Abstract
Identification of the right parental combinations to maximize heterosis is the major goal of hybrid breeding, which could be achieved through identification of heterotic groups. The main objective of this study was to identify promising heterotic groups for future rice breeding programs. A collection of 359 rice genotypes of diverse origins of China and abroad, composed of inbreds, maintainers, restorers, and temperature-sensitive genic male sterile (TGMS) lines were genotyped using 10K SNP chips. The SNP data set was subjected to genomic analyses for estimation of genetic divergence and diversity. Significant variations were observed in the germplasm with the identification of six different genetic groups. These lines were assigned to the genetic groups independent of their origin. Taking an account of commercially used heterotic groups present in each cluster, three cytoplasmic male sterile (CMS) lines and 14 inbred and restorer lines with moderate to high genetic distances selected from five heterotic patterns were crossed and obtained 42 F1 hybrids. A total of 14 hybrids were found with significant maximum mid- and better-parent heterosis, namely, TaifengA × Guang122, TaifengA × Wushansimiao, and TaifengA × Minghui63 for earliness; Guang8A × Huazhan for dwarf stature; and Guang8A × Huanghuzhan-1, TaifengA × Yuexiangzhan, Guang8A × Minhui3301, TianfengA × Guang122, Guang8A × Yahui2115, TianfengA × Huanghuazhan, TianfengA × Minghui63, TianfengA × Minhui3301, TaifengA × Gui99, and Guang8A × Yuenongsimiao for yield and yield-related traits. Mid-parent and better-parent heterotic F1 hybrids were in positive correlation with the genetic distances as that manifested by commercially used heterotic groups, encouraging the use of genotypic data for identification of heterotic groups. Our study provides an informative strategy for the development of early maturing, lodging resistant and high-yielding commercial hybrids and cultivars in future heterosis breeding programs.
Keywords: heterotic groups, heterotic patterns, hybrid rice, SNP, accession, genetic distance
1 Introduction
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is a staple food for over half of the world’s population. The continuous increase in rice consumption due to population increase (Khush, 2013) necessitates for higher rice production, which could be potentially achieved through rice genetic improvement. The development of hybrid varieties with high yield potential and resistance against disease and responsiveness to climatic changes could fulfill the future rice demands. In hybrid breeding, the most crucial element is identification of high-yielding heterotic patterns to achieve the maximum heterosis (Zhao et al., 2015). Genomic analyses could play a vital role in this regard. A heterotic group is a set of genetically related genotypes that show similar hybrid performance when crossed with individuals from another genetically distinct germplasm group (Melchinger and Gumber, 1984). Genetic relationship between genotypes of various accessions serves as one of the basic criteria for the outyielding potential of these heterotic groups (Thomson et al., 2008). The identification of heterotic groups in different germplasm pools is important for hybrid breeding (Xie et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2014). In general, the more divergent the heterotic groups are, the higher heterosis the offsprings have (Reif et al., 2005). Some studies, however, have reported the otherwise, which necessitates to include the phenotypic evaluation along with molecular marker data to explore both phenotypic and molecular diversity.
High genetic variations were detected in the Asian rice germplasm (Huang et al., 2012), which were divided into three indica subpopulations (South China origin, Southeast Asia origin, and IRRI inbred lines) and two japonica subpopulations (tropical and temperate; Wang et al., 2018a). The works on other groups like the aromatic rice have elucidated further diversity in the rice germplasm in different parts of the world (Civan et al., 2019). Identification of the heterotic groups among these various genetic stocks could be of immense importance for future hybrid breeding.
In hybrid rice crops, heterotic groups can be determined through marker-based genotyping (He et al., 2012). Molecular characterization of genetic diversity, population structure, and genetic relationships among breeding materials within a given set of genotypes will help to understand the use of the collected germplasm for further improvements, such as selecting parental lines and assigning to heterotic groups (Wu et al., 2016). So far, different kinds of molecular markers were used for diversity and divergence analyses in different species (Huang et al., 2012; Ali et al., 2016; Bueno-Sancho et al., 2017). Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) is the most abundant and robust DNA sequence variation present in plant genomes, feasible for automated high-throughput genotyping and available for multiple assay options using different technology platforms to meet the demand for genetic studies and molecular breeding in crop plants (Steemers and Gunderson, 2007; Bernardo et al., 2009; Singh et al., 2015). Only superior parents do not necessarily produce superior heterotic combinations; rather, parents from different heterotic groups with high divergence (Reif et al., 2005) would give elite heterotic combinations (Zeng et al., 2007).
China is considered as the center of origin of indica rice and serves as a leading and major contributor of the world’s hybrid rice breeding (Cheng et al., 2007). Substantial diversity present in the region could be used to identify potential heterotic groups (Huang et al., 2012). Nowadays, the maintainer (sterile) lines and restorer lines have been derived from two major heterotic groups, widely used in the three-line indica hybrid rice breeding programs of China (Wang et al., 2006; Wang and Lu, 2006). The three-line system was first developed by Long Ping Yuan in the 1970s, which consists of a sterile restorer and a maintainer line (Yuan, 1986).
Presently, there has been little rigorous effort considering the genetic diversity and divergence for identification of the heterotic groups exploitable for hybrid rice development. Therefore, the present investigation was made to identify the heterotic groups based on genotypic characteristics of rice accessions of the South China origin, along with reference out group accessions from the United States, Philippines, Pakistan, Iran, and Thailand.
2 Materials and Methods
2.1 Plant Materials and DNA Extraction
A set of 352 Indica and seven Japonica genotypes were selected from different regions of China (Guangdong, Fujian, Guangxi, Hainan, Heilongjiang, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangsu, Jiangxi, Jilin, Sichuan, Yunnan, Taibei, Anhui, Chongqing, and Zhejiang), Philippines, United States, Pakistan, Iran, and Thailand. The set of these 359 lines was composed of 183 inbred lines, 53 maintainers, 120 restorers, one temperature-sensitive genic male sterile (TGMS) line, and two unidentified lines (Supplementary Table S1). These materials were used for genotyping through 10k SNP chips. The genomic DNA was extracted by cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) method (Saghai-Maroof et al., 1984), and the quality and concentration of DNA were examined by agarose gel electrophoresis and Nano-Drop.
2.2 SNP Genotyping and In Silico Analysis of Sequence Data
We performed SNP genotyping via genotyping by target sequencing (GBTS) protocol GenoBaits, which is based on sequence capture in solution (also called a liquid chip). A 10K liquid rice chip developed by Mol Breeding Biotechnology Co., Ltd, Shijiazhuang, China was deployed. The protocol includes the steps of DNA library construction and probe hybridization, which was described in detail previously (Guo et al., 2019).
Sequence data generated by probe-in-solution target sequencing were subjected to in silico analysis as follows: the sequencing data were first checked for quality control; two-terminal reads were merged using FLASH, and sequencing data were then compared with the reference Nipponbare MSU 7.0 genome using BBMap. The alignment results were saved in the SAM/BAM (binary alignment map) format. SNP variants were detected from the BAM files using FreeBayes. The final variant calling was generated through GATK (2.4) (using Haplotype Caller in the gVCF mode) and joint genotyping (using Genotype GVCFs). The VCF file developed was filtered using criteria of MAF (minor allele frequency) > 0.05 and missing data > 80% at both the genotype and SNP marker levels. Only bi-allelic SNP markers with genotype quality > 20 and read depth > 5 were retained after using Vcftools v.0.1.12b (Danecek et al., 2011) and PLINK v1.07 (Purcell et al., 2007) for filtering.
2.3 Genomic Data Analyses
The final set of SNP data was subjected to genomic analyses for estimation of divergence and diversity. The genetic clusters were identified through discriminant analyses of principal component (DAPC) using the ADEGENET package implemented in R-software (Jombart et al., 2010). DAPC represents the non-parametric analyses which attempt to identify the genetic clusters without considering the origin of lines or their status as breeding lines (maintainer, restorer, etc.). Various numbers of clusters could be considered, and the lines were assigned to these clusters based on their genetic makeup. Thus, the DAPC analyses were run considering the possible clusters ranging from K = 2 to K = 10, where the most probable number of clusters was identified through the Bayesian Information Criteria (BIC) values (Jombart et al., 2010). The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method implemented in R-software based on their genetic distances, while the distribution of lines from the two ecotypes, various locations, and types of breeding lines was constructed in MEGA software. Information regarding diversity was estimated with POPPR applied on the GenLight object for populations defined based on ecotypes, locations of origin, and types of breeding lines (Kamvar et al., 2014). Genetic distances between heterotic groups were estimated through the Identity by Stat Distance Matrix method using TASSEL 5 software (Bradbury et al., 2007).
2.4 Plant Materials, Crossing, Field Experimentation, and Collection of Phenotypic Data
A total of 17 genotypes, composed of three maintainers, five inbreds, and nine restorer lines, were selected from five deduced heterotic groups (G-I, G-II, G-IV, G-V, and G-VI) on the basis of early maturity and high yielding performance with genetic distances ranging from 19.3 to 35.9% (Supplementary Table S6). In the late season of 2020, the three female lines, that is, TianfengA (C2330), TaifengA (C2230), and Guang8A (C2228), were crossed with the 14 male lines and obtained 42 new F1 hybrids. All the F1 hybrids and their parents were evaluated in Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) with three replications at Baiyun experimental base Guangzhou during early season of 2021. Observations were recorded on six earliness and yield-related traits, that is, days to 50% heading, plant height, panicles per plant, number of grains per panicle, 1,000-grain weight, and grain yield per plant.
2.5 Phenotypic Data Analyses
Analysis of variance was performed using Statistix 8.1. The mid parent and better parent (heterobeltiosis) were worked out as suggested by Dan et al. (2014) in Microsoft excel 2013. The correlation graphs of heterosis and genetic distances were also constructed in Microsoft excel 2013
3 Results
3.1 Summary Statistics on the SNPs
The 10,268 sites were evenly distributed on the short arm, centromere, and long arm of all the 12 chromosomes, as assessed for 359 rice genotypes. The number of SNPs on chromosomes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12 were 1,345, 1,097, 1,261, 914, 814, 899, 789, 672, 552, 573, 677, and 675, respectively. The average physical distance between SNPs is about 34.08 Kb based on a genome size of 350 Mb. The average minor allele frequency and the number of missing sites were 0.21989 and 0, respectively, whereas the proportion of heterozygous sites was 1.52% (Supplementary Table S2).
3.2 Diversity of the Breeding Population
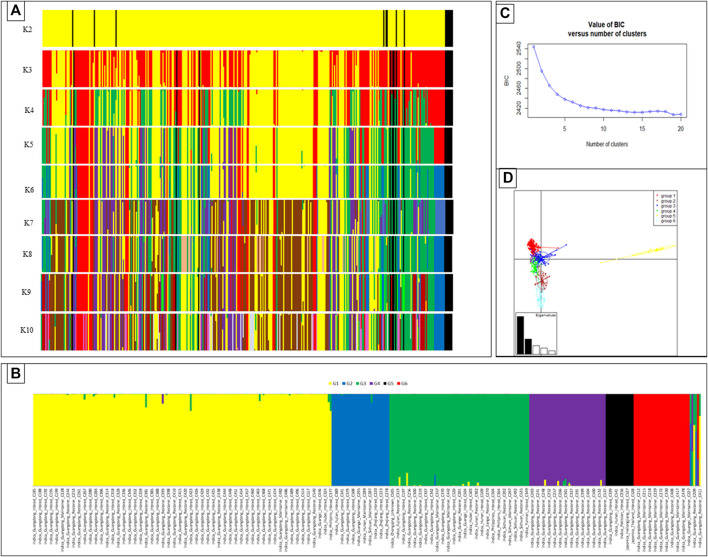
Divergent groups were identified using discriminate analysis of principal components (DAPC) to represent potential diversity in the rice germplasm tested in this study. Grouping was made considering different K levels (K2-K10) of the DAPC analyses (Figure 1A). While considering the BIC values and principal component analysis grouping, six different genetic groups were considered the optimum within the rice germplasm (Figures 1B,C). In terms of the distribution of these genetic groups, G1 was dominant in the overall Indica germplasm, while the entire Japonica genotypes were grouped within a single group, that is, G5, with limited divergence among Japonica lines.
FIGURE 1.
DAPC of rice accessions collected from different provinces in South China, Philippines, Thailand, Iran, Pakistan, and United States. Possible DAPC clusters ranging from K2 to K10 (A). The cluster of 359 rice genotypes of diverse origins into different genetic groups set a siding geographical origin for the optimal K-value (K = 6) in DAPC (B). Bayesian information criteria (BIC) supported six distinct genetic groups (C). The Eigen values of the analysis suggest that the first two components explained the maximum genetic structure of the data set. Scatter plot of the 359 accessions divided into six genetic groups (D).
Considering the geographical origin, the most prevalent genetic group, that is, G1, contained most of the genotypes from the Guangdong origins, with a few genotypes from Guangxi, Hainan, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangxi, Sichuan, and Philippines present (≤3). Genetic group G2 was represented mainly by the lines from Zhejiang (all genotypes placed in this group), and group 3 contained all genotypes of the Yunnan origin along with few genotypes from diverse origins. Group G5 had all the genotypes of Heilongjiang, Jilin, Pakistan, and United States. A few of Guangdong and Jiangsu genotypes also belonged to this genetic group. Some of the Guangdong and Guangxi genotypes were assigned to group G6 (Figure 1B).
The distribution of the four types of breeding lines (inbred lines, maintainers, restorers, and the TGMS line) was also assessed to various genetic groups. DAPC results showed that the inbred lines, maintainers, and restorers were distributed across different genetic groups, and no genetic group was specific to any type of breeding lines. G1 was predominantly composed of the inbred lines, along with some maintainer and restorer lines. G6 was mainly represented by maintainer lines and very few restorers but no inbred lines. G3 was represented by all types of breeding lines, while G4 was represented by the restorers and a few maintainer lines (Figure 1B and Supplementary Table S3). This was in line with the cluster analysis-based grouping where all types were dispatched across different groups. Thus, all the genetic groups had substantial variability for these lines to be utilized for breeding purposes (Figure 1B and Supplementary Table S3).
3.3 Diversity Across Ecotypes and Breeding Lines
Low genetic diversity was recorded between groups (ranging from 0.144 to 0.303; Table 1). G’st values between groups (ranging from 0.324 to 0.427) indicated high divergence between heterotic groups suitable for future breeding programs. For all types of grouping patterns, the global heterozygosity value was 0.304. At the subspecies level, the highest value of 0.291 of diversity index was calculated for Indica subspecies containing 704 alleles, whereas a low diversity index of 0.107 was manifested by Japonica subspecies with 14 alleles only. The divergence calculated at subspecies level grouping was the maximum (0.548), as expected (Table 1). The number of alleles and diversity index in breeding lines ranged from 2 to 366 and from 0.003 to 0.304, respectively. Inbred lines showed the maximum value (0.304) of diversity index, followed by restorers (0.282), whereas the divergence value was the maximum (0.093) between breeding lines (Table 1). The genetic groups also revealed a high value of divergence (G’st = 0.427). Moreover, allelic frequencies of genetic groups ranged between 12 and 322, whereas the minimum value (12) was manifested by the group with unassigned lines and the maximum by group 1 (K1); however, the diversity index ranged between 0.182 and 0.303. Group 2 (K2) revealed the second highest value (0.244) of diversity index, followed by the group with unassigned lines (UN) with 0.243. K2 and K3 contained accessions from eight and 11 different locations, respectively, and thus had high diversity indices (Table 1).
TABLE 1.
Amount of diversity index, heterozygosity, divergence, and number of alleles in ecotypes, breeding lines, locations, and genetic groups.
| Grouping | Category | Sample size | Number of alleles | Diversity index | Total heterozygosity | Gst | G’st |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice Ecotypes | Indica | 352 | 704 | 0.291 | 0.304 | 0.095 | 0.548 |
| Japonica | 7 | 14 | 0.107 | ||||
| Breeding lines | Unknown | 2 | 4 | 0.139 | 0.304 | 0.051 | 0.093 |
| Inbred | 183 | 366 | 0.304 | ||||
| Maintainer | 53 | 106 | 0.254 | ||||
| Restorer | 120 | 240 | 0.282 | ||||
| TGMS | 1 | 2 | 0.003 | ||||
| Genetic Group | K1 | 161 | 322 | 0.202 | 0.304 | 0.324 | 0.427 |
| K2 | 31 | 62 | 0.244 | ||||
| K3 | 75 | 150 | 0.303 | ||||
| K4 | 41 | 82 | 0.191 | ||||
| K5 | 15 | 30 | 0.144 | ||||
| K6 | 30 | 60 | 0.182 | ||||
| UN | 6 | 12 | 0.243 |
3.4 Identification of Heterotic Groups
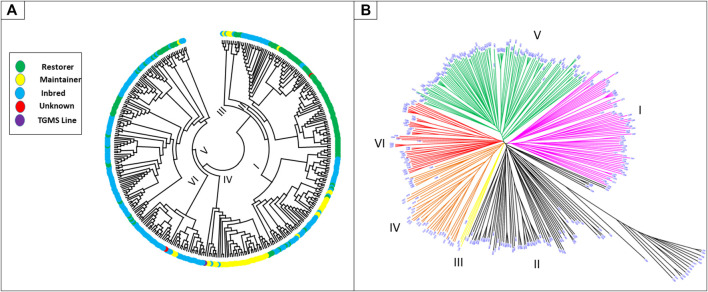
Genetic grouping was further confirmed via cluster analysis. The maximum number of accessions was recorded in cluster V (32.31%), followed by cluster II with (25.07%; Supplementary Table S4; Figure 2B). Similarly, cluster I contained 18.66% accessions in total, which was further divided into two subgroups, GI (12.3%) and GII (6.4%). Cluster II was further divided into four subgroups, GI (1.7%), GII (8.1%), GIII (4.2%), and GIV (11.1%). Cluster III was the smallest group that shared 1.39% of the accessions, whereas clusters IV and VI contained 10.6 and 11.14% of the total accessions, respectively (Supplementary Table S4).
FIGURE 2.
Distribution of breeding lines (inbreds, maintainers, restorers, TGMS, and unknown) into different clusters (A). Phylogenetic tree, showing the overall distribution of 359 rice accessions into six different clusters (B).
Indica lines were clustered into six groups, while those of Japonica were located only in cluster II with high divergence from the rest accessions of the cluster (Figure 2B). The grouping of “Indica”-type rice lines in this group could be due to potential mismatches or erroneous labeling of these lines. Based on genetic information, inbred lines were dominant in clusters I, V, and VI; restorer lines were dominant in cluster II; and maintainer lines were dominant in clusters I and IV (Figure 2A and Supplementary Table S6). In cluster I, inbred lines (42), restorers (11), and maintainers (14) from 11 locations, and all the accessions from Zhejiang and Yunnan were present. The early developed and widely used maintainers, such as Zhenshan 97B (C288), BoB (C296), II-32B (C299), and the maintainer LongtefuB (C290) used in the development of high-yielding hybrids in South China, were also clustered into this group. Maintainer lines Gang46B (C368) and XiandangB (C293) were found very close to the commercial maintainer LongtefuB (C290) in cluster I (Figure 2B). Similarly, cluster II consisted of 19 inbreds, 69 restorers, and two maintainers from 14 locations. The most famous commercially used restorer lines Minghui63 (C281, C375), Guanghui998 (C203), and Gui99 (C536) were present in this group. Moreover, restorer lines R122 (C298), R308 (C251), R368 (C257), and R428 (C245), recently used for commercial hybrids, were also grouped in cluster II. The positions of restorer lines R998-3 (C533), R108 (C502), R122-3 (C537), Guang122 (C373), R721 (C303), R308-2 (C534), R390-1(C247), R290 (C299), R498 (C309), and R889 (C308) were close to the commercially used restorers. Cluster III was the smallest cluster with only two inbred (C377, C511) and three maintainer lines, which include the widely used maintainer 9311B (C235). Cluster IV was dominated by maintainers (32 out of 38 lines), including the widely used maintainers TianfengB (C330), WufengB (C272), RongfengB (C219), TaifengB (C230), HengfengA (C227), and Guang8B (C228). The maintainers in cluster IV are known as modern maintainer lines in China. Some other maintainer lines, such as JifengB (C217), WFB-TFB-derived (C418), and ZaofengB (C216), were closely related (Figure 2B) to the commercially used lines. Cluster V was composed of inbred lines (84) and restorers (32) but no maintainers. Although accessions from five different origins contributed to the cluster, the predominant location and breeding lines were Guangdong and inbred lines, respectively. Among the restorers in this cluster, Yuehesimiao (C190), R308 (C251), and Huazhan (C250) were widely used restorers. Using these commercially used lines as a close reference, we found three inbred lines, Yuehesimiao2 (C267), Guanghong3-3 (C538), and Yuexianzhan8 (C199), and two restorer lines, R721 (C303) and R308-2 (C534), which may also serve as heterotic group in the development of high-yielding hybrids. Moreover, cluster VI consisted of 40 inbreds and three maintainers from four locations. Similar to cluster V, Cluster VI also showed the greater contribution of inbred lines from Guangdong. The widely used maintainer YexiangB (C231) and the most famous aromatic Guangdong Simiao and the inbred varieties, Meixiangzhan 2 (C487), Xiangyaxiangzhan (C344), and Xiangzhuxiangsimiao (C428), were all placed in this cluster (Figure 2B). The presence of commercially used heterotic groups in all the six clusters indicated that we have six herterotic groups’ clusters in our germplasm.
3.5 Identification of Heterotic Patterns Between Groups
All the rice accessions have been divided into six clusters (heterotic groups), and the heterotic patterns could be deduced based on the accessions which served already as the parental lines of the heterotic hybrid combinations that existed, widely used for commercial production in China. It was as follows:
3.5.1 Heterotic Pattern I (Cluster I × Cluster II)
Many famous maintainer lines, such as Zhenshan97B (C288), BoB (C296), LongtefuB (C290), and II-32B (C299), were located in Cluster I, while the famous restorer line Minghui63 (C281), R2156 (C263), R998 (C203), and Gui 99 (C201), were placed in Cluster II (Table 2 and Figure 2B). Many heterotic hybrids widely used for commercial production in China, such as Shanyou 63 (Zhenshan 97A/Minghui 63), Boyou 998 (BoA/R998), and ShanyouGui99 (Zhenshan 97A/Gui99), confirmed this pattern. It indicated that the hybrids derived from accessions of Cluster I and Cluster II had better heterosis; therefore, Cluster I and Cluster II could be a heterotic pattern. All the early-maturing inbred lines from Zhejiang Province and four accessions from Yunnan were located in Cluster I, which could be used for breeding new maintainer lines.
TABLE 2.
Heterotic groups used for commercial hybrid production, genetic distance, and their deduced heterotic patterns.
| Female parent (A) | Cluster | Male parent (R) | Cluster | Commercial hybrid | Genetic distance | Heterotic patterns |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AnfengA (C478) | IV | Yuehesimiao (C190) | V | Antianyouyuehesimiao | 0.351 | IV × V |
| Guang8A (C228) | IV | Yuehesimiao (C190) | V | Guang8youyuehesimiao | 0.277 | IV × V |
| HengfengA (C227) | IV | Yuehesimiao (C190) | V | Hengfengyouyuehesimiao | 0.290 | IV × V |
| TaifengA (C230) | IV | Yuehesimiao (C190) | V | Taiyouyuehesimiao | 0.285 | IV × V |
| LongtepuA (290) | I | Yuehesimiao (C190) | V | Teyouyuehesimiao | 0.294 | I × V |
| TianfengA (C330) | IV | R122 (C298) | II | Tianyou122 | 0.341 | IV × II |
| TianfengA (C330) | IV | R308 (C251) | V | Tianyou308 | 0.314 | IV × V |
| TianfengA (C330) | IV | R368 (C257) | II | Tianyou368 | 0.309 | IV × II |
| TianfengA (C330) | IV | R428 (C245) | II | Tianyou428 | 0.331 | IV × II |
| WufengA (C272) | IV | Yuehesimiao (190) | V | Wuyouyuehesimiao | 0.292 | IV × V |
| Zhenshan97B (C288) | I | Minghui63 (C281) | II | Shan you 63 | 0.379 | I × II |
| BoB (C296) | I | R998 (C203) | II | Boyou998 | 0.369 | I × II |
| Zhenshan97A (C288) | I | Gui 99 (C536) | II | shan you Gui99 | 0.368 | I × II |
| TianfengA (330) | IV | Guanghui 998(C203) | II | Tianyou 998 | 0.330 | IV × II |
| WufengB (C272) | IV | R998 (C203) | II | Wuyou 998 | 0.325 | IV × II |
| 9311B (C235) | III | Huazhan (C250) | V | Quanyouhuazhan | 0.304 | III × V |
| RongfengB (C219) | IV | R463 (C269) | I | Rongyou 463 | 0.317 | IV × I |
| Guang8A (C228) | IV | Yuenongsimiao (C265) | V | Guang8youyuenongsimiao | 0.289 | IV × V |
| Quan9311-A(235) | III | Wushansimiao (C320) | V | Quanyousimiao | 0.310 | III × V |
| Taifeng B(C230) | IV | R208(C248) | II | Rongyou Taiyou 208 | 0.325 | IV × II |
| Jifeng B (C217) | IV | R1002 (C242) | II | Jifng you 1,002 | 0.335 | IV × II |
| Tianfeng B(C330) | IV | Huazhan(C250) | V | Tian you huazhan | 0.308 | IV × V |
| Wufeng B(C272) | IV | R308(C251) | V | Wuyou 308 | 0.331 | IV × V |
| Wufeng B(C272) | IV | Huazhan(C250) | V | Wuyouhuazhan | 0.320 | IV × V |
| Wufeng B(C272) | IV | Hanhui1179(C239) | V | Wuyou1179 | 0.314 | IV × V |
| Tianfeng B (C330) | IV | R305(C381) | V | Taiyou 305 | 0.327 | IV × V |
| Tianfeng B (C330) | I | R398 (C243) | IV | Taiyou 398 | 0.291 | I × IV |
| Jifeng B (C217) | I | V1100(C300) | IV | Jiyou 1,100 | 0.317 | I × IV |
| Te B (C290) | I | R721(C303) | V | Teyou 721 | 0.315 | I × V |
| YexiangB (C231) | VI | Fuhui 676 (C319) | II | Yexiangyou 676 | 0.315 | VI × II |
| Mean | 0.319 | |||||
| Minimum | 0.277 | |||||
| Maximum | 0.379 |
3.5.2 Heterotic Pattern II (Cluster IV × Cluster II)
A number of super hybrid rice varieties were derived from this crossing pattern, including Tianyou998 from TianfengB (C330) and R998 (C203), Wuyou998 from WufengB (C272) and R998 (C203), Taifengyou 208 from TaifengB (C230) and R208 (C248), and Jifengyou 1,002 from JifengB (C217) and R1002 (C242). All the female parents of these hybrids were taken from cluster IV, and male parents were taken from cluster II (Table 2).
3.5.3 Heterotic Pattern III (Cluster IV × Cluster V)
The super rice hybrid “Tianyouhuazhan” was derived from TianfengB (C330) and Huazhan (C250), “Wuyou308” from Wufeng B (C272) and R308 (C251), Wuyouhuazhan from WufengB (C272) and Huazhan (C250), Wuyou1179 from WufengB (C272) and Hanghui1179 (C239), and Taiyou305 from TaifengB (C230) and R305 (C381), all supporting this heterotic group pattern.
3.5.4 Heterotic Pattern IV (Cluster III × Cluster V)
The famous hybrid Quanyousimiao was derived from 9311B (C235) and Wushansimiao (C320), and Quanyouhuazhan was derived from 9311B (C235) and Huazhan (C250), supporting this heterotic pattern.
3.5.5 Heterotic Pattern V (Cluster IV × Cluster I)
The widely planted early-maturing hybrid Taiyou398 derived from TaifengB(C230) and R398 (C243) and Jiyou 1,100 derived from Jifeng B (C217) and V1100 (C300) supported this pattern.
3.5.6 Heterotic Pattern VI (Cluster I × Cluster V)
The high-yielding hybrid rice hybrid Teyou 721 derived from LongtefuB (C290) and R721 (C303) supported this pattern.
3.5.7 Heterotic Pattern VII (Cluster VI × Cluster II)
The fine-quality hybrid Yexiangyou 676 supported this pattern as it was derived from YexiangB (C231) and Fuhui676 (C319).
All the six Clusters I–VI had already been involved in the seven heterotic patterns mentioned above, so these clusters could be considered as heterotic groups.
3.6 Heterotic Group and Genetic Distance
The diversity analyses of DAPC-based groups revealed significant diversity for all the heterotic groups, that is, K1 (0.202), K2 (0.244), K3 (0.303), K4 (0.191), K5 (0.144), K6 (0.182), and UN (0.283; Table 1). Similarly, the G’st value (0.427) also summarized the overall mean diversity (distances) between the heterotic groups, which were at the optimum level (Table 1). Genetic distances between the heterotic groups, the deduced heterotic groups of commercially used hybrids, and their nearby heterotic groups spotted on the Neighbor Joining tree (Figure 2B) were estimated through the Identity by state (IBS) matrix ranging between 0.01 and 0.391 with a mean value of 0.276 (Supplementary Table S5). The maximum genetic distance (0.391) was observed for the heterotic group Gang46B (C368) × R498 (C309), followed by Gang46B (C368) × Minghui63 (C281) (0.389), whereas the minimum genetic distance (0.010) was noted for R301-1 (C251) × R308-2 (C534), followed by (0.013) R998-3 (C533) × R998-1 (C203). However, the majority groups were found very close to the average (0.28) genetic distances (Supplementary Table S5). Among commercially used heterotic groups, the maximum genetic distance (0.379) was observed for Zhenshan 97B (C288) × Minghui63 (C281) of the deduced heterotic pattern (GI ×GII), followed by Bo B (C296) × R998 (C203) and Zhenshan 97A (288) × Gui 99 (536) with genetic distances of 0.369 and 0.368, respectively, from heterotic patterns (GI × GII) (Table 2). Majority of the commercially used heterotic groups showed greater genetic distances than the overall mean genetic distance of 0.276, which reflected that the genetic distances between heterotic groups have a positive effect on heterosis.
3.7 Variability for Earliness and Yield-Related Phenotypic Traits in F1 Hybrids and Their Parents
Analysis of variance revealed highly significant (p < 0.01) differences among genotypes for days to 50% heading, plant height, panicles per plant, number of grains per panicle, 1,000-grain weight, and grain weight per plant (Table 3; Supplementary Table S7). Days to 50% heading ranged from 76.33 to 101.67 days, with a net difference of 25.34 days (Supplementary Table S8). The plant heights varied from 88.00 to 131.00 cm, with a net difference of 43 cm and a majority of the F1 hybrids close to the mean (110.60 cm). The mean values of 4.33 to 11.00 panicles per plant were observed among genotypes. Almost all F1 hybrids revealed above-average performance for panicles per plant. For grains per panicle, the genotypes ranged from 30.41 to 173.61, showing a wide range of variability. A majority of hybrids showed above-average performance, and none of the hybrids was observed at par to the minimum. The mean values for 1,000-grain weight varied from 20.893 to 32.013 g. For grain yield per plant, the mean values of the genotypes ranged between 9.48 and 40.35 g, among which the maximum grain yield was produced by the three hybrids Guang8A × Yuenongsimiao (40.350 g), TaifengA × Gui99 (36.480 g), and TaifengA × Guang122 (35.250 g), followed by two other F1 hybrids, TaifengA × Minghui63 (31.537 g) and TaifengA × Huanghuazhan (30.823 g).
TABLE 3.
Analysis of variance for earliness, plant height, yield, and yield-related traits.
| S.No | Traits | GMS | Ems | F-ratio | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Days to 50% heading (#) | 120.63 | 1.13 | 106.54*** | 1.19 |
| 2 | Plant height (cm) | 192.77 | 5.38 | 35.82*** | 2.12 |
| 3 | Panicles per plant (#) | 6.42 | 0.44 | 14.61*** | 8.95 |
| 4 | Grains per panicle (#) | 2,222.70 | 175.78 | 12.64*** | 10.93 |
| 5 | 1,000-grains weight (g) | 59.06 | 0.08 | 743.82*** | 1.09 |
| 6 | Grains weight per plant (g) | 100.44 | 2.97 | 33.85*** | 7.52 |
3.8 Heterosis Estimates on the Basis of Phenotypic Performance
Heterosis over the mid parent and the best parent (heterobeltiosis) was studied in 38 F1 hybrids for various traits. For heading date, significant negative heterosis over mid and better parents was exhibited by nine and two F1 hybrids, respectively. Negative heterosis over the mid parent ranged from −0.36% (Guang8A × Huanghuazhan-1) to −9.49% (TaifengA × Guang122), whereas ranging from 0.55% (Guang8A × Wushansimiao) to 10.02% (TianfengA × Huanghuazhan), 18 F1 hybrids manifested mid parent-positive heterosis (Table 4). The better-parent heterotic performance ranged from −1.47% (Guang8A×Huazhan) to −2.97% (TaifengA × Guang122). Better-parent significantly positive heterosis ranged between 1.83% (Guang8A × Huanghuazhan-1) and 27.57% (TianfengA × Minhui3301). For heading date, negative heterosis is favored because it leads to earliness. A total of 19 F1 hybrids showed mid-parent heterosis and three F1 hybrids showed better-parent heterosis with negative values, in which nine mid parents and two better parents reached a significance level. Plant height revealed low to moderate levels of positive mid- and better-parent heterosis for a majority of F1 hybrids. One F1 hybrid (Guang8A × Huazhan) showed negative mid-parent and better-parent heterosis (−4.04%). A total of 10 F1 hybrids revealed positive mid-parent heterosis for panicles per plant, and maximum heterotic values were exhibited by the F1 hybrid Guang8A × Huanghuazhan-1 (31.30%). Only one F1 hybrid (Guang8A × Huanghuazhan-1) showed positive heterobeltiosis (14.24%) for panicles per plant. However, the remaining F1 hybrids manifested negative heterosis over the better parent (Table 4).
TABLE 4.
Mid-parent and better-parent heterosis estimates for days to 50% heading, plant height, panicles per plant, and genetic distances between their corresponding parents.
| Cross code | F1 hybrid name | Days to 50% heading | Plant height | Panicles per plant | GD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPH | BPH | MPH | BPH | MPH | BPH | |||
| C330 × C373 | TianfengA × Guang122 | 4.55** | 18.22** | 16.99** | 20.83** | −13.31** | −20.2** | 0.34 |
| C330 × C205 | TianfengA × Huanghuazhan-1 | 2.61** | 19.63** | 6.53** | 17.55** | −10.3 | −22.8** | 0.3 |
| C330 × C250 | TianfengA × Huazhan (HZ) | 5.95** | 20.56** | 12.81** | 23.99** | −22.59** | −24.1** | 0.31 |
| C330 × C375 | TianfengA × Minghui63 | 2.50** | 24.3** | 16.00** | 30.43** | −4.99 | −15.2** | 0.35 |
| C330 × C472 | TianfengA × Wushansimiao | 4.56** | 17.76** | 5.71** | 21.59** | 1.24 | 0 | 0.29 |
| C330 × C447 | TianfengA × Huanghuazhan | 10.02** | 25.7** | 7.74** | 16.92** | −32.45** | −35.5** | 0.24 |
| C330 × C268 | TianfengA × Minhui3301 | 3.02** | 27.57** | 17.26** | 31.69** | −0.01 | −25.3** | 0.35 |
| C330 × C493 | TianfengA × Chenghui727 | 6.75** | 25.7** | 10.65** | 27.28** | −17.30** | −30.4** | 0.34 |
| C330 × C492 | TianfengA × Yahui2115 | 9.02** | 27.1** | 9.40** | 34.47** | −26.48** | −36.7** | 0.36 |
| C330 × C201 | TianfengA × Gui99 | 4.72** | 19.16** | 8.18** | 21.97** | 4.7 | −1.28 | 0.34 |
| C330 × C282 | TianfengA × Yuexiangzhan | 3.79** | 21.5** | 13.75** | 30.56** | −10.24 | −27.9** | 0.31 |
| C330 × C386 | TianfengA × Yuenongsimiao | 7.16** | 22.43** | 9.56** | 21.59** | −0.03 | −17.7** | 0.27 |
| C230 × C373 | TaifengA × Guang122 | −9.49** | −2.97** | 5.39** | 7.82** | −29.29** | −31.9** | 0.33 |
| C230 × C205 | TaifengA × Huanghuazhan-1 | −0.96 | 9.32 | 4.30** | 8.61** | 5.57 | −12.6** | 0.31 |
| C230 × C250 | TaifengA × Huazhan (HZ) | −2.95** | 4.66** | 3.82** | 7.7** | −11.66* | −17.2** | 0.29 |
| C230 × C375 | TaifengA × Minghui63 | −7.58** | 5.93** | 6.09** | 12.46** | 14.07** | −2.31 | 0.33 |
| C230 × C472 | TaifengA × Wushansimiao | −8.73** | −2.54** | 0.36 | 8.72** | −3.57 | −6.9 | 0.31 |
| C230 × C447 | TaifengA × Huanghuazhan | −0.59 | 7.63 | 0.66 | 3.17* | −8.2 | −16.1** | 0.24 |
| C230 × C268 | TaifengA × Minhui3301 | −5.07** | 11.02** | 11.55** | 18.12** | 20.63** | −12.6** | 0.32 |
| C230 × C493 | TaifengA × Chenghui727 | −0.38 | 11.02 | 11.03** | 20.27** | 6.38 | −13.8** | 0.31 |
| C230 × C492 | TaifengA × Yahui2115 | −1.34 | 8.9 | 3.92** | 19.93** | −13.89* | −28.7** | 0.33 |
| C230 × C201 | TaifengA × Gui99 | −1.38 | 6.36 | 0.58 | 6.91** | −0.63 | −10.3* | 0.32 |
| C230 × C282 | TaifengA × Yuexiangzhan | −2.10** | 8.47** | 1.2 | 9.4** | 28.89** | 0 | 0.32 |
| C230 × C386 | TaifengA × Yuenongsimiao | −2.54** | 5.51** | 1.57 | 6.34** | −17.41** | −34.5** | 0.29 |
| C228 × C373 | Guang8A × Guang122 | 2.76** | 2.2** | 8.33** | 1.99** | −26.33** | −33** | 0.27 |
| C228 × C205 | Guang8A × Huanghuazhan-1 | −0.36 | 1.83* | 5.65** | 5.65** | 31.30** | 14.24** | 0.23 |
| C228 × C250 | Guang8A × Huazhan (HZ) | −1.47 | −1.47 | −4.04** | −4.39** | −39.86** | −40.3** | 0.22 |
| C228 × C375 | Guang8A × Minghui63 | −1.73** | 4.03** | 6.02** | 7.85** | −9.37 | −18.2** | 0.31 |
| C228 × C472 | Guang8A × Wushansimiao | 0.55 | 1.49 | −1.91 | 1.89 | −24.06** | −25.9** | 0.19 |
| C228 × C319 | Guang8A × Fuhui676 | 5.54** | 11.72** | 7.35** | 19.88** | −29.89** | −39** | 0.29 |
| C228 × C447 | Guang8A × Huanghuazhan | 0.73 | 1.1 | 3.77** | 2.2 | −10.05 | −13* | 0.22 |
| C228 × C268 | Guang8A × Minhui3301 | −3.57** | 4.03** | 6.64** | 8.37** | 24.13** | −6.51 | 0.29 |
| C228 × C493 | Guang8A × Chenghui727 | −0.89 | 2.2** | −0.3 | 3.56* | 2.28 | −13* | 0.29 |
| C228 × C492 | Guang8A × Yahui2115 | −1.43 | 0.73 | 3.08** | 13.81** | −19.41** | −29.9** | 0.33 |
| C228 × C201 | Guang8A × Gui99 | 0 | 0 | 2.26 | 4.29** | −15.65** | −19.5** | 0.28 |
| C228 × C307 | Guang8A × Ce64 | 2.36** | 3.3** | 10.48** | 3.14* | −25.00** | −33.3** | 0.28 |
| C228 × C282 | Guang8A × Yuexiangzhan | −1.07 | 1.47 | 7.67** | 11.61** | −15.21* | −31.2* | 0.24 |
| C228 × C386 | Guang8A × Yuenongsimiao | 2.55** | 2.93** | 3.12** | 3.66* | −17.21** | −31.2** | 0.21 |
| Mean | 0.67 | 9.96 | 6.40 | 13.47 | −8.29 | −20.10 | 0.29 | |
| Minimum | −9.49 | −2.97 | −4.04 | −4.39 | −39.86 | −40.30 | 0.19 | |
| Maximum | 10.02 | 27.57 | 17.26 | 34.47 | 31.30 | 14.24 | 0.36 | |
More than half of the F1 hybrids depicted significant positive mid-parent heterosis for grains per panicle (Table 5). Heterotic effects varied from 17.49% (Guang8A × Huanghuazhan) to 74.39% (Guang8A × Minghui63) over their mid parents. Significantly positive better-parent heterosis was recorded on 14 F1 hybrids, ranging from 16.73% (TianfengA × Minhui3301) to 45.01 (Guang8A × Yahui2115). A majority of the F1 hybrids showed significant positive mid- and better-parent heterosis for 1,000-grain weight (Table 5). The F1 hybrids TaifengA × Minghui63 and TaifengA × Minhui3301 revealed the highest values of 20.37 and 17.98% over their mid- and better-parental inbred lines, respectively. Regarding mid-parent heterosis for grain yield per plant, 18 and 15 F1 hybrids manifested significant positive mid- and better-parent heterosis, respectively (Table 5). Mid-parent significantly positive heterosis ranged from 20.73% (TianfengA × Minhui3301) to 94.99% (TaifengA × Gui99). The latter promising F1 hybrid was followed by four other high-yielding hybrids, Guang8A × Yuenongsimiao (77.00%), TaifengA × Huanghuazhan-1 (71.19%), TaifengA × Guang122 (60.08%), and TaifengA × Minghui63 (59.01%). For better-parent heterosis, the F1 hybrid TaifengA × Gui99 (71.03%) exhibited the most significant positive heterotic effects.
TABLE 5.
Mid-parent and better-parent heterosis estimates for grains per panicle, 1,000-grain weight, grain weight per panicle, and genetic distances between their corresponding parents.
| Cross code | F1 hybrid name | Grains per panicle | 1,000-grain weight | Grain weight per plant | GD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPH | BPH | MPH | BPH | MPH | BPH | |||
| C330 × C373 | TianfengA × Guang122 | 60.06** | 33.85** | 13.25** | 8.58** | 11.1 | 7.88** | 0.34 |
| C330 × C205 | TianfengA × Huanghuazhan-1 | 23.07** | 17.79* | −1.98** | −9.73** | 45.34** | 22.53** | 0.3 |
| C330 × C250 | TianfengA × Huazhan (HZ) | 13.00 | 12.03 | 7.16** | −3.61** | −47.86** | −43.2** | 0.31 |
| C330 × C375 | TianfengA × Minghui63 | 62.23** | 2.77 | 16.40** | 14.05** | 34.61** | 25** | 0.35 |
| C330 × C472 | TianfengA × Wushansimiao | 5.03 | 4.77 | 8.70** | 1.19 | 52.45** | 20.2* | 0.29 |
| C330 × C447 | TianfengA × Huanghuazhan | 39.58** | 32.63** | 6.57** | −0.15 | 21.95* | 21.01* | 0.24 |
| C330 × C268 | TianfengA × Minhui3301 | 50.48** | 16.73* | 18.63** | 15.14** | 20.73* | 14.7 | 0.35 |
| C330 × C493 | TianfengA × Chenghui727 | 19.54* | 12.91 | 5.99** | −1.3* | 26.13** | 14.05 | 0.34 |
| C330 × C492 | TianfengA × Yahui2115 | 29.25** | 23.98** | 6.46** | 6.33** | 4.04 | 3.08 | 0.36 |
| C330 × C201 | TianfengA × Gui99 | −3.41 | −4.69 | 2.96** | 1.99** | −20.94* | −30.8** | 0.34 |
| C330 × C282 | TianfengA × Yuexiangzhan | 18.26* | 11.33 | 9.18** | 2.5** | 9.25 | 2.23 | 0.31 |
| C330 × C386 | TianfengA × Yuenongsimiao | 5.21 | −12.6* | 1.75* | −4.6** | 49.39** | 32.15** | 0.27 |
| C230 × C373 | TaifengA × Guang122 | 37.44** | 27.57** | 7.86** | 7.28** | 60.08** | 55.22** | 0.33 |
| C230 × C205 | TaifengA × Huanghuazhan-1 | 18.10* | 9.78* | −8.05** | −18.9** | 71.19** | 44.51** | 0.31 |
| C230 × C250 | TaifengA × Huazhan (HZ) | 13.54 | 2.13 | 16.43** | 9.46** | −11.76 | −20.9** | 0.29 |
| C230 × C375 | TaifengA × Minghui63 | 73.99** | 16.57 | 20.37** | 17.11** | 59.01** | 37.86** | 0.33 |
| C230 × C472 | TaifengA × Wushansimiao | 14.93 | 2.82 | 7.66** | 4.93** | −43.67** | −55.5** | 0.31 |
| C230 × C447 | TaifengA × Huanghuazhan | −11.34 | −24.3** | 6.37** | 4.39** | 23.41** | 22.64** | 0.24 |
| C230 × C268 | TaifengA × Minhui3301 | 60.62** | 36.71** | 20.11** | 17.98** | 10.32 | 4.67 | 0.32 |
| C230 × C493 | TaifengA × Chenghui727 | 3.54 | −2.5 | 12.30** | 0.11 | 3.47 | −6.31 | 0.31 |
| C230 × C492 | TaifengA × Yahui2115 | 34.40** | 24.65** | 8.87** | 3.97** | 25.88** | 24.54** | 0.33 |
| C230 × C201 | TaifengA × Gui99 | 11.12 | −1.96 | 4.61** | −1.12 | 94.99** | 71.03** | 0.32 |
| C230 × C282 | TaifengA × Yuexiangzhan | 10.73 | −6.25 | 9.61** | 7.79** | 8.01 | 0.92 | 0.32 |
| C230 × C386 | TaifengA × Yuenongsimiao | 21.65** | −7.58 | 5.63** | 3.73** | 27.29** | 12.75 | 0.29 |
| C228 × C373 | Guang8A × Guang122 | 43.94** | 20.37** | 2.93** | −1.86* | −6.54 | −14 | 0.27 |
| C228 × C205 | Guang8A × Huanghuazhan-1 | −6.02 | −10.1 | −4.74** | −19** | 27.23* | 12.52 | 0.23 |
| C228 × C250 | Guang8A × Huazhan (HZ) | 40.59** | 39.38** | −0.29 | −2.29** | −9.66 | −22.8** | 0.22 |
| C228 × C375 | Guang8A × Minghui63 | 74.39** | 10.48 | 9.70** | 2.42** | 17.85 | 15.52 | 0.31 |
| C228 × C472 | Guang8A × Wushansimiao | 8.38 | 8.11 | 6.29** | 4.48** | 20.84 | −0.52 | 0.19 |
| C228 × C319 | Guang8A × Fuhui676 | 53.68** | 23.17** | 6.92** | −0.1 | 36.89** | 24.58* | 0.29 |
| C228 × C447 | Guang8A × Huanghuazhan | 17.49* | 11.64 | −4.55** | −6.82** | 41.11** | 34.5** | 0.22 |
| C228 × C268 | Guang8A × Minhui3301 | 15.7 | −10.3 | 5.58** | −0.53 | −7.18 | −16.3* | 0.29 |
| C228 × C493 | Guang8A × Chenghui727 | 12.05 | 5.83 | −2.12** | −15.9** | 41.43** | 34.77** | 0.29 |
| C228 × C492 | Guang8A × Yahui2115 | 51.16** | 45.01** | 1.95* | −6.5** | 16.97 | 9.72 | 0.33 |
| C228 × C201 | Guang8A × Gui99 | 20.31** | 18.72* | −1.90* | −10.9** | −1.7 | −9.44 | 0.28 |
| C228 × C307 | Guang8A × Ce64 | 44.50** | 29.73** | 0.14 | −3.3** | 9.87 | 0.74 | 0.28 |
| C228 × C282 | Guang8A × Yuexiangzhan | 13.29 | 6.65 | 10.98** | 8.12** | 5.67 | −6.08 | 0.24 |
| C228 × C386 | Guang8A × Yuenongsimiao | 21.36** | 0.81 | −0.01 | −2.46** | 77.00** | 60.33** | 0.21 |
| Mean | 26.89 | 11.28 | 6.26 | 0.854 | 21.16 | 10.63 | 0.29 | |
| Minimum | −11.34 | −24.30 | −8.05 | −19.00 | −47.86 | −55.50 | 0.19 | |
| Maximum | 74.39 | 45.01 | 20.37 | 17.98 | 94.99 | 71.03 | 0.36 | |
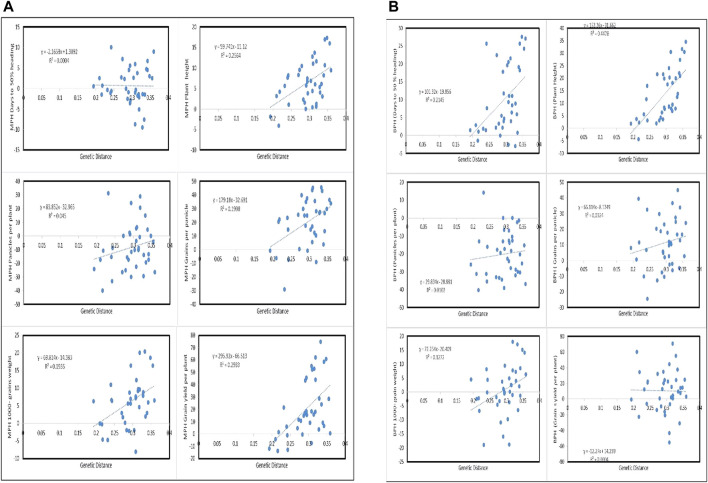
3.9 Genetic Distance Effects on Heterosis
Genetic distances between the parents of 38 F1 hybrids were estimated through IBS in TASSEL 5, which ranged between 19.00 and 36.00% (Table 5). For days to 50% heading, F1 hybrids of significant mid-parent-negative and mid-parent-positive heterosis manifested slightly negative correlation with genetic distances, whereas better-parent heterosis showed positive correlation with the genetic distances (Figure 3B). Similarly, heterosis over mid and better parents for plant height, panicles per plant, number of grains per panicles, and 1000-grain weight also showed positive association with the genetic distances. A majority of the F1 hybrids with highly significant heterosis were present at the maximum end of genetic distances (Figures 3A,B). Mid-parent heterosis for grain yield per plant in F1 hybrids was found in positive correlation with the genetic distances in their corresponding parents, whereas better-parent heterosis was observed in slightly negative correlation with genetic distances (Figures 3A,B).
FIGURE 3.
Representation of mid-parent (A) and better-parent (B) heterosis association of F1 hybrids with the genetic distances between their corresponding parents.
4 Discussion
Despite the success of hybrid rice since 1970s (Lin et al., 2020), the understanding of the heterosis group and heterotic pattern in rice is very limited (Wang et al., 2014). The maximum benefit out of the heterotic vigor could be achieved through the assessment of diversity and divergence in the rice germplasm for identification of the potential heterotic groups, for which high-throughput genotyping is of great help (Zhao et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2018b). In this study, heterotic groups were identified using a 10K SNP chip, in different Indicia and Japonica genotypes selected from different origins of China and abroad, including 183 inbred lines, 53 maintainers, 120 restorers, one TGMS line, and two unknowns.
Divergence analyses revealed the existence of six subgroups among subspecies, breeding lines, origins, and genetic groups. Up to K6, DAPC-based grouping was stable and was supported by both PCA and BIC analyses. Along with the overall variability in the tested germplasm, substantial variability was observed in each genetic group, geographically collected lines, and breeding lines. Geographical distribution of lines could also contribute to the existence of subgroups (Zhang et al., 2011). However, in this study, a no-population subdivision was observed due to geography/locations, except that lines from two regions, that is, Zhejiang and Yunnan, were grouped only in a single group (G2 and G3, respectively). Effective evaluation of diversity provides a considerable scope of choice of parents before hybridization (Pandey et al., 2011). Phylogenetic analysis showed that genotypes obtained from different origins had significant variation and were assigned into different groups. Huang et al. (2012) also find out a large-scale genetic variation in the Asian cultivated rice germplasm. Moreover, cluster analysis also confirmed that there are six different clusters, and the maintainers were distributed in three independent clusters. Almost similar principal components were identified in previous studies (Rathnathunga and Geekiyanage, 2015, 2016, 2017; Rathnathunga et al., 2016), which recommended variable levels of diversity in various rice germplasms.
Estimation of phenotypic and genotypic diversity provides useful information for the establishment of heterotic patterns (Agre et al., 2019). As all the six clusters contained the commercially used high-yielding parents, each cluster was considered as the basis for heterotic groups. From all commercially used hybrids and new combinations, seven heterotic patterns were identified. The higher genetic distance among the commercially used lines reflected positive association with heterosis; thus, new heterotic groups with higher genetic distances could be predicted. As suggested previously, significant differences among the rice genotypes were expected to provide better hybrid vigor (Prasanna et al., 2010; Mvuyekure et al., 2018).
Following the heterotic pattern of cluster IV × cluster II, the best modern maintainer lines in cluster IV could be used with the best restorers of cluster II in the development of high-yielding hybrids. Elite inbred lines from cluster V can be used as male parents of two lines and three lines of hybrid rice. Moreover, Cluster V was predominated by inbred cultivars of the Guangdong origin, which usually have good grain quality and better resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight, and is suitable to be deployed in breeding new restorer lines.
Considering the aforementioned findings, 14 inbred and restorer lines from groups I, II, V, and VI were crossed with three CMS lines from group IV. The mean performance for various parameters revealed a substantial variability. The F1 hybrids obtained from the partial diallel crosses and their parents revealed significant variations for all the studied traits, which can provide an ample scope for further improvement. A majority of the F1 hybrids showed higher mean performance than their parents. In agreement with our study, significant variation for yield and yield-related traits among rice genotypes was observed previously (Singh et al., 2006; Prasad et al., 2013; Ganapati et al., 2014; Asem et al., 2019).
Heterosis is critical for the estimation and development of new plant population (Cheng et al., 2019; Venkatesan et al., 2019; Rasheed et al., 2021). Although the overall heterosis for heading date and plant height was at low and moderate levels, some TaifengA progenies and Guang8A × Huazhan for plant height manifested significant negative heterosis over the mid and best parents, similar to other studies (Selvaraj et al., 2011; Kumar et al., 2012). Four F1 hybrids of TaifengA showed significant earliness and can be used for developing early maturing and lodging-resistant dwarf stature hybrids. The number of panicles per plant also showed moderate levels of significant positive heterosis, where the F1 hybrids such as TaifengA × Minhui3301 exhibited maximum heterosis. Corroborating results of similar nature heterosis were reported (Gnanamalar and Vivekanandan, 2013; Rukmini et al., 2014; Lingaiah et al., 2019). Quantitative traits, that is, grain weight, grain number per panicle, and number of panicles, positively contribute to the yield (Rasheed et al., 2021). High levels of mid- and better-parent heterosis were found for the number of grains per panicle, and all the three maternal lines showed significant heterotic effects with different inbred and restorer lines in our study, which is in accordance with the previous findings (Priyanka et al., 2014; Lingaiah et al., 2019). Similarly, for 1,000-grain weight, which is one of the key components of yield, F1 hybrids TaifengA × Minghui63 and TianfengA × Minhui3301 were found with moderately significant positive heterosis over the mid and better parents, and TaifengA × Minhui3301, TianfengA × Guang122, and TaifengA × Huazhan showed mid-parent heterosis and TianfengA × Minghui63 manifested heterobeltiosis only. Mostly significant positive mid- and better-parent heterotic performances were recorded for 1,000-grain weight (Lingaiah et al., 2019). In the case of grain yield per plant, a majority of F1 hybrids were found with above-average positive heterosis. High levels of significant positive heterosis over mid and better parents were manifested by F1 progenies such as TaifengA × Gui99, which can be used as potential sources for the development of high-yielding hybrids in future breeding. Advocating results of high heterosis over mid parents and better parents were reported previously (Zhang et al., 1994; Alzona and Arraudeau, 1995).
In the present study, a majority of mid-parent and best-parent heteroses were with positive association with genetic distances. Except mid-parent heterosis for days to 50% heading and better-parent heterosis for grain yield per plant, which were found in slightly negative correlation with genetic distances, all the studied traits exhibited positive correlation with the genetic distances. Considering the genetic variation as a source for heterotic gain, several studies were conducted to unveil the relationship between genetic distances and heterosis for predicting the heterosis effect and found that to some extent, heterosis is positively associated with genetic distances (Lee et al., 1989; Smith et al., 1997; Zhao et al., 2009). Although greater achievement of hybrid breeding depends on the identification of complementary heterotic groups (Reif et al., 2007; Zhao et al., 2015), the heterotic groups in rice are still not clearly defined (Xie et al., 2012). Corroborating results were obtained by maximizing the genetic distances for separation of maize lines into groups, showing the advantage of a significant yield over within-group crosses. Thus, the groups estimated by increasing the genetic distances could be a meaningful source for heterotic group development (Suwarno et al., 2014). Wang et al. (2014) estimated the magnitude of yield heterosis among selected heterotic groups with greater genetic distances and observed that hybrids had more yield than their parents, with an average of 24.1% mid-parent heterosis, which is in line with our findings. Similarly, the molecular marker approach was used to estimate the genetic distances between breeding lines for dividing the germplasm into heterotic groups (Prasanna et al., 2010). Singh et al. (2015) also estimated the genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship among 128 diverse rice germplasms using 50K rice SNP chips. Haplotype analysis separated the 128 genotypes into four major heterotic groups, revealing that the genotypes are grouped on the basis of their genetic makeup (genetic distances).
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, considering the mid-parent and better-parent significant heterosis and promising mean performance, our results have identified 14 heterotic combinations, that is, TaifengA × Guang122, TaifengA × Wushansimiao, and TaifengA × Minghui63 for earliness; Guang8A × Huazhan for dwarf stature; and Guang8A × Huanghuzhan-1, TaifengA × Yuexiangzhan, Guang8A × Minhui3301, TianfengA × Guang122, Guang8A × Yahui2115, TianfengA × Huanghuazhan, TianfengA × Minghui63, TianfengA × Minhui3301, TaifengA × Gui99, and Guang8A × Yuenongsimiao for yield and yield-related traits. F1 hybrid heterosis over the mid and better parents was in positive correlation with the genetic distances. These F1 Hybrids should be used in the development of early-maturing, lodging-resistant, and high-yielding commercial hybrids and cultivars in future heterosis breeding programs after multilocation and multiyear testing. The use of genetic distance must complement with phenotypic characterization for identification of heterotic groups and generation of promising hybrids.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Rice Research Institute, Guangdong Academy of Agricultural Sciences, for providing a research-conducive environment.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found here: The variation data reported in this paper have been deposited in the Genome Variation Map (GVM) (Song et al., 2018) in Big Data Center (BIG Data Center Members, 2018), Beijing Institute of Genomics (BIG), Chinese Academy of Science, under accession numbers GVM000300 at http://bigd.big.ac.cn/gvm/getProjectDetail?project=GVM000300.
Author Contributions
FW and IH conceived the original idea and collected the literature review. DL and SA provided technical expertise to streamline the basic idea. CF, SA, and MA validated the methodology. WL and JL performed formal analysis. YL provided the required resources. MZ helped in data curation. IH, DL, and SA wrote, edited, and reviewed the manuscript. FW supervised the project and funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Presidential fund of Guangdong Academy of Agricultural Sciences Guangzhou, China (BZ202002); the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province (2018B020206002); the Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System (CARS-01-18); the Common Key Technology Innovation Team for Agricultural Seed Industry of Guangdong Province (2020KJ106, 2021KJ106); and the Discipline Team of Agricultural Competitive Industries in Guangdong Academy of Agricultural Sciences (202101TD).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2022.811124/full#supplementary-material
References
- Agre P., Asibe F., Darkwa K., Edemodu A., Bauchet G., Asiedu R., et al. (2019). Phenotypic and Molecular Assessment of Genetic Structure and Diversity in a Panel of Winged Yam (Dioscorea Alata) Clones and Cultivars. Sci. Rep. 9, 18221. 10.1038/s41598-019-54761-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S., Soubeyrand S., Gladieux P., Giraud T., Leconte M., Gautier A., et al. (2016). Cloncase: Estimation of Sex Frequency and Effective Population Size by Clonemate Resampling in Partially Clonal Organisms. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 16, 845–861. 10.1111/1755-0998.12511 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alzona A. V., Arraudeau M. A. (1995). Heterosis in Yield Components of upland rice. Philippine J. Crop Sci. 17, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Asem I. D., Nongthombam A., Shaheen K., Heisnam N. D., Yurembam R., Asem R., et al. (2019). Phenotypic Characterization, Genetic Variability and Correlation Studies Among Ten Chakhao (Scented) rice of Manipur. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 8, 612–618. 10.20546/ijcmas.2019.802.070 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardo A. N., Bradbury P. J., Ma H., Hu S., Bowden R. L., Buckler E. S., et al. (2009). Discovery and Mapping of Single Feature Polymorphisms in Wheat Using Affymetrix Arrays. BMC Genomics 10, 251. 10.1186/1471-2164-10-251 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIG Data Center Members (2018). Database Resources of the BIG Data Center in 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 446 (D1), D14–D20. 10.1093/nar/gkx897 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury P. J., Zhang Z., Kroon D. E., Casstevens T. M., Ramdoss Y., Buckler E. S. (2007). TASSEL: Software for Association Mapping of Complex Traits in Diverse Samples. Bioinformatics 23, 2633–2635. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bueno-Sancho V., Persoons A., Hubbard A., Cabrera-Quio L. E., Lewis C. M., Corredor-Moreno P., et al. (2017). Pathogenomic Analysis of Wheat Yellow Rust Lineages Detects Seasonal Variation and Host Specificity. Gen. Biol. Evol. 9, 3282–3296. 10.1093/gbe/evx241 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S.-H., Zhuang J.-Y., Fan Y.-Y., Du J.-H., Cao L.-Y. (2007). Progress in Research and Development on Hybrid rice: A Super-domesticate in China. Ann. Bot. 100, 959–966. 10.1093/aob/mcm121 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Z., Xiao C., Huang X., Lin L., Xu M., Cao X., et al. (2019). Combining Ability and Heritability Analysis Provide Insights into Variability for Multiple Agronomic Traits in Two-Line Hybrid Black rice. Int. J. Agri. Biol. 22, 737–742. 10.17957/IJAB/15.1123 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Civáň P., Ali S., Batista-Navarro R., Drosou K., Ihejieto C., Chakraborty D., et al. (2019). Origin of the Aromatic Group of Cultivated rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Traced to the Indian Subcontinent. Genome Bio. Evol. 11, 832–843. 10.1093/gbe/evz039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dan Z., Liu P., Huang W., Zhou W., Yao G., Hu J., et al. (2014). Balance between a Higher Degree of Heterosis and Increased Reproductive Isolation: A Strategic Design for Breeding Inter-subspecific Hybrid rice. PLoS ONE 9, e93122–8. 10.1371/journal.pone.0093122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danecek P., Auton A., Abecasis G., Albers C. A., Banks E., DePristo M. A., et al. (2011). The Variant Call Format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 27, 2156–2158. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganapati R. K., Rasul M. G., Mian M., Sarker U. (2014). Genetic Variability and Character Association of T-Aman rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Int. J. Plant Biol. Res. 2, 1013–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Gnanamalar R. P., Vivekanandan P. (2013). Genetic Architecture of Grain Quality Characters in rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Eurp. J. Exptl. Biol. 3, 275–279. [Google Scholar]
- Guo Z., Wang H., Tao J., Ren Y., Xu C., Wu K., et al. (2019). Development of Multiple SNP Marker Panels Affordable to Breeders through Genotyping by Target Sequencing (GBTS) in maize. Mol. Breed. 39, 37. 10.1007/s11032-019-0940-4 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- He Z.-z., Xie F.-m., Chen L.-y., Dela Paz M. A. (2012). Genetic Diversity of Tropical Hybrid rice Germplasm Measured by Molecular Markers. Rice Sci. 19, 193–201. 10.1016/S1672-6308(12)60040-7 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Huang X., Kurata N., Wei X., Wang Z.-X., Wang A., Zhao Q., et al. (2012). A Map of rice Genome Variation Reveals the Origin of Cultivated rice. Nature 490, 497–501. 10.1038/nature11532 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jombart T., Devillard S., Balloux F. (2010). Discriminant Analysis of Principal Components: a New Method for the Analysis of Genetically Structured Populations. BMC Genet. 11, 94. 10.1186/1471-2156-11-94 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamvar Z. N., Tabima J. F., Grünwald N. J. (2014). Poppr: An R Package for Genetic Analysis of Populations with Clonal, Partially Clonal, And/or Sexual Reproduction. PeerJ 2, e281. 10.7717/peerj.281 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khush G. S. (2013). Strategies for Increasing the Yield Potential of Cereals: Case of rice as an Example. Plant Breed 132, 433–436. 10.1111/pbr.1991 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Singh S., Singh S. P. (2011). Heterosis for Yield and Yield Components in Basmati rice. Asian J. Agric. Res. 6 (1), 21–29. 10.3923/ajar.2012.21.29 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M., Godshalk E. B., Lamkey K. R., Woodman W. W. (1989). Association of Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms Among maize Inbreds with Agronomic Performance of Their Crosses. Crop Sci. 29, 1067–1071. 10.2135/cropsci1989.0011183X002900040050x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Z., Qin P., Zhang X., Fu C., Deng H., Fu X., et al. (2020). Divergent Selection and Genetic Introgression Shape the Genome Landscape of Heterosis in Hybrid rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 117, 4623–4631. 10.1073/pnas.1919086117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingaiah N., Raju C. H. S., Radhika K., Sarla N., Venkanna V., Reddy D. V. V. (2019). Nature and Magnitude of Heterosis and Inbreeding Depression for Grain Yield and Yield Attributing Traits in Nutritional Rich rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Crosses. J. Pharma. Phytochem. 8, 3508–3513. [Google Scholar]
- Melchinger A. E., Gumber R. K. (1984). in Overview of Heterosis and Heterotic Groups in Agronomic Crops: Concepts and Breeding of Heterosis in Crop Plants. Editors Larnkey K. R., Staub J. E. (Madison, WI: Crop Sci. Soci. America; ), 29–44. 10.2135/cssaspecpub25.c3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mvuyekure S. M., Sibiya J., Derera J., Nzungize J., Nkima G. (2018). Application of Principal Components Analysis for Selection of Parental Materials in rice Breeding. J. Genet. Genomic Sci. 3, 10. 10.24966/ggs-2485/100010 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey P., Anurag P. J., Tiwari D., Yadav S., Kumar B. (2011). Genetic Variability, Diversity and Association of Quantitative Traits with Grain Yield in rice (Oryza Sativa L.). J. Bio-sci. 17, 77–82. 10.3329/jbs.v17i0.7110 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad G. S., Krishna K. V. R., Rao L. V. S., Chaithanya U. (2013). Quantitative Analysis of rice Genotypes (Oryza Sativa L.). Int. J. Innov. Res. Dev. 2, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Prasanna B. M., Pixley K., Warburton M. L., Xie C.-X. (2010). Molecular Marker-Assisted Breeding Options for maize Improvement in Asia. Mol. Breed. 26, 339–356. 10.1007/s11032-009-9387-3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Priyanka K., Jaiswal H. K., Waza S. A. (2014). Combining Ability and Heterosis for Yield, its Component Traits and Some Grain Quality Parameters in rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Jans 6, 495–506. 10.31018/jans.v6i2.489 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell S., Neale B., Todd-Brown K., Thomas L., Ferreira M. A. R., Bender D., et al. (2007). PLINK: a Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81, 559–575. 10.1086/519795 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed A., Ashfaq M., Sajjad M. (2021). Combining Ability and Heterosis Analysis for Grain Yield Traits in fine Long Grain rice (Oryza Sativa L.). J. Anim. Plant Sci. 31, 764–772. 10.36899/JAPS.2021.3.0266 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rathnathunga E. U. U., Geekiyanage S. (2015). Potential Flowering Time Mutants of Sri Lankan Traditional rice Variety “Sulai”, National Symposium on Agriculture. Sri Lanka: Eastern University. [Google Scholar]
- Rathnathunga E. U. U., Geekiyanage S. (2016). Within Variety Flowering Time Variation Leads to Yield Variation in Sri Lankan Traditional rice “Sudu Wee”. Ceylon J. Sci. 45, 25–37. 10.4038/cjs.v45i2.7386 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rathnathunga E. U. U., Geekiyanage S. (2017). Morphological Diversity of Sri Lankan Traditional rice Varieties “Pachchaperumal” and “Suduru Samba”. Open Agric. 2, 552–560. 10.1515/opag-2017-0058 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rathnathunga E. U. U., Senanayake S. G. J. N., Dissanayake N., Seneweera S., Geekiyanage S. (2016). Vegetative Growth and Yield Associated Flowering Time Variation in Sri Lankan rice “Hondarawala”. J. Agric. Sci. 11, 42–52. 10.4038/jas.v11i1.8079 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Reif J. C., Hallauer A. R., Melchinger A. E. (2005). Heterosis and Heterotic Patterns in maize. Maydica 50, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Reif J. C., Gumpert F.-M., Fischer S., Melchinger A. E. (2007). Impact of Interpopulation Divergence on Additive and Dominance Variance in Hybrid Populations. Genet 176, 1931–1934. 10.1534/genetics.107.074146 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rukmini D. K., Parimala K., Cheralu C. (2014). Heterosis for Yield and Quality Traits in rice (Oryza Sativa L.). J. Res. ANGRAU. 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Saghai-Maroof M. A., Soliman K. M., Jorgensen R. A., Allard R. W. (1984). Ribosomal DNA Spacer-Length Polymorphisms in Barley: Mendelian Inheritance, Chromosomal Location, and Population Dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 81, 8014–8018. 10.1073/pnas.81.24.8014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj C. I., Nagarajan P., Thiyagaraj K., Bharathi M., Rabindran R. (2011). Studies on Heterosis and Combining Ability of Well Known Blast Resistant Rice Genotypes with High Yielding Varieties of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Int. J. Plant Breed. Genet. 5, 111–129. 10.3923/ijpbg.2011.111.129 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Singh S. P., Singhar G. S., Parray G. A., Bhat G. N. (2006). Genetic Variability and Character Association Studies in rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Agri. Sci. Dig. 26, 212–214. [Google Scholar]
- Singh N., Jayaswal P. K., Panda K., Mandal P., Kumar V., Singh B., et al. (2015). Single-Copy Gene Based 50 K SNP Chip for Genetic Studies and Molecular Breeding in rice. Sci. Rep. 5, 11600. 10.1038/srep11600 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S. C., Chin E. C. L., Shu H., Smith O. S., Wall S. J., Senior M. L., et al. (1997). An Evaluation of the Utility of SSR Loci as Molecular Markers in maize (Zea mays L.): Comparisons with Data from RFLPS and Pedigree. Theor. Appl. Genet. 95, 163–173. 10.1007/s001220050544 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Song S., Tian D., Li C., Tang B., Dong L., Xiao J., et al. (2018). Genome Variation Map: a Data Repository of Genome Variations in BIG Data Center. Nucleic Acids Res. 46 (D1), D944–D949. 10.1093/nar/gkx986 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steemers F. J., Gunderson K. L. (2007). Whole Genome Genotyping Technologies on the BeadArray Platform. Biotechnol. J. 2, 41–49. 10.1002/biot.200600213 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwarno W. B., Pixley K. V., Palacios-Rojas N., Kaeppler S. M., Babu R. (2014). Formation of Heterotic Groups and Understanding Genetic Effects in a Provitamin A Biofortified Maize Breeding Program. Crop Sci. 54, 14–24. 10.2135/cropsci2013.02.0096 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson M. J., Septiningsih E. M., Suwardjo F., Santoso T. J., Silitonga T. S., McCouch S. R. (2007). Genetic Diversity Analysis of Traditional and Improved Indonesian rice (Oryza Sativa L.) Germplasm Using Microsatellite Markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 114, 559–568. 10.1007/s00122-006-0457-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan M., Karthikeyan P., Mohan B. V. (2019). Gene Action and Heterosis for Yield and its Component Traits in rice (Oryza Sativa L.) through Line X Tester Analysis under saline Condition. Plant Arch. 19, 2021–2028. [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. J., Lu Z. M. (2006). Evolvement and Analysis of Genetic Diversity in Indica Hybrid rice (Oryza Sativa L.) in China. Jiangsu. J. Agric. Sci. 22, 192–198. [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. J., Lu Z. M., Wan J. M. (2006). Genetic Diversity of Parental Lines in Indica Hybrid rice Based on Phenotypic Characters and SSR Cluster Analysis. Rice Sci. 20, 475–480. 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2006.05.004 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Qiu F., Larazo W., dela Paz M. A., Xie F. (2014). Heterotic Groups of Tropical Indica rice Germplasm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 128, 421–430. 10.1007/s00122-014-2441-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Mauleon R., Hu Z., Chebotarov D., Tai S., Wu Z., et al. (2018a). Genomic Variation in 3,010 Diverse Accessions of Asian Cultivated rice. Nature 557, 43–49. 10.1038/s41586-018-0063-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Cai Q., Xie H., Wu F., Lian L., He W., et al. (2018b). Determination of Heterotic Groups and Heterosis Analysis of Yield Performance in Indica rice. Rice Sci. 25, 261–269. 10.1016/j.rsci.2018.08.002 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y., San Vicente F., Huang K., Dhliwayo T., Costich D. E., Semagn K., et al. (2016). Molecular Characterization of CIMMYT maize Inbred Lines with Genotyping-By-Sequencing SNPs. Theor. Appl. Genet. 129, 753–765. 10.1007/s00122-016-2664-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie F., Guo L., Ren G., Hu P., Wang F., Xu J., et al. (2012). Genetic Diversity and Structure of Indica Rice Varieties from Two Heterotic Pools of Southern China and IRRI. Plant Genet. Resour. 10, 186–193. 10.1017/s147926211200024x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Xie F., He Z., Esguerra M. Q., Qiu F., Ramanathan V. (2013). Determination of Heterotic Groups for Tropical Indica Hybrid rice Germplasm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 127, 407–417. 10.1007/s00122-013-2227-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan L. P. (1986). Hybrid rice in China. Rice Sci. 1, 8–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng M. Q., Ji H. L., Li J. Y., Sansen J. (2007). Formation and Development on the Conception of Heterotic Group and Their Heterotic Pattern in maize (Zea mays L.). Acta Agric. Boreali-sin. 22, 30–37. 10.16819/j.1001-7216.1986.01.002 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Q., Gao Y. J., Yang S. H., Ragab R. A., Maroof M. A. S., Li Z. B. (1994). A Diallel Analysis of Heterosis in Elite Hybrid rice Based on RFLPs and Microsatellites. Theoret. Appl. Genet. 89-89, 185–192. 10.1007/BF00225139 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang P., Li J., Li X., Liu X., Zhao X., Lu Y. (2011). Population Structure and Genetic Diversity in a rice Core Collection (Oryza Sativa L.) Investigated with SSR Markers. PLoS One 6, e27565. 10.1371/journal.pone.0027565 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Q. Y., Zhu Z., Zhang Y. D., Zhao L., Chen T., Zhang Q. F., et al. (2009). Analysis on Correlation between Heterosis and Genetic Distance Based on Simple Sequence Repeat Markers in Japonica rice. Rice Sci. 23, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao K., Tung C.-W., Eizenga G. C., Wright M. H., Ali M. L., Price A. H., et al. (2011). Genome-wide Association Mapping Reveals a Rich Genetic Architecture of Complex Traits in Oryza Sativa . Nat. Commun. 2, 467. 10.1038/ncomms1467 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y., Li Z., Liu G., Jiang Y., Maurer H. P., Würschum T., et al. (2015). Genome-based Establishment of a High-Yielding Heterotic Pattern for Hybrid Wheat Breeding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, 15624–15629. 10.1073/pnas.1514547112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found here: The variation data reported in this paper have been deposited in the Genome Variation Map (GVM) (Song et al., 2018) in Big Data Center (BIG Data Center Members, 2018), Beijing Institute of Genomics (BIG), Chinese Academy of Science, under accession numbers GVM000300 at http://bigd.big.ac.cn/gvm/getProjectDetail?project=GVM000300.