Abstract
Background:
Assessment of caregiver needs is a recommended standard of care in pediatric oncology. Caregivers of pediatric brain tumor survivors (PBTS) are a subgroup that may be at highest psychosocial risk. This study examined psychosocial functioning of caregivers of PBTS in comparison to caregivers of youth without cancer history. We hypothesized that caregivers of PBTS would exhibit more psychological symptoms, higher caregiver burden, and lower perceptions of social support than caregivers of comparison youth.
Procedure:
As part of a five-site study, we utilized a matched-sample design to evaluate psychosocial functioning of 301 caregivers of 189 PBTS (ages 8-15) who were 1-5 years post-treatment, and 286 caregivers of 187 comparison youth matched for sex, race, and age. Caregivers completed measures of psychological symptoms, caregiver burden, and perceptions of social support. Repeated measures mixed models compared outcomes between groups and examined differences based on caregiver sex. Socioeconomic status (SES) was examined as a moderator of significant main effects.
Results:
Caregivers of PBTS reported similar levels of psychological symptoms to caregivers of comparison youth. Mothers of PBTS mothers reported higher caregiver burden and lower perceptions of social support than mothers of comparison youth. Low SES exacerbated group differences in caregiver burden.
Conclusions:
Mothers of PBTS may have more caregiving responsibilities and perceive less social support, but reported similar levels of psychological symptoms to comparison mothers; fathers of PBTS were similar to comparison fathers. The mechanisms involved in this complex psychosocial dynamic require further investigation.
Keywords: oncology, pediatric, brain tumors, psychosocial, caregivers
Introduction
Pediatric cancer is a randomly occurring stressful life event that impacts the entire family, with possible psychosocial effects that last into survivorship.1 From a behavioral science perspective, all caregivers appraise their child’s cancer as stressful; some struggle to adapt, whereas others cope effectively.2 Thus, current standards of psychosocial care in pediatric oncology call for ongoing assessment of caregiver psychosocial functioning, with access to appropriate support and interventions as needed.1,3-4 Advances in treatment have led to an increasing number of children and adolescents who are surviving cancer of all types, including brain tumors.5 However, pediatric brain tumor survivors (PBTS) are at high risk for significant medical and psychosocial late effects, with fewer psychosocial supports available during survivorship than during treatment.6,7 The Disability-Stress-Coping model considers the impact of chronic illness in a socio-ecological and family context.8 From this perspective, the stress of childhood illness along with high levels of caregiver burden and low levels of social support may put caregivers of PBTS at risk for psychological symptoms.
Caregivers of children with cancer evidence increased psychological symptoms (e.g., symptoms of anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder) during the first months of treatment.1,9-11 Yet caregiver psychological symptoms beyond the first year of treatment are less consistent, with some studies evidencing ongoing heightened symptoms3,12-14; others demonstrating improved adjustment7,15 and return to baseline psychological functioning16; and still others reporting improvements from baseline psychological functioning (e.g., post-traumatic growth17,18). This lack of concordance has likely been impacted by a variety of methodological issues, including sample heterogeneity (i.e., pooling caregivers of youth of varying ages, diagnoses, prognoses, treatment regimens, stages of treatment), and variations in measurement. However, it also possible that differences in findings accurately reflect variability in stress and caregiving demands, as well as available support.8 Without a comparison group,14 it is impossible to know if the psychological functioning of caregivers of youth with cancer differs substantially from caregivers of youth without cancer history. Since parenting can be universally challenging, there is a need for more robust research designs with widely used measures and sound comparison groups.
PBTS represent a unique group of cancer survivors who are not often differentiated from youth surviving other types of cancer in studies of caregiver psychosocial functioning,14,15,18,19 resulting in critical gap in understanding the PBTS caregiver experience. Caring for PBTS involves numerous demands that may differ from caring for survivors of other cancer types in terms of more neurotoxic treatments, differing prognoses, and increased risk for late effects.6,7 The Disability-Stress-Coping model and qualitative studies suggest that more burden and less social support leads to gaps in caregivers’ ability to meet their own needs during survivorship.8,20,21 Unfortunately, no previous work compared the psychosocial functioning of caregivers of PBTS to that of caregivers of youth without a cancer history using quantitative measures, so it is unclear whether caregivers of PBTS experience more challenges with burden and social support than caregivers of youth in general, or if caregiver burden and low support lead to more psychological symptoms.
In addition to the potentially unique experience of caring for PBTS, individual factors may impact caregiver psychosocial functioning, including parent gender and family socioeconomic status (SES). Across the illness trajectory, mothers of youth with cancer evidence worse psychosocial outcomes than fathers.10,22,23 This may be attributable to mothers often taking on the primary caregiver role and perceptions of inadequate social support.13 Additionally, SES has been associated with worse caregiver psychosocial outcomes, with effects lasting into survivorship.1,24.
Drawing from the Disability-Stress-Coping model,8 this study examined psychosocial outcomes among mothers and fathers of PBTS compared to a sample of caregivers of matched comparison youth, with the primary outcome being psychological symptoms, and secondary outcomes being caregiver burden and perceptions of social support. Viewing pediatric cancer as a randomly occurring stressful life event,2 a classmate comparison sample allowed us to examine whether psychological functioning of caregivers of PBTS differs significantly from that of caregivers from similar sociodemographic backgrounds, but without the additional demands of caring for PBTS. We hypothesized that caregivers of PBTS would report worse psychosocial functioning than caregivers of comparison youth across primary (psychological symptoms) and secondary outcomes (caregiver burden and perceptions of social support). We further examined differences in outcomes based on caregiver sex (i.e., comparing mothers to fathers), and SES was examined as moderator of significant main effects.
Methods
Data for this paper were part of a larger study examining psychosocial late effects of brain tumors on youth and their families. The initial study involved a school-based assessment in the classrooms of PBTS followed by a home-based assessment with PBTS and matched comparison peers, as well as their caregivers.25 This study presents data regarding caregiver functioning from the home-based assessment.
Participants and Procedure
Following institutional ethics board approval, PBTS were identified from tumor registries at five pediatric cancer centers in the United States and Canada. Inclusion criteria were: a) current age 8-15 years, b) history of treatment for a primary intracranial tumor, and c) 1-5 years off treatment without disease progression. PBTS were excluded if they or their caregivers were not fluent in English; had a pre-existing neurobehavioral disorder (e.g., neurofibromatosis or tuberous sclerosis); or were receiving full-time special education. Caregivers of PBTS who met criteria were contacted to obtain permission to contact with schools.25 Following completion of classroom data collection, caregivers of PBTS were recruited to participate in a home visit and complete 1:1 assessments. Caregivers provided written informed consent and completed parent-reported measures. If a parent in a two-caregiver home declined to participate, their demographic information was obtained from the participating caregiver.
Comparison group.
Classmates who returned consent forms were eligible for participation. The participating classmate of the same sex, race, and closest in birthdate to each PBTS was identified as a possible comparison child. Caregivers of each comparison child candidate were contacted and invited to participate in home-based assessments identical to the PBTS group. If the first-choice comparison family declined, the next most closely matched classmate was contacted. All comparison families were screened to ensure the absence of any child with a chronic health condition. Families provided written consent and were compensated for their time.
Measures
Demographic Characteristics.
Caregivers provided information about socio-demographic characteristics, including age, occupation, and highest level of education completed, and the number of children in the home. Race and ethnicity were self-reported by caregivers using US Census categories, consistent with the National Institutes of Health Inclusion of Women, Minorities, and Children policy. SES was measured using the Revised Duncan Scale scores of occupational prestige.26 Age at diagnosis and dates of treatment were abstracted from the medical record for PBTS.
Psychological symptoms.
Caregiver psychological symptoms were assessed using the Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI),27 a 53-item questionnaire that assesses the presence and severity of psychological symptoms over the past seven days, rated on a 4-point scale. This measure yields subscales for nine dimensions of psychological distress (e.g., depression, anxiety) and three global indices of functioning (i.e., Global Severity Index (GSI), Positive Symptom Distress, and Positive Symptom Total). GSI raw scores were utilized for study analyses, and normative T-scores were used descriptively. For the GSI, T-scores above 63 are considered clinically elevated.26 Studies indicate good reliability and validity,28 and the GSI demonstrated excellent internal consistency in this sample (α = .96 - .97).
Caregiver burden.
Caregiver burden was assessed using the Impact on Family Scale, Version G (IOF-G).29,30 This 27-item instrument assesses the impact of caring for children on caregivers, rated on a 4-point scale. Items on this measure are applicable to caregivers of children with and without medical conditions (e.g., “children cause financial problems for the family,” “it is hard to find a reliable person to take care of my child.”). The measure assesses five dimensions of burden (financial impact, disruption of planning, caretaker burden, familial burden, coping) which are summed to create a total impact score. Higher scores indicate greater caregiver burden. Validation studies indicate good reliability and validity,30 and the measure demonstrated good internal consistency in this sample (α =.81 - .92).
Social support.
Caregiver perceptions of social support were assessed using the Medical Outcomes Study Social Support Survey (MOS-SSS).31,32 This 19-item measure assesses caregivers’ perception of and satisfaction with existing social supports. The measure assesses four dimensions of social support (emotional/informational, tangible, affectionate, and positive social interaction) which are summed to create a total score. Higher scores indicate greater satisfaction with social support. Acceptable reliability and validity have been reported,31 and the measure demonstrated good internal consistency in this sample (α = .88 - .91).
Analyses
Descriptive statistics were computed for variables of interest. Outcomes for caregivers of PBTS and comparison youth were examined using a repeated measures mixed model (SAS Proc Mixed) with an unstructured covariance matrix. Models were run separately for male and female caregivers, each compared to respective caregivers of comparison youth. Adjustments for multiple comparisons were made using the Holm’s step-down procedure (SAS Proc MultTest) for the pre-specified primary and secondary outcomes. Following significant tests for global outcomes, we conducted post-hoc analyses to explore which subscales contribute to the difference, using the same procedure described above. Effect sizes were estimated using the sex-specific standard deviation. Exploratory mixed models were run to examine differences in study outcomes based on caregiver sex (e.g., comparing PBTS mothers to PBTS fathers). Moderation analyses were conducted to examine the impact of SES (high vs. low based on median split) on the significance of main effects. Finally, Pearson correlations were conducted to examine relations between primary and secondary outcomes.
Results
Demographic and Background Information
Caregivers of 218 PBTS with completed study classroom visits were eligible for the study, and 301 caregivers of 188 PBTS (86%) agreed to complete parent-reported measures. The final sample included 182 female and 119 male caregivers constituting 100% and 82% of those living in the child’s primary home. A comparison family was recruited from 185 the classrooms of PBTS (85%) with 286 caregivers completing self-report measures, including 185 (99%) and 101 male (73%) caregivers. Demographic variables were not significantly different between caregivers of PBTS and comparison youth, except for ethnicity (Table 1). More caregivers of PBTS identified as Hispanic relative to caregivers of comparison youth. Family demographic variables were not significantly different between families with one versus two participating caregivers. Among PBTS, average age at brain tumor diagnosis was 7.39 years (SD = 3.06), and age at last treatment was 8.26 years (SD = 2.72). The average time from diagnosis to recruitment was 3.78 years (SD = 1.97), and age at recruitment was 11.29 years (SD = 2.33).
TABLE 1.
Demographic Characteristics of Caregivers of Pediatric Brain Tumor Survivors (PBTS) and Caregivers of Classroom Comparison Peers
| Characteristic | PBTS Caregivers (N=301) |
Comparison Caregivers (N=286) |
p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Father agea | 41.78 ± 6.36 | 42.84 ± 6.52 | .19 |
| Mother age | 40.33 ± 6.24 | 41.04 ± 6.08 | .30 |
| Father education | 14.29 ± 2.64 | 14.58 ± 2.57 | .35 |
| Mother education | 14.26 ± 2.17 | 14.63 ± 2.23 | .11 |
| Father occupationb | 53.58 ± 20.57 | 55.81 ± 20.40 | .35 |
| Mother occupationb | 40.41 ± 22.23 | 43.66 ± 23.62 | .17 |
| % Married/partnered | 86% | 89% | .10 |
| Race | .21 | ||
| % White | 89% | 91% | |
| % Black | 4% | 6% | |
| % Asian | 2% | 2% | |
| % Other Race | 5% | 0% | |
| Ethnicity | .01* | ||
| % Non-Hispanic | 95% | 98% | |
| % Hispanic | 5% | 2% | |
| Number of children living at home | 2.44 ± 1.01 | 2.49 ± 1.04 | .52 |
| Age of target child | 11.29 ± 2.32 | 11.26 ± 2.29 | .90 |
p < .05
Note. Plus minus values are means ± standard deviation.
The number of fathers in the sample (n = 101-119) is lower than the number of mothers (n = 182-185) because many of the families were single parent households.
Revised Duncan scores of occupational prestige.24
Caregiver Psychosocial Functioning
Psychological Symptoms.
No significant differences in the level of total psychological symptoms based were found for mothers or fathers of PBTS relative to caregivers of comparison youth (Table 2). Approximately 14% of mothers of PBTS and 11% of mothers of comparison youth endorsed clinically elevated psychological symptoms; 17% of fathers of PBTS and 18% of fathers of comparison youth endorsed clinically elevated psychological symptoms. Chi-square analyses indicated no significant group differences in the proportion of caregivers with elevated psychological symptoms (χ2(1) = .52, p = .47). While GSI scores were not significantly different, exploratory analyses of depression and anxiety were conducted. No significant differences emerged for mothers or fathers of PBTS relative to caregivers of comparison youth (d < 0.10).
TABLE 2.
Psychosocial Functioning among Caregivers of Pediatric Brain Tumor Survivors (PBTS) and Caregivers of Classroom Comparison Peers
| Measure | PBTS Caregivers |
Comparison Caregivers |
Holm’s Adjusted p value |
Effect Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brief Symptom Inventory | ||||
| Fathers | ||||
| Global Severity Index† | 52.20 ± 1.00 | 50.4 ± 1.2 | 1.00 | 0.11 |
| Positive Symptom Total | 12.65 ± 0.97 | 11.42 ± 1.06 | ||
| Positive Symptom Distress | 1.28 ± 0.05 | 1.14 ± .05 | ||
| Mothers | ||||
| Global Severity Index† | 51.00 ± 0.80 | 49.8 ± 0.8 | 1.00 | 0.05 |
| Positive Symptom Total | 14.37 ± 0.77 | 13.60 ± 0.82 | ||
| Positive Symptom Distress | 1.32 ± 0.03 | 1.21 ± 0.04 | ||
| Impact on Family Scale – Version G | ||||
| Fathers – Total | 21.88 ± 1.55 | 17.48 ± 1.92 | .23 | 0.23 |
| Financial impact | 3.80 ± 0.24 | 2.90 ± 0.31 | ||
| Disruption of planning | 7.90 ± 0.54 | 6.27 ± 0.71 | ||
| Caretaker burden | 4.69 ± 0.36 | 3.78 ± 0.46 | ||
| Familial burden | 5.49 ± 0.49 | 4.56 ± 0.55 | ||
| Coping | 7.04 ± 0.16 | 7.32 ± 0.20 | ||
| Mothers – Total | 27.95 ± 0.51 | 23.86 ± 0.41 | <.01** | 0.65 |
| Financial impact | 4.60 ± 0.10 | 3.80 ± 0.08 | <.01** | 0.65 |
| Disruption of planning | 8.92 ± 0.19 | 8.54 ± 0.17 | <.01** | 0.57 |
| Caretaker burden | 6.08 ± 0.14 | 5.21 ± 0.10 | <.01** | 0.53 |
| Familial burden | 7.36 ± 0.16 | 6.32 ± 0.13 | <.01** | 0.54 |
| Coping | 7.02 ± 0.15 | 7.73 ± 0.16 | <.01** | −0.34 |
| MOS Social Support Survey | ||||
| Fathers – Total | 371.8 ± 8.81 | 389.4 ± 8.29 | .60 | −0.19 |
| Emotional/informational support | 68.87 ± 2.24 | 71.77 ± 2.06 | ||
| Tangible support | 74.33 ± 2.00 | 77.94 ± 1.89 | ||
| Affectionate support | 80.48 ± 1.99 | 84.91 ± 1.85 | ||
| Positive support | 74.46 ± 2.23 | 76.50 ± 2.10 | ||
| Satisfaction with support | 74.11 ± 2.18 | 78.23 ± 2.18 | ||
| Mothers – Total | 377.4 ± 7.62 | 407.6 ± 6.93 | .04* | −0.31 |
| Emotional/informational support | 74.39 ± 1.64 | 79.35 ± 1.51 | .04* | −.23 |
| Tangible support | 68.45 ± 2.01 | 74.97 ± 1.89 | .04* | −0.25 |
| Affectionate support | 82.36 ± 1.83 | 88.90 ± 1.33 | .03* | −0.30 |
| Positive support | 74.84 ± 1.78 | 82.81 ± 1.59 | .02* | −0.31 |
| Satisfaction with support | 75.77 ± 1.81 | 81.75 ± 1.69 | .04* | −0.25 |
p < .01
p < .05
Normative T-scores reported in table. Analyses were run with Raw Scores.
Note. Plus minus values are means ± standard error.
Caregiver Burden.
A significant main effect for group status (PBTS vs. comparison) was found for mothers only, with a medium-to-large effect size (Table 2). Mothers of PBTS reported higher global levels of burden than mothers of comparison youth. Subscales of the IOF-G were examined for mothers to explore various dimensions of caregiver burden that contributed to global burden. Results demonstrated a significant main effect of group status on all subscales, such that mothers of PBTS reported higher levels of financial impact, disruption of planning, caretaker burden, familial burden, and significantly lower levels of coping than mothers of comparison youth. No significant differences in caregiver burden emerged between fathers of PBTS and fathers of comparison youth (Table 2).
Perceptions of Social Support.
A significant main effect for group status (PBTS vs. comparison) was found for mothers only. Mothers of PBTS reported significantly lower perceptions of global social support than mothers of comparison youth. Subscales of the MOS-SSS were examined for mothers to explore various dimensions of perceived social support that may have contributed to global perceptions of social support. Results demonstrated a significant main effect of group status on all social support subscales; mothers of PBTS reported significantly lower perceived emotional/informational support, tangible support, affectionate support, positive support, and satisfaction with support relative to mothers of comparison youth. No significant differences in perceptions of social support emerged between fathers of PBTS and fathers of comparison youth (Table 2).
Within-Group Characteristics Impacting Outcomes
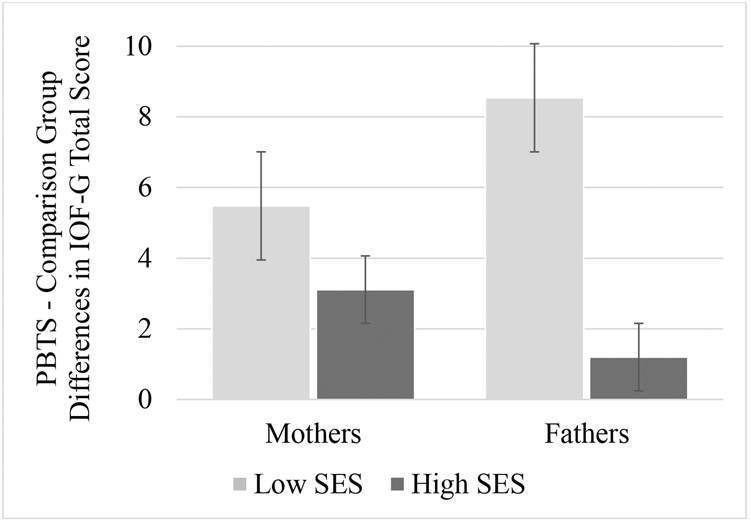
Exploratory mixed model analyses were conducted to examine whether there were significant differences in secondary outcomes between mothers and fathers within the same group (i.e., comparing mothers of PBTS with fathers of PBTS). Results revealed no significant differences in caregiver burden (p = .88) or perceptions of social support (p = .60) between mothers and fathers of PBTS. Mixed models were further utilized to examine whether caregiver SES moderated PBTS-comparison group differences in caregiver burden and perceptions of social support. There was a significant moderating effect of SES on group differences in caregiver burden (F(4, 200) = 8.07, p < .001; Figure 1). Specifically, mothers of PBTS reported significantly higher caregiver burden than mothers of comparison youth in both high (p < .01) and low SES groups (p < .01). Fathers of PBTS reported significantly higher levels of caregiver burden than fathers of comparison youth in the low SES group only (p < .01). Among fathers in the high SES group, there were no significant differences in caregiver burden between the PBTS and comparison groups (p = .69). There was no significant moderating effect of SES on caregiver perceptions of social support (p = .56).
FIGURE 1.
Moderation. Pediatric Brain Tumor Survivors (PBTS) – Comparison Group differences in Caregiving Burden, as a Function of Socioeconomic Status (SES)
Note. Impact on Family Scale, Version G (IOF-G)
Associations between Primary and Secondary Outcomes
We examined associations between primary and secondary outcomes among caregivers of PBTS only. Small positive correlations were found between caregiver symptoms and level of burden (r = .12), and negative correlations were found between psychological symptoms and social support (r = −.31). Finally, caregiver burden was negatively correlated with perceptions of social support (r = −.18). All associations were statistically significant (p > .05) and accounted for small amounts of variance.
Discussion
Assessment and treatment of caregiver needs is a recommended standard of care in pediatric oncology.1,3 Despite long-term challenges documented for PBTS, no studies have examined psychosocial late effects of caregivers of PBTS relative to caregivers of youth without cancer history. Additionally, caregivers of PBTS are rarely differentiated from caregivers of children surviving other types of cancer, even though PBTS may have more complex and challenging late effects. Identifying psychosocial needs of caregivers of PBTS has the potential to improve screening and access to evidence-based interventions, as well as inform the field about the long-term psychosocial effects of caring for a child with a brain tumor.
Contrary to hypotheses based on the Disability-Stress-Coping model,8 this study found no significant differences in psychological symptoms for caregivers of PBTS relative to caregivers of comparison youth. Despite the additional challenges of managing late effects for PBTS, the results from this study suggest that, as a group, caregivers of PBTS are at no higher risk for psychological symptoms than the general population. Notably, caregivers of PBTS with the highest levels of perceived burden and lowest perceived support reported the most elevated psychological symptoms. While this is line with the Disability-Stress-Coping model,8 these associations explained a small portion of the variance in psychological symptoms, suggesting that other factors influence psychological symptoms for caregivers of PBTS.
Elevations in secondary outcomes among caregivers of PBTS suggest ongoing caregiving challenges, particularly for mothers and fathers with low SES, in addition to gaps in social supports. Relative to caregivers of youth without cancer history, mothers of PBTS may have more demands for caregiving due to late effects commonly experienced by PBTS, including neurocognitive sequelae and challenges with social functioning.7,25,33,34 Indeed, there are numerous facets of caregiving required to manage the needs of PBTS,35 and addressing these needs can present a significant strain on caregivers.36 Although the Disability-Stress-Coping model8 hypothesizes that higher caregiver burden and perceptions of lower social support would put caregivers of PBTS at risk for elevated psychological symptoms,37 the magnitude of these associations in our sample were modest. It is likely that other protective factors, such as stress processing (e.g., appraisal, coping skills), play a role in this dynamic. Indeed, teaching coping skills to caregivers of youth with recently diagnosed cancer can alleviate psychological symptoms of distress.38,39 Future, longitudinal work is needed to better understand protective factors over time and whether coping skills learned during treatment continue to promote adaptive psychological functioning during survivorship.
Our findings add to a growing body of literature suggesting that most caregivers of children with cancer are resilient when faced with the challenge of their child’s illness.17,19 .This notion coincides with longitudinal studies of caregiver distress, which suggests that most caregivers adjust to the stressor of pediatric cancer treatment within the first year and continue to do well over time.9,15 A subset of caregivers who struggle to adjust initially may be at highest risk for long-term elevations in psychological symptoms.15,22 A deeper understanding of individual as well as familial differences in effective coping and support strategies may improve intervention for these caregivers.40 Families of PBTS could provide a rich sample for this work given evidence of adaptive psychological functioning in the context of complex and ongoing caregiving demands. In addition to understanding individual processes, a next step could be to examine longitudinal risk and resilience within the family system (e.g., between caregiving dyads) to evaluate interdependence between family members and consider ways that family dynamics may contribute to psychological outcomes.40,41
Caring for PBTS may be especially challenging for families with limited resources. We found that low SES exacerbated differences in caregiving burden between caregivers of PBTS and comparison youth (Figure 1). These findings fit the Disability-Stress-Coping model8 and corroborate evidence documenting increased burden among families who are faced with co-occurring sociodemographic stressors alongside caring for a child with cancer,24,36,42 although to date, most attention has been given to mothers of youth on active treatment. However, results from our study suggest that the impact of low SES may extend into survivorship for both mothers and fathers of PBTS. While these factors did not result in impaired psychological functioning among caregivers of PBTS, they may have contributed to diminished quality of life. In samples of caregivers of PBTS at the end of tumor-directed therapy, higher levels of caregiver strain were associated with low caregiver quality of life.37 Moreover, increased challenges with family management,43 or incorporating management of medical conditions into daily life, have been associated with lower quality of life among caregivers of adolescent and young adult PBTS.35
While caregivers in our sample did not report high levels of psychological symptoms, it is important to note that the long-term impact of high burden and perceptions of low social support is not currently known. Clinical providers are encouraged to conduct family-centered assessments that go beyond the evaluation of caregiver distress. Our results suggest that caregivers may report few psychological symptoms, and yet mothers may still endorse high caregiving burden and desire greater social support. Providers are encouraged to listen to caregivers’ concerns, ask questions to identify areas of burden, and consider ways to connect families to resources that can support needs outside of the clinic setting, as most PBTS have only yearly or semi-yearly follow-up in survivorship clinics.
Several limitations of the current work should also be noted. The cross-sectional nature of the study precludes the identification of causal factors that may be linked to outcomes. Our relatively small cohort of fathers limited our ability to confirm significant sex differences. Indeed, fathers are generally underrepresented in pediatric research,44 which may contribute to limited understanding of sex differences in caregiver psychosocial needs. Future, longitudinal work with families is essential to gaining a better understanding of the processes underlying the resilience of caregivers of PBTS. Future research with more diverse families, incorporating other important facets of the Disability-Stress-Coping model,8 is also important for testing more robust, complex associations among factors that may inform evidence-based interventions.
This study used a rigorous, matched-comparison design to examine psychosocial functioning of caregivers of PBTS in comparison to caregivers of youth without cancer history. Caregivers of PBTS demonstrated considerable resilience, evidencing psychological functioning within the normal range despite elevations in maternal caregiver burden and perceptions of low social support. Based on these findings, we recommend that future research longitudinally examine factors that promote resilience in the context of high caregiving needs, particularly processes of appraisal and coping, as well as the interrelated functioning of the family unit, in the context of a child’s cancer diagnosis, treatment, and survivorship. Clinicians should continue to screen families for distress, but also consider evaluating other aspects of family functioning, including caregiver burden, social support, and other socio-ecological resources, to ensure comprehensive supportive care in survivorship.
Acknowledgements:
This work was supported by awards from the American Cancer Society (RSGPB-03-098-01-PBP) and the National Cancer Institute (RO3 CA097740-02).
Abbreviation
- PBTS
Pediatric brain tumor survivors
- SES
Socioeconomic status
- BSI
Brief Symptom Inventory
- GSI
Global Symptom Index
- IOF-G
Impact on Family Scale, Version G
- MOS-SSS
Medical Outcomes Study Social Support Survey
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest Statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Data Availability Statement:
Data utilized in the manuscript are available from the anchor author (K. Vannatta) upon reasonable request.
References
- 1.Kearney JA, Salley CG, Muriel AC. Standards of psychosocial care for parents of children with cancer. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015;62 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):S632–S683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lazarus RS, Folkman S. Stress, appraisal, and coping. Springer Publishing Company, Inc, NY, NY. 1984. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kazak AE, Abrams AN, Banks J, et al. Psychosocial assessment as a standard of care in pediatric cancer. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015;62 Suppl 5:S426–S459. doi: 10.1002/pbc.25730 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wiener L, Kazak AE, Noll RB, Patenaude AF, Kupst MJ. Standards for the psychosocial care of children with cancer and their families: An introduction to the special issue. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015;62 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):S419–S424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Truitt G, Boscia A, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS. CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2011-2015. Neuro Oncol. 2018;20(suppl_4):iv1–iv86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gunn ME, Lähdesmäki T, Malila N, Arola M, Grönroos M, Matomäki J, Lähteenmäki PM. Late morbidity in long-term survivors of childhood brain tumors: a nationwide registry-based study in Finland. Neuro Oncol. 2015;17(5):747–56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zebrack BJ, Gurney JG, Oeffinger K, et al. Psychological outcomes in long-term survivors of childhood brain cancer: a report from the childhood cancer survivor study. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(6):999–1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wallander JL, Varni JW. Effects of pediatric chronic physical disorders on child and family adjustment. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1998;39(1):29–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Katz LF, Fladeboe K, King K, et al. Trajectories of child and caregiver psychological adjustment in families of children with cancer. Health Psychol. 2018;37(8):725–735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pai AL, Greenley RN, Lewandowski A, Drotar D, Youngstrom E, Peterson CC. A meta-analytic review of the influence of pediatric cancer on parent and family functioning. J Fam Psychol. 2007;21(3):407–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.van Warmerdam J, Sutradhar R, Kurdyak P, Lau C, Pole JD, Nathan PC, Gupta S. Long-term mental health outcomes in mothers and siblings of children with cancer: A population-based, matched cohort study. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(1):51–62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hutchinson KC, Willard VW, Hardy KK, Bonner MJ. Adjustment of caregivers of pediatric patients with brain tumors: a cross-sectional analysis. Psychooncology. 2009;18(5):515–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Witt WP, Litzelman K, Wisk LE, Spear HA, Catrine K, Levin N, Gottlieb CA. Stress-mediated quality of life outcomes in parents of childhood cancer and brain tumor survivors: a case-control study. Qual Life Res. 2010;19(7):995–1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.van Warmerdam J, Zabih V, Kurdyak P, Sutradhar R, Nathan PC, Gupta S. Prevalence of anxiety, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder in parents of children with cancer: A meta-analysis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2019. Jun;66(6):e27677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Howard Sharp KM, Fisher RS, Clark OE, et al. Long-term trajectories of depression symptoms in mothers of children with cancer. Health Psychol. 2020;39(2):89–98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Quin S The long-term psychosocial effects of cancer diagnosis and treatment on children and their families. Soc Work Health Care. 2004;39(1-2):129–49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Turner-Sack AM, Menna R, Setchell SR, Maan C, Cataudella D. Psychological functioning, post-traumatic growth, and coping in parents and siblings of adolescent cancer survivors. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2016;43(1):48–56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Phipps S, Long A, Willard VW, et al. Parents of children with cancer: At-risk or resilient?. J Pediatr Psychol. 2015;40(9):914–925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rosenberg AR, Wolfe J, Bradford MC, Shaffer ML, Yi-Frazier JP, Curtis JR, Syrjala KL, Baker KS. Resilience and psychosocial outcomes in parents of children with cancer. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2014;61(3):552–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Christen S, Mader L, Baenziger J, et al. "I wish someone had once asked me how I'm doing": Disadvantages and support needs faced by parents of long-term childhood cancer survivors. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2019;66(8):e27767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kelada L, Wakefield CE, Carlson L, Hetherington K, McGill BC, McCarthy MC, Miles G, Cohn RJ, Sansom-Daly UM. How parents of childhood cancer survivors perceive support from their extended families. J Child Fam Stud. 2019. Jun;28(6):1537–47. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Vrijmoet-Wiersma CM, van Klink JM, Kolk AM, Koopman HM, Ball LM, Maarten Egeler R. Assessment of parental psychological stress in pediatric cancer: a review. J Pediatr Psychol. 2008;33(7):694–706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rensen N, Steur LM, Schepers SA, et al. Gender-specific differences in parental health-related quality of life in childhood cancer. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2019;66(7):e27728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pelletier W, Bona K. Assessment of financial burden as a standard of care in pediatric oncology. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015;62 Suppl 5:S619–S631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Salley CG, Hewitt LL, Patenaude AF, Vasey MW, Yeates KO, Gerhardt CA, Vannatta K. Temperament and social behavior in pediatric brain tumor survivors and comparison peers. J Pediatr Psychol. 2015. Apr;40(3):297–308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Entwisle DR, Astone NM. Some practical guidelines for measuring youth’s race/ethnicity and socioeconomic status. Child Dev. 1994;65:1521–40 [Google Scholar]
- 27.Derogatis LR, Spencer PM. Brief symptom inventory: BSI. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Derogatis LR, Melisaratos N. The brief symptom inventory: an introductory report. Psychol Med. 1983. Aug;13(3):595–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Stein RE, Jessop DJ. The impact on family scale revisited: further psychometric data. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2003. Feb 1;24(1):9–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Stein REK, Riessman CK. The development of an Impact-on-Family Scale: preliminary findings. Med Care 1980;18:465–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sherbourne CD, Stewart AL. The MOS social support survey. Soc Sci Med. 1991;32(6):705–714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Priede A, Andreu Y, Martínez P, Conchado A, Ruiz-Torres M, González-Blanch C. The factor structure of the Medical Outcomes Study-Social Support Survey: A comparison of different models in a sample of recently diagnosed cancer patients. J Psychosom Res. 2018;108:32–38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gunn ME, Mört S, Arola M, Taskinen M, Riikonen P, Möttönen M, Lähteenmäki PM. Quality of life and late-effects among childhood brain tumor survivors: a mixed method analysis. Psychooncology. 2016. Jun;25(6):677–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hocking MC, McCurdy M, Turner E, et al. Social competence in pediatric brain tumor survivors: application of a model from social neuroscience and developmental psychology. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015;62(3):375–384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Deatrick JA, Barakat LP, Knafl GJ, et al. Patterns of family management for adolescent and young adult brain tumor survivors. J Fam Psychol. 2018;32(3):321–332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.SanGiacomo N, Toth J, Hobbie W, et al. Challenges to family management for caregivers of adolescent and young adult survivors of childhood brain tumors. J Pediatr Oncol Nurs. 2019;36(6):402–412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Quast LF, Turner EM, McCurdy MD, Hocking MC. Health-related quality of life in parents of pediatric brain tumor survivors at the end of tumor-directed therapy. J Psychosoc Oncol. 2016;34(4):274–90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sahler OJ, Dolgin MJ, Phipps S, et al. Specificity of problem-solving skills training in mothers of children newly diagnosed with cancer: results of a multisite randomized clinical trial. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(10):1329–1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Phipps S, Fairclough DL, Noll RB, et al. In-person vs. web-based administration of a problem-solving skills intervention for parents of children with cancer: Report of a randomized noninferiority trial. EClinicalMedicine. 2020;24:100428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Compas BE, Bemis H, Gerhardt CA, et al. Mothers and fathers coping with their children's cancer: Individual and interpersonal processes. Health Psychol. 2015;34(8):783–793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kenny DA. Commentary: Dyadic analyses of family data. J Pediatr Psychol. 2011;36(5):630–633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bemis H, Yarboi J, Gerhardt CA, et al. Childhood cancer in context: Sociodemographic factors, stress, and psychological distress among mothers and children. J Pediatr Psychol. 2015;40(8):733–743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Deatrick JA, Mullaney EK, Mooney-Doyle K. Exploring family management of childhood brain tumor survivors. J Pediatr Oncol Nurs. 2009;26(5):303–311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Phares V, Lopez E, Fields S, Kamboukos D, Duhig AM. Are fathers involved in pediatric psychology research and treatment?. J Pediatr Psychol. 2005;30(8):631–643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Data utilized in the manuscript are available from the anchor author (K. Vannatta) upon reasonable request.