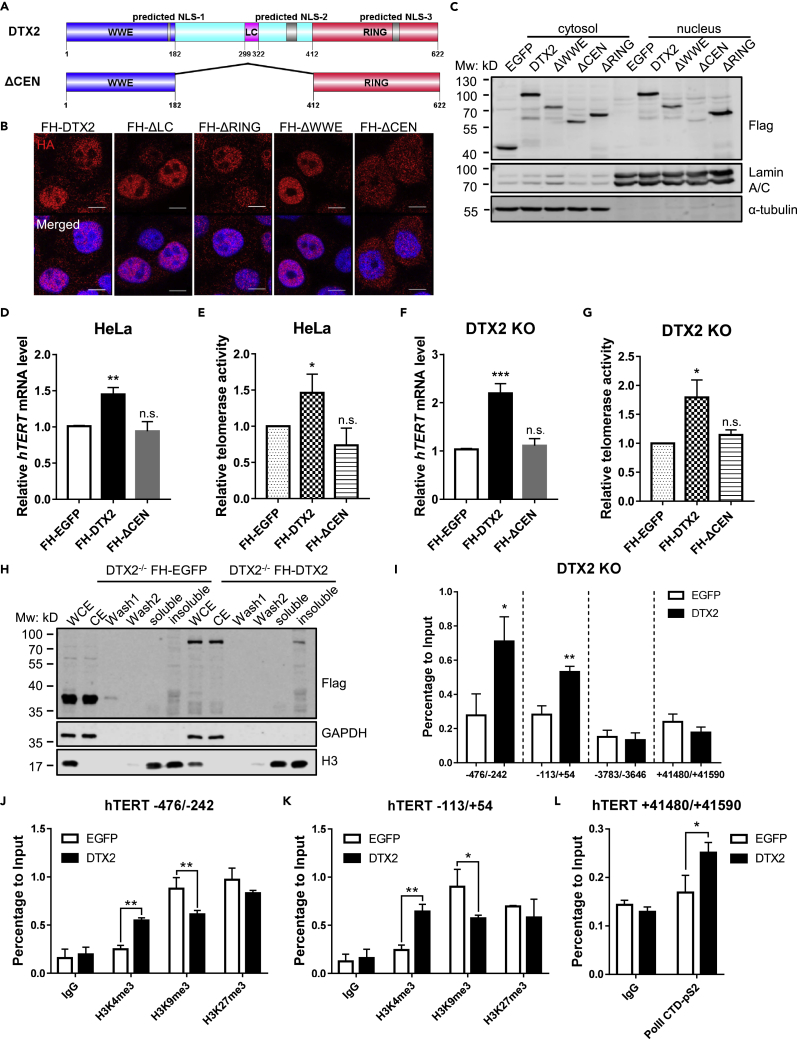
Figure 4.
DTX2 can localize to the nucleus and bind to the hTERT core promoter
(A) Schematic diagram of predicted nuclear localization signals (NLS) of DTX2 and the ΔCEN mutant.
(B and C) Full-length FH-DTX2 and its truncation mutants were expressed in HeLa cells. The localization of various DTX2 proteins was examined by immunostaining with an anti-HA antibody (scale bar: 10 μm) (B) and western blotting following cell fractionation using the indicated antibodies (C). FH-EGFP-expressing cells served as negative controls for fractionation.
(D and E) HeLa cells expressing full-length DTX2 or the ΔCEN mutant were assayed by RT-qPCR and qTRAP to determine the relative hTERT mRNA level (D) and telomerase activity (E). Data were shown as mean ± SD (N = 3). p values were calculated using Student’s t test. ∗p< 0.05; ∗∗p<0.01; n.s., not significant.
(F and G) DTX2 KO cells (#20) expressing full-length DTX2 or the ΔCEN mutant were assayed by RT-qPCR and qTRAP to determine the relative hTERT mRNA level (F) and telomerase activity (G). Data were shown as mean ± SD (N = 3). p values were calculated using Student’s t test. ∗p< 0.05; ∗∗∗p< 0.001; n.s., not significant.
(H) DTX2 KO line #20 expressing FH-EGFP or FH-DTX2 were fractionated for the chromatin association assay. Various fractions were subjected to immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies. WCE, whole cell extract. CE, cytosolic extract. Wash 1 & 2, nucleoplasmic fraction. Soluble & insoluble, chromatin fractions sensitive or resistant to micrococcal nuclease digestion.
(I) ChIP-qPCR analysis was done using cells from (H) and an anti-HA antibody. Primers span areas within the hTERT core promoter region (−113/+54 and −476/−242), upstream (∼3.7 kb) of hTERT TSS (−3,783/−3,646), or in the last exon (+41,480/+41,590). Enrichment of specific regions was normalized to input. Data were shown as mean ± SD (N = 3). p values were calculated using Student’s t test. ∗p< 0.05; ∗∗p< 0.01.
(J and K) ChIP-qPCR analysis was done using cells from (H) and anti-H3K4me3, anti-H3K9me3, and anti-H3K27me3 antibodies. Primers span areas within the hTERT core promoter region [−113/+54 (J) and −476/−242 (K)]. Enrichment of specific regions was normalized to input. Data were shown as mean ± SD (N = 2). p values were calculated using Student’s t test. ∗p< 0.05; ∗∗p< 0.01. (L) ChIP-qPCR analysis was done using cells from (H) and anti-Pol II-pS2 antibody. Primers span areas in the last exon of hTERT (+41,480/+41,590). Enrichment of specific regions was normalized to input. Data were shown as mean ± SD (N = 2). p values were calculated using Student’s t test. ∗p< 0.05.