Abstract
This rapid review examines how the mental health of adults in the general population in Germany changed during the COVID-19 pandemic. We conducted a systematic literature search and included 68 publications as of July 30 2021. The underlying studies were classified according to their suitability for representative statements for the general population and for estimating changes in mental health over time. In addition, the observation period and operationalisation of outcomes were considered.
The first wave of infection and the summer plateau were mapped by 65% of the studies. Studies that were particularly suitable for representative statements due to their research design showed mixed results, which tend to indicate a largely resilient adult population with a proportion of vulnerable individuals. A predominantly negative development of mental health was described by results from more bias-prone study designs. Routine data analyses showed decreases in outpatient and especially inpatient care, increased use of a crisis service, mixed results for outpatient diagnoses, incapacity to work and mortality as well as indications of shifts in the spectrum of diagnoses. As the current evidence is ambiguous, generalised statements should be reflected in favour of a differentiated view. There is a need for research on the further course of the pandemic, specific risk groups and the prevalence of mental disorders.
Keywords: COVID-19 PANDEMIC, SARS-COV-2, MENTAL HEALTH, MENTAL DISORDER, RAPID REVIEW, GENERAL POPULATION
1. Introduction
As a multidimensional stressor, the COVID-19 pandemic and the associated infection control measures pose risks to the mental health of the population at various levels [1–3]. The individual experience of insecurity and anxiety of an infection, the loss of protective factors for mental health (e.g. social and leisure activities, access to care services), the burden of infection protection measures [5–7], the loss of relatives [4] and immediate physical, neurological and psychological symptoms of a COVID-19 infection [8] can have negative consequences for mental health. Longer-term consequences [1, 2] are being discussed in the event of an economic recession caused by the pandemic [9–11]. The increase in risk factors that already existed before the pandemic may also create additional mental health burdens, such as a higher risk of domestic violence [11–13] or increased loneliness [14, 15] in the wake of contact restrictions and widespread closures. In principle, it can be expected that the longer the duration or chronification of stressors, the more difficult it becomes to cope successfully [10].
Against this background, the British Psychiatric Association predicted a ‘tsunami of mental disorders’ as early as May 2020 [17]. Experts also expect an increase in mental stress and disorders in Germany [3, 18, 19]. However, the current findings on the development of the mental health of the population during the COVID-19 pandemic are heterogeneous overall and difficult to assess due to their methodological diversity. Thus, studies from other countries as well as international reviews find, on the one hand, a (partly extreme) increase in psycho-social stress and a subsequent increase in mental disorders [20–26], but on the other hand, no lasting increase in psychopathology [27–30]. In addition to the inconsistency of the results of international studies, conclusions for Germany are also made difficult by significant differences between the countries in the course of the pandemic. In particular, the development of the number of cases and deaths, the resulting burden on the health care system as well as the measures taken to protect against infection, to stabilise the economy and to provide social security differed between the countries.
Since research reacted very quickly to the crisis situation, there is now both a high number of empirical studies and a large variation of the research methodology used [31]. The high demand for reliable findings as a basis for evidence-based policy decisions (e.g. to minimise risks and adapt care services) makes it understandable why rapid solutions are used for immediate data collection or prompt publication of the work on preprint servers even before the quality-assuring peer review. However, this practice makes it necessary to examine the quality and generalisability of the available work for the general population in order to describe the state of research.
This rapid review therefore explores how mental health developed in the adult general population in Germany during the COVID-19 pandemic, taking into account the respective research methodology of the available studies.
2. Methododology
Against the background of time and personnel limitations, the methodology of the present review is based on the standards proposed by the Competence Network Public Health on COVID-19 for conducting a rapid review in the context of the current pandemic [32, 33].
2.1 Literature search
The search was based on the PECO criteria (Population: General population in Germany; Exposure: COVID-19 pandemic; Comparison: before/after or after COVID outbreak in Germany; Outcome: Mental health) with the following inclusion and exclusion criteria:
Inclusion criteria
Target population: General population in Germany (and subgroups according to region, age, marital status, employment)
Age group: Adult
Observation period: During the COVID-19 pandemic
Constructs shown: Mental health as the main outcome
Publication of a temporal comparison (against measurement time points before the start of the pandemic or during the pandemic)
Publication language: German/English
Exclusion criteria
Publication type: Reviews, Opinions, Comments, Letters to the Editor
Methodology: Qualitative data
Presentation of study methodology: Methodology not presented with sufficient transparency in published abstracts or on posters
Analysis design: Exclusively correlation analyses without reporting of frequencies or their changes in the general population.
Target population: Subgroups beyond the above selected sociodemographic characteristics (e.g. people with pre-existing mental disorders, health workers, students).
Systematic search
The search was based on the literature database created by the library of the Robert Koch Institute in the course of the COVID-19 pandemic (accessed 30.07.2021). Since the beginning of the pandemic, all publications identified by means of several search strings (Annex Table 1) in the PubMed and Embase databases and the additionally searched preprint servers arXiv, bioRxiv, ChemRxiv, medRxiv, Preprints.org, Research Square and Social Science Research Network (SSRN) have been entered into this database on a weekly basis. The literature database was searched for texts on mental health using two search strings defined by filter terms (Annex Table 1). All texts extracted in this way were filtered for their reference to Germany using a third search string.
Offline search
Given the acute need for information with a correspondingly rapid development of scientific publications as well as other dissemination formats, such as reports, study websites, press releases or reports from health insurance funds, it can be assumed that not all findings or publications on the development of mental health in the German general population during the COVID-19 pandemic are already listed in international databases. Based on this, the literature search was extended to include the following areas:
Systematic search in the World Health Organization (WHO) database ‘COVID-19. Global literature on corona virus disease’ (Accessed 10.06.2021; Search string see Annex Table 1)
Websites of COVID-19 related studies in the general population listed on the website of the German Data Forum (RatSWD) (last update of already identified studies 30.07.2021)
Publications and literature lists from the Competence Network Public Health on COVID-19 [35] (last update 30.07.2021)
Search via Google search engine (access until 08.07.2021; Search string see Annex Table 1); press releases and current reports or studies by, among others, service providers and suppliers of the health care system (e.g. health insurance funds, Central Institute for Statutory Health Insurance in Germany, hospital statistics).
Screening of bibliographies of COVID-19 related reviews, statements and policy briefs for relevant studies and publications (as of 10.06.2021)
Screening for relevant COVID-19 related studies and publications listed on the website of the German Society for Psychiatry, Psychotherapy, Neurology and Psychosomatics (DGPPN) (accessed 10.06.2021) [36].
Title, abstract and full text screening
After piloting the procedure in the review team and excluding duplicates, the title and abstract screen was carried out by an experienced person (EM). More than 20% of the titles were additionally checked by at least one other person in the team. If the assessment of inclusion or exclusion of a publication was ambiguous, no exclusion was carried out conservatively. All remaining publications were reviewed in full text by at least two people. The publications that were ambiguous in this step were discussed in a team of three people and included or excluded in an iterative process based on the criteria mentioned above. In the course of this process, the first data extraction of the individual publications took place. Information was systematically transferred to a table created for this purpose. For individual publications, the respective data type (primary data, routine data) was identified, on the basis of which the publications were grouped.
2.2 Classification of included publications
For a meaningful summary of the findings against the background of the research methodology used and the resulting scope of the empirical results, the included publications were systematised in three ways as follows:
1) Observation periods
In order to assess the extent to which the current state of research allows statements about the entire course of the pandemic since March 2020, the observation periods of the included studies were recorded with the help of half-monthly intervals. Their distribution over the entire period was considered, irrespective of whether results were also reported for them individually. Periods were included for which data were available for at least one week from the respective halves of the month. If this was not the case for any half of the month, the study was assigned to the period in which the most study days occurred. To classify the observation periods, the development of the pandemic in Germany was divided into four phases (wave 1 to 3 and summer plateau 2020) following Schilling et al. [37] as well as Tolksdorf et al. [38] and illustrated with the case and death figures of COVID-19 (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
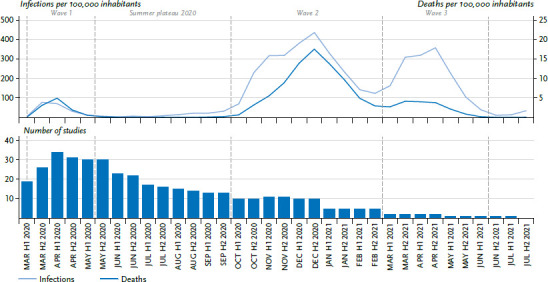
Number of studies included in the review and development of the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany according to incidence and deaths per 100,000 inhabitants
Source: COVID-19 cases reported to RKI, own research
Source: COVID-19 cases reported to RKI until 2021-08-25, own research, own calculations and graphs. Included are all cases reported to the RKI with age indications ranging from 0 to 120. The division into phases was done based on Schilling et al. [37] and Tolksdorf et al. [38]
2) Study design of the data used
Two criteria were used to assess the suitability of the study design of the data analysed in the publications for drawing conclusions about the development of mental health in the general population during the COVID-19 pandemic:
Criteria 1: Representativeness of the data for the general population
To assess the suitability of the data used in a publication for representative estimates in the general population, primary data was distinguished from routine data.
Routine data are generated in the course of standard documentation and billing in health care processes or in official statistics and represent these as a complete survey without sampling [39]. They are available from different data holders at different levels and thereby differ with regard to their population-based representativeness. For example, data from a single clinic or health insurance fund represent its health care provision without distortion, but may deviate from other clinics or health insurance funds as well as from the nationwide inpatient care or the entirety of persons with statutory health insurance [40].
In primary data collections, a sample of the target population is included in a study. The best approximation to an estimate representative of the general population in Germany is provided by random sampling (probability sampling). Samples can be drawn (a) from the total population with known selection probability [41] or (b) from an access panel with a stratified sampling design if necessary [41, 42]. The persons drawn are invited and motivated to participate. Ideally, measures are implemented to recruit participants from hard-to-reach population groups [41]. Possible biases due to the study design (design effects) and the non-participation of certain population groups (non-response) can be identified and taken into account in the data analysis, for example with weighting factors [43]. In contrast, in studies with non-probability samples (samples without random selection), interested persons participate on their own initiative by accepting non-personalised invitations that are primarily distributed by the media [41]. Thus, participation depends, among other things, on knowing about the study, one’s own motivation to participate and access to the providing medium. These samples can thus be systematically biased by selection effects in a methodologically uncontrollable way and therefore represent less reliable sources of information for the general population [41, 42]. In a methodological study conducted before the pandemic, for example, an overrepresentation of participants with psychological problems by a factor of about 2.5 was found in such a sample [44]. In order to avoid the risk of biased estimates or to be able to assess the uncertainty of the estimates, the use of non-probability samples to study the mental health of the general population during the COVID-19 pandemic is even explicitly discouraged from a methodological point of view [45]. Nevertheless, this pragmatic form of sampling is frequently used and results of corresponding studies find their way into the scientific and public discourse. In order to enable it to be differentiated, the present review differentiated between probability and non-probability samples.
Criteria 2: Estimation of changes over time during the pandemic
An essential prerequisite for a robust assessment of change over time is repeated measurement points that are identical in terms of study design (i.e. sample, survey mode, etc.) and outcome measurement. [46]. Trend studies, i.e. repeated and representative cross-sectional or panel surveys with identical study designs, are particularly suitable for this purpose [46, 47]. In these studies, characteristic values collected at different points in time are compared at group level between two samples. In one-off, representative cross-sectional studies, it is possible to assess changes over time by comparing them with norm samples, other reference surveys and retrospective surveys. However, possible sources of error such as recall bias, mode effects or deviating sample composition must be included in the interpretation [48]. Representative cohort or longitudinal studies offer the possibility of identifying changes in specific population groups via intra individual analyses, but can lose representativeness due to the drop out of individuals over time [47, 49].
Synopsis of the criteria: Classification in study types
To assess the suitability of the study methodology of the data underlying the publications for assessing temporal changes during the pandemic in the general population, a total of seven study types were defined by combining the two criteria listed above (Annex Table 2):
Within the primary data studies (Category I), the studies with randomly drawn samples were divided into trend studies with random sampling from the general population (study type A) or an access panel (study type B). One-time cross-sectional surveys with random sampling were assigned to study type C, in which the comparison over time took place via retrospective queries or comparisons with other reference surveys without consideration of possible design differences. Cohort studies with random sampling in non-randomly selected regions and without sample augmentation to compensate for drop out were assigned to study type D. Primary data studies with non-probability samples were subdivided into longitudinal studies with repeatedly interviewed participants (study type E) and cross-sectional studies (study type F). Routine data (Category II) were not subdivided, as they are usually available at different points in time and – given the same coding and analysis – can be compared over time.
As comparatively reliable estimates for changes in mental health in the general population during the pandemic, study types A, B, D and, to a limited extent, C, as well as routine data can be contrasted with study types E and F, which are more susceptible to bias.
3) Operationalisation of mental health outcomes
To assess how comprehensive and valid the multi-faceted topic of mental health was captured in the included studies, the mental health outcomes were classified according to the measured construct and its operationalisation. The survey was subdivided into (a) indicators of positive mental health, (b) indicators of mental distress, (c) indicators of acute symptoms of a mental disorder and (d) indicators of health care provision and mortality.
The inventories used to measure the indicators include different possibilities for analysis and interpretation, both with regard to the construct being measured and to pandemic-related changes over time: Non-standardised items or single items of established inventories have limited validity for the measurement of the construct due to a lack of studies on reliability and validity [50]. In contrast, standardised measurement inventories are validated for a defined construct and – given a comparable study design – allow comparison with previous studies and ideally with reference values from norm samples. These also include screening instruments in which currently present symptoms of a mental disorder are queried and thus persons with a high symptom burden can be identified. The frequency of a mental disorder, as it would be diagnosed in a standardized clinical interview, can, however, be both overestimated and underestimated by screening instruments [see e.g. 51]. Documented diagnoses in the health care system (incl. in reports of incapacity for work) presuppose the utilisation of medical or psychotherapeutic services as well as the recognition and documentation of mental disorders by those providing treatment, which means that, among other things, persons with unmet treatment needs are not depicted [52–54].
2.3 Systematic extraction of study results
The central results already extracted from the publications in a first step were prepared in tabular form according to the criteria listed here (Annex Table 3, Annex Table 4) and presented in the text. The systematised data extraction was carried out under quality assurance by at least two other independent persons in each case (Annex Table 3).
3. Results
3.1 Literature search
A total of 1,843 publications relating to Germany were identified using the various search strategies (as of 30.07.2021). With the help of a multi-stage inclusion and exclusion process (Figure 1), 68 publications were included in the review.
Figure 1.
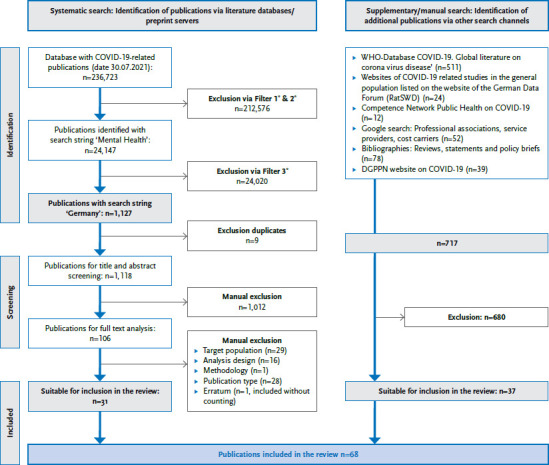
Flowchart on the inclusions and exclusions of the literature search
Source: Own table
* Explanation: Filter 1, 2, 3 see Annex Table 1
3.2 Classification of included studies
Observation periods
At the time of the literature search, the observation periods largely referred to the time of the first wave of infection of the COVID-19 pandemic, which still had relatively low incidence and death rates of people infected with SARS-CoV-2 compared to the later waves (Figure 2). From the second half of March onwards, more than 20 studies were available in each half of the month. For the 2020 summer plateau between the first and second waves, published data from at least 13 studies were also available. However, with the turn of the year 2020/2021, the number of studies decreased sharply: While eight to nine studies were still available in the respective halves of the month for the second wave in 2020, there were only one to five studies for the second and third waves in 2021.
Representativeness of the sampling for the general population and the estimation of changes over time during the pandemic
The review included 44 publications based on 25 primary data sources (Category I) and 24 publications based on 18 routine data sources (Category II) (Table 1).
Table 1.
Included studies and publications by category and study type
Source: Own table
| Category | Study type | Included publications | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of studies or data sources | Number of publications | References | ||
| Total | 43 | 68 plus Erratum | [14, 16, 55–121] | |
| I Primary data analysis | ||||
| Total | 25 | 44 | [14, 16, 55–97] | |
| A | 6 | 16 | [16, 55–69] | |
| B | 2 | 5 | [70–74] | |
| C | 3 | 3 plus Erratum | [75–78] | |
| D | 1 | 2 | [79, 80] | |
| E | 4 | 5 | [81–85] | |
| F | 9 | 13 | [14, 86–97] | |
| II Routine data analysis | ||||
| Total | 18 | 24 | [98–121] | |
Among the primary data sources, a total of 16 publications from six trend studies with randomly drawn samples from the general population (study type A), five publications from two trend studies with randomly drawn samples from an access panel (study type B) and three further representative cross-sectional studies with one publication each (study type C) were identified. Two publications originated from a cohort study with a random initial sample in non-randomly selected regions (study type D). Four longitudinal studies with five publications (study type E) and nine cross-sectional studies with 13 resulting publications were based on non-probability samples.
In summary, a total of 26 publications based on 12 primary data sources were available in the study types A, B, C and D, which are considered reliable for statements with regard to the general population. In contrast, there were 18 publications from 13 studies in the study types E and F, which are more susceptible to bias. Taking all study categories into account, it became apparent that more than two thirds of all publications (50 of 68) and studies or data sources (30 of 43) could be assigned to the study types (A, B, C, D, routine data) that were assessed as reliable.
3.3 Classification and results related to mental health outcomes
(a) Indicators of positive mental health
For indicators of positive mental health, results on life satisfaction, well-being and resilience were reported from a total of eight studies in 16 publications (Annex Table 3, Annex Table 4). The measurement was carried out with individual items as well as with standardised inventories. With the exception of study type D, results are available for these indicators from all study types.
For the first pandemic months, stable life satisfaction [16, 62] and stable well-being [16, 56, 65, 67] were reported on the basis of study type A until July 2020 compared to previous years. A later survey showed reduced life satisfaction [63, 64] and a slightly reduced well-being for January and February 2021 [63, 64]. However, the stable median values of the overall group in the first months of the pandemic concealed divergent developments in subgroups: Life satisfaction increased among people with low income or low education, but decreased among the self-employed [66] and people with high education or high income [65] and especially among women [67] as the pandemic progressed [63, 64]. Well-being increased among those living alone, was unchanged among couples without children and single parents, and decreased among couples with children [62].
Similarly, study type B papers reported consistently stable life satisfaction from early March 2020 to mid-July 2021 [74]. At the beginning of the pandemic, resilience was unchanged compared to 2018 values [72, 73], but decreased until early June 2020 [73].
A study of study type C also reported a decrease in life satisfaction in May and June 2020 compared to 2019, which was most evident among women, those with minor children, and those with low education [78].
Study type F papers exclusively reported decreases in life satisfaction in April and May 2020 respectively [97], in well-being in the first weeks of April [95] and for both indicators since October 2020 compared to earlier months in the pandemic [86]. An intra-individual decrease in life satisfaction and positive and negative affect was also observed from March to May 2020 in Study Type E among employed full-time workers [84].
(b) Indicators of mental burden
The measurement of feelings of anxiety or dejection, which are counted among the indicators of psychological stress (Annex Table 4), was mainly carried out with individual items from standardised instruments. Results were reported in six publications from three studies. COVID-19 related anxiety and distress were measured with both single-item and standardised instruments and reported in three studies with four publications. Situational distress and psychosocial stress were primarily measured with standardised instruments and reported in a total of 13 publications from eight studies.
Study types A and B consistently showed increased anxiety at the beginning of the pandemic, which decreased in all population groups during April 2020 [61, 72] and subsequently remained stable until March 2021 [72] and July 2020 [59, 60], respectively. In the case of dejection, the slightly increased level at the beginning of the pandemic stagnated until the end of April 2020 [74, 72] and continued to rise until March 2021 in the youngest age group [74]. While no increased psychosocial stress was found in study type A in the Mannheim region for May 2020 [56], it was increased in study type B in March 2020 [74] and changed over time: Anxiety declined until September 2020, increased until the end of April 2021 (especially among young adults) and declined again from May 2021 [74]. Another Type B study showed increased stress levels in February 2021 compared to the summer months of 2020 [70, 71].
Parents of minor children in study type C also reported an increase in stress experience at the time of the highest stress to date compared to January 2020 [76, 77].
Longitudinally, an increase in psychosocial stress was detected in study type D for May 2020 in all age groups. This was stronger in regions with higher incidence and in individuals who tested positive for COVID-19 [80]. Accordingly, in a sample of healthy adults in study type E, intra-individual daily stressors were reduced between the end of March and mid-May 2020 [81, 83]. At the group level, another study of this type found a decrease in COVID-19 specific anxiety from March to June 2020, while longitudinally, an increase was found in about 10% of the sample [82].
Findings from study type F showed elevated psychological distress for almost all reported indicators, which increased over the course of the pandemic. For April to May 2020, increased anxiety [97] and COVID-19 specific fears with a subsequent decrease below the baseline level [93, 94] and a continuous increase [14] for distress were reported. Stress levels were estimated to be moderate [95] in April 2020 and very high [91, 92, 94] in the first months of the pandemic, remaining at a stable high [94] level until July 2020 and increasing steadily until September 2020 [14]. For the first 20 days of the lockdown in April and November 2020, the burden remained high [90].
(c) Indicators of acute symptoms of mental disorder
Of a total of 25 primary data studies, 18 used standardised screening instruments to measure acute symptoms of a mental disorder. Results were reported in 31 publications (Annex Table 3 and Annex Table 4). In addition to screening for general psychopathological symptoms, the focus was primarily on depressive and anxiety symptoms.
Either no changes or decreases in psychopathological symptoms were reported from study type A compared to pre-pandemic comparison periods, apart from one finding of higher median scores in depressive and anxiety symptoms in May to June 2020 compared to the same months in 2018 [55]. Nationwide, depressive symptoms remained unchanged in the months after the outbreak compared to the months before [57, 58]. In the Mannheim region, too, no difference was detected in depressive and anxiety symptoms or somatoform disorder symptoms compared to 2018 [56]. A study with two survey periods during the pandemic (April to June 2020 [16, 65, 67] and January to February 2021 [63, 64]) did show an increase in depressive and anxiety symptoms compared to 2019, especially at the level of incident individual symptoms [68]. However, the significantly higher value compared to 2019 was in line with the results from 2016 [16, 65, 67]. With regard to individual symptoms, a decrease in fatigue/lack of energy as well as concentration difficulties was described for the first lockdown in 2020 compared to the same period in 2019 [57, 58]. A decrease in the median value of depressive symptoms was also observed in all population groups during the course of the pandemic from March to July 2020 [59]. Decreases were also described for psychopathological symptoms from mid-March compared to the month before (except for the elderly and persons with low-income) [69].
Results from study type C are based on comparisons with norm samples of the respective inventories and showed no changes in psychopathological symptoms for persons over 65 years of age for April 2020 compared to 2018 [75], while in the group of parents of minor children a slight increase could be found for both depressive and anxiety symptoms (retrospectively assessed for the time of subjectively highest stress) compared to 2010 [76, 77].
In the trend analysis of a longitudinal study of study type D, i.e. when comparing the survey points at group level, the proportions of those with current depressive symptoms or a generalised anxiety disorder were higher in May 2020 than two to seven years earlier in the initial sample [79, 80]. Longitudinally, symptoms increased among persons in the age range 18 to 60 years, but not among the elderly (ibid.). This intra-individual increase was most evident in the youngest age group (20 to 39 years) as well as in regions with a high incidence of infection and among persons tested for COVID-19 (ibid.).
In trend analyses of study type E, reduced psychopathological symptoms were found from the end of March to mid-May 2020 compared to the last measurement point before the pandemic [81, 83], unchanged psychopathology in the first lockdown week in March compared to February 2020 [85] as well as a decrease in depressive symptoms and symptoms of generalised anxiety disorder over the course of April to June 2020 [82]. Despite the findings, the analysis of intra-individual changes consistently pointed to a group of about 8% [83] to 10% [82, 85] of the study participants who experienced an increase in psychological symptoms during the pandemic, and as many as 25% with increases in the severity of depressive symptoms [82]. Another group of 8% to 9% initially developed increased psychological symptoms, which were reduced again within a few weeks [81, 83, 85]. However, the majority reported stable and in some cases even improved mental health (ibid.).
From study type F, elevated levels of psychopathological symptoms were reported almost exclusively. In mid-March to mid-April 2020, the median scores for depressive and anxiety symptoms were significantly elevated in two samples compared to pre-pandemic reference samples and were interpreted as an indication of a possible increase [89] or as an expression of psychological distress [95]. The frequency of depressive symptoms was reported in several studies between 14% and over 35% of participants in the period from March to June 2020 [87, 88, 90–92, 94, 96] and was consistently interpreted as a strong increase in the population [88, 90–92, 94, 96] or as an indication of this [87]. The level was described as stably elevated until the end of July 2020 [94] and a further increase was observed in November 2020 [90]. A comparable strong increase was described at the beginning of the pandemic for symptoms of generalised anxiety disorder with a relative frequency of about 15% to 20% of the participants [88, 90–94, 96]. Immediately afterwards, the symptoms dropped again slightly, but remained at an elevated level in the further course of the pandemic until the end of July [90] and in the second lockdown in November 2020 [94]. The values were interpreted as an up to eight-fold increase compared to 2013 [93] and a two- to ten-fold increase in generalised anxiety disorder compared to reference samples from 2008 and 2017 [94] in the population during the pandemic. In the same period, there were increased sample proportions with symptoms of panic disorder [88, 96] or obsessive-compulsive disorder [96] compared to prevalences from 2012 and 2013 respectively.
(d) Indicators of care patterns and mortality
Results on indicators of care provision and mortality were reported in 24 publications from 18 data sources. Various parameters like the use of a crisis service (two publications from one data source), outpatient care for mental disorders (three publications from two data sources), incapacity to work due to mental disorders (nine publications from six data sources), inpatient care for mental disorders (seven publications from six data sources) and mortality in the context of mental disorders (three publications from three data sources) were evaluated.
The utilisation of the crisis helpline ‘TelefonSeelsorge’ at the end of March 2020 showed an increase, which declined again in the following weeks [117, 118]. It particularly concerned counselling topics in the spectrum of health, relationships and violence and was higher in federal states with stricter infection control measures [118].
In outpatient mental health care, an increase in GPs’ first diagnoses of anxiety disorders was reported in the period March to June 2020, affecting more people aged over 30 years and with diagnosis of asthma and COPD [106]. In contrast, a decrease was reported for outpatient first diagnoses of depression among persons aged ≥65 years, for whom physician contacts, referrals and hospital admissions from psychiatric or neurological practices also declined [107]. There were fluctuations in the number of treatment cases among medical and psychological psychotherapists and specialists in psychosomatic medicine and psychotherapy. This fell below the previous year’s level from mid-March to the end of May and from November to the end of 2020 [121]. In June 2020, only these two groups of doctors showed a significant increase. Declines were also recorded in psychotherapeutic individual and group therapies as well as substitution therapy for drug addiction, which remained consistently below the 2019 level from mid-March 2020 [121].
Developments in incapacity to work due to mental disorders (IW) differed between the health insurance funds. BARMER [101] and BKK[103] observed a decrease in sick leave in the first months of the pandemic. DAK [104] and AOK [99] found a decrease in incapacity to work cases in 2020. In contrast, the KKH registered an increase in the number of cases of incapacity for work (IW) in the first half of 2020 [108] and the TK in the number of days of IW in 2020 [119, 120]. The BKK also recorded an increase in the number of sick days in November 2020 and at the beginning of 2021 [103]. According to the KKH, the case duration increased overall in 2020 [109, 110], whereby according to the DAK, short incapacity for work cases decreased in 2020, while cases with a duration of over six weeks increased [104]. The DAK reported shifts in the spectrum of diagnoses causing incapacity for work in 2020, with increases in anxiety disorders, reactions to severe stress and adjustment disorders [104].
In the area of inpatient care for mental disorders, there were decreases in the scope and shifts in clinical characteristics: For AOK-insured persons, the number of inpatient cases in psychiatric, psychotherapeutic and psychosomatic clinics and departments fell below the 2019 level from March 2020 to February 2021 [100]. From mid-March to early April 2020, the decline in diagnoses of mental and behavioral disorders (as coded in ICD-10 chapter V) was rather high compared to other indications [98]. One hospital group also reported a decline in admissions to day clinic and inpatient admissions from mid-March to the end of May 2020 [102], which affected various main diagnosis groups to varying degrees. At the same time, the length of stay of inpatient cases with coded diagnoses of mental and behavioral disorders fell considerably in another hospital network [111]. For psychiatric emergencies, there was a decrease in presentations [111, 113, 114] in the period from the beginning of the pandemic to the end of May, and only one hospital found no change in the absolute number of psychiatric emergencies [112]. At the same time, an increase in repeat presentations for psychiatric emergencies and changes in diagnostic spectrum and psychopathological findings were observed, with formal thought disorder, hopelessness and social withdrawal documented more frequently, while suicidality remained unchanged [114]. Among psychiatric emergencies [114] and psychiatric consultations [112] where a substantive relationship of the complaints to the COVID-19 pandemic was identified, the proportion of persons with suicide attempts was increased compared to cases unrelated to the COVID-19 pandemic.
A change in mortality in the context of mental disorders is evident for the number of deaths due to intoxication, which was higher in 2020 than in 2019 nationwide [105]. In contrast, for suicide rates in the city of Leipzig, no differences can be detected between different phases of infection control measures (light vs. heavy restrictions) nor to the temporal developments of previous years [116]. In preliminary evaluations, the nationwide suicide rates show a slight decrease in cases for 2020 compared to 2019 [115].
4. Discussion
Given the extensive and diverse body of studies, this rapid review aims to provide a comprehensive assessment of the development of the mental health of the adult population in Germany during the COVID-19 pandemic. For this purpose, as of July 30 2021, 68 relevant publications were identified and included in the review. The data used in the publications was classified with regard to the observation period, the research methodology used to answer the research question and the content. Based on the extracted main results, the state of research is summarised in the following and further research needs are derived.
The data of 65% of the included publications referred to the first wave of infection and the summer plateau 2020. In comparison, the level of information for the second and third waves from autumn 2020 to summer 2021 is much more limited and limits a comprehensive assessment of the entire course of the pandemic.
At the present time, the primary data studies show a large variation of the research methodology used across the study types A to F as defined here. More than half of the studies conducted and slightly less than half of the publications resulting from them were accounted for by study types E and F. These do not represent reliable sources of information for the general population due to the potential bias of the results, even though they can provide valuable information through the analysis of correlations or, above all, intra-individual changes. Despite their high visibility in scientific discourse due to a relatively high number of publications, these results should be placed into context with current studies less prone to bias and thus be interpreted with caution. Compared to primary data analyses, routine data analyses also evaluated a high number of data sources, from which, however, far fewer publications emerged.
From the broad spectrum of mental health topics, the studies conducted primarily focused on indicators of a current symptoms of a mental disorder using validated screening inventories. Indicators of mental distress and positive mental health ranked second and third, respectively. No study used standardized diagnostic procedures to determine the frequency of mental disorders according to established classification systems. Consequently, no evidence-based statement can yet be made, about the development of the prevalence of mental disorders in particular.
The comparison of results across all indicators indicates dependencies on the study design: The cross-sectional study types A, B and C, which were assessed as more suitable for a reliable estimation for the general population due to a representatively designed random sample, reported predominantly mixed results. If anything, the results suggest that the adult general population was rather resilient during the study period and that their mental health remained relatively stable despite increasing stress. First included publications with more recent data collection pointed to a deterioration in life satisfaction from the turn of the year 2020/2021. The necessity of a socially differentiated approach was illustrated by findings showing that a stable population mean value is based on diametrically opposed developments in different population groups. From the more bias-prone study type F with non-probability samples, predominantly results of a negative development of mental health and a strong increase of stress were reported. However, against the background of possible selection effects [42, 44, 45] compared to the general population, these findings should be interpreted cautiously as indications of changes in individual subgroups that need to be identified more precisely. In longitudinal studies of type D and E, both intra-individual deterioration and improvement of mental health were observed. Again, longitudinal analyses indicated that stable scores over time in the overall group may be due to contrasting trends in subgroups. Results based on routine data analyses in the context of mental health showed predominantly decreases in outpatient and inpatient case numbers or services, increases in the use of a crisis service, mixed results for the development of outpatient diagnoses, incapacity to work and mortality, as well as indications of shifts in the diagnostic spectrum and in clinical characteristics of treated cases.
In summary, the current scientific evidence can be considered inconclusive. Taking into account the study methodology used, statements of a dramatic deterioration in the mental health of the adult population during the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany in particular should therefore be questioned in favour of a more differentiated view.
Comparable to this, the first international systematic reviews also reported a heterogeneous picture [31]. In addition to significant increases [24] and decreases [27] in psychopathological symptoms, there was a tendency for mental health problems to increase at the beginning of the pandemic, which decreased [30] almost to the initial level after a few weeks. This observation corresponds to the findings from study types A, B and C outlined for Germany. Results of opposing trends in subgroups analogous to the findings from study types A and E were also reported [122]. However, a comprehensive evaluation of the international findings, in consideration of research methodology, regional differences in the course of the pandemic and special features prior to the outbreak, is still pending.
A psychological reaction of people to a crisis as profound as the global COVID-19 pandemic is to be expected within an appropriate and healthy range of experience and behaviour. Reduced well-being, increased mental distress or partly transient (single) symptoms of mental disorders alone do not imply a need for clinical treatment compared to manifest mental disorders with long-term functional limitations [31]. Since the development of mental disorders requiring treatment is often preceded by chronic overload and stress with a longer incubation period, measures should nevertheless be taken to prevent them and to promote mental health [see e.g. 3, 123], as implied by the available research on the experience of stress.
The limitations of the present rapid review include the following aspects: As the focus was on the mental health of the general population, studies in specific populations such as students, people with mental disorders or health workers were not included. Not all sources of potential bias were considered in the classification of included studies (e.g. survey mode, response or drop-out rates [41]). Furthermore, no established risk of bias tool was used, as systematic biases were explicitly considered as an object of the review question.
In principle, it should be noted that trends that already existed before the pandemic were not distinguished from temporal changes during the pandemic in most publications, neither empirically nor in the discussion of results. The latter can therefore not always be interpreted as causally linked to the pandemic.
From the present results, focal points of the current need for research can be derived:
For a comprehensive assessment of the course of the pandemic so far, results are needed for the second and third waves of infection. Since the increase in the number of cases and deaths as well as the (continued) duration of infection protection measures were comparatively higher during the latter, changed and increased risks for mental health can be assumed compared to the first wave, such as the chronification of stressors as well as the continued loss of resources [3]. Surveillance of the mental health of the population is also necessary after the infection waves have subsided, among other things because mental disorders can be preceded by longer sub-clinical or prodromal phases (precursor phases) and thus there may be a time-delayed increase in psychopathology [3]. In addition, it should be noted that in the past, economic recessions have been associated with an increase in mental disorders and suicides in the population, which may also contribute to an increased burden of disease in the context of a pandemic [2, 9, 10, 124].
Similar vulnerable and highly stressed groups for the development or worsening of psychopathological symptoms are described across all study designs and also across countries. In addition to people with mental disorders and health workers, these include young people, women and families with young children. International reviews also point to a widening of social inequalities in mental health in the wake of the pandemic by education, insecure income or unemployment [125]. The systematic identification of risk groups in Germany could take place in a second step on the basis of the present research. It is necessary for target group-oriented health promotion, prevention and care planning and could be included in future pandemic and crisis management.
Internationally, too, it is demanded that studies whose design allows a reliable and differentiated assessment of temporal changes in the general population should be carried out as a matter of priority [45, 126]. Trend and cohort studies in particular can contribute to the identification of subgroups that are particularly affected or at risk and test previous indications of the reversibility of negative effects as well as favourable factors. The results should be reported in a socially stratified manner in order to uncover possibly opposing developments in different population groups.
Research gaps remain for a variety of aspects of mental health, including key indicators such as incidence and prevalence of mental disorders and functional limitations, burden of disease and mortality associated with mental distress and disorders. While the standardised diagnosis of mental disorders before the pandemic showed a stable prevalence in the population (survey 1997–1999 vs. 2009–2012 [127, 128]), the assessment of current changes in care needs requires a renewed psycho-diagnostic data collection.
Finally, the direct effects of contracting COVID-19 or requiring intensive medical treatment [129, 130] may also have a negative impact on mental health and may be reflected in changes at the population level in the short or long term, especially against the background of higher case numbers during the later waves of infection. Consequently, population-based studies should capture these two events where possible and take them into account when examining mental health trends.
In the coming months, the publication of further research results on mental health in Germany during the COVID-19 pandemic can be expected. Since methodologically high-quality studies in particular require a longer planning phase, the longer the pandemic lasts, the greater the number of studies that allow valid statements at the population level as well as over time and that contribute to closing some of the research gaps mentioned. For effective mental health surveillance, study results must be systematically pooled and comparatively evaluated on an ongoing basis. Knowledge of the current situation and the temporal development dynamics of mental health in Germany can contribute to actors from health promotion, prevention, care and relevant political departments developing targeted and evidence-based approaches in order to manage the COVID-19 pandemic.
Key statements
A variety of studies with divergent research methodologies examined the development of mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Study results differed depending on the study design used, among other factors.
Despite increasing stress, the results tend to show relatively stable mental health in the adult population.
Stable values over time in the overall group are partly due to opposing trends in subgroups.
Systematic mental health surveillance is needed for evidence-based crisis management during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Annex Table 1.
Applied search strings in databases
Source: Own table
| DATA BANK | SEARCH STRATEGY |
|---|---|
| Weekly updated database of studies related to the COVID-19 pandemic (as of 30.07.2021) |
Search string PUBMed 1: (‘Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2’ [Supplementary Concept] OR ‘COVID-19’ [Supplementary Concept] OR ‘covid 19 diagnostic testing’ [Supplementary Concept] OR ‘covid 19 drug treatment’ [Supplementary Concept] OR ‘covid 19 serotherapy’[Supplementary Concept] OR ‘covid 19 vaccine’ [Supplementary Concept] OR ‘Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2’[tiab] OR ncov*[tiab] OR covid*[tiab] OR sars-cov-2[tiab] OR ‘sars cov 2’[tiab] OR ‘SARS Coronavirus 2’[tiab] OR ‘Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome CoV 2’[tiab] OR ‘Wuhan coronavirus’[tiab] OR ‘Wuhan seafood market pneumonia virus’[tiab] OR ‘SARS2’[tiab] OR ‘2019-nCoV’[tiab] OR ‘hcov-19’[tiab] OR ‘novel 2019 coronavirus’[tiab] OR ‘2019 novel coronavirus*’[tiab] OR ‘novel coronavirus 2019*’ [tiab] OR ‘2019 novel human coronavirus*’[tiab] OR ‘human coronavirus 2019’[tiab] OR ‘coronavirus disease-19’ [tiab] OR ‘corona virus disease-19’[tiab] OR ‘coronavirus disease 2019’[tiab] OR ‘corona virus disease 2019’[tiab] OR ‘2019 coronavirus disease’[tiab] OR ‘2019 corona virus disease’[tiab] OR ‘novel coronavirus disease 2019’ [tiab] OR ‘novel coronavirus infection 2019’[tiab] OR ‘new coronavirus*’[tiab] OR ‘coronavirus outbreak’[tiab] OR ‘coronavirus epidemic’[tiab] OR ‘coronavirus pandemic’[tiab] OR ‘pandemic of coronavirus’[tiab]) AND (‘2019/12/01’[PDAT] : ‘2099/12/31’[PDAT]) |
|
Search string PUBMed 2: (‘wuhan’[tiab] or china[tiab] or hubei[tiab]) AND (‘Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2’[Supplementary Concept] OR ‘COVID-19’ [Supplementary Concept] OR ‘covid 19 diagnostic testing’[Supplementary Concept] OR ‘covid 19 drug treatment’[Supplementary Concept] OR ‘covid 19 serotherapy’[Supplementary Concept] OR ‘covid 19 vaccine’[Supplementary Concept] OR ‘coronavirus*’[tiab] OR ‘corona virus*’[tiab] OR ncov[tiab] OR covid* [tiab] OR sars*[tiab]) | |
|
Search string Embase 1: (‘severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2’:ti,ab OR ‘severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2’/exp OR ‘covid 19’/exp OR ncov*:ti,ab OR covid*:ti,ab OR ‘sars cov 2’:ti,ab OR ‘sars-cov-2’:ti,ab OR ‘sars coronavirus 2’:ti,ab OR ‘sars coronavirus 2’/exp OR ‘severe acute respiratory syndrome cov 2’:ti,ab OR ‘wuhan coronavirus’: ti,ab OR ‘wuhan seafood market pneumonia virus’:ti,ab OR sars2:ti,ab OR ‘2019-ncov’:ti,ab OR ‘hcov-19’:ti,ab OR ‘novel 2019 coronavirus’:ti,ab OR ‘2019 novel coronavirus*’:ti,ab OR ‘novel coronavirus 2019’/exp OR ‘2019 novel human coronavirus*’:ti,ab OR ‘human coronavirus 2019’:ti,ab OR ‘coronavirus disease-19’:ti,ab OR ‘corona virus disease-19’:ti,ab OR ‘coronavirus disease 2019’:ti,ab OR ‘coronavirus disease 2019’/exp OR ‘corona virus disease 2019’:ti,ab OR ‘2019 coronavirus disease’:ti,ab OR ‘novel coronavirus 2019*’:ti,ab OR ‘novel coronavirus disease 2019’:ti,ab OR ‘novel coronavirus infection 2019’:ti,ab OR ‘2019 corona virus disease’:ti,ab OR ‘new coronavirus*’:ti,ab OR ‘coronavirus outbreak’:ti,ab OR ‘coronavirus epidemic’:ti,ab OR ‘coronavirus pandemic’:ti,ab OR ‘pandemic of coronavirus’:ti,ab OR ‘severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 vaccine’/exp OR ‘covid 19 vaccine’/exp) AND (2020:py OR 2021:py) | |
|
Search string Embase 2: (wuhan:ti,ab OR china:ti,ab OR hubei:ti,ab) AND (‘severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2’:ti,ab OR ‘severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2’/exp OR ‘severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2’ OR ‘covid*’:ti,ab OR ‘covid 19’/exp OR ‘covid 19’ OR coronavirus*:ti,ab OR ‘corona virus*’:ti,ab OR ncov:ti,ab OR covid*:ti,ab OR sars*:ti,ab OR ‘sars coronavirus 2’/exp) + additional hand research/evaluation of the preprint servers arXiv, bioRxiv, ChemRxiv, medRxiv, Preprints.org, Research Square and Social Science Research Network (SSRN) | |
| Endnote Smartgroups | Search string ‘Mental Health’: Smartgroup 1: Mental OR psychological OR psychosocial OR Psychisch OR psychische OR psychischer OR psychischen OR depression OR anxiety OR Angst Smartgroup 2: mentale OR Resilienz OR resilience OR Lebenszufriedenheit OR life satisfaction OR PTSD OR Wellbeing OR Wohlbefinden OR Suizid OR suicide Search string ‘Deutschland’: Smartgroup 3: German OR Germany OR deutsch OR Deutschland OR deutsche OR deutscher |
| Data bank of the World Health Organization (08.06.2021) https://search.bvsalud.org/global-literature-on-novel-coronavirus-2019-ncov/ | Search string as a combination of the endnote search terms (tw:(Mental OR psychological OR psychosocial OR Psychisch OR psychische OR psychischer OR psychischen OR depression OR anxiety OR Angst OR mentale OR Resilienz OR resilience Lebenszufriedenheit OR life satisfaction OR PTSD OR Wellbeing OR Wohlbefinden OR Suizid OR suicide)) AND (tw:(German OR Germany OR deutsch OR Deutschland OR deutsche OR deutscher)) |
| Google search | ENGLISH: (Covid OR Corona OR pandem*) AND German* AND (Mental OR disorder OR wellbeing OR distress OR substance OR missuse OR violence OR abuse) GERMAN: Covid AND German* AND Psych* Krankenkasse OR Krankenversicherung OR Routinedaten AND Corona OR Covid AND Psych |
Annex Table 2.
Classification of study type
Source: Own table
| Random sample of the general population | Random sample from an access panel | Adaptation and design weighting | Non-Probability Sample | Trend Design | Cohort Design | Identical assessment of the outcome over several measurement points | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study type I: PRIMARY DATA | ||||||||
| A | Representative cross-sectional study with random sample from the general population and possibility of comparison with identically surveyed cross-sectional study in trend | X | X | X | In part | X | ||
| B | Representative cross-sectional study with random sample from an ACCESS-Panel and possibility of comparison with identically surveyed cross-sectional study in trend | X | X | X | In part | X | ||
| C | Representative cross-sectional study with random sample and one-time survey | X | ||||||
| D | Cohort study with random sample at t1 | X | X | X | ||||
| E | Cohort study with non-probability sample at t1 | X | X | X | ||||
| F | Cohort study with non-probability sample | X | In part | |||||
| Study type II: ROUTINE DATA | ||||||||
Annex Table 3 Publication.
Category I: Primary data
Abbreviations used:
M = median, SD = standard deviation, cut-off = fixed limit of an instrument from which a certain interpretation of the results applies, n = sample size, N = full survey, OP = observation period, CP = comparison period, t1 = measurement time 1, t2 = measurement time 2., difference = calculation of the intra-individual deviation of different measurement times
| STUDY TYPE A: Representative cross-sectional studies in trend design with random sampling from the general population and identical survey design of the temporal comparative data [1–16] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study or data basis and publications (including observation period etc.) | Results | |||
| Outcome | Operationalisation/measuring instrument | Description and interpretation by authors of the publication | ||
|
Data basis: SOEP-CoV
Survey study (telephone): special study with two survey waves of the Socio-Economic Panel (SOEP) based on offline random sampling (households of the general population, persons aged 18-over 80); comparison over time between the samples and additionally with identically surveyed outcomes in previous years’ SOEP surveys. First wave: 31.03.–04.07.2020; second wave: 01.01.–28.02.2021 [1] Entringer T, Krieger M (2020): OP: 01.04.–30.06.2020 (n=5,529, division into three pandemic phases) [2] Entringer T, Kröger H (2020): OP: 01.04.– 26.4.2020 (n=3,599) [3] Entringer T, Kröger H, Schupp J et al. (2020): OP: 01.04.–26.04.2020 (n=3,599) [4] Kritikos AS, Graeber D, Seebauer J (2020): OP: 01.04.–24.05.2020 (n=3,052) [5] Liebig S, Buchinger L, Entringer T et al. (2020): OP: 01.04.–04./05.07.2020 (n=5,617) [6] Seebauer J, Kritikos AS, Graeber D (2021): OP: 01.04.–04./05.07.2020 versus CP 2019 (n=5,617) [14] Entringer T, Kröger H (2021): OP: 01.01.–28.02.2021 versus CP: 31.03.–04.07.2020 or previous years (n=6,013) [13] Entringer T, Kröger H (2021): OP: 01.01.–28.02.2021 versus CP: 31.03.2020–04.07.2020 or previous years (n=6,013) |
a | Satisfaction of life
compared to 2015–2019 |
Short scale L-1 (Scale 0–10) |
Unchanged in general population until 30.06.2020 at 7.44 similar to previous year [2]; reduction at the beginning of 2021 to 7.2 [13, 14]
Reduction among self-employed [4]; especially reduction among women [5] also in further course of the pandemic [13, 14] Increase for single people; unchanged among couples without children and single parents; reduction for couples with children [1] Increase among people with low income, low education; decrease among people with high income, high education – reduction of socioeconomic differences [3], is also evident as the pandemic continues [13] |
| a | Wellbeing
compared to 2007–2019 |
Four single items (Scale 1–5) |
Unchanged in general population [2, 3, 5]: 14.7 in 2020, similar to previous year. Small and not significant reduction to 14.5 in 2021 [13, 14]
Increase for single people; unchanged among couples without children and single parents; reduction for couples with children [1] |
|
| c | Depressive and anxiety symptoms
compared to 2016, 2019 |
PHQ-4
(M, Scale 1–12) |
Increase in general population compared to 2019; however, unchanged compared to 2016 [2, 3, 5]. In the OP 01.04–30.06.2020, the value is 2.4 [2, 3, 5] and in the OP 01.01–28.02.2021, the value is 2.2 [13, 14]. In 2019 it was 1.9 and in 2016 it was 2.3
Increase of incidence of depressive symptoms in general population compared to 2019: 21% depressive symptoms not present at any time in OP vs. 38% in CP [6] Particularly affected by an increase are people with a migration background [3, 13, 14], women and younger people [13, 14]; longitudinally, the situation worsened considerably for female self-employed workers [6] |
|
|
Data basis: Mannheim Corona Study
Survey study (online): special study of the German Internet Panel (GIP) based on offline random sampling: repeated weekly survey of approx. 3,600 people aged 18–75 in each case in the period 20.03.–09.07.2020, daily survey of an average of 489 people; comparison over time by showing weekly progression [7] Mata J, Wenz A, Rettig T et al. (2020): OP: 20.03.–09.07.2020 [8] Blom A G, Wenz A, Rettig T et al. (2020): OP: 20.03.–09.07.2020 [9] Naumann E, Mata J, Reifenscheid M et al. (2020): OP: 20.03.–16.04.2020 |
b | Anxiety | State-Trait Anxiety Inventory short scale
Until week 4: Five items (M; cut-off >2) [9] from week 5: Two items [7, 8] |
Decrease of the initially increased level of anxiety in the general population already during the first lockdown from 20 March to 16 April to 1.9 [9], in the further course of the pandemic until July stable, very slightly decreasing level to 1.70 and 1.66 respectively (taken from graphical representation) [7, 8]
Decline in all population groups, strongest among young people [9] |
| c | Depressive symptoms | from week 5: PHQ-2 | Decrease in general population over the course of the pandemic [7] from 1.50 to 1.43 (from graphical representation) in all population groups, no increase in vulnerable groups | |
|
Data basis: GEDA-EHIS 2019/2020
Survey study (telephone) of the European Health Interview Survey (EHIS) for Germany in the general population aged 15-over 80 (n=23,001, approx. 1,300 persons per month); comparison over the time before, during and after the lockdown in Germany (from 16.03.2020) within the surveyed study sample and presentation of monthly progression [11] Damerow S, Rommel A, Prütz F et al. (2020): OP: 04/2010–09/2020 (n=23,001) versus CP: 04/2019–03/2020 [15] Cohrdes C, Yenikent S, Wu J et al. (2021): OP: 01.01.–30.06.2020 versus CP: CW 1–11 2020, CW 12–18 2020, CW 19–31 2020 (n=9,011) |
c | Depressive symptoms | PHQ-8 (>9) | Unchanged in general population [11] 6.6% of population in CW 15–26 2020 compared to 8.3% CW 15–26 2019. |
| c | Individual symptoms PHQ-8 over time |
Decrease of two symptoms in general population (lack of energy; concentration problems) [11] 18.1% of population report concentration problems (CW 15–26 vs. 21.9% CW 15–26 2019) [11] and 50.7% of population report lack of energy (CW 15–26 vs. 64.0% CW 15–26 2019) [11]
Decrease in lack of energy in general population during CW 12–18 2020 (first lockdown) compared to CW 1–11 2020, subsequent increase in CW 19–31 2020 to level of CW 1–11 2020 [15] |
||
|
Data basis: Study of Ulm University
Survey study (personal interview) using the random route method in the general population aged 14–95; temporal comparison of the sample surveyed before and after the lockdown in Germany (from 16.03.2020) [12] Sachser C, Olaru G, Pfeiffer E et al. (2021): OP: 10.02.–15.03.2020 versus CP 16.03.–25.04.2020 (n=2,503) |
c | Psychopathological symptoms | Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI-18) |
Decrease in general population from M=3.73; SD=6.39 compared to M=5.00; SD=7.93 in the CP [12]
Unchanged in OP compared to CP for older people and people with low income |
|
Data basis: Study of the Universities of Mainz and Leipzig
Survey study (personal interview) using the random route method in the general population aged 14–95; temporal comparison with analogue study conducted in 2018 [16] Beutel ME, Hettich N, Ernst M et al. (2021): OP: 02.05.–29.06.2020 (n=2,503) compared to CP: May–July 2018 (n=2,516) |
c | Depressive and anxiety symptoms | PHQ-4 (M) |
Increase of depressive symptoms to M=1.14; SD=1.23 compared to M=0.89; SD=1.21 in the CP [16]
Increase of anxiety symptoms to M=1.05; SD=1.31 compared to M=0.77; SD=1.17 in the CP [16] |
|
Data basis: Regional Study of the Central Institute of Mental Health Mannheim
Survey study (written) in the Mannheim area in the general population aged 18–65; comparison over time with study from 2018 with the same survey design [10] Kuehner C, Schultz K, Gass P et al. (2020): OP: 24.04.–23.05.2020 compared to CP 2018 (n=721) |
a | Wellbeing | WHO-5-Well-Being-Index | Unchanged in general population to 2018 (2020: M=56.52; 2018: M=56.83) [10] |
| b | Psychosocial distress | PHQ-D Stress Module (total) | Unchanged in general population compared to 2018 [10] | |
| c | Symptoms and syndrome diagnosis: Depressive disorder, anxiety disorder, Somato-form disorder Comorbidity syndrome diagnosis. | Screening-based syndrome diagnoses from PHQ-D
Sum values of the respective symptoms |
Unchanged in general population (Mannheim region) in OP versus CP (PHQ-D syndrome diagnosis 2020: 29.4%; 2018: 26.8%; PHQ-D comorbidity diagnosis 2020: 20.3%; 2018: 8.9%) [10] | |
| STUDY TYPE B: Representative cross-sectional studies in trend design with random sampling from an access panel and identical survey design of the temporal comparative data [17–21] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study or data basis and publications (including observation period etc.) | Results | |||
| Outcome | Operationalisation/measuring instrument | Description and interpretation by authors of the publication | ||
|
Data basis: COSMO – COVID-19 Snapshot Monitoring
Survey study (online): weekly each approx. 1,000 persons aged 18–74 years since 03.03.2020 with random drawing via a panel provider. A representative distribution of the data by age × gender as well as federal state is aimed for. Education is not taken into account. Comparison over time by presenting the weekly course, partly additional comparison with previous norm data. [21] COSMO – COVID-19 Snapshot Monitoring: Resilience (2021): OP: until 01.06.2021 [20] COSMO – COVID-19 Snapshot Monitoring: Resources and stresses (2021): OP: until 14.07.2021 [19] Gilan D, Röthke N, Blessin M et al. (2020): OP: t1: 24.03.2020, t2: 31.03.2020, t3: 21.04.2020 each compared with norm sample |
a | Satisfaction of life – information until 14.07.2021 | Single item (Scale 1–7) | Unchanged in general population and stable over the course of the pandemic (until 14.07.2021): M=4.6 to M=4.8 [20] |
| b | Situational stress – information until 14.07.2021 | Single item | High burden in general population at the beginning of the pandemic (52% burdened) – decline to 33% in September 2020, since then increase to peak of 61% in early February 2021, decline since early May 2021 to approximately the level of summer 2020 [20]
Increase in all age groups since September 2020, especially in the 18–29 age group (69% burdened in January and April 2021); decrease since May 2021 [20] |
|
| b | Mental distress (anxiety, dejection) – information until 09.03.2021 | Five single items from GAD-7, ADS, IES-R (M) |
Increase in anxiety in general population at onset of pandemic (24.03.2020: M=0.77; SD=0.94 and 31.03.2020: M=0.75; SD=0.91) compared to norm sample (M=0.50; SD=0.64), decline until end of April 2020 (M=0.60; SD=0.83) [19], then level relatively unchanged until 09.03.2021 [20]
Increase in dejection in the general population at the beginning of the pandemic (M=0.66; SD=0.88) compared to the norm sample (M=0.43; SD=0.70), level unchanged until April 2020 [19], increase in younger people until 09.03.2021 [20] Risk factors for high psychological stress: young age, female gender, having children, single parent, migration background, living alone or more than two persons in household [19] |
|
| a | Resilience – Information until 14.07.2021 | Brief-Resilience-Scale (BRS) |
Unchanged in general population at start of pandemic (M=3.45; SD=0.85) compared to norm sample 2018 (M=3.49; SD=0.84) [19, 21], decrease over course of pandemic [21] (24.03.2020: M=3.43 compared to 01.06.2021: M=3.25)
Older people more resilient than younger people, older people more resilient during the pandemic also compared to the 2018 norm sample [21] |
|
|
Data basis: German-Depression-Barometer
Survey study (online): COVID-19 focus conducted twice since the beginning of the pandemic in general population aged 18–69 years; based on RESPONDI panel; comparison over the time of the two observation periods [18] Stiftung Deutsche Depressionshilfe 2020 (2020): OP: 06/2020 + 07/2020 (n=5,178) [17] Stiftung Deutsche Depressionshilfe 2021 (2021): OP: 02/2021 (n=5,135) |
b | Mental distress | Single items |
Increase in the feeling of low mood in the general population(71% perceive second lockdown as depressing compared to 59% in the first lockdown compared to 36% in summer 2020) [17, 18]
Increase in severe family stress in the general population (25% in the second lockdown compared to 16% in summer 2020) [17] Increase in general population’s perception that fellow citizens are inconsiderate (second lockdown 46% vs. first lockdown 40%) [17] |
| STUDY TYPE C: Representative, one-off cross-sectional studies with random drawing without an identical survey design of the temporal comparative data [22–25] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study or data basis and publications (including observation period etc.) | Results | |||
| Outcome | Operationalisation/measuring instrument | Description and interpretation by authors of the publication | ||
|
Data basis: Corona-COMPASS-Study
Survey study (online) with a random sample from a commercial panel (payback panel, no possibility for participants to self-select); eligible population with online access aged 18–70 (n=8,977, of which 5,844 were interviewed twice), comparison over time with previous SOEP surveys (see study type A) [24] Huebener M, Waights S, Spiess K et al. (2020): OP: 01.05.–01.07.2020 versus CP 2018 (n=8,977) |
a | Satisfaction of life | Short scale L-1 (Scale 0–10) |
Decrease in general population compared to 2018: M=6.95 compared to M=7.36 [24]
Decrease among parents with children younger than 16 years, women and people with low education; highest life satisfaction among older persons (>65 years) [24] |
|
Data basis: Parent Study of the Berlin University Alliance
Survey study (telephone, online) of parents of minor children aged 18–73 years, random sample of Germanspeaking households with minor children; comparison over time with previous norm samples and retrospective self-assessment. [23] Calvano C, Engelke L, Di Bella J et al. (2021): Survey from 03.08.11.08.2020; (n=1,024) plus erratum [25] |
b | Stress experience | Parental Stress Scale (total) for time of subjectively highest stress (OP) and for January 2020 (CP) | Increase in general population (parents of minor children) at time of highest exposure so far during pandemic versus retrospective estimate for January 2020: M=36.93; SD=10.45 compared to pre-COVID-19 M=34.72; SD=10.63 [23] |
| c | Depressive and anxiety symptoms | PHQ-4 (M) for time of subjectively highest stress (OP) |
Increase in general population (parents of minor children) at time of highest stress compared to pre-pandemic norm sample; depressive symptoms:
M=1.38 in the OP compared to M=0.94 in the CP; symptoms of anxiety: M=1.14 in the OP compared to M=0.82 in the CP [23, 25] |
|
|
Data basis: Study of the elderly population aged 65 and over by the University of Leipzig
Survey study (telephone), random sample of older people aged 65–94 in the general population; comparison over time with previous norm samples. [22] Röhr S, Reininghaus U, Riedel-Heller S G (2020): OP 06.04.–25.04.2020 |
c | Psychopathological symptoms | Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI-18) | Unchanged in general population (persons 65 years and older) compared to pre-pandemic norm levels (M: 1.4 vs. 2.0; 1.6 vs. 1.6; 2.2 vs. 2.4 and 5.1 vs. 6.0) [22] |
| STUDY TYPE D: Cohort studies with representative initial sample and random sampling at t1 [26, 27] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study or data basis and publications (including observation period etc.) | Results | |||
| Outcome | Operationalisation/measuring instrument | Description and interpretation by authors of the publication | ||
|
Data basis: NAKO Health Study
Survey study (online): special longitudinal survey of the NAKO Health Study; baseline survey t1 as random sample from 18 study regions (2014–2019, n=205,219); comparison over time with t2: re-participants at t2 aged 20–74 years (n=113,928, approx. 55% of t1, no difference in re-participation by age, gender, lower in north-eastern study sites). [26] Peters A, Rospleszcz S, Greiser K H et al (2020): OP: 30.04.–29.05.2020 (n=113,928) versus CP (t1: 2014–2019) [27] Berger K, Riedel-Heller S, Pabst A et al. (2021): OP: 30.04.–29.05.2020 (n=113,928) versus CP (t1: 2014–2019) |
c | Depressive symptoms | PHQ-9 Cut-Off: >9
Total; mean difference to t1 |
Increase in the general population (in the study sites) to 8.8% (t2) compared to 6.4% (t1) and by an average of 0.3 compared to CP [27].
Increase is only seen in persons under 60 years of age in the mean difference of 0.38+/-0.02 points [26]; clearest increase in youngest age group; stronger in regions with higher incidence and in persons tested positive for COVID-19 [26] |
| c | Symptoms of generalised anxiety disorder | GAD-7 Cut-Off: >9
Total; mean difference to t1 |
Increase in the general population (in the study sites) to 5.7% (t2) compared to 4.3% (t1) and 0.45 for women and for men 0.2 [27]
Increase is only seen in persons under 60 years of age in the mean difference of 0.38+/-0.02 points [26]; clearest increase in youngest age group; stronger in regions with higher incidence and in persons tested positive for COVID-19 [26] |
|
| b | Psychosocial stress burden | PHQ-D stress module
Total; mean difference at t1 |
Increase in the general population (in the study sites) in the mean difference by 0.36+/-0.02 points in all age groups [26]
Increase stronger in regions with higher incidence and in individuals who tested positive for COVID-19 [26] |
|
| STUDY TYPE E: Longitudinal studies with non-probability initial sample at t1 [28–32] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study or data basis and publications (including observation period etc.) | Results | |||
| Outcome | Operationalisation/measuring instrument | Description and interpretation by authors of the publication | ||
|
Data basis: LORA – Longitudinal Resilience Assessment
Survey study (online) as a special survey of the LORA study (=prospective study of healthy adults with a focus on resilience, Rhine-Main region): since 31.03.2020 with the start of the first lockdown in Germany, implementation of eight weekly surveys; participants aged 18–50 years (M=31.5±8.4), 69% female without differences to the LORA initial sample; comparison over the time during the pandemic and compared to the last measurement before the outbreak event [29, 32] Ahrens KF, Neumann RJ, Kollmann B et al. (2021): OP: from 31.03. through eight weekly surveys (t1: n=523, t8: n=451) compared to CP: last measurement before pandemic |
b | Everyday burdens per week | Amount | Decrease in sample to [32] to 41.2±22.3 in week 8 versus 60.0±27.2 before the pandemic [29] |
| c | Mental symptoms | GHQ-28 Difference, M | Average decrease [32] in sample to 16.2±7.1 in weeks 5 to 8 versus 20.5±9.7 before the pandemic [29]
Identification of three subgroups when analysing intra-individual changes: continuous increase in psychological symptoms at around 8%; at 9% initial increase and rapid decrease; at 83% improvement or unchanged from pre-pandemic levels [29, 32] |
|
|
Data basis: Longitudinal study (project to classify the factorial structure of protective factors influencing health at Saarland University)
Survey study (online), sampling from self-recruiting WiSo panel (sampling procedure not documented in publication); participants aged 20–95 years (M=55.0; SD=13.9), 53.6% female; comparison over time between t1 (before pandemic outbreak) and t2. [31] Schäfer S K, Sopp M R, Schanz C G et al. (2020): t1: 17.02.–23.02.2020, t2: 16.03.–22.03.2020; n=1,591 |
c | Psychopathological symptoms | Mini-Symptom Checklist Difference |
Unchanged in entire group (i.e. on average without taking individual change into account).
Intra-individual increase at about 10%, decrease at about 8%, unchanged for about 82% of the sample from t1 to t2 [31] |
|
Data basis: Longitudinal study with adults working fulltime
Survey study (mode not stated); sample from representative online panel: full-time working adults aged 18–69; 59.6% female; comparison over time using four survey time points with t1 before pandemic [30] Zacher H, Rudolph C W (2020): OP: t1: 12/2019, t2: 03/2020; t3: 04/2020, t4: 05/2020 (n=979) |
a | General satisfaction of life | Single item (Scale 1 to 7) | Intra-individual decrease in general satisfaction of life between March and May 2020, no change between December 2019 and March 2020 [30] |
| a | Wellbeing | Items of the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (Short Form) | Intra-individual decrease of positive and negative affect between March and May 2020, no change between December 2019 and March 2020 [30] | |
|
Data basis: CORA – Longitudinal Study of the Charité Berlin
Survey study (online), pandemic-initiated with self-selecting baseline sample at t1 in general population and three follow-up surveys; inclusion with participation in at least one follow-up survey (n=2,376 people (age 18–82) were willing to be interviewed again [see 33]) selective sample with 76.7% female; 89.6% higher education or health workers; Temporal comparison over time over the course of the pandemic [28] Bendau A, Plag J, Kunas S et al. (2020): OP: 27.03.–15.06.2020 (t1: 03/2020, t2: 04/2020, t3: 05/2020, t4: 06/ 2020) |
c | Depressive and anxiety symptoms | PHQ-4 (Cut-Off >5); M, Median, Difference |
Decrease in sample from 31.0% (t1) to 22.6% (t4) [28]
Continuous decrease in the mean value of the sample across all measurement points; especially decrease in symptom severity; decrease in the median value from 4 (t1) to 3 (t4) [28] Intra-individual increase in about 25% of the sample from t1 to t4 [28] |
| c | Depressive symptoms | PHQ-2 (Cut-Off >2); M, Median, Difference |
Decrease in sample from 32.7% (t1) to 25.3% (t4) [28]
Continuous decrease in the mean value of the sample across all measurement points; especially decrease in symptom severity; no decrease in the median value [28] Intra-individual increase in about 25% of the sample from t1 to t4 [28] |
|
| c | Symptoms of generalised anxiety disorder | GAD-2 (Cut-Off >2); M, Median, Difference |
Decrease in sample from 36.4% (t1) to 24.9% (t4) [28]
Continuous decrease in the mean value of the sample across all measurement points; especially decrease in symptom severity; decrease in the median value from 2 (t1) to 1 (t4) [28] Intra-individual increase in about 10% of the sample from t1 to t4 [28] |
|
| b | COVID-19-related anxiety | C-19-A M, Median, Difference | Continuous decrease in the mean value of the sample across all measurement points; decrease in the median value from 9 (t1) to 4 (t4) [28]
Intra-individual increase in about 10% of the sample from t1 to t4 [28] |
|
| STUDY TYPE F: Cross-sectional studies with online non-probability sample [33–45] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study or data basis and publications (including observation period etc.) | Results | |||
| Outcome | Operationalisation/measuring instrument | Description and interpretation by authors of the publication | ||
|
Data basis: Online survey of the LVR-Klinikum Essen
Cross-sectional survey 1 (10.03.–27.07.2020): Sample composition differs from the general population at all evaluation points (approx: 70% female, 75% with high education (at least Abitur), 61% younger than 44 years). Standardisation by calculation of weighting factors for the distribution of characteristics in the general population is not described. Since the second wave of infection, the study has been continued as a new cross-sectional study. [34] Moradian S, Bäuerle A, Schweda A et al. (2021): OP: 15.03.–04.04.2020 versus CP: 02.11–22.11.2020; adjustment of the two samples has been conducted (n=7,288) [35] Bäuerle A, Steinbach J, Schweda A et al. (2020): OP: 10.03.–05.05.2020; temporal comparison with retrospective assessment of the same instrument before the pandemic (n=15,037) [36] Bäuerle A, Teufel M, Musche, V et al. (2020): OP: 10.03.–05.05.2020 compared to norm sample, adjustment of samples not described (n=15,037) [37] Hetkamp M, Schweda A, Bäuerle A et al. (2020): OP: 10.03.–30.04.2020; comparison over time in the pandemic and against CP: norm sample, adjustment of samples not described (n=16,245) [38] Skoda EM, Spura A, De Bock F et al. (2021): OP: 10.03.–27.07.2020; comparison over time with norm sample before the pandemic and during the pandemic by dividing into five pandemic phases (n=16,918) |
c | Depressive symptoms | PHQ-2 (Cut-Off >2), M | 14.3% (OP) in sample vs. 7.6% (CP: retrospective assessment of instrument before pandemic); mean difference significant; interpreted as increase, especially among persons with pre-existing mental disorder [35]
14.3% (OP) in sample versus 5.6% (CP: norm sample); interpreted as increase [36] Lockdown 2 > Lockdown 1 in samples; interpreted as increase [34] Increase in sample from 8% in initial phase to 17% during phase 2 and 21% during phase 3 (crisis, lockdown), stable level afterwards; plus increase compared to 5.6% in pre-COVID-sample [38] |
| c | Symptoms of generalised anxiety disorder | GAD-2 (Cut-Off >2), M | 19.7% (OP) in sample vs. 9.0% (CP: retrospective assessment of instrument before pandemic); mean difference significant; interpreted as increase [35] | |
| c | Symptoms of generalised anxiety disorder | GAD-7 (Cut-Off >9, at least moderate symptoms) | 16.8% (OP) in sample vs. ~ 6% (CP: norm sample); interpreted as increase [36]
Increase in the sample over the course of the pandemic from 7% to 37% to 22%. Comparison with norm sample interpreted as up to 8-fold increase in prevalence in population exposed to COVID-19 [37] Increase in sample from 9% in initial phase to 22% each during phases 2 and 3 (crisis, lockdown), then slight drop to still higher level (22% and 20% respectively) compared to baseline values; plus increase in sample compared to norm sample of ~ 6%, interpreted as 2 to 10-fold increase in fear during pandemic [38] Unchanged in samples during the pandemic: lockdown 1=lockdown 2 [34] |
|
| b | Mental distress | Distress Thermometer (Cut-Off >3) | 65.2% (OP) in sample vs. 51.8% (CP: retrospective assessment of instrument before the pandemic); mean difference significant; interpreted as increase [35]
65.2% (OP) in sample vs. 39% (CP: norm sample); interpreted as increase [36] Unchanged in samples during the pandemic: lockdown 1=lockdown 2 [34] Increase in sample from 51% in initial phase to 63% during phase 2 and 60% during phase 3 (crisis, lockdown), then stable level of 58%; plus increase in sample compared to norm sample with 39% [38] |
|
| b | COVID-19 related anxiety | Single item (Scale 1–7) | Increase in sample at the beginning of the pandemic, then decrease below baseline level [37, 38] | |
|
Data basis: CORA [see 28] Initial sample – Charité Berlin
Survey study (online; self-selecting) in general population 18 years and older; selective composition: 70.1% female; 82.4% higher education (at least university entrance qualification); comparison over time with norm sample before pandemic, adjustment of samples not described [33] Petzold MB, Bendau A, Plag J et al. (2020): OP: 27.03.–06.04.2020 (n=6,509) versus CP: Publication from 2010 |
c | Depressive and anxiety symptoms | PHQ-4, M | 4.15 in sample vs. 1.76 in norm sample; interpreted as hypothesis-generating indication of possible increase [33] |
|
Data basis: Initial sample of a longitudinal study of the University Tübingen
Survey (online; self-selecting) in general population aged 18–85 years with the aim of identifying protective factors for mental health; selective composition: 76.6% female; 81.4% higher education (at least university entrance qualification); comparison over time with representative pre-pandemic data without sample adjustment. [39] Bauer LL, Seiffer B, Deinhart C et al. (2020): OP: 08.04.–26.04.2020 versus CP: representative data from 2013 (n=3,700) |
c | Depressive symptoms | PHQ-9 (>9,. at least moderate msymptoms) | 31.4% in OP compared to 8.1% in CP; interpreted as an increase in the prevalence of depressive disorders [39] |
| c | Symptoms of panic disorder | PHQ-Panic Module Long Version | 5.7% in OP vs. 2.0% in CP; interpreted as increase in the prevalence of panic disorders [39] | |
| c | Symptoms of generalised anxiety disorder | GAD-7 (>9, less. moderate symptoms) | 7.4% in OP compared to 2.2% in CP; interpreted as an increase in the prevalence of generalised anxiety disorders [39] | |
|
Data basis: Online survey of the Charité Berlin
Survey (online; self-selecting) in general population aged 18–81 years; 75.5% female; temporal comparison over the course of the pandemic (monthly) [40] Liu S, Heinzel S, Haucke MN et al. (2020): OP: April–September 2020 (n=1,903) |
b | COVID-19 related stress | COVID-19 Peritraumatic Distress Index (CPDI) | Increase of reported psychological distress in the sample over the survey period. Women, young people and lonely people were particularly affected [40] |
|
Data basis: Online survey of the Medizinische Hochschule Hannover
Survey study (online; self-selecting) in general population aged: M=40.4; SD=11.7; 83% female (separate reporting for women and men); years of education: M=15.9; SD=4.2), comparison over time with norm samples, among others, adjustment of the sample not described [41] Jung S, Kneer J, Krüger T (2020): OP: 01.04.–15.04.2020 (n=3,545) |
b | Psychosocial stress burden | PHQ Stress-Module | Women 6.40 and men: 6.19 in sample – men and women are in the range of mild psychosocial stress (Defined range: 5–9) [41] |
| c | Depressive and anxiety symptoms | PHQ-4; (M) | Women in the sample 3.91 vs. 1.71 in reference sample; men in the sample: 3.21 vs. 1.31 in reference sample; interpreted as mental distress [41] | |
| a | Wellbeing | WHO-5 (M) | Women 51.44 vs. 72.6 in reference sample (or: vs. healthy individuals who have an average score of 75); men: 47.52 vs. 68.28 in reference sample (or: vs. healthy individuals who have an average score of 75); interpreted as psychological distress [41] | |
|
Data basis: Initial sample of a longitudinal study of the Justus Liebig University Giessen
Survey study (online; self-selecting) in general population aged 18 years and older; selective composition: 79.5% female; 62.8% students; comparison over time with prevalences of mental disorders based on psychodiagnostic interview and representative data, adjustment of sample not described [42] Munk AJL, Schmidt NM, Alexander N (2020): OP: 27.03.–03.04.2020 (n=949) |
c | Symptoms ‘Any mental disorder’ | All instruments listed here | 50.6% vs. 27.9% 12-month prevalence in general population; interpreted as increase [42] |
| c | Depressive symptoms | Beck-Depression-Inventory | 35.3% vs. 7.7% 12-month prevalence in general population; interpreted as increase [42] | |
| c | Symptoms of generalised anxiety disorder | GAD-7 | 12.0% vs. 2.2% 12-month prevalence in general population; interpreted as increase [42] | |
| c | Symptoms of panic disorder | PHQ-Panic module | 5.4% vs. 2.0% 12-month prevalence in general population; interpreted as increase [42] | |
| c | Symptoms of obsessive compulsive disorder | Obsessive-Compulsive Inventory-R | 21.4% vs. 3.6% 12-month prevalence in general population; interpreted as increase [42] | |
|
Data basis: Online survey of the universities Marburg and Gießen
Survey study (online; self-selecting) in general population aged 18–81 years; 74.8% female; comparison over time using retrospective assessment of the same measure before the first lockdown [43] Schwinger M, Trautner M, Kärchner H et al. (2020): OP: 01.04–28.05.2020 (n=1,086) |
a | General satisfaction of life | Four Items of the Temporal Satisfaction with Life Scale M | 2.65 in sample on OP vs. 3.04 retrospective data; interpreted as strong decrease [43] |
| b | Anxiousness, depressivity | Three items each of the State-Trait-Anxiety-Depression-Inventory (STADI) M | Depressivity 1.91 in sample on OP vs. 1.71 retrospective data; interpreted as moderate increase [43]
Anxiousness 2.02 in sample on OP vs. 1.79 retrospective data; interpreted as moderate increase [43] |
|
|
Data basis: Online survey of the universities Göttingen and Regensburg
Survey study (online; self-selecting) in general population aged 18–88 years; (n=1,744, 72.2% female); comparison over time with reference sample from 2010, sample adjustment by random deletion of female participants (n=1,001, 52.2% female) [45] Schelhorn I, Ecker A, Bereznai J et al. (2020): OP: 08.04.–01.06.2020 |
c | Depressive symptoms | ICD-10-Symptom-Rating (ISR)
(> Cut-Offs for moderate or severe symptoms) |
13% moderate and 5% severe symptoms in sample vs. 4.8% and 1.1% in reference sample; interpreted as an indication of possible increase[45]
Particularly in women and in young people, the symptoms are more severe [45] |
|
Data basis: Online survey of the Universities Witten/Herdecke, …
Survey study (online, participant recruitment via snowball system); comparison over time by dividing the sample into three cohorts over the survey period [44] Büssing A, Rodrigues Recchia D, Dienberg T et al. (2021): OP: June 2020 (n=1,333), July–September 2020 (n=823), October–January 2021 (n=625) |
a | Wellbeing | WHO-5-Well-being Index (Total) | Decrease in the OP October–January 2021 compared to OP June 2020 and OP July–October 2020 [44] |
| a | Satisfaction of life | Brief Multidimensional Life Satisfaction Scale | Decrease in the OP October–January 2021 compared to OP June 2020 and OP July–October 2020 [44] | |
Category II: Routine Data
Abbreviations used:
AU = Incapacity for work; EBM = Uniform value scale for billing statutory health insurance services, IRR = Incidence Rate Ratio; PEPP = fixed rate remuneration system in psychiatry and psychosomatics (PEPP); AMDP = Working Group for Methodology and Documentation in Psychiatry; Information on Coded Diagnoses (FXX.X) according to the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-10)
| ROUTINE DATA [46–69] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study or data basis and publications (including observation period etc.) | Results | |||
| Outcome | Outcome | |||
|
Data basis: Outpatient care data from the National Association of Statutory Health Insurance Physicians
Data from persons with statutory health insurance who use SHI-accredited medical care; first to second quarter 2020 data from 16 of the 17 SHI-accredited medical associations (excluding Bremen), third to fourth quarter 2020 from 15 (excluding Bremen and Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania). [68] Mangiapane S, Zhu L, Czihal T et al. (2020): 14 defined observation periods in 2020: t0: 01.01.–03.03.; t1: 04.03.–10.03.; t2: 11.03.–17.03.; t3: 18.03.–24.03.; t4: 25.03.–31.03.; t5: 01.04.–28.04.; t6: 29.04.–26.05.; t7: 27.05.–30.06.; t8: 01.07.–28.07.; t9: 29.07.–25.08.; t10: 26.08.–30.09.; t11: 01.10.–04.11.; t12: 05.11.–02.12.; t13: 03.12.–31.12. compared to the corresponding comparison periods in 2019 |
e | Utilisation of outpatient care by medical and psychological psychotherapists and specialists in psychosomatic medicine and psychotherapy | Number of treatment cases |
Decrease compared to the same period of the previous year in the periods t2 to t6 with the strongest decrease at t4 with 36.5% and 39.8%, one-time increase at t7 by 24.4% and 17.8%;at t8-t11 fluctuations around the level of the previous year, t12–t13 decrease by 14.9% and 12.4% compared to the same period of 2019;
Changes over time roughly comparable to other doctor groups with the exception of the comparatively strong increase at t7 [68] |
| e | Utilisation of outpatient psychotherapy | Number of treatment cases for psychotherapeutic services for individual therapy (section 35.2.1 EBM) and group therapy (section 35.2.2 EBM) | Individual therapy: decrease compared to previous year’s period from t2 to t6 with strongest decrease at t3 by 23.3%, then increase compared to previous year’s periods until t11 with strongest increase at t11 (3.8%), then decrease again in t13 by 3,0% [68]
Group therapies decrease compared to previous year’s periods from t2 to t8 with strongest decrease at t5 by 59.8%, in t9 to t11 roughly unchanged at previous year’s level, decrease again at t12 and t13 by up to 16.4% [68] |
|
| e | Utilisation of outpatient substitution treatment | Number of treatment cases for substitution treatment for drug dependence (section 1.8 EBM) | Decrease compared to previous year’s period from t3 to t8 with strongest decrease at t4 by 13.0%, from t9 to t13 fluctuating below previous year’s level with decrease between 1.1% and 3.2% [68] | |
|
Data basis: Outpatient care data from the Disease Analyzer-Database (IQVIA)
Data from people with use of medical practices that are part of the panel of the Disease Analyzer Database (IQVIA) [54] Jacob L, Smith L, Koyanagi A et al. (2020): 03–06/2020 vs. 03–06/2019 (n=1,140 GP practices, n=1,854,742 people with treatment cases in 01–06/2020). [55] Michalowsky B, Hoffmann W, Bohlken J et al. (2020): 02–05/2020 compared to 02–05/2019 (n=1,095 GP or internal medicine practices and n=960 specialist practices, of which n=155 neurological and psychiatric practices; n=2,447,356 persons aged ≥65 years with treatment cases) |
e | Outpatient diagnostic incidence and prevalence of anxiety disorders in GP practices | Number of persons with (first) diagnosis of F41.0–3 or F41.8–9 | Increase in diagnoses by 19% in 2020 compared to 2019, increase in first diagnoses by 21% [54] |
| e | Outpatient diagnostic incidence of anxiety disorders in GP practices by age | Number of persons with first diagnosis of F41.0–3 or F41.8–9 by age | Decrease in the proportion of 18–30 year olds to 16.8% in 2020 compared to 20.3% in 2019 [54] | |
| e | Comorbidity of outpatient incident diagnoses in general practitioners of anxiety disorders | Number of persons with first diagnosis of F41.0–3 or F41.8–9 and diagnosis of nine somatic disorders | Increase in people with comorbid COPD in 2020 to 9.4% compared to 7.9% in 2019 and with comorbid asthma to 11.3% in 2020 compared to 9.7% in 2019 [54] | |
| e | Utilisation of outpatient care by psychiatric/neurological practices among persons aged ≥65 years | Number of physician contacts in psychiatric/neurological practices | Increase of 13% in March, decrease of 18% in April and 12% in May compared to 2019; rather small decrease compared to 7 other doctor groups with a mean of 5% (rank 3) [55] | |
| e | Referral or admission to outpatient or inpatient care by psychiatric/neurological practices among persons aged ≥65 years | Number of referrals or admissions in outpatient or inpatient care by psychiatric/neurological practices | Decrease of 22% in referrals and 40% in admissions in March to May 2020 compared to 2019 [55] | |
| e | Outpatient diagnosis of depression for persons aged ≥65 years | Number of Persons with first diagnosis F32–33 | Decrease of 13% in 2020 compared to 2019 [55] | |
|
Data basis: Work incapacity data for KKH
Data of those compulsorily and voluntarily insured with the KKH (excluding the unemployed and pensioners), n=812,000 [57] [56] KKH Kaufmännische Krankenkasse (2020): 01–06/2020 compared to 01–06/2019 [58] KKH Kaufmännische Krankenkasse (2021): 2020 compared to 2019 [57] KKH Kaufmännische Krankenkasse (2021): 2020 compared to 2019 and 2019 compared to 2018 |
e | Incapacity to work cases | Number of cases with incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis | Increase of approx. 80% compared to 2019 [56] |
| e | Duration of incapacity to work by gender | Number of days per case of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis | Increase for women by ‘just under 4 days’, for men by ‘almost five days’ in 2020 compared to 2019 [58] | |
| e | Duration of incapacity to work | Number of days per case of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis | Increase of 4.2 days in 2020 compared to 2019, larger increase than from 2018 to 2019 of 3.9 days [57] | |
|
Data basis: Incapacity to work for BARMER
Data from working people aged 15–64 who are insured with BARMER [49] BARMER (2020): 01–06/2020 compared to 2019 |
e | Number of work days lost due to sickness | Proportion of days with incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis in all insured days | Decrease of 5.5% in the period April–June 2020 compared to April–June 2019 [49] |
|
Data basis: Incapacity to work data for BKK
Data from employees insured with participating BKKs [51] BBK (2021): 01/2020 –04/2021 |
e | Number of work days lost due to sickness | Proportion of days with incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis in all insured days | Decrease from March (0.83%) to May 2020 (0.70%), renewed increase as of November 2020 (0.78%) and February/March 2021 (0.80%) [51] |
|
Data basis: Incapacity to work data for DAK
Data from employed persons insured with the DAK [52] DAK Gesundheit (2021): 01–12/2020 compared to 01–12/2019 |
e | Incapacity to work cases | Number of cases of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis per 100 insured persons | Decrease in 2020 compared to 2019 for women from 9.3 to 8.8 and for men from 5.7 to 5.1 [52] |
| e | Duration of incapacity to work | Number of days per case of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis | Decrease in short case durations (1–7 days) by 20% in 2020 compared to 2019, increase in long case durations (>6 weeks) by 6% in 2020 compared to 2019 [52] | |
| e | Work incapacity cases according to diagnosis | Number of days of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis per 100 insured persons according to individual diagnoses | Changes in 2020 vs. 2019: decrease in somatoform disorder (F45) by 6%, almost unchanged in depression (F32+33) with an increase of 0.3%; increase in other anxiety disorders (F41) by 5%, reactions to severe stress and adjustment disorders (F43) by 8% and other neurotic disorders (F48) by 7% [52] | |
|
Data basis: Incapacity to work data for AOK
Data from employees insured with the AOK, n=approx. 13 million [47] Wissenschaftliches Institut der AOK (WIdO) (2020): 01.01.–31.08.2020 compared to 01.01.–31.08.2019 |
e | Incapacity to work cases | Number of cases of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis per 100 insured persons | Decrease to 11.1 in the period January to August 2020 from 12.0 in the comparison period in 2019 [47] |
| e | Duration of incapacity to work | Number of days per case of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis | Increase to 29.3 in the period January to August 2020 from 25.9 days in the same period in 2019 [47] | |
|
Data basis: Work incapacity data for TK
Data from persons insured with TK who are subject to social insurance or registered as unemployed, n=5.4 million [67] Techniker Krankenkasse (2021): 2020 compared to 2019 [66] Techniker Krankenkasse (2021): 01–12/2020 com-pared to 2019/ 2018 |
e | Days of incapacity to work | Number of days of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis per 100 years insured | Increase of 5.1 days for men and 14.4 days for women in 2020 compared to 2019 [67] |
| e | Change in sick leave from 2019 to 2020 compared to 2018 to 2019 | Change in number of days with incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis | Increase of 0.11 days from 2019 to 2020 (2.98) compared to increase from 2018 to 2019 (2.89) [66] | |
|
Data basis: Emergency admission of the psychiatric clinic of the Hannover Medical School
Data of persons aged ≥18 years who presented at the psychiatric emergency admission of Hannover Medical School and had medical contact with psychiatrists [62] Seifert J, Meissner C, Birkenstock A et al. (2021): 16.03.–24.05.2020 compared to 16.03.–24.05.2019, n=374 presentings |
e | Psychiatric emergencies according to clinical characteristics | Number of cases with F-diagnosis, after repeated presentations within one month and suicide attempts before presentation | Decrease in case numbers of 21.4% in the period 16.03.–24.05.2020 compared to the same period in 2019, at the same time increase in the number of repeated presentations within one month to 30.2% compared to 20.4% in 2019; unchanged proportion of suicide attempts [62] |
| e | Psychiatric emergencies according to diagnoses | Number of diagnoses of mental disorders in the main diagnostic groups F1–F4 and F6, as well as ‘other’ (F0, F5, and F7–9) | Decrease to 15.2% in the period 16.03–24.05.2020 from 22.2% in the same period in 2019 for affective disorders (F32–33), at the same time increase for personality and behavioural disorders (F6) to 12.3% from 7.8%, unchanged proportion for F1, F2, F4 and ‘other’ [62] | |
| e | Aspects of the psycho-pathological findings | Documentation of 65 selected symptoms of psychopathological findings according to AMDP system | Increase in the period 16.03.–24.05.2020 compared to the same period in 2019 for formal thinking disorder (75.7% compared to 65.1%), hopelessness (13.9% compared to 5.3%) and social withdrawal (14.4% compared to 8.0%), all others unchanged (including suicidality) [62] | |
| e | Relation between psychiatric emergencies and the COVID-19-pandemic | Explicit documentation of the association of the case with the COVID-19-pandemic by the treating psychiatrist | A relation between the presentation and the COVID-19-pandemic was documented for 20.1% of all persons; among these, the proportion of persons with suicide attempts increased 3-fold compared to cases without a connection to the COVID-19-pandemic [62] | |
|
Data basis: Emergency admission of the Central Institute of Mental Health Mannheim
Data of persons that presented in the emergency admission of the Central Institute of Mental Health Mannheim [61] Hoyer C, Ebert A, Szabo K et al. (2020): 01.01.–19.04.2020 compared to 01.01.–21.04.2019 |
e | Presentations in psychiatric emergency admission | Number of presentations in psychiatric emergency admission | Decrease of 26.6% in presentation rates 18.03.–14.04./01.01.–17.03 in 2020 compared to 2019 [61] |
| e | Presentations in psychiatric emergency admission according to diagnosis | Number of presentations in psychiatric emergency admission by main diagnosis group | Decrease of 42.3% in showcase rates 18.03.–14.04./01.01.–17.03 in 2020 compared to 2019 for affective disorders [61] | |
|
Data basis: Emergency admission and consultation requirements of the Klinikum rechts der Isar, Technische Universität München
Data from people who presented at the central interdisciplinary emergency admission of the Klinikum rechts der Isar, Technische Universität München [60] Aly L, Sondergeld R, Holzle P et al. (2020): 21.03.–01.05.2020 vs 23.03.–03.05.2019 (n=3,549 total number of all presentations in emergency admission) |
e | Psychiatric emergencies | Number of cases with corresponding coding according to Manchester-Triage-System or ICD-10 | Unchanged absolute number of psychiatric emergencies as well as distribution among ICD main diagnosis groups, but increase in the share of all presentations to 5% compared to 3% in the previous year [60] |
| e | Psychiatric consultation requirements, connection with the COVID-19-pandemic | Proportion of cases with psychiatric consultation requests with content related to the COVID-19-pandemic and with suicide attempts | A substantive link to the COVID-19-pandemic was found in 21%; among these, an increased proportion of suicide attempts (22%) was observed compared to those without a COVID-19 link (6%) [60] | |
|
Data basis: Emergency admission and inpatient care in HELIOS-Clinics
Persons admitted as psychiatric emergencies to one of n=67 hospitals of the HELIOS Group with main diagnosis F00–F69 [59] Fasshauer JM, Bollmann A, Hohenstein S et al. (2021): 13.03.–21.05.2020 vs. 01.01.–12.03.2020; 13.03.–21.05.2019 (n=13,151 total number of all psychiatric emergency admissions) |
e | Psychiatric Emergencies | Number of cases with main diagnosis F00–F69 | Decrease in 13.03.–21.05.2020 compared to the previous months in 2020 (IRR 0.68) and the comparative period in 2019 (IRR 0.70), affected all main diagnosis groups [59] |
| e | Length of stay for psychiatric diagnosis | Number of days of inpatient treatment for cases with main diagnosis F00–F69 | Decrease in length of stay to 9.8 in 13.03.–21.05.2020 compared to 14.7 in the previous months in 2020 and 16.4 in the comparative period in 2019, respectively [59] | |
|
Data basis: AOK inpatient care data
Data of inpatient treatment among insured persons of the AOK, n=27 million [46] Wissenschaftliches Institut der AOK (WIdO) (2020): 16.03.–05.04.2020 compared to 16.03.2019–05.04.2019 [48] Wissenschaftliches Institut der AOK (WIdO) (2021): 01/2020–02/2021 compared to 01–12/2019 |
e | Inpatient treatment cases | Number of inpatient treatment cases for F-diagnoses | Decrease of 49% in 16.03.–05.04.2020 compared to the same period in 2019, thus comparatively strong decrease (rank 6) among the 21 treatment events considered [46] |
| e | Inpatient cases in psychiatric, psychotherapeutic and psychosomatic clinics and departments | Number of treatment cases in specialised hospitals or departments for psychiatry and psychotherapy, child and adolescent psychiatry and psychotherapy and psychosomatic medicine and psychotherapy that bill according to the PEPP system | Decrease compared to 2019 in the entire observation period, most pronounced in April 2020 by 31% as well as in January 2021 by 21%, least pronounced in September 2020 by 5% [48] | |
|
Data basis: LVR clinics inpatient care data
Data of persons who were admitted to one of n=9 psychiatric clinics of the Landschaftsverband Rheinland (LVR) as day-clinic patients or inpatients [50] Zielasek J, Vrinssen J, Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E (2021): 18.03.–31.05.2020 compared to 18.03.–31.05.2019 (n=10,545 treatment cases) |
Day-clinic and inpatient admissions per day | Number of admitted cases to day-clinic and inpatient care (planned admissions and emergencies) per day in clinics for psychiatry, child and adolescent psychiatry, psychosomatic medicine, geriatrics and addiction treatment | Decrease of 25% in the period 18.03.–31.05.2020 compared to the same period in 2019 [50] | |
| Day-clinic patient and inpatient cases by diagnosis | Discharge diagnosis according to main diagnosis groups | Decrease in the period 18.03.–31.05.2020 compared to the same period in 2019 for intelligence disorders (F7) with 51%, neurotic, stress and somato-form disorders (F4) with 35%, affective disorders (F3) with 34% and personality and behavioural disorders (F6) with 31%, organic mental disorders including Alzheimer’s (F0/G3) with 10% and schizophrenia, schizotypal and delusional disorders (F2) with 9% [50] | ||
|
Data basis: Statistics on narcotics-related deaths from the Land Offices of Criminal Investigation
[53] The Federal Government Drug Commissioner (2021): 2020 compared to 2019 |
e | Deaths due to narcotics use | Total number of deaths in all federal states | Increase of 13% to 1,581 in 2020 compared to 1,398 in 2019 [53] |
|
Data basis: Telephone counselling ‘Telefonseelsorge’
Data from persons who made contact with the nation-wide telephone counselling ‘Telefonseelsorge’ in one of n=91 counselling centres [64] Arendt F, Markiewitz A, Mestas M et al. (2020): 01.01.–31.03.2020 compared to 01.01.–31.03.2019 (contact via telephone) [65] Armbruster S, Klotzbücher V (2020): 01.01.2019–28.04.2020 (contact via telephone or online) |
e | Calls to telephone counselling | Number of calls to telephone counselling | Increase to approx. 700 calls more per day at the end of March 2020 compared to the same period in 2019 [64] |
| e | Contacts to telephone counselling | Number of contacts to telephone counselling per day (telephone and online) | Increase of approx. 20% around 22.03.2020, after approx. three weeks of decline, in April still increased compared to previous year’s level; stronger increase in federal states with stricter infection control measures [65] | |
| e | Reasons for contacting telephone counselling | Central counselling topics for each contact to telephone counselling | Increase in counselling topics ‘mental and physical health’, ‘relationship/social issues’ and ‘violence’ [65] | |
|
Data basis: Cause of death statistics of the city of Leipzig
[63] Radeloff D, Papsdorf R, Uhlig K et al. (2020): 16.03.–24.05.2020 compared to 16.03.–24.05.2019 and previous years 2010–2019; 3 phases depending on the limitation of social contacts and mobility: No restriction (01.01.–16.03.2020), moderate restriction (17.–21.03., 06.06.–30.09.2020), severe restriction (22.03.–05.06.2020) compared to previous years as of 2010 |
e | Suicide rate | Number of suicides per 100,000 life years | Decrease in suicide rate from 16.8 (time without restrictions) to 7.2 (time of severe restraints) due to unexpectedly high suicide rates in 2019 and early 2020; unchanged values in comparison none vs. mild and mild vs. severe restraints; no differences between expected and observed trends based on previous year trends [63] |
|
Data basis: Cause of death statistics of the Federal Statistical Office
[69] Federal Statistical Office (2021): 2020 vs. 2019 |
e | Suicide | Total number of suicides (cause of death X60–X84) | Decrease in suicides to n=8,565 in 2020 compared to n=9,041 in 2019 [69] |
Annex Table 3: Publication - Included References
- 1.Entringer T, Krieger M. (2020) Alleinlebende verkraften die Pandemie erstaunlich gut. Spotlights of the SOEP-CoV Study. DIW, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 2.Entringer T, Kröger H. (2020) Einsam, aber resilient – Die Menschenhabenden Lockdown besser verkraftet als vermutet. DIW aktuell, Vol 6. Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 3.Entringer T, Kröger H, Schupp J, et al. (2020) Psychische Krise durch COVID-19? Sorgen sinken, Einsamkeit steigt, Lebenszufriedenheit bleibt stabil. SOEPpapers on Multidisciplinary Panel Data Research 1087. DIW, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kritikos AS, Graeber D, Seebauer J. (2020) Corona-Pandemie wird zur Krise für Selbständige. DIW aktuell, Vol 47. Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 5.Liebig S, Buchinger L, Entringer T, et al. (2020) Ost- und Westdeutschland in der Corona-Krise: Nachwendegeneration im Osten erweist sich als resilient. DIW Wochenbericht 38. Berlin, P. 721–729 [Google Scholar]
- 6.Seebauer J, Kritikos AS, Graeber D. (2021) Warum vor allem weibliche Selbstständige Verliererinnen der COVID-19-Krise sind. DIW Wochenbericht 15. Berlin, P. 261–269 [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mata J, Wenz A, Rettig T, et al. (2020) Health behaviors and mental health before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: A longitudinal population-based survey. PsyArXiv [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Blom AG, Wenz A, Rettig T, et al. (2020) Die Mannheimer Corona-Studie: Das Leben in Deutschland im Ausnahmezustand. Bericht zur Lage vom 20. März bis 09. Juli 2020. https://www.uni-mannheim.de/gip/corona-studie (As at 30.07.2021)
- 9.Naumann E, Mata J, Reifenscheid M, et al. (2020) Die Mannheimer Corona-Studie: Schwerpunktbericht zum Angstempfinden in der Bevölkerung. Untersuchungszeitraum 20. März bis 16. April 2020. https://www.uni-mannheim.de/media/Einrichtungen/gip/Corona_Studie/Schwerpunktbericht_Angstempfinden_Mannheimer_Corona_Studie.pdf (As at 30.07.2021)
- 10.Kuehner C, Schultz K, Gass P, et al. (2020) Mental Health Status in the Community During the COVID-19-Pandemic. Psychiat Prax 47:361-369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Damerow S, Rommel A, Prütz F, et al. (2020) Developments in the health situation in Germany during the initial stage of the COVID-19 pandemic for selected indicators of GEDA 2019/2020-EHIS. Journal of Health Monitoring 5(4):3–20. https://edoc.rki.de/handle/176904/7550.2 (As at 17.10.2021) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sachser C, Olaru G, Pfeiffer E, et al. (2021) The immediate impact of lockdown measures on mental health and couples’ relationships during the COVID-19 pandemic – results of a representative population survey in Germany. Soc Sci Med 278:113954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Entringer T, Kröger H. (2021) Psychische Gesundheit im zweiten COVID-19 Lockdown in Deutschland. SOEPpapers on Multidisciplinary Panel Data Research 1136. DIW, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 14.Entringer T, Kröger H. (2021) Weiterhin einsam und weniger zufrieden – Die COVID-19-Pandemie wirkt sich im zweiten Lockdown stärker auf das Wohlbefinden aus. DIW aktuell, Vol 67. Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cohrdes C, Yenikent S, Wu J, et al. (2021) Indications of Depressive Symptoms During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Germany: Comparison of National Survey and Twitter Data. JMIR Ment Health 8(6):e27140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Beutel ME, Hettich N, Ernst M, et al. (2021) Mental health and loneliness in the German general population during the COVID-19 pandemic compared to a representative pre-pandemic assessment. Sci Rep 11(1):14946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stiftung Deutsche Depressionshilfe (2021) Deutschland-Barometer Depression 2021: COVID-19 und die Folgen für die psychische Gesundheit. https://www.deutsche-depressionshilfe.de/pressematerial-barometer-depression (As at 21.06.2021)
- 18.Stiftung Deutsche Depressionshilfe (2020) Deutschland-Barometer Depression 2020: COVID-19 und die Folgen für die psychische Gesundheit. https://www.deutsche-depressionshilfe.de/presse-und-pr/downloads (As at 21.06.2021)
- 19.Gilan D, Röthke N, Blessin M, et al. (2020) Psychomorbidity, Resilience, and Exacerbating and Protective Factors During the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic. Dtsch Arztebl Int 117(38):625–630 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.COSMO – COVID-19 Snapshot Monitoring (2021) Ressourcen und Belastungen. https://projekte.uni-erfurt.de/cosmo2020/web/topic/vertrauen-zufriedenheit-ressourcen/20-belastungen/ (As at 30.07.2021)
- 21.COSMO – COVID-19 Snapshot Monitoring (2021) Resilienz. https://projekte.uni-erfurt.de/cosmo2020/web/topic/vertrauen-zufriedenheit-ressourcen/10-resilienz/ (As at 30.07.2021)
- 22.Röhr S, Reininghaus U, Riedel-Heller SG. (2020) Mental wellbeing in the German old age population largely unaltered during COVID-19 lockdown: results of a representative survey. BMC Geriatrics 20(1):489–489 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Calvano C, Engelke L, Di Bella J, et al. (2021) Families in the COVID-19 pandemic: parental stress, parent mental health and the occurrence of adverse childhood experiences-results of a representative survey in Germany. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry (Epub) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Huebener M, Waights S, Spiess K, et al. (2020) Parental Well-Being in Times of COVID-19 in Germany. Goebel J, Liebig S, Richter D, et al. SOEPpapers on Multidisciplinary Panel Data Research 1099. DIW, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 25.Calvano C, Engelke L, Di Bella J, et al. (2021) Correction to: Families in the COVID-19 pandemic: parental stress, parent mental health and the occurrence of adverse childhood experiences-results of a representative survey in Germany. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry (Epub) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Peters A, Rospleszcz S, Greiser KH, et al. (2020) The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Self-Reported Health. Dtsch Arztebl Int 117(50):861–867 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Berger K, Riedel-Heller S, Pabst A, et al. (2021) Einsamkeit während der ersten Welle der SARS-CoV-2 Pandemie – Ergebnisse der NAKO-Gesundheitsstudie. PsyArXiv [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bendau A, Plag J, Kunas S, et al. (2020) Longitudinal changes in anxiety and psychological distress, and associated risk and protective factors during the first three months of the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany. Brain Behav e01964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ahrens KF, Neumann RJ, Kollmann B, et al. (2021) Differential impact of COVID-related lockdown on mental health in Germany. World Psychiatry 20(1):140–141 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zacher H, Rudolph CW. (2021) Individual differences and changes in subjective wellbeing during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. Am Psychol 76(1):50–62 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schäfer SK, Sopp MR, Schanz CG, et al. (2020) Impact of COVID-19 on Public Mental Health and the Buffering Effect of a Sense of Coherence. Psychother Psychosom 89:386-392 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ahrens KF, Neumann RJ, Kollmann B, et al. (2021) Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on mental health in Germany: longitudinal observation of different mental health trajectories and protective factors. Transl Psychiatry 11(1):392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Petzold MB, Bendau A, Plag J, et al. (2020) Risk, resilience, psychological distress, and anxiety at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany. Brain Behav 10:e01745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Moradian S, Bäuerle A, Schweda A, et al. (2021) Differences and similarities between the impact of the first and the second COVID-19-lockdown on mental health and safety behaviour in Germany. J Public Health (Oxf) (Epub) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bäuerle A, Steinbach J, Schweda A, et al. (2020) Mental Health Burden of the COVID-19 Outbreak in Germany: Predictors of Mental Health Impairment. J Prim Care Community Health 11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bäuerle A, Teufel M, Musche V, et al. (2020) Increased generalized anxiety, depression and distress during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional study in Germany. J Public Health 42(4):672–678 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hetkamp M, Schweda A, Bäuerle A, et al. (2020) Sleep disturbances, fear, and generalized anxiety during the COVID-19 shut down phase in Germany: relation to infection rates, deaths, and German stock index DAX. Sleep Med 75:350-353 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Skoda E-M, Spura A, De Bock F, et al. (2021) Change in psychological burden during the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany: fears, individual behavior, and the relevance of information and trust in governmental institutions. Bundesgesundheitsblatt – Gesundheitsforschung – Gesundheitsschutz 64(3):322–333 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bauer LL, Seiffer B, Deinhart C, et al. (2020) Associations of exercise and social support with mental health during quarantine and social-distancing measures during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional survey in Germany. medRxiv [Google Scholar]
- 40.Liu S, Heinzel S, Haucke MN, et al. (2021) Increased Psychological Distress, Loneliness, and Unemployment in the Spread of COVID-19 over 6 Months in Germany. Medicina 57(1):53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jung S, Kneer J, Krüger THC. (2020) Mental Health, Sense of Coherence, and Interpersonal Violence during the COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown in Germany. J Clin Med 9(11):3708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Munk AJL, Schmidt NM, Alexander N, et al. (2020) COVID-19-Beyond virology: Potentials for maintaining mental health during lockdown. PLoS ONE 15(8):e0236688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Schwinger M, Trautner M, Kärchner H, et al. (2020) Psychological Impact of Corona Lockdown in Germany: Changes in Need Satisfaction, Well-Being, Anxiety, and Depression. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(23):9083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Büssing A, Rodrigues Recchia D, Dienberg T, et al. (2021) Dynamics of Perceived Positive Changes and Indicators of Well-Being Within Different Phases of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front Psychiatry 12:685975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Schelhorn I, Ecker A, Bereznai J, et al. (2020) Depression symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic in different regions in Germany. PsyArXiv [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wissenschaftliches Institut der AOK (WIdO) (2020) Starker Rückgang der Krankenhaus-Fallzahlen durch Coronavirus-Lockdown bei planbaren Eingriffen, aber auch bei Notfällen. Pressemitteilung. https://www.wido.de/fileadmin/Dateien/Dokumente/News/2020_06_29_PM_WIdO-Report_Krankenhaus-Fallzahlen_im_Coronavirus-Lockdown.pdf (As at 22.02.2021)
- 47.Wissenschaftliches Institut der AOK (WIdO) (2020) Fehlzeiten in der Pandemie: Weniger Krankmeldungen, aber längere Krankheitsdauer wegen psychischer Erkrankungen. Pressemitteilung. https://www.wido.de/fileadmin/Dateien/Dokumente/News/Pressemitteilungen/2020/wido_pra_pm_fehlzeiten_im_pandemiejahr_1020.pdf (As at 22.02.2021)
- 48.Wissenschaftliches Institut der AOK (WIdO) (2021) WIdO-Analyse zu Krankenhausbehandlungen in der zweiten Pandemiewelle: Erneute Fallzahlrückgänge bei planbaren Eingriffen und Notfällen. Pressemitteilung. https://www.wido.de/fileadmin/Dateien/Dokumente/News/Pressemitteilungen/2021/wido_kra_pm_fallzahlrueckgaenge_wegen_covid-19_erg_0321.pdf (As at 21.04.2021)
- 49.BARMER (2020) Barmer-Analyse – Corona beeinflusst massiv den Krankenstand. https://www.barmer.de/presse/presseinformationen/pressemitteilungen/gesundheitsreport-273324 (As at 22.02.2021)
- 50.Zielasek J, Vrinssen J, Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E. (2021) Utilization of Inpatient Mental Health Care in the Rhineland During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front Public Health 9:593307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.BBK (2021) Monatlicher Krankenstand. https://www.bkk-dachverband.de/statistik/monatlicher-krankenstand (As at 10.06.2021)
- 52.DAK Gesundheit (2021) Psychreport 2021. Entwicklung der psychischen Erkrankungen im Job: 2010 – 2020. IGES, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 53.Die Drogenbeauftragte der Bundesregierung (2021) Zahl der an illegalen Drogen verstorbenen Menschen während der Coronapandemie um 13 Prozent gestiegen Drogenbeauftragte Ludwig: „Suchthilfe und Gesundheitsversorgung von schwerstabhängigen Menschen muss auch in der Krise weitergehen!“ https://www.drogenbeauftragte.de/presse/detail/zahl-der-an-illegalen-drogen-verstorbenen-menschen-waehrend-der-coronapandemie-um-13-prozent-gestiegen/ (As at 21.04.2021)
- 54.Jacob L, Smith L, Koyanagi A, et al. (2020) Impact of the coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on anxiety diagnosis in general practices in Germany. J Psychiatr Res (Epub) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Michalowsky B, Hoffmann W, Bohlken J, et al. (2020) Effect of the COVID-19 lockdown on disease recognition and utilisation of healthcare services in the older population in Germany: a cross-sectional study. Age Ageing 50(2):317–325 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.KKH Kaufmännische Krankenkasse (2020) Krankenstand explodiert – vor allem bei Frauen. https://www.kkh.de/presse/pressemeldungen/krankenstand-corona (As at 22.02.2021)
- 57.KKH Kaufmännische Krankenkasse (2021) Psyche: Berufstätige länger krank. https://www.kkh.de/presse/pressemeldungen/psyche (As at 22.02.2021)
- 58.KKH Kaufmännische Krankenkasse (2021) Kinder, Karriere, Corona-Koller: Frauen leiden seelisch mehr. https://www.kkh.de/presse/pressemeldungen/psycheo (As at 22.02.2021)
- 59.Fasshauer JM, Bollmann A, Hohenstein S, et al. (2021) Emergency hospital admissions for psychiatric disorders in a German-wide hospital network during the COVID-19 outbreak. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 56:1469–1475 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Aly L, Sondergeld R, Holzle P, et al. (2020) The COVID-19 pandemic has not changed the number but the type of psychiatric emergencies: A comparison of care data between 2019 and 2020. Nervenarzt 91(11):1047–1049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Hoyer C, Ebert A, Szabo K, et al. (2020) Decreased utilization of mental health emergency service during the COVID-19 pandemic. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci (Epub) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Seifert J, Meissner C, Birkenstock A, et al. (2021) Peripandemic psychiatric emergencies: impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on patients according to diagnostic subgroup. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 271(2):259–270 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Radeloff D, Papsdorf R, Uhlig K, et al. (2021) Trends in suicide rates during the COVID-19 pandemic restrictions in a major German city. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci 30:E16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Arendt F, Markiewitz A, Mestas M, et al. (2020) COVID-19 pandemic, government responses, and public mental health: Investigating consequences through crisis hotline calls in two countries. Soc Sci Med 265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Armbruster S, Klotzbücher V. (2020) Lost in lockdown? COVID-19, social distancing, and mental health in Germany. Discussion Paper Series. University of Freiburg [Google Scholar]
- 66.TK (2021) Trotz Corona: Krankenstand 2020 deutlich gesunken – psychische Erkrankungen nehmen weiter zu. Pressemitteilung. https://www.tk.de/presse/themen/praevention/gesundheitsstudien/trotz-corona-krankenstand-sinkt-anstieg-psychischer-diagnosen-2099838 (As at 22.02.2021)
- 67.TK (2021) Gesundheitsreport Arbeitsunfähigkeit 2021. Techniker Krankenkasse, Hamburg [Google Scholar]
- 68.Mangiapane S, Zhu L, Kretschmann J, et al. (2021) Veränderung der vertragsärztlichen Leistungsinanspruchnahme während der COVID-Krise. Tabellarischer Trendreport für das Jahr 2020. https://www.zi.de/fileadmin/images/content/Publikationen/Trendreport_4_Leistungsinanspruchnahme_COVID_2021-04-19.pdf (As at 21.04.2021)
- 69.Statistisches Bundesamt (2021) Erste vorläufige Ergebnisse der Todesursachenstatistik für 2020 mit Daten zu COVID-19 und Suiziden. Pressemitteilung Nr. 327 vom 8. Juli 2021. https://www.destatis.de/DE/Presse/Pressemitteilungen/2021/07/PD21_327_23211.html (As at 30.07.2021)
Annex Table 4.
Indicators
Category I: Primary data
| OUTCOME TYPE A: INDICATORS OF POSITIVE MENTAL HEALTH | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study type | Indicator | Inventory | Data source/Study | Publication |
| Construct: Satisfaction of life | ||||
| A | Satisfaction of life | Short scale L-1 (Scale 0–10) | SOEP | [1–7] |
| B | Satisfaction of life | Single item (Scale 1–7) | COSMO | [8] |
| C | Satisfaction of life | Short scale L-1 (Scale 0–10) | Corona COMPASS | [9] |
| E | Satisfaction of life | Single item (1 to 7) | Longitudinal study of people in full-time employment | [10] |
| F | Satisfaction of life | Four items of the Temporal Satisfaction with Life Scale | Online survey of the universities Marburg and Giessen | [11] |
| F | Satisfaction of life | Brief Multidimensional Life Satisfaction Scale | Online survey of the universities Witten/Herdecke, … | [12] |
| Construct: Wellbeing | ||||
| A | Wellbeing | Four single items (Scale 1–5): Positive and negative affect | SOEP | [1, 2, 4–7] |
| A | Wellbeing | WHO-5-Well-Being-Index | Study of the Central Institute of Mental Health Mannheim | [13] |
| E | Wellbeing | Items of the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (Short Form) | Longitudinal study of people in full-time employment | [10] |
| F | Wellbeing | WHO-5 | Online survey of the Medizinische Hochschule Hannover | [14] |
| F | Wellbeing | WHO-5-Well-Being-Index | Online survey of the universities Witten/Herdecke, … | [12] |
| Construct: Resilience | ||||
| B | Resilience | Brief-Resilience-Scale (BRS) | COSMO | [15, 16] |
| 3 Constructs | 8 Data sources/Studies | [1–16] | ||
| OUTCOME TYPE B: INDICATORS OF MENTAL BURDEN | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study type | Indicator | Inventory | Study | Publication |
| Construct: Feelings of anxiety, dejection | ||||
| A | Anxiety | State-Trait Anxiety Inventory short scale until week 4: Five items (M; cut-off >2) from week 5: Two items | The Mannheim Corona Study | [17–19] |
| B | Mental distress (anxiety, dejection) | Five single items from GAD-7, ADS, IES-R (M) | COSMO | [8, 15] |
| F | Anxiety, depression | State-Trait-Anxiety-Depression-Inventory (STADI) | Online survey of the universities Marburg and Giessen | [11] |
| Construct: COVID-19-related anxiety and distress | ||||
| E | COVID-19 specific anxiety | C-19-A | CORA Longitudinal study | [20] |
| F | COVID-19 related anxiety | Single item (Scale 1–7) | Online survey of the LVR-Clinic Essen | [21, 22] |
| F | COVID-19 related stress | COVID-19 Peritraumatic Distress Index (CPDI) | Online survey by Charité | [23] |
| Construct: Situational burden and psychosocial stress | ||||
| A | Psychosocial distress | PHQ-D Stress Module (Total) | Study of the Central Institute of Mental Health Mannheim | [13] |
| B | Situational stress | Single item | COSMO | [8] |
| B | Mental distress | Single item | German Depression Barometer | [24, 25] |
| C | Stress experience | Parental Stress Scale (Total) | Parent study of the Berlin University Alliance | [26, 27] Erratum |
| D | Psychosocial distress | PHQ-D stress module (Total); mean difference at t1 | NAKO | [28] |
| E | Everyday burdens per week | Amount | LORA | [29, 30] |
| F | Psychosocial distress | PHQ-D Stress Module | Online survey of the Medizinische Hochschule Hannover | [14] |
| F | Mental distress | Distress Thermometer (Cut-Off >3) | Online survey of the LVR-Clinic Essen | [22, 31–33] |
| 3 Constructs | 13 Data sources/Studies | |||
| OUTCOME TYPE C: INDICATORS OF ACUTE SYMPTOMS OF MENTAL DISORDER | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study type | Indicator | Inventory | Study | Publication |
| General psychopathological symptoms | ||||
| A | Psychopathological symptoms | Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI-18) | Study of Ulm University | [34] |
| A | Symptoms and syndrome diagnosis: depressive disorder, anxiety disorder, somatic disorder; psychosocial distress comorbidity syndrome diagnosis | Screening-based syndrome diagnoses from PHQ-D total values of the respective symptomatology | Study of the Central Institute of Mental Health Mannheim | [13] |
| C | Psychopathological symptoms | Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI-18) | Study of the elderly population aged 65 and over by the University Leipzig | [35] |
| E | Mental symptoms | GHQ-28 median value | LORA | [29, 30] |
| E | Psychopathological symptoms | Mini-Symptom Checklist | Longitudinal study of Saarland University | [36] |
| F | Symptoms ‘Any mental disorder’ | Beck-Depression-Inventory, GAD-7, PHQ-Panic Module, Obsessive-Compulsive Inventory-Revised | Initial sample of a longitudinal study of the Justus Liebig University Giessen | [37] |
| Depressive and anxiety symptoms | ||||
| A | Depressive and anxiety symptoms | PHQ-4 (M) | SOEP | [1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 38] |
| A | Depressive and anxiety symptoms | PHQ-4 (M) | Study of the universities Mainz and Leipzig | [39] |
| C | Depressive and anxiety symptoms | PHQ-4 (M) | Parent study of the Berlin University Alliance | [26, 27] Erratum |
| E | Depressive and anxiety symptoms | PHQ-4 (Cut-Off >5); M | CORA Longitudinal study | [20] |
| F | Depressive and anxiety symptoms | PHQ-4; (M) | Online survey of the Medizinische Hochschule Hannover | [14] |
| F | Depressive and anxiety symptoms | PHQ-4; (M) | CORA initial sample in the cross-section | [40] |
| Depressive symptoms | ||||
| A | Depressive symptoms | PHQ-8 (>9) | GEDA-EHIS | [41, 42] |
| A | Depressive symptoms | Individual symptoms PHQ-8 over time | GEDA-EHIS | [41, 42] |
| A | Depressive symptoms | from week 5 PHQ-2 | The Mannheim Corona Study | [18] |
| D | Depressive symptoms | PHQ-9 (Cut-Off: >9 total; median difference) | NAKO | [28, 43] |
| E | Depressive symptoms | PHQ-2 (Cut-Off >2) | CORA Longitudinal study | [20] |
| F | Depressive symptoms | PHQ-2 (Cut-Off >2) | Online survey of the LVR-Clinic Essen | [22, 31–33] |
| F | Depressive symptoms | PHQ-9 (>9, at least moderate Symptomatology) | Initial sample of a longitudinal study of the University Tübingen | [44] |
| F | Depressive symptoms | Beck-Depression-Inventory | Initial sample of a longitudinal study of the Justus Liebig University Giessen | [37] |
| F | Depressive symptoms | ICD-10-Symptom-Rating (ISR) | Online survey of the universities Göttingen and Regensburg | [45] |
| Symptoms of anxiety disorder | ||||
| D | Symptoms of generalised anxiety disorder | GAD-7 (Cut-Off: >9, total; median difference to t1) | NAKO | [28, 43] |
| E | Symptoms of generalised anxiety disorder | GAD-2 (Cut-Off >2) | CORA Longitudinal study | [20] |
| F | Symptoms of generalised anxiety disorder | GAD-7 (Cut-Off >9, at least moderate Symptomatology) | Online survey of the LVR-Clinic Essen | [21, 22, 32, 33] |
| F | Symptoms of generalised anxiety disorder | GAD-2 (Cut-Off >2) | Online survey of the LVR-Clinic Essen | [31] |
| F | Symptoms of panic disorder | PHQ Panic Module Long Version | Initial sample of a longitudinal study of the University Tübingen | [44] |
| F | Symptoms of generalised anxiety disorder | GAD-7 (>9, at least moderate symptoms) | Initial sample of a longitudinal study of the University Tübingen | [44] |
| F | Symptoms of generalised anxiety disorder | GAD-7 | Initial sample of a longitudinal study of the Justus Liebig University Giessen | [37] |
| F | Symptoms of panic disorder | PHQ-Panic module | Initial sample of a longitudinal study of the Justus Liebig University Giessen | [37] |
| Symptoms of obsessive compulsive disorder | ||||
| F | Symptoms of obsessive compulsive disorder | Obsessive-Compulsive Inventory-Revised | Initial sample of a longitudinal study of the Justus Liebig University Giessen | [37] |
| 5 Constructs | 18 Data sources/Studies | |||
Category II: Routine data
| INDICATORS OF CARE PATTERNS AND MORTALITY OF MENTAL DISORDERS | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Indicator | Operationalisation | Data body or holder | Publication |
| Area of care: Crisis service | |||
| Calls to telephone counselling | Number of calls to telephone counselling | Telephone counselling (nationwide) | [46] |
| Contacts to telephone counselling | Number of contacts to telephone counselling per day (telephone and online) | Telephone counselling (nationwide) | [47] |
| Reasons for contacting telephone counselling | Central counselling topics for each contact to telephone counselling | Telephone counselling (nationwide) | [47] |
| Area of care: Outpatient care | |||
| Utilisation of outpatient care by medical and psychological psychotherapists and specialists in psychosomatic medicine and psychotherapy | Number of treatment cases | Contractual physician billing data from the Central Research Institute of Ambulatory Health Care in Germany | [48] |
| Utilisation of outpatient psychotherapy | Number of treatment cases for psychotherapeutic services for individual therapy (section 35.2.1 EBM) and group therapy (section 35.2.2. EBM) | Contractual physician billing data from the Central Research Institute of Ambulatory Health Care in Germany | [48] |
| Utilisation of outpatient substitution treatment | Number of treatment cases for substitution treatment for drug dependence (section 1.8 EBM) | Contractual physician billing data from the Central Research Institute of Ambulatory Health Care in Germany | [48] |
| Outpatient diagnostic incidence and prevalence of anxiety disorders in GP practices | Number of persons with (first) diagnosis of F41.0–3 or F41.8–9 | Physician billing data from the practice panel of the Disease Analyser Database (IQVIA) | [49] |
| Outpatient diagnostic incidence of anxiety disorders in GP practices by age | Number of persons with first diagnosis of F41.0–3 or F41.8–9 by age | Physician billing data from the practice panel of the Disease Analyser Database (IQVIA) | [49] |
| Comorbidity of outpatient incident diagnoses in general practitioners of anxiety disorders | Number of persons with first diagnosis of F41.0–3 or F41.8–9 and diagnosis of 9 somatic disorders | Physician billing data from the practice panel of the Disease Analyser Database (IQVIA) | [49] |
| Utilisation of outpatient care by psychiatric/neurological practices among persons aged ≥65 years | Number of physician contacts in psychiatric/neurological practices | Physician billing data from the practice panel of the Disease Analyser Database (IQVIA) | [50] |
| Referral or admission to outpatient or inpatient care by psychiatric/neurological practices among persons aged ≥65 years | Number of referrals or admissions in outpatient or inpatient care by psychiatric/neurological practices | Physician billing data from the practice panel of the Disease Analyser Database (IQVIA) | [50] |
| Outpatient diagnosis of depression for persons aged ≥65 years | Number of persons with first diagnosis F32–33 | Physician billing data from the practice panel of the Disease Analyser Database (IQVIA) | [50] |
| Area of care: Incapacity to work | |||
| Incapacity to work cases | Number of cases with incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis | Data about incapacity to work from KKH | [51] |
| Duration of incapacity to work by gender | Number of days per case of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis | Data about incapacity to work from KKH | [52] |
| Duration of incapacity to work | Number of days per case of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis | Data about incapacity to work from KKH | [53] |
| Number of work days lost due to sickness | Proportion of days per case of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis | Data about incapacity to work from BARMER | [54] |
| Number of work days lost due to sickness | Proportion of days per case of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis | Data about incapacity to work from BKK | [55] |
| Incapacity to work cases | Number of cases of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis 100 per insured persons | Data about incapacity to work from DAK | [56] |
| Duration of incapacity to work | Number of days per case of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis | Data about incapacity to work from DAK | [56] |
| Work incapacity cases according to diagnosis | Number of days of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis per 100 insured persons according to individual diagnoses | Data about incapacity to work from DAK | [56] |
| Incapacity to work cases | Number of cases of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis per 100 insured persons | Data about incapacity to work from AOK | [57] |
| Duration of incapacity to work | Number of days per case of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis | Data about incapacity to work from AOK | [57] |
| Days of incapacity to work | Number of days of incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis per 100 years of insured persons | Data about incapacity to work from TK | [58] |
| Change in sick leave from 2019 to 2020 compared to 2018 to 2019 | Change in number of days with incapacity to work due to F-diagnosis | Data about incapacity to work from TK | [59] |
| Area of care: Stationary care | |||
| Psychiatric emergencies according to clinical characteristics | Number of cases with F-diagnosis, after repeated presentations within one month and suicide attempts before presentation | Routine data from the emergency department of the psychiatric clinic of the Medizinische Hochschule Hannover | [60] |
| Psychiatric emergencies according to diagnoses | Number of diagnoses of mental disorders in the main diagnostic groups F1–F4 and F6, as well as ‘other’ (F0, F5, and F7–9) | Routine data from the emergency department of the psychiatric clinic of the Medizinische Hochschule Hannover | [60] |
| Aspects of the psychopathological findings | Documentation of 65 selected symptoms of psychopathological findings according to AMDP system | Routine data from the emergency department of the psychiatric clinic of the Medizinische Hochschule Hannover | [60] |
| Linking the psychiatric emergency to the COVID-19 pandemic | Explicit documentation of the association of the case with the COVID-19 pandemic by the treating psychiatrist | Routine data from the emergency department of the psychiatric clinic of the Medizinische Hochschule Hannover | [60] |
| Presentations in psychiatric emergency admission | Number of presentations in psychiatric emergency admission | Routine data of emergency admission of the Central Institute of Mental Health Mannheim | [61] |
| Presentations in psychiatric emergency admission after diagnosis | Number of presentations in psychiatric emergency admission by main diagnosis group | Routine data of emergency admission of the Central Institute of Mental Health Mannheim | [61] |
| Psychiatric emergencies | Number of cases with corresponding coding according to Manchester Triage System or ICD-10 | Routine data of emergency admission and inpatient care of the Klinikum rechts der Isar, Technische Universität München | [62] |
| Psychiatric consultation requirements, connection with the COVID-19 pandemic | Proportion of cases with psychiatric consultation requests with content related to the COVID-19 pandemic and with suicide attempts | Routine data of emergency admission and inpatient care of the Klinikum rechts der Isar, Technische Universität München | [62] |
| Psychiatric emergencies | Number of cases with main diagnosis F00–F69 | Routine data of emergency admission and inpatient care in HELIOS-Clinic | [63] |
| Length of stay for psychiatric diagnosis | Number of days of inpatient treatment for cases with main diagnosis F00–F69 | Routine data of emergency admission and inpatient care in HELIOS-Clinic | [63] |
| Inpatient treatment cases | Number of inpatient treatment cases for F-diagnoses | Data about incapacity to work from AOK | [64] |
| Inpatient cases in psychiatric, psychotherapeutic and psychosomatic clinics and departments | Number of treatment cases in specialised hospitals or departments for psychiatry and psychotherapy, child and adolescent psychiatry and psychotherapy, and psychosomatic medicine and psychotherapy that bill according to the PEPP system | Data about incapacity to work from AOK | [65] |
| Day-clinic and inpatient admissions per day | Number of admitted cases to day-clinic and inpatient care (planned admissions and emergencies) per day in clinics for psychiatry, child and adolescent psychiatry, psychosomatic medicine, geriatrics and addiction treatment | LVR clinics inpatient care data | [66] |
| Day-clinic and inpatient cases by diagnosis | Discharge diagnosis according to main diagnosis groups | LVR clinics inpatient care data | [66] |
| Subject area: Mortality | |||
| Deaths due to narcotics use | Total number of deaths in all federal states | Statistics on narcotics-related deaths from the Land Offices of Criminal Investigation | [67] |
| Suicide rate | Number of suicides per 100,000 life years | Cause of death statistics of the city of Leipzig | [68] |
| Suicide | Total number of suicides (cause of death ICD X60-X84) | Cause of death statistics (nationwide) of the Federal Statistical Office | [69] |
| 5 Care or subject areas | 18 Data sources | [46-69] | |
Annex Table 4: Publication - Included References
- 1.Entringer T, Kröger H. (2020) Einsam, aber resilient – Die Menschenhabenden Lockdown besser verkraftet als vermutet. DIW aktuell, Vol 6, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 2.Entringer T, Kröger H. (2021) Weiterhin einsam und weniger zufrieden – Die COVID-19-Pandemie wirkt sich im zweiten Lockdown stärker auf das Wohlbefinden aus. DIW aktuell, Vol 67, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kritikos AS, Graeber D, Seebauer J. (2020) Corona-Pandemie wird zur Krise für Selbständige. DIW aktuell, Vol 47, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 4.Liebig S, Buchinger L, Entringer T, et al. (2020) Ost- und Westdeutschland in der Corona-Krise: Nachwendegeneration im Osten erweist sich als resilient. DIW Wochenbericht 38. Berlin, P. 721–729 [Google Scholar]
- 5.Entringer T, Krieger M. (2020) Alleinlebende verkraften die Pandemie erstaunlich gut. Spotlights of the SOEP-CoV Study. DIW, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 6.Entringer T, Kröger H, Schupp J, et al. (2020) Psychische Krise durch COVID-19? Sorgen sinken, Einsamkeit steigt, Lebenszufriedenheit bleibt stabil. SOEPpapers on Multidisciplinary Panel Data Research 1087. DIW, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 7.Entringer T, Kröger H. (2021) Psychische Gesundheit im zweiten COVID-19 Lockdown in Deutschland. SOEPpapers on Multidisciplinary Panel Data Research 1136. DIW, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 8.COSMO – COVID-19 Snapshot Monitoring (2021) Ressourcen und Belastungen. https://projekte.uni-erfurt.de/cosmo2020/web/topic/vertrauen-zufriedenheit-ressourcen/20-belastungen/ (As at 30.07.2021)
- 9.Huebener M, Waights S, Spiess K, et al. (2020) Parental Well-Being in Times of COVID-19 in Germany. Goebel J, Liebig S, Richter D, et al., SOEPpapers on Multidisciplinary Panel Data Research 1099. DIW, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zacher H, Rudolph CW. (2021) Individual differences and changes in subjective wellbeing during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. Am Psychol 76(1):50–62 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Schwinger M, Trautner M, Kärchner H, et al. (2020) Psychological Impact of Corona Lockdown in Germany: Changes in Need Satisfaction, Well-Being, Anxiety, and Depression. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(23):9083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Büssing A, Rodrigues Recchia D, Dienberg T, et al. (2021) Dynamics of Perceived Positive Changes and Indicators of Well-Being Within Different Phases of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front Psychiatry 12:685975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kuehner C, Schultz K, Gass P, et al. (2020) Mental Health Status in the Community During the COVID-19-Pandemic. Psychiat Prax 47:361-369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jung S, Kneer J, Krüger THC. (2020) Mental Health, Sense of Coherence, and Interpersonal Violence during the COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown in Germany. J Clin Med 9(11):3708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gilan D, Röthke N, Blessin M, et al. (2020) Psychomorbidity, Resilience, and Exacerbating and Protective Factors During the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic. Dtsch Arztebl Int 117(38):625–630 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.COSMO – COVID-19 Snapshot Monitoring (2021) Resilienz. https://projekte.uni-erfurt.de/cosmo2020/web/topic/vertrauen-zufriedenheit-ressourcen/10-resilienz/ (As at 30.07.2021)
- 17.Blom AG, Wenz A, Rettig T, et al. (2020) Die Mannheimer Corona-Studie: Das Leben in Deutschland im Ausnahmezustand. Bericht zur Lage vom 20. März bis 09. Juli 2020. https://www.uni-mannheim.de/gip/corona-studie (As at 30.07.2021)
- 18.Mata J, Wenz A, Rettig T, et al. (2020) Health behaviors and mental health before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: A longitudinal population-based survey. PsyArXiv [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Naumann E, Mata J, Reifenscheid M, et al. (2020) Die Mannheimer Corona-Studie: Schwerpunktbericht zum Angstempfinden in der Bevölkerung. Untersuchungszeitraum 20. März bis 16. April 2020. https://www.uni-mannheim.de/media/Einrichtungen/gip/Corona_Studie/Schwerpunktbericht_Angstempfinden_Mannheimer_Corona_Studie.pdf (As at 30.07.2021) [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bendau A, Plag J, Kunas S, et al. (2020) Longitudinal changes in anxiety and psychological distress, and associated risk and protective factors during the first three months of the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany. Brain Behav e01964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hetkamp M, Schweda A, Bäuerle A, et al. (2020) Sleep disturbances, fear, and generalized anxiety during the COVID-19 shut down phase in Germany: relation to infection rates, deaths, and German stock index DAX. Sleep Med 75:350-353 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Skoda EM, Spura A, De Bock F, et al. (2021) Change in psychological burden during the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany: fears, individual behavior, and the relevance of information and trust in governmental institutions. Bundesgesundheitsbl 64(3):322–333 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Liu S, Heinzel S, Haucke MN, et al. (2021) Increased Psychological Distress, Loneliness, and Unemployment in the Spread of COVID-19 over 6 Months in Germany. Medicina 57(1):53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Stiftung Deutsche Depressionshilfe (2020) Deutschland-Barometer Depression 2020: COVID-19 und die Folgen für die psychische Gesundheit. https://www.deutsche-depressionshilfe.de/presse-und-pr/downloads (As at 21.06.2021)
- 25.Stiftung Deutsche Depressionshilfe (2021) Deutschland-Barometer Depression 2021: COVID-19 und die Folgen für die psychische Gesundheit. https://www.deutsche-depressionshilfe.de/pressematerial-barometer-depression (As at 21.06.2021)
- 26.Calvano C, Engelke L, Di Bella J, et al. (2021) Families in the COVID-19 pandemic: parental stress, parent mental health and the occurrence of adverse childhood experiences-results of a representative survey in Germany. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry (Epub) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Calvano C, Engelke L, Di Bella J, et al. (2021) Correction to: Families in the COVID-19 pandemic: parental stress, parent mental health and the occurrence of adverse childhood experiences-results of a representative survey in Germany. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry (Epub) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Peters A, Rospleszcz S, Greiser KH, et al. (2020) The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Self-Reported Health. Dtsch Arztebl Int 117(50):861–867 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ahrens KF, Neumann RJ, Kollmann B, et al. (2021) Differential impact of COVID-related lockdown on mental health in Germany. World Psychiatry 20(1):140–141 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ahrens KF, Neumann RJ, Kollmann B, et al. (2021) Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on mental health in Germany: longitudinal observation of different mental health trajectories and protective factors. Transl Psychiatry 11(1):392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bäuerle A, Steinbach J, Schweda A, et al. (2020) Mental Health Burden of the COVID-19 Outbreak in Germany: Predictors of Mental Health Impairment. J Prim Care Community Health 11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bäuerle A, Teufel M, Musche V, et al. (2020) Increased generalized anxiety, depression and distress during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional study in Germany. J Public Health 42(4):672–678 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Moradian S, Bäuerle A, Schweda A, et al. (2021) Differences and similarities between the impact of the first and the second COVID-19-lockdown on mental health and safety behaviour in Germany. J Public Health (Oxf) (Epub) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sachser C, Olaru G, Pfeiffer E, et al. (2021) The immediate impact of lockdown measures on mental health and couples’ relationships during the COVID-19 pandemic – results of a representative population survey in Germany. Soc Sci Med 278:113954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Röhr S, Reininghaus U, Riedel-Heller SG. (2020) Mental wellbeing in the German old age population largely unaltered during COVID-19 lockdown: results of a representative survey. BMC Geriatrics 20(1):489–489 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Schäfer SK, Sopp MR, Schanz CG, et al. (2020) Impact of COVID-19 on Public Mental Health and the Buffering Effect of a Sense of Coherence. Psychother Psychosom 89:386-392 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Munk AJL, Schmidt NM, Alexander N, et al. (2020) COVID-19-Beyond virology: Potentials for maintaining mental health during lockdown. PLoS ONE 15(8):e0236688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Seebauer J, Kritikos AS, Graeber D. (2021) Warum vor allem weibliche Selbstständige Verliererinnen der COVID-19-Krise sind. DIW Wochenbericht 15, Berlin, P. 261–269 [Google Scholar]
- 39.Beutel ME, Hettich N, Ernst M, et al. (2021) Mental health and loneliness in the German general population during the COVID-19 pandemic compared to a representative pre-pandemic assessment. Sci Rep 11(1):14946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Petzold MB, Bendau A, Plag J, et al. (2020) Risk, resilience, psychological distress, and anxiety at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany. Brain Behav 10:e01745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Damerow S, Rommel A, Prütz F, et al. (2020) Developments in the health situation in Germany during the initial stage of the COVID-19 pandemic for selected indicators of GEDA 2019/2020-EHIS. Journal of Health Monitoring 5(4):3–20. https://edoc.rki.de/handle/176904/7550.2 (As at 21.06.2021) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Cohrdes C, Yenikent S, Wu J, et al. (2021) Indications of Depressive Symptoms During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Germany: Comparison of National Survey and Twitter Data. JMIR Ment Health 8(6):e27140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Berger K, Riedel-Heller S, Pabst A, et al. (2021) Einsamkeit während der ersten Welle der SARS-CoV-2 Pandemie – Ergebnisse der NAKO-Gesundheitsstudie. PsyArXiv [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bauer LL, Seiffer B, Deinhart C, et al. (2020) Associations of exercise and social support with mental health during quarantine and social-distancing measures during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional survey in Germany. medRxiv [Google Scholar]
- 45.Schelhorn I, Ecker A, Bereznai J, et al. (2020) Depression symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic in different regions in Germany. PsyArXiv [Google Scholar]
- 46.Arendt F, Markiewitz A, Mestas M, et al. (2020) COVID-19 pandemic, government responses, and public mental health: Investigating consequences through crisis hotline calls in two countries. Soc Sci Med 265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Armbruster S, Klotzbücher V. (2020) Lost in lockdown? COVID-19, social distancing, and mental health in Germany. Discussion Paper Series. University of Freiburg, Freiburg [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mangiapane S, Zhu L, Kretschmann J, et al. (2021) Veränderung der vertragsärztlichen Leistungsinanspruchnahme während der COVID-Krise. Tabellarischer Trendreport für das Jahr 2020. https://www.zi.de/fileadmin/images/content/Publikationen/Trendreport_4_Leistungsinanspruchnahme_COVID_2021-04-19.pdf (As at 21.04.2021)
- 49.Jacob L, Smith L, Koyanagi A, et al. (2020) Impact of the coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on anxiety diagnosis in general practices in Germany. J Psychiatr Res (Epub) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Michalowsky B, Hoffmann W, Bohlken J, et al. (2020) Effect of the COVID-19 lockdown on disease recognition and utilisation of healthcare services in the older population in Germany: a cross-sectional study. Age Ageing 50(2):317–325 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.KKH Kaufmännische Krankenkasse (2020) Krankenstand explodiert – vor allem bei Frauen. https://www.kkh.de/presse/pressemeldungen/krankenstand-corona (As at 22.02.2021)
- 52.KKH Kaufmännische Krankenkasse (2021) Kinder, Karriere, Corona-Koller: Frauen leiden seelisch mehr. https://www.kkh.de/presse/pressemeldungen/psycheo (As at 21.04.2021)
- 53.KKH Kaufmännische Krankenkasse (2021) Psyche: Berufstätige länger krank. https://www.kkh.de/presse/pressemeldungen/psyche (As at 22.02.2021)
- 54.BARMER (2020) Barmer-Analyse – Corona beeinflusst massiv den Krankenstand. https://www.barmer.de/presse/presseinformationen/pressemitteilungen/gesundheitsreport-273324 (As at 22.02.2021)
- 55.BBK (2021) Monatlicher Krankenstand. https://www.bkk-dachverband.de/statistik/monatlicher-krankenstand (As at 10.06.2021)
- 56.DAK Gesundheit (2021) Psychreport 2021. Entwicklung der psychischen Erkrankungen im Job: 2010 – 2020. IGES, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wissenschaftliches Institut der AOK (WIdO) (2020) Fehlzeiten in der Pandemie: Weniger Krankmeldungen, aber längere Krankheitsdauer wegen psychischer Erkrankungen. Pressemitteilung. https://www.wido.de/fileadmin/Dateien/Dokumente/News/Pressemitteilungen/2020/wido_pra_pm_fehlzeiten_im_pandemiejahr_1020.pdf (As at 22.02.2021)
- 58.TK (2021) Gesundheitsreport Arbeitsunfähigkeit 2021. Techniker Krankenkasse, Hamburg [Google Scholar]
- 59.TK (2021) Trotz Corona: Krankenstand 2020 deutlich gesunken – psychische Erkrankungen nehmen weiter zu. Pressemitteilung. https://www.tk.de/presse/themen/praevention/gesundheitsstudien/trotz-corona-krankenstand-sinkt-anstieg-psychischer-diagnosen-2099838 (As at 22.02.2021)
- 60.Seifert J, Meissner C, Birkenstock A, et al. (2021) Peripandemic psychiatric emergencies: impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on patients according to diagnostic subgroup. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 271(2):259–270 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Hoyer C, Ebert A, Szabo K, et al. (2020) Decreased utilization of mental health emergency service during the COVID-19 pandemic. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci (Epub) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Aly L, Sondergeld R, Holzle P, et al. (2020) The COVID-19 pandemic has not changed the number but the type of psychiatric emergencies: A comparison of care data between 2019 and 2020. Nervenarzt 91(11):1047–1049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Fasshauer JM, Bollmann A, Hohenstein S, et al. (2021) Emergency hospital admissions for psychiatric disorders in a German-wide hospital network during the COVID-19 outbreak. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 56:1469–1475 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Wissenschaftliches Institut der AOK (WIdO) (2020) Starker Rückgang der Krankenhaus-Fallzahlen durch Coronavirus-Lock-down bei planbaren Eingriffen, aber auch bei Notfällen. Pressemitteilung. https://www.wido.de/fileadmin/Dateien/Dokumente/News/2020_06_29_PM_WIdO-Report_Krankenhaus-Fallzahlen_im_Coronavirus-Lockdown.pdf (As at 21.04.2021)
- 65.Wissenschaftliches Institut der AOK (WIdO) (2021) WIdO-Analyse zu Krankenhausbehandlungen in der zweiten Pandemiewelle: Erneute Fallzahlrückgänge bei planbaren Eingriffen und Notfällen. Pressemitteilung. https://www.wido.de/fileadmin/Dateien/Dokumente/News/Pressemitteilungen/2021/wido_kra_pm_fallzahlrueckgaenge_wegen_covid-19_erg_0321.pdf (As at 22.02.2021)
- 66.Zielasek J, Vrinssen J, Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E. (2021) Utilization of Inpatient Mental Health Care in the Rhineland During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front Public Health 9:593307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Die Drogenbeauftragte der Bundesregierung (2021) Zahl der an illegalen Drogen verstorbenen Menschen während der Coronapandemie um 13 Prozent gestiegen Drogenbeauftragte Ludwig: „Suchthilfe und Gesundheitsversorgung von schwerstabhängigen Menschen muss auch in der Krise weitergehen!“ https://www.drogenbeauftragte.de/presse/detail/zahl-der-an-illegalen-drogen-verstorbenen-menschen-waehrend-der-coronapandemie-um-13-prozent-gestiegen/ (As at 21.04.2021)
- 68.Radeloff D, Papsdorf R, Uhlig K, et al. (2021) Trends in suicide rates during the COVID-19 pandemic restrictions in a major German city. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci 30:E16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Statistisches Bundesamt (2021) Erste vorläufige Ergebnisse der Todesursachenstatistik für 2020 mit Daten zu COVID-19 und Suiziden. Pressemitteilung Nr. 327 vom 8. Juli 2021. https://www.destatis.de/DE/Presse/Pressemitteilungen/2021/07/PD21_327_23211.html (As at 30.07.2021)
Funding Statement
The review was carried out within the framework of the project ‘Establishment of a national Mental Health Surveillance at the RKI (MHS)’, which is funded by the German Federal Ministry of Health (Chapter 1504 Title 54401, Duration 03/2019–12/2021).
Footnotes
The German version of the article is available at: www.rki.de/journalhealthmonitoring
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank the team at the library of the Robert Koch Institute for setting up and continuously updating the database of COVID-19-related publications that was made available to us for our literature search.
Disclaimer
Note: External contributions do not necessarily reflect the opinions of the Robert Koch Institute
References
- 1.Riedel-Heller S, Richter D. (2021) Psychological consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic in the general public. Public Health Forum 29(1):54–56 [Google Scholar]
- 2.Riedel-Heller SG, Richter D. (2020) COVID-19-Pandemie trifft auf Psyche der Bevölkerung: Gibt es einen Tsunami psychischer Störungen? Psychiat Prax 47(08):452–456 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Brakemeier EL, Wirkner J, Knaevelsrud C, et al. (2020) Die COVID-19-Pandemie als Herausforderung für die psychische Gesundheit: Erkenntnisse und Implikationen für die Forschung und Praxis aus Sicht der Klinischen Psychologie und Psychotherapie. Z Klin Psychol Psychother 49(1):1–31 [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bühring P. (2020) Psychological stress in the COVID-19 pandemic: General uncertainty. Deutsches Arzteblatt international 117(43):A2049–A2050 [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brooks SK, Webster RK, Smith LE, et al. (2020) The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: rapid review of the evidence. The Lancet 395(10227):912–920 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hossain MM, Sultana A, Purohit N. (2020) Mental health outcomes of quarantine and isolation for infection prevention: a systematic umbrella review of the global evidence. Epidemiology and health 42:e2020038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Röhr S, Müller F, Jung F, et al. (2020) Psychosoziale Folgen von Quarantänemaßnahmen bei schwerwiegenden Coronavirus-Ausbrüchen: ein Rapid Review. Psychiat Prax 47:179-189 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dreßing A, Hosp J, Kuehner C, et al. (2021) Neuropsychiatrische Folgen der COVID-19-Pandemie. Fortschritte der Neurologie-Psychiatrie 89(6):296–301 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dragano N, Conte A, Pförtner TK, et al. (2020) Gesundheitliche Folgen von Wirtschaftskrisen: epidemiologische Studien zur Weltfinanzkrise 2007/2008. https://www.public-health-covid19.de/images/2020/Ergebnisse/Hintergrund_Gesundheitliche_Folgen_von_Wirtschaftskrisen_KNPH_01_01072020.pdf (As at 09.09.2021)
- 10.Brenner MH, Bhugra D. (2020) Acceleration of Anxiety, Depression, and Suicide: Secondary Effects of Economic Disruption Related to COVID-19. Frontiers in psychiatry 11:592467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Simon FAJ, Schenk M, Palm D, et al. (2021) The Collateral Damage of the COVID-19 Outbreak on Mental Health and Psychiatry. International journal of environmental research and public health 18(9) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Steinert J, Ebert C. (2020) Gewalt an Frauen und Kindern in Deutschland während COVID-19-bedingten Ausgangsbeschränkungen: Zusammenfassung der Ergebnisse. https://drive.google.com/file/d/19Wqpby9nwMNjdgO4_FCqql-fYyLJmBn7y/view (As at 30.07.2021)
- 13.Kofman YB, Garfin DR. (2020) Home is not always a haven: The domestic violence crisis amid the COVID-19 pandemic. Psychol Trauma 12(S1):S199–S201 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Liu S, Heinzel S, Haucke MN, et al. (2021) Increased Psychological Distress, Loneliness, and Unemployment in the Spread of COVID-19 over 6 Months in Germany. Medicina 57(1):53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Müller F, Röhr S, Reininghaus U, et al. (2021) Social Isolation and Loneliness during COVID-19 Lockdown: Associations with Depressive Symptoms in the German Old-Age Population. International journal of environmental research and public health 18(7):3615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Entringer T, Kröger H. (2020) Einsam, aber resilient –Die Menschenhabenden Lockdown besser verkraftet als vermutet. DIW aktuell, Vol 6., Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 17.Royal College of Psychiatrists (2020) Psychiatrists see alarming rise in patients needing urgent and emergency care and forecast a ‘tsunami’ of mental illness. Press release. https://www.rcpsych.ac.uk/news-and-features/latest-news/detail/2020/05/15/psychiatrists-see-alarming-rise-in-patients-needing-urgent-and-emergency-care (As at 13.06.2021)
- 18.Zielasek J, Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E. (2020) COVID-19-Pandemie: Psychische Störungen werden zunehmen. Dtsch Arztebl 117(21):A-1114–1117 [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bundespsychotherapeutenkammer (2020) Corona-Pandemie und psychische Erkrankungen. BPtK-Hintergrund zur Forschungslage, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 20.Daly M, Sutin AR, Robinson E. (2020) Longitudinal changes in mental health and the COVID-19 pandemic: evidence from the UK Household Longitudinal Study. Psychological medicine:1–10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pierce M, Hope H, Ford T, et al. (2020) Mental health before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal probability sample survey of the UK population. The Lancet Psychiatry 7(10):883–892 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sønderskov KM, Dinesen PT, Santini ZI, et al. (2020) The depressive state of Denmark during the COVID-19 pandemic. Acta neuropsychiatrica 32(4):226–228 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fiorillo A, Sampogna G, Giallonardo V, et al. (2020) Effects of the lockdown on the mental health of the general population during the COVID-19 pandemic in Italy: Results from the COMET collaborative network. European psychiatry: the journal of the Association of European Psychiatrists 63(1):e87–e87 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Twenge JM, Joiner TE. (2020) U.S. Census Bureau-assessed prevalence of anxiety and depressive symptoms in 2019 and during the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic. Depress Anxiety 37(10):954–956 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vindegaard N, Benros ME. (2020) COVID-19 pandemic and mental health consequences: Systematic review of the current evidence. Brain, behavior, and immunity 89:531-542 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Xiong J, Lipsitz O, Nasri F, et al. (2020) Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on mental health in the general population: A systematic review. Journal of affective disorders 277:55-64 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hyland P, Shevlin M, Murphy J, et al. (2021) A longitudinal assessment of depression and anxiety in the Republic of Ireland before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. Psychiatry Res 300:113905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fancourt D, Steptoe A, Bu F. (2021) Trajectories of anxiety and depressive symptoms during enforced isolation due to COVID-19 in England: a longitudinal observational study. The Lancet Psychiatry 8(2):141–149 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sønderskov KM, Dinesen PT, Santini ZI, et al. (2020) Increased psychological well-being after the apex of the COVID-19 pandemic. Acta neuropsychiatrica 32(5):277–279 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Robinson E, Sutin AR, Daly M, et al. (2021) A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal cohort studies comparing mental health before versus during the COVID-19 pandemic. medRxiv [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Richter D, Riedel-Heller S, Zuercher S. (2021) Mental health problems in the general population during and after the first lockdown phase due to the SARS-Cov-2 pandemic: Rapid review of multi-wave studies. Epidemiology and psychiatric sciences 30(e27):1–9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Seidler A, Nußbaumer-Streit B, Apfelbacher C, et al. (2021) Rapid Reviews in Zeiten von COVID-19 – Erfahrungen im Zuge des Kompetenznetzes Public Health zu COVID-19 und Vorschlag eines standardisierten Vorgehens. Gesundheitswesen 83(03):173–179 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tricco AC, Garritty CM, Boulos L, et al. (2020) Rapid review methods more challenging during COVID-19: commentary with a focus on 8 knowledge synthesis steps. J Clin Epidemiol 126:177-183 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rat für Sozial- und WirtschaftsDaten (RatSWD) (2021) Studien zur Corona-Pandemie. https://www.konsortswd.de/ratswd/themen/corona/studien/(As at 08.06.2021)
- 35.Kompetenznetz Public Health COVID-19 (2021) Ergebnisse des Kompetenznetz Public Health zu COVID-19. https://www.public-health-covid19.de/ergebnisse.html (As at 08.06.2021)
- 36.Deutsche Gesellschaft für Psychiatrie und Psychotherapie Psychosomatik und Nervenheilkunde e. V. (DGPPN) (2021) Corona-virus: Herausforderung auf allen Ebenen. https://www.dgppn.de/schwerpunkte/COVID-19.html (As at 08.06.2021)
- 37.Schilling J, Tolksdorf K, Marquis A, et al. (2021) Die verschiedenen Phasen der COVID-19-Pandemie in Deutschland: Eine deskriptive Analyse von Januar 2020 bis Februar 2021. Bundesgesundheitsbl 64(9):1093–1106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tolksdorf K, Buda S, Schilling J. (2021) Aktualisierung zur „Retrospektiven Phaseneinteilung der COVID-19-Pandemie in Deutschland“. Epid Bull 37(2021):3–4 [Google Scholar]
- 39.Geyer S, Jaunzeme J. (2014) Möglichkeiten und Grenzen von Befragungsdaten und Daten gesetzlicher Krankenversicherungen. In: Swart E, Ihle P, Gothe H, et al. (Eds) Routinedaten im Gesundheitswesen Handbuch Sekundärdatenanalyse: Grundlagen, Methoden und Perspektiven. Verlag Hans Huber, Bern, P. 223–233 [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jaunzeme J, Eberhard S, Geyer S. (2013) Wie „repräsentativ“ sind GKV-Daten? Bundesgesundheitsbl 56(3):447–454 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Cornesse C, Bosnjak M. (2018) Is there an association between survey characteristics and representativeness? A meta-analysis. Surv Res Methods 12(1) [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lehdonvirta V, Oksanen A, Räsänen P, et al. (2020) Social Media, Web, and Panel Surveys: Using Non-Probability Samples in Social and Policy Research. Policy Internet 13(1):134–155 [Google Scholar]
- 43.Haziza D, Beaumont JF. (2017) Construction of Weights in Surveys: A Review. Statistical Science 32(2):206–226 [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chauvenet A, Buckley R, Hague L, et al. (2020) Panel sampling in health research. The Lancet Psychiatry 7(10):840–841 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Pierce M, McManus S, Jessop C, et al. (2020) Says who? The significance of sampling in mental health surveys during COVID-19. The Lancet Psychiatry 7(7):567–568 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Schnell R, Hill PB, Esser E. (2018) Methoden der empirischen Sozialforschung. De Gruyter, Oldenbourg [Google Scholar]
- 47.Pforr K, Schröder J. (2015) Warum Panelstudien? GESIS Survey Guidelines. GESIS Leibniz-Institut für Sozialwissenschaften, Mannheim [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tourangeau R, Rips LJ, Rasinski K. (2000) The Psychology of Survey Response. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kristman V, Manno M, Côté P. (2004) Loss to Follow-Up in Cohort Studies: How Much is Too Much? European Journal of Epidemiology 19(8):751–760 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rammstedt B, Beierlein C, Brähler E, et al. (2015) Quality Standards for the Development, Application, and Evaluation of Measurement Instruments in Social Science Survey Research’. https://madoc.bib.uni-mannheim.de/54702/ (As at 09.09.2021)
- 51.Maske UE, Busch MA, Jacobi F, et al. (2015) Current major depressive syndrome measured with the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) and the Composite International Diagnostic Interview (CIDI): results from a cross-sectional population-based study of adults in Germany. BMC Psychiatry 15(1):77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Mack S, Jacobi F, Gerschler A, et al. (2014) Self-reported utilization of mental health services in the adult German population – evidence for unmet needs? Results of the DEGS 1-Mental Health Module (DEGS 1-MH). Int J Methods Psychiatr Res 23(3):289–303 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Maske UE, Hapke U, Riedel-Heller SG, et al. (2017) Respondents’ report of a clinician-diagnosed depression in health surveys: comparison with DSM-IV mental disorders in the general adult population in Germany. BMC Psychiatry 17(1):39–39 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Grobe TG, Kleine-Budde K, Bramesfeld A, et al. (2019) Prävalenzen von Depressionen bei Erwachsenen – eine vergleichende Analyse bundesweiter Survey- und Routinedaten. Gesundheitswesen 81(12):1011–1017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Beutel ME, Hettich N, Ernst M, et al. (2021) Mental health and loneliness in the German general population during the COVID-19 pandemic compared to a representative pre-pandemic assessment. Scientific reports 11(1):14946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kuehner C, Schultz K, Gass P, et al. (2020) Mental Health Status in the Community During the COVID-19-Pandemic. Psychiat Prax 47:361-369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Cohrdes C, Yenikent S, Wu J, et al. (2021) Indications of Depressive Symptoms During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Germany: Comparison of National Survey and Twitter Data. JMIR mental health 8(6):e27140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Damerow S, Rommel A, Prütz F, et al. (2020) Developments in the health situation in Germany during the initial stage of the COVID-19 pandemic for selected indicators of GEDA 2019/2020-EHIS. Journal of Health Monitoring 5(4):3–20. https://edoc.rki.de/handle/176904/7550.2 (As at 17.10.2021) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Mata J, Wenz A, Rettig T, et al. (2020) Health behaviors and mental health before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: A longitudinal population-based survey. PsyArXiv [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Blom AG, Wenz A, Rettig T, et al. (2020) Die Mannheimer Corona-Studie: Das Leben in Deutschland im Ausnahmezustand. Bericht zur Lage vom 20. März bis 09. Juli 2020. https://www.uni-mannheim.de/gip/corona-studie (As at 30.07.2021)
- 61.Naumann E, Mata J, Reifenscheid M, et al. (2020) Die Mannheimer Corona-Studie: Schwerpunktbericht zum Angstempfinden in der Bevölkerung. Untersuchungszeitraum 20. März bis 16. April 2020. https://www.uni-mannheim.de/media/Einrichtungen/gip/Corona_Studie/Schwerpunktbericht_Angstempfinden_Mannheimer_Corona_Studie.pdf (As at 30.07.2021)
- 62.Entringer T, Krieger M. (2020) Alleinlebende verkraften die Pandemie erstaunlich gut. Spotlights of the SOEP-CoV Study. DIW, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 63.Entringer T, Kröger H. (2021) Psychische Gesundheit im zweiten COVID-19 Lockdown in Deutschland. SOEPpapers on Multidisciplinary Panel Data Research 1136. DIW, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 64.Entringer T, Kröger H. (2021) Weiterhin einsam und weniger zufrieden – Die COVID-19-Pandemie wirkt sich im zweiten Lockdown stärker auf das Wohlbefinden aus. DIW aktuell, Vol 67. Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 65.Entringer T, Kröger H, Schupp J, et al. (2020) Psychische Krise durch COVID-19? Sorgen sinken, Einsamkeit steigt, Lebenszufriedenheit bleibt stabil. SOEPpapers on Multidisciplinary Panel Data Research 1087. DIW, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kritikos AS, Graeber D, Seebauer J. (2020) Corona-Pandemie wird zur Krise für Selbständige. DIW aktuell, Vol 47, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 67.Liebig S, Buchinger L, Entringer T, et al. (2020) Ost- und Westdeutschland in der Corona-Krise: Nachwendegeneration im Osten erweist sich als resilient. DIW Wochenbericht 38, Berlin, P. 721–729 [Google Scholar]
- 68.Seebauer J, Kritikos AS, Graeber D. (2021) Warum vor allem weibliche Selbstständige Verliererinnen der COVID-19-Krise sind. DIW Wochenbericht 15, Berlin, P. 261–269 [Google Scholar]
- 69.Sachser C, Olaru G, Pfeiffer E, et al. (2021) The immediate impact of lockdown measures on mental health and couples’ relationships during the COVID-19 pandemic – results of a representative population survey in Germany. Soc Sci Med 278:113954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Stiftung Deutsche Depressionshilfe (2021) Deutschland-Barometer Depression 2021: COVID-19 und die Folgen für die psychische Gesundheit. http://www.deutsche-depressionshilfe.de/pressematerial-barometer-depression (As at 21.06.2021)
- 71.Stiftung Deutsche Depressionshilfe (2020) Deutschland-Barometer Depression 2020: COVID-19 und die Folgen für die psychische Gesundheit. https://www.deutsche-depressionshilfe.de/presse-und-pr/downloads (As at 21.06.2021)
- 72.Gilan D, Röthke N, Blessin M, et al. (2020) Psychomorbidity, Resilience, and Exacerbating and Protective Factors During the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic. Deutsches Arzteblatt international 117(38):625–630 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.COSMO – COVID-19 Snapshot Monitoring (2021) Resilienz. https://projekte.uni-erfurt.de/cosmo2020/web/topic/vertrauen-zufriedenheit-ressourcen/10-resilienz/ (As at 30.07.2021)
- 74.COSMO – COVID-19 Snapshot Monitoring (2021) Ressourcen und Belastungen. https://projekte.uni-erfurt.de/cosmo2020/web/topic/vertrauen-zufriedenheit-ressourcen/20-belastungen/ (As at 30.07.2021)
- 75.Röhr S, Reininghaus U, Riedel-Heller SG. (2020) Mental wellbeing in the German old age population largely unaltered during COVID-19 lockdown: results of a representative survey. BMC geriatrics 20(1):489–489 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Calvano C, Engelke L, Di Bella J, et al. (2021) Families in the COVID-19 pandemic: parental stress, parent mental health and the occurrence of adverse childhood experiences-results of a representative survey in Germany. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry (Epub) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Calvano C, Engelke L, Di Bella J, et al. (2021) Correction to: Families in the COVID-19 pandemic: parental stress, parent mental health and the occurrence of adverse childhood experiences-results of a representative survey in Germany. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry (Epub) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Huebener M, Waights S, Spiess K, et al. (2020) Parental Well-Being in Times of COVID-19 in Germany. Goebel J, Liebig S, Richter D, et al., SOEPpapers on Multidisciplinary Panel Data Research 1099. DIW, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 79.Berger K, Riedel-Heller S, Pabst A, et al. (2021) Einsamkeit während der ersten Welle der SARS-CoV-2 Pandemie – Ergebnisse der NAKO-Gesundheitsstudie. PsyArXiv [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Peters A, Rospleszcz S, Greiser KH, et al. (2020) The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Self-Reported Health. Deutsches Arzteblatt international 117(50):861–867 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Ahrens KF, Neumann RJ, Kollmann B, et al. (2021) Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on mental health in Germany: longitudinal observation of different mental health trajectories and protective factors. Translational psychiatry 11(1):392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Bendau A, Plag J, Kunas S, et al. (2020) Longitudinal changes in anxiety and psychological distress, and associated risk and protective factors during the first three months of the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany. Brain and behavior e01964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Ahrens KF, Neumann RJ, Kollmann B, et al. (2021) Differential impact of COVID-related lockdown on mental health in Germany. World psychiatry: official journal of the World Psychiatric Association (WPA) 20(1):140–141 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Zacher H, Rudolph CW. (2021) Individual differences and changes in subjective wellbeing during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. The American psychologist 76(1):50–62 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Schäfer SK, Sopp MR, Schanz CG, et al. (2020) Impact of COVID-19 on Public Mental Health and the Buffering Effect of a Sense of Coherence. Psychotherapy and psychosomatics 89:386-392 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Büssing A, Rodrigues Recchia D, Dienberg T, et al. (2021) Dynamics of Perceived Positive Changes and Indicators of Well-Being Within Different Phases of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Frontiers in psychiatry 12:685975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Schelhorn I, Ecker A, Bereznai J, et al. (2020) Depression symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic in different regions in Germany. PsyArXiv [Google Scholar]
- 88.Bauer LL, Seiffer B, Deinhart C, et al. (2020) Associations of exercise and social support with mental health during quarantine and social-distancing measures during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional survey in Germany. medRxiv [Google Scholar]
- 89.Petzold MB, Bendau A, Plag J, et al. (2020) Risk, resilience, psychological distress, and anxiety at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany. Brain and behavior 10:e01745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Moradian S, Bäuerle A, Schweda A, et al. (2021) Differences and similarities between the impact of the first and the second COVID-19-lockdown on mental health and safety behaviour in Germany. Journal of public health (Oxford, England) (Epub) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Bäuerle A, Steinbach J, Schweda A, et al. (2020) Mental Health Burden of the COVID-19 Outbreak in Germany: Predictors of Mental Health Impairment. Journal of primary care & community health 11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Bäuerle A, Teufel M, Musche V, et al. (2020) Increased generalized anxiety, depression and distress during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional study in Germany. J Public Health 42(4):672–678 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Hetkamp M, Schweda A, Bäuerle A, et al. (2020) Sleep disturbances, fear, and generalized anxiety during the COVID-19 shut down phase in Germany: relation to infection rates, deaths, and German stock index DAX. Sleep Med 75:350-353 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Skoda EM, Spura A, De Bock F, et al. (2021) Change in psychological burden during the COVID-19 pandemic in Germany: fears, individual behavior, and the relevance of information and trust in governmental institutions. Bundesgesundheitsbl 64(3):322–333 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Jung S, Kneer J, Krüger THC. (2020) Mental Health, Sense of Coherence, and Interpersonal Violence during the COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown in Germany. Journal of clinical medicine 9(11):3708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Munk AJL, Schmidt NM, Alexander N, et al. (2020) COVID-19-Beyond virology: Potentials for maintaining mental health during lockdown. PloS one 15(8):e0236688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Schwinger M, Trautner M, Kärchner H, et al. (2020) Psychological Impact of Corona Lockdown in Germany: Changes in Need Satisfaction, Well-Being, Anxiety, and Depression. International journal of environmental research and public health 17(23):9083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Wissenschaftliches Institut der AOK (WIdO) (2020) Starker Rückgang der Krankenhaus-Fallzahlen durch Coronavirus-Lockdown bei planbaren Eingriffen, aber auch bei Notfällen. Pressemitteilung. https://www.wido.de/fileadmin/Dateien/Dokumente/News/2020_06_29_PM_WIdO-Report_Krankenhaus-Fallzahlen_im_Coronavirus-Lockdown.pdf (As at 22.02.2021)
- 99.Wissenschaftliches Institut der AOK (WIdO) (2020) Fehlzeiten in der Pandemie: Weniger Krankmeldungen, aber längere Krankheitsdauer wegen psychischer Erkrankungen. Pressemitteilung. https://www.wido.de/fileadmin/Dateien/Dokumente/News/Pressemitteilungen/2020/wido_pra_pm_fehlzeiten_im_pandemiejahr_1020.pdf (As at 22.02.2021)
- 100.Wissenschaftliches Institut der AOK (WIdO) (2021) WIdO-Analyse zu Krankenhausbehandlungen in der zweiten Pandemiewelle: Erneute Fallzahlrückgänge bei planbaren Eingriffen und Notfällen. Pressemitteilung. https://www.wido.de/fileadmin/Dateien/Dokumente/News/Pressemitteilungen/2021/wido_kra_pm_fallzahlrueckgaenge_wegen_covid-19_erg_0321.pdf (As at 21.04.2021)
- 101.BARMER (2020) Barmer-Analyse – Corona beeinflusst massiv den Krankenstand. https://www.barmer.de/presse/presseinformationen/pressemitteilungen/gesundheitsreport-273324 (As at 22.02.2021)
- 102.Zielasek J, Vrinssen J, Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E. (2021) Utilization of Inpatient Mental Health Care in the Rhineland During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Frontiers in public health 9:593307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.BBK (2021) Monatlicher Krankenstand. https://www.bkk-dachverband.de/statistik/monatlicher-krankenstand (As at 10.06.2021)
- 104.DAK Gesundheit (2021) Psychreport 2021. Entwicklung der psychischen Erkrankungen im Job: 2010 – 2020. IGES, Berlin [Google Scholar]
- 105.Die Drogenbeauftragte der Bundesregierung (2021) Zahl der an illegalen Drogen verstorbenen Menschen während der Coronapandemie um 13 Prozent gestiegen Drogenbeauftragte Ludwig: „Suchthilfe und Gesundheitsversorgung von schwerstabhängigen Menschen muss auch in der Krise weitergehen!“ https://www.drogenbeauftragte.de/presse/detail/zahl-der-an-illegalen-drogen-verstorbenen-menschen-waehrend-der-coronapandemie-um-13-prozent-gestiegen/ (As at 21.04.2021)
- 106.Jacob L, Smith L, Koyanagi A, et al. (2020) Impact of the coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on anxiety diagnosis in general practices in Germany. J Psychiatr Res (Epub) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Michalowsky B, Hoffmann W, Bohlken J, et al. (2020) Effect of the COVID-19 lockdown on disease recognition and utilisation of healthcare services in the older population in Germany: a cross-sectional study. Age and ageing 50(2):317–325 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.KKH Kaufmännische Krankenkasse (2020) Krankenstand explodiert – vor allem bei Frauen. https://www.kkh.de/presse/pressemeldungen/krankenstand-corona (As at 22.02.2021)
- 109.KKH Kaufmännische Krankenkasse (2021) Psyche: Berufstätige länger krank. https://www.kkh.de/presse/pressemeldungen/psyche (As at 22.02.2021)
- 110.KKH Kaufmännische Krankenkasse (2021) Kinder, Karriere, Corona-Koller: Frauen leiden seelisch mehr. https://www.kkh.de/presse/pressemeldungen/psycheo (As at 21.04.2021)
- 111.Fasshauer JM, Bollmann A, Hohenstein S, et al. (2021) Emergency hospital admissions for psychiatric disorders in a German-wide hospital network during the COVID-19 outbreak. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology 56:1469–1475 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Aly L, Sondergeld R, Holzle P, et al. (2020) The COVID-19 pandemic has not changed the number but the type of psychiatric emergencies: A comparison of care data between 2019 and 2020. Der Nervenarzt 91(11):1047–1049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Hoyer C, Ebert A, Szabo K, et al. (2020) Decreased utilization of mental health emergency service during the COVID-19 pandemic. European archives of psychiatry and clinical neuroscience (Epub) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Seifert J, Meissner C, Birkenstock A, et al. (2021) Peripandemic psychiatric emergencies: impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on patients according to diagnostic subgroup. European archives of psychiatry and clinical neuroscience 271(2):259–270 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Statistisches Bundesamt (2021) Erste vorläufige Ergebnisse der Todesursachenstatistik für 2020 mit Daten zu COVID-19 und Suiziden. Pressemitteilung Nr. 327 vom 8. Juli 2021. https://www.destatis.de/DE/Presse/Pressemitteilungen/2021/07/PD21_327_23211.html (As at 30.07.2021)
- 116.Radeloff D, Papsdorf R, Uhlig K, et al. (2021) Trends in suicide rates during the COVID-19 pandemic restrictions in a major German city. Epidemiology and psychiatric sciences 30:E16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Arendt F, Markiewitz A, Mestas M, et al. (2020) COVID-19 pandemic, government responses, and public mental health: Investigating consequences through crisis hotline calls in two countries. Soc Sci Med 265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Armbruster S, Klotzbücher V. (2020) Lost in lockdown? COVID-19, social distancing, and mental health in Germany. Discussion Paper Series. University of Freiburg [Google Scholar]
- 119.TK (2021) Trotz Corona: Krankenstand 2020 deutlich gesunken – psychische Erkrankungen nehmen weiter zu. Pressemitteilung. https://www.tk.de/presse/themen/praevention/gesundheitsstudien/trotz-corona-krankenstand-sinkt-anstieg-psychischer-diagnosen-2099838 (As at 22.02.2021)
- 120.TK (2021) Gesundheitsreport Arbeitsunfähigkeit 2021. Techniker Krankenkasse, Hamburg [Google Scholar]
- 121.Mangiapane S, Zhu L, Kretschmann J, et al. (2021) Veränderung der vertragsärztlichen Leistungsinanspruchnahme während der COVID-Krise. Tabellarischer Trendreport für das Jahr 2020. https://www.zi.de/fileadmin/images/content/Publikationen/Trendreport_4_Leistungsinanspruchnahme_COVID_2021-04-19.pdf (As at 21.04.2021)
- 122.Shevlin M, Butter S, McBride O, et al. (2021) Refuting the myth of a ‘tsunami’ of mental ill-health in populations affected by COVID-19: Evidence that response to the pandemic is heterogenous, not homogeneous. Psychological medicine:1–9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Petzold MB, Ströhle A, Plag J. (2020) COVID-19-Pandemie: Psychische Belastungen können reduziert werden. Dtsch Arztebl International 117(13):648–654 [Google Scholar]
- 124.Forbes MK, Krueger RF. (2019) The Great Recession and Mental Health in the United States. Clin Psychol Sci 7(5):900–913 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Gibson B, Schneider J, Talamonti D, et al. (2021) The impact of inequality on mental health outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review. Can Psychol 62(1):101–126 [Google Scholar]
- 126.Holmes EA, O’Connor RC, Perry VH, et al. (2020) Multidisciplinary research priorities for the COVID-19 pandemic: a call for action for mental health science. The Lancet Psychiatry 7(6):547–560 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Jacobi F, Höfler M, Strehle J, et al. (2014) Psychische Störungen in der Allgemeinbevölkerung: Studie zur Gesundheit Erwachsener in Deutschland und ihr Zusatzmodul Psychische Gesundheit (DEGS 1-MH). Der Nervenarzt 85:77-87 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Jacobi F, Höfler M, Strehle J, et al. (2016) Erratum zu: Psychische Störungen in der Allgemeinbevölkerung. Studie zur Gesundheit Erwachsener in Deutschland und ihr Zusatzmodul „Psychische Gesundheit“ (DEGS 1-MH). Der Nervenarzt 87:88-90 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Rogers JP, Watson CJ, Badenoch J, et al. (2021) Neurology and neuropsychiatry of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the early literature reveals frequent CNS manifestations and key emerging narratives. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry 92(9):932–941 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Moreno C, Wykes T, Galderisi S, et al. (2020) How mental health care should change as a consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic. The Lancet Psychiatry 7(9):813–824 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


