abrupt decline in kidney function, is a serious and deadly complication affecting one in five hospitalized patients (1,2). Previous studies have implicated AKI as an independent risk factor for death, with a more than four-fold higher likelihood of in-hospital mortality (3). Moreover, an episode of AKI is associated with not only in-hospital mortality but also reduced survivorship at 1 year across all AKI stages (4).
Previous studies have indicated that in-hospital mortality among patients with dialysis-requiring AKI has declined from 2000 to 2015 (5–7). Although the trend toward lower in-hospital mortality among patients with dialysis-requiring AKI is encouraging, this comprises only a small fraction of all patients with AKI (8), and mortality trends in patients with dialysis-requiring AKI may not be generalizable to mortality rates across all stages of AKI. To date, few studies have examined mortality trends among less severe stages of AKI. There has been some suggestion that in-hospital mortality among patients with a diagnosis code for AKI has decreased across time (9,10). However, the incidence of AKI using administrative coding has increased across the past two decades (8,11,12). This rise has been most pronounced among hospitalizations with stage 1 AKI (13), as defined by the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) consensus serum creatinine criteria (14). Therefore, temporal mortality reduction among hospitalized patients with AKI may represent increased coding of mild AKI rather than true reduction in mortality. Alternatively, increased AKI recognition as well as advances in the management of hospitalized patients may have translated into true improvement in AKI outcomes. Whether any potential mortality reduction persists beyond the initial hospitalization period is unknown.
The goal of this study was to examine recent short- and long-term mortality trends in hospitalized patients with AKI as defined by the consensus criteria. Quantifying long-term outcomes and trends of AKI is critical to understanding the population-level effect of AKI and may influence resource allocation post-AKI. We hypothesized that improved AKI recognition and care have led to decreasing mortality across all KDIGO AKI stages and that this mortality reduction is sustained at 1 year.
Materials and Methods
Data Source/Population
We conducted a retrospective cohort analysis of adult patients (22 years or older) admitted to an acute care facility in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) from October 1, 2008 to September 30, 2017, corresponding to VHA fiscal years 2009–2017. For simplicity, we will subsequently refer to this time period as 2009–2017. VHA is the largest integrated health care system in the United States. VHA data from the Corporate Data Warehouse include detailed individual patient demographic, clinical, laboratory, and vital status data.
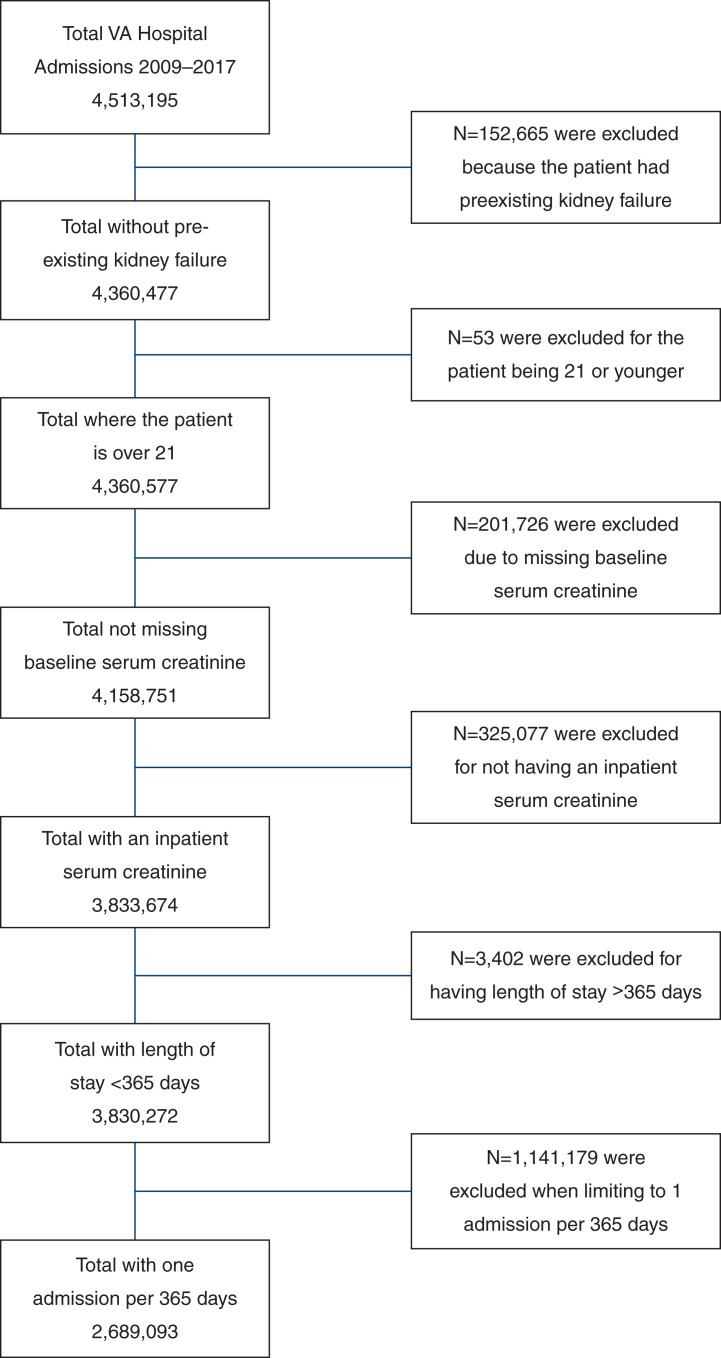
Hospitalizations were included if they had at least one inpatient serum creatinine result; there was no preadmission kidney failure (International Classification of Diseases, ninth revision, Clinical Modification [ICD-9-CM] 585.6 and International Classification of Diseases, tenth revision, Clinical Modification [ICD-10-CM] N18.6), including dialysis (Current Procedure Terminology [CPT] codes 90918, 90919, 90935, 90937, 90940, 90945, 90947, 90951–90970, 90989, 90993, 90997, and 90999) prior to admission; and the patients were not admitted to a long-term care facility. We included patients more than once only if their next hospitalization occurred >365 days from the previous included hospital admission. We excluded hospitalizations with a hospital length of stay >365 days.
This project was conducted at the University of Michigan and funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Research using VHA data for this project was approved by the institutional review boards of the University of Michigan and the Ann Arbor VHA.
Data Collection
We extracted Corporate Data Warehouse data for all patients with hospital admissions from October 1, 2008 to September 30, 2017. Data were collected through September 30, 2018 to ensure a full year of follow-up for all patients. Data extracted from the VHA national Corporate Data Warehouse included demographic information (age, sex, and race), inpatient and outpatient procedures and diagnoses (using CPT codes and ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM diagnoses), physician order entry, inpatient and outpatient serum creatinine values, and vital status. Baseline data were obtained for 365 days prior to each hospital admission, including ICD-9-CM or ICD-10-CM diagnoses and CPT codes for comorbid conditions.
AKI Definition.
The primary exposure of interest was hospitalization with AKI. The 2012 KDIGO AKI consensus guideline (13) recommends a serum creatinine definition for AKI that relies upon change in creatinine from a baseline. We defined the baseline creatinine by a hierarchical approach on the basis of the availability of (1) the mean outpatient creatinine between 365 and 7 days prior to admission, (2) the earliest outpatient value within the 7 days prior to admission (if no creatinine 7 days prior to admission was available), or (3) the lowest inpatient creatinine (if no outpatient creatinine in the year prior to admission was available). A 7-day cutoff was used to avoid selecting an elevated creatinine that may have been associated with the cause for hospitalization. We calculated the corresponding baseline eGFR according to the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation using race-based values where race was recorded and “non-Black” if race was missing (6% of the cohort).
AKI was ascertained and staged according to severity on the basis of the KDIGO serum creatinine definition. Stage 1 AKI was defined as a creatinine level increase ≥0.3 mg/dl (within 48 hours) or an increase of 1.5–1.9 times baseline (within 7 days). Stage 2 AKI is an increase of 2.0–2.9 times baseline. Stage 3 AKI is a serum creatinine level increase >3.0 times baseline, a serum creatinine ≥4.0 mg/dl and ≥0.5 mg/dl above baseline, or AKI requiring the initiation of dialysis. Dialysis-requiring AKI included those meeting creatinine criteria for AKI and additionally having a CPT code for dialysis (ICD-9-CM: 3995 and 5498; ICD-10-CM: 5A1D00Z, 5A1D60Z, and 3E1M39Z). In addition to KDIGO criteria, we also identified AKI separately using ICD-9-CM (584.9) or ICD-10-CM (N17.9) codes.
Mortality Outcomes.
We used two separate primary outcomes: all-cause in-hospital mortality and all-cause mortality 1 year from hospitalization (inclusive of in-hospital mortality). We determined the date of death using the Veterans’ Vital Status Files. The Vital Status Files combine multiple information sources to ascertain mortality with >97% sensitivity (15).
Covariates.
Patient demographics (preadmission age, sex, and race), comorbid conditions, and acute hospitalization characteristics were obtained from the Corporate Data Warehouse. We defined CKD as a baseline eGFR <60 ml/min per 1.73 m2, prehospital urine albumin-creatinine ratio >30 mg/g, or the presence of an ICD-9-CM or ICD-10-CM code for CKD in the 365 days prior to admission. All other baseline (prehospitalization) patient comorbid conditions were compiled using ICD-9-CM or ICD-10-CM codes for the 365 days prior to admission. Baseline comorbid conditions included CKD, hypertension, diabetes, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, peripheral vascular disease, malignancy, liver disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cerebrovascular accident, and transient ischemic attack. We additionally compiled hospitalization characteristics, including surgical procedures, hospital length of stay, intensive care unit (ICU) utilization, mechanical ventilation, sepsis, and vasopressor use. We used surgery Diagnosis Related Group codes to identify hospitalizations involving inpatient surgical procedures. A surgical Diagnosis Related Group indicates that a hospitalization involved a procedure commonly performed in the operating room. We identified hospitalizations involving an ICU stay by the specialty or bed section codes corresponding to the service location within the hospital. We used ICD-9 CM or ICD-10 codes for sepsis and septic shock to identify sepsis and mechanical ventilation.
Statistical Analyses
To assess mortality trends in the AKI and non-AKI cohorts separately, we performed time-to-event analysis using Cox proportional hazards models with hospital admission date as day 0. We censored patients at hospital discharge when estimating time to in-hospital mortality and at 365 days from hospital admission date for time to 1-year mortality. Our primary interest was to estimate trends in mortality over time. To accomplish this, we included year as a continuous linear variable in the model. We chose to model year as a continuous variable on the basis of visualization of the crude data demonstrating linear trends in in-hospital and 1-year mortality.
We constructed three models to understand potential reasons for the trend. Model 1 included demographic data, including race, sex, and preadmission age. Model 2 included preadmission comorbid diseases in addition to the covariates included in model 1. Comorbid diseases included CKD, hypertension, diabetes, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, peripheral vascular disease, malignancy, liver disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cerebrovascular accident, and transient ischemic attack. Model 3 incorporated hospitalization characteristics in addition to the covariates in model 3. This final model was built with the intent to incorporate markers of acute illness severity. Hospitalization characteristics included hospital admitting service, hospital length of stay, ICU utilization, mechanical ventilation, sepsis, and vasopressor use.
To account for the correlation between repeated hospitalizations for the same person, we estimated the variance using robust variance techniques (16,17). We examined patients with AKI and non-AKI in separate models. For each mortality outcome, we also tested for differences in the mortality trend between patients with and without AKI by fitting a model combining both sets of patients and including an interaction term between AKI and year. We consider a P value ≤0.05 to be statistically significant. Because we did observe a significant interaction, all subsequent modeling was performed stratified by whether patients had AKI. Analyses were conducted using SAS 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC).
Subgroup/Sensitivity Analyses
To address the issue that improvement in mortality reported in previous studies may be related to increased coding of mild AKI rather than true reduction in mortality, we examined crude in-hospital and 1-year mortality trends for hospitalized patients with an ICD-9-CM or ICD-10-CM code for AKI (as opposed to serum creatinine values in our primary analyses).
Additionally, we examined AKI-associated mortality trends among patients with baseline eGFR ≥60 ml/min per 1.73 m2, as the insult required to generate an AKI may be greater for those without than with CKD. Improvements in clinical treatment of AKI over time may appear more evident among this cohort.
Finally, to verify the assumption that time to event mortality conforms to a linear trend across time, we constructed separate Cox proportional hazards models with year as a categorical variable.
Results
Patient Population and Hospitalization Characteristics
After applying exclusion criteria, the study included 2,689,093 qualifying hospitalizations and 1,688,457 unique patients in VHA from 2009 to 2017 (Figure 1). The cohort included 548,782 hospitalizations with AKI and 2,140,311 hospitalizations without AKI. Patient demographic and hospitalization characteristics stratified by AKI status and time period appear in Table 1. The mean ages were 70 (SD 13) and 73 (SD 11) for patients without AKI and patients with AKI, respectively, and did not change substantially during the study period. Several comorbid diseases, including hypertension, CKD, and diabetes, were more prevalent among patients hospitalized with AKI as compared with non-AKI hospitalizations.
Figure 1.
Cohort derivation. VA, Veterans Affairs.
Table 1.
Hospitalization and patient characteristics by AKI status in US veterans, 2009–2017
| Variable | Total | 2009–2011 | 2012–2014 | 2015–2017 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No AKI | AKI | No AKI | AKI | No AKI | AKI | No AKI | AKI | |
| Hospitalizations, n | 2,140,311 | 548,782 | 710,859 | 179,127 | 714,610 | 183,195 | 714,842 | 186,460 |
| Women, n (%) | 122,004 (6) | 17,174 (3) | 37,209 (5) | 5254 (3) | 40,972 (6) | 5613 (3) | 43,823 (6) | 6307 (3) |
| Age, n (%) | ||||||||
| 22–29 | 4232 (0.2) | 282 (0.1) | 552 (0.1) | 59 (0.0) | 1294 (0.2) | 93 (0.1) | 2386 (0.3) | 130 (0.1) |
| 30–39 | 51,803 (2) | 3905 (0.7) | 11,785 (2) | 803 (0.4) | 17,064 (2) | 1275 (0.7) | 22,954 (3) | 1827 (1) |
| 40–49 | 74,275 (4) | 9341 (2) | 21,654 (3) | 2713 (2) | 24,334 (3) | 2935 (2) | 28,287 (4) | 3693 (2) |
| 50–59 | 221,534 (10) | 44,647 (8) | 75,113 (11) | 15,616 (9) | 72,879 (10) | 14,807 (8) | 73,542 (10) | 14,224 (8) |
| 60–69 | 606,161 (28) | 157,212 (29) | 203,484 (29) | 50,825 (28) | 205,469 (29) | 54,236 (30) | 197,208 (28) | 52,151 (28) |
| 70+ | 1,182,306 (55) | 333,395 (61) | 398,271 (56) | 109,111 (61) | 393,570 (55) | 109,849 (60) | 390,465 (55) | 114,435 (61) |
| Mean age (SD), yr | 70 (13) | 73 (11) | 71 (12) | 73 (11) | 70 (13) | 73 (11) | 70 (13) | 72 (11) |
| Race, n (%) | ||||||||
| Non-Hispanic White | 1,500,678 (70) | 357,856 (65) | 503,086 (71) | 117,846 (66) | 503,747 (71) | 120,496 (66) | 493,845 (69) | 119,514 (64) |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 385,185 (18) | 123,093 (22) | 123,407 (17) | 38,495 (22) | 127,877 (18) | 40,908 (22) | 133,901 (19) | 43,690 (23) |
| Hispanic | 100,029 (5) | 26,075 (5) | 28,022 (4) | 7094 (4) | 31,520 (4) | 7918 (4) | 40,487 (6) | 11,063 (6) |
| American Indian/ Alaska Native | 13,045 (0.6) | 2992 (0.5) | 3922 (0.6) | 818 (0.5) | 4451 (0.6) | 1034 (0.6) | 4672 (0.7) | 1140 (0.6) |
| Asian | 19,019 (0.9) | 5020 (0.9) | 5712 (0.8) | 1524 (0.9) | 6371 (0.9) | 1658 (0.9) | 6936 (1) | 1838 (1) |
| Other/unknown | 122,355 (6) | 33,746 (6) | 46,710 (7) | 13,350 (8) | 40,644 (6) | 11,181 (6) | 35,001 (5) | 9215 (5) |
| Baseline eGFR | ||||||||
| Baseline eGFR, mean (SD), ml/kg per 1.73 m2 | 74 (22) | 63 (26) | 73 (22) | 62 (26) | 75 (22) | 63 (26) | 75 (22) | 62 (26) |
| Baseline eGFR<60, n (%) | 551,439 (26) | 257,478 (47) | 192,473 (27) | 85,017 (48) | 179,168 (25) | 84,129 (46) | 179,798 (25) | 88,332 (47) |
| Comorbidity, n (%) a | ||||||||
| HTN | 952,322 (45) | 284,633 (52) | 302,976 (43) | 92,423 (52) | 321,636 (45) | 94,572 (52) | 327,710 (46) | 97,638 (52) |
| CKD, no DM | 147,179 (7) | 88,736 (16) | 44,240 (6) | 28,041 (16) | 48,276 (7) | 29,337 (16) | 54,663 (8) | 31,358 (17) |
| DM and CKD | 114,648 (5) | 84,929 (16) | 30,221 (4) | 23,494 (13) | 382,59 (5) | 28,021 (15) | 46,168 (7) | 33,414 (18) |
| DM, no CKD | 411,307 (19) | 110,957 (20) | 130,039 (18) | 36,573 (20) | 138,104 (19) | 36,669 (20) | 143,164 (20) | 37,715 (20) |
| No DM or CKD | 1,467,177 (69) | 264,160 (48) | 506,359 (71) | 91,019 (51) | 48,9971 (69) | 89,168 (49) | 470,847 (66) | 83,973 (45) |
| MI | 61,970 (3) | 19,268 (4) | 19,007 (3) | 6002 (3) | 20,882 (3) | 6220 (3) | 22,081 (3) | 7046 (4) |
| PVD | 157,595 (7) | 49,402 (9) | 49,936 (7) | 16,026 (9) | 52,878 (7) | 16,643 (9) | 54,781 (8) | 16,733 (9) |
| Cancer | 40,579 (2) | 11,838 (2) | 10,738 (2) | 3213 (2) | 14,533 (2) | 4227 (2) | 15,308 (2) | 4398 (2) |
| Liver | 64,460 (3) | 22,606 (4) | 12,704 (2) | 4767 (3) | 15,686 (2) | 6136 (3) | 36,070 (5) | 11,703 (6) |
| COPD | 393,858 (18) | 101,899 (19) | 123,677 (17) | 32,567 (18) | 133,521 (19) | 34,391 (19) | 136,660 (19) | 34,941 (19) |
| CVA/TIA | 161,232 (8) | 46,445 (9) | 52,794 (7) | 15,634 (9) | 56,623 (8) | 16,045 (9) | 51,815 (7) | 14,766 (8) |
| Illness severity, n (%) | ||||||||
| Surgical DRG | 898,982 (42) | 207,396 (38) | 303,204 (43) | 66,853 (37) | 302,539 (42) | 68,851 (38) | 293,239 (41) | 71,692 (38) |
| AKI stage | ||||||||
| Stage 1 | — | 451,427 (82) | — | 146,898 (82) | — | 150,626 (82) | — | 153,903 (83) |
| Stage 2 | — | 18,375 (3) | — | 5968 (3) | — | 6422 (4) | — | 5985 (3) |
| Stage 3 | — | 55,450 (10) | — | 18,306 (10) | — | 18,492 (10) | — | 18,652 (10) |
| AKI with dialysis | — | 23,530 (4) | — | 7955 (4) | — | 7655 (4) | — | 7920 (4.2) |
| ICU | 325,520 (15) | 122,307 (22) | 107,407 (15) | 40,493 (23) | 106,979 (15) | 40,247 (22) | 111,134 (16) | 41,567 (22) |
| Mechanical ventilation | 31,700 (2) | 42,095 (8) | 11,901 (2) | 15,707 (9) | 11,649 (2) | 14,973 (8) | 8150 (1) | 11,415 (6) |
| Sepsis | 46,136 (2) | 50,858 (9) | 7102 (1) | 11,466 (6) | 15,582 (2) | 17,453 (10) | 23,452 (3) | 21,939 (12) |
| Vasopressors use | 156,952 (7) | 54,685 (10) | 49,038 (7) | 17,211 (10) | 53,150 (7) | 18,196 (10) | 54,764 (8) | 19,278 (10) |
| LOS, mean (SD) | 6.1 (17.9) | 11.2 (24.9) | 6.6 (19.1) | 12.3 (27.3) | 5.9 (17.4) | 10.9 (23.8) | 5.8 (17.1) | 10.3 (23.4) |
Data are for hospitalizations. Characteristics of patients with multiple hospitalizations during the study period are represented more than once. HTN, hypertension; DM, diabetes mellitus; MI, myocardial infarction; PVD, peripheral vascular disease; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CVA/TIA, cerebrovascular accident/transient ischemic attack; DRG, Diagnosis Related Group; —, not applicable; ICU, intensive care unit; LOS, length of stay.
CKD includes eGFR<60 ml/min per 1.73 m2, urinary albumin-creatinine ratio >30 mg/g, or International Classification of Diseases, ninth revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) or International Classification of Diseases, tenth revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) code for CKD in the 365 days prior to admission. All other comorbid conditions are defined according to corresponding ICD-9-CM or ICD-10-CM codes.
Among all hospitalizations with AKI, 82% were KDIGO stage 1, 3% were KDIGO stage 2, and 14% were KDIGO stage 3 (including dialysis-requiring AKI). The relative makeup of AKI severity did not change across time. ICU utilization, mechanical ventilation, sepsis, and vasopressor use were more prevalent among hospitalizations with AKI.
Crude In-Hospital and 1-Year Mortality
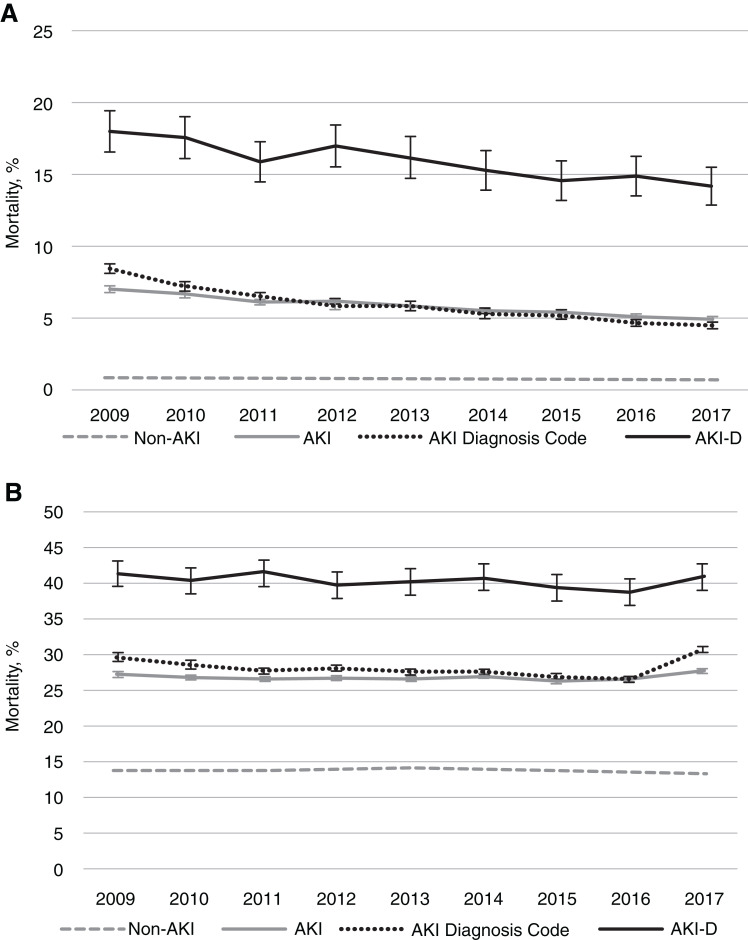
The number of hospitalizations at risk and crude mortality rate each year appear in Tables 2 and 3. Across 2009–2017, in-hospital mortality was 6% among hospitalizations with AKI compared with 1% among non-AKI hospitalizations. Sixty-seven percent of all hospital deaths occurred among those with AKI. Notably, in-hospital mortality was relatively similar by method of AKI ascertainment (6% with AKI diagnosis code and 6% with serum creatinine). One-year mortality rates among patients with and without AKI were 28% and 14%, respectively. The crude in-hospital and 1-year mortality trends stratified by AKI status appear in Figure 2.
Table 2.
Crude trends in in-hospital and 1-year mortality among US veterans with and without AKI, 2009–2012
| Patient Group | Total | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N at Risk | Rate | N at Risk | Rate | N at Risk | Rate | N at Risk | Rate | N at Risk | Rate | |
| In-hospital mortality | ||||||||||
| All hospitalized patients | 2,689,093 | 1.9 | 298,720 | 2.1 | 294,371 | 1.9 | 296,895 | 1.9 | 297,198 | 1.8 |
| AKI serum creatinine | 548,782 | 6.1 | 61,181 | 7.0 | 56,132 | 6.6 | 61,814 | 6.1 | 60004 | 6.1 |
| AKI diagnosis code | 329,573 | 5.9 | 23,614 | 8.4 | 26,859 | 7.2 | 31,606 | 6.5 | 34,282 | 5.8 |
| Non-AKI | 2,140,311 | 0.8 | 237,539 | 0.8 | 238,239 | 0.8 | 235,081 | 0.8 | 237,194 | 0.7 |
| AKI KDIGO stage | ||||||||||
| Stage 1 | 451,427 | 4.5 | 50,139 | 5.0 | 46,085 | 4.7 | 50,674 | 4.5 | 49,009 | 4.5 |
| Stage 2 | 18,375 | 13.8 | 2081 | 16.5 | 1844 | 16.7 | 2043 | 13.8 | 2102 | 13.1 |
| Stage 3 | 55,450 | 12.7 | 6188 | 14.7 | 5615 | 13.9 | 6503 | 12.0 | 6196 | 12.4 |
| AKI-D | 23,530 | 16.4 | 2773 | 18.0 | 2588 | 17.6 | 2594 | 15.9 | 2587 | 17.0 |
| AKI and eGFR≥60 ml/min per 1.73 m2 | 291,304 | 6.5 | 31,510 | 7.4 | 29,880 | 6.8 | 32,720 | 6.4 | 32,232 | 6.5 |
| AKI and eGFR <60 ml/min per 1.73 m2 | 257,478 | 5.8 | 29,671 | 6.6 | 26,252 | 6.4 | 29,094 | 5.7 | 27,772 | 5.7 |
| 1-yr mortality | ||||||||||
| All hospitalized patients | 2,689,093 | 16.4 | 298,720 | 16.4 | 294,371 | 16.4 | 296,895 | 16.4 | 297,198 | 16.6 |
| AKI | 548,782 | 27.7 | 61,181 | 27.2 | 56,132 | 26.7 | 61,814 | 26.6 | 60,004 | 26.7 |
| AKI diagnosis code | 329,573 | 30.7 | 23,614 | 29.6 | 26,859 | 28.6 | 31,606 | 27.7 | 34,282 | 28.1 |
| Non-AKI | 2,140,311 | 13.5 | 237,539 | 13.8 | 238,239 | 13.7 | 235,081 | 13.8 | 237,194 | 14.0 |
| AKI KDIGO stage | ||||||||||
| Stage 1 | 451,427 | 25.3 | 50,139 | 24.9 | 46,085 | 24.7 | 50,674 | 24.6 | 49,009 | 24.9 |
| Stage 2 | 18,375 | 36.1 | 2081 | 36.9 | 1844 | 32.8 | 2043 | 32.0 | 2102 | 31.5 |
| Stage 3 | 55,450 | 37.9 | 6188 | 37.0 | 5615 | 34.8 | 6503 | 35.0 | 6196 | 34.3 |
| AKI-D | 23,530 | 40.8 | 2773 | 41.3 | 2588 | 40.3 | 2594 | 41.4 | 2587 | 39.7 |
| AKI and eGFR≥60 ml/min per 1.73 m2 | 291,304 | 24.2 | 31,510 | 25.9 | 29,880 | 25.0 | 32,720 | 24.5 | 32,232 | 24.2 |
| AKI and eGFR<60 ml/min per 1.73 m2 | 257,478 | 29.7 | 29,671 | 29.6 | 26,252 | 29.8 | 29,094 | 29.2 | 27,772 | 29.5 |
eGFR refers to baseline preadmission eGFR. KDIGO, Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes; AKI-D, dialysis-requiring AKI.
Table 3.
Crude trends in in-hospital and 2-year mortality among US veterans with and without AKI, 2013–2017
| Patient Group | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N at Risk | Rate | N at Risk | Rate | N at Risk | Rate | N at Risk | Rate | N at Risk | Rate | |
| In-hospital mortality | ||||||||||
| All hospitalized patients | 293,974 | 1.8 | 306,633 | 1.7 | 304,526 | 1.7 | 300,969 | 1.6 | 295,807 | 1.5 |
| AKI serum creatinine | 60,651 | 5.8 | 62,540 | 5.5 | 63,492 | 5.4 | 62,358 | 5.0 | 60,610 | 4.9 |
| AKI diagnosis code | 36,822 | 5.8 | 41,349 | 5.2 | 43,222 | 5.1 | 45,101 | 4.6 | 46,718 | 4.5 |
| Non-AKI | 23,323 | 0.8 | 244,093 | 0.7 | 241,034 | 0.7 | 238,611 | 0.7 | 235,197 | 0.6 |
| AKI KDIGO stage | ||||||||||
| Stage 1 | 49,927 | 4.4 | 51,580 | 4.0 | 52,466 | 3.9 | 51,543 | 3.7 | 49,894 | 3.6 |
| Stage 2 | 229 | 10.6 | 2091 | 12.3 | 2049 | 11.8 | 2011 | 11.1 | 1925 | 11.2 |
| Stage 3 | 6080 | 11.7 | 6216 | 11.3 | 6427 | 12.0 | 6236 | 10.2 | 6089 | 10.0 |
| AKI-D | 2415 | 16.2 | 2653 | 15.3 | 2550 | 14.6 | 2668 | 14.9 | 2702 | 14.2 |
| AKI and eGFR≥60 ml/min per 1.73 m2 | 33,084 | 6.1 | 33,750 | 5.7 | 33,980 | 5.7 | 33,076 | 5.4 | 31,072 | 5.3 |
| AKI and eGFR <60 ml/min per 1.73 m2 | 27,567 | 5.5 | 28,790 | 5.1 | 29,512 | 5.2 | 29,282 | 4.6 | 29,538 | 4.6 |
| 1-yr mortality | ||||||||||
| All hospitalized patients | 293,974 | 16.6 | 306,633 | 16.7 | 304,526 | 16.4 | 300,969 | 16.5 | 295,807 | 16.4 |
| AKI | 60,651 | 26.6 | 62,540 | 26.9 | 63,492 | 26.2 | 62,358 | 26.5 | 60,610 | 27.7 |
| AKI diagnosis code | 36,822 | 27.6 | 41,349 | 27.6 | 43,222 | 26.9 | 45,101 | 26.6 | 46,718 | 30.7 |
| Non-AKI | 23,323 | 14.1 | 244,093 | 14.0 | 241,034 | 13.8 | 238,611 | 13.9 | 235,197 | 13.5 |
| AKI KDIGO stage | ||||||||||
| Stage 1 | 49,927 | 24.7 | 51,580 | 24.7 | 52,466 | 24.4 | 51,543 | 24.7 | 49,894 | 25.3 |
| Stage 2 | 229 | 30.8 | 2091 | 33.1 | 2049 | 31.4 | 2011 | 30.1 | 1925 | 36.1 |
| Stage 3 | 6080 | 35.0 | 6216 | 36.9 | 6427 | 33.8 | 6236 | 35.2 | 6089 | 37.9 |
| AKI-D | 2415 | 40.2 | 2653 | 40.7 | 2550 | 39.3 | 2668 | 38.7 | 2702 | 40.8 |
| AKI and eGFR≥60 ml/min per 1.73 m2 | 33,084 | 24.2 | 33,750 | 23.7 | 33,980 | 23.7 | 33,076 | 23.5 | 31,072 | 23.5 |
| AKI and eGFR<60 ml/min per 1.73 m2 | 27,567 | 29.6 | 28,790 | 30 | 29,512 | 30.5 | 29,282 | 29.3 | 29,538 | 29.7 |
eGFR refers to baseline preadmission eGFR. KDIGO, Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes; AKI-D, dialysis-requiring AKI.
Figure 2.
Crude mortality trends among US veterans stratified by AKI status, 2009–2017. (A) In-hospital mortality; (B) 1-year mortality. Vertical bars represent 95% confidence intervals. AKI-D, dialysis-requiring AKI.
AKI Severity.
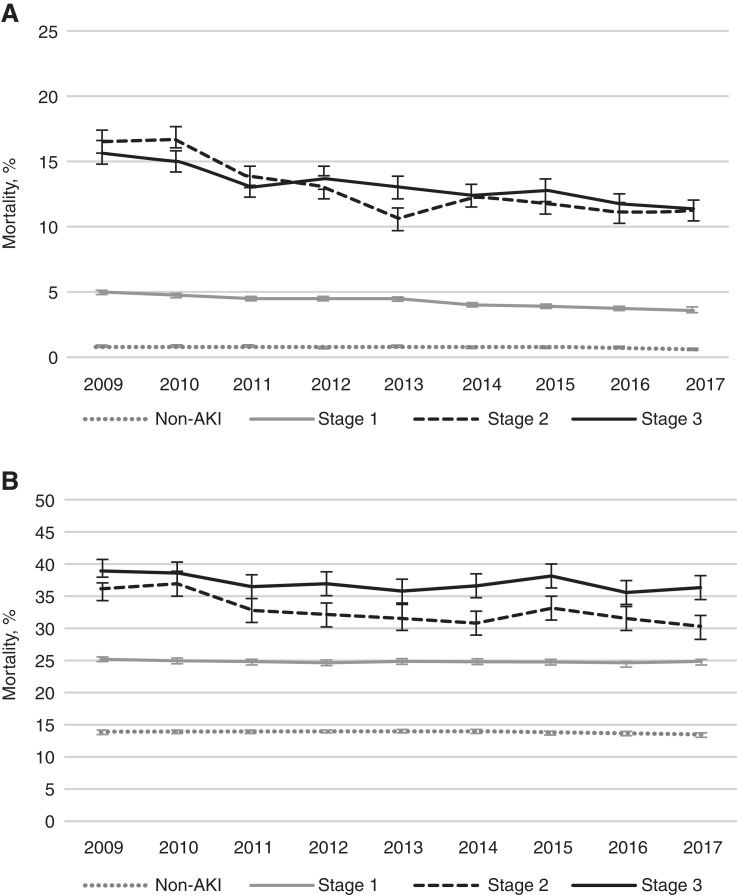
We observed higher in-hospital and 1-year mortality with increasing AKI severity by KDIGO stage. Among patients with dialysis-requiring AKI, 16% died during hospitalization, while 41% died within 1 year. Twenty-five percent of patients with KDIGO stage 1 AKI died within 1 year. AKI-associated mortality trends stratified by KDIGO stage appear in Figure 3.
Figure 3.
Crude mortality trends among US veterans stratified by Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes AKI stage, 2009–2017. (A) In-hospital mortality; (B) 1-year mortality. Stage 3 AKI includes AKI-D. Vertical bars represent 95% confidence intervals.
Baseline Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate.
In-hospital AKI-associated mortality rates were similar in those with a baseline eGFR <60 or ≥60 ml/min per 1.73 m2 (6% and 7%, respectively), whereas 1-year mortality was slightly higher in those with a baseline eGFR <60 ml/min per 1.73 m2 (30% versus 24%).
Mortality Trends
AKI-Associated Mortality Trends.
The crude and adjusted Cox proportional hazard models for in-hospital and 1-year mortality among hospitalizations with and without AKI appear in Table 4. From 2009 to 2017, there was a decline in the crude AKI-associated in-hospital mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 0.98 per year; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 0.98 to 0.99). This trend was slightly attenuated after accounting for patient demographics, comorbid conditions, and acute hospitalization characteristics (model 3 adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.99 per year; 95% CI, 0.99 to 1.00). Across the same time period, crude AKI-associated time to 1-year mortality went unchanged (HR, 1.00 per year; 95% CI, 1.00 to 1.00). However, when adjusting for demographics, comorbid conditions, and acute hospitalization characteristics, there was a statistically significant temporal reduction in time to AKI-associated mortality within 1 year (model 3 aHR, 1.00 per year; 95% CI, 0.99 to 1.00). Characteristics most strongly associated with in-hospital and 1-year AKI mortality include malignancy, liver disease, sepsis, mechanical ventilation, and AKI stage (Supplemental Table 1).
Table 4.
Crude and adjusted Cox proportional hazards models for trend in time to mortality among US veterans with AKI and non-AKI hospitalizations, 2009–2017
| Patient Group | Hazards Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted | Model 1a | Model 2b | Model 3c | |
| In hospital | ||||
| AKI | 0.98 (0.98 to 0.99) | 0.99 (0.98 to 0.99) | 1.00 (0.99 to 1.00) | 0.99 (0.99 to 1.00) |
| Non-AKI | 1.00 (0.99 to 1.00) | 1.03 (1.03 to 1.03) | 1.02 (1.02 to 1.02) | 1.01 (1.01 to 1.02) |
| 1 yr | ||||
| AKI | 1.00 (1.00 to 1.00) | 1.00 (1.00 to 1.01) | 1.00 (0.99 to 1.00) | 1.00 (0.99 to 1.00) |
| Non-AKI | 1.02 (1.02 to 1.03) | 1.03 (1.03 to 1.03) | 1.02 (1.02 to 1.02) | 1.02 (1.01 to 1.02) |
Hazards ratios are presented for year as a continuous variable.
Model 1 includes patients demographics, including preadmission age, sex, and race (Black or other).
Model 2 contains model 1 plus prehospital comorbid diseases, including hypertension, diabetes mellitus, CKD, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, peripheral vascular disease, malignancy, liver disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and cerebrovascular disease.
Model 3 contains model 2 plus acute hospitalization characteristics, including AKI stage, mechanical ventilation, intensive care unit utilization, sepsis, vasopressor use, hospital length of stay, and primary admitting service (surgical versus other).
In models with year as a categorical variable, we similarly observed modest changes in adjusted hazard for mortality for each subsequent year compared with the baseline (reference) year of 2009 (Supplemental Table 2).
Non–AKI-Associated Mortality Trends.
There was no change in crude in-hospital mortality among non-AKI hospitalizations (HR, 1.00 per year; 95% CI, 0.99 to 1.00), and there was a slightly higher in-hospital mortality in the fully adjusted model (aHR, 1.01 per year; 95% CI, 1.01 to 1.02). A similar trend was demonstrated at 1 year after non-AKI hospitalization (aHR, 1.02 per year; 95% CI, 1.01 to 1.02) (Table 4). Finally, in the additional models combining AKI and non-AKI hospitalizations, the AKI × year interaction term was significant for both in-hospital and 1-year mortality, confirming a difference in trend by AKI status.
Discussion
In this study examining mortality trends in a large national cohort of hospitalized veterans, in-hospital and 1-year mortality in patients with AKI declined modestly from 2009 to 2017. However, this trend was attenuated when accounting for changing patient and hospitalization characteristics, resulting in a relatively flat adjusted hazard for mortality. Further, our findings highlight the poor prognostic implications of having AKI, as more than one in four patients with AKI experienced death within 1 year of hospital admission.
Existing literature suggests that in-hospital mortality in those with AKI has rapidly declined. In an early analysis using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS), Waikar et al. (9) noted a nearly 50% reduction in in-hospital mortality from 1988 to 2002 among patients with AKI, falling from 40% to 20% (P<0.001). More recently, using NIS data from 2000 to 2011, Brown et al. (10) reported that although the number of in-hospital deaths associated with AKI nearly doubled, in-hospital AKI-associated mortality declined by 58% (22% to 99%). However, assessing AKI-associated mortality on the basis of claims data can present significant challenges and may not be an accurate representation of true trends. Claims data may inflate the apparent mortality reduction through increased recognition of mild AKI over time (11). Importantly, our study corroborated this issue, as it found a crude relative mortality reduction of 46% across 9 years when ascertaining AKI using diagnosis codes compared with 30% when ascertaining AKI by consensus creatinine criteria.
Other studies have examined mortality trends in dialysis-requiring AKI, as dialysis-requiring AKI is less susceptible to ascertainment bias. Hsu et al. (5) reported decreasing mortality during hospitalization with dialysis-requiring AKI from 2001 to 2009 (29% to 24%). However, even in-hospital mortality trends in dialysis-requiring AKI could overestimate mortality reduction, as changes in practices related to initiation of acute dialysis may affect trends over time. Our study among a national cohort of hospitalized patients with serum creatinine–defined AKI found a very small yearly reduction in AKI-associated mortality hazard from 2009 to 2017. Over a period of 10 years, this amounts to a modest reduction in mortality hazard (2017 aHR, 0.89 [reference 2009]; 95% CI, 0.83 to 0.85 [Supplemental Table 2]). Unfortunately, mortality among patients hospitalized with AKI remains high.
Despite recent emphasis on improving post-AKI care (18–20), we did not observe clinically significant improvement in the long-term mortality outcomes post-AKI. The long-term poor adverse health consequences associated with even mild AKI are highly significant, as one in four patients with stage 1 AKI died within a year of AKI hospitalization. Mortality was higher with worse AKI stage, and only 60% of patients with dialysis-requiring AKI survived to 1 year of hospitalization. Factors most strongly associated with death included men, malignancy, liver disease, sepsis, and mechanical ventilation. Such nonmodifiable factors reflect the role of significant comorbidity in contributing to long-term mortality. However, the significant excess mortality seen between hospital discharge and 1 year also presents an important opportunity to optimize postacute care. The lack of improvement in AKI-associated mortality in recent years is in stark contrast to the tremendous gains in mortality reduction among patients with kidney failure, another population with high comorbidity (21). Our findings point to an urgent need to continue identifying opportunities both to prevent AKI and to improve post-AKI outcomes.
This study has several limitations. VHA is composed of a population of predominantly men; however, our study included >28,000 AKI hospitalizations among women. AKI-associated mortality among those requiring ICU admission in our sample appeared lower than reported in other literature (22,23). However, VHA facilities represent community hospital settings where most patients seek care as opposed to large tertiary academic institutions. Although we adjusted for patient demographics and a robust set of comorbid diseases and markers of acute illness severity, we are unable to account for all confounders that may explain trends in mortality. Future work may elucidate whether post-AKI follow-up care, such as primary care and nephrology office visit, associates with long-term outcomes following AKI. It is also possible that in-hospital mortality may be underestimated, as some patients are transferred to tertiary hospitals for higher levels of care. However, a major strength of this study is the excellent ascertainment of mortality at 1 year by utilizing the VHA Vital Status Files.
Our study evaluating in-hospital and 1-year mortality among hospitalized patients experiencing a consensus creatinine-defined AKI provides valuable insight into the recent trends in AKI-associated mortality. In contrast to prior earlier studies, we found a relatively stable recent trend in in-hospital and 1-year mortality in those with AKI after accounting for changing patient and hospitalization characteristics. The poor prognostic implications of an episode of AKI persist, with overall 1-year mortality exceeding 25%. Our findings highlight the persistent urgent need for interventions to improve both short- and long-term outcomes in this vulnerable population.
Disclosures
N.R. Burrows reports employment with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. M. Heung reports consultancy agreements with Reata Pharmaceuticals and Wolters Kluwer (Lexicomp), receiving research funding from Spectral Medical Inc., receiving honoraria from the National Kidney Foundation, and serving as an associate editor of Advances in Chronic Kidney Disease. C.-y. Hsu has consulted for legal cases involving acute kidney disease or CKD; consults on an ad hoc basis for companies regarding kidney disease; and reports receiving honoraria from Satellite Healthcare, research funding from Satellite Healthcare, and royalties from UpToDate. M.E. Pavkov reports employment with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and serving on the Kidney Health Initiative Board of Directors. N. Powe reports receiving honoraria from the Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and serving as a scientific advisor or member of the Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, the University of Washington, Vanderbilt University, and Yale University. R. Saran reports consultancy agreements with KHK, Japan; receiving honoraria from Baylor Scott and White Health System, Fresenius Medical Care, the Japanese Society of Dialysis and Transplantation, Nutek Food Sciences, Reata, and the Renal Research Institute; serving as a scientific advisor or member of the National Kidney Foundation of Michigan Scientific Advisory Board and Reata Pharmaceuticals; and serving as an American Nephrologists of Indian Origin Steering Committee member and a World Federation of Noncommunicable Diseases International Advisory Council member. K. Zivin reports employment with the Department of Veterans Affairs and Mathematica. All remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Funding
This study was done under the auspices of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cooperative agreement number U58 DP006254 (to M. Heung [coinvestigator], R. Saran [principal investigator], and V. Shahinian [coinvestigator]). R. Sohaney was funded by National Institutes of Health training grant 5T32DK007378-40.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Brenda Gillespie for her contribution to the statistical methods and critical review of the manuscript.
This material is the result of work supported with resources and the use of facilities at the Ann Arbor Veterans Affairs Healthcare System, Ann Arbor, Michigan.
The findings and conclusions in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official position of the Department of Veterans Affairs or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
M. Heung, R. Saran, V. Shahinian, and R. Sohaney were responsible for study concept and design; R. Saran, D. Steffick, and H. Yin were responsible for data acquisition; all authors were responsible for data analysis and/or interpretation; M. Heung, V. Shahinian, R. Sohaney, D. Steffick, and H. Yin drafted the manuscript; and all authors were responsible for critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content.
Footnotes
Published online ahead of print. Publication date available at www.cjasn.org.
See related editorial, “Improved Survival after Acute Kidney Injury: Past and Future,” on pages 179–181.
Contributor Information
Collaborators: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Chronic Kidney Disease Surveillance Team, Rajiv Saran, Vahakn Shahinian, Michael Heung, Brenda Gillespie, Hal Morgenstern, William Herman, Kara Zivin, Deb Gipson, Zubin Modi, Jennifer Bragg-Gresham, Diane Steffick, Yun Han, Xiaosong Zhang, April Wyncott, Neil Powe, Tanushree Banerjee, Delphine Tuot, Chi-yuan Hsu, Joe Coresh, Charles McCulloch, Deidra Crews, Nilka Ríos Burrows, Mark Eberhardt, Alain Koyama, Juanita Mondesire, Meda E. Pavkov, Deborah Rolka, and Sharon Saydah
Supplemental Material
This article contains the following supplemental material online at http://cjasn.asnjournals.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.2215/CJN.01730221/-/DCSupplemental.
Supplemental Table 1. Adjusted Cox proportional mortality hazards models among United States veterans with an AKI hospitalization from 2009 to 2017.
Supplemental Table 2. Unadjusted and adjusted Cox proportional mortality hazard models among patients with and without AKI hospitalization from 2009 to 2017.
References
- 1.Susantitaphong P, Cruz DN, Cerda J, Abulfaraj M, Alqahtani F, Koulouridis I, Jaber BL; Acute Kidney Injury Advisory Group of the American Society of Nephrology : World incidence of AKI: A meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8: 1482–1493, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.United States Renal Data System : 2018 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States, Bethesda, MD, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2018. Available at: https://adr.usrds.org/2021/chronic-kidney-disease/4-acute-kidney-injury. Accessed September 30, 2021 [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wang HE, Muntner P, Chertow GM, Warnock DG: Acute kidney injury and mortality in hospitalized patients. Am J Nephrol 35: 349–355, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.See EJ, Jayasinghe K, Glassford N, Bailey M, Johnson DW, Polkinghorne KR, Toussaint ND, Bellomo R: Long-term risk of adverse outcomes after acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies using consensus definitions of exposure. Kidney Int 95: 160–172, 2019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hsu RK, McCulloch CE, Dudley RA, Lo LJ, Hsu CY: Temporal changes in incidence of dialysis-requiring AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol 24: 37–42, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brown JR, Rezaee ME, Hisey WM, Cox KC, Matheny ME, Sarnak MJ: Reduced mortality associated with acute kidney injury requiring dialysis in the United States. Am J Nephrol 43: 261–270, 2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Harding JL, Li Y, Burrows NR, Bullard KM, Pavkov ME: US trends in hospitalizations for dialysis-requiring acute kidney injury in people with versus without diabetes. Am J Kidney Dis 75: 897–907, 2020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pavkov ME, Harding JL, Burrows NR: Trends in hospitalizations for acute kidney injury - United States, 2000-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 67: 289–293, 2018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Waikar SS, Curhan GC, Wald R, McCarthy EP, Chertow GM: Declining mortality in patients with acute renal failure, 1988 to 2002. J Am Soc Nephrol 17: 1143–1150, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brown JR, Rezaee ME, Marshall EJ, Matheny ME: Hospital mortality in the United States following acute kidney injury. BioMed Res Int 2016: 4278579, 2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Grams ME, Waikar SS, MacMahon B, Whelton S, Ballew SH, Coresh J: Performance and limitations of administrative data in the identification of AKI. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9: 682–689, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Xue JL, Daniels F, Star RA, Kimmel PL, Eggers PW, Molitoris BA, Himmelfarb J, Collins AJ: Incidence and mortality of acute renal failure in Medicare beneficiaries, 1992 to 2001. J Am Soc Nephrol 17: 1135–1142, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sohaney R, Yin H, Shahinian V, Saran R, Steffick D, Nallamothu BK, Heung M: Trends in the incidence of acute kidney injury in a national cohort of US veterans. Am J Kidney Dis 77: 300–302, 2021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group : KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Available at: https://kdigo.org/guidelines/acute-kidney-injury/. Accessed September 30, 2021 [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sohn MW, Arnold N, Maynard C, Hynes DM: Accuracy and completeness of mortality data in the Department of Veterans Affairs. Popul Health Metr 4: 2, 2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.White H: A heteroskedasticity-consistent covariance matrix estimator and a direct test for heteroskedasticity. Econometrica 48: 817–838, 1980 [Google Scholar]
- 17.Huber PJ: The behavior of maximum likelihood estimates under nonstandard conditions. Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, 5: 221–233, 1967 [Google Scholar]
- 18.Siew ED, Peterson JF, Eden SK, Hung AM, Speroff T, Ikizler TA, Matheny ME: Outpatient nephrology referral rates after acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 23: 305–312, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Harel Z, Wald R, Bargman JM, Mamdani M, Etchells E, Garg AX, Ray JG, Luo J, Li P, Quinn RR, Forster A, Perl J, Bell CM: Nephrologist follow-up improves all-cause mortality of severe acute kidney injury survivors. Kidney Int 83: 901–908, 2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Silver SA, Adhikari NK, Bell CM, Chan CT, Harel Z, Kitchlu A, Meraz-Muñoz A, Norman PA, Perez A, Zahirieh A, Wald R: Nephrologist Follow-Up versus Usual Care after an Acute Kidney Injury Hospitalization (FUSION): A randomized controlled trial. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 16: 1005–1014, 2021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.United States Renal Data System : 2020 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States, Bethesda, MD, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2020. Available at: https://adr.usrds.org/2020/chronic-kidney-disease/3-mobidity-and-mortality-in-patients-with-ckd. Accessed September 30, 2021 [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mandelbaum T, Scott DJ, Lee J, Mark RG, Malhotra A, Waikar SS, Howell MD, Talmor D: Outcome of critically ill patients with acute kidney injury using the Acute Kidney Injury Network criteria. Crit Care Med 39: 2659–2664, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Barrantes F, Tian J, Vazquez R, Amoateng-Adjepong Y, Manthous CA: Acute kidney injury criteria predict outcomes of critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 36: 1397–1403, 2008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.