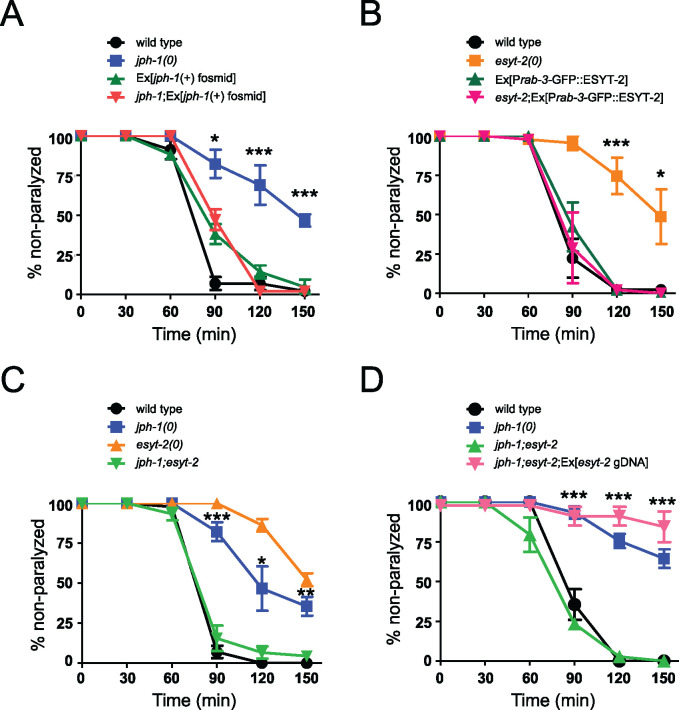
Figure 6.
jph-1 and esyt-2 null mutants are aldicarb resistant and exhibit mutual suppression. (A) jph-1(0) animals are resistant to aldicarb compared to wild-type animals. Aldicarb resistance was rescued by expression of a fosmid containing jph-1 genomic DNA (juEx3390). Statistical significance shown between jph-1(0) and jph-1; Ex[jph-1(+) fosmid]. (B) esyt-2(0) animals are resistant to aldicarb compared to wild-type animals. Aldicarb resistance was rescued by pan-neuronal expression of GFP::ESYT-2 [Prab-3-GFP::ESYT-2(juEx8112)]. Statistical significance shown between esyt-2(0) and esyt-2; Ex[Prab-3-GFP::ESYT-2]. (C) jph-1(0); esyt-2(0) double mutants exhibit a wild-type response to aldicarb. Statistical significance shown between jph-1(0) and jph-1; esyt-2. (D) Expression of esyt-2 genomic DNA (juEx7581) restores aldicarb resistance to jph-1(ju1683); esyt-2(ju1409) double mutants. Statistical significance shown between jph-1; esyt-2 and jph-1; esyt-2; Ex[esyt-2 gDNA]. 1 mM aldicarb. Thirteen to 15 animals tested per genotype per trial, n = 3 trials. Data are shown as individual data points and mean ± SEM. Statistics: One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test. ns, not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.