Important Compound Classes
Title
Difluorocyclohexyl Derivatives as IL-17 Modulators
Patent Publication Number
WO 2021/204801 A1
Publication Date
October 14, 2021
Priority Application
GB 2005153.8 and GB 2009617.8
Priority Date
April 7, 2020, and June 24, 2020
Inventors
Chovatia, P. T.; Foley, A. M.; Haslett, G. W.; Hutchings, M. C.; Johnson, J. A.; Lecomte, F. C.; Monck, N. J. T.; Quincey, J. R.; Rampalakos, K.; Reuberson, J. T.; Smalley, A. P.; Trani, G.; Vaidya, D. G.
Assignee Company
UCB Biopharma SRL, Belgium
Disease Area
Inflammatory and autoimmune diseases
Biological Target
IL-17
Summary
The interleukin (IL)-17 or IL-17A is a proinflammatory cytokine and the founder member of the IL-17 family. Subsequently, five additional members of the family (IL-17B to IL-17F) have been identified, including the most closely related, IL-17F (ML-1), which shares approximately 55% amino acid sequence homology with IL-17A. IL-17A and IL-17F are expressed by the recently defined autoimmune related subset of T helper cells, TH17, that also express IL-21 and IL-22 signature cytokines. IL-17A and IL-17F are expressed as homodimers but may also be expressed as the IL-17A/F heterodimer. IL-17A and IL-17F signal through the receptors IL-17R, IL-17RC, or an IL-17RA/RC receptor complex. Both IL-17A an IL-17F have been associated with a number of autoimmune diseases.
The present application describes a series of novel difluorocyclohexyl derivatives as IL-17 modulators for the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Further, the application discloses compounds, their preparation, use, pharmaceutical composition, and treatment.
Definitions
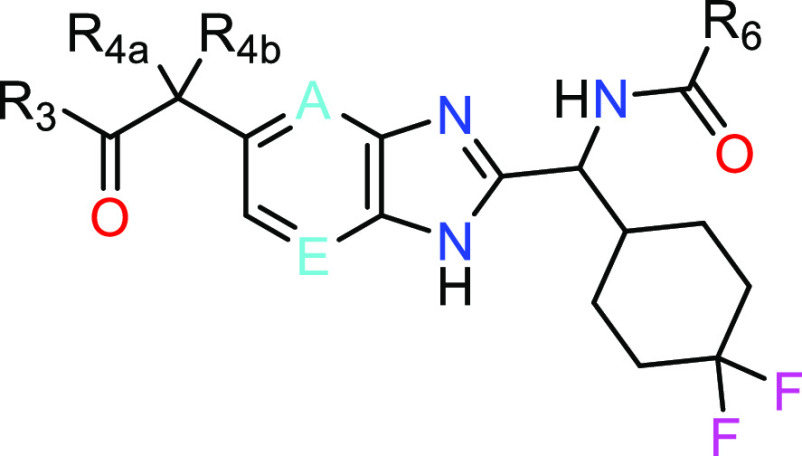
A = C-R1 or N; E = C-R2 or N; R3 = −NR3aR3b;
R4a = H, F, OH; or R4a = C1–4 alkyl, optionally substituted by one or more substituents;
R4b = H, F, or C1–4 alkyl; and
R6 = −OR6a or −NR6bR6c or R6 = C1–6 alkyl, C3–9 cycloalkyl, C3–9 cycloalkyl(C1–6)alkyl, aryl, aryl(C1–6) alkyl, C3–7 heterocycloalkyl, C3–7 heterocycloalkyl(C1–6)alkyl, heteroaryl or heteroaryl(C1–6) alkyl), any of which group may be optionally substituted by one or more substituents.
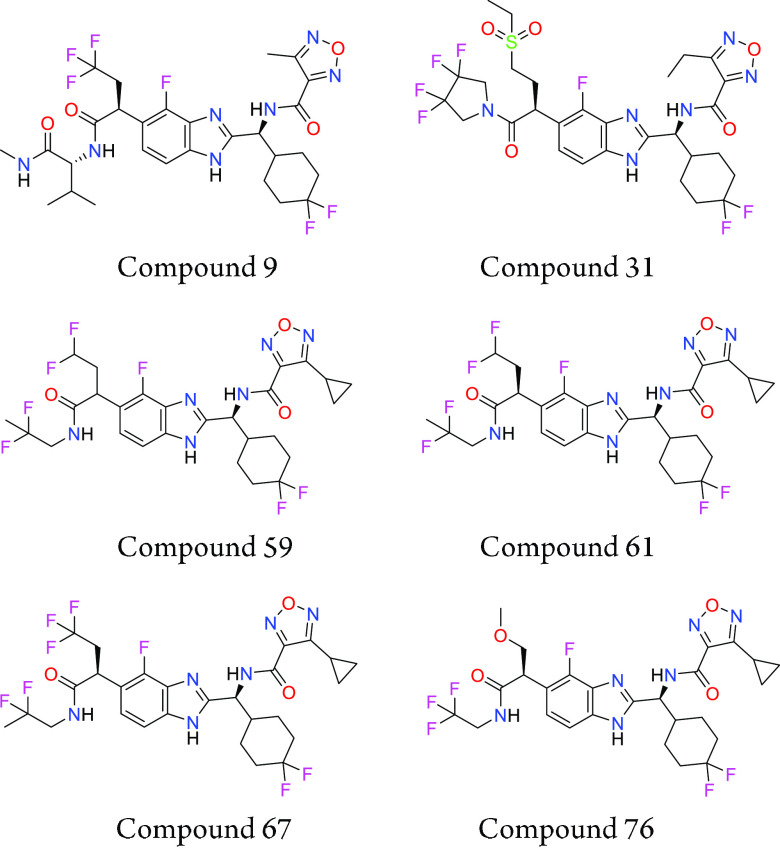
Key Structures
Biological Assay
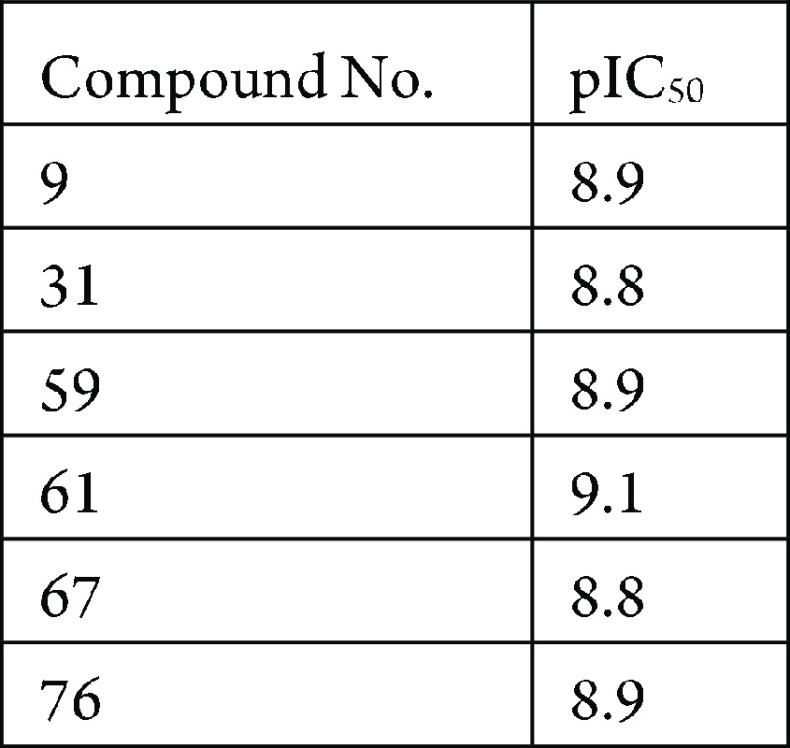
The inhibition of IL-17A-induced IL-6 release from the human dermal fibroblast (HDF) cell line assay was performed. The compounds described in this application were tested for their ability to inhibit IL-17. The IL-17 pIC50 are shown in the following table.
Biological Data
The table below shows representative compounds were tested for IL-17 inhibition. The biological data obtained from testing representative examples are listed in the following table.
Claims
Total claims: 21
Compound claims: 15
Pharmaceutical composition claims: 2
Method of treatment claims: 2
Use of compound claims: 2
Recent Review Articles
-
1.
Ghoreschi K.; Balato A.; Enerback C.; Sabat R.. Lancet 2021, 397, 754.
-
2.
Loft N.; Halling A.; Egeberg A.; Skov L.. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, 130.
-
3.
Marson J. W.; Snyder M. L.; Lebwohl M. G.. Med. Clin. North Am. 2021, 105, 627.
-
4.
Griffiths C. E. M.; Armstrong A. W.; Gudjonsson J. E.; Barker J. N. W. N.. Lancet 2021, 397, 1301.
-
5.
Stober C.Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 35, 101694.
-
6.
Higgins E.Medicine 2021, 49, 361.
The author declares no competing financial interest.