Abstract
Background
Novel devices target different facets of amblyopia risk factors (ARFs). Through birefringence, the Rebion blinq assesses binocular foveation. The Adaptica 2WIN is a multiradial infrared photorefractor that also estimates ocular alignment. PDI Check is a forced-choice, dynamic near-vision game for the autostereoscopic Nintendo 3DS.
Methods
New and returning patients to a pediatric ophthalmology clinic had concomitant confirmatory exams after all three vision screens had been validated with ROC curves, Bland–Altman plots, and Alaska Blind Child Discovery ellipsoid grades. Exam outcomes were classified by ARF visual acuity, strabismus, binocularity, and refractive errors following the 2021 AAPOS guidelines and Bosque–Hunter rubric for the blinq.
Results
A total of 202 ethnically diverse students aged 10±4 (4–19) years, 33% treatment-naïve, had a high (58%) prevalence of ARFs. Linear logMAR visual acuity, intereye differences, stereo and three-cone color correlated well between PDI Check and exams. Mean score on the 2WIN matched sphero-cylinder exam with ellipsoid scoring was 2.1±1.5. For AAPOS 2021 refractive plus strabismus, sensitivity/specificity for PDI Check was 68%/59%, 2WIN 72%/95%, and blinq 87%/32%. For the amblyopia or strabismus rubric, PDI Check was 79%/68%, 2WIN 56%/65%, and blinq 94%/37%.
Conclusion
Each device had advantages and disadvantages in screening this cohort of older, high-prevalence students, many of whom had already been treated. Validation methods should cover more than just refraction, as the new 2021 AAPOS guidelines do.
Keywords: amblyopia, vision screening, strabismus, validation
Video abstract

Point your smartphone at the code above. If you have a QR code reader, the video abstract will appear. Or use:
Introduction
Amblyopia is the most common condition causing vision impairment in children, and it theoretically could be completely cured with early consistent screening and thorough treatment.1 Conventional screening waits until children are old enough to perform monocular visual acuity screening, but instrument-based, objective methods can outperform conventional screening in terms of younger-age screening and higher validity for risk-factor detection.2 Despite monumental efforts, an ideal amblyopia-screening method has not yet been developed or optimized.3
Normal vision results from early and consistent focused, overlapped binocular images. Amblyopia is caused by three main vision disruptors — form deprivation, strabismus, and refractive error — presented to the brain during development. Deprivational amblyopia is usually the most severe, due to cataracts, corneal opacity, or eyelid deformity blocking out formed images. Refractive amblyopia is usually due to insufficiently accommodated hyperopia in one or more meridia in one or both eyes. Strabismic amblyopia usually results from constant esotropic or exotropic strabismus, while amblyopia is rarely associated with intermittent strabismus.4
Most amblyopia arises due to excess refractive error or strabismus. These result in ocular suppression and diminished best-corrected visual acuity and reduced stereopsis. Cases with large-angle or small-angle strabismus with anisometropia are also characterized by fixation instability in the amblyopic eye.5 Large-angle strabismus can be detected by a pediatrician or parent.6,7 Some vision screeners, such as infrared photorefractors, detect refractive error.8,9 Other devices quantify larger-angle strabismus,10 while the new Rebion blinq detects lack of foveal birefringence.11 Other amblyopia-screening enlists patient participation to quantify visual acuity, suppression, and stereopsis.12–14
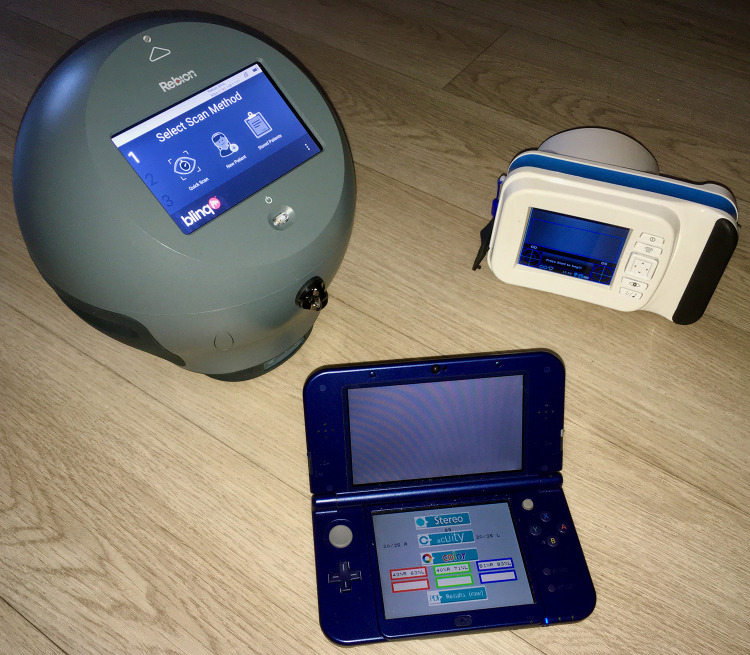
Gold standards for amblyopia definition comprise various amblyopia risk factors or amblyopia vision impacts that have been quantified to inform pediatric vision screening. The American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus (AAPOS) Vision Screening Committee presented two uniform guidelines in 200315 and 201316 and one recent 2021 summary17 of what confirmatory exam findings constitute amblyopia risk factors (Table 1). These uniform guidelines cover levels of refractive components, visual acuity, and strabismus. Amblyopia is also associated with fixation instability,18 diminished stereopsis, and suppression.19 A definition of “referral warranted” combines aspects of visual acuity and strabismus.20 We compared the performance of three entirely different electronic amblyopia-screening devices (Figure 1), with characteristics compared and contrasted in Table 2 for children old enough to communicate their amblyopia status.
Table 1.
Gold-standard exam criteria of amblyopia risk factors
| AAPOS 2003 | AAPOS 2013 | AAPOS 2021 | Hunter–MEPEDS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, young | 12 | 49 | 31 | 12 | 12 | 49 | |
| Age, older | 60 | 72 | 48 | 30 | 18 | 72 | 96 |
| Anisometropia | >1.50 D | >1.50 D | >2.00 D | >2.50 D | >1.25 D | >1.25 D | ≥1.00 D |
| Hyperopia | >3.50 D | >3.50 D | >4.00 D | >4.50 D | >4.00 D | >4.00 D | ≥4.00 D |
| Cylinder | >1.50 D | >1.50 D | >2.00 D | >2.00 D | >3.00 D | >1.75 D | ≥2.50 D |
| Myopia | <–3.00 D | <–3.00 D | <–3.00 D | <–3.00 D | <–3.00 D | <–2.00 D | ≤−6.00 D |
| Strabismus | Any | >8 PD | >8 PD | >8 PD | >8 PD | >8 PD | >2 PD heterotopia |
| Comment | Manifest | Manifest | Manifest | Manifest | Manifest | Manifest | ± surgery |
| Media opacity | >1 mm | >1 mm | >1 mm | >1 mm | >1 mm | >1 mm | History of |
| Visual acuity | 0.4/0.3 | >0.3 | Not | Not | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 unilat/0.5–0.3 |
| Intereye | ≥2 lines | ≥2 lines | ≥2 lines | ||||
| Stereo | Not stereo | Not stereo | Not stereo | Not stereo | Not stereo | ≥201 arc sec | |
| Special | Ptosis <1 MRD | Rubric | |||||
| References | J AAPOS 2003:314–316 | J AAPOS 2013 17:4 | J AAPOS 2022; | J AAPOS 2021;25:214, Oph Epid. 2006 13:253 | |||
Notes: Columns indicate three sets of AAPOS uniform guidelines separated by age-group and also the new set of cutoffs selected from a rubric for “referral-warranted” pediatric eye conditions proposed by David Hunter utilizing risk-factor levels from the Multi-Ethnic Pediatric Eye Disease (MEPEDS) study. Refractive risk factors are given in diopters (D), while strabismus is in prism diopters (PD). Visual acuity is presented in logMAR. In 2003, AAPOS sought ptosis within 1 mm of marginal reflex distance (MRD).
Figure 1.
Three vision-screening devices: Rebion blinq birefringent binocular foveation scanner (upper left), Adaptica 2WIN infrared multiradial autorefractor (upper right), and PDI Check dynamic forced-choice vision-screening game on the Nintendo 3DS (bottom).
Table 2.
Compared and contrasted aspects of the electronic vision-screening devices
| Rebion Blinq | Adaptica 2WIN | PDI Check | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | 1,800 g | 854 g | 336 g |
| Dimensions | 21.4×21.4×22.6 | 8.8×12.2×16.5 cm | 1.9×9.0×15.9 cm |
| AUC (2021 AAPOS ≥4 years) | 0.59 | 0.86 | 0.69 |
| AUC (Hunter rubric) | 0.49 | 0.60 | 0.74 |
| Speed | 25 seconds | 10 seconds | 90 seconds |
| Price | $9,000 | $6,500 | $300 (v. 0.2.9) |
| Room lighting | Dim | Dark | Any |
| Noise/sound | None | On–off warble | None |
| Version | Model BQ830, Pro version A.2.1 | 5 | 0.2.17 |
| Referral output | Clear laterality | Menu options — obscure | Refer not defined |
| IRC | Refer, pass, timed out, inconclusive | Target 2003 AAPOS chart | Select Va, stereo, and/or color |
| Screening age | 2–3 years to adult | 6 months to adult | 2–3 years to adult |
| Mechanism | Infrared radial birefringent scanning | Multiradial infrared eccentric photorefraction | Autostereoscopic barrier parallax screen |
| Office connect | WiFi — database report | WiFi and reports | WiFi, but no report yet |
| Targeting strengths | Microstrabismus, strabismic amblyopia | Refractive error, asymmetric corneal reflex, anisocoria | Ocular suppression, disrupted stereopsis, color-vision anomalies, malingering |
| Targeting weaknesses | Refractive error, bilateral ametropic amblyopia | Optic neuropathy | Refractive error, strabismus |
| Power | 20 V, 1.5 A DC | USB, conventional | USB, special |
| # Screened on battery charge | >10 | >40 | >100 |
| Battery life | 4–6 hours | 4–6 hours | 1 week |
| Breakage risk | High | Fair | Low |
Notes: Devices compared on the autostereoscopic Nintendo 3DS screen. AUC, area under the ROC curve; ROC, receiver-operating characteristic; IRC, instrument-referral criteria.
Methods
This comparative evaluation of screening tests complied with the Declaration of Helsinki and received approval from the institutional review board at Providence Alaska Medical Center. Parents provided written informed consent. Deidentified data are available for download at https://www.abcd-vision.org/references/Blinq.2WIN.PDI%20de-ID.pdf. Subjects were recruited from new and returning patients to a subspecialty pediatric eye clinic, and each patient had had a confirmatory eye examination according to AAPOS guidelines16 within the previous 6 months. Younger children (consistent with the AAPOS 12- to 72-month age range) had refraction at the phoropter or school-bus accommodation-relaxing skiascopy21 testing, with excess accommodation controlled with cycloplegia using cyclopentolate 1%. Older children had manifest refractions on phoropter testing with refinement to achieve maximal surround HOTV visual acuity on an M&S Systems monitor calibrated for room length. This study was undertaken during COVID-19 protocols, when routine cycloplegia was minimized to encourage social distancing. Motility included prism cover tests at distance and near and sensory testing including Worth four dot at a distance and near and Titmus Stereo Fly from 30 cm. In addition to ophthalmoscopy, optic nerve hypoplasia was confirmed on OPTOS ultra-widefield fundus photography.22 The three digital vision-screening devices were tested in random order without cycloplegia. Although it is possible to obtain readings with the infrared light passing though spectacle lenses, the 2WIN and blinq were tested without glasses.
Each child was screened with the blinq (model BQ830, pro version, version A.2.0 updated to A.2.1 after patient 23, B-00027-V). The room lights were dimmed and the patient was asked to gaze into the round window on the front of the device after focusing distance was confirmed by directing the aiming beam on skin away from the eyes. The first interpretation from the device (either pass, refer — right eye, refer — left eye, timed out, or inconclusive) was used for validation, even though some timed-out and inconclusive results prompted re-screening in cooperative children. The manufacturer recommends rescreenings for timed-out or inconclusive interpretations.
Each child was screened by the infrared photorefractor 2WIN (version 5.0; Adaptica). The Kaleidos case for the 2WIN23 and the infrared-transmitting occlusion wand10 were not used: the device was handheld in a dimmed examination room. The fixation bright, color blinking lights plus an audible fixation stimulus were used on all but three patients. Some autistic children preferred that the audible fixation be silenced. Pupil size, prism diopter, and gaze estimates were not analyzed. Instrument-referral criteria were formulated as sensitive, specific, and routine, optimizing accuracy for comparison utilizing receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
Each child was also screened with the PDI Check near-vision screening game (version 0.2.17) using an autostereoscopic barrier screen on a Nintendo 3DS development kit. The game presents three four-way, forced-choice, dynamic tasks to estimate monocular rivalry Landolt C visual acuity, stereopsis, monocular rivalry, and isoluminance gray trichromatic (red cone, green cone, and blue cone) color testing.24 Rivalry presentation of near visual acuity and monocular three-cone color testing can uncover suppression.25
The refractive estimate of the 2WIN was compared with actual refraction using Bland–Altman26 and the new ABCD composite ellipsoid27 methods. Each device was then validated using various uniform and adapted gold-standard exams. The 2021 and the 2003 AAPOS amblyopia risk factors, various measures of strabismus (cover test >8 prism-diopter manifest, any history of strabismus surgery or chemodenervation), ocular suppression (Worth dot testing, near or distance), and visual acuity were analyzed. The Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group (PEDIG) criteria for amblyopia, with visual acuity in either eye of logMAR 0.3 or worse or intereye difference of two lines or more was utilized to define amblyopia.28 The 24-point rubric for determination of ocular diagnoses the blinq might target20 (amblyopia and strabismus) were included as another validation outcome.
Results
Complete eye examinations and screening attempts with the blinq, 2WIN, and PDI Check were completed by 202 children aged 4–19 years (mean 10.2±3.6 years, median 9.6 years). The racial–ethnic mix of the cohort was white 103, black 24, Hispanic 21, Alaska native 19, Asian 19, and Middle Eastern two. The male-to-female mix was 104 to 98. Refractive error ranged from −9.75 myopia to 8.5 diopters hyperopia, with maximum cylinder 6.5 diopters. Patients who had undergone spectacle, patching, and/or surgical treatment comprised 136 of the 202 (67%), while 66 (33%) were treatment-naïve. Of the treatment-naïve, eleven were referred due to visual acuity screening and eight from photoscreening. The prevalence of eye disease in this cohort of older children was high, with 105 (52%) having 2003 AAPOS refractive risk factors and 115 (58%) having 2021 AAPOS school-age refractive and/or strabismic amblyopia risk factors. In the cohort were three with recent concussion, three with hysterical denial of vision, eleven with syndromes, 24 with prior strabismus surgery, one with ptosis, one with central partial cataracts, and four with optic nerve hypoplasia.
Inconclusive results were obtained for 21 eyes (15 patients) with the 2WIN and one with myopia exceeding instrument estimation, which we designated as −7 diopters sphere. Three patients did not complete the monocular color testing on the PDI Check. For the blinq, 13 had inconclusive initial results and 41 timed out. Photoscreening like 2WIN can yield quick reliable results in very young patients;29 however, if the other two instruments (PDI Check and blinq) had been tested on even younger patients, some would not have participated with fixation or screen interaction based on our experience.
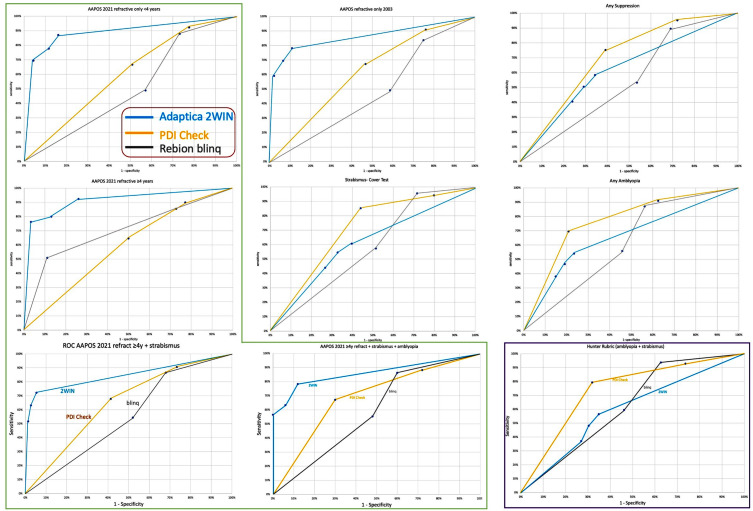
For a range of amblyopia-related examination findings, ROC curves were generated to compare the performance of the three types of instrument-based screening (Figure 2). Refractive subcomponents (hyperopia, astigmatism, myopia and anisometropia) on the 2WIN varied from more sensitive to more specific, and an ROC curve was constructed with “routine” as the instrument-referral criteria that yielded optimal accuracy.30 For 2021 AAPOS criteria for age <4 years, the sensitive alternative yielded 87% sensitivity, 84% specificity, and positive predictive value (PPV) of 80%. For AAPOS 2021 criteria for age ≥4 years, the regular instrument-referral criteria yielded 80% sensitivity, 78% specificity, and PPV of 88%. The blinq with any interpretation other than “pass” considered a referral for the AAPOS refractive criteria for age <4 years, high sensitivity of 88% was achieved at the expense of specificity of only 27% and PPV of 49%. For 2021 AAPOS refractive criteria for age ≥4 years, sensitivity was 85%, specificity 27%, and PPV 58%. On the PDI Check with instrument referral-criteria of ≥200 seconds of arc stereo, logMAR acuity ≥0.5, and delta acuity ≥0.4, the 2021 AAPOS younger (<4 y/o) refractive criteria yielded 67% sensitivity, 49% specificity, and PPV of 51%, while targeting the older 2021 refractive guidelines (≥4 y/o) achieved 65% sensitivity, 50% specificity, and PPV of 61%.
Figure 2.
ROC curves for amblyopia screening. Rebion blinq (gray), Adaptica 2WIN (teal blue), and PDI Check Nintendo 3DS game (orange) performance on detecting high prevalence of amblyopia risk factors and actual amblyopia and strabismus. Of the various exam outcomes, AAPOS 2021 outlined in green on the left and Bosque–Hunter rubric outlined in purple at lower right. Commonly referenced AAPOS 2003 (older triad of 2013) and aspects of manifest strabismus (cover test >8 prism diopters and “any” cases with prior strabismus surgery or chemodenervation) and diminished binocularity are also included.
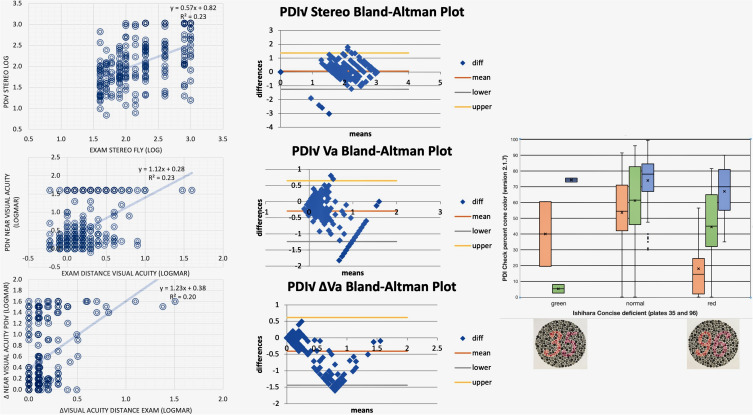
For those children with actual amblyopia and strabismus, blinq with first or second interpretation a referral, repeat “time-out”, or “inconclusive” had 94% sensitivity, 37% specificity, and PPV of 65%. Refraction determined by 2WIN was compared with actual refraction on Bland–Altman and ABCD ellipsoid tests (Figure 3). Stereopsis (log of arc seconds), monocular visual acuity (logMAR), and intereye differences in visual acuity were compared between PDI Check and confirmatory exams (Figure 4). The two objective tests were completed very quickly: about 5-10 seconds for the 2WIN refraction estimate and 15-25 seconds for the initial blinq result. The PDI Check took 1–2 minutes. During the confirmatory exam, color vision was evaluated using two of the Ishihara concise plates capable of sorting protanopia from deuteranopia: orange 3 and 9 and pink 5 and 6 on gray background dots such that correct answers would be 35 and 96. Those who only noticed 3_ and 9_ (n=2) and those who observed only _5 and _6 (n=11) were compared to 109 able to see all four numbers. Their results are compared to the averaged monocular trichromatic cone scores from the PDI Check in Figure 4.
Figure 3.
Refractive comparison between Adaptica 2WIN and optimal refraction. Bland–Altman plots with intraclass correlation (ICC) for vector-transformed astigmatism (J0 and J45) and spherical equivalent (left). ABCD ellipsoid spectacle comparison (right) for anisometropia, astigmatism, spherical equivalent (SphEq), and overall combined ellipsoid. Means ± SD given. The bar chart shows the proportion and number of patient/eyes for which 2WIN scored an A match (blur <1 logMAR), B match (blur 1–3 logMAR), C match (blur 4–6 logMAR), and poor match (7 logMAR and worse) and inconclusive photorefraction results.
Figure 4.
PDI Check near results compared to examination. Linear correlations far left, Bland–Altman plots center for stereo (top row; log arc seconds), logMAR visual acuity, and intereye difference (bottom row, logMAR). On the right, PDI Check mean, monocular trichromatic isoluminance gray cone is compared to exam results from Ishihara orange–pink vs gray “35” and “96” plates.
Discussion
Children capable of completing reliable sensory and objective confirmatory tests associated with the diagnosis of amblyopia successfully completed all three screening modalities. Each device demonstrated proficiencies and weaknesses. These patients came from a subspecialty pediatric eye practice, with many having already been treated for strabismus and/or amblyopia. Many had high refractive error. Only a third were treatment-naïve. Devices that target residual amblyopia risk factors, such as refractive error (2WIN) and visual acuity, suppression, and stereopsis (PDI Check), performed better that the blinq in many of these older, previously treated amblyopia students. Bosque et al found better performance with an earlier version of blinq when they restricted their cohort to patients aged <8 years, especially treatment-naïve amblyopic and/or strabismic patients.20 On the other hand, the blinq identified 100% of our patients with a recent history of concussion, and for the four patients with confirmed optic nerve hypoplasia, results were two referrals, one timed out twice, and one was inconclusive.
The 2WIN has a menu for fixation lights and sounds. The device has prompt refractive estimates from multi-radial infrared to off-axis photoscreening. It offers an optional add-on corneal reflex function (“CR”) that uses an infrared-transmitting occlusive wand for estimation and quantification of constant and intermittent strabismus.10 For some strabismic patients, the 2WIN refracted each eye separately. Had gaze estimates and/or sequential monocular refraction been further analyzed, 2WIN strabismus validation may have fared even better. The main 2WIN menu is not specifically adapted to simplified pediatric amblyopia screening, even though instrument-referral criteria in the software are capable of designating a “refer” or a “pass” from refractive findings, viewable with some menu clicking. Helpful PDF reports can be stored and printed from the 2WIN for pediatric health record-keeping. Early versions had less reproducibility than tabletop autorefractors.31 When the 2WIN was introduced in the US, instrument-referral criteria were developed to allow valid comparisons with the other multiradial infrared photoscreeners32,33 Updated instrument-referral criteria targetting the 2021 AAPOS Guidelines allow valid performance compared between 2WIN, the Welch Allyn Spot and the Plusoptix A12.30 Selection of the bright, twinkling fixation lights and the warble sound may result in underestimation of cycloplegic hyperopia compared to other photoscreeners with intentionally low-detail fixation methods, such as the GoCheck Kids modified smartphone.34
The blinq basic version was initially used in this study, before we upgraded to the Pro-version with enhanced on-screen reporting. The blinq can yield different interpretations after the patient views a circular window with a tiny, orange smiley face: refer (right or left), pass, timed out, or inconclusive. We employed the initial interpretation; however, Rebion recommends repeat screening if a “timed out” interpretation is obtained. Rebion suggests that the screening distance be determined by aiming the crossed lasers at the skin below the chin. During COVID, most of the students were wearing masks. Often, inaccurate distance was determined if the beams were aimed at mask material, so instead aim was occasionally directed at the skin of the forehead before actual screening was performed. In another study, an earlier version of blinq outperformed the Welch Allyn SureSight.11 The blinq can perform admirably with prior editions of the AAPOS validation criteria compared to the 2WIN, particularly in the identification of isolated small-angle strabismus.35 The blinq did not perform as well when modified to deliver outdoor, drive-by photoscreening.36 In a cohort of 300 younger children, all six of the six with amblyopia were detected by blinq, with specificity estimated at 85%.37 We suspect even better performance may have been observed with the software update had we taken the extra time to rescreen the 41 patients with “timed out” initial interpretations. Our referral options from the blinq utilized only the four categories of currently interpreted raw optical data (refer, pass, timed out, and inconclusive) plus whether the patient was capable of consistently viewing the device or not. We were not able to reprocess raw optical data or adjust internal optics by which the manufacturer might achieve even better validity on an ROC curve.
The PDI Check utilizes the autostereoscopic barrier screen of the Nintendo 3DS development kit to present a dynamic set of forced-choice video games, allowing graded estimation of monocular near visual acuity ± suppression, stereopsis, and color vision. The rapid presentation scheme from fine to coarse resolution allows normal subjects to complete the screening very quickly. The device has been calibrated with normal children and adults, as well as patients with amblyopia,25,38 strabismus, and color-vision deficiencies.24 In one study, patients familiar with computers and video games initially were more rapid in scoring acuity, stereopsis, and color (112±14 seconds) than non–English speaking villagers (234±25 seconds), but the PDI Check was faster than conventional testing plates and books.39
A strength of this study is simultaneous completion of the three screening modalities and confirmatory exams on a large number of ethnically diverse children. A weakness is that many of the children were beyond the age of ideal amblyopia therapy and many had already been treated, often successfully, for their initial diagnosis of amblyopia. Another weakness is that the corroborating examiner was not always blinded to the outcomes of the screenings. An advantage of the study is experienced, acuity-optimized, accommodation-reduced refractions, whereas a limitation was that several of the older children did not have cycloplegia. A weakness of the study was imperfect adherence to the Rebion recommendations for the blinq, with some initial fixation-distance measurements disturbed by COVID-19 masks or facial coverings and not all initial “timed out” or “inconclusive” interpretations followed by a second screening attempt. With the initial version of the blinq, three of our screening attempts were unsuccessful, due to incomplete electrical contact of the charger leading to battery drain. This was complete fixed in an update from Rebion. The ideal age for amblyopia screening is early in the first decade, but many of the children in this study were already older or in their teens. Three students using the PDI Check confessed inadvertent mischoice of stereo, but this version of the game did not allow updated scoring with repeat effort only with the stereo component. On the other hand, repeat scoring was possible with visual acuity and monocular cone color on PDI Check version 2.1.7.
It is easy to demonstrate that a new screening device is imperfect. It is much more difficult to envision, design, develop, and then market a device for low- and high-risk populations that is capable of contributing to a reduction in childhood blindness. Each of the devices described in this manuscript utilize different techniques to detect various objective risk factors associated with amblyopia and binocularity. The 2WIN is designed to estimate refractive error in adults, and thus is proficient at detecting refractive amblyopia risk factors in very young children. The PDI Check and blinq were not easily used by children under age 3 years. The PDI Check provides an unpatched form of monocular and depth testing in cooperative older children. The blinq is a more passive test, but still requires understanding and attention to stare at the tiny, orange, smiley-face fixation target inside the dark-gray device. The blinq uniquely can detect small-angle constant strabismus,35 which parents, pediatricians, and photorefractors can miss.
Developers of the devices provided personal thoughts. Dr Mario Angi said of the 2WIN that the bright fixation light can be turned on and off repeatedly to estimate part of the subjective compensation of hyperopia. However, it has to be considered that in a photorefractive screening, the refraction is measured on purpose without cycloplegia, because this offers the advantage of detecting only the component of hyperopia not compensated by accommodation, thus reducing the number of nonamblyopic hyperopic patients referred. The hope for the 2WIN is an economic, simple, rapid, and efficient battery of tests to be administered like an attractive game to screen amblyogenic factors in children. The dream for the 2WIN is to utilize the Kaleidos tube23 and integrate an infrared cover test that masks for a few seconds the right and left eye to enable rapid detection of both phorias and tropias before measurement of refraction.
Dr David Hunter, a developer of the blinq, recommended meticulous adherence to operator instructions, repeat screening of each “inconclusive” or “timed out,” interpretation and validation with “referral-warranted” eye disease and actual amblyopia, rather than just refractive risk factors. Dr Robert Arnold, a developer of vision testing on the autostereoscopic Nintendo 3DS, advised more independent calibration studies from normal young subjects and patients with amblyopia and color deficiency are needed. The hope is to transfer the vision game to a different autostereoscopic platform with a single 3D touch-screen interface. The dream is for simplified, rapid, dynamic presentation of sensory vision tasks to enable reliable screening and verification of vision in young and older patients.
Conclusion
Three novel portable vision-screening devices had separate overlapping and contrasted advantages and disadvantages in detecting risk factors of amblyopia, deficient binocularity, and vision impairment.
Acknowledgment
Thanks to Dr David Hunter for carefully reviewing our data and offering suggestions for consistent methodology using the new birefringent scanner.
Funding Statement
There is no funding to report.
Abbreviations
AAPOS, American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus; ABCD, Alaska Blind Child Discovery; ARF, amblyopia risk factor; AUC, area under the curve; logMAR, logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution; MEPEDS, Multi-Ethnic Pediatric Eye Disease Study; MRD, marginal reflex distance; PD, prism diopter; PPV, positive predictive value; ROC, receiver-operating characteristic.
Data Sharing
Data access: https://www.abcd-vision.org/references/Blinq.2WIN.PDI%20de-ID.pdf
Disclosure
Dr Arnold is a board member of PDI Check and Glacier Medical Software. He coordinates Alaska Blind Child Discovery, which has received discounted vision-screening technology from several vendors. He is an unpaid member of advisory boards for PlusoptiX, Adaptica, GoCheck Kids, iScreen, and NovaSight. He and Alex Damarjian have a patent for PDI Check pending. Dr. Angi has no financial conflicts to disclose. The authors have no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Wu C, Hunter DG. Amblyopia: diagnostic and therapeutic options. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006;141(1):175–184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Leman RE, Clausen MM, Bates J, Stark L, Arnold KK, Arnold RW. A comparison of patched HOTV visual acuity and photoscreening. J Sch Nurs. 2006;22(4):237–243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hunter D, Cotter S. Early diagnosis of amblyopia. Vis Neurosci. 2018;35:E013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Helveston EM. Understanding, detecting, and managing strabismus. Community Eye Health. 2010;23(72):12–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Birch EE, Subramanian V, Weakley DR. Fixation instability in anisometropic children with reduced stereopsis. J AAPOS. 2013;17(3):287–290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rosner J, Rosner J. Parents as screeners for strabismus in their children. J Visual Impair Blindness. 1988;82:193–194. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Arnold RW, Stange CA, Ryan C. The compared predictive value of Bruckner, acuity and strabismus from pediatric referrals. Am Orthopt J. 2006;56(1):15–21. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Angi MR, Bergamo L, Bisantis C. The binocular videorefractoscope for visual screening in infancy. Ger J Ophthalmol. 1993;2(3):182–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Angi MR, Pucci V, Forattini F, Formentin PA. Results of photorefractometric screening for amblyogenic defects in children aged 20 months. Behav Brain Res. 1992;49(1):91–97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Arnold SL, Arnold AW, Sprano JH, Arnold RW. Performance of the 2WIN photoscreener with “CR” strabismus estimation in high risk patients. Am J Ophthalmol. 2019;207:195–203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jost RM, Yanni SE, Beauchamp CL, et al. Beyond screening for risk factors: objective detection of strabismus and amblyopia. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014;132(7):814–820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Budai A, Czigler A, Miko-Barath E, et al. Validation of dynamic random dot stereotests in pediatric vision screening. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2019;257(2):413–423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wallace DK, Lazar EL, Melia M, et al. Stereoacuity in children with anisometropic amblyopia. J AAPOS. 2011;15(5):455–461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ohlsson J, Villarreal G, Sjostrom A, Abrahamsson M, Sjostrand J. Screening for amblyopia and strabismus with the Lang II stereo card. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2002;80(2):163–166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Donahue S, Arnold R, Ruben JB. Preschool vision screening: what should we be detecting and how should we report it? Uniform guidelines for reporting results from studies of preschool vision screening. J AAPOS. 2003;7(5):314–316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Donahue SP, Arthur B, Neely DE, Arnold RW, Silbert D, Ruben JB. Guidelines for automated preschool vision screening: a 10-year, evidence-based update. J AAPOS. 2013;17(1):4–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Arnold RW, Donahue SP, Silbert DI, et al. Uniform guidelines for pediatric vision screen validation 2021. J AAPOS.In Press. 2022; doi: 10.1016/jaapos.2021.09.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kelly KR, Cheng-Patel CS, Jost RM, Wang YZ, Birch EE. Fixation instability during binocular viewing in anisometropic and strabismic children. Exp Eye Res. 2019;183:29–37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Birch EE, Morale SE, Jost RM, et al. Assessing suppression in amblyopic children with a dichoptic eye chart. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016;57(13):5649–5654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bosque LE, Yamarino CR, Salcedo N, et al. Evaluation of the blinq vision scanner for detection of amblyopia and strabismus. J AAPOS. 2021.25:214 e1-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Arnold AW, Arnold SL, Sprano JH, Arnold RW. School bus accommodation-relaxing skiascopy. Clin Ophthalmol. 2019;13:1841–1851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Arnold AW, Eller AM, Smith KA, Grendahl RL, Winkle RK, Arnold RW. Direct nerve size determination and prevalent optic nerve hypoplasia in Alaska. Clin Ophthalmol. 2020;14:491–499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Martin SJ, Htoo HE, Hser N, Arnold RW. Performance of two photoscreeners enhanced by protective containers. Clin Ophthalmol. 2020;14:1427–1435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Arnold AW, Smith KA, Molina A, Damarjian AG, Arnold RW. Trichromatic enhanced dynamic color screening on the PDI Check Nintendo 3DS game. Clin Optom. 2021;(13):137–141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Smith KA, Arnold AW, Sprano JH, Arnold SL, Arnold RW. Performance of a quick screening version of the Nintendo 3DS PDI check game in patients with ocular suppression. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2019;56(4):234–237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Arnold R, Martin SJ, Beveridge JR, et al. Ellipsoid spectacle comparison of PlusoptiX, Retinomax and 2WIN autorefractors. Clin Ophthalmol. 2021;(15):3637–3648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.PEDIG. The clinical profile of moderate amblyopia in children younger than 7 years. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120(3):281–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Longmuir SQ, Boese EA, Pfeifer W, Zimmerman B, Short L, Scott WE. Practical community photoscreening in very young children. Multicenter Study. Pediatrics. 2013;131(3):e764–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Arnold RW, Silbert DI, Modjesky H. Instrument referral criteria for Plusoptix, SPOT and 2WIN targeting 2021 AAPOS guidelines. Clin Ophthalmol. In Press; 2022; doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S342666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ogbuehi KC, Almaliki WH, AlQarni A, Osuagwu UL. Reliability and reproducibility of a handheld videorefractor. Optom Vis Sci. 2015;92(5):632–641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kirk S, Armitage MD, Dunn S, Arnold RW. Calibration and validation of the 2WIN photoscreener compared to the PlusoptiX S12 and the SPOT. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2014;51(5):1–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Racano E, Alessi S, Pertile R. Comparison of 2Win and plusoptiX A12R refractometers with Retinomax handheld autorefractor keratometer. J AAPOS. 2019;23(5):276e1–276 e5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Levitt AH, Martin SJ, Arnold RW. Performance of glow-fixation GCK and 2WIN photoscreeners and Retinomax to uncover hyperopia. Clin Ophthalmol. 2020;14:2237–2244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Arnold RW. Comparative AAPOS validation of the blinq birefringent amblyopia screener with isolated small-angle strabismus. Clin Ophthalmol. 2020;14:325–329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Keffalos MA, Martin SJ, Arnold RW. Drive-by photoscreening: plusoptiX, 2WIN and blinq amblyopia detection during the COVID-19 pandemic. Clin Ophthalmol. 2021;15:775–782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Shah SS, Jimenez JJ, Rozema EJ, Nguyen MT, Preciado M, Mehta AM. Validation of the Pediatric Vision Scanner in a normal preschool population. J AAPOS. 2021. doi: 10.1016/j.jaapos.2021.03.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Smith KA, Damarjian AG, Molina A, Arnold RW. Calibrated measurement of acuity, color and stereopsis on a Nintendo 3DS game console. Clin Optom (Auckl). 2019;11:47–55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Martin SJ, Rowe KS, Hser N, et al. Compared near vision testing with the Nintendo 3DS PDI Check game on the Thai-Burma border. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2019;8(4):330–334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]