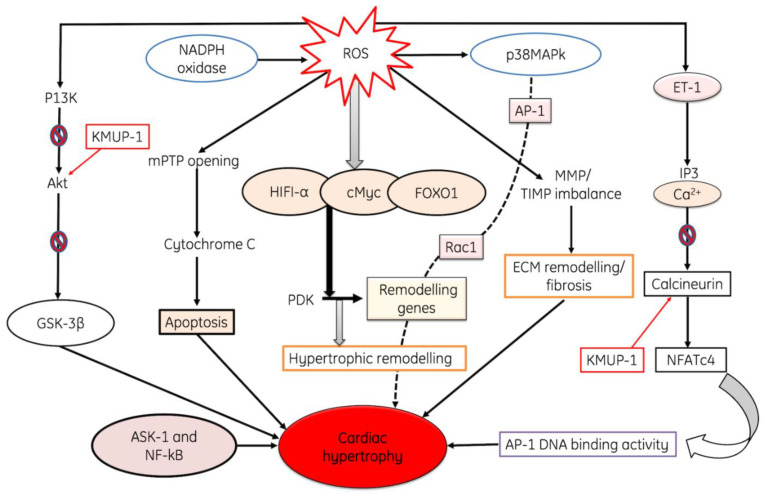
Figure 6.
The diagram shows ROS-induced cardiac hypertrophy through the up-regulation of various pathways. ROS induces the activation of endotjelin-1 protein which in turn causes break down of PIP3 into IP3 and DAG, both of these activates the calcium channels and releases calcium from endoplasmic reticulum. Liberation of Ca from ER inhibits the activation of Calcineurin, also mediated by KMUP-1, and finally causes cardiac hypertrophy through the activation of AP-1DNA binding activity of NFATc4. Moreover, ROS activates HIFI-1, FOXO-α and Myc pathways and leads to the activation of hypertrophic remodeling. ROS also induce cardiac hypertrophy through the opening of mPTP channel, release of cytochrome C and induction of apoptosis of myocardial muscles. Additionally, ROS induces inhibition of P13K, Akt and GSK-3β. All these pathways induce cardiac hypertrophy, where ET-1: Endothelin-1, mPTP: Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore, ASK-1: Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase-1, MMP. TIMP: Matrix metalloproteinase/Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases, AP-1: Activator protein 1, NF-κβ: Nuclear factor-κ Beta, KATP; ATP-sensitive potassium, NADPH oxidase: Nicotinamide dinucleotide phosphate reduced, p38MAPK; p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases, HIFA-α; Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha, FOXO1; Fork-head box transcription factors, PDK: Protein 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase, NLRP: Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, MCP: Monocyte Chemo-attractant Protein, TNF-α:Tumor necrosis factor alpha, IL-1β: Interleukin-1 beta.