Abstract
COVID-19 is a highly infectious disease caused by the viral pathogen SARS-CoV-2, causing an estimated 5.4 million fatalities globally in 2 years since its emergence in December 2019. On December 22, 2021, the U.S. FDA granted Emergency Use Authorization for the oral viral main protease inhibitor, Nirmatrelvir, to treat patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. This patent review reveals the structure–activity relationship of key inhibitors described in the patent WO 2021/250648 A1.
Important Compound Classes
Title
Nitrile-containing antiviral compounds.
Patent Publication Number
WO 2021/250648 A1 (https://patentscope.wipo.int)
Publication Date
December 16, 2021
Priority Application
US 63/073,982, 63/143,435, 63/170,158 and 63/194,241
Priority Date
September 3, 2020, January 29, 2021, April 2, 2021, May 28, 2021
Inventors
Owen, D. R.; Pettersson, M. Y.; Reese, M. R.; Sammons, M. F.; Tuttle, J. B.; Verhoest, P. R.; Wei, L.; Yang, Q.; Yang, X.
Assignee Company
Pfizer, Inc., USA
Disease Area
COVID-19
Biological Target
SARS-CoV-2 main protease
Summary
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a highly infectious disease caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). First reported in Wuhan, China in December 2019, it rapidly escalated into a global pandemic by April 2020. Infection symptoms include sore throat, dry cough, fever, headache, fatigue, and dyspnea. By December 31, 2021, the WHO reported 280 million cases worldwide, with an estimated 5.4 million fatalities. Treatment options up to mid-December 2021 were limited to intravenously administered monoclonal antibodies (e.g., Sotrovimab and Tocilizumab) and the nucleoside analogue Remdesivir. On December 22, 2021, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the oral antiviral drug, Nirmatrelvir, for treating patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in combination with Ritonavir.
Nirmatrelvir was designed to specifically target the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro), also known as 3 chymotrypsin-like protease (3CLpro). This viral protease plays a critical role in coronavirus polyprotein processing, cleaving the polyprotein in at least 11 places to yield functional viral proteins and enzymes required for its survival and propagation. It is a peptidomimetic, designed based on the natural 3CLpro polypeptide substrate recognition sequence: valine–leucine–glutamine. An electrophilic nitrile moiety was introduced at its C-terminus so that, after the drug binds into the 3CLpro active site, the nitrile can then subsequently react with 3CLpro’s Cys145 thiol (−SH) moiety, forming a covalent bond and thereby inhibiting the viral protease.
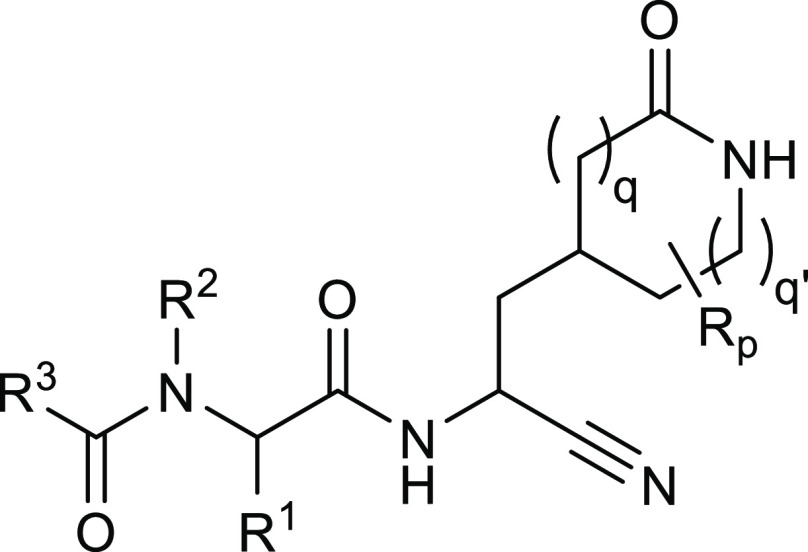
The present patent application describes 98 novel coronavirus 3CLpro peptidomimetic inhibitors that can be used to inhibit viral replication and can potentially be used for treating COVID-19. It also includes methods of administering a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of the inhibitor to COVID-19 patients.
Key Structures
The inventors described 98 novel structures with their synthetic methods. Key exemplified structures and their biological activities are shown vide infra.
Biological Assay
SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Ki values were determined in a biochemical SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) competition assay where the exemplified compounds were challenged with a fluorogenic peptide substrate in the presence of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro. EC50 values were determined in a cell-based assay using VeroE6 cells enriched for hACE2 expression and tested using SARS-CoV-2. Cell viability was measured using CellTiter-Glo (Promega) to quantify cellular ATP levels.
Biological Data
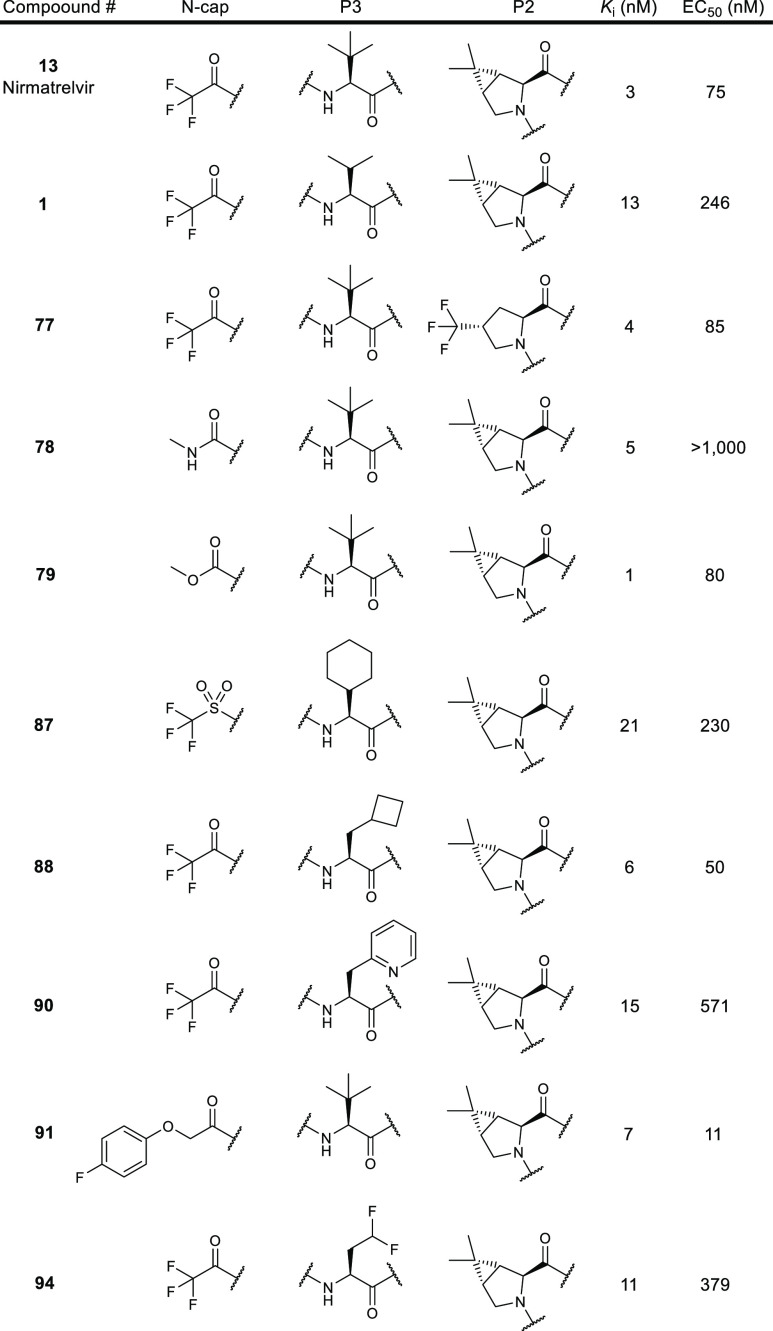
The SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Ki and EC50 data of key inhibitors are summarized
in the following table.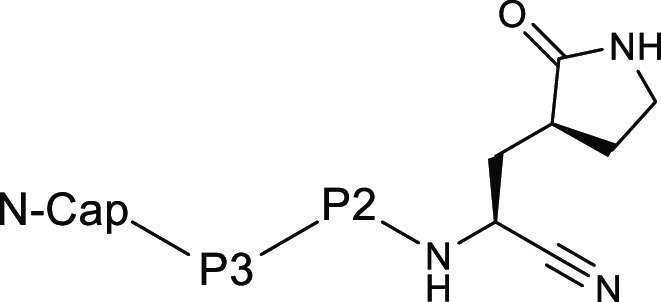
Recent Review Articles
-
1.
Owen D. R.; Allerton C. M. N.; Anderson A. S., Aschenbrenner L.; Avery M.; Berritt S.; Boras B.. Science 2021, 374, 1586; DOI: 10.1126/science.abl4784.
-
2.
Banerjee R.; Perera L.; Tillekeratne L. M. V.. Drug Discovery Today. 2021, 26, 804; DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2020.12.005.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (ASTAR), Singapore, for funding this patent review.
Glossary
Abbreviations
- 3CLpro
3 chymotrypsin-like protease
- ACE2
angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
- ATP
adenosine triphosphate
- COVID-19
Coronavirus Disease 2019
- FDA
Food and Drug Administration
- FRET
fluorescence resonance energy transfer
- EUA
Emergency Use Authorization
- Mpro
main protease
- SARS-CoV-2
severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
- WHO
World Health Organization
The author declares no competing financial interest.
This article is made available via the ACS COVID-19 subset for unrestricted RESEARCH re-use and analyses in any form or by any means with acknowledgement of the original source. These permissions are granted for the duration of the World Health Organization (WHO) declaration of COVID-19 as a global pandemic.