Abstract
The inactivating effect of ozone (O3)-based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) (O3/H2O2, O3/UV, and O3/UV/H2O2 systems) on antimicrobial-resistant bacteria (AMRB) and antimicrobial-susceptible bacteria (AMSB) in sewage treatment plant (STP) wastewater was investigated. The AMRB were grouped into six classes: carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE), extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacteriaceae (ESBL-E), multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter (MDRA), multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MDRP), methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE); these classes constituted the World Health Organization (WHO) global priority list of AMRB. The results indicate that O3-based advanced wastewater treatment inactivated all AMRB and AMSB (>99.9%) after 10 min of treatment, and significant differences (p < 0.5) were not observed in the disinfection of AMRB and AMSB by each treatment. Altered taxonomic diversity of micro-organisms based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing via O3/UV and O3/UV/H2O2 treatment showed that advanced wastewater treatments not only inactivated AMRB but also removed antimicrobial resistance genes (AMRGs) in the wastewater. Consequently, this study recommends the use of advanced wastewater treatments for treating the STP effluent, reducing environmental pollution, and alleviating the potential hazard to human health caused by AMRB, AMSB, and infectious diseases. Overall, this study provides a new method for assessing environmental risks associated with the spread of AMRB and AMSB in aquatic environments, while keeping the water environment safe and maintaining human health.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance (AMR), inactivation, ozonation, advanced oxidation process (AOPs), sewage treatment plant (STP), river environment
1. Introduction
The emergence and spread of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria (AMRB) has become a serious situation in clinical sites worldwide [1,2,3,4]. AMRB are widely detected in the aquatic environment [5,6,7,8,9]. The spread of AMRB not only makes it difficult to treat infectious diseases but also increases the risk of epidemics and aggravation. Taking effective measures to prevent the prevalence of AMRB has become urgent [10,11,12]. The connection between humans and the environment continues to complicate. With AMRB flowing into the aquatic environment, both direct infections associated with drinking and swimming and indirect infections through animals, agriculture, and fisheries are of concern [9,13,14,15,16,17]. The World Health Organization (WHO) launched a Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) based on the One Health approach. The goal of the plan is to provide optimal health for people, animals (domestic and wild), and the environment by considering interactions between all three systems [18,19,20]. This plan also requires every country to institute its own national action plan by performing extensive research on the occurrence, environmental fate, and risk assessment of AMRB flowing into water bodies [21]. Japan has implemented the Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance to prevent their prevalence [22,23,24].
Previous studies have reported that the effluent from sewage treatment plants (STPs) is one of the main sources of river pollution in urban areas, where the population is concentrated and the sewerage coverage is highly developed [25,26,27,28]. Some AMRB flowed into the river environment without being sufficiently inactivated by conventional disinfection processes, such as chlorine [27,29], which is widely used as a disinfection treatment in STPs worldwide [5,30]. In addition, various wastewater antimicrobials were also difficult to completely remove by the conventional sewage treatment process and entered the river environment. These residual antimicrobials have toxic effects on the aquatic ecosystem and become potential factors that promote the formation of new AMRB in the aquatic environment [31,32]. Therefore, evaluating the effectiveness of the advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) is becoming increasingly important for reducing the pollution load into rivers and creating environmental risks [33,34,35].
Several recent studies have evaluated the inactivation of AMRB in water using various disinfection methods, including the use of Fenton [36,37], ultrasonication [38], electrolysis [39], TiO2 [40], persulfate [41], graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) [42], UV/chlorine [43], and ozone (O3) [37,44]. Among these, O3 has a high oxidizing power (oxidation potential 2.1 V) [45] and is effective for decolorization, deodorization, sterilization, etc. [46]. It has been shown to be effective not only for inactivating pathogenic microorganisms [47,48] but also for removing micropollutants such as pharmaceutical residues and endocrine disruptors in wastewater [49,50]. In addition, by using O3 and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) together (O3/H2O2) or O3 and ultraviolet rays (O3/UV), hydroxyl radical (OH) [51] exhibits a stronger oxidizing power (oxidation potential 2.8 V) than that obtained using O3 alone; thus, it is possible to improve the efficiency of O3 treatment [52,53,54]. Nevertheless, research on the inactivation of AMRB and the development of countermeasures to reduce their impact remains limited [55,56]. Therefore, it seems necessary to investigate the inactivation of AMRB in wastewater in detail for a practical and comprehensive understanding of the environmental risks of AMRB in rivers. Previous research reported the inactivation profiles of AMRB obtained by treatment with O3 alone using actual wastewater from sewage treatment plants [57,58]. Given this situation, the current study evaluated the effectiveness of O3/H2O2, O3/UV, and O3/UV/H2O2 systems for inactivation of a group of AMRB and antimicrobial-susceptible bacteria (AMSB) in STP effluent to better understand the environmental risk management of AMRB in the water environment. Evaluating the inactivation of AMRB in real wastewater samples via O3-based AOPs will provide useful insights into the effectiveness of the inactivating effect of wastewater treatment in overcoming the challenge of water contamination and pollution by AMR.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microbes and Reagents
Six classes of AMRB were given global priority by the WHO [21,59] and are reported to be in the clinical range [3,60]—namely CRE, extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacteriaceae (ESBL-E), multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter (MDRA), multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MDRP), methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) were investigated.
The AMRB prevalence was analysed by screening microbes grown on different chromogenic agar methods: chromID CARBA (bioMérieux S.A., Marcy-l’Étoile, France) for detection of CRE, chromID ESBL for ESBL-E, chromID MRSA for MRSA, chromID VRE New for VRE, CHROMagar MDRA for MDRA, and CHROMagar MDRP for MDRP (Kanto Chemical Co., Inc., Tokyo, Japan). Similarly, AMSB was analysed by screening microbes grown on different chromogenic agar methods without antimicrobial agents: CHROMagar Acinetobacter for Acinetobacter, chromID S. aureus Elite for Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), chromID CPS Elite for Enterococcus, PASA medium (Nippon Becton Dickinson Company, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) for Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa), and XM-G agar (Nissui Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) for Escherichia coli (E. coli). Ultra-pure Milli-Q water (18.2 MΩ·cm; MilliporeSigma, Watford, UK) with pH adjusted to 7.0 and 10 M sterilized phosphate buffer were used for dilution. Analytical grade hydrogen peroxide (30%) and sodium thiosulfate (>98%) were purchased from FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation (Osaka, Japan).
2.2. Sampling
Samples were collected from an STP located in an urban area of Japan, as described previously [61]. The STP treats municipal sewage generated by a population of 420,000 individuals. The STP influent was first treated with conventional activated sludge and step anoxic/oxic treatment and discharged as the STP secondary effluent. The STP secondary effluent was treated with chlorine (contact with 0.9 mg NaClO/L for 15 min) for disinfection and discharged as the STP effluent. Three water types were collected from the STP: STP influent, STP secondary effluent, and STP effluent. Samples were collected in December 2018 on rain-free days when the recorded rainfall was >1 mm for the preceding two days [62]. The annual average chemical oxygen demand was 91, 19, and 17 mg/L for the STP influent, STP secondary effluent after biological treatment, and STP effluent, respectively. A stainless-steel pail sampler was used to collect wastewater samples, which were then placed in separate sterilized glass bottles. Sodium thiosulfate (0.5 g/L) was immediately added to each bottle for quenching residual chlorine [63,64]. Composite samplers could not be installed to sample the STP wastewater. Therefore, identical manual sampling at a fixed sampling frequency was used. All samples were immediately transported to the laboratory in a cooler box (within 2 h), stored in dark at 4 °C, and processed within 12 h.
2.3. Analytical Procedures
The number of each type of AMRB and AMSB in the samples was estimated following the protocols given by the manufacturers of growth mediums using previously described methods [65,66,67,68]. From every water sample, 1 mL was taken out and spread on separate agar plates and incubated at 37 ± 1 °C for 24 h in the dark. Then, the bacterial species were differentiated by the colour and morphology of the colonies [69,70,71]. The colonies were counted and the number of bacteria formed was expressed as colony-forming units per mL (CFU/mL). If the mean CFU was a whole number, the values were expressed as the nearest integer after applying the rounding off rule and counted as N.D. (not detected) if the values were <1. The relative reproducibility values (n = 3) for the AMRB (CRE, ESBL, MDRA, MDRP, MRSA, and VRE) were 15%, 27%, 18%, 12%, 20%, and 13%, respectively; those of AMSB (Acinetobacter, Enterococcus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus) were 9%, 13%, 15%, 7%, and 18%, respectively.
2.4. Inactivation of AMRB and AMSB by O3-Based AOPs
Inactivation of AMRB and AMSB by O3-based AOPs was investigated in a semi-batch reactor with an interior diameter of 10 cm and a height of 30 cm (effective volume of 2.2 L; Supplementary Materials Figure S1) [50]. The temperature of the test water was maintained at 20 °C through an external jacket by a thermostat water circulator (CTR-320, AGC Techno Glass Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). The test water was agitated continuously at 300 rpm with a magnetic stirrer (SRS710DA, Advantec Toyo Kaisha, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Preliminary experiments indicated that a mixture of different water samples is appropriate for the performance of model laboratory experiments to determine the feasibility of the present method. STP secondary effluent and STP influent were mixed at a ratio of 9:1 (v/v) as a model sample (STP wastewater) for evaluating the inactivation of AMRB by O3-based AOPs, in accordance with a previous report [29,57,61] and the results in Section 3.1.
O3 was generated by an O3 generator (ED-OG-R6, Ecodesign Inc., Saitama, Japan) and injected into the reactor at a flow rate of 0.3 L/min with a concentration of 6.8 mg/L, which corresponded to a feed rate of 1.2 mg/L/min. This feed rate is similar to that used in a previous research on the effectiveness of O3 treatment on a wide range of microbes [63,72,73] and micropollutants [74,75]. This feed rate was similar to that used in STPs (7 ± 7 mg/L for 15 ± 5 min) [76]. UV irradiation was supplied by a 9 W low-pressure mercury lamp (TCGU60-250ZP, Miyakawa Corp., Tokyo, Japan) with a peak wavelength of 254 nm and an intensity of 2.8 mW/cm2, as reported in previous research [77,78]. The UV lamp was introduced into the reactor and kept separate from the water by using a quartz jacket. The initial H2O2 concentration was set at 5 mg/L (as effective concentration), as suggested in previous research [79,80].
The experiments were started by sparging O3 gas continuously into the filled reactor. A portion of the reactor solution (20 mL) was sampled at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, and 10 min after the experiment started. These durations were determined by using the average contact times in Japanese STPs, which implement ozonation before discharging the effluent into rivers [76], and by previously reported values [74,81]. The O3 consumption was calculated from the balance in gas and liquid phases during the experiment [82,83]. Sodium thiosulfate was immediately added to each sample at a concentration of 1.0 g/L to mitigate the effects of any residual O3 and H2O2 and to quench reactive oxygen species such as hydroxyl radicals [63,64]. The samples were then stored at 4 °C in dark and processed within 12 h. Bacterial numbers and species survived from the treatment were analysed with differences in colony colour and morphology, as described in Section 2.3.
2.5. Bacterial Community Structure Analysis
Genomic DNA was extracted from the water samples using an Extrap Soil DNA Kit Plus v.2 (Nippon Steel Eco-Tech Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). The concentrations and purifications of DNA were determined by a Qubit® 3.0 fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) using a Qubit® dsDNA BR Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) [84]. The V1–V2 region of the 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene of bacteria was used to characterise the bacterial communities [85,86]. For PCR amplification, the universal bacterial primers 27F/338R [87,88] were used. PCR was carried out in a T100 Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA) in accordance with previous studies [89,90]. The PCR cycle consisted of a 3 min denaturation cycle at 95 °C, which was followed by 25 cycles at 95 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 30 s, 72 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 5 min. Electrophoresis was conducted in 1.5% agarose gel using a Mupid-2plus System (Advance Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) to examine the quality of PCR products [90], and the genes were sequenced on a MiSeq platform (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and a previous report [57].
Sequence data were pre-processed and analysed in Flora Genesis software (Repertoire Genesis Inc., Osaka, Japan). Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were picked by the open-reference method at a 97% identity level and annotated from the prefiltered Greengenes Database v.13.8 by the UCLUST algorithm [91,92]. Representative sequences of each OTU were extracted, and taxonomy was assigned by the Ribosomal Database Project classifier at a confidence threshold of 0.80 [93,94].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The data of the tested traits were analysed by Microsoft Excel software. A paired t-test was performed to evaluate the difference in inactivation rates between AMRB and AMSB at p < 0.05 as statistical significance.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Occurrence of AMRB and AMSB in the STP Wastewater
Table 1 shows the occurrence of AMRB and AMSB in STP wastewater. All AMRB targeted in this study were detectable in the STP influent. The detection concentrations of AMRB ranged from 58 to 814 CFU/mL in the STP influent, N.D. to 201 CFU/mL in the STP secondary effluent, and N.D. to 34 CFU/mL in the STP effluent. These results show that AMRB were widely present in the wastewater, and they were almost removed in the wastewater treatment process of the STP; however, some of them (ESBL-E, MRSA, Enterococcus, and Staphylococcus aureus) were discharged into the river as effluent after chlorine disinfection treatment. These results were similar to those reported previously [71]. On the other hand, the number of AMSB ranged from 96 to 30,000 CFU/mL, N.D. to 836 CFU/mL, and N.D. to 219 CFU/mL for the STP influent, STP secondary effluent, and STP effluent, respectively. Inactivation of MRSA and S. aureus by chlorine disinfection was gradual, which may be attributed to stronger cell walls than those of other bacteria, which render them resistant to multiple environmental conditions [95,96].
Table 1.
Occurrence of AMRB and AMSB in sewage treatment plant (STP) influent, STP secondary effluent, and STP effluent.
| Bacteria | Bacteria Counts (CFU/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| STP Influent | STP Secondary Effluent |
STP Effluent | |
| CRE | 317 | 201 | 1 |
| ESBL-E | 814 | 182 | 34 |
| MDRA | 323 | 19 | 2 |
| MDRP | 98 | N.D. | N.D. |
| MRSA | 58 | 7 | 6 |
| VRE | 200 | 3 | N.D. |
| Acinetobacter | 391 | 38 | 8 |
| Enterococcus | 2528 | 836 | 219 |
| Escherichia coli | 30,000 | 115 | N.D. |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 117 | N.D. | N.D. |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 96 | 8 | 17 |
CRE: carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae, ESBL-E: extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae, MDRA: multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter, MDRP: multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, MRSA: methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, VRE: vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus, and N.D.: Not detected).
3.2. O3-Based AOP Inactivation of AMRB and AMSB in STP Wastewater
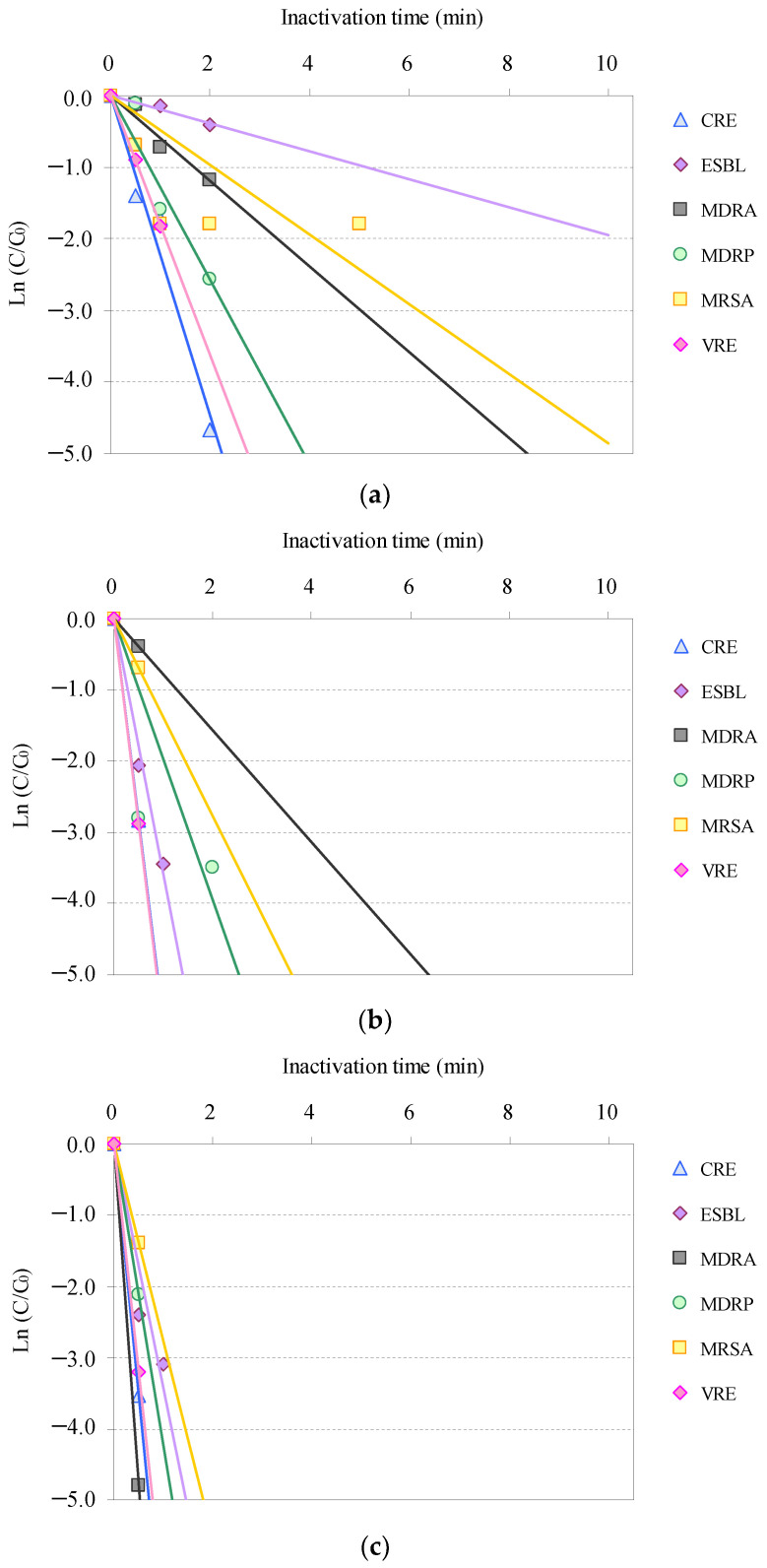
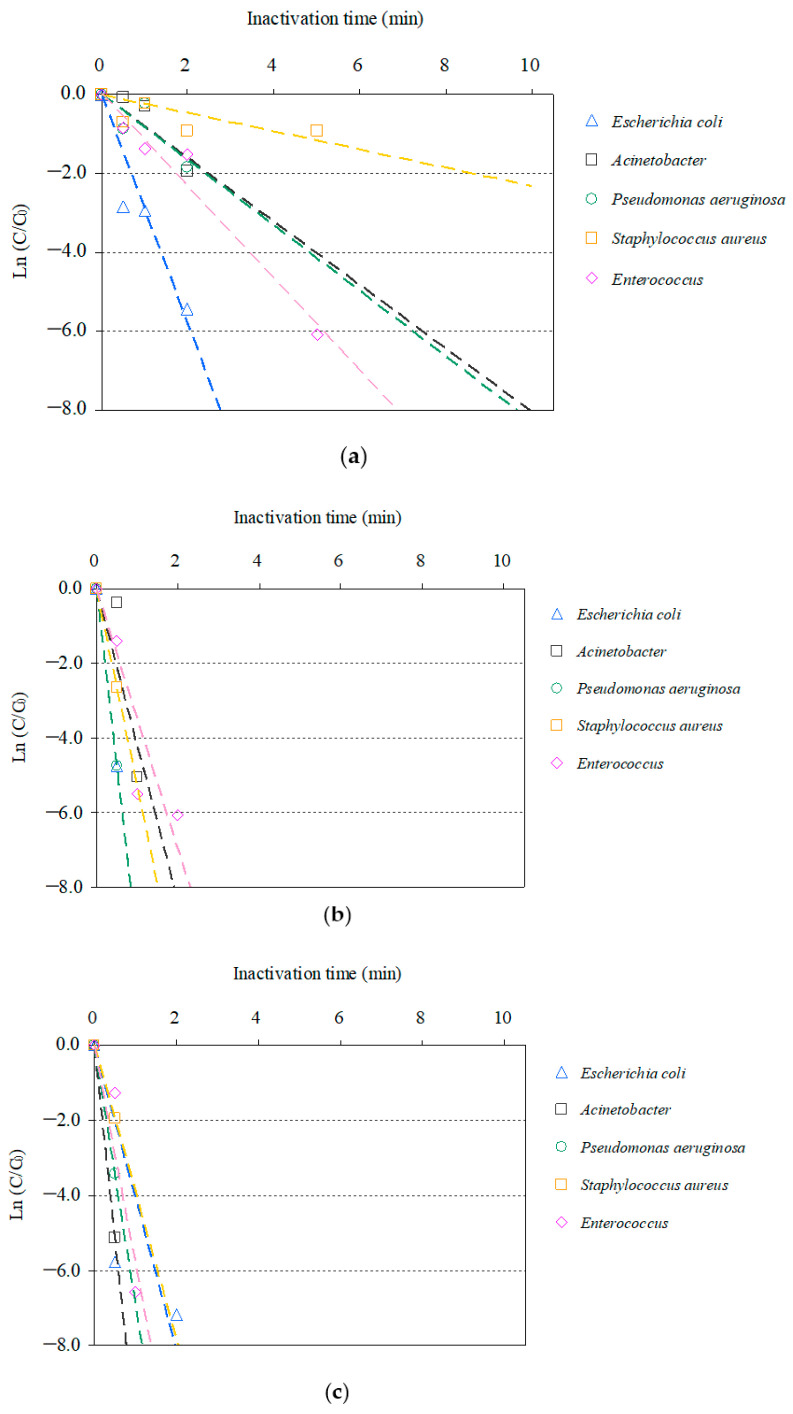
Time-dependent inactivation profiles associated with the inactivation of the AMRB and AMSB in the STP wastewater via O3/H2O2, O3/UV, and O3/UV/H2O2 treatments are summarized in Figure 1 and Figure 2. Although the inactivation time differed among bacteria, all targeted AMRB and AMSB contained in the STP wastewater were inactivated by O3-based AOPs.
Figure 1.
Relative residual antimicrobial-resistant bacteria (AMRB) under O3-based AOP treatment (C0: initial bacterial counts; C: bacterial counts after treatment): (a) O3/H2O2, (b) O3/UV, (c) O3/UV/H2O2. (CRE: carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae, ESBL-E: extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae, MDRA: multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter, MDRP: multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, MRSA: methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and VRE: vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus).
Figure 2.
Relative residual antimicrobial-susceptible bacteria (AMSB) under O3-based AOPs treatment (C0: initial bacterial counts, C: bacterial counts after treatment): (a) O3/H2O2, (b) O3/UV, (c) O3/UV/H2O2.
Inactivation of the AMRB and AMSB by O3-based AOPs followed pseudo-first-order kinetics, as previously reported for O3 disinfection of multiple bacteria and viruses [47,48,79,97]. CRE, MDRP, and VRE were rapidly inactivated >99% after 2 min; and ESBL-E and MDRA were inactivated >99% after 5 min in O3/H2O2 treatment. Meanwhile, MRSA was inactivated more gradually than other AMRB, with >99% inactivation after 10 min.
Similar profiles of inactivation for AMSB were observed: E. coli and P. aeruginosa were inactivated >99% after 2 min; and Acinetobacter and Enterococcus were inactivated >99% after 5–10 min. S. aureus was slowly inactivated with >99% inactivation after 10 min. In addition, no significant difference (p < 0.05) was observed in the effects of chlorination on AMRB and AMSB. These results are similar to those described in the previous section, supporting the effectiveness of the inactivation of AMRB in wastewater via ozonation.
Combined use of UV and O3 remarkably improved inactivation efficiencies. All targeted AMRB and AMSB were rapidly inactivated by O3/UV and O3/UV/H2O2 treatment. Within 1 min, >99% inactivation was completed for CRE, ESBL-E, MDRA, MDRP, MRSA, and VRE. In addition, synergistic improvement in inactivation was observed in O3/UV/H2O2 treatment. The inactivation rates after 0.5 min of treatment with O3/UV and O3/UV/H2O2 were 94% and 97% for CRE, 87% and 91% for ESBL-E, 32% and 99% for MDRA, 94% and 88% for MDRP, 50% and 75% for MRSA, and 94% and 96% for VRE, respectively. AMSB was also rapidly inactivated during both the treatments, and >99% inactivation was completed within 1 min for Acinetobacter, Enterococcus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus. The improvement in the inactivation rate by the combined use of UV irradiation was related to the bactericidal activity of UV and the hydroxyl radicals generated as catalysts for O3 [47,79,98,99].
3.3. Distribution of the Inactivation Rate Constants of AMRB and AMSB by O3-Based AOP Treatment
The distribution inactivation rate constants for AMRB and AMSB in O3/H2O2, O3/UV, and O3/UV/H2O2 processes are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2.
Reaction rate constants for each AMRB and AMSB during O3-based AOP treatment for STP wastewater. (* Reported values from the previous research [57].)
| Bacteria | Inactivation Rate (min−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3/H2O2 | O3/UV | O3/UV/H2O2 | O3 * | |
| CRE | 2.239 | 5.668 | 7.054 | 1.978 |
| ESBL-E | 0.196 | 3.586 | 3.431 | 0.539 |
| MDRA | 0.596 | 0.785 | 9.576 | 0.311 |
| MDRP | 1.290 | 1.976 | 4.242 | 0.523 |
| MRSA | 0.368 | 1.386 | 2.773 | 0.274 |
| VRE | 1.817 | 5.748 | 6.398 | 2.508 |
| Acinetobacter | 1.649 | 4.187 | 10.225 | 0.426 |
| Enterococcus | 1.165 | 3.496 | 5.776 | 0.725 |
| Escherichia coli | 2.902 | 9.479 | 4.056 | 2.515 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 1.610 | 9.716 | 6.870 | 0.295 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 0.230 | 5.278 | 3.892 | 0.129 |
The mean reaction rate constants for AMRB and AMSB were 1.1 ± 0.8 and 1.5 ± 1.0 min−1 for O3/H2O2, 3.2 ± 2.2 and 6.4 ± 3.0 min−1 for O3/UV, and 5.6 ± 2.6 and 6.2 ± 2.6 min−1 for O3/UV/H2O2, respectively. Interestingly, no significant differences were observed in the inactivation rates between AMRB and AMSB. Inactivation rate constants were improved by the combined use of UV irradiation with O3; the reaction rate constants of O3/UV and O3/UV/H2O2 treatments were significantly (p < 0.05) enhanced when compared with O3/H2O2 treatment for both AMRB and AMSB. Meanwhile, a statistically significant difference was not observed between the inactivation caused by O3/UV and O3/UV/H2O2 treatments. The estimated half-lives generally ranged from <0.1 to 1 min. The detailed distribution of half-lives for AMRB and AMSB are summarized in Table S1 (Supplementary Materials).
Previous research reported that the inactivation rate constants for AMRB and AMSB in wastewater subjected to O3 treatment ranged from 0.3 to 2.5 min−1 (1.0 ± 1.0 min−1) for AMRB and 0.1 to 2.5 min−1 (0.8 ± 1.0 min−1) for AMSB [57]. By comparing these reported values with those obtained in this study, significant differences (p < 0.05) were observed between O3, O3/UV, and O3/UV/H2O2 treatments, which showed that O3/UV treatment is more effective than conventional O3/H2O2 treatment. These results demonstrate that O3-based AOPs are effective for inactivation of AMRB and AMSB in wastewater. The present findings are generally similar to the results obtained with other bacteria, pathogenic microorganisms [63,100,101], and chemical pollutants [46,49,102], thereby supporting the performance of the O3-based AOP for pollutants in the wastewater.
The present research established the effectiveness of O3-based AOP treatment for the inactivation of AMRB together with AMSB in real wastewater samples. Application of this treatment system to developing regions and countries should be encouraged worldwide for preventing the spread of infectious diseases at the stream stage. Its cost-effectiveness is also important for practical application. The use of this system to prevent the spread of infectious diseases originating from wastewater seems urgent currently. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report to show the behaviour of AMRB and AMSB under O3/H2O2, O3/UV, and O3/UV/H2O2 treatments in real STP wastewater. These findings will contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the environmental risks associated with AMRB in aquatic environments.
3.4. Bacterial Community Structure Analysis
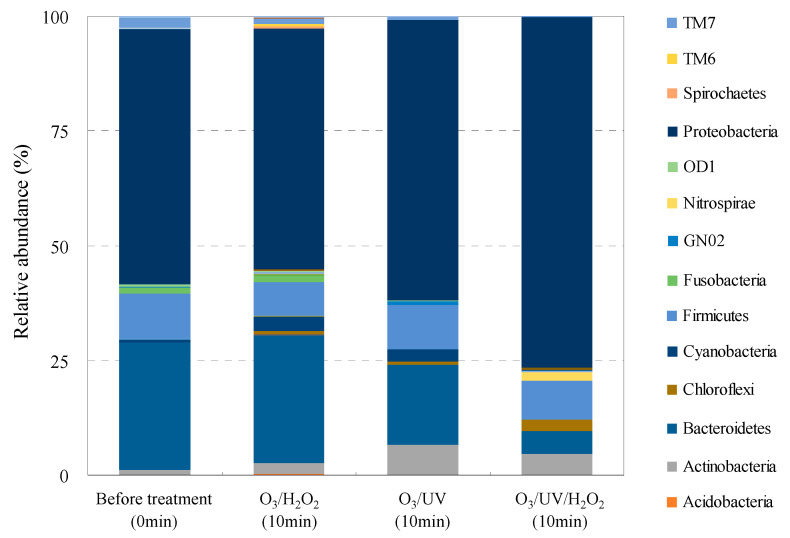
Variations in the bacterial community structure before and after ozonation based on taxonomic affiliation of OTUs are summarized in Figure 3. The bacterial 16S rRNA reads collected from the STP wastewater samples were 142,696 at the start of treatment and 187,671 after O3/H2O2 treatment, 147,834 after O3/UV treatment, and 142,275 after O3/UV/H2O2 treatment (5787 OTUs in total). The STP wastewater samples hosted 40 bacterial phyla, 117 classes, 205 orders, 361 families, and 690 genera.
Figure 3.
Taxonomic diversity of bacterial communities in O3-based AOP-treated wastewater samples.
Interestingly, O3/UV and O3/UV/H2O2 treatment changed the constitution of phyla in the STP effluent. The constitution was Proteobacteria (55%), Bacteroidetes (28%), Firmicutes (10%), TM7 (2%), and Fusobacteria (1%) before O3-based treatment; Proteobacteria (61%), Bacteroidetes (17%), Firmicutes (10%), Actinobacteria (7%), and Cyanobacteria (3%) after O3/UV treatment; and Proteobacteria (76%), Firmicutes (8%), Bacteroidetes (5%), Actinobacteria (5%), and Chlorobi (2%) after O3/UV/H2O2 treatment. Meanwhile, the constitution of phyla was almost similar in O3/H2O2 treatment: Proteobacteria (53%), Bacteroidetes (28%), Firmicutes (7%), Cyanobacteria (3%), and Actinobacteria (2%). The genus Acinetobacter, comprising the major antimicrobial-resistant bacteria, also showed a reduced read rate. By comparing these results with the reports on changes in sewage flora following O3 treatment [57,58], it is observed that the changes in the bacterial community structure composition are almost similar for O3 and O3-based AOP treatment. The overall results suggest the importance of introducing advanced wastewater treatment for removal of AMRB and AMRGs, although some of them are not completely removed [103,104,105]. This seems reasonable considering the existence of multiple microorganisms [103,106,107] and AMRGs [108,109,110,111] in wastewater.
Recent research provides insights into the environmental risk assessment of both AMRB and AMRGs [8,35,112]. The risk of infection by AMRB in water and via the ecosystem is increasing, and further development of AMRB in the presence of residual antimicrobials or AMRGs in water is now progressing [12,113,114,115]. Further, the present study might provide invaluable information to prevent infectious diseases from the aquatic environment, including wastewater. The results improve our understanding of environmental pollution associated with AMRB and AMRGs in aquatic environments. Our findings will contribute to enhance the effectiveness of the advanced wastewater treatment systems not only at STPs but also at medical facilities such as hospitals, for reducing the discharge of AMRB and AMRGs into rivers and keeping aquatic environments safe.
3.5. Efficiency of the Inactivation of AMRB and AMSB Based on O3 Consumption
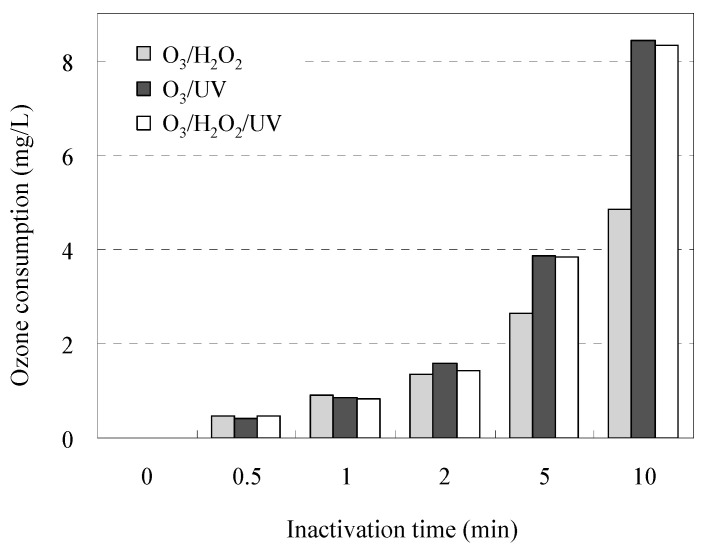
The time-dependent profiles of O3 consumption during inactivation of AMRB and AMSB are shown in Figure 4. The O3/UV and O3/UV/H2O2 treatment consumed up to 1.7-fold O3 (1.2 ± 0.4 times by O3/UV and 1.2 ± 0.4 times by O3/UV/H2O2 as mean) compared with the O3/H2O2 treatment. The difference in the time-dependent profiles associated with the inactivation of AMRB and AMSB is related to O3 consumption by contaminants in wastewater samples during the experiment; these results agree with the distribution of reaction rate constants, as shown in Table 2. These results suggest that a long treatment process is required to achieve sufficient inactivation of a wide range of AMRB species, depending on the concentration of multiple pollutants in the wastewater.
Figure 4.
O3 consumption over time in STP wastewater in each treatment system.
Recent research has shed light on the environmental risk assessment of both AMRB and AMSB [8,35,112,116]. In addition, AMRB carrying antimicrobial-resistance genes (AMRGs) are also present in wastewater and river water and act as potential factors that promote the formation of new AMRB in the aquatic environment through transformations [117,118,119]. The risk of infection by AMRB in water and via the ecosystem and the development of AMRB in the presence of residual antimicrobials or AMRGs in the water environment are now being assessed [113,114,120]. Latest research reported the importance of introducing advanced wastewater treatment systems not only for wastewater at STPs but also for hospital effluents from medical facilities [30,121,122,123]. Meanwhile, it is important to maintain a balance between costs and efficiency by optimizing the operations cost of wastewater treatment along with the management of wastewater treatment plants [82,124,125]. Ozonated-fine bubble (O3-FB) technologies would be useful for implementing efficient and effective treatments based on O3 by improving the efficiency of O3 consumption [126,127,128]. The results should prove valuable in improving our understanding of environmental pollution caused by AMRB and AMRGs in aquatic environments. Our findings will contribute to enhance the effectiveness of the advanced wastewater treatment systems at STPs for reducing the discharge of AMRB and AMRGs into rivers, while keeping aquatic environments safe.
4. Conclusions
The effectiveness of inactivation induced by O3-based AOPs for AMRB and AMSB in STP wastewater was evaluated. The results showed that various AMRB are present in the wastewater and that O3-based AOPs are an effective inactivating treatment for both AMRB and AMSB. Inactivation rate constants were improved by the combined use of UV irradiation with O3. The estimated inactivation rate constants for AMRB and AMSB were 1.1 ± 0.8 and 1.5 ± 1.0 min−1 for O3/H2O2, 3.2 ± 2.2 and 6.4 ± 3.0 min−1 for O3/UV, and 5.6 ± 2.6 and 6.2 ± 2.6 min−1 for O3/H2O2, respectively, with half-lives generally ranging from < 0.1 to 1 min. The difference in the time-dependent profiles of inactivation for AMRB and AMSB was attributed to O3 consumption by contaminants in wastewater during treatment. The taxonomic diversity analysis of micro-organisms based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing showed changes in constitution of phyla after treatment, indicating that O3-based AOPs inactivated not only AMRB but also AMRGs present in the treated water. The overall results present a novel approach for preventing environmental risks associated with the spread of AMRB, AMSB, and infectious diseases originating from aquatic environments and contribute toward safety of water environments and human health. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report to show the effectiveness of O3/H2O2, O3/UV, and O3/UV/H2O2 treatments for inactivation of AMRB and AMSB present in real STP wastewater.
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff of the STPs for providing water samples.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded from https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antibiotics11020210/s1, Table S1: Half-life of each AMRB and AMSB during O3-based AOP for the model STP wastewater, Figure S1: Semi-batch ozone reactor used for experiments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: T.A. and T.H.; investigation: T.A. and T.H.; methodology: T.A., M.U. and T.H.; formal analysis: T.A. and M.U.; writing—original draft: T.A., M.U. and T.H.; writing—review and editing: T.A., M.U. and T.H.; supervision: T.A.; funding acquisition: T.A.; project administration: T.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Lake Biwa–Yodo River Water Quality Preservation Organization (Japan); the River Foundation (Japan); the Kurita Water and Environment Foundation (Japan); the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (16K16218 and 20H02289); the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan (21HA1002); and the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) (JP21fk0108131) in the form of research grants and scholarships.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Bush K., Courvalin P., Dantas G., Davies J., Eisenstein B., Huovinen P., Jacoby G.A., Kishony R., Kreiswirth B.N., Kutter E., et al. Tackling antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011;9:894–896. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Laxminarayan R., Duse A., Wattal C., Zaidi A.K.M., Wertheim H.F.L., Sumpradit N., Vlieghe E., Hara G.L., Gould I.M., Goossens H., et al. Antibiotic resistance-the need for global solutions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013;13:1057–1098. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70318-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mulani M.S., Kamble E.E., Kumkar S.N., Tawre M.S., Pardesi K.R. Emerging strategies to combat eskape pathogens in the era of antimicrobial resistance: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2019;10:539. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Roope L.S.J., Smith R.D., Pouwels K.B., Buchanan J., Abel L., Eibich P., Butler C.C., Tan P.S., Walker A.S., Robotham J.V., et al. The challenge of antimicrobial resistance: What economics can contribute. Science. 2019;364:eaau4679. doi: 10.1126/science.aau4679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rizzo L., Manaia C., Merlin C., Schwartz T., Dagot C., Ploy M.C., Michael I., Fatta-Kassinos D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013;447:345–360. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Berendonk T.U., Manaia C.M., Merlin C., Fatta-Kassinos D., Cytryn E., Walsh F., Burgmann H., Sorum H., Norstrom M., Pons M.N., et al. Tackling antibiotic resistance: The environmental framework. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015;13:310–317. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ben Y., Fu C., Hu M., Liu L., Wong M.H., Zheng C. Human health risk assessment of antibiotic resistance associated with antibiotic residues in the environment: A review. Environ. Res. 2019;169:483–493. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2018.11.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pazda M., Kumirska J., Stepnowski P., Mulkiewicz E. Antibiotic resistance genes identified in wastewater treatment plant systems—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019;697:134023. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yoshizawa N., Usui M., Fukuda A., Asai T., Higuchi H., Okamoto E., Seki K., Takada H., Tamura Y. Manure compost is a potential source of tetracycline-resistant Escherichia coli and tetracycline resistance genes in Japanese farms. Antibiotics. 2020;9:76. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9020076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Walsh T.R. Emerging carbapenemases: A global perspective. Int. J. Antimicrob. Age. 2010;36:S8–S14. doi: 10.1016/S0924-8579(10)70004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.de Lastours V., Chau F., Roy C., Larroque B., Fantin B. Emergence of quinolone resistance in the microbiota of hospitalized patients treated or not with a fluoroquinolone. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014;69:3393–3400. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Katagiri M., Kuroda M., Sekizuka T., Nakada N., Ito Y., Otsuka M., Watanabe M., Kusachi S. Comprehensive genomic survey of antimicrobial-resistance bacteria in the sewage tank replacement with hospital relocation. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021;14:5563–5574. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S336418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Müller A., Stephan R., Nüesch-Inderbinen M. Distribution of virulence factors in esbl-producing Escherichia coli isolated from the environment, livestock, food and humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2016;541:667–672. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Swift B.M.C., Bennett M., Waller K., Dodd C., Murray A., Gomes R.L., Humphreys B., Hobman J.L., Jones M.A., Whitlock S.E., et al. Anthropogenic environmental drivers of antimicrobial resistance in wildlife. Sci. Total Environ. 2019;649:12–20. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Li L.-G., Huang Q., Yin X., Zhang T. Source tracking of antibiotic resistance genes in the environment—Challenges, progress, and prospects. Water Res. 2020;185:116127. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Neher T.P., Ma L., Moorman T.B., Howe A., Soupir M.L. Seasonal variations in export of antibiotic resistance genes and bacteria in runoff from an agricultural watershed in Iowa. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;738:140224. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sun J., Jin L., He T., Wei Z., Liu X., Zhu L., Li X. Antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in agricultural soils from the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;740:140001. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Harbarth S., Balkhy H.H., Goossens H., Jarlier V., Kluytmans J., Laxminarayan R., Saam M., Van Belkum A., Pittet D. Antimicrobial resistance: One world, one fight! Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2015;4:49. doi: 10.1186/s13756-015-0091-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Walsh T.R. A one-health approach to antimicrobial resistance. Nat. Microbiol. 2018;3:854–855. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0208-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Booton R.D., Meeyai A., Alhusein N., Buller H., Feil E., Lambert H., Mongkolsuk S., Pitchforth E., Reyher K.K., Sakcamduang W., et al. One health drivers of antibacterial resistance: Quantifying the relative impacts of human, animal and environmental use and transmission. One Health. 2021;12:100220. doi: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2021.100220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.World Health Organization (WHO) Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2015. pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- 22.The Government of Japan . National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Government of Japan; Tokyo, Japan: 2016. pp. 1–69. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Muraki Y., Yagi T., Tsuji Y., Nishimura N., Tanabe M., Niwa T., Watanabe T., Fujimoto S., Takayama K., Murakami N., et al. Japanese antimicrobial consumption surveillance: First report on oral and parenteral antimicrobial consumption in Japan (2009–2013) J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2016;7:19–23. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2016.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ohkusa Y., Sugawara T., Kawanohara H., Kamei M. Evaluation of the global action plan on antimicrobial resistance in Japan during its first eighteen months. Drug Discov. Ther. 2018;12:182–184. doi: 10.5582/ddt.2018.01011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Auguet O., Pijuan M., Borrego C.M., Rodriguez-Mozaz S., Triadó-Margarit X., Giustina S.V.D., Gutierrez O. Sewers as potential reservoirs of antibiotic resistance. Sci. Total Environ. 2017;605:1047–1054. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Qiao M., Ying G.G., Singer A.C., Zhu Y.G. Review of antibiotic resistance in china and its environment. Environ. Int. 2018;110:160–172. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wang J., Chu L., Wojnárovits L., Takács E. Occurrence and fate of antibiotics, antibiotic resistant genes (args) and antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB) in municipal wastewater treatment plant: An overview. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;744:140997. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Makowska N., Bresa K., Koczura R., Philips A., Nowis K., Mokracka J. Urban wastewater as a conduit for pathogenic gram-positive bacteria and genes encoding resistance to β-lactams and glycopeptides. Sci. Total Environ. 2021;765:144176. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Azuma T., Otomo K., Kunitou M., Shimizu M., Hosomaru K., Mikata S., Ishida M., Hisamatsu K., Yunoki A., Mino Y., et al. Environmental fate of pharmaceutical compounds and antimicrobial-resistant bacteria in hospital effluents, and contributions to pollutant loads in the surface waters in Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2019;657:476–484. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Khan N.A., Ahmed S., Farooqi I.H., Ali I., Vambol V., Changani F., Yousefi M., Vambol S., Khan S.U., Khan A.H. Occurrence, sources and conventional treatment techniques for various antibiotics present in hospital wastewaters: A critical review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020;129:115921. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2020.115921. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rodriguez-Mozaz S., Chamorro S., Marti E., Huerta B., Gros M., Sànchez-Melsió A., Borrego C.M., Barceló D., Balcázar J.L. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in hospital and urban wastewaters and their impact on the receiving river. Water Res. 2015;69:234–242. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.11.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sabri N.A., van Holst S., Schmitt H., van der Zaan B.M., Gerritsen H.W., Rijnaarts H.H.M., Langenhoff A.A.M. Fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes during conventional and additional treatment technologies in wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;741:140199. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rizzo L., Fiorentino A., Anselmo A. Advanced treatment of urban wastewater by UV radiation: Effect on antibiotics and antibiotic-resistant E. coli strains. Chemosphere. 2013;92:171–176. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.03.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhang Y., Zhuang Y., Geng J., Ren H., Xu K., Ding L. Reduction of antibiotic resistance genes in municipal wastewater effluent by advanced oxidation processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016;550:184–191. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hiller C.X., Hübner U., Fajnorova S., Schwartz T., Drewes J.E. Antibiotic microbial resistance (AMR) removal efficiencies by conventional and advanced wastewater treatment processes: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019;685:596–608. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Vorontsov A.V. Advancing fenton and photo-fenton water treatment through the catalyst design. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019;372:103–112. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.04.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ahmed Y., Zhong J., Yuan Z., Guo J. Simultaneous removal of antibiotic resistant bacteria, antibiotic resistance genes, and micropollutants by a modified photo-fenton process. Water Res. 2021;197:117075. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Juretic H., Montalbo-Lomboy M., van Leeuwen J., Cooper W.J., Grewell D. Hydroxyl radical formation in batch and continuous flow ultrasonic systems. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015;22:600–606. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2014.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yang S.-Q., Cui Y.H., Li J.Y., Lv X.D., Liu Z.Q. Determination methods for steady-state concentrations of HO· and SO4·− in electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere. 2020;261:127658. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Di Paola A., García-López E., Marcì G., Palmisano L. A survey of photocatalytic materials for environmental remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012;211–212:3–29. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.11.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zhang R., Wang X., Zhou L., Liu Z., Crump D. The impact of dissolved oxygen on sulfate radical-induced oxidation of organic micro-pollutants: A theoretical study. Water Res. 2018;135:144–154. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.02.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Yang Y., Li X., Zhou C., Xiong W., Zeng G., Huang D., Zhang C., Wang W., Song B., Tang X., et al. Recent advances in application of graphitic carbon nitride-based catalysts for degrading organic contaminants in water through advanced oxidation processes beyond photocatalysis: A critical review. Water Res. 2020;184:116200. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Chan P.Y., Gamal El-Din M., Bolton J.R. A solar-driven UV/chlorine advanced oxidation process. Water Res. 2012;46:5672–5682. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.07.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yu G., Wang Y., Cao H., Zhao H., Xie Y. Reactive oxygen species and catalytic active sites in heterogeneous catalytic ozonation for water purification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020;54:5931–5946. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c00575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Jiang J.Q. Research progress in the use of ferrate(VI) for the environmental remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007;146:617–623. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Loeb B.L. Forty years of advances in ozone technology. A review of ozone: Science & Engineering. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2018;40:3–20. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lee O.M., Kim H.Y., Park W., Kim T.H., Yu S. A comparative study of disinfection efficiency and regrowth control of microorganism in secondary wastewater effluent using UV, ozone, and ionizing irradiation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015;295:201–208. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ofori I., Maddila S., Lin J., Jonnalagadda S.B. Ozone initiated inactivation of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus in water: Influence of selected organic solvents prevalent in wastewaters. Chemosphere. 2018;206:43–50. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hansen K.M.S., Spiliotopoulou A., Chhetri R.K., Escolà Casas M., Bester K., Andersen H.R. Ozonation for source treatment of pharmaceuticals in hospital wastewater—Ozone lifetime and required ozone dose. Chem. Eng. J. 2016;290:507–514. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.01.027. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Azuma T., Otomo K., Kunitou M., Shimizu M., Hosomaru K., Mikata S., Mino Y., Hayashi T. Removal of pharmaceuticals in water by introduction of ozonated microbubbles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019;212:483–489. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2018.11.059. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kusvuran E., Gulnaz O., Samil A., Erbil M. Detection of double bond-ozone stoichiometry by an iodimetric method during ozonation processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010;175:410–416. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ribeiro A.R., Nunes O.C., Pereira M.F.R., Silva A.M.T. An overview on the advanced oxidation processes applied for the treatment of water pollutants defined in the recently launched directive 2013/39/eu. Environ. Int. 2015;75:33–51. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2014.10.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ferrando-Climent L., Gonzalez-Olmos R., Anfruns A., Aymerich I., Corominas L., Barceló D., Rodriguez-Mozaz S. Elimination study of the chemotherapy drug tamoxifen by different advanced oxidation processes: Transformation products and toxicity assessment. Chemosphere. 2017;168:284–292. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zhao X., Su H., Xu W., Hu X., Xu Y., Wen G., Cao Y. Removal of antibiotic resistance genes and inactivation of antibiotic-resistant bacteria by oxidative treatments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021;778:146348. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Anthony E.T., Ojemaye M.O., Okoh O.O., Okoh A.I. A critical review on the occurrence of resistomes in the environment and their removal from wastewater using apposite treatment technologies: Limitations, successes and future improvement. Environ. Pollut. 2020;263:113791. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Congilosi J.L., Aga D.S. Review on the fate of antimicrobials, antimicrobial resistance genes, and other micropollutants in manure during enhanced anaerobic digestion and composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021;405:123634. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Azuma T., Hayashi T. Disinfection of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in sewage and hospital effluent by ozonation. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2021;43:413–426. doi: 10.1080/01919512.2021.1906095. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Azuma T., Usui M., Hayashi T. Evaluation of the effectiveness of ozone treatment of hospital wastewater. J. Med. Hyg. Use Ozone. 2021;28:91–100. [Google Scholar]
- 59.World Health Organization (WHO) Antibiotic-Resistant “Priority Pathogens”—A Catalogue of 12 Families of Bacteria That Pose the Greatest Threat to Human Health. [(accessed on 28 December 2021)]. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2017/bacteria-antibiotics-needed/en/
- 60.Alekshun M.N., Levy S.B. Molecular mechanisms of antibacterial multidrug resistance. Cell. 2007;128:1037–1050. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Azuma T., Hayashi T. On-site chlorination responsible for effective disinfection of wastewater from hospital. Sci. Total Environ. 2021;776:145951. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Japan Meteorological Agency 2019 Weather Statistics. [(accessed on 28 December 2021)]; Available online: http://www.jma.go.jp/jma/index.html.
- 63.Zheng J., Su C., Zhou J., Xu L., Qian Y., Chen H. Effects and mechanisms of ultraviolet, chlorination, and ozone disinfection on antibiotic resistance genes in secondary effluents of municipal wastewater treatment plants. Chem. Eng. J. 2017;317:309–316. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.02.076. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Dunkin N., Weng S., Coulter C.G., Jacangelo J.G., Schwab K.J. Impacts of virus processing on human norovirus gi and gii persistence during disinfection of municipal secondary wastewater effluent. Water Res. 2018;134:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.01.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Lamba M., Graham D.W., Ahammad S.Z. Hospital wastewater releases of carbapenem-resistance pathogens and genes in urban india. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017;51:13906–13912. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b03380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Glady-Croue J., Niu X.-Z., Ramsay J.P., Watkin E., Murphy R.J.T., Croue J.P. Survival of antibiotic resistant bacteria following artificial solar radiation of secondary wastewater effluent. Sci. Total Environ. 2018;626:1005–1011. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Haller L., Chen H., Ng C., Le T.H., Koh T.H., Barkham T., Sobsey M., Gin K.Y.H. Occurrence and characteristics of extended-spectrum β-lactamase- and carbapenemase- producing bacteria from hospital effluents in singapore. Sci. Total Environ. 2018;615:1119–1125. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Serna-Galvis E.A., Vélez-Peña E., Osorio-Vargas P., Jiménez J.N., Salazar-Ospina L., Guaca-González Y.M., Torres-Palma R.A. Inactivation of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae by photo-fenton: Residual effect, gene evolution and modifications with citric acid and persulfate. Water Res. 2019;161:354–363. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.06.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Hrenovic J., Ivankovic T., Ivekovic D., Repec S., Stipanicev D., Ganjto M. The fate of carbapenem-resistant bacteria in a wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 2017;126:232–239. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.bioMérieux (France) Manufacturer’s Protocol for Chromid® Chromogenic Media. [(accessed on 28 December 2021)]. Available online: http://www.biomerieux.fr/diagnostic-clinique/milieux-de-culture.
- 71.Azuma T., Hayashi T. Effects of natural sunlight on antimicrobial-resistant bacteria (AMRB) and antimicrobial-susceptible bacteria (AMSB) in wastewater and river water. Sci. Total Environ. 2021;766:142568. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Heß S., Gallert C. Sensitivity of antibiotic resistant and antibiotic susceptible Escherichia coli, Enterococcus and Staphylococcus strains against ozone. J. Water Health. 2015;13:1020–1028. doi: 10.2166/wh.2015.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Wen G., Liang Z., Xu X., Cao R., Wan Q., Ji G., Lin W., Wang J., Yang J., Huang T. Inactivation of fungal spores in water using ozone: Kinetics, influencing factors and mechanisms. Water Res. 2020;185:116218. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Verlicchi P., Al Aukidy M., Zambello E. What have we learned from worldwide experiences on the management and treatment of hospital effluent?—An overview and a discussion on perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2015;514:467–491. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kharel S., Stapf M., Miehe U., Ekblad M., Cimbritz M., Falås P., Nilsson J., Sehlén R., Bester K. Ozone dose dependent formation and removal of ozonation products of pharmaceuticals in pilot and full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;731:139064. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Japan Sewage Works Association . Statistics of Sewerage. Japan Sewage Works Association; Tokyo, Japan: 2018. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- 77.Mezzanotte V., Antonelli M., Citterio S., Nurizzo C. Wastewater disinfection alternatives: Chlorine, ozone, peracetic acid, and UV light. Water Environm. Res. 2007;79:2373–2379. doi: 10.2175/106143007X183763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Mohapatra D.P., Brar S.K., Tyagi R.D., Picard P., Surampalli R.Y. Analysis and advanced oxidation treatment of a persistent pharmaceutical compound in wastewater and wastewater sludge-carbamazepine. Sci. Total Environ. 2014;470–471:58–75. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.09.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.He H., Zhou P., Shimabuku K.K., Fang X., Li S., Lee Y., Dodd M.C. Degradation and deactivation of bacterial antibiotic resistance genes during exposure to free chlorine, monochloramine, chlorine dioxide, ozone, ultraviolet light, and hydroxyl radical. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019;53:2013–2026. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b04393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Rubio-Clemente A., Chica E., Peñuela G. Total coliform inactivation in natural water by UV/H2O2, UV/US, and UV/US H2O2 systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019;26:4462–4473. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3297-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Azuma T., Ishiuchi H., Inoyama T., Teranishi Y., Yamaoka M., Sato T., Yamashita N., Tanaka H., Mino Y. Detection of peramivir and laninamivir, new anti-influenza drugs, in sewage effluent and river waters in Japan. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0131412. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Nielsen U., Hastrup C., Klausen M.M., Pedersen B.M., Kristensen G.H., Jansen J.L.C., Bak S.N., Tuerk J. Removal of apis and bacteria from hospital wastewater by MBR plus O3, O 3+H2O 2, PAC or ClO2. Water Sci. Technol. 2013;67:854–862. doi: 10.2166/wst.2012.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Paucar N.E., Kim I., Tanaka H., Sato C. Ozone treatment process for the removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in wastewater. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2019;41:3–16. doi: 10.1080/01919512.2018.1482456. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Szekeres E., Baricz A., Chiriac C.M., Farkas A., Opris O., Soran M.-L., Andrei A.S., Rudi K., Balcázar J.L., Dragos N., et al. Abundance of antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community composition in wastewater effluents from different romanian hospitals. Environ. Pollut. 2017;225:304–315. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.01.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Jeon Y.-S., Park S.-C., Lim J., Chun J., Kim B.S. Improved pipeline for reducing erroneous identification by 16s rrna sequences using the illumina miseq platform. J. Microbiol. 2015;53:60–69. doi: 10.1007/s12275-015-4601-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Zhang J., Ding X., Guan R., Zhu C., Xu C., Zhu B., Zhang H., Xiong Z., Xue Y., Tu J., et al. Evaluation of different 16s rrna gene v regions for exploring bacterial diversity in a eutrophic freshwater lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2018;618:1254–1267. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Deng M., Chen J., Gou J., Hou J., Li D., He X. The effect of different carbon sources on water quality, microbial community and structure of biofloc systems. Aquaculture. 2018;482:103–110. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.09.030. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Quartaroli L., Silva C.M., Silva L.C.F., Lima H.S., de Paula S.O., Dias R.S., Carvalho K.B., Souza R.S., Bassin J.P., da Silva C.C. Effect of the gradual increase of salt on stability and microbial diversity of granular sludge and ammonia removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2019;248:109273. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Sun Z., Li G., Wang C., Jing Y., Zhu Y., Zhang S., Liu Y. Community dynamics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbes in an estuary reservoir. Sci. Rep. 2014;4:6966. doi: 10.1038/srep06966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Yu P., Sun Y., Huang Z., Zhu F., Sun Y., Jiang L. The effects of ectomycorrhizal fungi on heavy metals’ transport in pinus massoniana and bacteria community in rhizosphere soil in mine tailing area. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020;381:121203. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Bokulich N.A., Subramanian S., Faith J.J., Gevers D., Gordon J.I., Knight R., Mills D.A., Caporaso J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods. 2013;10:57–59. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Greay T.L., Gofton A.W., Zahedi A., Paparini A., Linge K.L., Joll C.A., Ryan U.M. Evaluation of 16s next-generation sequencing of hypervariable region 4 in wastewater samples: An unsuitable approach for bacterial enteric pathogen identification. Sci. Total Environ. 2019;670:1111–1124. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Wang Q., Garrity G.M., Tiedje J.M., Cole J.R. Naive bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rrna sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007;73:5261–5267. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00062-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Edgar R.C. Sintax: A simple non-bayesian taxonomy classifier for 16s and its sequences. bioRxiv. 2016:074161. doi: 10.1101/074161. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Guidelines for Environmental Infection Control in Health-Care Facilities Recommendations of CDC and the Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee (HICPAC) CDC; Atlanta, GA, USA: 2013. [(accessed on 28 December 2021)]. pp. 1–241. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/environmental/index.html. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Garcia A.B., Vinuela-Prieto J.M., Lopez-Gonzalez L., Candel F.J. Correlation between resistance mechanisms in Staphylococcus aureus and cell wall and septum thickening. Infect. Drug. Resist. 2017;10:353–356. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S146748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Torii S., Itamochi M., Katayama H. Inactivation kinetics of waterborne virus by ozone determined by a continuous quench flow system. Water Res. 2020;186:116291. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.116291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Burns N., Hunter G., Jackman A., Hulsey B., Coughenour J., Walz T. The return of ozone and the hydroxyl radical to wastewater disinfection. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2007;29:303–306. doi: 10.1080/01919510701463206. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Giannakis S., Voumard M., Grandjean D., Magnet A., De Alencastro L.F., Pulgarin C. Micropollutant degradation, bacterial inactivation and regrowth risk in wastewater effluents: Influence of the secondary (pre)treatment on the efficiency of advanced oxidation processes. Water Res. 2016;102:505–515. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.06.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Malvestiti J.A., Dantas R.F. Disinfection of secondary effluents by O3, O3/H2O2 and UV/H2O2: Influence of carbonate, nitrate, industrial contaminants and regrowth. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018;6:560–567. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2017.12.058. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Ding W., Jin W., Cao S., Zhou X., Wang C., Jiang Q., Huang H., Tu R., Han S.F., Wang Q. Ozone disinfection of chlorine-resistant bacteria in drinking water. Water Res. 2019;160:339–349. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Itzel F., Jewell K.S., Leonhardt J., Gehrmann L., Nielsen U., Ternes T.A., Schmidt T.C., Tuerk J. Comprehensive analysis of antagonistic endocrine activity during ozone treatment of hospital wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018;624:1443–1454. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Alexander J., Knopp G., Dötsch A., Wieland A., Schwartz T. Ozone treatment of conditioned wastewater selects antibiotic resistance genes, opportunistic bacteria, and induce strong population shifts. Sci. Total Environ. 2016;559:103–112. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Choi Y., He H., Dodd M.C., Lee Y. Degradation kinetics of antibiotic resistance gene meca of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) during water disinfection with chlorine, ozone, and ultraviolet light. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021;55:2541–2552. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c05274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Li S., Zhang C., Li F., Hua T., Zhou Q., Ho S.H. Technologies towards antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) removal from aquatic environment: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021;411:125148. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Czekalski N., Imminger S., Salhi E., Veljkovic M., Kleffel K., Drissner D., Hammes F., Bürgmann H., von Gunten U. Inactivation of antibiotic resistant bacteria and resistance genes by ozone: From laboratory experiments to full-scale wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016;50:11862–11871. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b02640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Stange C., Sidhu J.P.S., Toze S., Tiehm A. Comparative removal of antibiotic resistance genes during chlorination, ozonation, and uv treatment. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health. 2019;222:541–548. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2019.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Sekizuka T., Yatsu K., Inamine Y., Segawa T., Nishio M., Kishi N., Kuroda M. Complete genome sequence of a blakpc-2-positive Klebsiella pneumoniae strain isolated from the effluent of an urban sewage treatment plant in Japan. mSphere. 2018;3:e00314-18. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00314-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Gomi R., Matsuda T., Yamamoto M., Chou P.H., Tanaka M., Ichiyama S., Yoneda M., Matsumura Y. Characteristics of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in wastewater revealed by genomic analysis. Antimicrob. Age Chemother. 2018;62:e02501-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02501-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Sekizuka T., Inamine Y., Segawa T., Kuroda M. Characterization of NDM-5- and CTX-M-55-coproducing Escherichia coli gsh8m-2 isolated from the effluent of a wastewater treatment plant in Tokyo bay. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019;12:2243–2249. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S215273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Teixeira P., Tacão M., Pureza L., Gonçalves J., Silva A., Cruz-Schneider M.P., Henriques I. Occurrence of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in a portuguese river: blaNDM, blaKPC and blaGES among the detected genes. Environ. Pollut. 2020;260:113913. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.113913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Piña B., Bayona J.M., Christou A., Fatta-Kassinos D., Guillon E., Lambropoulou D., Michael C., Polesel F., Sayen S. On the contribution of reclaimed wastewater irrigation to the potential exposure of humans to antibiotics, antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes—Nereus cost action es1403 position paper. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020;8:102131. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2018.01.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Le Page G., Gunnarsson L., Snape J., Tyler C.R. Integrating human and environmental health in antibiotic risk assessment: A critical analysis of protection goals, species sensitivity and antimicrobial resistance. Environ. Int. 2017;109:155–169. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Pepper I.L., Brooks J.P., Gerba C.P. Antibiotic resistant bacteria in municipal wastes: Is there reason for concern? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018;52:3949–3959. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b04360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Adachi F., Sekizuka T., Yamato M., Fukuoka K., Yamaguchi N., Kuroda M., Kawahara R. Characterization of fri carbapenemase-producing Enterobacter spp. Isolated from a hospital and the environment in Osaka, Japan. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021;76:3061–3062. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkab284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Verlicchi P. Trends, new insights and perspectives in the treatment of hospital effluents. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health. 2021;19:100217. doi: 10.1016/j.coesh.2020.10.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Hocquet D., Muller A., Bertrand X. What happens in hospitals does not stay in hospitals: Antibiotic-resistant bacteria in hospital wastewater systems. J. Hosp. Infect. 2016;93:395–402. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2016.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.King T.L.B., Schmidt S., Essack S.Y. Antibiotic resistant Klebsiella spp. From a hospital, hospital effluents and wastewater treatment plants in the umgungundlovu district, kwazulu-natal, south africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;712:135550. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Araújo S., Sousa M., Tacão M., Baraúna R.A., Silva A., Ramos R., Alves A., Manaia C.M., Henriques I. Carbapenem-resistant bacteria over a wastewater treatment process: Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in untreated wastewater and intrinsically-resistant bacteria in final effluent. Sci. Total Environ. 2021;782:146892. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146892. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Bombaywala S., Mandpe A., Paliya S., Kumar S. Antibiotic resistance in the environment: A critical insight on its occurrence, fate, and eco-toxicity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021;28:24889–24916. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-13143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Verlicchi P. Hospital Wastewaters: Characteristics, Management, Treatment and Environmental Risks. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2017. pp. 1–243. [Google Scholar]
- 122.Khan M.T., Shah I.A., Ihsanullah I., Naushad M., Ali S., Shah S.H.A., Mohammad A.W. Hospital wastewater as a source of environmental contamination: An overview of management practices, environmental risks, and treatment processes. J. Water Proc. Eng. 2021;41:101990. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.101990. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Nguyen A.Q., Vu H.P., Nguyen L.N., Wang Q., Djordjevic S.P., Donner E., Yin H., Nghiem L.D. Monitoring antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater treatment: Current strategies and future challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2021;783:146964. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Kovalova L., Siegrist H., von Gunten U., Eugster J., Hagenbuch M., Wittmer A., Moser R., McArdell C.S. Elimination of micropollutants during post-treatment of hospital wastewater with powdered activated carbon, ozone, and UV. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013;47:7899–7908. doi: 10.1021/es400708w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Wardenier N., Liu Z., Nikiforov A., Van Hulle S.W.H., Leys C. Micropollutant elimination by O3, UV and plasma-based aops: An evaluation of treatment and energy costs. Chemosphere. 2019;234:715–724. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Yao K., Chi Y., Wang F., Yan J., Ni M., Cen K. The effect of microbubbles on gas-liquid mass transfer coefficient and degradation rate of cod in wastewater treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2016;73:1969–1977. doi: 10.2166/wst.2016.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Gao Y., Duan Y., Fan W., Guo T., Huo M., Yang W., Zhu S., An W. Intensifying ozonation treatment of municipal secondary effluent using a combination of microbubbles and ultraviolet irradiation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019;26:21915–21924. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05554-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Movahed S.M.A., Sarmah A.K. Global trends and characteristics of nano- and micro-bubbles research in environmental engineering over the past two decades: A scientometric analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021;785:147362. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.