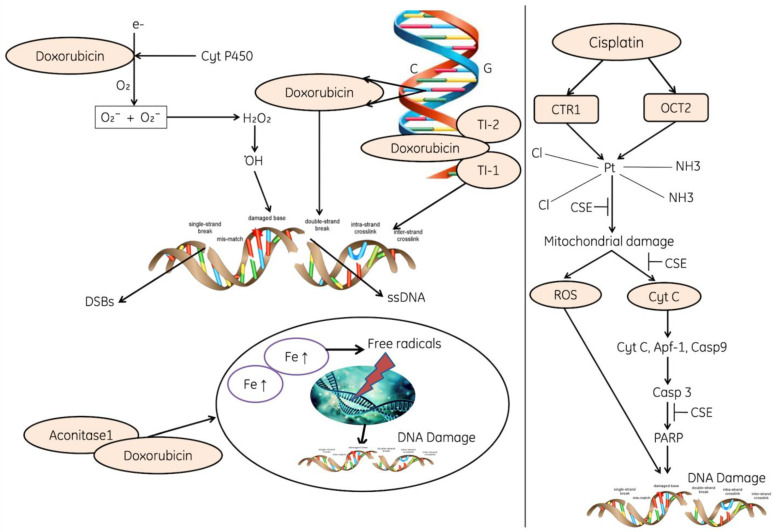
Figure 11.
The diagram reflecting the role of cisplatin and Doxorubicin in the initiation of oxidative stress and molecular changes. Cisplatin activates the CTR1 and OCT2, damage in mitochondria (perforations), release of cytochrome, apoptosis and fragmentation in DNA. Doxorubicin induces the production of superoxides and peroxide production; ROS inhibit the enzymatic activities. Doxorubicin directly binds to the aconitase enzymes, enters into the nucleus and leads the ROS-induced DNA damage, where CRT1: The copper transporter CTR1 regulates1, OCT2; Organic cation transporter 2, PARP: poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase, APf-1: Apoptotic protease factor 1, Cyt C: Cytochrome C, Casp3, 9: Caspase3 and 9, and DSBs: Double-stranded breaks.NH3, Cl, CSE. Note: Dot (.) designates free radical.