Extended Data Fig. 2 |. Effects of tethered RNA on HR.
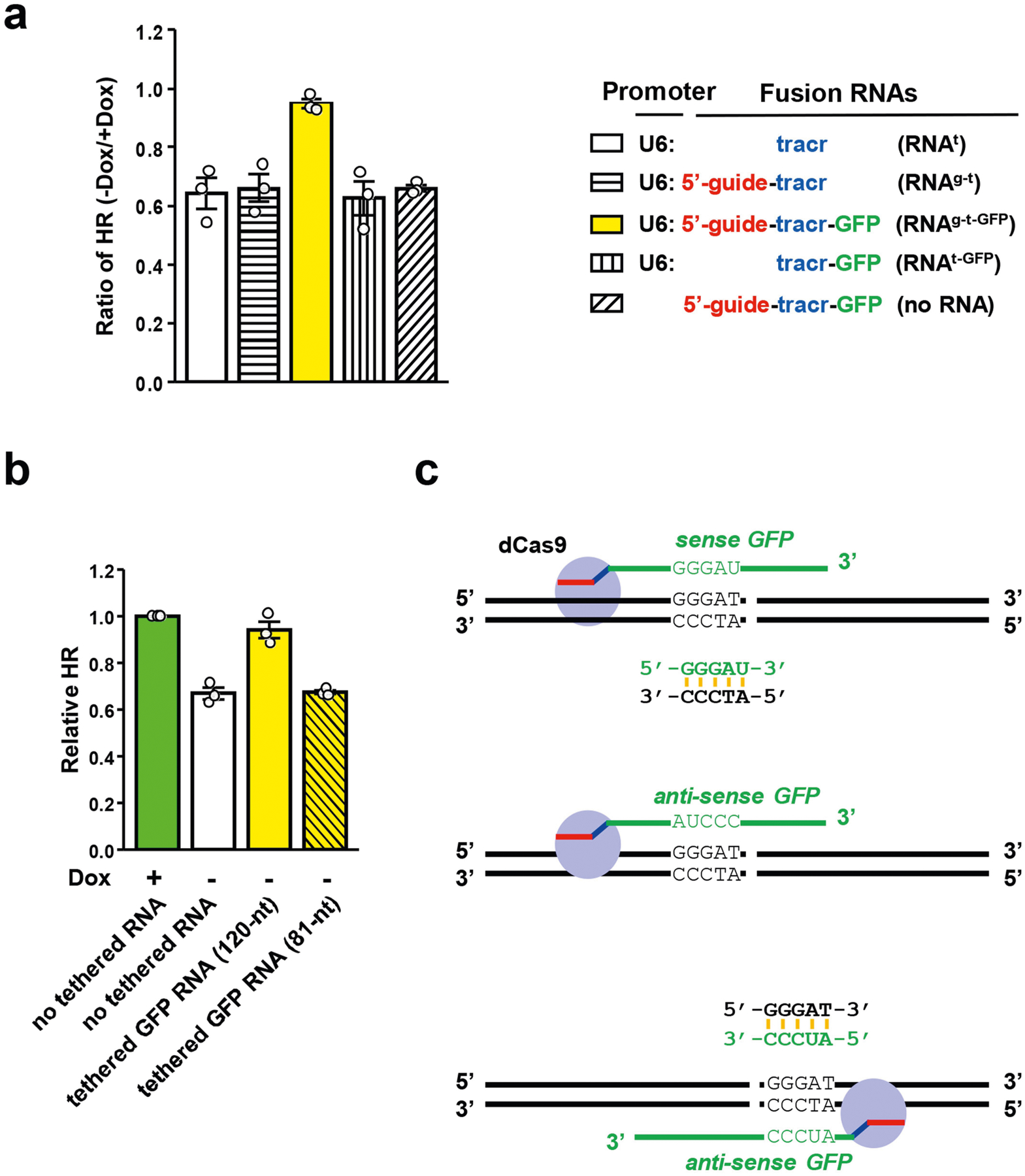
a, The indicated fusion RNAs were tethered to a unique sequence 5′ to the I-SceI site in sceGFP. HR efficiency in cells expressing various fusion RNAs was analysed by qPCR in the transcriptionally on and off states. For each RNA, the HR level in the transcriptionally on state is defined as 1. The ratios of HR levels between the transcriptionally off and on states (−Dox/+Dox) were determined. Data are mean ± s.e.m. (n = 3 independent experiments). b, Two fusion RNAs containing 120-nt or 81-nt GFP sequence were tethered to a unique sequence 5′ to the I-SceI site in sceGFP. Relative HR efficiencies in cells expressing either of the two fusion RNAs or no fusion RNA were measured by qPCR in the transcriptionally off state (−Dox). The HR efficiency of cells expressing no fusion RNA in the transcriptionally on state (+Dox) serves as a reference. Data are mean ± s.e.m. (n = 3 independent experiments). c, Schematic to explain why only sense GFP RNA and not anti-sense GFP RNA can hybridize DNA when tethered 5′ to the I-SceI site. It also explains why anti-sense GFP RNA can hybridize DNA when tethered 3′ to the I-SceI site.
