Abstract
Plants will face increased heat stress due to rising global temperatures. Heat stress affects plant reproductive development and decreases productivity; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms of these processes are poorly characterized. Plant small RNAs (sRNAs) have important regulatory roles in plant reproductive development following abiotic stress responses. We generated sRNA transcriptomes of reproductive bud stages at three different time points to identify sRNA‐mediated pathways responsive to heat stress in flax ( Linum usitatissimum ). With added sRNA transcriptomes of vegetative tissues, we comprehensively annotated miRNA and phasiRNA‐encoding genes (PHAS) in flax. We identified 173 miRNA genes, of which 42 are newly annotated. Our analysis revealed that 141 miRNA genes were differentially accumulated between tissue types, while 18 miRNA genes were differentially accumulated in reproductive tissues following heat stress, including members of miR482/2118 and miR2275 families, known triggers of reproductive phasiRNAs. Furthermore, we identified 68 21‐PHAS flax loci from protein‐coding and noncoding regions, four 24‐PHAS loci triggered by miR2275, and 658 24‐PHAS‐like loci with unknown triggers, derived mostly from noncoding regions. The reproductive phasiRNAs are mostly downregulated in response to heat stress. Overall, we found that several previously unreported miRNAs and phasiRNAs are responsive to heat stress in flax reproductive tissues.
Keywords: flax, heat stress, microRNA, phasiRNA
1. INTRODUCTION
Agricultural production is negatively impacted by climate change, especially because of higher temperatures. The global yield of three main staple crops is estimated to be reduced by 3.2%–6.0% per 1°C increase in global mean temperature (Zhao et al., 2017). The effect of higher temperature is greater on reproductive development, especially through impacts on pollen development, pollination, and embryo formation (Hedhly et al., 2009). Although there are studies that assess the impacts of higher temperature on growth, physiological processes, and yields on crops such as wheat, maize, rice, canola, and flax (Cross et al., 2003; Pokharel et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2016; Zhao et al., 2017), limited knowledge is available on the underlying molecular mechanisms that play roles in heat stress; such knowledge would enable the development of thermo‐tolerant crops.
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) are major players in heat tolerance (Hasanuzzaman et al., 2013). HSPs are produced in response to heat stress after activation by heat stress transcription factors (HSFs) such as MULTIPROTEIN BRIDGING FACTOR 1C, WRKYGQK motif‐containing proteins, and basic leucine zipper proteins (He et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2017). Multiple thermosensors initiate HSF activation after sensing heat stress. The conserved heat tolerance process in plants involves regulatory cascades of heat‐responsive genes as well as other regulators such as noncoding RNAs that play a role in modulation of gene expression, and these noncoding molecules are yet to be identified.
Plant sRNAs are implicated in modulating expression of genes related to heat stress (He et al., 2019). These sRNAs are regulatory elements that modulate gene expression, genome‐wide, by transcriptional and post‐transcriptional gene silencing. Typically, sRNAs are 20–24 nucleotides (nt) in length and are diced by DICER‐LIKE proteins (DCLs) from hairpin or double stranded RNA precursors formed by RNA‐DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASEs (RDRs). The sRNAs form a silencing complex with Argonaute (AGO) proteins to modulate the expression of genes and transposable elements (TEs). The major classes of plant sRNAs are as follows: microRNAs (miRNAs), phased secondary small interfering RNAs (phasiRNAs), and secondary small interfering RNA (siRNAs) (Axtell, 2013; Axtell et al., 2006; Fei et al., 2013; Reinhart et al., 2002; Zhai et al., 2011).
The miRNAs are the key regulators in the attenuation of gene expression, by transcript cleavage and degradation or translation inhibition in a homology‐dependent manner (Zhai et al., 2011). There have been reports of heat‐responsive miRNAs such as miR398, miR156, miR159, miR160, miR167, miR396, and miR408 during vegetative and reproductive stages of plants like Arabidopsis, sunflower, maize, and tomato (Giacomelli et al., 2012; Guan et al., 2013; He et al., 2019; Keller et al., 2020; Lin et al., 2018; Stief et al., 2014). PhasiRNAs are generated from mRNA transcripts of coding and noncoding regions of the genome mainly after the cleavage of trigger miRNAs (Fei et al., 2013; Johnson et al., 2009; Zhai et al., 2011). A special class of phasiRNAs that are produced from trans‐acting siRNA loci (TAS) is called tasiRNAs (Fei et al., 2013; Howell et al., 2007). In Arabidopsis, tasiRNAs from the TAS1 locus are found to target transcripts of HEAT‐INDUCED TAS1 TARGET 1 (HTT1) and HTT2 proteins that accumulate in response to heat stress (Li et al., 2014). Complete loss of reproductive 24‐nt phasiRNAs after knock out of DCL5, a reproductive phasiRNA pathway gene, in maize, produces male sterility at high temperatures (Teng et al., 2020), while mutation in reproductive 21‐nt phasiRNAs‐generating loci produces photoperiod‐ and thermo‐sensitive male sterility in rice (Fan et al., 2016; Zhou et al., 2012).
Flax is a widely cultivated crop species from the family Linaceae known for oil, fiber, and medicinally important compounds. Heat stress in flax reduces boll formation and seed set, and it may be due to the failure of pollen tubes to reach ovules (Cross et al., 2003). In this study, flax plants were subjected to 7‐ and 14‐day heat treatments after flower initiation in a growth chamber to simulate heat stress conditions in the field. We harvested three reproductive bud stage tissues at three time points and generated sRNA transcriptomes to identify sRNA‐mediated pathways responsive to heat stress. With added publicly available sRNA transcriptomes of leaves, stem, and root, we comprehensively annotated miRNA‐ and phasiRNA‐ spawning genes (PHAS) in flax. We found that several miRNAs and both types of reproductive phasiRNAs (21 and 24 nt) are mostly downregulated in response to heat stress. Overall, we found that several previously unreported flax miRNAs and phasiRNAs are responsive to heat stress in reproductive tissues.
2. RESULTS
2.1. Comprehensive annotation of miRNA in flax
In the latest release of miRBase version 22 (http://www.mirbase.org), there are 124 miRNA precursors deposited for flax, mainly identified from computational approaches (Barvkar et al., 2013). There are studies that annotated flax miRNAs based on sRNA sequencing in control, nutrient, saline, and alkaline stress conditions (Melnikova et al., 2016; Yu et al., 2016), but their miRNA lists are not available from miRBase; these studies predicted a high number of novel candidate miRNAs (233–475), in addition to observing known miRNAs, suggesting that most of them may be false positives. Because the highly studied model plant Arabidopsis only has a few hundred miRNAs, caution may be warranted for reports of more than 100 novel miRNAs in a species (Axtell & Meyers, 2018). Further, all these flax miRNA identifications were carried out using an older scaffold‐based genome (Wang et al., 2012). Recently, a chromosome‐scale genome assembly has been released for flax (You et al., 2018).
To comprehensively annotate miRNA precursors in the latest flax genome assembly version 2 (ASM22429v2) (You et al., 2018), sRNA libraries were sequenced from leaves, stem, and root tissues. In addition, to identify heat‐responsive miRNAs in flax, sRNA transcriptomes from reproductive bud stages (Figure S1a) at three time points were sequenced (see Section 4 for details). In total, we generated 24 sRNA libraries, and clean reads (after removing rRNA/tRNA sequences) were used for miRNA prediction (Table S1). To accurately identify miRNA precursors, we used ShortStack and miR‐PREFeR, some of the best‐performing miRNA annotation tools in terms of precision and accuracy (Johnson et al., 2016; Lei & Sun, 2014). We identified 173 candidate miRNA precursors yielding 106 nonredundant mature miRNAs (Figure 1, outer circle; Table S2). Among them, 131 precursors produced known miRNAs, while 42 precursors generated novel miRNAs which contained at least five variants (mismatches plus unaligned nucleotides) with Viridiplantae miRNAs derived from miRBase version 22. We identified miRNAs from 31 known miRNA families; among them, the families having the greatest numbers of precursors encoded into the genome were miR167 (14), miR482/2118 (12), miR156 (11), miR166 (9), and miR160 (9) (Figure S1b, Table S2).
FIGURE 1.
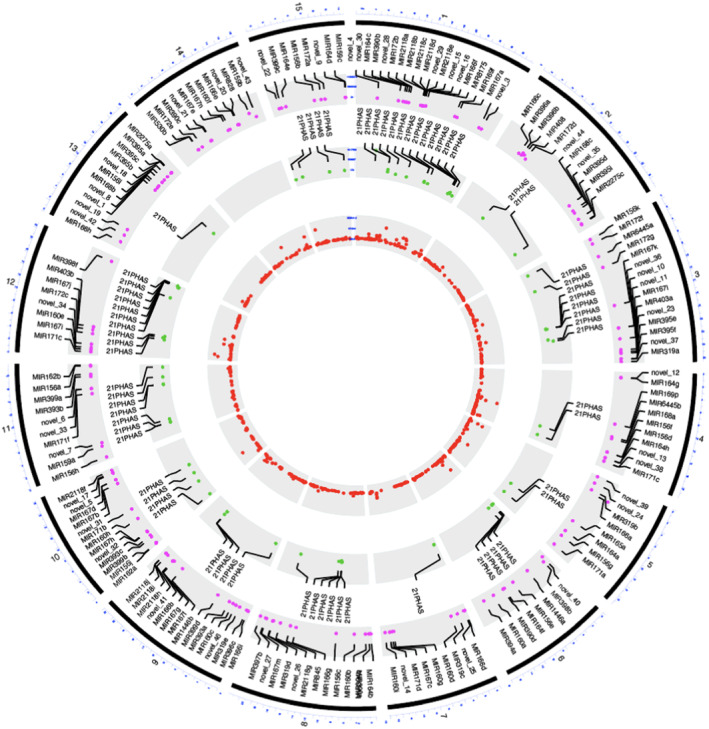
Genome‐wide distribution of MIR genes and PHAS loci in flax. Chromosomal position of 173 MIR genes (outer circle, pink dots), 68 21‐PHAS loci (middle circle, green dots), and 662 24‐PHAS/24‐PHAS‐like loci (inner cycle, red dots). The MIR genes and 21‐PHAS loci were annotated in each chromosome. The outermost cycle represents chromosomes from 1 to 15 as numbered
2.2. Differentially accumulating miRNA precursors in flax tissues and heat treatments
miRNA species (miRNA–miRNA* pairs) are produced from precise cleavage of stem‐loop RNA precursors, called miRNA precursors. The miRNA species accumulate differentially to perform their roles in developmental processes in vegetative and reproductive tissues. To assess miRNA precursor abundance, we summed the abundance of sRNAs that mapped to the entire region of the hairpin, and this was used also for subsequent differential expression (DE) analyses. We used this approach for DE of miRNA loci because it accounts for the abundance of the miRNA mature sequence, its variants, and the star sequence, instead of using the abundance value of the single mature miRNA. Here, we characterized the abundance of miRNA loci in different tissue stages and summarized the results (Table 1). In total, we found 140 miRNA loci varying in abundance between vegetative and reproductive tissues; among them, 89 were enriched in vegetative tissues (Figure 2a, Table S3), while 51 were enriched in reproductive tissues (Figure 2b, Table S3). Vegetative tissue‐enriched miRNA loci were divided into four sets based on their enrichment into different vegetative tissues. Set I represents miRNA loci more abundant in both leaves and root and includes members of miRNA families miR160, miR156, miR166, miR393, miR395, miR845, miR482, and several novel miRNAs (22, 26, and 46). Set II represents miRNA loci enriched mostly in root tissues only and composed of members of miR164, miR156, miR395, miR159, miR399, miR394, and several novel miRNAs (20, 38, and 13). Set III, mostly enriched in both stem and root tissues, is composed of members of miR8175, miR396, miR395, miR169, miR172, miR171, miR159, and novel miRNAs (15, 16, 25,17, 10, 14, 11, 36, and 3). Set IV‐related loci were enriched mostly in leaves only and composed of members related to miR167, miR171, miR166, miR162, miR172, miR396, miR530, miR396, miR6445, miR168, miR397, miR408, miR398, and several novel miRNAs (9, 31, 39, and 12). We divided the group of miRNA loci that were enriched more in reproductive tissues into three sets (Set V, VI, and VII). Set V, mostly enriched in all three reproductive tissues along with stem and root, includes members of miR156, miR319, and miR482/2118. Set VI, mostly enriched in reproductive tissues, includes members of miR171, miR390, miR1446, miR482/2118, miR2275, miR169, and novel miRNAs (30, 24, and 7). The last, Set VII, includes miRNA loci that were enriched in reproductive tissues and leaves, and consists of members of miR160, miR393, miR164, miR403, miR171, miR167, and novel miRNAs (5, 18, 33, 23, and 43).
TABLE 1.
Differentially accumulated miRNA precursors in different tissues of flax
| Leaves | Stem | Root | B_2_4 | B_5_7 | B_8_10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves | 30D, 18U | 35D, 46U | 28D, 40U | 33D, 31U | 28D, 27U | |
| Stem | 11D, 32U | 16D, 36U | 16D, 25U | 21D, 25U | ||
| Root | 45D, 42U | 51D, 39U | 53D, 31U | |||
| B_2_4 | 5 D, 0U | 14D, 4U | ||||
| B_5_7 | 2D, 2U |
Note: miRNAs that were significantly accumulated in different tissues were denoted as downregulated (D) and upregulated (U) (p < .05, FDR < .05, Table S3). B_2_4 indicates bud stage 1 with buds 2–4 mm in length, B_5_7 indicates bud stage 2 with buds 5–7 mm in length, and B_8_10 indicates bud stage 3 with buds 8–10 mm in length.
FIGURE 2.
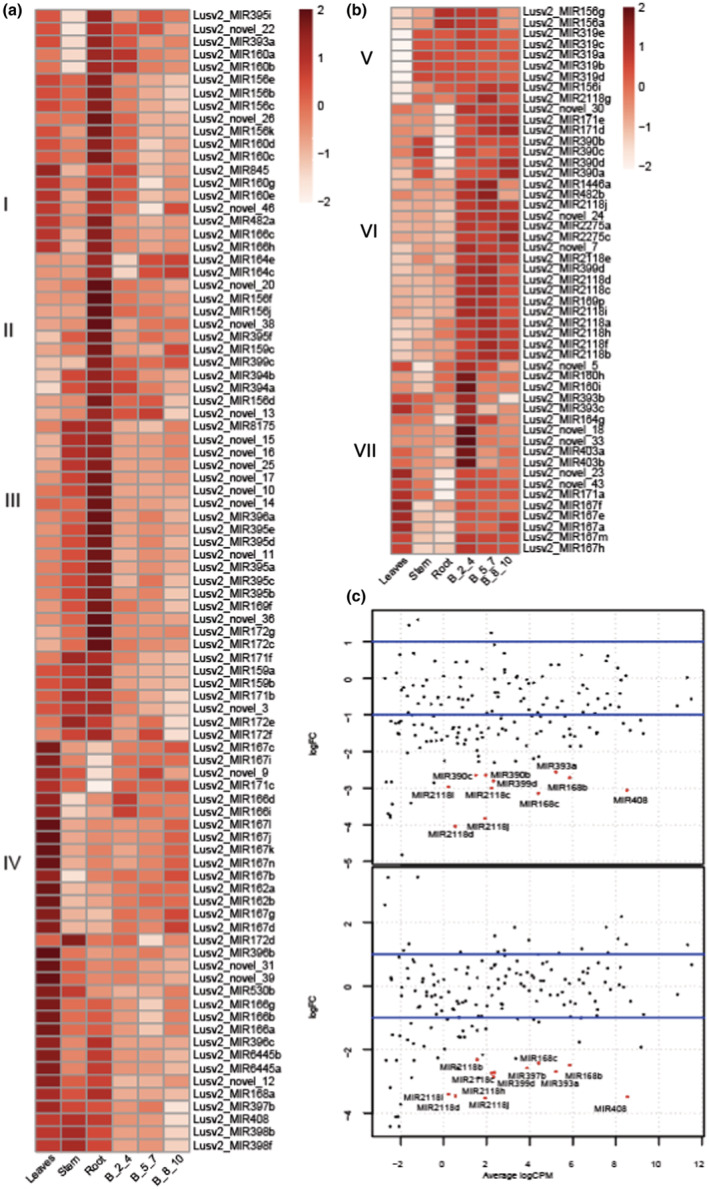
Differentially accumulated MIR genes in different tissues type and heat treatments. (a) Heatmap showing differentially accumulated MIR genes enriched in vegetative tissues with four sets of MIR genes: Set I, enriched in leaves and root; Set II, enriched in roots; Set III, enriched in stem and roots; and Set IV, enriched in leaves. (b) Similar to (a) except enriched in reproductive tissues, and with three sets of MIR genes: Set V, enriched in all reproductive tissues and stem/roots; Set VI, enriched in reproductive tissues; and Set VII, enriched in reproductive tissues and leaves. The key at right shows z‐score. B_2_4 indicates bud stage 1 with 2–4 mm in length, B_5_7 indicates bud stage 2 with 5–7 mm in length, and B_8_10 indicates bud stage 3 with 8–10 mm in length. (c) Smear plot showing differentially accumulated microRNAs (miRNAs) in reproductive bud stages: Upper track, bud stage 1 before (B_2_4) and after 14 days (B_2_4_F) of heat treatment; and in lower tack, bud stage 2 before (B_5_7) and after 14 days (B_5_7_F) of heat treatment
In this study, we subjected flax to two heat treatments during flowering as reported in (Cross et al., 2003) (more in Section 4 for details); and these heat treatments resulted in differential abundances of a total of 18 miRNA loci (Figure 2c, Figure S2a, Table S4). These were mostly downregulated due to heat stress, with one exception: miR8175 (Figure S2b). The downregulated miRNA loci under heat stress are members of the families of miR482/2118, miR390, miR168, and miR393a, miR399d, miR397b, miR408, and novel_7. Compared with other bud stages, bud stage 2 is the most sensitive to heat stress, and 11 miRNA loci were differentially accumulated after 7 days of heat treatment. There were no differentially accumulated miRNA loci identified between the two different treatments in all stages, but with an increased number of heat stress days, from 7 to 14, more miRNA loci were differentially expressed (Table 2). Overall, members of the miR482/2118 family were enriched in reproductive tissues and they initiate the production of 21‐nt reproductive phasiRNAs (Pokhrel, Huang, Bélanger, et al., 2021).
TABLE 2.
Differentially accumulated microRNA (miRNA) precursors in flax due to heat treatments
| B_2_4 | B_5_7 | B_8_10 | B_2_4_S | B_5_7_S | B_8_10_S | B_2_4_F | B_5_7_F | B_8_10_F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B_2_4 | 1D, 0U | 11D, 0U | |||||||
| B_5_7 | 10D, 1U | 12D, 0U | |||||||
| B_8_10 | 1D, 0U | 0D, 0U | |||||||
| B_2_4_S | 0D, 0U | ||||||||
| B_5_7_S | 0D, 0U | ||||||||
| B_8_10_S | 0D, 0U |
Note: miRNAs that were significantly accumulated in different tissues were denoted as downregulated (D) and upregulated (U) (p < .05, FDR < .05, Table S4). B_2_4 indicates bud stage 1 with buds 2–4 mm in length, B_5_7 indicates bud stage 2 with buds 5–7 mm in length, and B_8_10 indicates bud stage 3 with buds 8–10 mm in length. "_S" and "_F" in the codes indicate 7 and 14 days of heat treatment.
2.3. Genome‐wide identification of phasiRNAs in flax
Plant genomes encode loci that produce secondary siRNAs that are generated from a miRNA cleavage site within a polyadenylated RNA; these are generated in a phased pattern and are called PHAS loci. These loci can be derived from both protein‐coding (mRNA) and noncoding (long, noncoding RNA or lncRNA) transcripts. We used small RNA libraries from both vegetative and reproductive tissues to identify PHAS loci in flax. We identified 68 21‐PHAS loci (i.e., loci‐generating 21‐nt phasiRNAs) from both coding and noncoding regions (Figure 1, middle circle; Table 3; Table S5). Out of 68 loci, 51 were enriched in reproductive tissues (Figure 3a), while 17 loci were enriched in vegetative tissues (Figure S3a). We identified three loci of miR390‐TAS3, the most conserved phasiRNA pathway in land plants (Xia et al., 2015) (example locus in Figure 3b). We found two noncoding TAS‐like (TASL) loci enriched in leaves and reproductive tissues triggered by miR167h (example locus in Figure 3c, miR167 variants in Figure 3d) and another 12 noncoding loci enriched in reproductive tissues with unknown triggers (Figure 3a). We found triggers of at least 30 21‐PHAS loci, including miR167 as a trigger for a locus encoding a metal tolerance protein, miR168 for AGO1, miR393 for AFB2, miR6445 for NAC, miR408 for a laccase‐encoding gene, and miR482/2118 for noncoding reproductive 21‐PHAS loci that were recently described (Pokhrel, Huang, Bélanger, et al., 2021). The other gene families for which triggers were not identified included genes encoding BHLH, SCD, RING‐type, Zf‐C3H4, and BZIP domain‐containing proteins, a eukaryotic translation initiation factor, and an E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (Table 3).
TABLE 3.
Summary of 21‐PHAS loci and their triggers identified in flax
| Trigger miRNA | Locus type, name, or encoded protein | Number of loci |
|---|---|---|
| Lusv2_MIR167h/j | Metal tolerance protein | 3 |
| Lusv2_MIR167h | Noncoding | 2 |
| Lusv2_MIR168a | AGO1 | 2 |
| Lusv2_MIR482/2118 | Noncoding | 13 |
| Lusv2_MIR390 | TAS3 | 3 |
| Lusv2_MIR393b | AFB2 | 2 |
| Lusv2_MIR408 | Laccase | 2 |
| Lusv2_MIR6445a | NAC | 3 |
| N.D. | Noncoding | 13 |
| N.D. | Other protein‐coding genes | 25 |
Note: Detailed information for these loci can be found in Table S5.
Abbreviations: AFB2, AUXIN SIGNALING F‐BOX 2; AGO, Argonaute protein; microRNA, miRNA; NAC, NAC domain‐containing protein; N.D., not determined.
FIGURE 3.
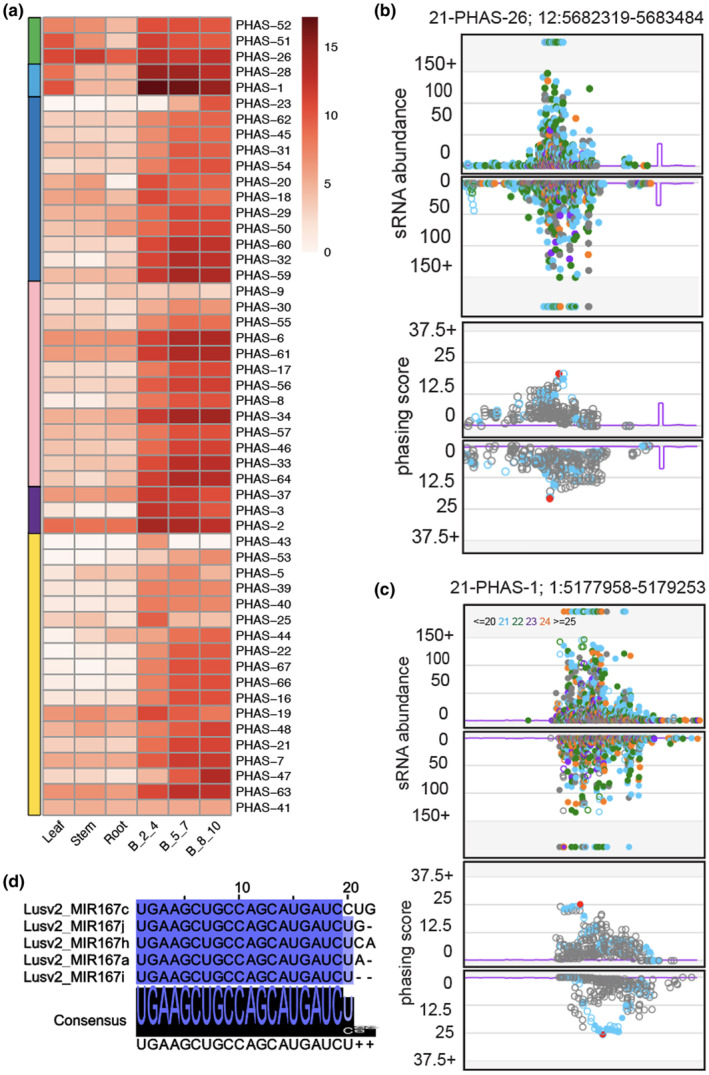
Characterization of reproductive 21‐nt phased secondary small interfering RNAs (phasiRNAs) in flax. (a) Expression of reproductive‐enriched multi‐microRNA (miRNA) triggered 21‐nt reproductive phasiRNAs in different tissue types. Left color‐coded panel indicates different trigger miRNA and their phasiRNA: green, miR390 triggered TAS3 loci; light blue, miR167 triggered TASL loci; dark blue, noncoding loci with unknown trigger, noncoding loci with miR482/2118 trigger; purple, miR167 derived metal protein‐related loci; and yellow, all other protein‐coding loci with unknown triggers. The key at right indicates the abundance in unit of log2(RP20M). B_2_4, B_5_7, and B_8_10 indicate bud stages 1, 2, and 3, respectively. (b) Upper track: Abundance (RP10M) of small RNAs (sRNAs) in both strands of an example TAS3 locus padded with 250 base pairs, each side. Name and coordinates of the PHAS locus are indicated in top. sRNA sizes are denoted by colors, as indicated at top. Below track: Phasing score of the same locus; the red dot indicates the highest phased sRNA position. (c) Similar to (b) for an example TASL locus as indicated in the top. (d) Alignment of members of miR167 in flax. The intensity of blue color denotes the conservation in nucleotide level. The consensus sequence of the alignment is shown with a sequence logo
Recently, 24‐nt phasiRNAs were reported in several eudicots (Pokhrel, Huang, & Meyers, 2021; Xia et al., 2019); thus, we looked for the conservation of this pathway in flax. We identified four 24‐PHAS loci triggered by miR2275 and an additional 658 24‐PHAS‐like loci with unknown triggers (Figure 1, inner circle; Figure S3; Table S6). These 24‐PHAS‐like loci passed the software's filtering criteria for PHAS loci, and the loci were mostly derived from nonrepetitive regions of the genome. However, when we examined a subset in our genome browser (Nakano et al., 2020), we found these loci display poor phasing, with phasing scores ranging from 15 to 20. Due to their poor phasing and unknown triggering mechanism, it is more likely that these 24‐nt sRNAs could be hc‐siRNAs that are abundant at specific stages of reproductive development, misidentified as 24‐nt phasiRNAs as previously described (Polydore et al., 2018). However, a subset of these loci may be derived from a 12‐nt phasing mechanism similar to the 24‐nt phasiRNAs of Solanaceous species (Xia et al., 2019).
2.4. Differentially expressed phasiRNAs
Because the two classes of phasiRNAs enriched in anthers of angiosperms demonstrate short periods of peak abundance (Pokhrel, Huang, Bélanger, et al., 2021; Pokhrel, Huang, & Meyers, 2021; Xia et al., 2019), we examined the differential accumulation of these reproductive phasiRNAs. We found among 68 21‐PHAS loci present in flax that 40 loci were differentially expressed, with most (37) being downregulated in heat‐treated samples (Table S7). Among the differentially expressed loci, 37 loci were enriched in reproductive tissues, 12 of which are 21‐PHAS loci targeted by miR482/2118, three encode metal tolerance proteins (triggered by miR167h/f), nine are noncoding loci with unknown triggers, and the remaining 13 loci are from other protein‐coding genes (Figure 4a, Table S7). Both Stages 1 and 2 had similar numbers of 21‐PHAS differentially expressed during 7 and 14 days of heat treatments; however, for Stage 3, the 14‐day heat treatment increased the number of differentially accumulated 21‐PHAS loci (Table 4).
FIGURE 4.
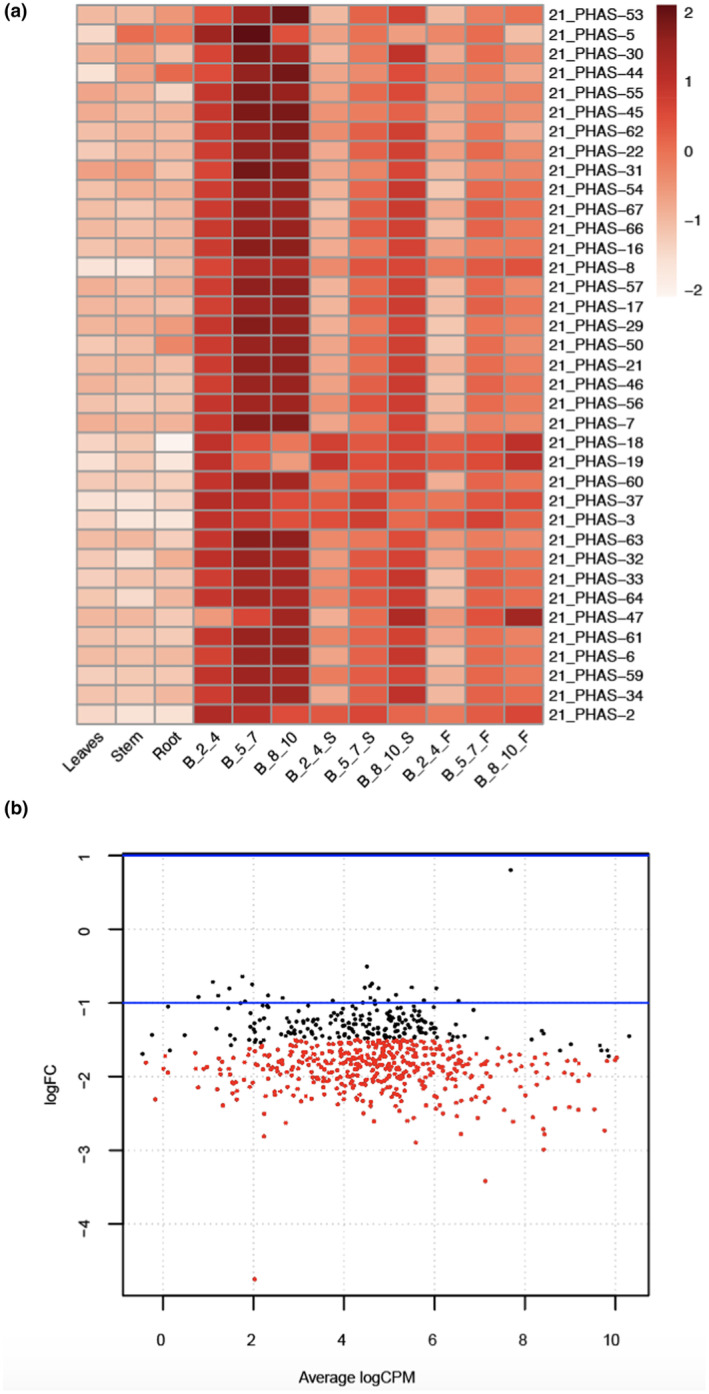
Profiling of differential accumulation of reproductive 21‐ and 24‐nt phased secondary small interfering RNAs (phasiRNAs) in flax. (a) Differential accumulation of 21‐nt reproductive phasiRNAs in reproductive stages after heat treatments. B_2_4, B_5_7, and B_8_10 indicate bud stage 1, 2 and 3 respectively. S and F indicates 7 and 14 days of heat treatment. The key at right indicates z‐score. (b) Smear plot showing differentially accumulated 24‐nt phasiRNAs in bud stage 1 before (B_2_4) and after 14 days (B_2_4_F) of heat treatment
TABLE 4.
Differentially accumulated 21‐PHAS loci in flax due to heat treatments
| B_2_4 | B_5_7 | B_8_10 | B_2_4_S | B_5_7_S | B_8_10_S | B_2_4_F | B_5_7_F | B_8_10_F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B_2_4 | 2D, 8U | 7D, 21U | 32D, 0U | 33D, 0U | |||||
| B_5_7 | 0D, 2U | 34D, 1U | 31D, 0U | ||||||
| B_8_10 | 16D, 1U | 30D, 2U | |||||||
| B_2_4_S | 0D, 0U | ||||||||
| B_5_7_S | 0D, 0U | ||||||||
| B_8_10_S | 19D, 0U |
Note: 21‐PHAS loci that were significantly accumulated in different tissues and heat treatment were denoted as downregulated (D) and upregulated (U) (p < .05, FDR < .05, Table S7). B_2_4 indicates bud stage 1 with buds 2–4 mm in length, B_5_7 indicates bud stage 2 with buds 5–7 mm in length, and B_8_10 indicates bud stage 3 with buds 8–10 mm in length."_S" and "_F" in the codes indicate 7 and 14 days of heat treatment.
In the case of 24‐PHAS loci, for bud stages 1 and 2, 14 days of heat treatment resulted in more downregulated 24‐PHAS loci compared with 7 days of heat treatment, although the abundance of 24‐PHAS loci in bud stage 3 did not change due to either of the heat treatments (Table 5). Each of the four reproductive 24‐PHAS loci triggered by miR2275 was downregulated in heat‐treated samples, while 450 24‐PHAS‐like loci were also downregulated by heat, out of 658 total loci (Figure 4b, Table S8).
TABLE 5.
Differentially accumulated 24‐PHAS loci in flax due to heat treatments
| B_4_2 | B_5_7 | B_8_10 | B_2_4_S | B_5_7_S | B_8_10_S | B_2_4_F | B_5_7_F | B_8_10_F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B_2_4 | 62D,0 U | 449D,0 U | |||||||
| B_5_7 | 68D,0 U | 143D, 0 U | |||||||
| B_8_10 | 1D,0 U | 0D,0 U | |||||||
| B_2_4_S | 0D, 0 U | ||||||||
| B_5_7_S | 0D, 0 U | ||||||||
| B_8_10_S | 0D, 0 U |
Note: 24‐PHAS loci that were significantly accumulated in different tissues were denoted as downregulated (D) and upregulated (U) (p < .05, FDR < .05, Table S8). B_2_4 indicates bud stage 1 with buds 2–4 mm in length, B_5_7 indicates bud stage 2 with buds 5–7 mm in length, and B_8_10 indicates bud stage 3 with buds 8–10 mm in length. "_S" and "_F" in the codes indicate 7 and 14 days of heat treatment.
3. DISCUSSION
We conducted a genome‐wide annotation of miRNAs and phasiRNAs in flax. On the basis of the updated criteria of miRNA annotation (Axtell & Meyers, 2018), we comprehensively identified 173 MIR genes that generated miRNAs from 31 known families and 42 novel miRNAs. As miRNAs play important regulatory roles in plant growth and reproductive development, we found that most of the miRNA loci (141 out of 173) were preferentially accumulated in a tissue‐specific manner. Further, we categorized differentially accumulated miRNAs loci based on their enrichment in vegetative and reproductive tissues. Because miRBase (v22) contains only 124 MIR genes for flax, most of which were identified using computational prediction based on the flax genome sequence, our current analysis would substantially improve the miRBase data for flax.
Furthermore, we identified 68 21‐PHAS loci that include three TAS3 loci, two TASL loci, and additional loci from coding and noncoding regions. We found no PHAS loci related to PPR genes or NB‐LRR defense genes, which is surprising as these are conserved and numerous PHAS loci in many eudicots (Zhai et al., 2011). There are cases of the near absence or absence of PHAS loci at PPR genes in all Solanaceous species, although some of the Solanaceous species (petunia and Nicotiana) harbor few PHAS loci related to NB‐LRR defense genes (Baldrich et al., 2021). Instead of protein‐coding PHAS loci triggered by miR482/2118 members, we found that these miRNAs initiate the production of reproductive tissue‐enriched 21‐nt phasiRNAs from noncoding loci in flax, a eudicot (Pokhrel, Huang, Bélanger, et al., 2021; and this study). We identified several miRNAs and phasiRNA pathways in flax that are responsive to heat stress. The two members of miR390, the conserved trigger of TAS3, were downregulated under heat stress, although the abundance of TAS3 derived phasiRNAs did not change significantly. We found no miR167 members to be differentially accumulated under heat stress, but we observed a reduction in phasiRNAs from miR167‐triggered metal tolerance proteins phasing pathways that were enriched in reproductive tissues.
In recent studies, conservation of the miR2275‐24‐PHAS pathway in angiosperms was reported, including several eudicots (Pokhrel, Huang, & Meyers, 2021; Xia et al., 2019); the pathway is also conserved in flax, but with few (only four) 24‐PHAS loci. Here, we identified a larger number (658) of 24‐PHAS‐like loci that are reproductive tissue‐enriched but that lack obvious trigger miRNAs, possibly similar to the Solanaceous 24‐nt phasiRNAs (Xia et al., 2019) or possibly some sort of loci of reproductive‐tissue‐enriched hc‐siRNAs. We found that all 24‐PHAS and 450 24‐PHAS‐like loci were heat responsive and all are downregulated due to heat stress.
Notably, we observed downregulation of the reproductive phasiRNA triggers, miR482/2118 and miR2275 in response to heat treatments, as well as the reproductive 21‐ and 24‐nt phasiRNAs triggered by these miRNAs, respectively. In rice, mutations in the precursors of two 21‐PHAS loci resulted in temperature‐sensitive genic male sterility (Fan et al., 2016; Zhou et al., 2012), although in maize, knockdown of DCL5, a gene responsible for the production of reproductive 24‐nt phasiRNAs, greatly reduced the phasiRNAs and resulted in temperature‐sensitive male sterile phenotype (Teng et al., 2020). Cross et al. reported that two heat treatments reduce boll formation and seed set in flax (Cross et al., 2003), the same conditions that we used; however, the molecular mechanisms underlying these results are unknown. We hypothesize that a decrease in abundance of rate‐limiting trigger miRNAs due to heat stress results in the downregulation of reproductive phasiRNAs that ultimately produces sterility phenotypes in flax. Future studies are needed to elucidate a mechanistic understanding of the roles for miRNA‐phasiRNAs in reproductive development under heat stress.
4. METHODS
4.1. Heat stress treatment and plant materials
Flax cultivar “Stormont cirrus” was grown in a walk‐in Conviron growth chamber with 16‐/8‐h light/dark cycle with 25/20°C temperatures, respectively. From 1‐month‐old seedlings, leaves, stem, and root tissues were harvested and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen. After 2 weeks following the initiation of flowering, two groups of seedlings, each containing at least nine plants, were transferred to a new growth chamber where during the day (16 h) cycle, temperatures would increase at ~3°C/h from 20°C to 40°C, over a 7‐h period, held at 40°C for 1 h, and decreased at the same rate for 7 h. The heat treatment was continued for 14 days, and samples of three bud stages (Figure S1a) were harvested before initiation of heat stress, and after 7 and 14 days during peak heat stress (40°C), from two groups as two biological replicates, and frozen immediately in liquid nitrogen. We sampled two replicates for three different bud stages at three different time points (before heat stress, 7 and 14 days after heat treatment), resulting in 18 total libraries; six more libraries from other tissue types, for a total of 24, were subsequently used.
4.2. RNA extraction, libraries preparation, and sequencing
Total RNA from all flax vegetative and reproductive tissues was extracted using the PureLink Plant RNA Reagent (ThermoFisher Scientific, cat. #12322012) following the manufacturer's instructions with minor modifications. RNA quality was determined by running denaturing gels, and quantity was assessed using Qubit. First, sRNAs (20–30 nt) were size selected in a 15% polyacrylamide/urea gel and used for sRNA library preparation. An input amount 5 μg of total RNA was used for library construction. The sRNA libraries were constructed following manufacturer's instruction using the NEBNext Small RNA Library Preparation set for Illumina (NEB, cat # E7300).
4.3. Data analysis and visualization
Preprocessing and filtering of sRNA libraries were conducted as previously described (Pokhrel, Huang, Bélanger, et al., 2021). Two miRNA identification tools: ShortStack and miR‐PREFeR were used (Johnson et al., 2016; Lei & Sun, 2014) for genome‐wide MIR gene identification. To increase the sensitivity of miRNA detection (a result of increased supporting data), in ShortStack, two libraries were used at a time using default parameters except −mismatch 0 and −mincov 10. As ShortStack has relatively high precision and accuracy, miRNA loci predicted using miR‐PREFeR were again re‐evaluated with ShortStack, and only the loci with passed the criteria were included in the final set. The miRNA loci from two tools/runs were merged in BEDTools using the “merge” command with default parameters with –s –c 4,6 –o distinct (Quinlan & Hall, 2010).
PHAS loci were also identified using two tools, PHASIS (Kakrana et al., 2017) with a p‐value cut‐off of .001 and number of phase cycle (k) = 7 and ShortStack (Johnson et al., 2016) with default parameters except −mismatch 0 and −mincov 10. BEDTools was used to merge PHAS loci from two different softwares (Quinlan & Hall, 2010). 24‐PHAS loci with unknown triggers were annotated as 24‐PHAS‐like loci. Target prediction was carried out by sPARTA (Kakrana et al., 2014) with a target cut off score of ≤5. The sRNA abundance and phasing score were viewed at a customized browser (Nakano et al., 2020). The 250 base pairs were padded in both upstream and downstream of predicted PHAS loci and subsequently used as the de novo annotated set for analysis by BLASTX (Altschul et al., 1997) against UniRef90. The summed abundance of sRNAs from given locus was calculated by ShortStack using –locifile parameter. Differential analysis (p < .05, false discovery rate [FDR] < .05) of sRNA loci was conducted in R using the edgeR package (Robinson et al., 2010). Circular plots were constructed using OmicCircos (Hu et al., 2014) for the chromosomal distributions of miRNAs and phasiRNAs generating loci. pheatmap (https://rdrr.io/cran/pheatmap/) was used to draw heatmaps in R.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest associated with the work described in this manuscript.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
B.C.M. and S.P. designed the research; S.P. performed the experiments and analyzed the data; S.P. and B.C.M wrote and revised the manuscript.
Supporting information
Figure S1. Reproductive buds staging and miRNA precursors in flax.
A. Bud stages used for sequencing in flax, B_2_4: 2–4 mm buds, B_5_7: 5–7 mm buds, and B_8_10: 8–10 mm buds. B. Number of precursors encoded into the genome of flax for each miRNA families. miRNA family with more than 3 precursors were included.
Figure S2. Differential accumulation of miRNAs due to heat stress in flax.
A. Differential accumulation of miRNAs in reproductive buds after heat stress. The key at right indicates z‐score. B_2_4: 2–4 mm buds, B_5_7: 5–7 mm buds, and B_8_10: 8–10 mm buds. S and F indicates seven and fourteen days of heat treatment.
B. Smear plot showing differentially accumulated miRNAs in bud stage 2 (before B_5_7) and after 7 days (B_5_7_S) of heat treatment.
Figure S3. Accumulation of vegetative‐enriched 21‐nt phasiRNAs and all 24‐nt phasiRNA in flax.
A. Accumulation pattern of vegetative‐enriched 21‐nt phasiRNAs in different tissues. The key at right indicates the abundance in units of log2(RP20M). B_2_4: 2–4 mm buds, B_5_7: 5–7 mm buds, and B_8_10: 8–10 mm buds.
B. Accumulation of 24‐nt reproductive phasiRNAs derived from 24‐PHAS/24‐ PHAS‐like loci in different tissues. The key at right indicates the abundance in units of log2(RP20M). B_2_4: 2–4 mm buds, B_5_7: 5–7 mm buds, and B_8_10: 8–10 mm buds.
Figure S4. 24‐nt phasiRNAs differentially accumulated after heat‐stress treatment in flax.
Differential accumulation of 24‐nt phasiRNAs from 454 loci in reproductive buds after heat stress. The key at right indicates z‐score. B_2_4: 2–4 mm buds, B_5_7: 5–7 mm buds, and B_8_10: 8–10 mm buds. S and F indicates seven and fourteen days of heat treatment.
Table S1. Small RNA libraries used in the study.
Table S2. Genome‐wide identification of miRNA precursors in flax.
Table S3. Differentially accumulated miRNA loci and enrichment analyis, in different tissues of flax.
Table S4. miRNA loci differentially accumulated under heat treatment in flax.
Table S5. 21‐PHAS loci, their triggers, and annotation in flax.
Table S6. 24‐PHAS loci and their abundances in different tissues of flax.
Table S7. Differentially accumulated 21‐PHAS loci, and their abundances in different heat treatments of flax.
Table S8. Differentially accumulated 24‐PHAS loci due to different heat treatments of flax reproductive buds.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank members of the Meyers lab for helpful discussions and Joanna Friesner for assistance with editing. We thank Mayumi Nakano for assistance with data handling. This work was supported by resources from the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center and the University of Missouri–Columbia plus the William H. Danforth Plant Science Fellow Award (to S.P.).
Pokhrel, S. , & Meyers, B. C. (2022). Heat‐responsive microRNAs and phased small interfering RNAs in reproductive development of flax. Plant Direct, 6(2), e385. 10.1002/pld3.385
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
All the sRNA data generated during this study were deposited in NCBI's SRA (Sequence Read Archive) under the accession numbers PRJNA669702and PRJNA768110.
REFERENCES
- Altschul, S. F. , Madden, T. L. , Schäffer, A. A. , Zhang, J. , Zhang, Z. , Miller, W. , & Lipman, D. J. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI‐BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 3389–3402. 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axtell, M. J. (2013). Classification and comparison of small RNAs from plants. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 64, 137–159. 10.1146/annurev-arplant-050312-120043 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axtell, M. J. , Jan, C. , Rajagopalan, R. , & Bartel, D. P. (2006). A two‐hit trigger for siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell, 127(3), 565–577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axtell, M. J. , & Meyers, B. C. (2018). Revisiting criteria for plant microRNA annotation in the era of big data. Plant Cell, 30, 272–284. 10.1105/tpc.17.00851 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldrich, P. , Bélanger, S. , Kong, S. , Pokhrel, S. , Tamim, S. , Teng, C. , Schiebout C., Gurazada, S. G. R. , Pallavi, G. , Patel, P. , Razifard, H. , Nakano, M. , Dusia, A. , Meyers, B. C., & Frank, M. H. (2021). The evolutionary history of small RNAs in the Solanaceae. bioRxiv. 10.1101/2021.05.26.445884 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Barvkar, V. T. , Pardeshi, V. C. , Kale, S. M. , Qiu, S. , Rollins, M. , Datla, R. , Gupta, V. S. , & Kadoo, N. Y. (2013). Genome‐wide identification and characterization of microRNA genes and their targets in flax (Linum usitatissimum): Characterization of flax miRNA genes. Planta, 237, 1149–1161. 10.1007/s00425-012-1833-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross, R. H. , McKay, S. A. B. , McHughen, A. G. , & Bonham‐Smith, P. C. (2003). Heat‐stress effects on reproduction and seed set in Linum usistatissimum L. (flax). Plant, Cell and Environment, 26, 1013–1020. 10.1046/j.1365-3040.2003.01006.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y. , Yang, J. , Mathioni, S. M. , Yu, J. , Shen, J. , Yang, X. , … Zhang, Q. (2016). PMS1T, producing phased small‐interfering RNAs, regulates photoperiod‐sensitive male sterility in rice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113, 15144–15149. 10.1073/pnas.1619159114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fei, Q. , Xia, R. , & Meyers, B. C. (2013). Phased, secondary, small interfering RNAs in posttranscriptional regulatory networks. Plant Cell, 25, 2400–2415. 10.1105/tpc.113.114652 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacomelli, J. I. , Weigel, D. , Chan, R. L. , & Manavella, P. A. (2012). Role of recently evolved miRNA regulation of sunflower HaWRKY6 in response to temperature damage. The New Phytologist, 195, 766–773. 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04259.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Q. , Lu, X. , Zeng, H. , Zhang, Y. , & Zhu, J. (2013). Heat stress induction of miR398 triggers a regulatory loop that is critical for thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal, 74, 840–851. 10.1111/tpj.12169 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasanuzzaman, M. , Nahar, K. , Alam, M. M. , Roychowdhury, R. , & Fujita, M. (2013). Physiological, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms of heat stress tolerance in plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14, 9643–9684. 10.3390/ijms14059643 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He, J. , Jiang, Z. , Gao, L. , You, C. , Ma, X. , Wang, X. , … Liu, L. (2019). Genome‐wide transcript and small RNA profiling reveals transcriptomic responses to heat stress. Plant Physiology, 181, 609–629. 10.1104/pp.19.00403 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedhly, A. , Hormaza, J. I. , & Herrero, M. (2009). Global warming and sexual plant reproduction. Trends in Plant Science, 14, 30–36. 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.11.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell, M. D. , Fahlgren, N. , Chapman, E. J. , Cumbie, J. S. , Sullivan, C. M. , Givan, S. A. , Kasschau, K. D. , & Carrington, J. C. (2007). Genome‐wide analysis of the RNA‐DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE6/DICER‐LIKE4 pathway in arabidopsis reveals dependency on miRNA‐ and tasiRNA‐directed targeting. The Plant Cell, 19, 926–942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y. , Yan, C. , Hsu, C. H. , Chen, Q. R. , Niu, K. , Komatsoulis, G. A. , & Meerzaman, D. (2014). Omiccircos: A simple‐to‐use R package for the circular visualization of multidimensional omics data. Cancer Informatics, 13, 13–20. 10.4137/CIN.S13495 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C. , Kasprzewska, A. , Tennessen, K. , Fernandes, J. , Nan, G. L. , Walbot, V. , … Bowman, L. H. (2009). Clusters and superclusters of phased small RNAs in the developing inflorescence of rice. Genome Research, 19, 1429–1440. 10.1101/gr.089854.108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, N. R. , Yeoh, J. M. , Coruh, C. , & Axtell, M. J. (2016). Improved placement of multi‐mapping small RNAs. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics, 6(7), 2103–2111. 10.1534/g3.116.030452 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakrana, A. , Hammond, R. , Patel, P. , Nakano, M. , & Meyers, B. C. (2014). SPARTA: A parallelized pipeline for integrated analysis of plant miRNA and cleaved mRNA data sets, including new miRNA target‐identification software. Nucleic Acids Research, 42, 1–13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakrana, A. , Li, P. , Patel, P. , Hammond, R. , Anand, D. , Mathioni, S.M. & Meyers, B.C. (2017). PHASIS: A computational suite for de novo discovery and characterization of phased, siRNA‐generating loci and their miRNA triggers. bioRxiv. 10.1101/158832 [DOI]
- Keller, M. , Schleiff, E. , & Simm, S. (2020). miRNAs involved in transcriptome remodeling during pollen development and heat stress response in Solanum lycopersicum. Scientific Reports, 10, 10694. 10.1038/s41598-020-67833-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei, J. , & Sun, Y. (2014). miR‐PREFeR: An accurate, fast and easy‐to‐use plant miRNA prediction tool using small RNA‐Seq data. Bioinformatics, 30, 2837–2839. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu380 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li, S. , Liu, J. , Liu, Z. , Li, X. , Wu, F. , & He, Y. (2014). HEAT‐INDUCED TAS1 TARGET1 mediates thermotolerance via heat stress transcription factor A1a‐directed pathways in arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 26, 1764–1780. 10.1105/tpc.114.124883 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J. S. , Kuo, C. C. , Yang, I. C. , Tsai, W. A. , Shen, Y. H. , Lin, C. C. , … Jeng, S. T. (2018). MicroRNA160 modulates plant development and heat shock protein gene expression to mediate heat tolerance in Arabidopsis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9, 68. 10.3389/fpls.2018.00068 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnikova, N. V. , et al. (2016). Identification, expression analysis, and target prediction of flax genotroph MicroRNAs under normal and nutrient stress conditions. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 1–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, M. , McCormick, K. , Demirci, C. , Demirci, F. , Gurazada, S. G. R. , Ramachandruni, D. , … Meyers, B. C. (2020). Next‐generation sequence databases: RNA and genomic informatics resources for plants. Plant Physiology, 182, 136–146. 10.1104/pp.19.00957 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pokharel, M. , Chiluwal, A. , Stamm, M. , Min, D. , Rhodes, D. , & Jagadish, S. V. K. (2020). High night‐time temperature during flowering and pod filling affects flower opening, yield and seed fatty acid composition in canola. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 206, 579–596. 10.1111/jac.12408 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pokhrel, S. , Huang, K. , Bélanger, S. , Zhan, J. , Caplan, J. L. , Kramer, E. M. , & Meyers, B. C. (2021). Pre‐meiotic 21‐nucleotide reproductive phasiRNAs emerged in seed plants and diversified in flowering plants. Nature Communications, 12, 4941. 10.1038/s41467-021-25128-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pokhrel, S. , Huang, K. , & Meyers, B. C. (2021). Conserved and non‐conserved triggers of 24‐nucleotide reproductive phasiRNAs in eudicots. The Plant Journal, 107(5), 1–14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polydore, S. , Lunardon, A. , & Axtell, M. J. (2018). Several phased siRNA annotation methods can frequently misidentify 24 nucleotide siRNA‐dominated PHAS loci. Plant Direct, 2, 1–13. 10.1002/pld3.101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan, A. R. , & Hall, I. M. (2010). BEDTools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics, 26, 841–842. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart, B. J. , Weinstein, E. G. , Rhoades, M. W. , Bartel, B. , & Bartel, D. P. (2002). MicroRNAs in plants. Genes & Development, 16, 1616–1626. 10.1101/gad.1004402 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, M. D. , McCarthy, D. J. , & Smyth, G. K. (2010). edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics, 26, 139–140. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stief, A. , Altmann, S. , Hoffmann, K. , Pant, B. D. , Scheible, W. R. , & Bäurle, I. (2014). Arabidopsis miR156 regulates tolerance to recurring environmental stress through SPL transcription factors. Plant Cell, 26, 1792–1807. 10.1105/tpc.114.123851 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng, C. , Zhang, H. , Hammond, R. , Huang, K. , Meyers, B. C. , & Walbot, V. (2020). Dicer‐like 5 deficiency confers temperature‐sensitive male sterility in maize. Nature Communications, 11. 10.1038/s41467-020-16634-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D. , Heckathorn, S. A. , Mainali, K. , & Tripathee, R. (2016). Timing effects of heat‐stress on plant ecophysiological characteristics and growth. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 1629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. , Hobson, N. , Galindo, L. , Zhu, S. , Shi, D. , McDill, J. , … Deyholos, M. K. (2012). The genome of flax (Linum usitatissimum) assembled de novo from short shotgun sequence reads. The Plant Journal, 72, 461–473. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.05093.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia, R. , Chen, C. , Pokhrel, S. , Ma, W. , Huang, K. , Patel, P. , … Meyers, B. C. (2019). 24‐nt reproductive phasiRNAs are broadly present in angiosperms. Nature Communications, 10. 10.1038/s41467-019-08543-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia, R. , Xu, J. , Arikit, S. , & Meyers, B. C. (2015). Extensive families of miRNAs and PHAS loci in Norway spruce demonstrate the origins of complex phasiRNA networks in seed plants. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 32, 2905–2918. 10.1093/molbev/msv164 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- You, F. M. , Xiao, J. , Li, P. , Yao, Z. , Jia, G. , He, L. , … Cloutier, S. (2018). Chromosome‐scale pseudomolecules refined by optical, physical and genetic maps in flax. The Plant Journal, 95, 371–384. 10.1111/tpj.13944 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y. , Wu, G. , Yuan, H. , Cheng, L. , Zhao, D. , Huang, W. , … Guan, F. (2016). Identification and characterization of miRNAs and targets in flax (Linum usitatissimum) under saline, alkaline, and saline‐alkaline stresses. BMC Plant Biology, 16, 124. 10.1186/s12870-016-0808-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, J. , Jeong, D. H. , de Paoli, E. , Park, S. , Rosen, B. D. , Li, Y. , … Meyers, B. C. (2011). MicroRNAs as master regulators of the plant NB‐LRR defense gene family via the production of phased, trans‐acting siRNAs. Genes & Development, 25, 2540–2553. 10.1101/gad.177527.111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S. S. , Yang, H. , Ding, L. , Song, Z. T. , Ma, H. , Chang, F. , & Liu, J. X. (2017). Tissue‐specific transcriptomics reveals an important role of the unfolded protein response in maintaining fertility upon heat stress in arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 29, 1007–1023. 10.1105/tpc.16.00916 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C. , Liu, B. , Piao, S. , Wang, X. , Lobell, D. B. , Huang, Y. , … Asseng, S. (2017). Temperature increase reduces global yields of major crops in four independent estimates. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 114, 9326–9331. 10.1073/pnas.1701762114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H. , Liu, Q. , Li, J. , Jiang, D. , Zhou, L. , Wu, P. , … Zhuang, C. (2012). Photoperiod‐ and thermo‐sensitive genic male sterility in rice are caused by a point mutation in a novel noncoding RNA that produces a small RNA. Cell Research, 22, 649–660. 10.1038/cr.2012.28 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. Reproductive buds staging and miRNA precursors in flax.
A. Bud stages used for sequencing in flax, B_2_4: 2–4 mm buds, B_5_7: 5–7 mm buds, and B_8_10: 8–10 mm buds. B. Number of precursors encoded into the genome of flax for each miRNA families. miRNA family with more than 3 precursors were included.
Figure S2. Differential accumulation of miRNAs due to heat stress in flax.
A. Differential accumulation of miRNAs in reproductive buds after heat stress. The key at right indicates z‐score. B_2_4: 2–4 mm buds, B_5_7: 5–7 mm buds, and B_8_10: 8–10 mm buds. S and F indicates seven and fourteen days of heat treatment.
B. Smear plot showing differentially accumulated miRNAs in bud stage 2 (before B_5_7) and after 7 days (B_5_7_S) of heat treatment.
Figure S3. Accumulation of vegetative‐enriched 21‐nt phasiRNAs and all 24‐nt phasiRNA in flax.
A. Accumulation pattern of vegetative‐enriched 21‐nt phasiRNAs in different tissues. The key at right indicates the abundance in units of log2(RP20M). B_2_4: 2–4 mm buds, B_5_7: 5–7 mm buds, and B_8_10: 8–10 mm buds.
B. Accumulation of 24‐nt reproductive phasiRNAs derived from 24‐PHAS/24‐ PHAS‐like loci in different tissues. The key at right indicates the abundance in units of log2(RP20M). B_2_4: 2–4 mm buds, B_5_7: 5–7 mm buds, and B_8_10: 8–10 mm buds.
Figure S4. 24‐nt phasiRNAs differentially accumulated after heat‐stress treatment in flax.
Differential accumulation of 24‐nt phasiRNAs from 454 loci in reproductive buds after heat stress. The key at right indicates z‐score. B_2_4: 2–4 mm buds, B_5_7: 5–7 mm buds, and B_8_10: 8–10 mm buds. S and F indicates seven and fourteen days of heat treatment.
Table S1. Small RNA libraries used in the study.
Table S2. Genome‐wide identification of miRNA precursors in flax.
Table S3. Differentially accumulated miRNA loci and enrichment analyis, in different tissues of flax.
Table S4. miRNA loci differentially accumulated under heat treatment in flax.
Table S5. 21‐PHAS loci, their triggers, and annotation in flax.
Table S6. 24‐PHAS loci and their abundances in different tissues of flax.
Table S7. Differentially accumulated 21‐PHAS loci, and their abundances in different heat treatments of flax.
Table S8. Differentially accumulated 24‐PHAS loci due to different heat treatments of flax reproductive buds.
Data Availability Statement
All the sRNA data generated during this study were deposited in NCBI's SRA (Sequence Read Archive) under the accession numbers PRJNA669702and PRJNA768110.


