Significance
In Photosystem II (PSII), O2 reduction by is often discussed but has not been demonstrated. Here, we show in PSII membranes that can reduce O2 to superoxide, but only when bicarbonate is absent from its binding site on the nonheme Fe2+. Bicarbonate’s role in PSII was recently shown to involve a regulatory/protective redox-tuning mechanism linking PSII function to CO2 concentration. A key aspect is the presence of stable causing release of bicarbonate from its site on Fe2+. Here, we show that under these conditions, O2 binds to the empty site on the Fe2+ and is reduced by . This unexpected reaction may be a further indication of cross-talk between the regulation of PSII and CO2 fixation.
Keywords: photosynthesis, photoinhibition, redox signaling, photoregulation, reactive oxygen species
Abstract
Photosystem II (PSII), the water/plastoquinone photo-oxidoreductase, plays a key energy input role in the biosphere. , the reduced semiquinone form of the nonexchangeable quinone, is often considered capable of a side reaction with O2, forming superoxide, but this reaction has not yet been demonstrated experimentally. Here, using chlorophyll fluorescence in plant PSII membranes, we show that O2 does oxidize at physiological O2 concentrations with a t1/2 of 10 s. Superoxide is formed stoichiometrically, and the reaction kinetics are controlled by the accessibility of O2 to a binding site near , with an apparent dissociation constant of 70 ± 20 µM. Unexpectedly, could only reduce O2 when bicarbonate was absent from its binding site on the nonheme iron (Fe2+) and the addition of bicarbonate or formate blocked the O2-dependant decay of . These results, together with molecular dynamics simulations and hybrid quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics calculations, indicate that electron transfer from to O2 occurs when the O2 is bound to the empty bicarbonate site on Fe2+. A protective role for bicarbonate in PSII was recently reported, involving long-lived triggering bicarbonate dissociation from Fe2+ [Brinkert et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113, 12144–12149 (2016)]. The present findings extend this mechanism by showing that bicarbonate release allows O2 to bind to Fe2+ and to oxidize . This could be beneficial by oxidizing and by producing superoxide, a chemical signal for the overreduced state of the electron transfer chain.
Photosystem II (PSII) is the water/plastoquinone photo-oxidoreductase that uses the energy of red light to drive the oxidation of water and the reduction of plastoquinone (PQ). This process leads to the formation of a radical pair on the chlorophyll PD1•+ and pheophytin PheoD1•−. The electron hole is transferred from the chlorophyll cation radical, PD1•+, via a redox-active tyrosine (TyrZ) to the Mn4O5Ca cluster, where, after four sequential photochemical turnovers, two water molecules are oxidized on the luminal side of the membrane. The electron is transferred from the pheophytin anion radical (PheoD1•−) via a nonexchangeable plastoquinone (QA), which acts as a one-electron relay, to an exchangeable plastoquinone (QB), the terminal electron acceptor (1–3). QB accepts two electrons and takes up two protons from the aqueous phase to form QBH2 before it is released as a PQH2 into the PQ/PQH2 pool in the membrane (4). From here, the PQH2 delivers electrons to cytochrome b6f complex, the subsequent enzyme of the photosynthetic electron transfer chain.
As photochemical charge separation is intrinsically a one-photon-per-electron process, two photochemical turnovers are required to form PQH2, with the one-electron reduced semiquinone, , formed as an intermediate. Semiquinones can be very reactive, but is rendered thermodynamically stable by the environment provided by its binding site on the D1 protein (4). The electron on is still able to back-react via with the S2 and S3 states, the two semistable intermediates of the water oxidizing enzyme (5). This back-reaction occurs by thermal repopulation of the intermediate radical pairs between and . can either repopulate P*, which can decay radiatively (5, 6), or it undergoes direct charge recombination, forming the chlorophyll triplet state, 3P680 (7–9). As expected for a long-lived chlorophyll triplet state, it reacts with dioxygen to form a highly reactive singlet oxygen species, 1O2, which causes photodamage (10, 11).
On the electron acceptor-side of PSII (Fig. 1), the reduced forms of the electron transfer cofactors can potentially reduce oxygen, forming superoxide radical () by a one-electron transfer to O2. This would be a wasteful leak of electrons, and the formed could be damaging and act as redox signal within the cell. During forward electron transfer, has a half-time of ∼1 ms (1) and is unlikely to react with O2. However, when, for example, QB and the PQ pool are reduced, is longer lived, and it is then more likely to reduce oxygen. Oxygen reduction by is often discussed in the literature (12–16), but clear experimental evidence for this reaction has not been reported. Here, using PSII membranes, we have directly tested for electron transfer from to O2 and for formation of superoxide. We show the reaction does occur, and we characterized the reaction in terms of the O2 binding site using biochemical and computational approaches. The results indicate the reaction constitutes an unexpected regulatory mechanism involving bicarbonate.
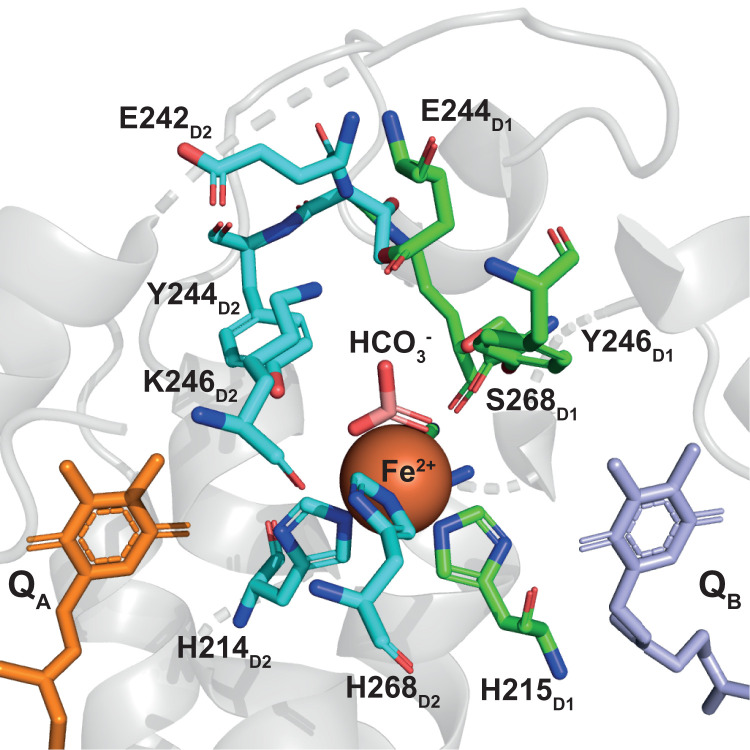
Fig. 1.
The quinone-iron complex in PSII. The nonheme iron shown as a red sphere and the bicarbonate in pink. The amino acid side chains involved in the hydrogen-bonding network are shown, green if belonging to D1 and cyan if belonging to D2. Data from the 1.9-Å crystal structure (PDB ID: 3WU2) (41).
Results
Oxidation by O2.
Fig. 2A (orange trace) shows the stability of generated in low-PQ PSII membranes (SI Appendix, Fig. S1) under anaerobic conditions and with the concentration of monitored using chlorophyll fluorescence (17, 18). To generate this state, a dark-adapted sample was illuminated with three saturating flashes in the presence of the exogenous electron donor, NH2OH, at 250 µM, a concentration that was sufficient to donate electrons to the Mn cluster but low enough to avoid overreduction and loss of the Mn cluster in the majority of centers (SI Appendix, Materials and Methods, and, for example, ref. 19). This treatment resulted in the trapping of stable in ∼50% of the centers, based on a comparison to maximum fluorescence. The decay of in the other centers is mainly due to 1) forward electron transfer in the millisecond timescale (18) as a result of the incomplete removal of the PQ pool and 2) charge recombination ( and ) in the seconds timescale (20) in centers where electron donation from NH2OH was insufficient to eliminate these back reactions. In the absence of O2, the stable fluorescence signal from showed a slow decay with a half-time of ∼600 s. A decay rate for with similar kinetics has previously been correlated with the decay of TyrD• and attributed to charge recombination between these two states (21), which could explain the slow decay of observed here.
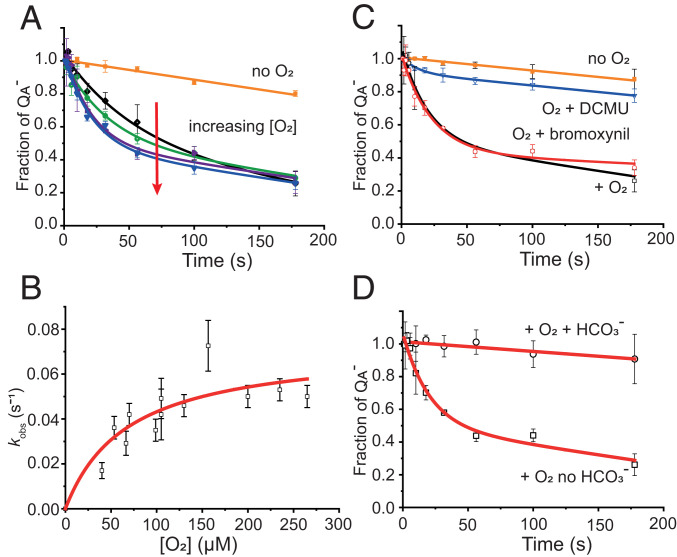
Fig. 2.
Kinetics of reoxidation by O2. Fraction of obtained after three saturating flashes of a degassed sample of PSII membrane fragments (60 nM PSII cores) in the presence of 250 µM hydroxylamine in a 40 mM MES buffer, 5 mM MgCl, pH 6.5. The data in A, C, and D were fitted to Eq. 1. (A) Orange symbols represent the decay in the absence of added oxygen, and the data were fitted with a linear decay. Other symbols represent the decay in the presence of oxygen in the concentration range from 40 ± 3 µM (black symbols) to 155 ± 6 µM (blue symbols). Data were fitted with Eq. 1. (B) Observed kinetic rate constants obtained from the fitting of the kinetic data with Eq. 1 plotted in function of the concentration of added oxygen. Data were fitted with the hyperbole of Eq. 2. (C) Effect of the addition of QB site inhibitors. Control experiments with (open black symbols) and without (closed orange symbols) oxygen are shown for comparison; 10 µM DCMU (open blue symbols) or 100 µM bromoxynil (open red symbols) was added prior to the degassing step and the kinetics were measured upon the addition of 110 ± 5 µM oxygen. (D) Effect of the addition of 1 mM bicarbonate (open circles) at the degassing step prior to the addition of oxygen is compared with a control kinetics in the absence of bicarbonate (open squares). Kinetics were recorded upon addition of 110 ± 5 µM oxygen.
The decay of the trapped state was significantly accelerated when O2 was added back to the medium (Fig. 2A), which provided clear experimental evidence for the reduction of O2 by . Fig. 2A also shows that the rate of oxidation accelerated as the O2 concentration increased. The observed fluorescence decays were found to be biphasic, with a fast exponential decay rate that depended on the O2 concentration and a slow decay rate that was independent of the O2 concentration. The slower phase corresponded to that observed in the absence of oxygen. The kinetic data were fitted using a linear combination of the fast exponential phase and a slow, linear decay,
| [1] |
where kobs is the pseudo first-order rate constant for reoxidation at a fixed O2 concentration, b is the slope, and c is the intercept of the linear decay observed in the absence of O2. This biphasic behavior indicated heterogeneity in the preparation, where most of the centers were susceptible to reactions with O2, but a smaller fraction remained unreactive. We demonstrate in the following that this heterogeneity appears to be related to bicarbonate binding to the nonheme iron. We investigated whether the effect of “connectivity” influenced the kinetics observed here in Fig. 2. Connectivity is a phenomenon seen in fluorescence when PSII shares an extended antenna, leading to a situation where there is a significant probability that excitation energy can visit more than one closed center before finding an open PSII. This results in a nonlinear relationship between fluorescence intensity and concentration (22, 23). We found that connectivity has a negligible effect on the present experiment (SI Appendix, Fig. S2).
Fig. 2B shows the observed rate constants (kobs) for the fast, exponential phase of the decay, measured in pseudo first-order conditions and plotted as a function of the added concentration of O2. The plot shows saturation behavior characteristic of the presence of a discrete binding site. This binding site becomes saturated above ∼150 µM O2 (SI Appendix, Fig. S3). The data were fitted with a hyperbolic curve (Eq. 2) from which the apparent Kd was calculated to be 70 ± 20 µM and a rate constant, at physiological O2 concentrations, to be 0.07 s−1, corresponding to a half-time of ∼10 s (10.6 ± 0.8 s). The pseudo first-order rate constant kobs for reoxidation at a fixed oxygen concentration was estimated as
| [2] |
where ksat is the rate constant when the binding site is fully occupied, and is the apparent dissociation constant. The second-order rate constant, calculated from the linear fit, was found to be 340 ± 83 M−1 s−1.
Influence of Herbicides on the Reactivity to Oxygen.
To test if the driving force determines the rate of the electron transfer, kinetics was measured by modulating the reduction potential of by binding herbicides into the QB site.
Different classes of herbicides shift the potential in different directions: by +50 mV (−144 mV to −94 mV) with 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea (DCMU), and by −50 mV (−144 mV to −194 mV) with bromoxynil (24). These herbicide-induced shifts in the Em result in differential effects on the kinetics of recombination (SI Appendix, Fig. S4), thereby confirming herbicide binding under our experimental conditions. Fig. 2C shows the kinetics of reoxidation at 110 ± 5 μM O2 concentration. With DCMU, the reaction was essentially blocked, whereas with bromoxynil, the reaction was virtually unaffected. Similar behavior was observed when the experiment was performed at lower O2 concentration (40 ± 3 µM) (SI Appendix, Fig. S5). The effect of DCMU appears to be too drastic to be due to the small change in the reduction potential, and it is thus attributed to a structural effect of DCMU binding rather than a redox effect on the quinone (in the following, we discuss DCMU binding having a redox effect on the nonheme iron and on the binding of bicarbonate as viable options to explain its effect). The lack of a bromoxynil effect, on the other hand, suggests that the rate of O2 reduction by is not determined by the thermodynamic driving force between and . As bromoxynil occupies the QB site (bromoxynil binding data on flash 1 is provided in SI Appendix, Fig. S6B), this result eliminates the possibility that or QBH2 donates electrons to O2, allowing the to decay by forward electron transfer.
Influence of Bicarbonate on Reoxidation Kinetics.
The degassing used to make the PSII anaerobic is also expected to remove CO2 and, at this pH (pH 6.5), bicarbonate from solution. The degassing is thus expected to result in partial loss of bicarbonate from PSII. Fig. 2D shows that addition of bicarbonate after degassing the sample, eliminated electron transfer from to O2. A control experiment using 1 mM NaCl instead of NaHCO3− had no effect on the kinetics of oxidation by O2 (SI Appendix, Fig. S7A). Addition of bicarbonate also blocked reoxidation by O2 in the presence of the herbicides (Fig. 2B and SI Appendix, Fig. S8).
Fig. 2D thus suggests that bicarbonate binding to the nonheme Fe2+ controls electron transfer from to O2. To test the specificity of this effect, sodium formate, which is known to bind in the bicarbonate site on the nonheme Fe2+, was added (SI Appendix, Fig. S7B). Formate, at 100 mM, a concentration known to be competitive with bicarbonate (25, 26), behaved like bicarbonate: it prevented from reducing O2 (SI Appendix, Fig. S7B). Because the effect is not specific to bicarbonate, this suggests electron transfer from to O2 requires that nonheme Fe2+ lacks the carboxylic acid and thus that the O2 is reduced when bound to the Fe2+.
Superoxide as the Product of the Reaction.
The electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spin trap 5-(diisopropoxyphosphoryl)-5-methyl-1-pyrroline-N-oxide (DIPPMPO) was used to demonstrate formation under continuous illumination (Fig. 3A). This spin trap forms trapped radical adducts with either or the more reactive OH•, but these can be distinguished by their different EPR spectra (27). The experiments in Fig. 3A were done in the presence of catalase, which removes peroxide (formed by dismutation of the ), which could give rise to OH• by Fenton chemistry. The presence of residual OH• forms a spectroscopically distinct adduct with DIPPMPO (28); it can be deconvoluted from the be spin adduct and quantified as being less than 20% of the OH• adduct (SI Appendix, Figs. S9 and S10 EPR deconvolution).
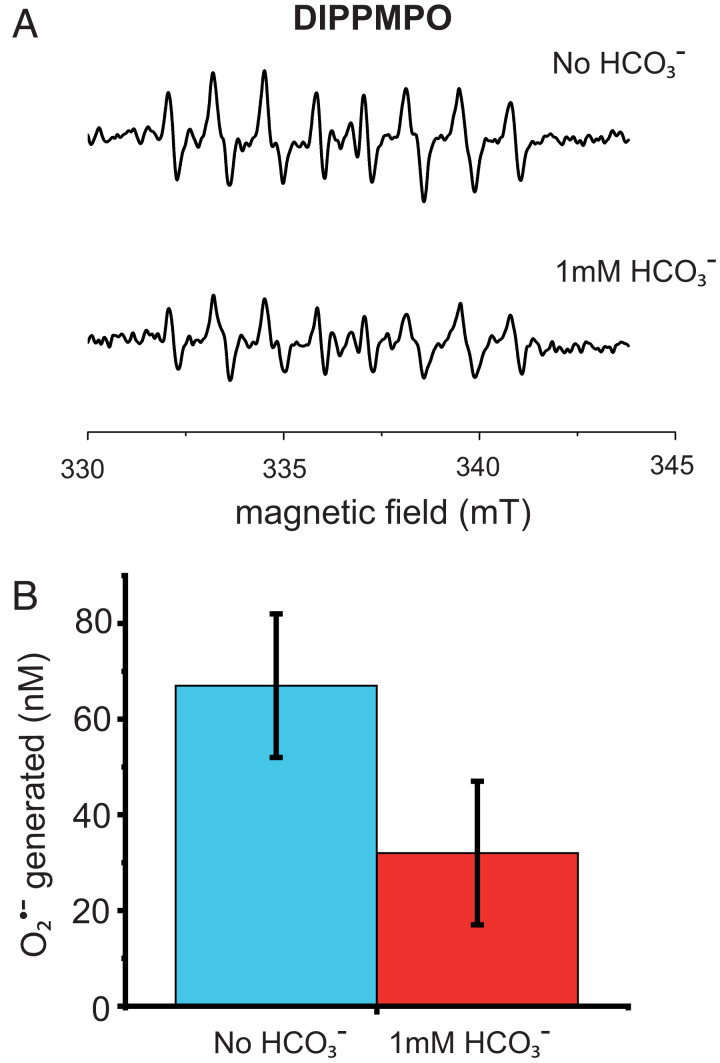
Fig. 3.
EPR characterization of ROS. (A) Generation of produced in the absence (Top) and in the presence (Bottom) of 10 mM bicarbonate measured by EPR using the spin probe DIPPMPO. PSII membrane fragments (600 nM PSII cores) in 40 mM MES buffer, 5 mM MgCl, pH 6.5. The sample was illuminated with 50 µM photons m−2 s−1 red light (590 nm longpass filter) for 20 min. (B) quantified as reduced cyt c in the absence (blue bar) and in the presence (red bar) of 1 mM bicarbonate. A total of 40 to 50% was obtained after three saturating flashes of a degassed sample of PSII membrane fragments (60 nM PSII cores) in the presence of 250 µM hydroxylamine in a 40 mM MES buffer, 5 mM MgCl, pH 6.5.
Fig. 3A shows that the concentration of formed under these conditions was diminished by ∼30% when the experiment was done in the presence of 12 mM bicarbonate. The higher bicarbonate concentration was used to maintain the bicarbonate ratio to PSII in the EPR experiment, in which 12 times more PSII is required to obtain appropriate signal to noise.
The spin-trapping EPR experiment showing the formation of was insufficiently sensitive to allow its exact quantification. A more sensitive approach is to monitor the reduction of cytochrome c (cyt c) by by its absorption change at 550 nm (29). Fig. 3B shows the amount of reduced cyt c from the reaction of with O2, in a sample containing 60 nM PSII. The sample was treated as described for the fluorescence kinetics measurements (Materials and Methods). The experiment was performed in the presence and absence of 1 mM bicarbonate, and the amount of reduced cyt c, which is equivalent to the amount of generated, was found to be 32 ± 16 nM and 68 ± 16 nM respectively. The bicarbonate-dependent decrease in the amount of reduced cyt c corresponds to ∼50% of the concentration of PSII and thus approximately the same amount of present prior to O2 addition. This confirms that decay upon the addition of O2 is due to stoichiometric formation. Control experiments showed that the direct reduction of cyt c by PSII was negligible, consistent with previous reports (e.g., ref. 30). Interference by H2O2 and OH• on the cyt c reduction was prevented by the presence of catalase (Materials and Methods).
The residual cyt c reduction occurring after the addition of bicarbonate does not arise from the present prior to O2 addition, as all of that is accounted for by the bicarbonate-sensitive . Other electron transfer components have been suggested as possible reductants of O2 forming , including cyt b559 (31) and QBH2 (14) as well as the PQH2 pool (15, 32), which could be present as a residual in our low PQ preparation. Furthermore, small amounts of contaminant Photosystem I (PSI) in the PSII-enriched thylakoid membrane (BBY)-prep (Materials and Methods) could represent another possible source of . While such effects would be expected to occur to a minor extent in the dark, they could also be driven by an actinic effect of the measuring flashes. Despite their weak intensity, their frequency might result in sufficient photochemistry during the time course of the experiment to account for the observed residual -mediated cyt c reduction (SI Appendix, Fig. S11). This would be consistent with the observation that experiments run in the presence of DCMU show a further decrease in the amount of reduced cyt c.
Production When Is Generated by Continuous Illumination.
The accumulation was also studied by cyt c reduction under constant illumination (SI Appendix, Fig. S12). After 2 min of illumination (50 μmol photons m−2 s−1 red light), an average of 736 ± 10 nM reduced cyt c was generated, and when 1 mM HCO3− was present, this was diminished by approximately half (351 ± 60 nM). This is consistent with what we observed in the single flash stoichiometric experiments. When the same experiment was done by using 20 min of illumination without HCO3−, an average of 2,076 ± 10 nM reduced cyt c was generated, while in the presence of HCO3−, 1,457 ± 60 nM reduced cyt c was formed. The effect of HCO3− on decreasing the formation of reduced cyt c seemed to diminish at longer illumination periods, suggesting that other routes for production of , such as cytochrome b559 and PQH2 and perhaps involving 1O2, might play a role upon prolonged illumination. Furthermore, the prolonged illumination leads to an increased probability of being formed that in turn favors bicarbonate dissociation even in the presence of 1 mM bicarbonate in solution (33, 34).
When the DCMU was present in the absence of added bicarbonate, 2 min of illumination resulted in hardly detectable amounts of reduced cyt c, while after 20 min of illumination, the amount was 626 ± 70 nM (SI Appendix, Fig. S12). These results differ from those shown in Fig. 2B, where DCMU was found to be less effective than bicarbonate for inhibiting the reduction of O2 in the dark. The more pronounced effect of DCMU under continuous light could result from other reactions generating reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as long-lived PheoD1•− and/or 3Chl-mediated 1O2 formation.
Mechanism of Reduction of O2.
To probe possible molecular mechanisms of O2 reduction, we performed quantum chemical density functional theory (DFT) calculations and hybrid quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to assess the electronic structure of the nonheme iron site and its reactivity with molecular oxygen (Fig. 4 and SI Appendix, Fig. S13). In our DFT models, we first optimized the structure of the nonheme iron site with either or an O2 ligand bound to the Fe2+ ion or in the absence of either ligand. The DFT models suggested that the O2 can bind with a high affinity (∼−4 kcal mol−1) to the nonheme Fe2+, forming a 2.4-Å covalent bond between the Fe2+ and the O2. We next added an electron on QA and reoptimized the models. The DFT calculations suggested that the electron was localized on QA, forming in the -bound form and when no exchangeable ligand on the iron was modeled (Fig. 4A). In contrast, in the dioxygen-bound form, the electron instantly moved from to O2 during the calculations, leading to formation of an species (Fig. 4 B–D). By varying the Fe-O2 distance, we observed that the electron transfer from was triggered at around 2.6 Å, when a chemical bond forms between the dioxygen and iron (SI Appendix, Fig. S14). The findings thus suggest that the nonheme iron catalyzes O2 reduction/superoxide formation (Fig. 4 B and D). Our calculations also suggested that the presence of led to weakening of the affinity for the iron due to electrostatic repulsion, in accordance with experimental evidence (33). The calculations also support that the Fe3+ form of the nonheme iron can still bind , whereas both O2 and favor the Fe2+ form (SI Appendix, Fig. S15).
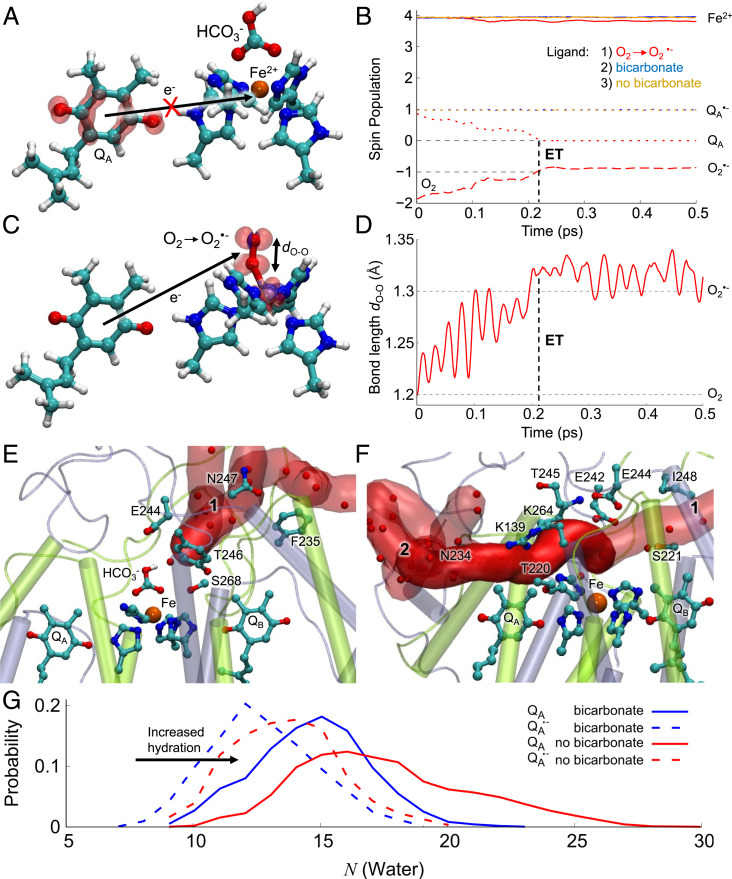
Fig. 4.
O2 reduction mechanism, bicarbonate binding, and accessibility of the nonheme Fe site of PSII. Structure and spin densities from DFT models of the (A) HCO3−-bound and (C) O2-bound forms of the nonheme iron (the state without HCO3− is shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S13F). The figure shows the spin density difference (red/blue sphere ±0.001e for alpha/beta spin) after adding an electron into the system, with only the QA and iron/histidine residues shown for clarity (SI Appendix, Fig. S13). (B) Spin population during the QM/MM MD simulations for HCO3−-bound (in blue) and without HCO3−-bound (in orange) and the O2-bound forms (in red) on the Fe2+ (solid lines), QA (dotted lines), and O2 (dashed line). (D) The O-O bond length during electron transfer from QA. (E and F) Snapshot at 150 ns of the water-filled tunnels formed around the QA site during MD simulations in (E) with the HCO3−-bound form and (F) without the HCO3−. (G) Histogram of water molecules in tunnels 1 and 2 connecting to the iron from the bulk solvent. The bicarbonate blocks water entry to the nonheme iron site.
Hybrid QM/MM MD simulations were also done to study the dynamics of the electron transfer process in more detail, including the effects of temperature (Fig. 4 B and D, SI Appendix, Fig. S14, Materials and Methods). This was done by initiating the simulations from a state in which was relaxed in classical molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The reduction of QA tightened the local hydrogen bonds between the plastoquinone and His214/Phe261 relative to the neutral QA state, which stabilized the reduced form by further subtle conformational changes in the surrounding helices. Consistent with our results obtained from the DFT models, we found that QA remained reduced throughout the 2 ps QM/MM MD simulation when HCO3− was bound or when no exchangeable ligand on the iron was modeled. In contrast, the electron was rapidly transferred during the initial 0.2 ps to the Fe-bound O2, forming a species.
To probe structural effects linked to dissociation of HCO3− on longer nano-to-microsecond timescales, we performed classical atomistic MD simulations of PSII embedded in a lipid membrane, with the QA site modeled either as oxidized or as semiquinone, . During the 200 ns MD simulations, we observed two water-filled tunnels, 1 and 2, that connect the stromal side of the membrane to the nonheme Fe center, while the QA site remained sequestered from water molecules (Fig. 4 E–G, SI Appendix, Fig. S15). In simulations without an exchangeable ligand modeled on the nonheme iron, we observed a significant increase in the hydration state of the tunnels compared to the simulations performed when the was bound (Fig. 4G). Conformational changes around Lys264 seem to regulate the accessibility of the tunnel to the nonheme iron site (Fig. 4 E and F, SI Appendix, Fig. S15 A and B). We note that the water-filled tunnels are large enough for dioxygen diffusion into the site. These findings fit with the model in which occupation of the binding site on the nonheme iron prevents O2 from binding there.
Discussion
Electron Donation from to O2.
Here, we trapped the state in PSII membranes with a depleted PQ pool by illuminating in the presence of low concentrations of the electron donor, NH2OH, under anaerobic conditions. The is stable in a significant fraction of centers because forward electron transfer is blocked due to QB being reduced or absent in the PQ-depleted PSII. In addition, cannot recombine with the stable S0 or S1 states on the minutes timescale of the experiment (5). The presence of was monitored using chlorophyll fluorescence (17, 35). This “trapped” undergoes a slow decay (t1/2 = 5 min) that may correspond to the recombination of the electron on with a relatively stable oxidized species, such as TyrD• (21) (Fig. 2A).
We used this experimental system to test if the trapped would react with added O2. Upon addition of O2, the lifetime of the trapped was found to decrease, with the reaction rate increasing with increased O2 concentration and saturating above ∼150 µM O2 (SI Appendix, Fig. S3). The kinetics of the O2-induced decay showed a single exponential curve, consistent with a pseudo first-order reaction at a fixed concentration, with a transition to a zero-order reaction above 150 µM O2, thus resulting in a half-time of ∼10 s under physiological O2 concentrations (270 µM) (Fig. 2B).
The reaction rate did not appear to be affected by the thermodynamic driving force, as judged by the lack of effect of the phenolic herbicide, bromoxynil, which is known to lower the Em of the redox couple (24) (Fig. 2C and SI Appendix, Fig. S4 TyrD recomb). DCMU binding is expected to increase the Em of the couple and thus potentially slow down the O2 reduction. However, DCMU binding strongly inhibited the electron transfer from to O2 (Fig. 2C). The DCMU inhibition was so significant that it seems unlikely to result from the predicted +50 mV change in reduction potential. Possible explanations for the DCMU-induced inhibition of O2 reduction by include minor structural/conformational effects, redox effects on the nonheme iron, which may affect bicarbonate binding (see The Nonheme Iron as the Binding Site for O2).
Bicarbonate and Formate Inhibition of O2 Reduction.
Under the conditions of the fluorescence measurements, the bicarbonate was expected to be depleted from its binding site on the nonheme Fe2+ because 1) the degassing of the sample to make it anaerobic is expected to lower the concentration of CO2 and thus of the bicarbonate; and 2) the presence of greatly decreases the affinity of the bicarbonate for its binding site on the nonheme iron (33). Therefore, we tested the effect of adding back bicarbonate prior to the addition of O2. Bicarbonate readdition is expected to lower the Em of and thus to increase the driving force for O2 reduction. Instead, we found that bicarbonate addition completely blocked electron transfer from to O2 (Fig. 2D). This finding suggests that O2 reduction occurs when it is bound to the nonheme iron in the empty bicarbonate site.
Formate had the same effect as bicarbonate. This lack of formate/bicarbonate specificity contrasts with the specific roles of bicarbonate in optimizing proton-coupled electron transfer (26, 34, 36) and in redox tuning for regulation and photoprotection (33), roles that are not shared by formate. This lack of specificity of bicarbonate-versus-formate binding is consistent with the inhibition of O2 reduction being a steric effect, with either bicarbonate or formate binding occluding the O2 binding site on the nonheme iron. The occlusion of the nonheme iron binding site by bicarbonate was also indicated by the MD simulations.
Formation of Superoxide.
EPR spin trapping and cyt c reduction confirmed that was the product of the reaction of with O2 (Fig. 3) and that this reaction was blocked by bicarbonate addition. The cytochrome reduction method allowed the to be quantified, and its concentration was found to be close to that of the . A second fraction of was formed in the dark in a reaction that was not inhibited by bicarbonate addition and was unrelated to the oxygen-dependent decay of . We have not characterized the electron source of this fraction of formation, but we note that there are several possible candidates, including PQH2 bound to PSII or in the membrane, cyt b559, and PSI (14, 15, 31, 32).
Physiological Significance: Rates and Conditions.
(In Redox and Mechanistic Considerations, we discuss the possibility of faster rates of O2 reduction by , but in this section, we discuss the slower rate measured using the experimental approach used here.) The rate of electron transfer from to O2 (t1/2 ∼ 10 s) implies that under conditions where the QB and quinone pool are oxidized, the reduction of O2 is too slow to compete with the forward electron transfer rate of t1/2 ∼ 1 ms (35) even when bicarbonate is absent (34). When the quinone pool is fully reduced, a large proportion of and will recombine with a t1/2 ∼ 1.5 s (20), i.e., much faster than the rate of electron transfer of the to O2 reaction reported here. However, when forward electron transfer from is blocked in centers where either S1 or S0 are present, the reaction with O2 could be the dominant reoxidation pathway, provided the bicarbonate is absent from its binding site on the nonheme iron. Such conditions are likely to occur when CO2 levels are limiting, as previously discussed (33).
Physiological conditions other than those where the PQ pool is reduced are likely to exist in which electrons are trapped on long enough to allow bicarbonate release and reduction of O2 to be a relevant reaction. These circumstances could include those associated with assembly and photoactivation of PSII, photoinhibition, and repair, in which is longer lived (9, 37–39). An intermediate state in PSII assembly is structurally modified by the binding of assembly factors (Psb27, Psb28, and Psb34) that cause the bicarbonate site on the nonheme iron to be occupied instead by a glutamate (39). This iron coordination mirrors the situation that exists in the purple bacterial reaction centers. From the present results, we expect such assembly intermediates of PSII to be unable to reduce O2 from . As the QB site is significantly modified in this assembly intermediate, it seems likely that will recombine with TyrZ•(H+) via a direct tunneling step between P+ and , given the high potential of the couple prior to photo-assembly of the Mn4CaO5 cluster (9, 39).
The Nonheme Iron as the Binding Site for O2.
The single saturable site for O2 reduction and its complete inhibition by bicarbonate indicate that the nonheme Fe2+ is the O2 binding and reduction site. DFT and QM/MM calculations reported here further support this assignment. Our calculations showed that reduction of O2 by is favorable when oxygen binds to the Fe2+ in the absence of bicarbonate binding to that site. This result contrasts with a previously proposed mechanism involving direct oxidation of by O2 (12–14), which is expected to require close contact between the oxygen and the semiquinone (40). The crystal structure (41) and the MD simulations indicate that this is unlikely because the QA is not exposed to the solvent.
In enzymes, transition metals and Fe2+ in particular often activate O2 for reduction, overcoming the intrinsic spin-transition that makes O2, a ground state triplet, anomalously stable. It seems that this is also the case in PSII. This mechanism seems reasonable given that bicarbonate dissociates from the iron when is long-lived (33).
The DCMU inhibition of O2 reduction may also be taken as an indication that the nonheme Fe2+ is the O2 binding site. DCMU binding shifts the redox potential of the Fe3+/Fe2+ couple 120 mV to higher values, while other herbicides/inhibitors (atrazine and o-phenanthroline) induced much smaller shifts (42–44). Whether the DCMU inhibition of O2 reduction reflects a perturbation of the electronic structure of the Fe2+ (as manifest by the redox shift), minor structural changes, or both of these is unclear. These effects could be responsible for DCMU inhibiting bicarbonate binding and dissociation (45, 46). Given the conditions of our experiment, it is possible that DCMU binding prevents bicarbonate loss, leaving the nonheme Fe2+ site occupied. This would explain the lack of O2 reduction (Fig. 2). The observation that addition of bicarbonate to a DCMU-treated sample eliminates the residual O2 reduction (SI Appendix, Fig. S10) is consistent with bicarbonate depletion is very limited when DCMU is present.
The suggestion that the nonheme Fe2+ could play an oxygen reduction role was already discussed (47), although superoxide was suggested to bind to the Fe2+, and then to undergo further reduction to form OH•. In this mechanism, the superoxide was suggested to arise from oxygen reduction by directly, a reaction that seems unlikely based on the present work. The direct catalytic role for the nonheme iron in oxygen reduction and its control by the bicarbonate, reported here, have not been discussed previously, as far as we are aware.
Redox and Mechanistic Considerations.
Nominally, the electron transfer from to O2 is thermodynamically unfavorable, based on the Em of = −144 mV, a value that is shifted to −70 mV in the absence of bicarbonate (33), and thus, it is more oxidizing than Em = −160 mV for (48). However, given the very low concentration of compared to O2, its functional potential is likely to be closer to ∼0 mV (13), rendering the overall process thermodynamically favorable. In addition, it seems likely that the binding of the O2 to the iron will change the redox potential of the couple.
Given the thermodynamic driving force and the ∼8 Å distance between and O2, rapid (∼ps) reaction rates are expected, as indeed observed in the QM/MM MD simulation, when O2 was already bound to the iron. The measured reaction rates are, however, much slower (t1/2 ∼10 s), and this could be due to the reaction rates being limited by O2 diffusion along the constricted channels to the iron binding site (Fig. 4 E and F and SI Appendix, Fig. S14). This diffusional restriction could limit the measured rate in the experiments performed, i.e., when an anaerobic sample is mixed with oxygenated buffer. The possibility arises that under aerobic conditions, O2 may be already within the access channel and thus have more rapid access to the nonheme iron. This raises the possibility that in vivo the reduction of O2 by could be faster than reported here.
The Fe3+/Fe2+ couple has an Em of +430 mV at this pH (44). The Fe2+ is located between the quinones QA and QB, but there is no evidence of a distinct redox role of the metal in the electron transfer process between the two quinones (49). Similarly, while the DFT and QM/MM calculations indicate that both Fe3+ and Fe2+ are stable with HCO3− bound, no Fe3+ is formed during the electron transfer process with O2 bound, suggesting that the Fe2+ has a catalytic rather than redox role in enabling the electron transfer to O2 (Fig. 4 and SI Appendix, Fig. S14).
Bicarbonate Regulatory Mechanism.
Recently, it was shown that the dissociation of bicarbonate leads to an increase in the reduction potential of , and consequently, the presence of decreased the bicarbonate affinity for its binding site on the nonheme iron (33). The redox-tuning/bicarbonate-binding relationship suggested the following photoregulation/protection model: 1) when the intracellular CO2 concentration is low and PSII is exposed to light, limitations in CO2 fixation result in the overreduction of the electron transfer chain, leading to the formation of a long-lived ; 2) the long-lived triggers the dissociation of the bicarbonate by lowering its affinity for the nonheme iron; 3) the loss of the bicarbonate raises the Em of , increasing the energy gap between the and PheoD1/PheoD1•− redox couples (33); 4) this increased energy gap disfavors the back-reaction, preventing the formation of P+•Pheo•−, the precursor of the chlorophyll triplet state (7) that reacts with O2 to form damaging 1O2 (9).
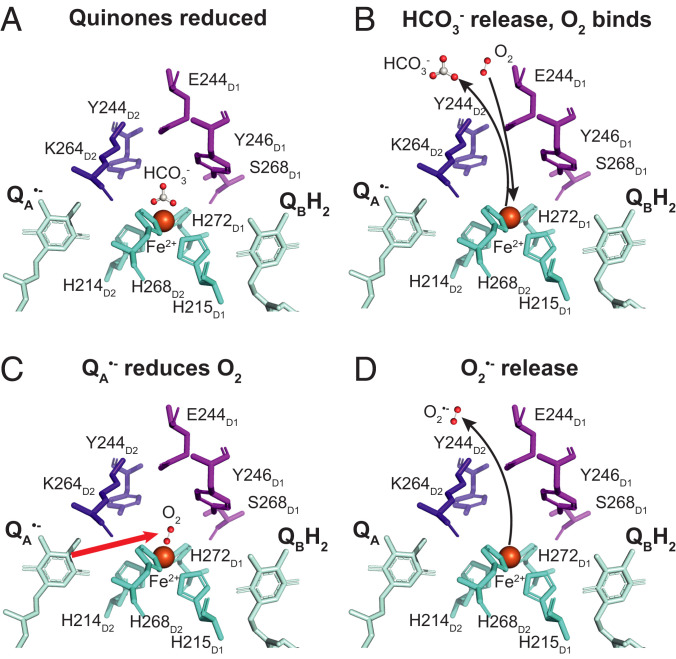
Our current findings that can reduce O2 and that bicarbonate binding prevents this reaction suggest another layer of complexity on the regulatory and protective role of bicarbonate in PSII (Fig. 5). Under normal functional conditions (light, high intracellular CO2, stomata open), the lifetime is expected to be short, the bicarbonate is bound, and formation is blocked (Fig. 5A), leading to minimal electron leaks. However, when the intracellular CO2 concentration is low, the electron transfer chain is reduced, and long-lived is formed, which favors bicarbonate release (Fig. 5B). Under these conditions, O2 can bind to the Fe2+ and then be reduced by , forming QA and (Fig. 5C), which is then released (Fig. 5D).
Fig. 5.
Structural scheme showing the working model for O2 reduction by in PSII. (A) When photosynthesis is limited by low CO2, illumination results in the reduction of the PQ pool, QB and QA. (B) The presence of long-lived changes the dissociation constant of the bicarbonate ligand on the nonheme Fe2+, leading to its release and allowing O2 to enter the channel and to bind to the Fe2+. (C) When the O2 is bound to the Fe2+, it is rapidly reduced by the electron coming from . (D) The superoxide formed is released from the Fe2+ and diffuses away.
The slow rate (t1/2 = 10 s) for reoxidation of will only have small effects on relieving the electron transfer block. It is debatable whether this will constitute a significant benefit to the system. As mentioned previously, this slow rate appears to represent the diffusional limit when O2 is added to a fully anaerobic system, and it seems quite possible that faster rates may occur in equilibrated aerobic conditions. The possibility of faster O2 reduction notwithstanding, low concentrations of superoxide can act as a signal, either directly or by dismutation to form hydrogen peroxide (11, 50, 51). Superoxide formation is stoichiometric and could accumulate, and a signaling role does not necessarily require a high concentration. PSI is usually considered the major source of superoxide (11, 15, 50). However, the different locations of the two photosystems in the thylakoid membrane and the specific localization of superoxide dismutases near PSI could allow the produced by PSII to play a role in regulation.
Relevance to Previous Studies.
The phosphorylation of the D1 protein in PSII, which is associated with the migration of damaged PSII from the grana to the stroma lamellae during PSII repair cycle, was shown to decrease production (52). This was confirmed in STN8 kinase knockout mutant strains in rice that showed enhanced production under high light (53). In both cases, it was suggested that a conformational change induced by the phosphorylation (or the lack of it in the absence of the kinase in the knockout mutant) was responsible for the formation of due to the reduction of oxygen by QB•−. Considering 1) that the experiments in ref. 52 were performed in high light, 2) the improved understanding of the redox properties of QB (4), and 3) the findings in the present work, it seems more likely that is responsible for the oxygen reduction and that the phosphorylation restricts O2 accessibility to the nonheme iron, perhaps by favoring bicarbonate binding.
PsbS knockout mutants in rice were shown to produce more due to a proposed decrease in the reduction potential compared to the wild type under high light conditions (54). More recently, while investigating the role of PsbS on the efficiency of water use in field crops, a correlation between stomatal conductance and the QA redox state was reported (55). As hydrogen peroxide is a signal involved in stomatal opening, and as superoxide rapidly dismutates forming hydrogen peroxide, it is possible that the superoxide generated by reported here contributes to this signaling pathway.
Small carboxylic acids, such as acetate and glycolate, can replace bicarbonate at the nonheme iron binding site in vivo (56, 57) and could thereby protect against photooxidative stress under low-CO2 conditions (33, 56, 57). The mechanism involves redox tuning of QA and the associated binding effects of bicarbonate (33). The observation here (SI Appendix, Fig. S7B) that formate can replace bicarbonate in blocking oxygen access to the iron and thus to reduction by extends this model suggesting a potential role for carboxylic acids in controlling superoxide-initiated signaling.
Materials and Methods
Isolation of the PSII Complex.
Market spinach (Spinacia oleracea) was used for the isolation of PSII-enriched thylakoid membranes (BBY). Samples were prepared following the protocol from ref. 24, obtaining samples with a lower content of QB. To obtain samples with a lower QB content, preparation was the same, but samples were additionally treated with Triton X-100 at a concentration of 2.5% per milligram chlorophyll and for an incubation period of 50 min.
Reoxidation Using Fluorometry.
All fluorescence measurements were recorded using a Fluorometer FL3000 (Photon Systems Instruments) and carried out in the dark. For the kinetic measurements, the samples were prepared in a septum sealed cuvette. Final concentrations were 60 nM PSII and 250 µM hydroxylamine in working buffer (40 mM of 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid [MES] and 15 mM of MgCl2 pH 6.5). A dark-adaptation period was set to 15 min, during which the samples were mixed and oxygen was removed by flushing with argon. was trapped in 40 to 50% of centers by three saturating flashes spaced by 120 s at room temperature. Fluorescence was monitored from submilliseconds to 100 s after each flash. Oxygen was readded to the system with a gas-tight syringe by adding oxygenated buffer to the degassed samples in different proportions. The ratio of oxygenated to degassed buffer was such that the final concentration of oxygen in the sample ranged from 30 to 230 μM. Final O2 concentrations, upon each addition, were monitored using the Ocean Optics Neofox Phase oxygen sensor. In the cases where oxygenated buffer was added without bicarbonate, the buffer was bubbled with air passed through Ca(OH)2 to remove any dissolved in the buffer due to the equilibrium of the atmospheric CO2 (58). When necessary, 1 mM bicarbonate, 10 μM DCMU, or 100 μM bromoxymil was added to the PSII samples prior to the degassing step. Further experimental details are provided in SI Appendix.
ROS Formation from O2 Reacting with a Fixed Stable Amount of Using cyt c Reduction.
Reduction of cyt c was used to quantify the concentration of generated based on known concentrations of and O2. A fixed amount of was generated following the protocol previously described for the fluorescence measurements: anaerobic, 250 μM hydroxylamine, three saturating flashes, resulting in the formation of 40 to 50% being stably trapped. The experiment was initiated by the addition of oxygenated buffer corresponding to a specific final concentration of O2, and after 2 min, the concentration of reduced cyt c was determined. The experiment was performed in the presence and in the absence of 1 mM bicarbonate using 60 nM PSII samples with 250 μM hydroxylamine in 40 mM MES and 15 mM MgCl2 pH 6.5 with additional 20 μM cyt c and 500 U mL−1 catalase. Catalase was added to remove any H2O2 generated by spontaneous dismutation of , which could oxidize cyt c by diminishing the signal. The samples containing were treated in the same way as for the fluorescence studies. The cyt c absorbance spectrum was measured using a Shimadzu UV-1601PC UV-Visible spectrophotometer, and the absorbance peak at 550 nm was used to determine the concentration of reduced cyt c. SI Appendix provides details on the ROS formation studied under continuous light conditions using cyt c reduction.
Formation Studied Using EPR.
was trapped using DIPPMPO and spectra measured with Magnettech Miniscope MS5000. The 50-μL capillary tubes contained 60 μg mL−1 PSII, 10 mM DIPPMPO (28), 500 U mL−1 catalase, and 12 mM bicarbonate. Samples were illuminated for 2, 10, and 20 min using 50 μmol photons m−2 s−1 of red light (590 nm longpass filter) prior to measuring spectra. PSII in working buffer had removed when necessary by either bubbling with dry N2 or with air through Ca(OH)2 (58). Catalase and DIPPMPO were added after removal from the buffer. Spectra were measured at room temperature with 9.2-GHz microwave frequency, 100-kHz modulation frequency, 2-Gauss modulation amplitude, 3,363-Gauss field center, 150-Gauss sweep width, 3-mW microwave power, and 60-s sweep-time (59). Methylene blue was used to artificially generate 1O2 to establish that there was no interference between 1O2 generated and DIPPMPO.
Molecular Simulations.
All simulations were based on the 1.9-Å resolution crystal structure of PSII from Thermosynechococcus vulcanus (PDB ID: 3WU2) (41), which provided a better resolved QA/nonheme iron site compared to the cryoEM structure of S. oleracea (PDB ID:3JCU) (60). The plant and cyanobacterial structures are highly similar around the region studied, and the results obtained are thus likely to apply for both systems (SI Appendix, Fig. S16). The crystal structure of PSII from T. vulcanus (PDB ID: 3WU2) (41) was embedded in a 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine membrane and solvated with TIP3P water molecules and 100 mM NaCl concentration. The total system comprised ca. 425,000 atoms. Parameters for all cofactors were derived from in-house DFT calculations (cf. refs. 61–63), and the remaining system was treated using the CHARMM36 force field (64). Four independent MD simulations, 200 ns each, were carried out with the QA site modeled either in the oxidized or anionic semiquinone () state, and the nonheme iron center modeled with HCO3−-bound or without the HCO3−. The MD simulations were performed in an NPT ensemble at T = 300 K and P = 1 atmosphere and using a 1 fs integration timestep. Long-range electrostatics was treated using the particle mesh Ewald method. The system was gradually relaxed for 4 ns with harmonic restraints of 1 kcal mol−1 Å−1, followed by 20-ns equilibration without restraints, and the 200-sns production runs. All classical MD simulations were performed using NAMD2 (65), and simulations were analyzed using VMD (66). Tunnels leading to the nonheme Fe site were analyzed using CAVER (67).
DFT Active Site Models and QM/MM Calculations.
DFT models comprising the nonheme Fe2+, its four coordinating histidine residues (His215D1, His272D1, His214D2, His268D2), the QA plastoquinone, Glu244D1, Tyr246D1, Ser268D1, Glu242D2, Tyr244D2, and Lys264D2 in addition to three crystal water molecules and the CO32-/HCO3−/O2 ligand were built based on the crystal structure of PSII (PDB ID: 3WU2) (41). The Fe2+ iron was modeled in its high spin state, and anti-ferromagnetically coupled to O2 using the broken symmetry DFT approach. The quantum chemical models comprised around 160 atoms. Protein residues were cut between Cβ and Cα atoms, except for glutamate and lysine residues, which were cut at the Cγ and Cβ bond. Terminal carbon atoms were saturated by hydrogen atoms and kept fixed during geometry optimizations at the B3LYP-D3/def2-SVP/def2-TZVP (Fe)/ε = 4 level (68–70). A polarizable dielectric medium using the COSMO (71) was used to model solvation effects. Single point calculations were performed at the B3LYP-D3/def2-TZVP/ε = 4 level as well as by using with B3LYP* (72), CAM-B3LYP (73), CAMh-B3LYP (74), and BHLYP (68) functionals. All calculations were performed using TURBOMOLE v. 7.2/v. 7.5 (75) and the electronic structure was visualized using VMD (66). Hybrid QM/MM calculations were performed based on the MD relaxed crystal structure of PSII (Molecular Simulations). The QM region was defined as in the DFT models but by additionally including the backbone of Ala260D2 and Phe261D2 to provide stabilization of the semiquinone at the QA site. Link atoms were introduced between Cα and Cβ atoms, and the QM/MM systems were relaxed using an adopted basis Newton-Raphson optimizer, followed by QM/MM dynamics at T = 310 K using a 1-fs integration time step. A 12-Å sphere around the QM region was allowed to relax during the QM/MM simulations. The QM/MM calculations were initiated from the state with an HCO3− or O2 bound to the nonheme Fe site. All QM/MM calculations were performed using an in-house version of the CHARMM/TURBOMOLE interface (76).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Royal Society Wolfson Research Merit Award (to A.W.R.), Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council Grants BB/K002627/1 (to A.W.R.) and BB/R00921X (to A.F. and A.W.R.), the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation (V.R.I.K.), and the Technische Universität München (TUM) Global Incentive Fund, funded under the Excellence Strategy of the Federal Government and the Länder (to V.R.I.K. and A.W.R.) as part of the TUM-Imperial College strategic partnership. This work was also supported by the Swedish National Infrastructure for Computing (SNIC 2020/1-38, SNIC 2021/1-40) at the High Performance Computing Centre, partially funded by the Swedish Research Council through Grant Agreement 016-07213.
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at https://www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.2116063119/-/DCSupplemental.
Data Availability
All study data are included in the article and/or SI Appendix.
References
- 1.Rappaport F., Diner B., Primary photochemistry and energetics leading to the oxidation of the (Mn)4Ca cluster and to the evolution of molecular oxygen in Photosystem II. Coord. Chem. Rev. 252, 259–272 (2008). [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dau H., Zaharieva I., Principles, efficiency, and blueprint character of solar-energy conversion in photosynthetic water oxidation. Acc. Chem. Res. 42, 1861–1870 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cardona T., Sedoud A., Cox N., Rutherford A. W., Charge separation in photosystem II: A comparative and evolutionary overview. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1817, 26–43 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.De Causmaecker S., Douglass J. S., Fantuzzi A., Nitschke W., Rutherford A. W., Energetics of the exchangeable quinone, QB, in Photosystem II. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 116, 19458–19463 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rutherford A. W., Crofts A. R., Inoue Y., Thermoluminescence as a probe of Photosystem II photochemistry. The origin of the flash-induced glow peaks. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 682, 457–465 (1982). [Google Scholar]
- 6.Van Gorkom H. J., Electron transfer in photosystem II. Photosynth. Res. 6, 97–112 (1985). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rutherford A. W., Paterson D. R., Mullet J. E., A light-induced spin-polarized triplet detected by EPR in photosystem II reaction centers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 635, 205–214 (1981). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Keren N., Berg A., van Kan P. J., Levanon H., Ohad I., Mechanism of Photosystem II photoinactivation and D1 protein degradation at low light: The role of back electron flow. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94, 1579–1584 (1997). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Johnson G. N., Rutherford A. W., Krieger A., A change in the midpoint potential of the quinone QA in Photosystem II associated with photoactivation of oxygen evolution. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 1229, 202–207 (1995). [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rutherford A. W., Osyczka A., Rappaport F., Back-reactions, short-circuits, leaks and other energy wasteful reactions in biological electron transfer: Redox tuning to survive life in O(2). FEBS Lett. 586, 603–616 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dietz K.-J., Turkan I., Krieger-Liszkay A., Redox- and reactive oxygen species-dependent signaling into and out of the photosynthesizing chloroplast. Plant Physiol. 171, 1541–1550 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cleland R. E., Grace S. C., Voltammetric detection of superoxide production by photosystem II. FEBS Lett. 457, 348–352 (1999). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pospísil P., Production of reactive oxygen species by photosystem II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1787, 1151–1160 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pospíšil P., Production of reactive oxygen species by photosystem II as a response to light and temperature stress. Front. Plant Sci. 7, 1950 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kozuleva M. A., Ivanov B. N., Vetoshkina D. V., Borisova-Mubarakshina M. M., Minimizing an electron flow to molecular oxygen in photosynthetic electron transfer chain: An evolutionary view. Front. Plant Sci. 11, 211 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Frankel L. K., Sallans L., Limbach P. A., Bricker T. M., Oxidized amino acid residues in the vicinity of Q(A) and Pheo(D1) of the photosystem II reaction center: Putative generation sites of reducing-side reactive oxygen species. PLoS One 8, e58042 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Crofts A. R., Wraight C. A., The electrochemical domain of photosynthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 726, 149–185 (1983). [Google Scholar]
- 18.Vass I., Kirilovsky D., Etienne A.-L., UV-B radiation-induced donor- and acceptor-side modifications of photosystem II in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Biochemistry 38, 12786–12794 (1999). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Guiles R. D., et al. , The S0 state of photosystem II induced by hydroxylamine: Differences between the structure of the manganese complex in the S0 and S1 states determined by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Biochemistry 29, 486–496 (1990). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bouges-Bocquet B., Limiting steps in photosystem II and water decomposition in Chlorella and spinach chloroplasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 292, 772–785 (1973). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Johnson G. N., Boussac A., Rutherford A. W., The origin of 40–50°C thermoluminescence bands in Photosystem II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 1184, 85–92 (1994). [Google Scholar]
- 22.Joliot A., Joliot P., Etude cinétique de la réaction photochimique libérant l’oxygène au cours de la photosynthèse. C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris 258, 4622–4625 (1964). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lavergne J., Trissl H. W., Theory of fluorescence induction in photosystem II: Derivation of analytical expressions in a model including exciton-radical-pair equilibrium and restricted energy transfer between photosynthetic units. Biophys. J. 68, 2474–2492 (1995). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Krieger-Liszkay A., Rutherford A. W., Influence of herbicide binding on the redox potential of the quinone acceptor in photosystem II: Relevance to photodamage and phytotoxicity. Biochemistry 37, 17339–17344 (1998). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Govindjee J. J., Eaton-Rye J. J., Electron transfer through photosystem II acceptors: Interaction with anions. Photosynth. Res. 10, 365–379 (1986). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sedoud A., et al. , Semiquinone-iron complex of photosystem II: EPR signals assigned to the low-field edge of the ground state doublet of QA•-Fe2+ and QB•-Fe2+. Biochemistry 50, 6012–6021 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Steffen-Heins A., Steffens B., EPR spectroscopy and its use in planta—A promising technique to disentangle the origin of specific ROS. Front. Environ. Sci. 3, 15 (2015). [Google Scholar]
- 28.Abbas K., et al. , Medium-throughput ESR detection of superoxide production in undetached adherent cells using cyclic nitrone spin traps. Free Radic. Res. 49, 1122–1128 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ananyev G., Renger G., Wacker U., Klimov V., The photoproduction of superoxide radicals and the superoxide dismutase activity of Photosystem II. The possible involvement of cytochrome b559. Photosynth. Res. 41, 327–338 (1994). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Larom S., Salama F., Schuster G., Adir N., Engineering of an alternative electron transfer path in photosystem II. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 9650–9655 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bondarava N., et al. , Putative function of cytochrome b559 as a plastoquinol oxidase. Physiol. Plant. 138, 463–473 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Borisova-Mubarakshina M. M., Vetoshkina D. V., Ivanov B. N., Antioxidant and signaling functions of the plastoquinone pool in higher plants. Physiol. Plant. 166, 181–198 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Brinkert K., De Causmaecker S., Krieger-Liszkay A., Fantuzzi A., Rutherford A. W., Bicarbonate-induced redox tuning in Photosystem II for regulation and protection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113, 12144–12149 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Shevela D., Eaton-Rye J. J., Shen J.-R., Govindjee, Photosystem II and the unique role of bicarbonate: A historical perspective. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1817, 1134–1151 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.de Wijn R., van Gorkom H. J., Kinetics of electron transfer from Q(a) to Q(b) in photosystem II. Biochemistry 40, 11912–11922 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cox N., et al. , The semiquinone-iron complex of photosystem II: Structural insights from ESR and theoretical simulation; evidence that the native ligand to the non-heme iron is carbonate. Biophys. J. 97, 2024–2033 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nixon P. J., Trost J. T., Diner B. A., Role of the carboxy terminus of polypeptide D1 in the assembly of a functional water-oxidizing manganese cluster in photosystem II of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803: Assembly requires a free carboxyl group at C-terminal position 344. Biochemistry 31, 10859–10871 (1992). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zimmermann K., et al. , Herbicide binding and thermal stability of photosystem II isolated from Thermosynechococcus elongatus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1757, 106–114 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zabret J., et al. , Structural insights into photosystem II assembly. Nat. Plants 7, 524–538 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wass J. R. T. J., Ahlberg E., Panas I., Schiffrin D. J., Quantum chemical modelling of the rate determining step for oxygen reduction on quinones. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 8, 4189–4199 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Umena Y., Kawakami K., Shen J.-R., Kamiya N., Crystal structure of oxygen-evolving photosystem II at a resolution of 1.9 Å. Nature 473, 55–60 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wraight C. A., Modulation of herbicide-binding by the redox state of Q400, an endogenous component of Photosystem II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 809, 320–330 (1985). [Google Scholar]
- 43.Diner B. A., Petrouleas V., Light-induced oxidation of the acceptor-side Fe(II) of Photosystem II by exogenous quinones acting through the QB binding site. II. Blockage by inhibitors and their effects on the Fe(III) EPR spectra. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 893, 138–148 (1987). [Google Scholar]
- 44.Diner B. A., Petrouleas V., Q400, the non-heme iron of the photosystem II iron-quinone complex. A spectroscopic probe of quinone and inhibitor binding to the reaction center. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 895, 107–125 (1987). [Google Scholar]
- 45.Snel J. F. H., van Rensen J. J. S., Kinetics of the reactivation of the Hill reaction in CO2-depleted chloroplasts by addition of bicarbonate in the absence and in the presence of herbicides. Physiol. Plant. 57, 422–427 (1983). [Google Scholar]
- 46.Blubaugh D. J., Govindjee, Comparison of bicarbonate effects on the variable chlorophyll a fluorescence of CO2-depleted and non-CO2-depleted thylakoids in the presence of diuron. Z. Naturforsch. C 39, 378–381 (1984). [Google Scholar]
- 47.Pospísil P., Arató A., Krieger-Liszkay A., Rutherford A. W., Hydroxyl radical generation by photosystem II. Biochemistry 43, 6783–6792 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wardman P., Reduction potentials of one‐electron couples involving free radicals in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 18, 1637–1755 (1989). [Google Scholar]
- 49.Chernev P., Zaharieva I., Dau H., Haumann M., Carboxylate shifts steer interquinone electron transfer in photosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 5368–5374 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Schmitt F.-J., et al. , Reactive oxygen species: Re-evaluation of generation, monitoring and role in stress-signaling in phototrophic organisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1837, 835–848 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Noctor G., Reichheld J.-P., Foyer C. H., ROS-related redox regulation and signaling in plants. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 80, 3–12 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Chen L., et al. , Protecting effect of phosphorylation on oxidative damage of D1 protein by down-regulating the production of superoxide anion in photosystem II membranes under high light. Photosynth. Res. 112, 141–148 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Poudyal R. S., Nath K., Zulfugarov I. S., Lee C.-H., Production of superoxide from photosystem II-light harvesting complex II supercomplex in STN8 kinase knock-out rice mutants under photoinhibitory illumination. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 162, 240–247 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zulfugarov I. S., et al. , Production of superoxide from Photosystem II in a rice (Oryza sativa L.) mutant lacking PsbS. BMC Plant Biol. 14, 242 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Głowacka K., et al. , Photosystem II Subunit S overexpression increases the efficiency of water use in a field-grown crop. Nat. Commun. 9, 868 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Roach T., Sedoud A., Krieger-Liszkay A., Acetate in mixotrophic growth medium affects photosystem II in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and protects against photoinhibition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1827, 1183–1190 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Messant M., et al. , Glycolate induces redox tuning of photosystem II in vivo: Study of a photorespiration mutant. Plant Physiol. 177, 1277–1285 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Korshunov S., Imlay J. A., Detection and quantification of superoxide formed within the periplasm of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 188, 6326–6334 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Fufezan C., Rutherford A. W., Krieger-Liszkay A., Singlet oxygen production in herbicide-treated photosystem II. FEBS Lett. 532, 407–410 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Wei X., et al. , Structure of spinach photosystem II-LHCII supercomplex at 3.2 Å resolution. Nature 534, 69–74 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Ugur I., Rutherford A. W., Kaila V. R. I., Redox-coupled substrate water reorganization in the active site of Photosystem II—The role of calcium in substrate water delivery. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1857, 740–748 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Boussac A., et al. , The low spin-high spin equilibrium in the S2-state of the water oxidizing enzyme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 1859, 342–356 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Suomivuori C.-M., Winter N. O. C., Hättig C., Sundholm D., Kaila V. R. I., Exploring the light-capturing properties of photosynthetic chlorophyll clusters using large-scale correlated calculations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 12, 2644–2651 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Huang J., et al. , CHARMM36m: An improved force field for folded and intrinsically disordered proteins. Nat. Methods 14, 71–73 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Phillips J. C., et al. , Scalable molecular dynamics on CPU and GPU architectures with NAMD. J. Chem. Phys. 153, 044130 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Humphrey W., Dalke A., Schulten K., VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 14, 33–38, 27–28 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Chovancova E., et al. , CAVER 3.0: A tool for the analysis of transport pathways in dynamic protein structures. PLoS Comput. Biol. 8, e1002708 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Becke A. D., Density‐functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 98, 5648–5652 (1993). [Google Scholar]
- 69.Lee C., Yang W., Parr R. G., Development of the Colle–Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 37, 785–789 (1988). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Schäfer A., Horn H., Ahlrichs R., Fully optimized contracted Gaussian basis sets for atoms Li to Kr. J. Chem. Phys. 97, 2571–2577 (1992). [Google Scholar]
- 71.Klamt A., Schüürmann G., COSMO: A new approach to dielectric screening in solvents with explicit expressions for the screening energy and its gradient. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 799–805 (1993). [Google Scholar]
- 72.Reiher M., Salomon O., Artur Hess B., Reparameterization of hybrid functionals based on energy differences of states of different multiplicity. Theor. Chem. Acc. 107, 48–55 (2001). [Google Scholar]
- 73.Yanai T., Tew D. P., Handy N. C., A new hybrid exchange–correlation functional using the Coulomb-attenuating method (CAM-B3LYP). Chem. Phys. Lett. 393, 51–57 (2004). [Google Scholar]
- 74.Shao Y., Mei Y., Sundholm D., Kaila V. R. I., Benchmarking the performance of time-dependent density functional theory methods on biochromophores. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 16, 587–600 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Ahlrichs R., Bär M., Häser M., Horn H., Kölmel C., Electronic structure calculations on workstation computers: The program system turbomole. Chem. Phys. Lett. 162, 165–169 (1989). [Google Scholar]
- 76.Riahi S., Rowley C. N., The CHARMM-TURBOMOLE interface for efficient and accurate QM/MM molecular dynamics, free energies, and excited state properties. J. Comput. Chem. 35, 2076–2086 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All study data are included in the article and/or SI Appendix.