Abstract
Background
During the COVID-19 pandemia, non-invasive mechanical ventilation (NIV) has been largely applied. Few data are available about predictors of NIV failure in critical COVID-19 patients admitted to ICU. The aim of this study is to analyze clinical and laboratory features able to predict non-invasive ventilation success in avoiding endotracheal intubation.
Methods
A retrospective observational study was performed in our COVID-19 ICU during a 6-month period. Demographic, clinical, laboratory, imaging, and outcome data were extracted from electronic and paper medical records and anonymously collected.
Results
Eighty-two severe COVID-19 patients were supported by NIV at ICU admission. The median PaO2/FiO2 ratio was 125 [98.5–177.7]. NIV failed in 44 cases (53%). Patients who experienced NIV failure had a higher Charlson Comorbidity Index (median value 4) compared to those who were dismissed without endotracheal intubation (median 2, p < 0.0001). At Cox regression analysis, the Charlson Comorbidity Index represented a predictive factor related to NIV failure. PaO2/FiO2, CPK, INR, and AT III at ICU admission showed a significant relationship with the outcome, when single variables were adjusted for the Charlson Comorbidity Index.
Conclusion
The Charlson Comorbidity Index may be helpful to stratify patients’ risk of NIV failure in a severe COVID-19 population; even if this study, retrospective design does not allow definitive conclusions.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s44158-022-00038-7.
Keywords: COVID-19, ARDS, Non-invasive mechanical ventilation, Intensive care unit, Predictive factor
Background
The most relevant clinical manifestation of COVID-19 [1] is the development of interstitial pneumonia, evolving in about 5–15% of cases to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), requiring admission in intensive care [2]. Older age and the presence of multimorbidities are related to a higher risk of mortality, and the Charlson Comorbidity Index, which is used by geriatricians to predict 10 years of mortality, can predict COVID-19 mortality with an exponential increase in the odds ratio by each point of score [3].
Chinese [4], British [5], American [6], and Australian [7] guidelines recommended safe endotracheal intubation and initiation of invasive mechanical ventilation in critically ill COVID-19 patients. Two objectives justified this approach: (a) to reduce the airborne dispersion of viral particles, preventing contagion between healthcare personnel [8]; (b) avoid the onset of sudden cardiac arrest and death in patients with severe hypoxia [9]. Although experts support the use of early endotracheal intubation to prevent “self-inflicted lung injury” (SILI) [10], a meta-analysis suggests that the timing of endotracheal intubation does not affect mortality and morbidity in critically ill COVID-19 patients [11]. Moreover, patients requiring endotracheal intubation after non-invasive mechanical ventilation (NIV) failure showed the same mortality rate compared to those intubated without NIV trial attempts [12].
Therefore, these results could justify a cautious “wait-and-see” approach, favoring the use of NIV as the primary respiratory support modality in critical COVID-19 patients. However, a scoping review performed by Radovanovic et al. [9] showed that few studies examined the role of NIV in critical COVID-19 patients requiring ICU admission. Furthermore, data on mortality in NIV patients admitted to ICUs are poorly reported, such as studies on clinical and laboratory predictors related to NIV failure or success in patients with COVID-19.
The aim of the present retrospective study is to analyze clinical and laboratory features present at ICU admission and able to predict NIV failure in COVID-19 patients.
Material and method
Patients’ enrollment
This retrospective observational study enrolled all patients admitted to a university hospital COVID ICU (“Da Procida” Hospital, Salerno, Italy) from 14th October 2020 to 30th April 2021. Inclusion criteria were age > 18 years old, positive reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction nasopharyngeal swab test for SARS-CoV-2 infection, acute respiratory failure (defined as PaO2/FiO2 ≤ 300 [13]) eligible for NIV, ICU length of stay (LOS) ≥ 48 h. Exclusion criteria were ICU LOS < 48 h and other major causes requiring ICU admission, i.e., spontaneous cerebral hemorrhage, trauma, post-operative complications in COVID patients.
NIV management and sedation protocol
A “patient eligible for NIV” is defined as a conscious and cooperative subject requiring NIV support by oral-nasal mask, full-face mask or helmet, in both pressure support ventilation (PSV) and continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) modalities and not requiring endotracheal intubation within 3 h ICU admission. NIV was provided by conventional ICU mechanical ventilators. To enhance patients' compliance, a continuous infusion of dexmedetomidine (0.6–1.2 mcg/kg/h) and morphine bolus (5 mg iv) when required, was used. Sedation was adjusted stepwise to achieve a Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale (RASS) level of 0, -1 [14]. Awakening prone position ventilation was adopted according to patients' tolerance and aimed to be continued for 3 h at least [15].
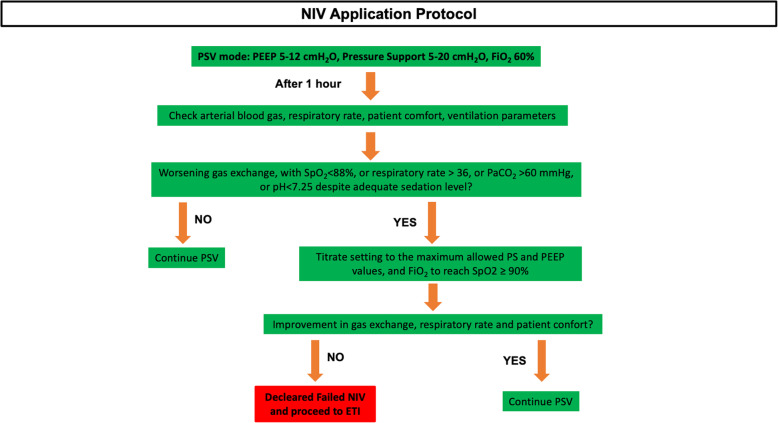
Figure 1 shows details about the NIV application protocol. NIV was continued whenever possible and based on the patient’s tolerance. When FiO2 was < 50%, respiratory rate < 30 breaths per minute, expiratory tidal volume > 5 mL/kg body weight expected with a pressure support < 10 cmH2O, and PEEP < 8 cmH2O, NIV was progressively suspended, and a high-flow nasal oxygen (HFNO) was started based on arterial blood gas (ABG) data. HFNO was also used during patients’ mobilization on a chair and meals [16].
Fig. 1.
NIV protocol. The figure shows the NIV protocol adopted for the patients admitted to ICU. When patients started with CPAP mode at ICU admission, we set a PEEP value ranging between 5 and 12 cmH2O and FiO2 60%. After 1 h, the clinician evaluated gas exchanges, by arterial blood gas analysis, respiratory rate, and patient’s comfort. In case of worsening gas exchange with SpO2 < 88%, or respiratory rate > 36, or PaCO2 > 60 mmHg, or pH < 7.25 despite adequate sedation level, the patient stopped CPAP and started NIV in PSV mode according to our protocol. On the contrary case, the patient continued CPAP mode ventilation
NIV failure was defined according to ERS/ATS guidelines [17], as the persistence of a low PaO2/FiO2 ratio (less than 100 mmHg despite optimal NIV settings) and high respiratory rate (> 36/min). In order to avoid endotracheal intubation, NIV was titrated with a maximum pressure support of 20 cmH2O, maximum PEEP of 10–12 cmH2O and FiO2 set to obtain an oxygen saturation higher than 90%. We checked in the single patient in order to avoid barotrauma and intolerance.
In case of persistent or worsening of gas exchanges (oxygen saturation < 88%, respiratory rate > 36/min), patient’ inability to protect airways (i.e., coma or convulsive disorder) or to manage abundant tracheal and/or bronchial secretions, and hemodynamic or electrocardiographic instability, intensivists proceeded to endotracheal intubation and started invasive mechanical ventilation.
Therapy
We provided all therapies as part of our standard care pathway. All patients, following the available scientific evidence, received: intravenous dexamethasone (6 mg iv, once a day for 10 days) and subcutaneous enoxaparin (50 I.U./kg, once a day as prophylaxis dosing, or bid in case of thrombosis suspected or confirmed). In addition, in selected cases and according to the best available evidence, we administered tocilizumab, remdesivir, and eculizumab.
Data collection
Demographic, clinical, laboratory, imaging, and outcome data were extracted from electronic and paper medical records and anonymously collected on a digital sheet (Excel, Microsoft). A detailed description of collected data is provided in Supplementary File 1.
We used the Charlson Comorbidity Index (Supplementary File 2) to identify the chronic conditions which might impact long-term survival [18]. Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score [19] and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio were calculated [20].
We reported the patient’s length of stay (LOS) in the pneumology/infectious disease ward, defined as the days from emergency room (ER) to ICU admission, ICU LOS, NIV-days, and ICU survival rates.
Statistical analysis
We performed statistical analysis with MedCalc® Statistical Software version 19.6 (MedCalc Software Ltd, Ostend, Belgium; https://www.medcalc.org; 2020) and R software (R Core Team 2020, R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL https://www.R-project.org/).
No statistical sample size assessment was performed a priori, and the sample size was the number of patients requiring NIV during the study period, meeting inclusion and exclusion criteria. We reported the number of missing data and carried out the statistics based on available ones (Supplementary Table 1).
To investigate the influence of clinical and laboratory variables on the main outcome, NIV failure, we performed univariate Cox regression analysis. Categorical variables with a frequency ≤ 5 cases were excluded. First, Hazard-ratio (HR), 95% confidence interval (CI95%) and p-value were computed. Considering Charlson Comorbidity Index as an independent risk factor related to poor outcomes in COVID-19 patients [21], in a second step, each variable was adjusted for Charlson Comorbidity Index. Adjusted HR (HRAdj) with CI95% were computed.
For significant models, the performance was analyzed with the receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve [22]. The area under the curve (AUC) and CI95% were computed. The best cut-off value using the Youden’s (J) index [23], sensibility (Se, defined as the true positive rate, and specificity (Sp, defined as the true negative rate), with CI95%, were computed. Finally, we compared ROC curves for the single significative variable, adjusted variable for the Charlson Comorbidity Index, and Charlson Comorbidity Index. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Furthermore, a subgroup analysis between patients who experienced NIV failure and those who did not was performed and details about statistical methods and results are provided in Supplementary file 1. We reported the data in tables and graphics.
Results
On admission, 82 patients required NIV (70.1%), representing the studied sample. Table 1 reports the details of the population’s main characteristics.
Table 1.
Demographic and clinical features of the sample
| Main characteristics of the population (82 patients) | |
|---|---|
| Demographic data | |
| Variable | Result |
| Sex, male (%) | 62 (75.6%) |
| Age (years) | 67.0 [56.5–73.0] |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.8 [25.3–31.3] |
| NIV-day | 5.0 [3.0–8.5] |
| Ward LOS (days) | 3.0 [0.0–7.0] |
| ICU LOS (days) | 8.0 [5.0–12.0] |
| Survived (%) | 37 (45.1%) |
| Comorbidities | |
| Variable | Result |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | 3 [1–4] |
| Hypertension (%) | 45 (54.9%) |
| Obesity (%) | 27 (32.9%) |
| Diabets (%) | 22 (26.8%) |
| COPD (%) | 15 (18.3%) |
| CAD (%) | 10 (12.2%) |
| CKD (%) | 4 (4.9%) |
| Endocrinological disease (%) | 4 (4.9%) |
| Atrial fibrillation (%) | 4 (4.9%) |
| DVT (%) | 3 (3.7%) |
| CVD (%) | 3 (3.7%) |
| Asthma (%) | 3 (3.7%) |
| Autoimmune disease (%) | 3 (3.7%) |
| Hematological disease (%) | 2 (2.4%) |
| OSAS (%) | 2 (2.4%) |
| Neurological disorder (%) | 2 (2.4%) |
| Liver disease (%) | 1 (1.2%) |
| Arterial blood gas analysis and ventilation parameters | |
| Variable | Result |
| pH | 7.46 [7.43–7.48] |
| PaO2(mmHg) | 89.5 [75.0–106.2] |
| PaCO2(mmHg) | 37.5 [33.0–42.0] |
| PaO2/FiO2 | 125.0 [98.5–177.7] |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 1.3 [1.1–1.8] |
| CPAP (%) | 13 (15.9%) |
| PSV (%) | 69 (84.1%) |
| PEEP (cmH2O) | 10 [10–10] |
| Pressure support (cmH2O) | 7.5 [6.0–10.0] |
The table reports demographic and clinical features. Frequencies are expressed as numbers and percentages (%). Continuous variables are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) or median, first and third quartile [q1–q3]. BMI, body mass index; LOS, length of stay; CAD, coronary artery disease; DVT, deep vein thrombosis; CVD, cerebral-vascular disease; CKD, chronic kidney disease; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; OSAS, obstructive sleep apnea syndrome; CPAP, continuous positive airway pressure; PSV, pressure support ventilation; PEEP, positive end-expiratory pressure
PSV was the most common modality used for NIV (84.1%), and the median NIV-day was 5.0 [3.0–8.5] (minimum and maximum, respectively, 1.0 and 18.0 days); 37 patients (45.1%) were discharged alive from the ICU. NIV-failed and NIV-successful groups consisted of 44 and 38 patients, respectively. Tables 2, 3, and 4 show detailed results of statistical comparison between the groups, such as described in Supplementary file 1. The survival rate in NIV-successful group resulted higher than NIV-failed group (94.7% vs 2.3%, p-value < 0.0001, Table 2).
Table 2.
NIV-failed vs NIV-successful groups: demographic, comorbidities, blood gas analysis, and ventilation setting parameter statistical analysis
| Variable | NIV-failed (n = 44) | NIV-successful (n = 38) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic data | |||
| Male gender (%) | 28 (63.6%) | 34 (89.5%) | 0.0069 |
| Age (years) | 69.4 ± 7.8 | 59.0 ± 12.4 | < 0.0001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.4 [25.1–31.0] | 28.7 [25.2–38.0] | 0.1215 |
| NIV day (days) | 5.0 [3.0–9.0] | 4.5 [3.0–8.0] | 0.7931 |
| Ward LOS (days) | 4.0 [0.0–7.0] | 3.0 [0.0–7.0] | 0.8540 |
| ICU LOS (day) | 10.0 [7.0–13.0] | 5.0 [4.0–8.0] | < 0.0001 |
| Survived (%) | 1 (2.3%) | 36 (94.7%) | < 0.0001 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | 4 [3–4] | 2 [1–3] | <0.0001 |
| Hypertension (%) | 28 (63.6%) | 17 (44.7%) | 0.0863 |
| Obesity (%) | 12 (27.3%) | 15 (39.5%) | 0.2411 |
| Diabets (%) | 15 (34.1%) | 7 (18.4%) | 0.1103 |
| COPD (%) | 12 (27.3%) | 3 (7.9%) | 0.0236 |
| CAD (%) | 8 (18.2%) | 2 (5.3%) | 0.0764 |
| CKD (%) | 3 (6.8%) | 1 (2.6%) | 0.3801 |
| Endocrinological disease (%) | 4 (9.1%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.0567 |
| Atrial fibrillation (%) | 3 (6.8%) | 1 (2.6%) | 0.3801 |
| DVT (%) | 2 (4.5%) | 1 (2.6%) | 0.6453 |
| CVD (%) | 3 (6.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.1010 |
| Asthma (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (7.9%) | 0.0579 |
| Autoimmune disease (%) | 3 (6.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.1010 |
| Hematological disease (%) | 1 (2.3%) | 1 (2.6%) | 0.9163 |
| OSAS (%) | 1 (2.3%) | 1 (2.6%) | 0.9163 |
| Neurological disorder (%) | 2 (4.5%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.1833 |
| Liver disease (%) | 1 (2.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.3498 |
| Arterial blood gas analysis and ventilation parameters | |||
| pH | 7.45 [7.44–7.49] | 7.46 [7.43–7.48] | 0.8280 |
| PaO2(mmHg) | 81.0 [74.0–106.7] | 91.0 [77.2–104.4] | 0.7977 |
| PaCO2(mmHg) | 36.0 [30.2–42.0] | 39.0 [34.5–42.2] | 0.2650 |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 1.5 [1.3–1.9] | 1.2 [1.0–1.6] | 0.0070 |
| PaO2/FiO2 | 111.0 [93.0–182.7] | 127.0 [116.2–173.2] | 0.2379 |
| CPAP (%) | 3 (6.8%) | 10 (26.3%) | 0.0166 |
| PEEP (cmH2O) | 10.0 [10.0–10.0] | 10.0 [10.0–11.0] | 0.4785 |
| Pressure support (cmH2O) | 6.0 [5.0–10.0] | 9.0 [7.0–10.0] | 0.0393 |
The table reports the statistical comparison of demographic, comorbidities, blood gas analysis, and ventilation setting parameters between the groups. Frequencies are expressed as numbers and percentages (%). Continuous variables are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) or median, first and third quartile [q1–q3]. In case of missing data, statistics were performed on available data. Differences in frequencies were tested with the chi-square test. Differences in continuous variables were tested with two-tailed Student’s t-test (equal variance) or Welch’s test (unequal variance) or, for not normally distributed continuous variables, the Mann-Whitney test. All tests were performed with an α = 0.05, and a p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant
Table 3.
NIV-failed vs NIV-successful groups: laboratory findings and therapies statistical analysis
| Variable | Overall (n = 82) | NIV-failed (n = 44) | NIV-successful (n = 38) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory results | ||||
| Glicemia (mg/dL) | 139.0 [117.0–177.0] | 160.5 [129.5–202.5] | 123.5 [112.0–154.0] | 0.0039 |
| Azotemia (mg/dL) | 60.5 [46.2–71.0] | 63.5 [49.5–96.0] | 60.0 [45.0–69.0] | 0.2284 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.74 [0.61–0.96] | 0.73 [0.56–1.09] | 0.74 [0.66–0.91] | 0.7802 |
| eGFR (mL/min) | 95.5 [73.3–106.7] | 91.5 [66.7–99.3] | 100.8 [88.8–113.3] | 0.0104 |
| Total protein (g/dL) | 6.0 ± 0.6 | 6.1 ± 0.6 | 6.1 ± 0.6 | 0.7854 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 0.7 [0.6–0.9] | 2.9 ± 0.3 | 3.1 ± 0.4 | 0.0051 |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 3.0 ± 0.4 | 0.8 [0.6–0.9] | 0.7 [0.5–0.9] | 0.4540 |
| Ammonium (μg/dL) | 84.0 [65.0–113.0] | 84.0 [63.0–110.7] | 85.5 [67.5–115.5] | 0.9250 |
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 138.0 [136.0–140.0] | 138.0 [136.0–143.0] | 138.0 [136.0–140.0] | 0.3287 |
| Potassium (mEq/L) | 4.4 ± 0.5 | 4.2 ± 0.4 | 4.6 ± 0.5 | 0.0013 |
| Clorum (mEq/L) | 102.0 [99.5–104.0] | 103.0 [100.2–105.7] | 102.0 [99.0–103.0] | 0.1595 |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 8.5 [8.1–8.8] | 8.4 [8.1–8.6] | 8.6 [8.3–8.9] | 0.0443 |
| Magnesium (mg/dL) | 2.2 ± 0.3 | 2.3 [2.0–2.5] | 2.2 [2.0–2.4] | 0.8127 |
| AST (U/L) | 31.5 [25.0–48.2] | 29.0 [23.0–45.5] | 34.0 [27.0–50.0] | 0.3218 |
| ALT (U/L) | 37.0 [26.0–56.0] | 30.0 [20.0–42.5] | 49.5 [28.0–79.0] | 0.0016 |
| LDH (U/L) | 413.0 [319.5–598.0] | 456.5 [348.0–614.5] | 387.5 [299.0–550.0] | 0.1344 |
| CPK (U/L) | 69.5 [40.5–141.5] | 61.5 [45.0–132.0] | 82.0 [34.0–156.0] | 0.7168 |
| Troponin (ng/L) | 11.3 [5.0–21.3] | 13.5 [8.4–38.6] | 6.0 [3.7–13.9] | 0.0008 |
| Mioglobin (ng/mL) | 62.3 [37.8–110.9] | 75.5 [39.2–169.5] | 49.9 [32.5–91.5] | 0.0894 |
| CK-MB (ng/mL) | 1.7 [1.1–2.8] | 2.1 [1.3–3.9] | 1.3 [0.9–1.9] | 0.0038 |
| BNP (pg/mL) | 53.0 [33.0–123.2] | 86.0 [46.5–196.2] | 34.0 [21.0–58.0] | 0.0001 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 13.7 [12.2–14.6] | 13.1 [12.1–13.9] | 14.3 [12.4–14.9] | 0.0327 |
| WBC (× 103) | 11.0 [8.1–13.3] | 11.8 [9.1–13.3] | 10.1 [7.6–13.3] | 0.1017 |
| Neutrophil (× 103) | 9.6 [7.0–11.7] | 10.3 [8.0–12.0] | 8.4 [6.9–10.9] | 0.0542 |
| Lymphocytes | 727 [536–999] | 758 ± 330 | 850 ± 348 | 0.2255 |
| Eosinophil | 85 [48–154] | 96 [53–156] | 78 [39–149] | 0.2906 |
| Monocyte | 437 [318–627] | 433 [317–580] | 476 [322–700] | 0.5121 |
| Basophil | 13 [8–24] | 13 [10–24] | 12 [5–21] | 0.2182 |
| Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio | 12.1 [8.8–18.0] | 15.1 [10.4–19.7] | 10.3 [7.4–14.4] | 0.0080 |
| Platelet (× 103) | 266.6 ± 103.9 | 247.4 ± 104.6 | 288.8 ± 99.9 | 0.0714 |
| aPTT (sec) | 29.9 [26.8–32.8] | 31.2 [29.3–34.0] | 27.9 [25.9–30.6] | 0.0041 |
| INR | 1.13 [1.04–1.23] | 1.19 [1.04–1.31] | 1.12 [1.04–1.18] | 0.0921 |
| Firbinogen (mg/dL) | 538.5 [471.0–670.0] | 505.5 [424.5–588.0] | 596.0 [512.0–699.0] | 0.0166 |
| D-dimer (ng/mL) | 1060.0 [680.7–2495.0] | 1460.0 [860.0–3825.0] | 820.0 [530.0–1260.0] | 0.0037 |
| AT III (%) | 86.3 ± 15.9 | 82.4 ± 16.2 | 90.8 ± 14.4 | 0.0161 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 7.3 [3.6–12.7] | 8.9 [5.1–14.2] | 6.1 [3.6–9.4] | 0.0762 |
| PCT (ng/mL) | 0.10 [0.06–0.23] | 0.13 [0.09–0.35] | 0.08 [0.05–0.14] | 0.0141 |
| SOFA score | 3 [3–4] | 4 [3–5] | 3 [3–4] | 0.0808 |
| Therapies | ||||
| Tocilizumab (%) | 16 (19.5%) | 6 (13.6%) | 10 (26.3%) | 0.1490 |
| Eculizumab (%) | 2 (2.4%) | 1 (2.3%) | 1 (2.6%) | 0.9163 |
| Remdesivir (%) | 6 (7.3%) | 2 (4.5%) | 4 (10.5%) | 0.2997 |
The table reports the statistical comparison of laboratory findings and therapies between the groups. Frequencies are expressed as numbers and percentages (%). Continuous variables are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) or median, first and third quartile [q1–q3]. In case of missing data, statistics were performed on available data. Differences in frequencies were tested with the chi-square test. Differences in continuous variables were tested with two-tailed Student’s t-test (equal variance) or Welch’s test (unequal variance) or, for not normally distributed continuous variables, the Mann-Whitney test. All tests were performed with an α = 0.05, and a p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant
Table 4.
NIV-failed and NIV-successful groups: chest CT scan feature statistical analysis
| Variable | Overall (n = 58) | NIV-failed (n = 31) | NIV-successful (n = 27) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥ 4 involved lobes (%) | 54 (93.1%) | 28 (90.3%) | 26 (96.3%) | 0.3705 |
| Ground-glass opacity (%) | 51 (87.9%) | 30 (96.8%) | 21 (77.8%) | 0.0281 |
| Consolidation (%) | 43 (74.1%) | 21 (67.7%) | 22 (81.5%) | 0.2373 |
| Lymphoadenopathy (%) | 27 (46.6%) | 16 (51.6%) | 11 (40.7%) | 0.4117 |
| Interstitial septum thickening (%) | 12 (20.7%) | 8 (25.8%) | 4 (14.8%) | 0.3068 |
| Crazy paving (%) | 8 (13.8%) | 3 (9.7%) | 5 (18.5%) | 0.3343 |
| Pneumomediastinum (%) | 9 (15.5%) | 7 (22.6%) | 2 (7.4%) | 0.1145 |
| Bronchogram (%) | 6 (10.3%) | 4 (12.9%) | 2 (7.4%) | 0.4968 |
| Pleural effusion (%) | 8 (13.8%) | 3 (9.7%) | 5 (18.5%) | 0.3343 |
| Emphysema (%) | 8 (13.8%) | 6 (19.4%) | 2 (7.4%) | 0.1920 |
| Pneumothorax (%) | 5 (8.6%) | 3 (9.7%) | 2 (7.4%) | 0.7607 |
| Cavitation (%) | 5 (8.6%) | 3 (9.7%) | 2 (7.4%) | 0.7607 |
| Adjacent pleural thickening (%) | 7 (12.1%) | 7 (22.6%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.0090 |
| Subcutaneous emphysema (%) | 6 (10.3%) | 6 (19.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.0167 |
| Pericardial effusion (%) | 3 (5.2%) | 1 (3.2%) | 2 (7.4%) | 0.4771 |
| Iodinate contrast (%) | 28 (48.3%) | 17 (54.8%) | 11 (40.7%) | 0.2880 |
| Pulmonary thromboembolism (%) | 2 (7.1%) | 2 (11.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.2378 |
The table reports the statistical comparison of chest CT scan features between the groups. Frequencies are expressed as numbers and percentages (%). Differences in frequencies were tested with the chi-square test (α = 0.05) and a p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant
Single-variable Cox regression analysis showed that age, the Charlson Comorbidity Index, suffering from COPD and CAD, calcium, CPK, troponin, CK-MB, INR, and AT III were factors related to NIV failure (for details, see Table 5). When single variables were adjusted for the Charlson Comorbidity Index, only PaO2/FiO2 (HRAdj 0.99, CI95% 0.98–1.00, p-value 0.0181), CPK (HRAdj 1.00, CI95% 1.00–1.00, p-value 0.0064), INR (HRAdj 2.32, CI95% 1.10–4.85, p-value 0.0262), and AT III (HRAdj 0.98, CI95% 0.96–0.99, p-value 0.0249) showed a significant relationship with the considered outcome.
Table 5.
Cox regression analysis
| Variable | Univariate Cox regression | Multivariate Cox regression (adjusted for the Charlson Comorbidity Index) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (CI95%) | p-value | HRAdj (CI95%) | p-value | |
| Gender, male | 0.82 (0.42–1.59) | 0.5533 | 0.84 (0.43–1.65) | 0.6143 |
| Age | 1.04 (1.00–1.07) | 0.0372 | 1.00 (0.95–1.05) | 0.9315 |
| BMI | 0.99 (0.92–1.05) | 0.6700 | 1.00 (0.94–1.07) | 0.9212 |
| Ward LOS | 1.00 (0.97–1.03) | 0.9638 | 0.99 (0.96–1.03) | 0.7481 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | 1.32 (1.10–1.57) | 0.0024 | – | – |
| Hypertension | 1.11 (0.58–2.12) | 0.7499 | 0.81 (0.41–1.59) | 0.5380 |
| Obesity | 1.34 (0.65–2.78) | 0.4287 | 1.76 (0.83–3.74) | 0.1381 |
| Diabets | 1.70 (0.89–3.26) | 0.1065 | 0.98 (0.45–2.13) | 0.9592 |
| COPD | 2.33 (1.13–4.79) | 0.0212 | 1.51 (0.69–3.30) | 0.2993 |
| CAD | 2.56 (1.16–5.64) | 0.0199 | 1.81 (0.80–4.11) | 0.1535 |
| pH | 0.15 (0.00–33.93) | 0.4953 | 17.11 (0.06–4463.02) | 0.3170 |
| PaO2 | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | 0.7803 | 0.99 (0.98–1.00) | 0.0843 |
| PaCO2 | 0.98 (0.94–1.03) | 0.4053 | 1.00 (0.96–1.03) | 0.9155 |
| Lactate | 1.36 (0.83–2.24) | 0.2244 | 0.88 (0.50–1.57) | 0.6719 |
| PaO2/FiO2 | 1.00 (0.99–1.00) | 0.3118 | 0.99 (0.98–1.00) | 0.0181 |
| FiO2 | 4.22 (0.58–30.40) | 0.1531 | 5.52 (0.66–46.00) | 0.1146 |
| Ventilation mode, PSV | 2.43 (0.74–7.92) | 0.1410 | 2.07 (0.63–6.84) | 0.2332 |
| PEEP | 1.10 (0.86–1.40) | 0.4339 | 1.11 (0.85–1.46) | 0.4305 |
| Pressure support | 0.89 (0.77–1.02) | 0.0852 | 0.91 (0.79–1.04) | 0.1846 |
| Glicemia | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | 0.0714 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.8372 |
| Azotemia | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | 0.7315 | 0.99 (0.99–1.00) | 0.3478 |
| Creatinine | 1.09 (0.63–1.88) | 07611 | 0.69 (0.39–1.23) | 0.2094 |
| eGFR | 0.99 (0.98–1.01) | 0.4092 | 1.00 (0.99–1.02) | 0.3930 |
| Total protein | 1.28 (0.52–3.16) | 0.5907 | 1.13 (0.47–2.71) | 0.7744 |
| Albumin | 0.49 (0.21–1.17) | 0.1079 | 0.52 (0.20–1.32) | 0.1673 |
| Bilirubin | 1.08 (0.80–1.45) | 0.6109 | 0.99 (0.74–1.32) | 0.9494 |
| Ammonium | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | 0.9765 | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | 0.6060 |
| Sodium | 1.00 (0.96–1.05) | 0.8205 | 1.00 (0.95–1.04) | 0.9191 |
| Potassium | 0.60 (0.33–1.08) | 0.0883 | 0.75 (0.41–1.37) | 0.3536 |
| Clorum | 1.00 (0.93–1.06) | 0.9048 | 0.98 (0.92–1.05) | 0.6350 |
| Calcium | 0.51 (0.28–0.93) | 0.0288 | 0.55 (0.29–1.03) | 0.0626 |
| Magnesium | 0.68 (0.27–1.71) | 0.4110 | 0.92 (0.36–2.34) | 0.8621 |
| AST | 1.01 (0.99–1.02) | 0.4030 | 1.01 (0.99–1.02) | 0.2631 |
| ALT | 0.99 (0.98–1.00) | 0.0599 | 0.99 (0.98–1.00) | 0.1900 |
| LDH | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.3968 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.4288 |
| CPK | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.0491 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.0064 |
| Troponin | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.0323 | 1.00 (0.99–1.00) | 0.0823 |
| Mioglobin | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.4230 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.9568 |
| CK-MB | 1.08 (1.01–1.16) | 0.0269 | 1.06 (0.98–1.15) | 0.1271 |
| BNP | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.1776 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.7786 |
| Hb | 0.86 (0.69–1.07) | 0.1800 | 0.95 (0.75–1.20) | 0.6466 |
| WBC | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.7677 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.6782 |
| Neutrophil | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.7523 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.7071 |
| Limphocyte | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.3318 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.2168 |
| Eosinophil | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.4216 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.7185 |
| Monocyte | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.7885 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.7783 |
| Basophil | 1.00 (1.00–1.01) | 0.2188 | 1.00 (0.99–1.00) | 0.4400 |
| Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio | 1.02 (0.99–1.06) | 0.1794 | 1.02 (0.99–1.06) | 0.2176 |
| Platelet | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.2903 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.8352 |
| aPTT | 1.03 (0.99–1.06) | 0.1466 | 1.03 (0.99–1.08) | 0.1072 |
| INR | 2.60 (1.27–5.34) | 0.0090 | 2.32 (1.10–4.85) | 0.0262 |
| Firbinogen | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.3873 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.8126 |
| D-dimer | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.1273 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.5689 |
| AT III | 0.97 (0.95–0.99) | 0.0015 | 0.98 (0.96–0.99) | 0.0249 |
| CRP | 1.00 (1.00–1.01) | 0.8349 | 1.00 (1.00–1.01) | 0.9794 |
| PCT | 1.05 (0.99–1.11) | 0.0758 | 1.06 (0.99–1.12) | 0.0738 |
| SOFA | 1.21 (0.91–1.61) | 0.1807 | 1.08 (0.83–1.40) | 0.5789 |
| Tocilizumab | 0.57 (0.24–1.36) | 0.2053 | 0.72 (0.30–1.76) | 0.4737 |
| Remdesivir | 0.73 (0.18–3.05) | 0.6699 | 0.96 (0.23–4.08) | 0.9607 |
The table reports the results of univariate and multivariate (considering the Charlson Comorbidity Index) Cox regression analysis for single variables. Hazard ratio (HR), adjusted HR (HRAdj) with CI95% were computed. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant
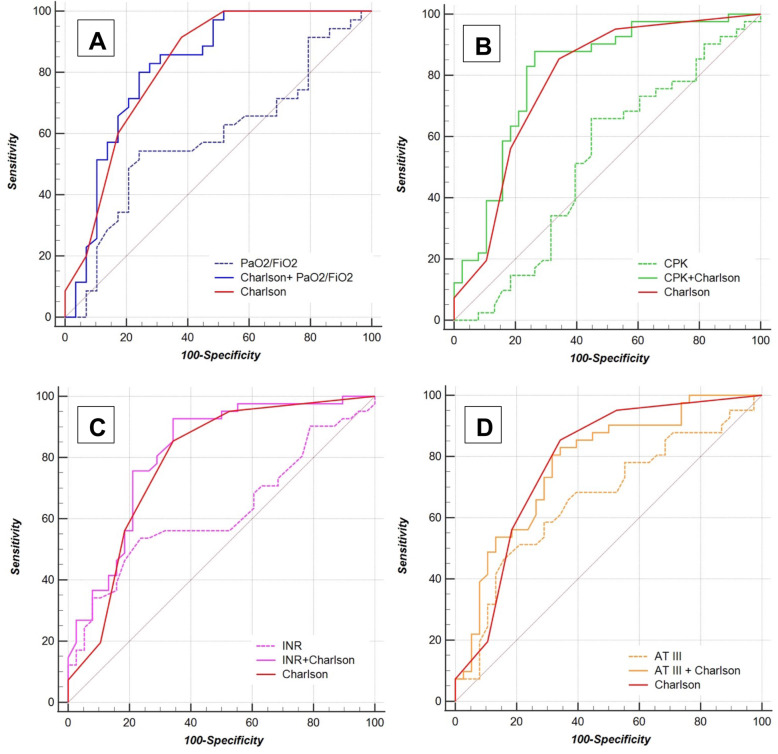
Briefly, Charlson Comorbidity Index ROC curve analysis (Fig. 2) showed an AUC of 0.784 (CI95% 0.677–0.869, p-value < 0.0001), with a Se and Sp for cut-off value of, respectively 85.4% (CI95% 70.8–94.4%) and 65.8% (CI95% 48.6–80.4%). For all significant variables, the adjustment for Charlson Comorbidity Index showed an increase in AUC statistically significant (see Fig. 3). Charlson Comorbidity Index + AT III model (Fig. 3D) showed an AUC of 0.776 (CI95% 0.668–0.862, p-value < 0.0001), with a Se and Sp for cut-off value of, respectively, 80.5% (CI95%65.1–91.2%) and 68.4% (CI95%51.3–82.5%). However, even single AT III model score showed a significant statistically AUC (0.662, CI95% 0.547–0.765, p-value 0.0092), with a Se 46.3% (CI95% 30.7–62.6%) and Sp 84.2% (CI95% 68.7–94.0%) for the cut-off value.
Fig. 2.
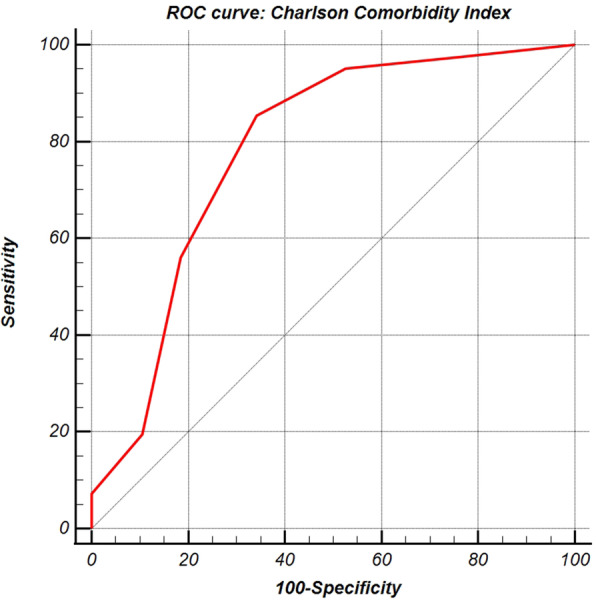
ROC curve analysis for the Charlson Comorbidity Index. The figure shows ROC curve analysis for the Charlson Comorbidity Index (AUC 0.784, CI95% 0.677–0.869, p-value < 0.0001). The coefficient for the score and cut-off values were: score model [Charlson] = 0.2762 * (Charlson), cut-off values > 0.5523 (J-index = 0.5116). Se and Sp were, respectively 85.4% (CI95% 70.8–94.4%) and 65.8% (CI95% 48.6–80.4%)
Fig. 3.
ROC curves analysis for single variables and adjusted for the Charlson Comorbidity Index. The figure shows ROC curve analysis for PaO2/FiO2 (A), for CPK (B), INR (C), and AT III (D). A Score model [PaO2/FiO2] = − 0.0028 * (PaO2/FiO2), cut-off values > − 0.3271 (J-index = 0.3015), Se 54.9% (CI95% 36.6–71.2%) and Sp 75.9% (CI95% 56.5–89.7%); score model [Charlson + PaO2/FiO2] = 0.4705 * (Charlson) − 0.0072 * (PaO2/FiO2), cut-off values > 0.2659 (J-index = 0.5586), Se 80.0% (CI95% 63.1–91.6%) and Sp 75.9% (CI95% 56.5–89.7%). The AUCs for single and adjusted model were, respectively, 0.586 (CI95% 0.456-0.708, p-value 0.2400) and 0.819 (CI95% 0.702–0.904, p-value < 0.0001). The adjustment for the Charlson Comorbidity Index showed a statistically significant difference for the AUC (p-value < 0.0001). When the Charlson Comorbidity Index and adjusted model score ROC curves were compared, the p-value was not statistically significant (0.9254). B Score model [CPK] = 0.0007 * (CPK), cut-off values ≤ 0.0558 (J-index = 0.2112), Se 65.8% (CI95% 49.4–79.9%), Sp 55.3% (CI95% 38.3–71.4%); score model [Charlson + CPK] = 0.2984 * (Charlson) + 0.0009 * (CPK), cut-off value > 0.9267 (J-index = 0.6149), Se 87.8% (CI95% 73.8–95.9%), Sp 73.7% (CI95% 56.9–86.6%). The AUCs for single and adjusted models were, respectively, 0.522 (CI95% 0.407–0.636, p-value 0.7390) and 0.807 (CI95% 0.703–0.887, p-value < 0.0001). The adjustment for Charlson Comorbidity Index showed a statistically significant difference for the AUC (p-value 0.0008). When the Charlson Comorbidity Index and adjusted model scores ROC curves were compared, the p-value was not statistically significant (0.3234). C Score model [INR] = 0.9573 * (INR), cut-off values > 1.1296 (J-index = 0.2997) Se 53.7% (CI95% 37.4–69.3%), Sp 76.3% (CI95% 59.8–88.6%); score model [Charlson +INR] = 0.2623 * (Charlson) + 0.8398 * (INR), cut-off value > 1.5220 (J-index = 0.5847), Se 92.7% (CI95% 80.1–98.5%), Sp 65.8% (CI95% 48.6–80.4%). The AUCs for single and adjusted model were, respectively, 0.621 (CI95% 0.505–0.728, p-value 0.0590) and 0.815 (CI95% 0.712–0.894, p-value < 0.0001). The adjustment for Charlson Comorbidity Index showed a statistically significant difference for the AUC (p-value 0.0051). When the Charlson Comorbidity Index and adjusted model scores ROC curves were compared, the p-value was not statistically significant (0.0805). D Score model [AT III] = − 0.0299 * (AT III), cut-off values > − 2.3655 (J-index = 0.3055), Se 46.3% (CI95% 30.7–62.6%), Sp 84.2% (CI95% 68.7–94.0%); score model [Carlson + AT III] = 0.1980 * (Charlson) − 0.0227 * (AT III), cut-off value > − 1.5922 (J-index = 0.4891), Se 80.5% (CI95% 65.1–91.2%), Sp 68.4% (CI95% 51.3–82.5%). The AUCs for single and adjusted models were, respectively, 0.662 (CI95% 0.547–0.765, p-value 0.0092) and 0.776 (CI95% 0.668–0.862, p-value < 0.0001). The adjustment for the Charlson Comorbidity Index showed a statistically significant difference for the AUC (p-value 0.0053). When the Charlson Comorbidity Index and adjusted model scores ROC curves were compared, the p-value was not statistically significant (0.8428)
Discussion
Several studies have been published on COVID-19 patients who underwent NIV outside ICU [9], while data are still required about NIV performed in the ICU setting. The NIV failure rate in ICU ranged from 17 to 47% [24, 25], with a mortality rate from 14 to 97% [12, 25, 26]. In this retrospective study, we showed that NIV was used in a large proportion of patients (70.1%) admitted to ICU to treat acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19, with a failure rate of 53.7%. Furthermore, patients who experienced failed NIV showed a higher mortality rate. Our data is in agreement with the evidence present in the international literature [12, 24–26].
Remarkably, patients who experienced NIV failure did not show a shorter NIV duration than patients who did not. Therefore, the correct patient selection based on clinical, laboratory, and imaging features can represent the “cornerstone” to reduce at least ICU distress, avoiding extenuating NIV “trial.” Our analysis points to suggest that patients who failed NIV represented a particular cluster, showing peculiar characteristics already presented at ICU admission that can be easily identified.
Patients who experienced NIV failure showed a higher Charlson Comorbidity Index than patients who did not. This data suggested that age and previous comorbidities, in detail, COPD, reduced patients’ reserve to respond to COVID-19-related inflammatory state. Furthermore, as showed by Cox regression analysis, Charlson Comorbidity Index represented a robust predictive factor related to NIV failure, with a high sensibility for cut-off value. The Charlson Comorbidity Index originally was developed to predict the risk of mortality within one year of hospitalization. During the current pandemia, the Charlson Comorbidity Index score, which considers the effects of both age and comorbidity, predicts death among COVID-19 patients by an exponential increase in the odds ratio at each score point [21]. Thus, the application of Charlson Comorbidity Index scoring in the context of the COVID-19 outbreak can be helpful to predict which ICU patient will experience NIV failure.
In our analysis, patients who experienced NIV failure showed the features of ongoing multiorgan impairment, expression of systemic disease, not only related to lung site. As reported by Zannella et al. [27], early multiorgan impairment due to the COVID-19 disease was already present at ICU admission, and it subsequently worsened during the ICU stay, mainly in non-survivors. In univariate Cox regression analysis, organ-specific injury markers, in detail cardiac and coagulation parameters, were able to predict NIV failure. However, when univariate models were adjusted for the Charlson Comorbidity Index, only PaO2/FiO2, CPK, INR, and AT III were single parameters able to predict NIV failure. Adjusted predictive models presented a good performance, as showed by AUC, with high sensibility and variable specificity for the cut-off values. When single variables were adjusted for the Charlson Comorbidity Index, the increase in AUC resulted statistically significant, but the comparisons between adjusted and single Charlson Comorbidity Index model scores did not show a statistically significant difference.
In our study PaO2/FiO2value at ICU admission did not show a statistically significant difference between the two groups but, instead, in the univariate Cox regression analysis, it resulted significantly related to NIV failure when adjusted for Charlson Comorbidity Index. Grasselli et al. [28], in a retrospective study, showed that PaO2/FiO2 was higher in younger patients than older patients, with an increased mortality rate in the latter. Chen et al. [29] reported that initial PaO2/FiO2< 122.17 mmHg should be considered a “warning sign” in patients with COVID-19 and guide the clinician to evaluate the need for endotracheal intubation and invasive mechanical ventilation. Coppadoro et al. [30] demonstrated that PaO2/FiO2 collected during helmet CPAP treatment and the number of comorbidities was independently associated with NIV failure. According to our results, PaO2/FiO2 should not be used as a single parameter to predict NIV failure but should be implemented with Charlson Comorbidity Index. The influence of the Charlson Comorbidity Index on the PaO2/FiO2 is poorly studied, and further analyses are needed.
In addition to lung damage, muscle weakness and elevation of serum CPK level were documented in around 20% severe SARS-CoV2 infection and could be interpreted as a manifestation of multiorgan damage [31]. In the present study, CPK levels between groups did not show a statistically significant difference. Still, both single and bivariate, Cox regression analysis showed that CPK levels could be considered a parameter able to predict NIV failure. Even though several factors could cause an increase in serum CPK, the pathogenesis of muscle damage in such patients remains unknown. It was suggested that a possible myotoxic effect of SARS-CoV2 should be carefully assessed particularly in severe SARS-CoV2 infection [32]. Our data indicated that serum CPK increasing could be considered a potential prognostic sign for muscle weakness and, consequently, failed NIV. Further investigations are necessary regarding this topic.
Evidence suggests that SARS-CoV-2 can cause a series of acquired coagulation disorders, producing endothelial damage, coagulation activation, and intravascular fibrin deposition. For severe COVID-19 patients, coagulation activation can lead to thrombus formation and even disseminated intravascular coagulation [33]. In our study, when adjusted for the Charlson Comorbidity Index, INR and AT III level were related to NIV failure, suggesting that early coagulation impairment and subliminal parameters alterations should be considered markers of severity or an ongoing stadium of the disease. It is interesting to note that D-dimer, the hallmark of severe COVID-19 patients, was not related to failed NIV, suggesting that alteration in INR and AT III could anticipate the “catastrophic” increase in D-dimer levels. Our results are in line with those reported in previous studies. Ouyang et al. [34], analyzing the temporal changes in laboratory markers of adult COVID-19 survivors and non-survivors, reported that INR was higher in non-survivors both in the first and latter tests. In the present analysis, AT III levels resulted higher in patients who had successful NIV and the single score model showed an AUC statistically significant, with a high specificity. Our results are in line with Tang et al. [35], reporting a statistically significant reduction in AT III occurred in non-survivors of COVID-19 patients compared to survivors after day 7 of admission. This reduction seems to persist until day 14.
Although we did not include chest CT findings in our model, ground glass opacity, adjacent pleural thickening, and subcutaneous emphysema presented a higher incidence in patients who experienced NIV failure. Ground glass opacity represents the most common CT imaging feature in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia [36]. At the same time, subcutaneous emphysema should be considered a premonitory sign for the development of more severe barotrauma. Subcutaneous emphysema should be encompassed in a range of clinical manifestations defined as “alveolar air leaks syndrome” [37]. Further findings are essential to clarify if its occurrence represents a severe index disease or the results of an inappropriate NIV setting [38].
Conclusions
Although NIV was extensively used in ICU as respiratory support to treat COVID-19 related ARDS, its failure is associated with high mortality. To stratify patients, it can be helpful to have predictive factors, available at the ICU admission. In the present analysis, factors able to identify patients at risk for NIV failure at ICU admission were the Charlson Comorbidity Index and its combination with PaO2/FiO2, CPK, INR, and AT III. Derived models showed higher AUC and higher sensibility for the cut-off point, suggesting a potential role for the identification of patients considered at risk of NIV failure. The main limitation of this study is represented by its retrospective design and its small sample size. Moreover, we provided a description of our population at ICU admission, and we did not evaluate how variables changed during ICU stay. Further studies are needed to clarify the role of endotracheal intubation and invasive mechanical ventilation to reduce mortality in the population considered at risk of NIV failure [39].
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Supplementary file 1.
Additional file 2: Supplementary file 2.
Additional file 3: Supplementary Table 1.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to all the nurses involved in the ICU patients’ care during the pandemic wave that hit Salerno University Hospital in 2020.
Abbreviations
- CI95%
95% confidence interval
- aPTT
Activated partial thromboplastin time
- ARDS
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- HRAdj
Adjusted HR
- AST
Alanine-amine transferase
- AT III
Antithrombin III
- AUC
Area under the curve
- ALT
Aspartate-amine transferase
- BMI
Body mass index
- BNP
Brain natriuretic peptide
- Ca
Calcium
- CT
Chest-tomography
- Χ2
Chi-square test
- CKD
Chronic kidney disease
- COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Cl
Clorum
- PaCO2
CO2partial pressure
- CPAP
Continuous positive airway pressure
- CAD
Coronary artery disease
- COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019
- CPK
Creatine kinase
- eGFR
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
- Hb
Hemoglobin concentration
- HR
Hazard-ratio
- INR
International normalized ratio
- LDH
Lactate dehydrogenase
- LOS
Length of stay
- Mg
Magnesium
- max
Maximum
- CK-MB
MB creatine kinase isoform
- min
Minimum
- NIV
Non-invasive mechanical ventilation
- FiO2
O2 fraction inspired
- PaO2
O2 partial pressure
- OSAS
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
- PLT
Platelets
- PEEP
Positive end-expiratory pressure
- K
Potassium
- PSV
Pressure support ventilation
- ROC
Receiver operating characteristics
- SILI
Self-inflicted lung injury
- Se
Sensibility
- SOFA
Sequential Organ Failure Assessment
- SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
- Na
Sodium
- Sp
Specificity
- SD
Standard deviation
- TnI
Troponin I
- WBC
White blood cell count
- WHO
World Health Organization
- J
Youden’s index
Authors’ contributions
Conceptualisation: AR, OP. Data Curation: AR, PT, AC, GL, GS, DB, FO, GLC, GP. Formal Analysis: AR. Investigation: AR, PT, AC, GL, GS, DB, FO, GLC, GP. Methodology. AR, OP, GS. Project Administration: OP. Resources: PT, AC, GL, GS, DB, FO, GLC, GP. Software: AR, PT. Supervision: OP. Visualization: AR, OP. Writing-Original Draft Preparation: AR, OP, GS. Writing—Review and Editing: AR, OP, GS, DB. All authors approved the final version.
Funding
None.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The local ethical committee (“Comitato Etico Campania Sud”) approved the present study (protocol ID 0008402010) and waived the need for patient consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan. China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fan E, Beitler JR, Brochard L, Calfee CS, Ferguson ND, Slutsky AS, Brodie D. COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: is a different approach to management warranted? Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(8):816–821. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30304-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mancusi C, Grassi G, Borghi C, Ferri C, Muiesan ML, Volpe M, Iaccarino G, Group S-RI Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with COVID-19 infection: The results of the SARS-RAS study of the Italian Society of Hypertension. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2021;28(1):5–11. doi: 10.1007/s40292-020-00429-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zuo MZ, Huang YG, Ma WH, Xue ZG, Zhang JQ, Gong YH, Che L Chinese Society of Anesthesiology Task Force on Airway M, Airway Management Chinese Society of Anesthesiology Task Force (2020) Expert recommendations for tracheal intubation in critically ill patients with noval coronavirus disease 2019. Chin Med Sci J (0):10.24920/003724. 10.24920/003724 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.Cook TM, El-Boghdadly K, McGuire B, McNarry AF, Patel A, Higgs A. Consensus guidelines for managing the airway in patients with COVID-19: guidelines from the Difficult Airway Society, the Association of Anaesthetists the Intensive Care Society, the Faculty of Intensive Care Medicine and the Royal College of Anaesthetists. Anaesthesia. 2020;75(6):785–799. doi: 10.1111/anae.15054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brown CA, 3rd, Mosier JM, Carlson JN, Gibbs MA. Pragmatic recommendations for intubating critically ill patients with suspected COVID-19. J Am Coll Emerg Physicians Open. 2020;1(2):80–84. doi: 10.1002/emp2.12063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Brewster DJ, Chrimes N, Do TB, Fraser K, Groombridge CJ, Higgs A, Humar MJ, Leeuwenburg TJ, McGloughlin S, Newman FG, et al. Consensus statement: Safe Airway Society principles of airway management and tracheal intubation specific to the COVID-19 adult patient group. Med J Aust. 2020;212(10):472–481. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kallet RH. 2020 year in review: mechanical ventilation during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. Respir Care. 2021;66(8):1341–1362. doi: 10.4187/respcare.09257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Radovanovic D, Coppola S, Franceschi E, Gervasoni F, Duscio E, Chiumello DA, Santus P. Mortality and clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia treated with non-invasive respiratory support: a rapid review. J Crit Care. 2021;65:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2021.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Marini JJ, Gattinoni L. Management of COVID-19 respiratory distress. JAMA. 2020;323(22):2329–2330. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.6825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Papoutsi E, Giannakoulis VG, Xourgia E, Routsi C, Kotanidou A, Siempos II. Effect of timing of intubation on clinical outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of non-randomized cohort studies. Crit Care. 2021;25(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03540-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Boscolo A, Pasin L, Sella N, Pretto C, Tocco M, Tamburini E, Rosi P, Polati E, Donadello K, Gottin L, Vianello A, Landoni G, Navalesi P, FERS, for the COVID-19 VENETO ICU Network. Valeri I, Andreatta G, Gandolfi L, Gadaldi A, Brumana N, Forin E, Correale C, Fregolent D, Pirelli PF, Marchesin D, Perona M, Franchetti N, Paolera MD, Simoni C, Falcioni T, Tresin A, Schiavolin C, Schiavi A, Vathi S, Sartori D, Sorgato A, Pistollato E, Linassi F, Golino GL, Frigo L, Serra E, Pittarello D, Tiberio I, Bond O, Michieletto E, Muraro L, Peralta A, Persona P, Petranzan E, Zarantonello F, Pettenuzzo T, Graziano A, de Cassai A, Bernardi L, Pianon R, Badii F, Bosco E, Agostini M, Trevisiol P, Farnia A, Peta M, Altafini L, Calò MA, Meggiolaro M, Lazzari F, Martinello I, Fullin G, Papaccio F, Toffoletto F, Bonato A, Sgarabotto C, Baratto F, Montacciani F, Parnigotto A, Gagliardi G, Gioconda F, Ongaro L, Baiocchi M, Danzi V, de Rosa S, Polati E, Donadello K, Gottin L, Zanatta P, Sinigaglia E, da Ros A, Marchiotto S, Bassanini S, Zamperini M, Daroui I, Mosaner W, Lembo R. Outcomes of COVID-19 patients intubated after failure of non-invasive ventilation: a multicenter observational study. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):17730. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96762-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ferguson ND, Fan E, Camporota L, Antonelli M, Anzueto A, Beale R, Brochard L, Brower R, Esteban A, Gattinoni L, Rhodes A, Slutsky AS, Vincent JL, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT, Ranieri VM. The Berlin definition of ARDS: an expanded rationale, justification, and supplementary material. Intensive Care Med. 2012;38(10):1573–1582. doi: 10.1007/s00134-012-2682-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ni YN, Wang T, Yu H, Liang BM, Liang ZA. The effect of sedation and/or analgesia as rescue treatment during noninvasive positive pressure ventilation in the patients with Interface intolerance after extubation. BMC Pulm Med. 2017;17(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12890-017-0469-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tan W, Xu DY, Xu MJ, Wang ZF, Dai B, Li LL, Zhao HW, Wang W, Kang J. The efficacy and tolerance of prone positioning in non-intubation patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and ARDS: a meta-analysis. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2021;15:17534666211009407. doi: 10.1177/17534666211009407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lewis SR, Baker PE, Parker R, Smith AF. High-flow nasal cannulae for respiratory support in adult intensive care patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021;3(3):CD010172. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010172.pub3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rochwerg B, Brochard L, Elliott MW, Hess D, Hill NS, Nava S, Navalesi PMOTSC, Antonelli M, Brozek J, Conti G et al (2017) Official ERS/ATS clinical practice guidelines: noninvasive ventilation for acute respiratory failure. Eur Respir J:50(2). 10.1183/13993003.02426-2016 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 18.Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(5):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, De Mendonca A, Bruining H, Reinhart CK, Suter PM, Thijs LG. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996;22(7):707–710. doi: 10.1007/BF01709751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zahorec R. Ratio of neutrophil to lymphocyte counts--rapid and simple parameter of systemic inflammation and stress in critically ill. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2001;102(1):5–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tuty Kuswardhani RA, Henrina J, Pranata R, Anthonius Lim M, Lawrensia S, Suastika K. Charlson comorbidity index and a composite of poor outcomes in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020;14(6):2103–2109. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.10.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988;44(3):837–845. doi: 10.2307/2531595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Youden WJ. Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer. 1950;3(1):32–35. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(1950)3:1<32::aid-cncr2820030106>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gaulton TG, Bellani G, Foti G, Frazer MJ, Fuchs BD, Cereda M. Early clinical experience in using helmet continuous positive airway pressure and high-flow nasal cannula in overweight and obese patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure from coronavirus disease 2019. Crit Care Explor. 2020;2(9):e0216. doi: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000000216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sivaloganathan AA, Nasim-Mohi M, Brown MM, Abdul N, Jackson A, Fletcher SV, Gupta S, Grocott MPW, Dushianthan A. University Hospital Southampton Critical C et al: Noninvasive ventilation for COVID-19-associated acute hypoxaemic respiratory failure: experience from a single centre. Br J Anaesth. 2020;125(4):e368–e371. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2020.07.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Baqi S, Naz A, Sayeed MA, Khan S, Ismail H, Kumar V, Somjimal H, Aneela J, Imtiaz S, Aftab S. Clinical characteristics and outcome of patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia at a public sector hospital in Karachi. Pakistan. Cureus. 2021;13(2):e13107. doi: 10.7759/cureus.13107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zanella A, Florio G, Antonelli M, Bellani G, Berselli A, Bove T, Cabrini L, Carlesso E, Castelli GP, Cecconi M, Citerio G, Coloretti I, Corti D, Dalla Corte F, de Robertis E, Foti G, Fumagalli R, Girardis M, Giudici R, Guiotto L, Langer T, Mirabella L, Pasero D, Protti A, Ranieri MV, Rona R, Scudeller L, Severgnini P, Spadaro S, Stocchetti N, Viganò M, Pesenti A, Grasselli G, COVID-19 Italian ICU Network Time course of risk factors associated with mortality of 1260 critically ill patients with COVID-19 admitted to 24 Italian intensive care units. Intensive Care Med. 2021;47(9):995–1008. doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06495-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Grasselli G, Zangrillo A, Zanella A, Antonelli M, Cabrini L, Castelli A, Cereda D, Coluccello A, Foti G, Fumagalli R, Iotti G, Latronico N, Lorini L, Merler S, Natalini G, Piatti A, Ranieri MV, Scandroglio AM, Storti E, Cecconi M, Pesenti A, COVID-19 Lombardy ICU Network. Agosteo E, Alaimo V, Albano G, Albertin A, Alborghetti A, Aldegheri G, Antonini B, Barbara E, Belgiorno N, Belliato M, Benini A, Beretta E, Bianciardi L, Bonazzi S, Borelli M, Boselli E, Bronzini N, Capra C, Carnevale L, Casella G, Castelli G, Catena E, Cattaneo S, Chiumello D, Cirri S, Citerio G, Colombo S, Coppini D, Corona A, Cortellazzi P, Costantini E, Covello RD, de Filippi G, Dei Poli M, Della Mura F, Evasi G, Fernandez-Olmos R, Forastieri Molinari A, Galletti M, Gallioli G, Gemma M, Gnesin P, Grazioli L, Greco S, Gritti P, Grosso P, Guatteri L, Guzzon D, Harizay F, Keim R, Landoni G, Langer T, Lombardo A, Malara A, Malpetti E, Marino F, Marino G, Mazzoni MG, Merli G, Micucci A, Mojoli F, Muttini S, Nailescu A, Panigada M, Perazzo P, Perego GB, Petrucci N, Pezzi A, Protti A, Radrizzani D, Raimondi M, Ranucci M, Rasulo F, Riccio M, Rona R, Roscitano C, Ruggeri P, Sala A, Sala G, Salvi L, Sebastiano P, Severgnini P, Sforzini I, Sigurtà FD, Subert M, Tagliabue P, Troiano C, Valsecchi R, Viola U, Vitale G, Zambon M, Zoia E. Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy region. Italy. JAMA. 2020;323(16):1574–1581. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.5394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chen J, Zhu YF, Du ZQ, Li WF, Zhang MJ, Zhao SD, Ying JW, Li Z, Miao HJ. Predictors of mechanical ventilation for COVID-19: combined data from three designated hospitals. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(24):13065–13071. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202012_24214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Coppadoro A, Benini A, Fruscio R, Verga L, Mazzola P, Bellelli G, Carbone M, Mulinacci G, Soria A, Noe B, et al. Helmet CPAP to treat hypoxic pneumonia outside the ICU: an observational study during the COVID-19 outbreak. Crit Care. 2021;25(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03502-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mao L, Jin H, Wang M, Hu Y, Chen S, He Q, Chang J, Hong C, Zhou Y, Wang D, Miao X, Li Y, Hu B. Neurologic manifestations of hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan. China. JAMA Neurol. 2020;77(6):683–690. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.1127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Islam B, Ahmed M, Islam Z, Begum SM. Severe acute myopathy following SARS-CoV-2 infection: a case report and review of recent literature. Skelet Muscle. 2021;11(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13395-021-00266-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Qiu H, Yuan L, Huang X, Zhou Y, Wu Q, Zheng R, Yang Q. Using the big data of internet to understand coronavirus disease 2019ʼs symptom characteristics: a big data study. Zhonghua er bi yan hou tou jing wai ke za zhi= Chinese journal of otorhinolaryngology head and neck surgery. 2020;55:E004. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20200225-00128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ouyang SM, Zhu HQ, Xie YN, Zou ZS, Zuo HM, Rao YW, Liu XY, Zhong B, Chen X. Temporal changes in laboratory markers of survivors and non-survivors of adult inpatients with COVID-19. BMC Infect Dis. 2020;20(1):952. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05678-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tang N, Li D, Wang X, Sun Z. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18(4):844–847. doi: 10.1111/jth.14768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Awulachew E, Diriba K, Anja A, Getu E, Belayneh F. Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging features of patients with COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiol Res Pract. 2020;2020:1023506. doi: 10.1155/2020/1023506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Joshi S, Bhatia A, Tayal N, Chaturvedi S, Ali SJ. Alveolar air leak syndrome a potential complication of COVID-19-ARDS - single center retrospective analysis. J Assoc Physicians India. 2021;69(1):22–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Elhakim TS, Abdul HS, Pelaez Romero C, Rodriguez-Fuentes Y. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax and subcutaneous emphysema in COVID-19 pneumonia: a rare case and literature review. BMJ Case Rep. 2020;13(12):13(12). doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-239489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lorenzoni G, Sella N, Boscolo A, Azzolina D, Bartolotta P, Pasin L, Pettenuzzo T, De Cassai A, Baratto F, Toffoletto F, et al. COVID-19 ICU mortality prediction: a machine learning approach using SuperLearner algorithm. J Anesth Analgesia Crit Care. 2021;1(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s44158-021-00002-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Supplementary file 1.
Additional file 2: Supplementary file 2.
Additional file 3: Supplementary Table 1.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.