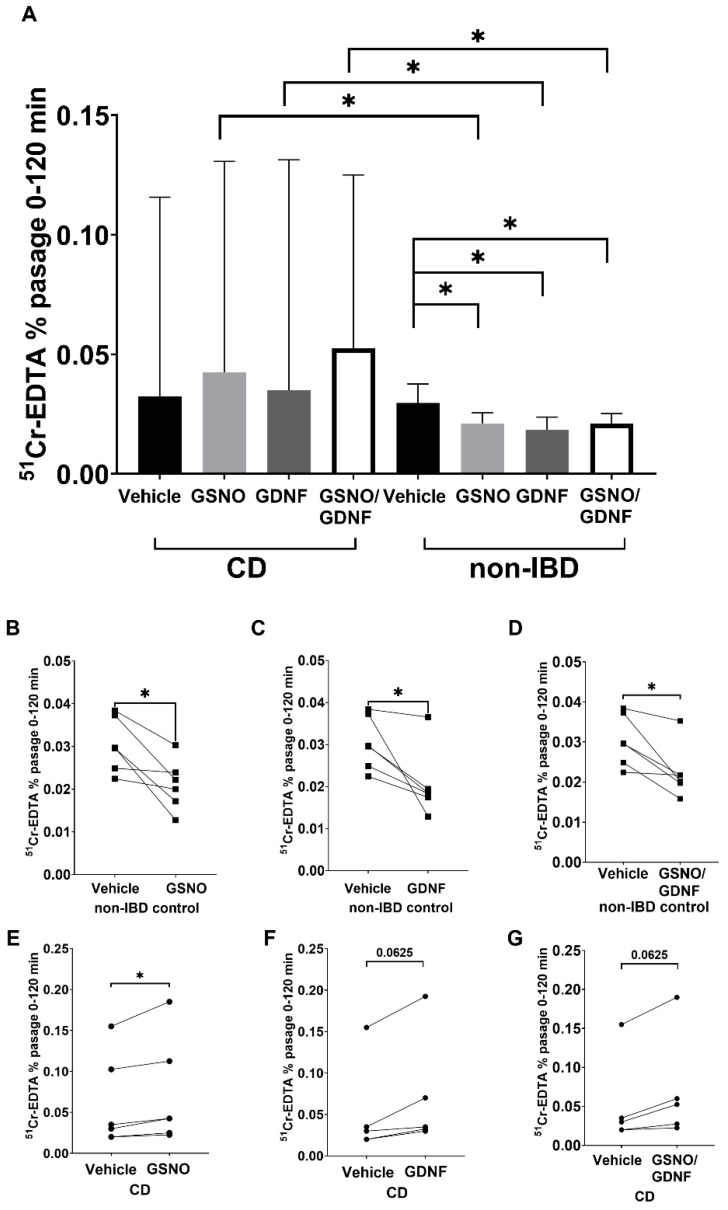
Figure 6.
Enteric glial cells (EGC) mediators increase epithelial barrier function in non-inflammatory bowel disease (non-IBD) controls while decrease it in Crohn’s disease (CD) patients. (A) Paracellular permeability of 51Chromium-EDTA (51Cr-EDTA) through the epithelium of non-IBD controls and in CD patients in the presence of vehicle or EGC mediator S-nitroglutathione (GSNO), glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), or the combination of both (GSNO/GDNF). (B) 51Cr-EDTA permeability through the epithelium of non-IBD controls with and without stimulation with GSNO. (C) 51Cr-EDTA permeability through the epithelium of non-IBD controls with and without stimulation with GDNF. (D) 51Cr-EDTA permeability through the epithelium of non-IBD controls with and without stimulation with GSNO/GDNF. (E) 51Cr-EDTA permeability through the epithelium of CD patients with and without stimulation with GSNO. (F) 51Cr-EDTA permeability through the epithelium of CD patients with and without stimulation with GDNF. (G) 51Cr-EDTA permeability through the epithelium of CD patients with and without stimulation with GSNO/GDNF. Mann–Whitney U test was used for comparisons between groups and Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test for paired data, * p < 0.05.