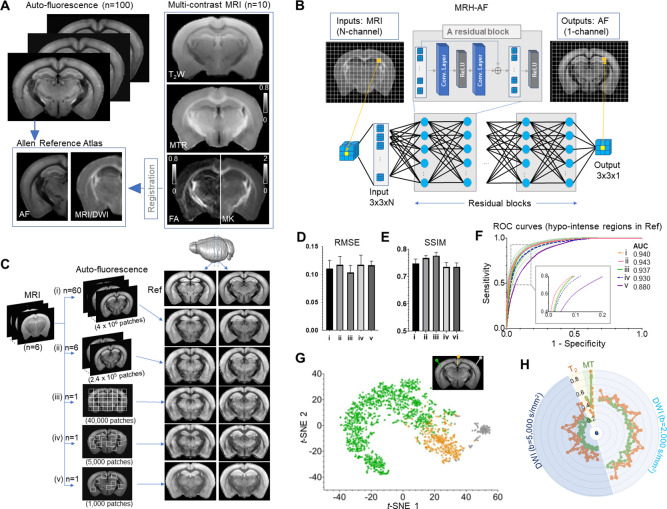
Figure 1. Connect multi-contrast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and auto-fluorescence (AF) data of the mouse brain using deep learning.
(A) T2-weighted (T2W), magnetization transfer ratio (MTR), and diffusion-weighted images (DWIs) were registered to the Allen Reference Atlas (ARA) space, from which 100 already registered AF data were selected and down-sampled to the same resolution of the MRI data. Parameter maps derived from DWI, for example, fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean kurtosis (MK), were also included in this study. (B) The deep convolutional neural network (CNN) contained 64 layers (two layers for each residual block × 30 residual blocks plus four additional layers at the input and output ends) and was trained using multiple 3 × 3 MRI patches as inputs and corresponding 3 × 3 patches from histology as targets. (C) The CNN was trained using the MRI data (n = 6) and different amounts of randomly selected AF data (i–v). The results generated by applying the CNN to a separate set of MRI data (n = 4) were shown on the right for visual comparison with the reference (Ref: average AF data from 1675 subject). (D–E) Quantitative evaluation of the results in C with respect to the reference using root mean square error (RMSE) and structural similarity indices (SSIM). The error bars indicate the standard deviations due to random selections of AF data used to train the network. (F) The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of the results in C in identifying hypo-intense structures in the reference and their areas under the curve (AUCs). The ROC curves from 25 separate experiments in (iii) (light green) show the variability with respect to the mean ROC curve (dark green) due to inter-subject variations in AF intensity. (G) The distribution of randomly selected 3 × 3 MRI patches in the network’s two-dimensional (2D) feature space, defined using the t-SNE analysis based on case (iii) in C, shows three clusters of patches based on the intensity of their corresponding patches in the reference AF data (turquoise: hyper-intense, orange: hypo-intense; gray: brain surfaces). (H) MRI signals from two representative patches with hyper-intense AF signals (turquoise) and two patches with hypo-intense AF signals (orange). The orange profiles show higher DWI signals and larger oscillation among them than the turquoise profiles (both at b = 2000 and 5000 s/mm2).
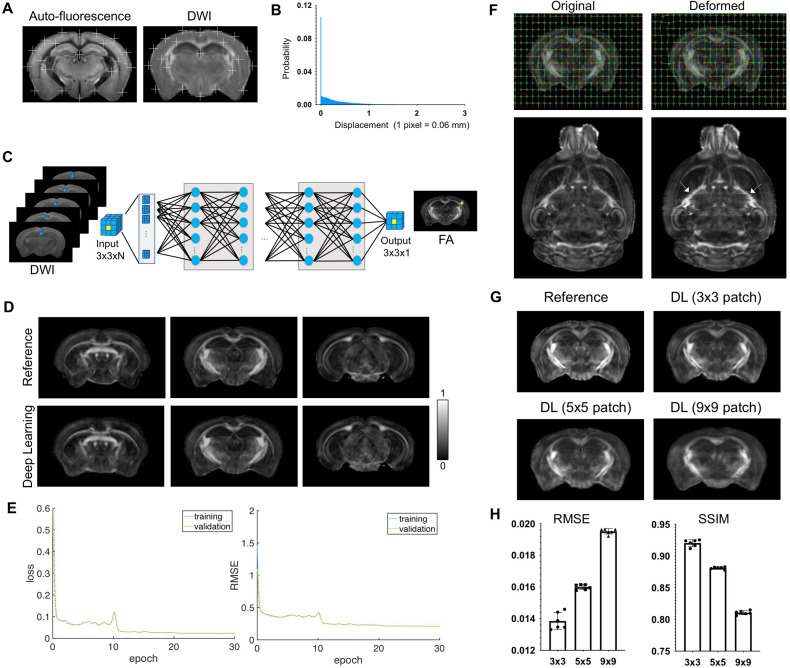
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Evaluate the effects of mismatches between input magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data and target auto-fluorescence (AF) data on deep learning outcomes.
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. Training convergence curves of MRH auto-fluorescence (MRH-AF) network (A–B) and MRH myelin basic protein (MRH-MBP) during transfer learning.
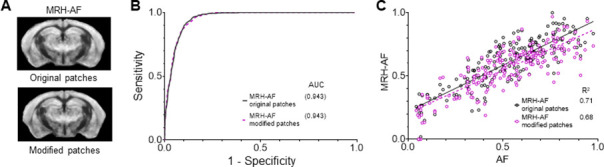
Figure 1—figure supplement 3. Evaluation of MRH auto-fluorescence (MRH-AF) results generated using modified 3 × 3 patches with nine voxels assigned the same values as the center voxel as inputs.