In the article titled “Responsive Inverse Opal Scaffolds with Biomimetic Enrichment Capability for Cell Culture” [1], there was an error in Figure 6e. The scale on the y-axis was written as 0-100, whereas it should have been 0-1000. This error was introduced during the production process, and the publisher apologises for this error. The corrected figure is shown below:
Figure 1.
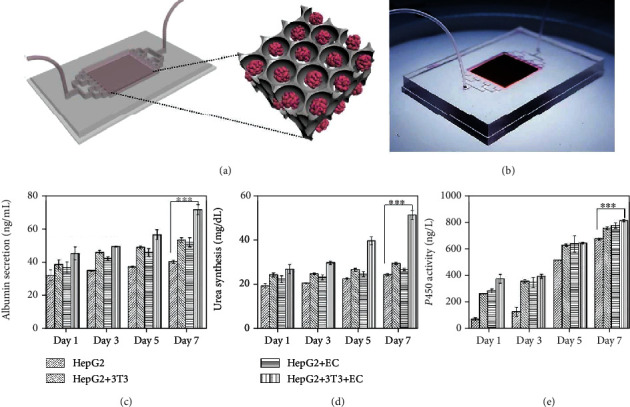
The applications of the GO hydrogel scaffolds in a liver-on-a-chip system. (a) Schematic of the construction of the liver-on-a-chip. (b) Image of the GO hydrogel scaffold-integrated liver-on-a-chip. (c–e) Albumin secretion (c), urea synthesis (d), and cytochrome P450 expression (e) of HepG2 after coculture with 3T3, ECs, and both 3T3 and ECs in the liver-on-a-chip system for 7 days; ∗∗∗p < 0.01.
References
- 1.Shao C., Liu Y., Chi J., Wang J., Zhao Z., Zhao Y. Responsive Inverse Opal Scaffolds with Biomimetic Enrichment Capability for Cell Culture. Research . 2019;2019, article 9783793:1–10. doi: 10.34133/2019/9783793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


