ABSTRACT
Infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus are a leading cause of mortality. Treating infections caused by S. aureus is difficult due to resistance against most traditional antibiotics, including β-lactams. We previously reported the presence of mutations in gdpP among S. aureus strains that were obtained by serial passaging in β-lactam drugs. Similar mutations have recently been reported in natural S. aureus isolates that are either nonsusceptible or resistant to β-lactam antibiotics. gdpP codes for a phosphodiesterase that cleaves cyclic-di-AMP (CDA), a newly discovered second messenger. In this study, we sought to identify the role of gdpP in β-lactam resistance in S. aureus. Our results showed that gdpP-associated mutations caused loss of phosphodiesterase function, leading to increased CDA accumulation in the bacterial cytosol. Deletion of gdpP led to an enhanced ability of the bacteria to withstand a β-lactam challenge (2 to 3 log increase in bacterial CFU) by promoting tolerance without enhancing MICs of β-lactam antibiotics. Our results demonstrated that increased drug tolerance due to loss of GdpP function can provide a selective advantage in acquisition of high-level β-lactam resistance. Loss of GdpP function thus increases tolerance to β-lactams that can lead to its therapy failure and can permit β-lactam resistance to occur more readily.
KEYWORDS: GdpP, Staphylococcus aureus, beta-lactams, cyclic-di-AMP, tolerance
INTRODUCTION
Staphylococcus aureus is an important pathogen that causes widespread nosocomial and community-associated infections in humans (1, 2). Along with possessing a vast array of virulence factors, S. aureus also harbors the ability to display antibiotic resistance and antibiotic tolerance that enable bacteria to evade the action of antibiotics used for treatment (3). While resistance is typically characterized by an increase in the MIC for a target antibiotic, tolerance is a phenomenon where the survival of cells in the presence of antibiotics is prolonged, without causing a change in drug MIC (4). β-lactams are an important class of antibiotics that are often the first choice of treatment for S. aureus infections, primarily due to their high safety and efficacy. Over the past several decades, β-lactam resistance among contemporary clinical strains of S. aureus has called for the use of second-line agents that are often less safe and effective (5).
β-Lactam resistance in S. aureus is classically mediated by penicillin binding protein 2a (PBP2a) and β-lactamase, which are encoded by mecA and blaZ respectively (6). While they have been well investigated, there is increasing evidence of the prevalence of nonclassical mechanisms of β-lactam resistance (7–9). Our previous studies that were targeted toward identifying nonclassical mechanisms of resistance detected missense and nonsense mutations in gdpP among every resistant passaged strain (10). Recent clinical surveillance studies also detected similar gdpP associated mutations among several β-lactam-nonsusceptible isolates, reiterating their clinical relevance (7, 11). GdpP (GGDEF domain protein containing phosphodiesterase [PDE]) contains two N-terminal transmembrane helices followed by a degenerated PAS domain (12), which acts as an internal sensor of oxygen and redox potential (13). This is followed by the degenerated GGDEF domain that is normally associated with cyclic-di-GMP cyclase (14) along with the DHH-DHHA1 domains that have phosphodiesterase activity, which gives GdpP the ability to cleave cyclic-di-AMP (CDA) (12). CDA is a newly discovered second messenger in bacteria and archaea that is synthesized from two molecules of ATP by the action of diadenylate cyclase (encoded by dacA) (12, 15). CDA has been deemed essential for bacterial cells and is implicated in a variety of cellular processes, such as ion homeostasis, cell size, and cell wall stress response among others in S. aureus (12, 16–18). GdpP, through its phosphodiesterase function, helps maintain the intracellular levels of CDA through its cleavage. In this study, we focused on determining the role of gdpP-associated mutations in surviving the antibacterial action of β-lactam drugs. Our results suggest that gdpP-associated mutations detected among laboratory-passaged and clinically isolated β-lactam-resistant or -nonsusceptible strains of S. aureus were loss-of-function mutations that led to enhanced CDA concentrations in bacterial cytosol. To the best of our knowledge, this study for the first time showed that gdpP mutations detected among clinical strains could lead to increased concentrations of CDA due to its loss of function. Enhanced CDA concentrations facilitated bacterial survival against β-lactam antibiotics by promoting drug tolerance but did not alter drug MICs. β-lactam drug tolerance achieved through loss of GdpP function in S. aureus can lead to its therapy failure. Our findings further indicate that GdpP loss-of-function mutations arise very early during the evolution of β-lactam resistance and provide new insights into how attaining drug tolerance can promote faster evolution of β-lactam resistance in S. aureus.
RESULTS
Mutations associated with gdpP cause loss of phosphodiesterase activity in laboratory-generated β-lactam-resistant passaged strains and clinical isolates.
Every resistant passaged strain previously obtained through passaging of COLnex and SF8300ex (lacking mecA and blaZ, the classical mediators of β-lactam resistance in wild-type COLn and SF8300 strains, respectively) had a missense or nonsense mutation in gdpP that led to an amino acid alteration or a premature truncation of GdpP, respectively (see Table S1a in the supplemental material; Fig. 1a). The nonsense mutations were such that they ablated the DHH-DHHA1 domains of GdpP, which mediate phosphodiesterase (PDE) activity to degrade CDA (Fig. 1a) (12). Recent clinical surveillance studies have also identified similar gdpP-associated mutations among β-lactam nonsusceptible S. aureus strains, further implicating their role in β-lactam resistance (see Table S4 and Fig. S1a in the supplemental material) (7, 11).
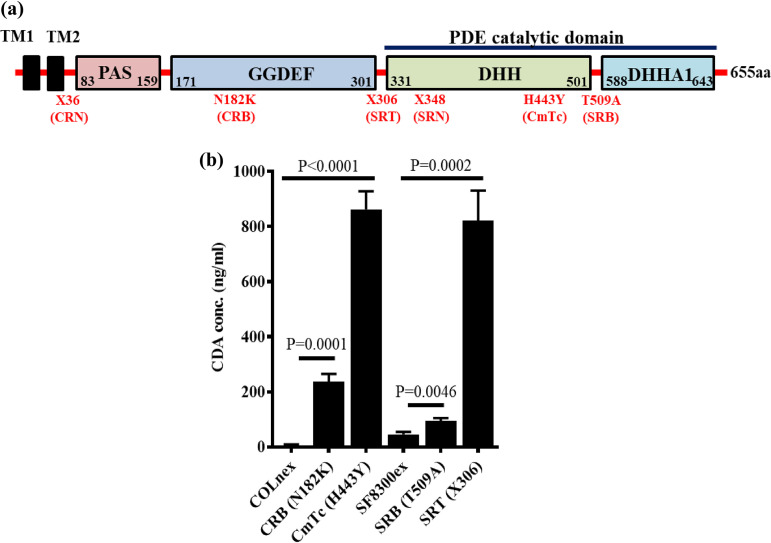
FIG 1.
Passaged strains accumulated loss-of-GdpP-function mutations. (a) Schematic diagram showing different domains of GdpP and mutations detected among passaged resistant strains. (b) Cyclic-di-AMP concentrations in the cytosol of passaged strains in comparison to their isogenic susceptible parental strains COLnex and SF8300ex. Concentrations of CDA were significantly higher in CRB and CmTc, respectively, compared to that of the wild-type, COLnex. Similarly, CDA concentrations were higher in SRB and SRT, respectively, compared to that of the wild-type, SF8300ex.
We hypothesized that the accumulated mutations of gdpP caused attenuated PDE function (Table S1a; Fig. 1a), leading to elevated CDA concentrations in passaged strains. To make this determination, we measured the CDA abundance of the resistant passaged strains and compared them to their susceptible parents (Table S1a). We evaluated a representative strain that had a nonsense mutation in gdpP (X306) that resulted in a premature truncation before the DHH-DHHA1 domains (SRT with X306) (Table S1a; Fig. 1a) and all of the strains that accumulated missense mutations in our passaging study (CRB with N182K, CmTc with H443Y, and SRB with T509A) (Fig. 1a; see also Table S1a). We detected that every strain, including those having a missense mutation, displayed elevated levels of CDA compared to their isogenic parents, COLnex and SF8300ex (Fig. 1b). SRT had ∼10-fold increased level of CDA. Notably, gdpP with the H443Y mutation (in the passaged strain CmTc) that substituted the 2nd histidine residue of the DHH residues with a tyrosine also yielded similarly high levels of CDA in the bacterial cytosol. Two other gdpP mutants, CRB (N182K) and SRB (T509A), had significantly elevated CDA amounts compared to their isogenic wild-type strains (Fig. 1b). These results indicated that the accumulated mutations in gdpP altered GdpP phosphodiesterase activity that ranged from partial attenuation to complete loss of function. Similarly, the majority of gdpP missense mutations identified through a recent clinical surveillance study were GdpP loss-of-function mutations (Table S4 and Fig. S1a and b). Of the 12 clinical strains analyzed for cytosolic CDA concentrations (strains 1 through 12), 9 were seen to have significantly increased CDA levels (Fig. S1b).
Loss of GdpP function leads to a growth defect and enhanced ability to withstand β-lactam challenge but does not change MIC against β-lactam antibiotics.
To determine the phenotypes associated with loss of GdpP function, gdpP was deleted from S. aureus SF8300, a clinical isolate that belongs to the USA300 background strain and from its isogenic mecA- and blaZ-excised variant, SF8300ex. This approach allowed us to evaluate the role of GdpP in isogenic background strains both with and without the classical mediators of β-lactam resistance. Deletion of gdpP caused increased accumulation of CDA in the bacterial cytosol and produced a growth defect compared to the isogenic wild-type strains (Fig. 2a and b). To assess if the observed ΔgdpP-related phenotypes were indeed due to loss of gdpP, we complemented the ΔgdpP mutants with constitutively expressing wild-type gdpP. We also transformed the wild-type and ΔgdpP mutant strains with an empty vector as control strains. gdpP complementation in ΔgdpP mutants restored their wild-type phenotypes (Fig. 2). Results of population analysis revealed that the ΔgdpP strains had at least a 2 to 3 log fold increase in the proportion of bacterial cells compared to their isogenic wild-type strains, indicating a heightened survival to β-lactam drug treatment (Fig. 2c). This also denoted that the observed phenotypes were attributed to gdpP. Since both mecA- positive and -negative strains (i.e., SF8300 and SF830ex, respectively) displayed a similar pattern of β-lactam resilience, it indicated that mecA (the major mediator of β-lactam resistance in S. aureus) likely did not play any important role in mediating the phenotypes that the ΔgdpP strains displayed (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material). In addition to the SF8300 ΔgdpP strain, we included another clinically relevant and epidemic-associated strain of S. aureus, MW2 (a member of the USA400 background), to confirm these findings (see Fig. S3 in the supplemental material). These results reiterated the notion that GdpP played an important role in surviving β-lactam challenge in S. aureus.
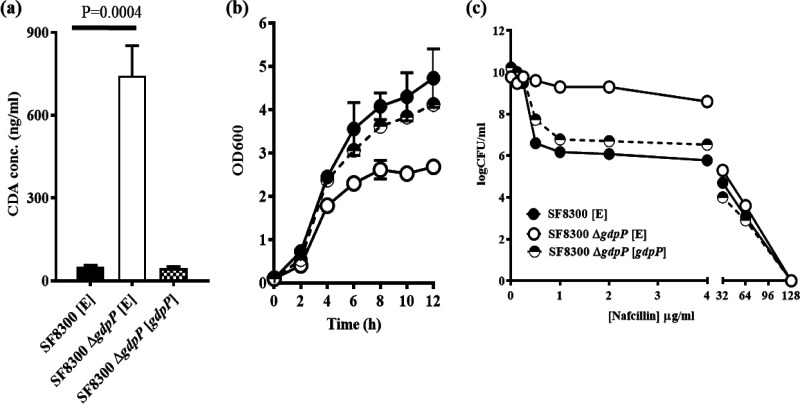
FIG 2.
Complementation with gdpP restored wild-type phenotypes in SF8300 strains. (a) CDA levels in the cytosol. Deletion of gdpP (SF8300 ΔgdpP [E]) caused a significant increase in the cytosolic CDA concentration compared to that of the wild-type (SF8300 [E]) and complemented (SF8300 ΔgdpP [gdpP]) strains. (b) Growth pattern in TSB medium. The deletion of gdpP in strain SF8300 (SF8300 ΔgdpP [E]) (open circles) caused a growth defect compared to the wild-type strain containing an empty vector, SF8300 [E] (completely filled circles). This growth defect was abolished when complemented with wild-type gdpP in strain SF8300 ΔgdpP [gdpP] (half-filled circles). (c) Population analysis with nafcillin. The deletion of gdpP in strain SF8300 ΔgdpP [E] (open circles) enabled the cells to survive a nafcillin challenge compared to wild-type SF8300 [E] (completely filled circles) and the complemented strain SF8300 ΔgdpP [gdpP] (half-filled circles).
To further our understanding of the role of GdpP, we focused our study on mecA-positive strains, which cause the majority of complicated and hard-to-treat S. aureus infections (5). To determine if CDA abundance alone was the factor driving the observed ΔgdpP-associated β-lactam-resilient phenotypes, the ΔgdpP mutant of SF8300 was complemented with gdpP obtained from the passaged strains, namely, CRB, CmTc, SRB, and SRT. An empty vector (E) and gdpP from SF8300 (Wt) were used as controls (Table S1a). The resultant isogenic strains displayed varying amounts of CDA (see Fig. S4a in the supplemental material). Growth assays (Fig. S4b) and population assays (Fig. S4c) showed a high correlation between CDA concentrations, bacterial growth attenuation, and increased proportion of resistant populations.
Since the results of the population analysis showed a very similar endpoint of killing of the isogenic strains (Fig. S4c), we sought to determine if gdpP loss-of-function-mediated enhanced β-lactam survival actually involved an MIC change. Results of the MIC assays did not show a substantial difference in MIC values between the strains (Table 1). Thus, deletion of gdpP did not produce a resistant phenotype when measured through an MIC assay.
TABLE 1.
MICs for strains used in this study
| Strains | MIC (μg/mL) for:a |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAF | CRO | FOX | CFZ | CPT | |
| SF8300 | 32 | >256 | 128 | 128 | 1 |
| SF8300 ΔgdpP | 32 | >256 | 128 | 128 | 1 |
NAF, nafcillin; CRO, ceftriaxone; FOX, cefoxitin; CFZ, cefazolin; CPT, ceftaroline.
Loss of GdpP function leads to increased tolerance to β-lactams.
Since deletion of gdpP allowed increased bacterial survival without a significant increase in the MIC values in the presence of β-lactams, we determined if the ΔgdpP strains mediated β-lactam tolerance. We performed tolerance assays using two representative β-lactam antibiotics (nafcillin and cefoxitin). The ΔgdpP strains in SF8300 (Fig. 3) and MW2 (see Fig. S5 in the supplemental material) backgrounds showed a classical (19) tolerance response, displaying an increased survival over time compared to its isogenic wild-type strain following treatment of antibiotics. Complementation with gdpP in the ΔgdpP strains restored their wild-type phenotype. These results led to the suggestion that ΔgdpP strains were able to survive a β-lactam challenge via drug tolerance.
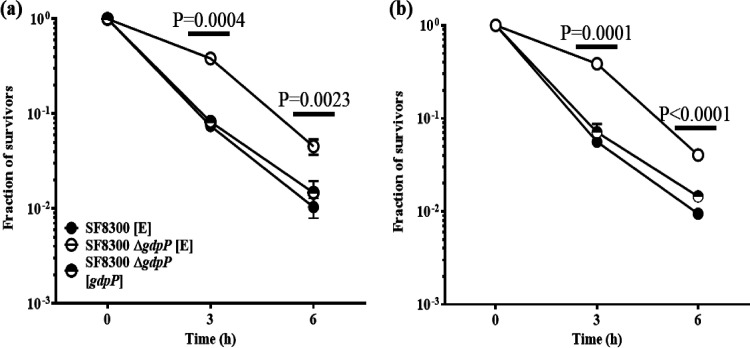
FIG 3.
Deletion of gdpP leads to β-lactam tolerance in SF8300 strains. β-Lactam tolerance assay carried out with nafcillin (128 μg/mL) (a) and cefoxitin (256 μg/mL) (b). The deletion of gdpP in the strain SF8300 ΔgdpP [E] (open circles) had a significant increase in the fraction of survivors and, thus, in tolerance when compared to that of the empty vector SF8300 [E] (filled circles) and the complemented strain SF8300 ΔgdpP [gdpP] (half-filled circles). P values were determined for SF8300 [E] versus SF8300 ΔgdpP [E].
GdpP loss-of-function mutations accumulate early in the process of β-lactam resistance and lead to faster evolution of β-lactam resistance.
As mentioned above, the reported mutations in gdpP among resistant strains were obtained through serial passaging of the susceptible parental strains in the presence of drugs that took several weeks to accomplish (20). While whole-genome sequencing enabled the identification of mutated genes, our study design did not inform about the specific stage of the passage at which the mutations were acquired. To determine this, we sequenced pbp4 and gdpP in one of the passaged strains, SRT (21), for which bacterial stock cultures from each day of passaging were available. SRT was obtained by passaging the susceptible SF8300ex (mecA and blaZ excised) strain in increasing concentrations of ceftaroline for 22 days. At day 22, SRT was able to grow in bacterial medium containing 256 μg/mL ceftaroline (21). The purified SRT clone that was used for subsequent studies showed high-level resistance to β-lactam drugs and had a pbp4 promoter and gene mutations in addition to having the X306 mutation in GdpP (Fig. 1a) (10). Bacteria from the daily stock cultures of SRT passage were streaked onto TSA plates, and three colonies from each day of passage were randomly chosen for sequencing of the gdpP and pbp4 promoter and gene. We detected that SRT acquired its gdpP-associated X306 mutation as early as on day 4 of passaging, during which bacteria were grown in media containing 0.5 μg/mL of ceftaroline. On day 4, SRT did not have any pbp4-related mutations, suggesting that gdpP-associated mutations were acquired very early during the evolution of resistance in SRT. Of note, we also detected gdpP mutations among passaged strains obtained in day 3, which were different from the X306 detected on day 4 (see Table S5 in the supplemental material).
To determine if tolerance mediated by loss of GdpP function could facilitate evolution of β-lactam resistance, we performed passaging of the susceptible SF8300ex and its isogenic ΔgdpP strains in two β-lactam antibiotics (nafcillin and cefoxitin). Results of this study revealed that the ΔgdpP strain was able to develop resistance faster compared to its isogenic SF8300ex strain (see Fig. S6 in the supplemental material). Thus, GdpP-mediated tolerance can lead to faster evolution of resistance.
Loss of GdpP function could lead to β-lactam treatment failure.
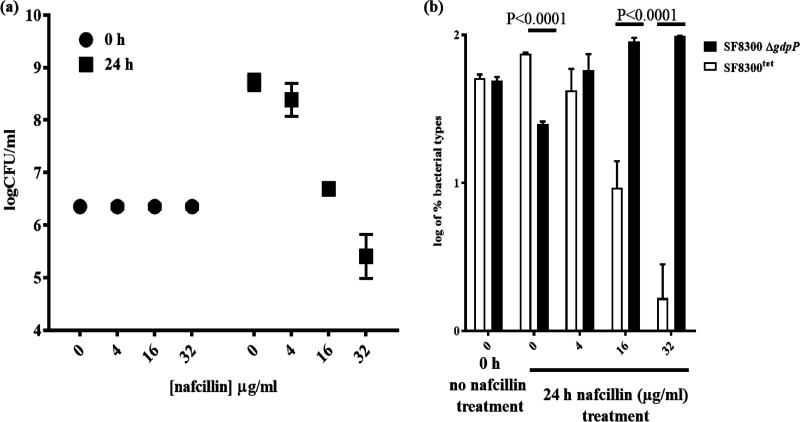
Since the therapeutic outcome of β-lactam tolerance due to loss of GdpP function is unknown, we created a tetracycline-resistant SF8300 (SF8300tet) strain by integrating pLL29 (single copy chromosomal integration vector) in its genome (22). The resultant SF8300tet strain displayed no difference in β-lactam resistance phenotypes when measured through MIC assays (see Table S6 in the supplemental material) or population analysis (see Fig. S7a in the supplemental material). There was also no change in CDA amounts in the bacterial cytosol (Fig. S7b) when compared to its isogenic wild-type strain, SF8300. To test the impact of ΔgdpP-induced tolerance on β-lactam treatment outcome, SF8300tet was mixed with the SF8300 ΔgdpP strain in a 1:1 ratio and was treated with different nafcillin concentrations. The resultant bacterial mixture was incubated for 24 h, upon which surviving bacterial CFU were enumerated by plating them onto Trypticase soy agar (TSA) plates. The bacterial titers of this assay at 24 h showed a stepwise decrease of total surviving bacteria in a nafcillin concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 4a). To determine the respective abundance of bacterial strains in the mixture, the surviving bacteria were selected onto TSA and TSAtet (TSA containing tetracycline) plates. The results of this analysis showed a preponderance of the SF8300 ΔgdpP strain (i.e., tetracycline-sensitive colonies) in the mixture (Fig. 4b). Furthermore, the ΔgdpP strain outcompeted the wild-type bacteria in a nafcillin concentration-dependent manner as well. These results suggested that the ΔgdpP strain could survive a β-lactam challenge better than its isogenic wild-type strain. The results of these experiments also revealed that at 24 h following incubation, the fraction of ΔgdpP strain was slightly attenuated compared to that of the wild-type strain without any antibiotic treatment, probably due to the inherent growth defect that the ΔgdpP strain displayed. This suggested that tolerance mediated by gdpP could indeed lead to β-lactam nonsusceptibility or therapy failure.
FIG 4.
Deletion of gdpP leads to β-lactam resistance. (a) Survival of 1:1 mixed cocultures of SF8300tet and SF8300 ΔgdpP strains upon treatment with nafcillin resulted in decreasing survival of bacterial CFU with increasing concentrations of nafcillin. (b) Fraction of SF8300tet and SF8300 ΔgdpP strains in the mixture showed that after 24 h of nafcillin treatment, SF8300 ΔgdpP strains had significantly increased survival than SF8300tet.
DISCUSSION
Previous work performed in Gram-positive firmicutes, such as Bacillus subtilis (23), Listeria monocytogenes (24), and S. aureus (12, 25) among others, has shown a broad role of CDA in controlling bacterial physiology, including osmoregulation, peptidoglycan metabolism, biofilm formation, and virulence and has also drawn associations between CDA levels to β-lactam resistance of bacteria. While reduction of CDA concentration (through inhibition of its synthesis machinery) in bacterial cells has been shown to sensitize bacteria to β-lactams, increased amount of CDA (via inhibition of its degradation machinery) produces resistance to β-lactam drugs (12). The mechanism(s) through which CDA modulates drug sensitivity/resistance, however, remains currently unknown.
A high-level association in detection of mutations in gdpP (the machinery that degrades CDA) among laboratory-generated and natural strains of S. aureus that were nonsusceptible or resistant to β-lactam drugs prompted us to determine their role in surviving β-lactam drug challenge (7, 20). Our results showed that the gdpP mutations, by virtue of their loss of function, enabled increased intracellular CDA concentration in S. aureus (Fig. 1b; see also Fig. S1b in the supplemental material), which in turn provided a significant fitness advantage in surviving β-lactam challenge in a manner that was dependent on CDA concentration. Experiments carried out to decipher an enhanced understanding of CDA’s role enabling better survival to a drug challenge indicated that increased CDA concentrations promoted β-lactam tolerance without altering drug resistance when measured through classical means, such as MIC or population analysis (Table 1; Fig. 2c). Although population analysis results showed homoresistance characteristics of bacterial strains with high CDA concentrations (Fig. 2c; see also Fig. S3c in the supplemental material), they indicated an almost identical endpoint of bacterial killing to that of wild-type bacteria. Thus, the term “resistance” in previous studies that associated CDA levels with drug resistance might have been used loosely. Antibiotic tolerance has recently emerged as an important factor that is distinct from traditional resistance, which reduces drug efficacy by producing slower killing of bacteria upon chemotherapeutic challenge (4, 19, 26). Indeed, our results show that acquisition of β-lactam tolerance through GdpP loss of function could lead to β-lactam therapy failure due to slower killing, thereby complicating treatment outcome (Fig. 3 and 4). These results are in alignment with previous studies that show that GdpP has a role in tolerance (27).
Recent studies have reported that increased mecA expression can enable S. aureus strains to display a β-lactam homoresistance phenotype (25), similar to that observed among strains with elevated CDA concentrations. Western blotting analysis did not indicate altered PBP2a expression among isogenic Wt and ΔgdpP strains used in this study (see Fig. S8a in the supplemental material). The results of Bocillin assay further showed unaltered expression of housekeeping PBPs (PBP1 through 4), suggesting that they were also likely not involved in GdpP-mediated β-lactam tolerance (Fig. S8b). We created two additional isogenic sets of strains (COLn and N315) to verify these results since the MW2 ΔgdpP strain showed slight overexpression of PBP4 in the Bocillin assay. Complementation with gdpP did not alter the PBP4 expression of the MW2 ΔgdpP strain (Fig. S8c), suggesting that the elevated PBP4 level is likely due to secondary site mutation(s) in this strain. Appearance of similar homoresistance phenotypes displayed by SF8300 and SF8300ex strains (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material) along with detection of loss of GdpP function mutations among natural strains (7, 11) (see Table S4 and Fig. S1b in the supplemental material) further supported the notion that GdpP-mediated effects are most likely carried out through mechanisms that are independent of bacterial PBPs. Strains containing truncated gdpP that were not susceptible to penicillins were also isolated from human and animal origin in recent studies (28, 29), further validating the clinical relevance of GdpP-associated effects of drug nonsusceptibility.
Appearance of GdpP loss-of-function mutation among one of the resistance-passaged strain, SRT, showed that its acquisition preceded mutations that enabled antibiotic resistance indicating that tolerance precedes resistance during evolution of antibiotic resistance (see Table S5 in the supplemental material). It also indicated that antibiotic tolerance is an independent biological phenomenon to that of resistance, which potentially employs separate mechanism(s) to aid antibiotic survival (19). This is likely the reason why GdpP loss-of-function mutations could be identified in natural strains that are nonsusceptible but not resistant to β-lactam drugs (7).
The mechanism through which GdpP loss of function enables β-lactam tolerance is unknown. Slower growth rate of the strains with elevated CDA levels does not seem to cause β-lactam tolerance, as both diminished and elevated CDA levels, which oppositely affects drug tolerance, reportedly inhibit bacterial growth (17). Thus, slower growth rate likely precludes β-lactam tolerance. Apart from a slightly smaller cell size, results of electron microscopic studies did not show much difference in bacterial gross cell morphologies, including that of the cell wall among the isogenic Wt and ΔgdpP strain pairs used in our study (see Fig. S9 in the supplemental material). This ruled out the possibility that an altered cell wall structure is the contributing factor for β-lactam tolerance, although further studies are required in order to determine this with more certainty. Previous studies have shown that CDA acts as a vital gatekeeper of ion transporting channels (most prominently that of potassium transporters, KdpFABC and KtrAB/AD potassium importers, and the CpaA potassium/sodium cation-proton antiporter) (16, 30), thereby controlling ion homeostasis in bacterial cells. It is thus imperative that elevated CDA concentrations due to GdpP loss of function would lead to reduced potassium ion concentrations in bacterial cells, which in turn would increase bacterial turgor pressure forcing bacteria to alter their cell structure and cell wall stiffness. Indeed, similar to our observation, GdpP loss-of-function mutants have previously been shown to display 30% smaller staphylococcal cell size (12). Since changes in cell shape in bacteria have recently been shown to influence antibiotic efficacy (31), it will be tempting to determine if changes in physical parameters, such as cell shape or stiffness brought in by CDA-mediated ionic imbalance, could contribute to β-lactam tolerance.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains and growth conditions.
Bacterial strains were grown in Trypticase soy broth (TSB) as previously described (21). Allelic replacements and complementation were carried out with the plasmids pKOR1 and pTXΔ, respectively (10). Tetracycline-resistant SF8300 (SF8300tet) was created by chromosomal integration of the plasmid pLL29 as previously described (22). Bacterial strains, plasmids, and primers used in this study are listed in Tables S1a and b, S2, S3, and S4 in the supplemental material.
Antibiotic resistance measurements.
MICs were determined by broth microdilution method as described previously (32). Briefly, 1 × 105 CFU were incubated for 48 h at 37°C in 0.2 mL cation-adjusted Mueller-Hinton broth (CAMHB) (BD Biosciences) containing increasing concentrations of antibiotic. MIC was recorded as the lowest concentration without growth at 48 h.
Population analyses were done by the agar method as previously described (21). Tetracycline (12.5 μg/mL) was added to the agar plates to select for the plasmid pTXΔ whenever stated. Briefly, a 10-μl volume of serially diluted culture was spotted onto agar plates containing various concentrations of antibiotic. The plates were incubated at 37°C for 72 h. Plates were read and expressed as CFU mL−1. Ceftobiprole and ceftaroline were provided by Johnson and Johnson Pharmaceutical Research and Development and (former) Forest Laboratories, respectively. All other antibiotics were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
CDA measurement in bacterial cell lysates.
CDA measurement was carried out as previously described (33) with a few modifications. Briefly, bacterial cells were collected after 6 h postculture, washed, and lysed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 1 mM EDTA using a FastPrep-24 homogenizer (MP Biomedicals). Bacterial cytosolic fraction was collected upon centrifugation. Aliquots of 40-μl cytosolic samples were mixed with 10 μL internal standard (20 ng/mL tenofovir, a phosphate group containing compound that is negatively charged in solution, similar to CDA), and 10 μL of the resulting mixture was injected into a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometer (LC-MS/MS) system. The LC-MS/MS system consisted of AB Sciex API 5000 tandem mass spectrometer, Shimadzu Prominence 20ADXR ultra-fast liquid chromatography (UFLC) pumps, and SIL-20ACXR autosampler. A Hypercarb analytical column (100 by 2.1 mm, 3 mm; Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) and mobile phases 100 mM ammonium acetate (Buffer A) and acetonitrile (Buffer B) were used for separation. Electrospray ionization in negative ion mode as the ion source and multiple reactions monitoring with ion pairs m/z 657/133 for CDA and m/z 286/133 for the internal standard were used for quantification. Calibration standards were prepared with synthetic CDA (Biolog) dissolved in the PBS containing 1 mM EDTA. The calibration range was 10 to 500 ng/mL with lower limit of quantification at 10 ng/mL.
Identification of GdpP function among clinical strains.
We cloned the gdpP gene from the clinical strains that contained missense mutations with a constitutively expressing plasmid, pTXΔ, and transformed the construct into a heterologous host, SF8300. The intracellular CDA abundance for each of these strains was measured through LC-MS/MS.
Bioinformatics and statistical analysis.
All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism. Comparisons between groups and determination of P values were carried out using two-tailed t test unless otherwise stated. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean for experiments performed in triplicates. Each experiment was performed in biological duplicates to ensure reproducibility. DNA sequence analysis was performed using DNAstar software. All other methods used in this study are presented in detail in the supplemental material.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Joseph Schaefer and Aubre Gilbert for their technical help. S.S.C. would like to thank Nick Carbonetti for critically reading the manuscript.
S.S.C. supervised L.B. and E.B. while he was at UCSF. R.P. and L.B. performed the key experiments in this manuscript. R.P. in addition performed all major experiments that were required for the manuscript revision and helped with manuscript preparation.
This work was funded by NIH grants 2R01AI100291 and R21AI142501 and startup funds provided by the University Systems of Maryland to S.S.C.
Footnotes
Supplemental material is available online only.
REFERENCES
- 1.Chatterjee SS, Otto M. 2013. Improved understanding of factors driving methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus epidemic waves. Clin Epidemiol 5:205–217. 10.2147/CLEP.S37071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lowy FD. 1998. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med 339:520–532. 10.1056/NEJM199808203390806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bui LMG, Conlon BP, Kidd SP. 2017. Antibiotic tolerance and the alternative lifestyles of Staphylococcus aureus. Essays Biochem 61:71–79. 10.1042/EBC20160061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Levin-Reisman I, Brauner A, Ronin I, Balaban NQ. 2019. Epistasis between antibiotic tolerance, persistence, and resistance mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:14734–14739. 10.1073/pnas.1906169116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chambers HF, Deleo FR. 2009. Waves of resistance: Staphylococcus aureus in the antibiotic era. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:629–641. 10.1038/nrmicro2200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Berger-Bachi B. 1999. Genetic basis of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Cell Mol Life Sci 56:764–770. 10.1007/s000180050023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Argudín MA, Roisin S, Nienhaus L, Dodemont M, de Mendonca R, Nonhoff C, Deplano A, Denis O. 2018. Genetic diversity among Staphylococcus aureus isolates showing oxacillin and/or cefoxitin resistance not linked to the presence of mec genes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 62:e00091-18. 10.1128/AAC.00091-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dordel J, Kim C, Chung M, Pardos de la Gándara M, Holden MT, Parkhill J, de Lencastre H, Bentley SD, Tomasz A. 2014. Novel determinants of antibiotic resistance: identification of mutated loci in highly methicillin-resistant subpopulations of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. mBio 5:e01000-13. 10.1128/mBio.01000-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Boonsiri T, Watanabe S, Tan X-E, Thitiananpakorn K, Narimatsu R, Sasaki K, Takenouchi R, Sato'o Y, Aiba Y, Kiga K, Sasahara T, Taki Y, Li F-Y, Zhang Y, Azam AH, Kawaguchi T, Cui L. 2020. Identification and characterization of mutations responsible for the β-lactam resistance in oxacillin-susceptible mecA-positive Staphylococcus aureus. Sci Rep 10:16907. 10.1038/s41598-020-73796-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chatterjee SS, Chen L, Gilbert A, da Costa TM, Nair V, Datta SK, Kreiswirth BN, Chambers HF. 2017. PBP4 mediates β-lactam resistance by altered function. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61:e00932-17. 10.1128/AAC.00932-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Argudín MA, Dodemont M, Taguemount M, Roisin S, de Mendonca R, Deplano A, Nonhoff C, Denis O. 2017. In vitro activity of ceftaroline against clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates collected during a national survey conducted in Belgian hospitals. J Antimicrob Chemother 72:56–59. 10.1093/jac/dkw380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Corrigan RM, Abbott JC, Burhenne H, Kaever V, Grundling A. 2011. c-di-AMP is a new second messenger in Staphylococcus aureus with a role in controlling cell size and envelope stress. PLoS Pathog 7:e1002217. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Taylor BL, Zhulin IB. 1999. PAS domains: internal sensors of oxygen, redox potential, and light. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:479–506. 10.1128/MMBR.63.2.479-506.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tal R, Wong HC, Calhoon R, Gelfand D, Fear AL, Volman G, Mayer R, Ross P, Amikam D, Weinhouse H, Cohen A, Sapir S, Ohana P, Benziman M. 1998. Three cdg operons control cellular turnover of cyclic di-GMP in Acetobacter xylinum: genetic organization and occurrence of conserved domains in isoenzymes. J Bacteriol 180:4416–4425. 10.1128/JB.180.17.4416-4425.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fahmi T, Port GC, Cho KH. 2017. c-di-AMP: an essential molecule in the signaling pathways that regulate the viability and virulence of Gram-positive bacteria. Genes (Basel) 8:197. 10.3390/genes8080197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Corrigan RM, Campeotto I, Jeganathan T, Roelofs KG, Lee VT, Gründling A. 2013. Systematic identification of conserved bacterial c-di-AMP receptor proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:9084–9089. 10.1073/pnas.1300595110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Corrigan RM, Grundling A. 2013. Cyclic di-AMP: another second messenger enters the fray. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:513–524. 10.1038/nrmicro3069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Huynh TN, Woodward JJ. 2016. Too much of a good thing: regulated depletion of c-di-AMP in the bacterial cytoplasm. Curr Opin Microbiol 30:22–29. 10.1016/j.mib.2015.12.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Brauner A, Fridman O, Gefen O, Balaban NQ. 2016. Distinguishing between resistance, tolerance and persistence to antibiotic treatment. Nat Rev Microbiol 14:320–330. 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Greninger AL, Chatterjee SS, Chan LC, Hamilton SM, Chambers HF, Chiu CY. 2016. Whole-genome sequencing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus resistant to fifth-generation cephalosporins reveals potential non-mecA mechanisms of resistance. PLoS One 11:e0149541. 10.1371/journal.pone.0149541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chan LC, Gilbert A, Basuino L, da Costa TM, Hamilton SM, Dos Santos KR, Chambers HF, Chatterjee SS. 2016. PBP4 mediates high-level resistance to new-generation cephalosporins in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:3934–3941. 10.1128/AAC.00358-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Luong TT, Lee CY. 2007. Improved single-copy integration vectors for Staphylococcus aureus. J Microbiol Methods 70:186–190. 10.1016/j.mimet.2007.04.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Luo Y, Helmann JD. 2012. Analysis of the role of Bacillus subtilis σM in β-lactam resistance reveals an essential role for c-di-AMP in peptidoglycan homeostasis. Mol Microbiol 83:623–639. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07953.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Whiteley AT, Garelis NE, Peterson BN, Choi PH, Tong L, Woodward JJ, Portnoy DA. 2017. c-di-AMP modulates Listeria monocytogenes central metabolism to regulate growth, antibiotic resistance and osmoregulation. Mol Microbiol 104:212–233. 10.1111/mmi.13622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pozzi C, Waters EM, Rudkin JK, Schaeffer CR, Lohan AJ, Tong P, Loftus BJ, Pier GB, Fey PD, Massey RC, O'Gara JP. 2012. Methicillin resistance alters the biofilm phenotype and attenuates virulence in Staphylococcus aureus device-associated infections. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002626. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Levin-Reisman I, Ronin I, Gefen O, Braniss I, Shoresh N, Balaban NQ. 2017. Antibiotic tolerance facilitates the evolution of resistance. Science 355:826–830. 10.1126/science.aaj2191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Griffiths JM, O'Neill AJ. 2012. Loss of function of the GdpP protein leads to joint β-lactam/glycopeptide tolerance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:579–581. 10.1128/AAC.05148-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ba X, Kalmar L, Hadjirin NF, Kerschner H, Apfalter P, Morgan FJ, Paterson GK, Girvan SL, Zhou R, Harrison EM, Holmes MA. 2019. Truncation of GdpP mediates β-lactam resistance in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother 74:1182–1191. 10.1093/jac/dkz013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sommer A, Fuchs S, Layer F, Schaudinn C, Weber RE, Richard H, Erdmann MB, Laue M, Schuster CF, Werner G, Strommenger B. 2021. Mutations in the gdpP gene are a clinically relevant mechanism for β-lactam resistance in meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus lacking mec determinants. Microbial Genomics 7:000623. 10.1099/mgen.0.000623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kim H, Youn SJ, Kim SO, Ko J, Lee JO, Choi BS. 2015. Structural studies of potassium transport protein KtrA regulator of conductance of K+ (RCK) C domain in complex with cyclic diadenosine monophosphate (c-di-AMP). J Biol Chem 290:16393–16402. 10.1074/jbc.M115.641340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Banerjee S, Lo K, Ojkic N, Stephens R, Scherer NF, Dinner AR. 2021. Mechanical feedback promotes bacterial adaptation to antibiotics. Nat Phys 17:403–409. 10.1038/s41567-020-01079-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chan LC, Basuino L, Diep B, Hamilton S, Chatterjee SS, Chambers HF. 2015. Ceftobiprole- and ceftaroline-resistant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59:2960–2963. 10.1128/AAC.05004-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Burhenne H, Kaever V. 2013. Quantification of cyclic dinucleotides by reversed-phase LC-MS/MS. Methods Mol Biol 1016:27–37. 10.1007/978-1-62703-441-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental material. Download AAC.01431-21-s0001.pdf, PDF file, 1.6 MB (1.6MB, pdf)