Abstract
Objective
To seek evidence for osteoradionecrosis (ORN) after dental extractions before or after intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) for head and neck cancer (HNC).
Methods
Medline/PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library were searched from 2000 until 2020. Articles on HNC patients treated with IMRT and dental extractions were analyzed by two independent reviewers. The risk ratios (RR) and odds ratios (OR) for ORN related to extractions were calculated using Fisher’s exact test. A one-sample proportion test was used to assess the proportion of pre- versus post-IMRT extractions. Forest plots were used for the pooled RR and OR using a random-effects model.
Results
Seven of 630 publications with 875 patients were eligible. A total of 437 (49.9%) patients were treated with extractions before and 92 (10.5%) after IMRT. 28 (3.2%) suffered from ORN after IMRT. ORN was associated with extractions in 15 (53.6%) patients, eight related to extractions prior to and seven cases related to extractions after IMRT. The risk and odds for ORN favored pre-IMRT extractions (RR = 0.18, 95% CI: 0.04–0.74, p = 0.031, I2 = 0%, OR = 0.16, 95% CI: 0.03–0.99, p = 0.049, I2 = 0%). However, the prediction interval of the expected range of 95% of true effects included 1 for RR and OR.
Conclusion
Tooth extraction before IMRT is more common than after IMRT, but dental extractions before compared to extractions after IMRT have not been proven to reduce the incidence of ORN. Extractions of teeth before IMRT have to be balanced with any potential delay in initiating cancer therapy.
Supplementary Information
The online version of this article (10.1007/s00066-021-01896-w) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Dental care, Osteoradionecrosis prevention, Radiation toxicity, Oropharyngeal cancer, Dental management
Introduction and objectives
Ionizing radiation (IR) inhibits wound healing and damaged irradiated tissue has reduced healing abilities [1]. IR of the oral and pharyngeal mucosa and the salivary glands leads to changes of the oral milieu, including decreasing pH and saliva quantity, and changes in bacterial composition [2, 3]. Oral hygiene is helpful for preserving teeth and reduces adverse side effects of radiotherapy (RT) [4]. A severe side effect is osteoradionecrosis (ORN), characterized by the exposure and devitalization of the bone, causing severe pain, swelling, or difficulties with eating. Poor dental status predisposes for dental decay and ORN if left untreated during, prior to, or after RT [5–7]. Therefore, it has become routine to evaluate the dental status and to extract non-restorable teeth prior to any high-dose radiotherapy for head and neck cancer (HNC) [4].
The rationale for extracting critical teeth before RT is that bone heals better before irradiation than after irradiation. In earlier studies, tooth extractions after RT have been reported to be associated with a high risk of ORN [8]. However, some authors observed that dental extractions prior to RT do not prevent ORN completely [9–11]. Currently, there is no conclusive evidence that dental extractions before irradiation offer a significant risk reduction for the development of ORN compared to dental extractions after RT, and there are no randomized controlled trials [12]. Reviews hold back on meta-analyses, and patients treated in the pre-intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) era were included [4, 13].
Nabil and Samman reported that the incidence of ORN varied between 12.9% in 1938 to almost 40% in the 1960s, and fell to 8.2% in 2003 [14]. More recent studies reported an ORN incidences of 0–5% after the introduction of intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) [15–17]. As IMRT represents a modern RT technique that can balance the dose of IR within small spatial volumes, it is unclear how technological advancements in the last decades have affected the need or the sequencing of dental care in the context of IMRT [18]. In this systematic review and meta-analysis using published patient data, we reviewed the existing literature in order to answer the question of whether dental extractions prior to intensity-modulated radiotherapy effectively decrease the risk of developing ORN.
Materials and methods
Data and data sources
This systematic review was conducted according to the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guideline [19]. In September 2019, a first search was conducted for the Medline/PubMed, the Embase, and the Cochrane Library online databases for articles published between 2000 and 2020 which report on head and neck cancer patients with dental extractions undergoing IMRT and developing ORN afterwards. The search included the specific arrangement of free terms and medical subject headings (MeSH) terms in the population, intervention, control, and outcome search design (PICO). Details of the search sequence are given in the supplementary figure Appendix 1.
Selection of studies
IMRT was introduced in the late 1990s. All published articles from the year 2000 onwards were included. Previous IMRT-only studies revealed an ORN incidence of approximately 5% [15–17]. Therefore, case reports and studies with less than 20 IMRT patients were excluded. Exact eligibility criteria are also listed under “Supplementary methods.”
Results
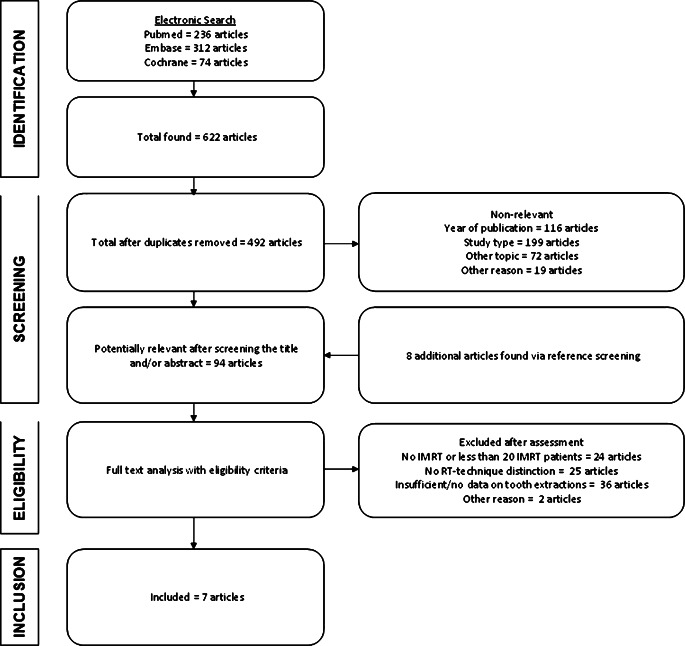
A first search was conducted on 28 September 2019 and a second search on 21 January 2020. As shown in the PRISMA flowchart (Fig. 1), 236 articles were found via Medline/PubMed, 312 articles via Embase, and 74 articles via the Cochrane library resulting in a total of 622 articles. After deleting duplicates, 492 articles remained for further processing. The articles were checked for the year of publication, the study type, and the main topic in the title and the abstract. Finally, 86 articles were submitted to qualitative analysis of the text. Eight additional articles were found in the references, resulting in 94 articles.
Fig. 1.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) flowchart. IMRT intensity-modulated radiotherapy, RT radiotherapy
After analysis and correspondence with authors, eligibility criteria were applied and 87 articles were excluded: 24 articles included patients without IMRT or IMRT was used in less than 20 patients; in 25 studies, distinguishing between patients treated with IMRT or other techniques was not possible for the entire cohort, only for specific subgroups, and absolute figures regarding ORN cases and extractions for IMRT were impossible; in 36 articles, there were incomplete data on dental extractions and individual ORN; the remaining 2 studies marked “other reasons” only reported on ORN grade ≥ 3 [10]. After the eligibility assessment, 7 studies that met our eligibility criteria were suitable for inclusion (Table 1).
Table 1.
Literature articles included
| Author | Year | Title | Study design | Location | Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ben-David et al. [19] | 2007 | Lack of osteoradionecrosis of the mandible after intensity-modulated radiotherapy for head and neck cancer: likely contributions of both dental care and improved dose distributions |
Retrospective Single center |
USA Michigan Ann Arbor |
1996–2005 |
| Gomez et al. [20] | 2011 | Correlation of osteoradionecrosis and dental events with dosimetric parameters in intensity-modulated radiation therapy for head and neck cancer |
Retrospective Single center |
USA New York |
2000-2007 |
| Maesschalck et al. [21] | 2016 | Comparison of the incidence of osteoradionecrosis with conventional radiotherapy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy |
Retrospective Single center |
Switzerland Geneva |
2002–2012 |
| Muraki et al. [22] | 2019 | Dental intervention against osteoradionecrosis of the jaws in irradiated patients with head and neck malignancy; a single-arm prospective study |
Prospective Single center |
Japan Kobe |
2015–2016 |
| Schuurhuis et al. [23] | 2018 | Patients with advanced periodontal disease before intensity-modulated radiation therapy are prone to develop bone healing problems; a 2-year prospective follow-up study |
Prospective Single center |
Netherlands Groningen |
2011–2013 |
| See Toh et al. [24] | 2018 | Dental extractions for preradiation dental clearance and incidence of osteoradionecrosis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy |
Retrospective Single center |
Singapore Singapore |
2011–2013 |
| Willaert et al. [25] | 2019 | Does intensity-modulated radiation therapy lower the risk of osteoradionecrosis of the jaw? A long-term comparative analysis |
Retrospective Single center |
Belgium Leuven |
2003–2010 |
The percentage of patients who had to undergo dental extractions before irradiation ranged from 18% [17, 26] to 90% [27] of the respective study populations. Post-IMRT extractions ranged from 7% [17, 27] to 22% [28]. Combined, 875 patients were treated, with 432 of them having dental extractions before irradiation versus 92 afterwards (Table 2).
Table 2.
Dental extractions before and after intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT)
| Author | Total IMRT patients, n | Edentulous at presentation, n (%) | Patients with extractions prior to IMRT, n (%) | Patients without extractions prior to IMRT, n (%) | Patients with extractions after IMRT, n (%) | Patient without extractions after IMRT, n (%)d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ben-David et al. [19]a | 176 | 16 (9) | 31 (18) | 122 (69) | 13 (7) | 163 (93) |
| Gomez et al. [20] | 168 | 7 (4) | 30 (18) | 138 (82) | 20 (12) | 148 (88) |
| Maesschalck et al. [21]a | 89 | 20 (22) | 46 (52) | 39 (44) | 9 (10) | 80 (90) |
| Muraki et al. [22] | 46 | 0 | 24 (52) | 22 (48) | 4 (9) | 42 (91) |
| Schuurhuis et al. [23] | 56 | 0 | 43 (77) | 13 (23) | 6 (11) | 50 (89) |
| See Toh et al. [24]b | 231 | 0 | 207 (90) | 25 (11) | 16 (7) | 215 (93) |
| Willaert et al. [25]c | 109 | 16 (15) | 51 (47) | 40 (37) | 24 (22) | 85 (78) |
| Total | 875 | 59 (7) | 432 (49) | 394 (45) | 92 (11) | 783 (89) |
IMRT intensity-modulated radiotherapy
aThe preradiation dental extraction percentages do not add up to 100% because extraction data were not available/known for some patients
bReported combined more cases as the total population
cThe preradiation dental extraction percentages do not add up to 100% because edentulous patients were not counted as “Patients without extractions prior to IMRT” and dental status was not available for 1 patient
dCalculated (total IMRT patients–patients with extractions after IMRT)
Overall, 28 (3.2%) patients developed osteoradionecrosis. Based on the authors’ statements or the localization of the ORN, eight ORN cases can be attributed to extractions prior to IMRT. Seven ORN cases can be accounted for by post-IMRT extractions. The remaining 13 cases were not triggered by dental extraction according to the reports (Table 3).
Table 3.
Timeline of dental extractions and manifestation of osteoradionecrosis (ORN)
| Author | Primary tumor location | TN stage | ORN location | ORN onset after IMRT (months) | Patient had pre-IMRT extraction | Patient had post-IMRT extraction | Pre-IMRT extraction related to ORN | Post-IMRT extraction related to ORN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ben-David et al. [19] | No ORN observed | |||||||
| Gomez et al. [20] | Floor of mouth | T2N1 | Mandible | 31 | No | n.a. | No | n.a. |
| Floor of mouth | T2N2b | Mandible | 32 | No | n.a. | No | n.a. | |
| Maesschalck et al. [21] | Oropharynx | T1 (n = 0) T2 (n = 2) T3 (n = 1) T4 (n = 6) | Mandible | 54 | n.a. | Yes | No | Yes |
| Oropharynx | Mandible | 23 | n.a. | No | No | No | ||
| Oropharynx | Mandible | 7 | n.a. | Yes | No | Yes | ||
| Oropharynx | Mandible | n.a. | n.a. | Yes | No | No | ||
| Oropharynx | Mandible | 32 | Probably | No | n.a. | No | ||
| Oropharynx | Mandible | 8 | n.a. | Yes | No | Yes | ||
| Oropharynx | Mandible | 28 | No | No | No | No | ||
| Oropharynx | Mandible | 31 | n.a. | Yes | No | Yes | ||
| Oropharynx | Mandible | 2 | Yes | No | Yes | No | ||
| Muraki et al. [22] | Hypopharynx | T3N0 | Mandible | 3 | No | No | No | No |
| Oropharynx | T4aN2b | Mandible | 11 | No | No | No | No | |
| Oropharynx | T3N0 | n.a. | 18 | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Schuurhuis et al. [23] | Oral Cavity or Oropharynx | n.a. | Mandible | 3 | Yes | n.a. | Yes | No |
| n.a. | Mandible | 7 | n.a. | Yes | No | Yes | ||
| n.a. | Mandible | 2 | n.a. | n.a. | No | No | ||
| n.a. | Transplant | 2 | n.a. | n.a. | No | No | ||
| See Toh et al. [24] | Nasopharynx | T1 (n = 1) T2 (n = 0) T3 (n = 2) T4 (n = 3) | Maxilla | 10 | Yes | No | 5/6 Yes a | No |
| Nasopharynx | Mandible | 6 | Yes | No | No | |||
| Nasopharynx | Mandible | 3 | Yes | No | No | |||
| Nasopharynx | Mandible | 1 | Yes | No | No | |||
| Nasopharynx | Mandible | 24 | Yes | No | No | |||
| Nasopharynx | Mandible | 4 | Yes | No | No | |||
| Willaert et al. [25] | Oropharynx (n = 3) Hypopharynx (n = 1) | n.a. | Mandible | 51.6 | n.a. | Yes | No | Yes |
| n.a. | Mandible | 54.3 | Yes | n.a. | Yes | No | ||
| n.a. | Mandible | 67.7 | n.a. | n.a. | No | No | ||
| n.a. | Mandible | 6.7 | n.a. | Yes | No | Yes | ||
IMRT intensity-modulated radiotherapy, n.a. not available
a In five of six cases, patients had teeth removed prior to irradiation at the areas that subsequently developed ORN. One case occurred spontaneously
Ben-David et al. [17] reported that dental records for 174 out of 176 patients were analyzed. While 16 patients presented edentulous, 157 were dentulous during IMRT. Dental extractions prior to IMRT were received by 30 patients, with two being the median number of teeth removed (range 1–8); 122 patients started IMRT without prior extractions; and 13 patients had extractions after irradiation. With a median follow-up of 34 months, they had no case of grade 2 or worse ORN (CTCAE v3.0) in the 176 patients. They did not observe any grade 1 ORN, because post-treatment panoramic X‑rays were taken only on clinical suspicion of ORN and not systematically.
Gomez et al. reported data for 168 patients [26]: 30 patients received extractions prior to IMRT and 20 patients after IMRT. Seven patients presented edentulous and 138 patients started IMRT without extractions. With a median follow-up of 37.4 months, they observed two cases of ORN, 31 and 32 months after the end of IMRT. None of the patients with ORN had pre-IMRT extractions and no patient underwent bone stripping as part of the surgical procedure.
Maesschalck et al. analyzed dental extraction reports available for 85 of 89 patients [29]: 46 of them received pre-IMRT extractions, nine patients received extraction after irradiation, and 20 patients were edentulous before IMRT. With a median follow-up of 3.2 (± 1.8) years, they observed nine cases of ORN in the 89 patients. ORN occurred with a median of 25 months (range 8–54 months). The authors stated on request that one patient had a dental extraction prior to IMRT which did not heal well, leading to ORN 2 months after IMRT. In four patients, dental extractions after IMRT were the trigger for ORN. In the remaining four cases, no connection between extraction and ORN was observed.
Muraki et al. specified data after request. Prior to IMRT, 24 out of 46 patients underwent extractions [30]. Four patients received post-IMRT extractions. In total, 97 teeth were extracted in the IMRT group. On completion of the study after 2 years, they observed three cases of jawbone exposure. Two patients had neither dental extraction before nor after IMRT. The first case of ORN occurred 3 months after IMRT in a patient with a lingual anterior lesion of the mandible; however, this was unrelated to the dentition status. The bone exposure healed within a month after a sequestrectomy was performed. The second case was due to an impacted wisdom tooth, not extracted prophylactically, and led to bone exposure 11 months after IMRT. This exposure healed after surgical debridement over a period of 13 months. The third patient had pre- and post-IMRT extractions and 18 months after IMRT, ORN was observed. Surgical trauma or dental extractions could not be causally linked ORN. Bone resorption led to a floating tooth, which was lost spontaneously, and bone exposure probably existed before the loss. The treatment from diagnosis of ORN until healing took 5 months (Table 3).
Schuurhuis et al. reported that of 56 patients, 43 were submitted to pre-IMRT extractions [20]. Five had full mouth clearance, rendering them edentulous. Median number of teeth extracted was seven (range 2–10 teeth). Six patients had one to three teeth extracted after IMRT. On completion of the study, with a median follow-up of 24 months (range 11–27 months), 10 patients with bone healing problems were reported. Three patients were diagnosed with delayed wound healing after pre-IMRT dental extraction, three with lingual mandibular sequestration (unrelated to dental extraction), and four with ORN. The first case of ORN occurred 3 months after IMRT at the site where a mandibular molar was extracted prior to irradiation. The second case developed 7 months after IMRT because of a non-healing socket, which was the result of a post-IMRT extraction. Another patient had pathological fracture 2 months after IMRT, where idiopathic ORN had preceded. The fourth case of ORN occurred in the transplanted fibula and thus was not related to pre-or post-IMRT dental extractions.
See Toh et al. reported on 231 patients, 207 needing extractions prior to IMRT, and 16 patients receiving post-IMRT extractions [27]. A total of 943 teeth were extracted, 4.1 teeth extracted per patient on average. With an average follow-up duration of 52 months, they observed six cases of ORN. Median duration for ORN to occur was 5 months (range 1–24 months). The authors stated that 5 patients had pre-IMRT extractions at the sites that developed ORN and that ORN was possibly the result of insufficient healing time of the extraction wounds before the start of IMRT.
Willaert et al. reported on 108 patients with documented details on their dental status out of a cohort of 109 patients treated with IMRT [28]. While 16 patients presented edentulous, 51 of 92 dentulous patients were treated with extractions prior to IMRT and 40 patients started irradiation without dental extractions; 24 patients underwent post-IMRT extractions. With a mean follow-up of 44.4 months (range 6–96 months), 4 patients suffered from ORN. Median interval to ORN diagnosis was 40 months (range 6.7–67.7 months). The authors stated that three out of four cases were related to dental extractions. One ORN case occurring after 54.3 months was related to extraction before, and two cases, occurring after 6.7 and 51.6 months, were related to extraction after IMRT.
Risk of developing dental extraction-related osteoradionecrosis
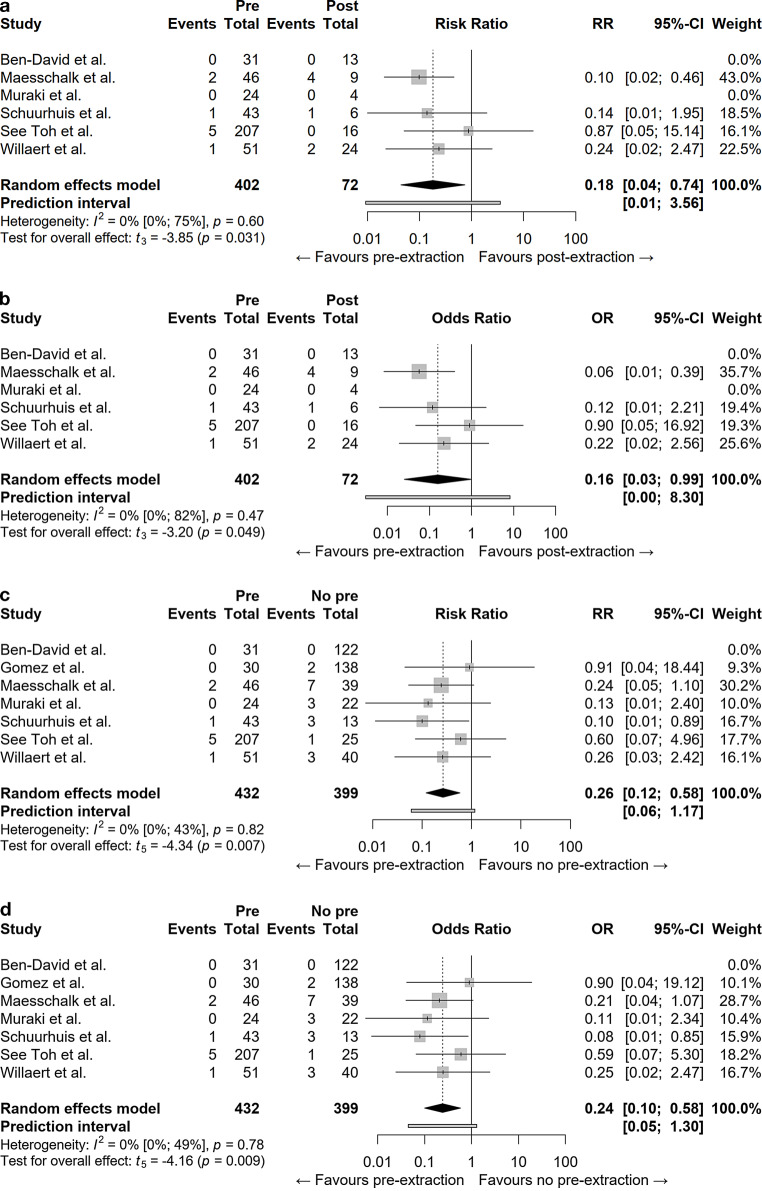
Significantly more (p < 0.001) patients underwent extraction before (n = 432) than after IMRT (n = 92). Further, having extractions prior to IMRT was associated with ORN development less often (8/432) than having extractions after IMRT (7/92) (p < 0.01). As shown in Fig. 2, the pooled risk ratio and odds ratio for ORN development after pre-IMRT extractions to ORN development after post-IMRT extractions were 0.18 (p = 0.031) and 0.16 (p = 0.049), respectively.
Fig. 2.
a Forest plot for the risk ratio (RR) of ORN development between pre-intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) extractions and post-IMRT extractions. b Forest plot for the odds ratio (OR) of ORN development between pre-IMRT extractions and post-IMRT extractions. c Forest plot for the RR of ORN development between pre-IMRT extractions and no pre-IMRT extractions. d Forest plot for the OR of ORN development between pre-IMRT extractions and no pre-IMRT extractions. CI confidence interval
Having pre-IMRT extractions resulted less often in ORN than not having pre-IMRT extractions. By taking all ORN cases into account which were not triggered by pre-IMRT extraction and comparing the patients who did not have pre-IMRT extractions (“No pre” in Fig. 2) to the pre-IMRT extraction group, the risk ratio and odds ratio also indicate an advantage for pre-IMRT extractions (RR = 0.26, p = 0.007, OR = 0.24, p = 0.009).
Lastly, as the prediction interval for the risk ratio and odds ratio includes the value one, no difference in the risk and odds of ORN-development between having extractions prior to IMRT, compared to having extractions after IMRT may be present upon repetition of testing. The same applies to having extractions prior to IMRT, compared to not having extractions prior to IMRT.
Discussion
Radiation-related damage to dentition is of multifactorial origin [21]. Adequate oral hygiene helps to prevent tooth decay and subsequent threats to the bone underneath [22, 23]. Oral hygiene impacts on the risk of caries, and thus on ORN [26]. Dental extractions can enhance ORN and dental extraction prior to IMRT seems to come with a reduced risk compared to dental extraction after IMRT in the present review of the literature. Our observation is in line with the prevailing opinion and current practice, but in contrast to recent reports [9–11]. The statistical difference in OR and RR was not large enough to be conclusive. All articles included in the present meta-analysis report on dental evaluation to identify critical teeth and had hygiene protocols during and after irradiation to prevent dental sequelae. Attribute differences in numbers of patients undergoing pre-IMRT extractions and post-IMRT extractions were present. A general consensus to extract critical teeth before radiotherapy on the one hand, and short follow-up duration and patients changing the treating institution after irradiation on the other hand being the most common of these. Thus, we cannot exclude that a detrimental effect of dental extractions prior to IMRT may be compensated by improved radiotherapy-techniques. The current data suggest that it seems to be premature to conclude that dental extractions before IMRT reduce the risk for ORN development after IMRT. Finally, the protocols from the analyzed studies regarding the pre-irradiation dental extractions and the introduction of the IMRT-technique result in an incidence of less than 5% of ORN, which leaves little room for improvement (Table 4; Refs. [5, 15–17, 20, 24–40]).
Table 4.
Osteoradionecrosis (ORN) incidence in studies with intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) patients
| Author | Year | IMRT patients (n) | ORN cases (n) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ben-David et al. [19] | 2007 | 176 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Huang et al. [31] | 2008 | 71 | 1 | 1.4 |
| Eisbruch et al. [32] | 2009 | 69 | 3 | 4.3 |
| Mendelhall et al. [41] | 2010 | 130 | 4 | 3.1 |
| Montejo et al. [33] | 2010 | 43 | 1 | 2.3 |
| Gomez et al. [20] | 2011 | 168 | 2 | 1.2 |
| Studer et al. [18] | 2011 | 304 | 5 | 1.6 |
| Nguyen et al. [34] | 2012 | 83 | 1 | 1.2 |
| Tsai et al. [35] | 2012 | 334 | 21 | 6.3 |
| Chen et al. [36] | 2015 | 1692 | 105 | 6.2 |
| Maesschalk et al. [21] | 2016 | 89 | 9 | 10.1 |
| Monroe et al. [37] | 2016 | 89 | 4 | 4.5 |
| Owosho et al. [26] | 2016 | 1023 | 44 | 4.3 |
| Caparrotti et al. [38] | 2017 | 1196 | 71 | 5.9 |
| Kojima et al. [8] | 2017 | 26 | 1 | 3.8 |
| Mohamed et al. [39] | 2017 | 1700 | 83 | 4.9 |
| Moon et al. [40] | 2017 | 225 | 9 | 4.0 |
| Schuurhuis et al. [23] | 2017 | 56 | 4 | 7.1 |
| See Toh et al. [24] | 2017 | 231 | 6 | 2.6 |
| Zhang et al. [42] | 2017 | 534 | 41 | 7.7 |
| Muraki et al. [22] | 2019 | 46 | 3 | 6.5 |
| Willaert et al. [25] | 2019 | 109 | 4 | 3.7 |
| Total | – | 8394 | 422 | 5.0 |
The current low rates of ORN since the introduction of IMRT put the focus on improvement and standardization of methods of detecting and reporting ORN. Similarly, the criteria for dental extraction must also be adapted for IMRT. A study conducted at the University Hospital of Zurich in 2011 compared two protocols for dental extractions in IMRT patients and showed that with the risk-adapted dental care treatment (RaDC), fewer teeth can be extracted (with 50% more patients receiving no extraction at all) without increasing the incidence of ORN [15]. However, the mean and median follow-up in the RaDC group was shorter (19/13 months) compared to the group with the conventional protocol (40/30 months). Therefore, protocols that motivate practitioners to easily extract teeth prior to RT should be discouraged. In times of an epidemiological shift from older and sometimes indifferent head and neck cancer patients with tobacco- and alcohol-induced tumors to younger human papilloma virus(HPV)-induced tumor patients, leaving as many teeth in place as possible may become more important in terms of life quality.
Limitations of this systematic review
The literature search for this systematic review included articles in English or German only, representing a linguistic selection bias, and several authors were not attenable to our requests for additional information on the data.
There is no suitable tool to assess the risk of bias of included studies and our approach to data interpretation. As five of seven studies were conducted retrospectively, a retrospective bias applies. The data presented in this review reflect the information provided by the authors of the studies. A selection bias for the retrospective selection of the patient population and the inclusion criteria is likely. Furthermore, a detection bias must also be present because ORN was defined and graded differently in various studies. Three patients with ORN out of two studies included in the present meta-analysis had ORN with unknown association with dental extractions. We decided to include the reports and put them in the group, which was the most accurate with the available information.
Moreover, the result is influenced by many confounders that we were unable to integrate into the calculation because of a lack of data. Such known confounders are, amongst others and not limited to, the exact dose at each extraction site, exact time interval between tooth extraction and treatment, nicotine and alcohol consumption, concomitant systemic treatments, and personal oral hygiene status at diagnosis.
Conclusion
Osteoradionecrosis (ORN) after intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) has become a rare complication. There is no conclusive evidence that dental extractions after IMRT will result in a higher risk of ORN than dental extractions prior to IMRT. However, a reduced risk of developing ORN with pre-IMRT dental extractions emerges after analysis of the current literature, because all research groups use pre-IMRT dental evaluation. Thus, pre-radiotherapy (RT) dental care and extractions remain the standard procedure to prevent dental complications from IMRT. To prove that pre-IMRT extractions decrease the risk of developing ORN, randomized, clinical trials with sufficient follow-up durations would be necessary, but unlikely to be performed due to the low incidence of ORN. Pre-RT dental extractions must be weighed against postponing cancer treatment and the chances of successful control of cancer on the basis of an interdisciplinary evaluation, setting priorities according to individual risks.
Supplementary Information
Funding
Open access funding provided by University of Zurich
Declarations
Conflict of interest
P. Balermpas, J.E. van Timmeren, D.J. Knierim, M. Guckenberger, and I.F. Ciernik declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
For this article no studies with human participants or animals were performed by any of the authors. All studies performed were in accordance with the ethical standards indicated in each case.
References
- 1.McGuire JD, Gorski JP, Dusevich V, Wang Y, Walker MP. Type IV collagen is a novel DEJ biomarker that is reduced by radiotherapy. J Dent Res. 2014;93(10):1028–1034. doi: 10.1177/0022034514548221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Muller VJ, Belibasakis GN, Bosshard PP, Wiedemeier DB, Bichsel D, Rucker M, Stadlinger B. Change of saliva composition with radiotherapy. Arch Oral Biol. 2019;106:104480. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2019.104480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gaetti-Jardim E, Jr., Jardim ECG, Schweitzer CM, da Silva JCL, Oliveira MM, Masocatto DC, Dos Santos CM. Supragingival and subgingival microbiota from patients with poor oral hygiene submitted to radiotherapy for head and neck cancer treatment. Arch Oral Biol. 2018;90:45–52. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2018.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jereczek-Fossa BA, Orecchia R. Radiotherapy-induced mandibular bone complications. Cancer Treat Rev. 2002;28(1):65–74. doi: 10.1053/ctrv.2002.0254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kojima Y, Yanamoto S, Umeda M, Kawashita Y, Saito I, Hasegawa T, Komori T, Ueda N, Kirita T, Yamada SI, Kurita H, Senga Y, Shibuya Y, Iwai H. Relationship between dental status and development of osteoradionecrosis of the jaw: a multicenter retrospective study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2017;124(2):139–145. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2017.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Katsura K, Sasai K, Sato K, Saito M, Hoshina H, Hayashi T. Relationship between oral health status and development of osteoradionecrosis of the mandible: a retrospective longitudinal study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;105(6):731–738. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2007.10.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kobayashi W, Teh BG, Kimura H, Kakehata S, Kawaguchi H, Takai Y. Comparison of osteoradionecrosis of the jaw after superselective intra-arterial chemoradiotherapy versus conventional concurrent chemoradiotherapy of oral cancer. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;73(5):994–1002. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2014.11.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Thorn JJ, Hansen HS, Specht L, Bastholt L. Osteoradionecrosis of the jaws: clinical characteristics and relation to the field of irradiation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;58(10):1088–1093. doi: 10.1053/joms.2000.9562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chang DT, Sandow PR, Morris CG, Hollander R, Scarborough L, Amdur RJ, Mendenhall WM. Do pre-irradiation dental extractions reduce the risk of osteoradionecrosis of the mandible? Head Neck. 2007;29(6):528–536. doi: 10.1002/hed.20538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Baker S, Verduijn GM, Petit S, Sewnaik A, Mast H, Koljenovic S, Nuyttens JJ, Heemsbergen WD. Long-term outcomes following stereotactic body radiotherapy boost for oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Oncol. 2019;58(6):926–933. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2019.1581375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Beech NM, Porceddu S, Batstone MD. Radiotherapy-associated dental extractions and osteoradionecrosis. Head Neck. 2017;39(1):128–132. doi: 10.1002/hed.24553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Eliyas S, Al-Khayatt A, Porter RW, Briggs P. Dental extractions prior to radiotherapy to the jaws for reducing post-radiotherapy dental complications. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;2:CD008857. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008857.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nabil S, Samman N. Risk factors for osteoradionecrosis after head and neck radiation: a systematic review. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2012;113(1):54–69. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2011.07.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nabil S, Samman N. Incidence and prevention of osteoradionecrosis after dental extraction in irradiated patients: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;40(3):229–243. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2010.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Studer G, Glanzmann C, Studer SP, Gratz KW, Bredell M, Locher M, Lutolf UM, Zwahlen RA. Risk-adapted dental care prior to intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) Schweiz Monatsschr Zahnmed. 2011;121(3):216–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Owosho AA, Tsai CJ, Lee RS, Freymiller H, Kadempour A, Varthis S, Sax AZ, Rosen EB, Yom SK, Randazzo J, Drill E, Riedel E, Patel S, Lee NY, Huryn JM, Estilo CL. The prevalence and risk factors associated with osteoradionecrosis of the jaw in oral and oropharyngeal cancer patients treated with intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT): the memorial sloan kettering cancer center experience. Oral Oncol. 2017;64:44–51. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2016.11.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ben-David MA, Diamante M, Radawski JD, Vineberg KA, Stroup C, Murdoch-Kinch CA, Zwetchkenbaum SR, Eisbruch A. Lack of osteoradionecrosis of the mandible after intensity-modulated radiotherapy for head and neck cancer: likely contributions of both dental care and improved dose distributions. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;68(2):396–402. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.11.059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.El-Bassiouni M, Ciernik IF, Davis JB, El-Attar I, Reiner B, Burger C, Goerres GW, Studer GM. [18FDG] PET-CT-based intensity-modulated radiotherapy treatment planning of head and neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;69(1):286–293. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.04.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P, Stewart LA, Group P-P. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. 2015;4:1. doi: 10.1186/2046-4053-4-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Schuurhuis JM, Stokman MA, Witjes MJH, Reintsema H, Langendijk JA, Vissink A, Spijkervet FKL. Patients with advanced periodontal disease before intensity-modulated radiation therapy are prone to develop bone healing problems: a 2-year prospective follow-up study. Support Care Cancer. 2018;26(4):1133–1142. doi: 10.1007/s00520-017-3934-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kielbassa AM, Hinkelbein W, Hellwig E, Meyer-Luckel H. Radiation-related damage to dentition. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7(4):326–335. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70658-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kielbassa AM, Schendera A, Schulte-Monting J. Microradiographic and microscopic studies on in situ induced initial caries in irradiated and nonirradiated dental enamel. Caries Res. 2000;34(1):41–47. doi: 10.1159/000016568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Silva AR, Alves FA, Antunes A, Goes MF, Lopes MA. Patterns of demineralization and dentin reactions in radiation-related caries. Caries Res. 2009;43(1):43–49. doi: 10.1159/000192799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Huang K, Xia P, Chuang C, Weinberg V, Glastonbury CM, Eisele DW, Lee NY, Yom SS, Phillips TL, Quivey JM. Intensity-modulated chemoradiation for treatment of stage III and IV oropharyngeal carcinoma: the university of California-San Francisco experience. Cancer. 2008;113(3):497–507. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Eisbruch A, Harris J, Garden AS, Chao CK, Straube W, Harari PM, Sanguineti G, Jones CU, Bosch WR, Ang KK. Multi-institutional trial of accelerated hypofractionated intensity-modulated radiation therapy for early-stage oropharyngeal cancer (RTOG 00-22) Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;76(5):1333–1338. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.04.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gomez DR, Estilo CL, Wolden SL, Zelefsky MJ, Kraus DH, Wong RJ, Shaha AR, Shah JP, Mechalakos JG, Lee NY. Correlation of osteoradionecrosis and dental events with dosimetric parameters in intensity-modulated radiation therapy for head-and-neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81(4):e207–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Toh YLS, Soong YL, Chim YX, Tan LT, Lye WK, Teoh KH. Dental extractions for preradiation dental clearance and incidence of osteoradionecrosis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy. J Investig Clin Dent. 2018;9(2):e12295. doi: 10.1111/jicd.12295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Willaert R, Nevens D, Laenen A, Batstone M, Politis C, Nuyts S. Does intensity-modulated radiation therapy lower the risk of osteoradionecrosis of the jaw? A long-term comparative analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019;48(11):1387–1393. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2019.04.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Maesschalck T, Dulguerov N, Caparrotti F, Scolozzi P, Picardi C, Mach N, Koutsouvelis N, Dulguerov P. Comparison of the incidence of osteoradionecrosis with conventional radiotherapy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Head Neck. 2016;38(11):1695–1702. doi: 10.1002/hed.24505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Muraki Y, Akashi M, Ejima Y, Hasegawa T, Miyawaki D, Shinomiya H, Nishii M, Otsuki N, Sasaki R, Nibu KI, Komori T. Dental intervention against osteoradionecrosis of the jaws in irradiated patients with head and neck malignancy: a single-arm prospective study. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019;23(3):297–305. doi: 10.1007/s10006-019-00783-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mendenhall WM, Amdur RJ, Morris CG, Kirwan JM, Li JG. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy for oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(11):2218–2222. doi: 10.1002/lary.21144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Montejo ME, Shrieve DC, Bentz BG, Hunt JP, Buchman LO, Agarwal N, Hitchcock YJ. IMRT with simultaneous integrated boost and concurrent chemotherapy for locoregionally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81(5):e845–52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.10.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Nguyen NP, Vock J, Chi A, Ewell L, Vos P, Mills M, Khan R, Almeida F, Davis R, Betz M, Jang S, Gelumbauskas S, Vo RP, Vinh-Hung V. Effectiveness of intensity-modulated and image-guided radiotherapy to spare the mandible from excessive radiation. Oral Oncol. 2012;48(7):653–657. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chen JA, Wang CC, Wong YK, Wang CP, Jiang RS, Lin JC, Chen CC, Liu SA. Osteoradionecrosis of mandible bone in patients with oral cancer—associated factors and treatment outcomes. Head Neck. 2016;38(5):762–768. doi: 10.1002/hed.23949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Monroe AT, Flesher-Bratt D, Morris CG, Peddada AV. Prospectively-collected, tooth-specific dosimetry correlated with adverse dental outcomes. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2016;122(2):158–163. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2016.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Caparrotti F, Huang SH, Lu L, Bratman SV, Ringash J, Bayley A, Cho J, Giuliani M, Kim J, Waldron J, Hansen A, Tong L, Xu W, O’Sullivan B, Wood R, Goldstein D, Hope A. Osteoradionecrosis of the mandible in patients with oropharyngeal carcinoma treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Cancer. 2017;123(19):3691–3700. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wong ATT, Lai SY, Gunn GB, Beadle BM, Fuller CD, Barrow MP, Hofstede TM, Chambers MS, Sturgis EM, Mohamed ASR, Lewin JS, Hutcheson KA. Symptom burden and dysphagia associated with osteoradionecrosis in long-term oropharynx cancer survivors: a cohort analysis. Oral Oncol. 2017;66:75–80. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.01.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Moon DH, Moon SH, Wang K, Weissler MC, Hackman TG, Zanation AM, Thorp BD, Patel SN, Zevallos JP, Marks LB, Chera BS. Incidence of, and risk factors for, mandibular osteoradionecrosis in patients with oral cavity and oropharynx cancers. Oral Oncol. 2017;72:98–103. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhang W, Zhang X, Yang P, Blanchard P, Garden AS, Gunn B, Fuller CD, Chambers M, Hutcheson KA, Ye R, Lai SY, Radwan MAS, Zhu XR, Frank SJ. Intensity-modulated proton therapy and osteoradionecrosis in oropharyngeal cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2017;123(3):401–405. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.05.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tsai CJ, Hofstede TM, Sturgis EM, Garden AS, Lindberg ME, Wei Q, Tucker SL, Dong L. Osteoradionecrosis and radiation dose to the mandible in patients with oropharyngeal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;85(2):415–420. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.05.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mendenhall WM, Amdur RJ, Morris CG, Kirwan JM, Li JG. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy for oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(11):2218–2222. doi: 10.1002/lary.21144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zhang W, Zhang X, Yang P, Blanchard P, Garden AS, Gunn B, Fuller CD, Chambers M, Hutcheson KA, Ye R, Lai SY, Radwan MAS, Zhu XR, Frank SJ. Intensity-modulated proton therapy and osteoradionecrosis in oropharyngeal cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2017;123(3):401–405. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.05.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.