Abstract
Currently, the world faces a novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) challenge and infected cases are increasing exponentially. COVID-19 is a disease that has been reported by the WHO in March 2020, caused by a virus called the SARS-CoV-2. As of 10 March 2021, more than 150 million people were infected and 3v million died. Researchers strive to find out about the virus and recommend effective actions. An unprecedented increase in pathogens is happening and a major attempt is being made to tackle the epidemic. This article presents deep learning-based COVID-19 detection using CT and X-ray images and data analytics on its spread worldwide. This article's research structure builds on a recent analysis of the COVID-19 data and prospective research to systematize current resources, help the researchers, practitioners by using in-depth learning methodologies to build solutions for the COVID-19 pandemic.
History shows that human has been suffering from several pandemics and a few were highly disastrous. The world is currently facing another pandemic and fighting against an invisible enemy, the novel COVID-19 coronavirus. The rapid spread of coronavirus disease has caused panic worldwide since December 2019. Hundreds of deaths and thousands of infections in almost every corner of the world have been observed. CoV RNA viruses are of the subfamily Coronavirinae, belong to the family Coronaviridae and order Nidovirales (order Nidovirales is composed of Coronaviridae, Arteriviridae, Mesovirididae, and Roniviridae families). Coronavirinae and Torovirinae are two subfamilies of the Coronaviridae family. The Coronavirinae subfamily consists of alpha CoV, beta CoV, gamma CoV, and delta CoV based on genomic structure. Hence, the rapidly increasing prevalence of the COVID-19 pandemic is facing major challenges in preventing the virus. By the end of December 2019, several patients with pneumonia of unidentified etiology were reported in Wuhan, China whose cause was later linked with a wet seafood wholesale market. In December 2019, the SAV-CoV-2 virus was initially described and linked with (COVID-19); on 11 March 2020, WHO proclaimed it a pandemic.1 The coronavirus pandemic continued, and as of 10 March 2021, more than 150 million people were infected and 3v million died.2 The researchers try their best to develop precise approaches to detect virus from huge datasets and recommend effective responses. According to world meter, total confirmed Coronavirus cases globally are 2 306 016, deaths are 158 028 and recovered are 588 634. On behalf of WHO, there are 2 164 111 confirmed COVID-19 cases, with confirmed deaths of 146 198 and a total of 213 countries, areas, or territories with COVID-19 cases.3
Chen et al.4 detected 2019-nCoV in 40 days of the start of the epidemic. They informed that “Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme II” (ACEII) from animals of the family of fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds, bats, or mammals could potentially bind RBD of 2019-nCoV, making them possibly natural hosts for the virus. They further revealed that 2019-COVID is mainly transmitted through respiratory droplets but could also spread through other means. They also insisted upon developing antibodies and small molecular inhibitors to stop the interaction of RBD and ACE2-receptor from containing the virus and its transmission.
The symptoms of COVID-19 could cause an ailment that might extend from mellow to extreme or even dangerous. The side effects as a symptom start between 2 and 14 days after one gets tainted. This period is known as the incubation period. The subjects showing symptoms or found positive are being kept inactive or quarantined either in isolation wards or camps under active medical custody. The disease's key symptoms include fever, chest pain, rapid heartbeat, cough, sore throat, and shortness of breath. Several infected people were found to develop pneumonia in both lungs ranging from mild to severe. In the worst infected cases, severe acute respiratory syndromes and kidney failure were also found, leading to deaths.
The virus normally spreads by respiratory droplets such as cough, contact from an infected person to the surrounding person. It may also spread by contacting objects that are polluted and then contacting the skin. The virus will live up to 72 hours on surfaces (NIH, 2020). The period between two and fourteen days from exposure to the start of symptoms is typically five days on average. A combination of different CT scan symptoms and X-rays could also be diagnosed for the infection.3
The preventions and precautions, typical recommendations of preventing infection spread are to wash hands with soap after every 20 seconds, covering face with handkerchief or elbow/arm while coughing and sneezing, avoiding less-cooked or raw meat, avoiding animal contact too. However, the best precaution is to avoid close contact with any person with the above-mentioned symptoms.
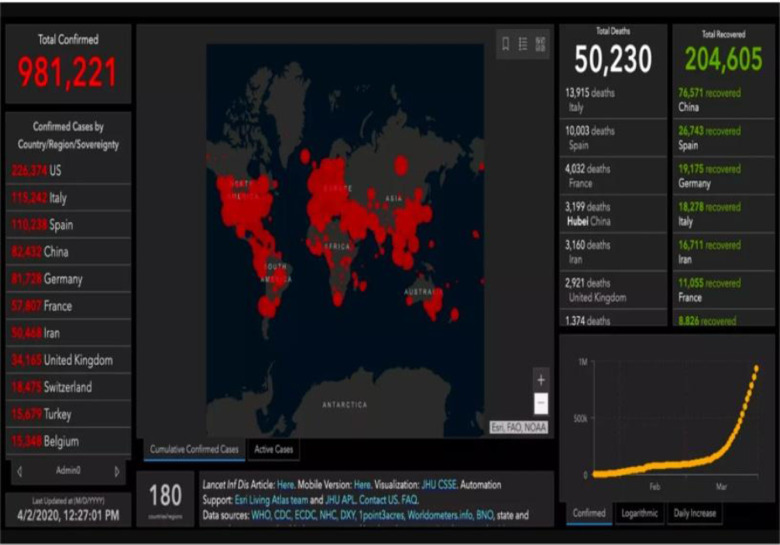
According to a database from Johns Hopkins University, more than 185 countries reported COVID-19 cases as of April 16. Figure 1 exhibits COVID-19 statistics.
Figure 1.
COVID-19 statistics of countries worldwide.
This analytical study presents a comprehensive, up-to-date literature survey highlighting important applications, community resources, trends, and data science research challenges in COVID-19. However, in such a dynamic, rapidly evolving epidemic, cannot aim for exhaustiveness. Nonetheless, it is hoped that the current analysis will provide a solid introduction in the field for all researchers interested in this area.
Further research is composed of several sections describing a brief literature survey, a short note on the role of deep learning in the epidemic, the impact of the epidemic, discussion, and conclusion.
DATA SCIENCE AND COVID-19
Data science is an interdisciplinary discipline that collects information and knowledge from many structural and unstructured sources using computational techniques, procedures, algorithms, and systems. In the article by van der Schaar and Alaa,5 five major healthcare challenges are identified where such technologies could help to address in the fight against COVID-19: (i) managing strong healthcare resources; (ii) remote patient treatment; (iii) well-informed policies; (iv) ability to handle uncertainty; and (v) acceptable clinical trials. Building on this, we start by summarizing some of the computer vision-based research that data scientists may contribute.
COMPUTER VISION-BASED COVID-19 DETECTION USING CT AND X-RAY IMAGES
Various studies employed MRI, CT scans, and X-Ray images for precise COVID-19 infection detection, a few detailed below.
Several hyper-endemic regions/countries could not produce a proper RT-PCR check with hundreds of thousands of suspicious cases. An effort to identify COVID-19 from CT images to resolve the lack of reagents is a good effort since well-trained machines could diagnose positive infection precisely and quickly from a huge collection.12,13 Shi et al.6 presented a fusion model consisted of iCOVIDX-Net + CNN for COVID 19 detection and F1-scores 0.91 reported on Chest X-ray images. Figure 2 exhibits a generalized training model for COVID-19 detection from X-ray images.
Figure 2.
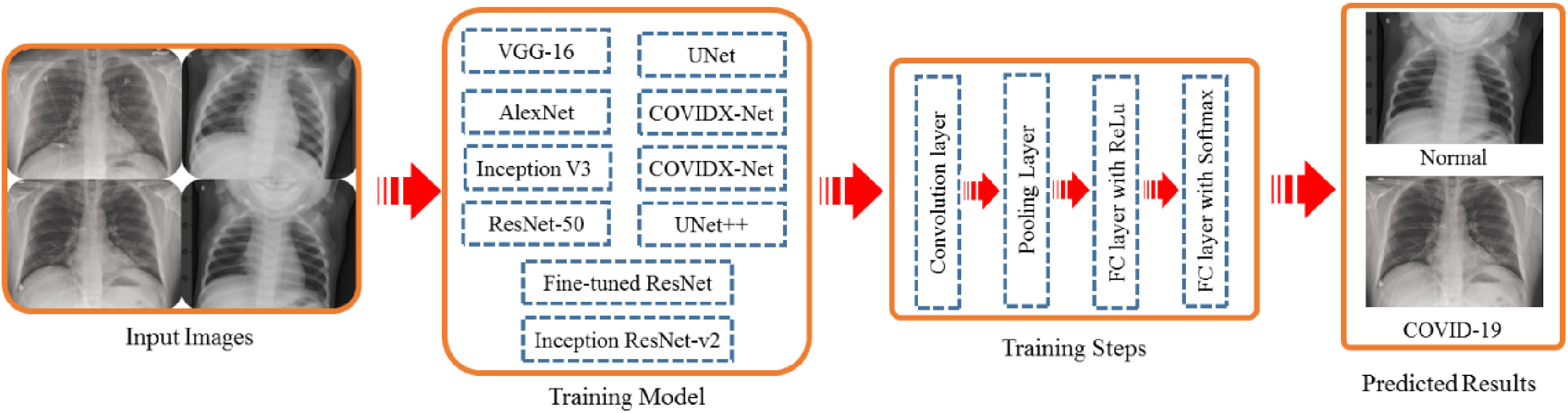
Training models fusion to detect COVID-19.
A fast and accurate COVID-19 diagnostic system using neural networks fusion methodology was proposed by Ardakani et al.7 They collected 1020 CT slices among the 108 laboratory-proven COVID-19 (COVID-19 Group) cases and 86 cases in the non-COVID-19 community of atypical and viral pneumonia. Ten esteemed neural network models fusion employed for COVID-19 infection detection. ResNet-101 and Xception outperformed all others.
Salman et al.8 experimented with chest X-ray images collected from GitHub, Kaggle, and Open-i repository. Six measures were adopted to analyze the proposed CNN model that detected 100% COVID-19 positive infection. Table 1 presents a comparisons of current state of art techniques for COVID19 detection using benchmark datasets along with results.
TABLE 1. COVID-19 detection: Current state of the art analysis and comparisons.
| References | Methodology | Data Type | Results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al.4 | Features model (C model), (R model), and (CR model). | CT scans | sensitivity (0.961) specificity (0.957) accuracy (0.959) AUC* 0.986 (0.966∼1.000) |
|
| Ardakani et al.7 | AlexNet, VGG-16, VGG-19, SqueezeNet, GoogleNet, MobileNet-V2, ResNet-18, ResNet-50, ResNet-101, and Xception |
CT scans | AUC (0.994) sensitivity (100); specificity, (99.02) accuracy (99.51%). |
|
| Salman et al.8 | Trained CNN to detect COVID-10 | Chest X-rays | sensitivity (100) specificity (100) accuracy (100), PPV (100) NPV (100) |
|
| Ozturk et al.10 | DarkNet model and YOLO | Chest X-rays | sensitivity (85.35) specificity (92.18) accuracy (87.02) precision (89.96) F1-score (97.37) |
|
| Butt et al.11 | 3D CNN, ResNet, image preprocessing method based on HU Value, Noisy Bayesian Function | CT scans | AUC 0.996 (95%CI: 0.989–1.00) sensitivity (98.2) specificity (92.2). |
|
| Toğaçar et al.14 | Features were extracted using CNN model (MobileNetV2, SqueezeNet). Finally, for features selection, Social Mimic optimization is employed. | X-ray images | Accuracy (99.27) | |
| Singh et al.16 | A fusion of CNN, ANN, and ANFIS models to classify infected patients from COVID-19 |
Chest CT images | Accuracy (1.9789) F-measure (2.0928) sensitivity (1.8262), specificity (1.6827) Kappa statistics (1.9276) |
|
| Wu et al.17 | Multi-view deep learning fusion model | CT images | AUC (0.732) accuracy (0.700) sensitivity (0.730) specificity (0.615) in validation set. For test set AUC (0.819) accuracy (0.760) sensitivity (0.811) specificity (0.615) |
|
| Ucar and Korkmaz18 | Deep Bayes-SqueezeNet based rapid diagnostic system | Chest X-ray images | COR (98.26) COM (98.26) accuracy (98.26) specificity (99.13) MCC (97.39) F1-score (98.25) |
|
| Hasan et al.19 | Q-Deformed Entropy Feature Extraction (QDE), convolutional neural network (CNN) feature extractor and LSTM Neural Network Classifier. | CT Images | Accuracy (99.68) TP COVID-19 (100) TP Healthy (100) TP Pneumonia (98.90) |
|
| Loey et al.20 | Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) and Convolutional Neural Networks (AlexNet, Googlenet, Resnet18) | Chest X-ray images | Googlenet 4 classes Test accuracy (80.56) F1-score (82.32) Recall (80.56) Precision (84.17) |
|
*AUC (Area Under Curve)Common benchmarking dataset.
Song et al.9 proposed deep learning-based lung computerized tomography (CT) identification system to identify the patients with Coronavirus disease. It could highlight the radiographic features of unusual pneumonia, particularly the GGO from gamma-ray imaging. For evaluation, the authors acquired CT images of eighty-eight COVID-19 septic patients. The data contained only crosswise images of the lung, imported to a deep learning-centered CT analysis system. By regulating hyper-constraints conferring to the corroboration set, authors attained an AUC of 0.91 in the image ratio and AUC of 0.95 in the inhabitant ratio.
Ozturk et al.10 introduced a new paradigm for automatically detecting COVID-19 for chest X-ray images (COVID versus no-founds) classification. Their model produced 98.08% classification precision for binary classes and 87.02% for multi-class case classes. The DarkNet is used as a classifier for the real-time target tracking method that only searched one time (YOLO). They also added 17 convolutionary layers and separate filters for each layer.
Toğaçar et al.14 restructured data classes with a preprocessing technique called the Fuzzy Color technology and stacked the images structured with the initial images. The next move was to train the stacked dataset using deep learning models (MobileNet V2, SqueezeNet) and use the social imitation optimization method to process the feature sets created by such a model. Efficient features were then combined with and classified using SVM. Chen et al.16 developed an ideal model by evaluating three models: the model of clinical features (Model C), (ii) radiological simultaneous features (Model R), (iii) multivariate analytical logistic regression combination model of clinic-radiological semantic features (CR model).
In the article by Ucar and Korkmaz,18 current experiments were overridden by an AI-based system. SqueezeNet is designed for diagnosing COVID-19 with a Bayesian optimization additive for its light network architecture. The proposed network worked better than current network designs and achieved a stronger diagnostic reliable COVID-19 with its fine balanced hyperparameters and expanded data collection.
Hasan et al.19 preprocessed CT images to minimize the impact of differences in intensity between CT scans. Histogram thresholding is employed to isolate CT lung scan history. Each CT lung scan undergoes a deep learning feature extraction and a Q-deformed entropy algorithm. A long-term memory (LSTM) neural network classifier classified the obtained characteristics. Loey et al.20 came out with GAN deep transfer learning in chest X-ray images to identify a coronavirus. The key motivation of this scientific analysis is the lack of COVID-19 data sets, especially in X-ray chest images. The key idea is to gather all available images for COVID-19 before the study is published and produce more images utilizing the GAN network to identify this virus with the highest precision available.
Wang et al.15 proposed a human–machine concerted policy, which was influenced to produce COVID-Net, where a human-focused ethical network strategy was pooled with machine-driven policy assessment to yield a network design that could be personalized for the recognition of COVID-19 patient identification from Chest radiograph (CXR) images. Algorithm influences procreative amalgamation as the machine-driven policy assessment approach built on complex chemistry between an initiator–examiner pair that toil in tandem to store sniffed data and train (method) to produce a deep neural network system that best satisfies the policy necessities.
Measuring patient well-being and forecasting imminent outcomes is a significant problem in precarious care research. With the topical developments and realization of machine learning and deep learning, many academics have embraced prototypes for medical forecasting to categorize specific diseases based on benchmarked datasets.21, 22
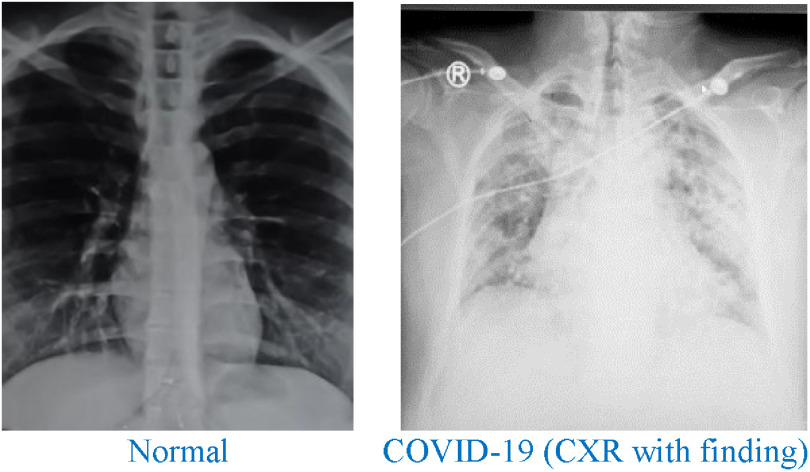
It is validated that deep learning models reliably outdo, particularly when an enormous sum of raw experimental time-series information is used as feedback features to the forecast models, as exhibited in Figure 3.23,24
Figure 3.
Sample chest X-ray (obtained with the patient's consent).
COVID-19 Datasets
A wide variety of open access Kaggle COVID-19 datasets are available for experiments and comparisons detailed below.
Covid-19 X rays Kaggle (2020), 10.34740/KAGGLE/DSV/1019469
Available https://www.kaggle.com/dsv/1019469.
coronavirus report Kaggle (2020)
https://www.kaggle.com/imdevskp/corona-virus-report.
Normal COVID-19 (CXR with finding)
CONCLUSION
Data scientists have been involved in predicting possible issues in the growth of COVID-19. Accordingly, this article has presented a recent overview and ongoing developments and COVID-19 detection trends using deep learning methodologies with CT and X-ray images. This article has also identified specific data science use cases that have the ability to assist in the pandemic by using machine learning techniques for data analysis/prediction. Present chest X-ray findings that have been identified as part of this comprehensive analysis, and most common problems are explored, highlighted. Finally, it would be beneficial for the data scientist to work harder for early disease prediction to avoid the spread of COVID-19.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the Research Project [Diagnosis of COVID-19 through Imaging Modalities using Deep Learning]; Prince Sultan University; Saudi Arabia [COVID19-CCIS-2020{54}].
Biography
Contact Amjad Rehman (Corresponding author) at drrehman70@gmail.com.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the Research Project [Diagnosis of COVID-19 through Imaging Modalities using Deep Learning]; Prince Sultan University; Saudi Arabia [COVID19-CCIS-2020{54}].
REFERENCES
- 1.(WHO), W. H. O. Accessed: 18/04/2020. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak situation. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019
- 2.Worldometer. Accessed: 10/05/2021. COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic. [Online]. Available: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/?
- 3.Business Insider. Accessed: 18/04/2020. Coronavirus-cases-maps-us-world-spread-symptoms-death-rate-2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.businessinsider.com/coronavirus-cases-maps-us-world-spread-symptoms-death-rate-2020-1#where-has-the-coronavirus-spread-1
- 4.Chen X., et al. , “A diagnostic model for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) based on radiological semantic and clinical features: A multi-center study,” Eur. Radiol., vol. 1, pp. 4893–4902, 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.van der Schaar M. and Alaa A., “How artificial intelligence and machine learning can help healthcare systems respond to COVID-19,” 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Shi F., et al. , “Large-scale screening of covid-19 from community-acquired pneumonia using infection size-aware classification,” arXiv:2003.09860, 2020. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 7.Ardakani A. A., Kanafi A. R., Acharya U. R., Khadem N., and Mohammadi A., “Application of deep learning technique to manage COVID-19 in routine clinical practice using CT images: Results of 10 convolutional neural networks,” Comput. Biol. Med., vol. 121, 2020, Art. no. 103795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Salman F. M., Abu-naser S. S., Alajrami E., Abu-Nasser B. S., and Alashqar B. A., “COVID-19 detection using artificial intelligence,” Int. J. Acad. Eng. Res., vol. 4, pp. 18–25, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Song Y., et al. , “Deep learning enables accurate diagnosis of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) with CT images,” medRxiv, 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 10.Ozturk T., Talo M., Yildirim E. A., Baloglu U. B., Yildirim O., and Acharya U. R., “Automated detection of COVID-19 cases using deep neural networks with X-ray images,” Comput. Biol. Med., vol. 121, 2020, Art. no. 103792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Butt C., Gill J., Chun D., and Babu B. A., “Deep learning system to screen coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia,” Appl. Intell., vol. 1, pp. 1–7, 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mughal B., Muhammad N., Sharif M., Rehman A., and Saba T., “Removal of pectoral muscle based on topographic map and shape-shifting silhouette,” BMC Cancer, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 1–14, 2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Iqbal S., Khan M. U. G., Saba T., and Rehman A., “Computer assisted brain tumor type discrimination using magnetic resonance imaging features,” Biomed. Eng. Lett., vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 5–28, 2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Toğaçar M., Ergen B., and Cömert Z., “COVID-19 detection using deep learning models to exploit social mimic optimization and structured chest X-ray images using fuzzy color and stacking approaches,” Comput. Biol. Med., vol. 121, 2020, Art. no. 103805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wang L. and Wong A., “COVID-Net: A tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 cases from chest X-ray images,” arXiv:2003.09871, 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Singh D., Kumar V., and Kaur M., “Classification of COVID-19 patients from chest CT images using multi-objective differential evolution-based convolutional neural networks,” Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis., pp. 1–11, 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 17.Wu X., et al. , “Deep learning-based multi-view fusion model for screening 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia: A multicentre study,” Eur. J. Radiol., 2020, Art. no. 109041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 18.Ucar F. and Korkmaz D., “COVIDiagnosis-Net: Deep Bayes-squeezenet based diagnostic of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from X-ray images,” Med. Hypotheses, 2020, Art. no. 109761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 19.Hasan A. M., Al-Jawad M. M., Jalab H. A., Shaiba H., Ibrahim R. W., and Al-Shamasneh A. A. R., “Classification of COVID-19 coronavirus pneumonia healthy lungs CT scans using Q-deformed entropy deep learning features,” Entropy, vol. 22, 2020, Art. no. 517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Loey M., Smarandache F., and M Khalifa N. E., “Within the lack of chest COVID-19 X-ray dataset: A novel detection model based on GAN and deep transfer learning,” Symmetry, vol. 12, 2020, Art. no. 651. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Saba T., Haseeb K., Ahmed I., and Rehman A., “Secure and energy-efficient framework using Internet of Medical Things for e-healthcare,” J. Infection Public Health, vol. 13, no. 10, pp. 1567–1575, 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Saba T., “Recent advancement in cancer detection using machine learning: Systematic survey of decades, comparisons and challenges,” J. Infection Public Health, vol. 13, no. 9, pp. 1274–1289, 2020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Saba T., “Automated lung nodule detection and classification based on multiple classifiers voting,” Microsc. Res. Techn., vol. 82, no. 9, pp. 1601–1609, 2019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Husham A., Alkawaz M. H., Saba T., Rehman A., and Alghamdi J. S., “Automated nuclei segmentation of malignant using level sets,” Microsc. Res. Techn., vol. 79, no. 10, pp. 993–997, 2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]