Abstract
Most cardiac arrhythmias at the whole heart level result from alteration of cell membrane ionic channels and intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) cycling with emerging spatiotemporal behavior through tissue-level coupling. For example, dynamically induced spatial dispersion of action potential duration, QT prolongation, and alternans are clinical markers for arrhythmia susceptibility in regular and heart-failure patients that originate due to changes of the transmembrane voltage (Vm) and [Ca2+]i. We present an optical-mapping methodology that permits simultaneous measurements of the Vm - [Ca2+]i signals using a single-camera without cross-talk, allowing quantitative characterization of favorable/adverse cell and tissue dynamical effects occurring from remodeling and/or drugs in heart failure. We demonstrate theoretically and experimentally in six different species the existence of a family of excitation wavelengths, we termed semasbestic, that give no change in signal for one dye, and thus can be used to record signals from another dye, guaranteeing zero cross-talk.
Keywords: optical mapping, semasbestic wavelength, isosbestic point, fluorescent dyes, transmembrane voltage, intracellular free calcium concentration, alternans
1. Introduction
Heart failure (HF) is a global epidemic, affecting more than 64 million people worldwide (James et al., 2018) and is increasing in prevalence. In the US, about 6.9 million people have been diagnosed with HF, with an expected 24% increase to nearly 8.5 million by 2030 (Benjamin et al., 2018). The prognosis is poor: 20% die within 1 year and 80% within 8 years, resulting in over 655,000 deaths annually (Virani et al., 2020) in the US alone. More than half of HF deaths are due to ventricular fibrillation (Packer, 1985), and despite decades of study, the mechanisms by which HF predisposes patients to these ventricular arrhythmias are not well-understood. As a result, few treatment options are available. It is, therefore, crucial to identify how HF leads to the development of life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias. Although it is well-known that fibrosis and myocardial ischemia (Tomaselli and Zipes, 2004) can cause conduction abnormalities and cardiac arrhythmias, there is growing recognition that abnormal intracellular calcium cycling plays a fundamental role in the pathology of HF (Hoeker et al., 2009; Aistrup et al., 2011). Many studies have shown that disruptions in intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) cycling, along with the complex voltage-calcium bidirectional coupling, can lead to action potential (AP) repolarization abnormalities that promote arrhythmias (Balijepalli and Kamp, 2008, 2011; Hoeker et al., 2009; Louch et al., 2010; Aistrup et al., 2011). This necessitates the development of effective methods that can investigate simultaneously the dynamics of the cell's transmembrane voltage (Vm) and [Ca2+]i in cardiac tissue.
Optical mapping, developed in the mid-1970s, is the perfect methodology for the study of Vm -[Ca2+]i in cardiac electrophysiology due to a high spatial and temporal resolutions. In essence the method originally consisted in measuring changes in Vm from changes in fluorescence intensity using Vm sensitive dyes. For example, electrochromic Vm dyes bind to the cell's membrane, and their absorption and emission spectra blue-shifts a few nanometers as the cell membrane depolarizes. By blocking the excitation light and part of the emission spectra with a long-pass-filter (LPF) placed over an electro-optical sensor (camera), fluorescence intensity is measured in practice (Figure 1). For small spectra shifts, the normalized change in fluorescence intensity (ΔF/F) is given by (F - F0) / F0, where F0 is the fluorescence intensity when the cell's membrane is polarized (the resting membrane potential), and F when the cell's membrane is depolarized (any other transmembrane potential) which to first approximation it is linearly proportional to the cell's transmembrane potential and thus closely reproduce the action potential (Figure 1D). With unprecedented high spatial and temporal resolution, optical mapping with Vm sensitive dyes have been used to characterize wave propagation across the tissue surface (Barone et al., 2020) and depth (Kelly et al., 2013), during regional ischemia (Sidorov et al., 2011) and provide evidence of reentrant waves as mechanisms of lethal arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation (Davidenko et al., 1992; Gray et al., 1998; Cherry and Fenton, 2008) that affect the electro-mechanical coupling (Christoph et al., 2018). Additionally, invasive and non-invasive techniques can also be characterized using optical mapping, such radio-frequency ablation outcome (Paredes et al., 2020; Pollnow et al., 2020), and low-energy defibrillation techniques (Li et al., 2011; Ji et al., 2017; Uzelac and Fenton, 2020). However, for a complete understanding of arrhythmic mechanisms, simultaneous measurements of Vm and [Ca2+]i are needed. Simultaneous measurement of Vm-[Ca+2]i reveals spatial dispersion of AP repolarization and [Ca+2]i transients (CaT) (Uzelac et al., 2017) which is one of the mechanisms leading to ventricular arrhythmias (Pastore et al., 1999; Watanabe et al., 2001; Gizzi et al., 2013).
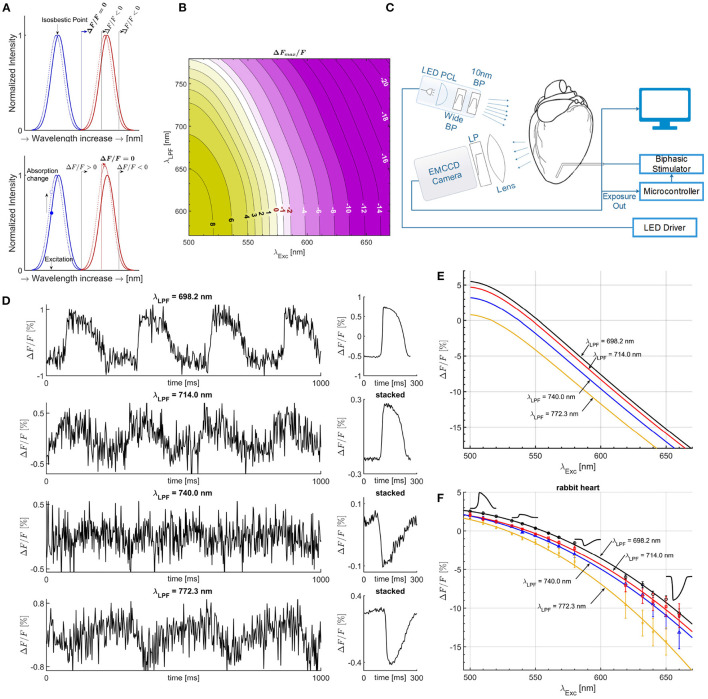
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of measurement with an electrochromic Vm dye. (A) The Gaussian absorption (blue) and emission curves (red) are good fits for a given electrochromic Vm dye for illustration purposes, with solid lines for polarized membrane and leftward shifted dotted lines for maximally depolarized membrane by a propagating AP. For excitation at the isosbestic point and for a given LPF on the camera side passing only part of the emission spectra, as illustrated with the solid (black) vertical lines, ΔF/F is always negative. ΔF/F = 0 can only be achieved if the entire emission spectrum is obtained (solid blue vertical line), thereby not dependent on the optical setup, the λLPF value. Excitation left of the isosbestic point results in an amplitude increase of the emission spectra due to absorption coefficient increase with the shift of the absorption spectra. Depending on the filter λLPF, overall ΔF/F sign can be negative or positive, and in between, there is a particular λLPF such that positive change cancels the negative change resulting in ΔF/F = 0, for specific λExc, termed semasbestic wavelength. (B) Theoretically calculated map of ΔF/F magnitude values as a function of λExc and λLPF, showing the transition from positive to negative ΔF/F, and continuous line of semasbestic wavelengths, ΔF/F = 0 isochrone line, for each λExc - λLPF pair. (C) Illustration of the experimental setup. (D) APs from optical mapping measurements on isolated rabbit heart near a semasbestic wavelength. A 10 nm wide BP excitation filter was used of 540 nm nominal center wavelength along different LPFs on the camera's side. Due to low ΔF/F values SNR is low. However, ensemble averaging (stacking) increases SNR without filtering in post-processing. (E) Quadratic fit curves from ΔF/F simulated values (B), for four different LPFs of the same λLPF values as LPF used in ΔF/F measurements on isolated hearts. (F) Quadratic fit curves from ΔF/F magnitude values for four different LPFs. Optical mapping recordings were performed on isolated rabbit heart for across a wide range of excitation wavelengths, from 500 to 660 nm. Zero crossings correspond to the semasbestic wavelengths. All λLPF values of LPFs are experimentally measured.
Historically, the first dual optical mapping systems were designed in 2000 by Choi and Salama (2000) with RH-237 Vm and Rhod-2 AM [Ca+2]i dyes, and by Laurita and Singal (2001) with Di-4-ANEPPS Vm and Indo-1 AM [Ca+2]i dyes. These systems used overlapping excitation bands for the two dyes with separate emission bands split and sent to the two photodetectors, one to measure Vm and one for [Ca+2]i with a spatial resolution of 16 × 16 pixels. Since then, other dual systems with higher resolution (Holcomb et al., 2009) have been developed, including those designed with a single camera for monolayers (Scull et al., 2012) and whole hearts (Lee et al., 2011, 2012a,b,c; Herron et al., 2012). The advantages of a single detector based systems include: (i) Significantly less expensive as they do not require multiple detectors/cameras; (ii) There is no need for spatial alignment of the detectors to have the same field of view, increasing complexity of setups, and possible decrease of the field of view (Holcomb et al., 2009); (iii) No need to use a dichroic mirror to separate the Vm and [Ca+2]i fluorescence signals for each sensor, decreasing light intensity, that is signal to noise ratio (SNR).
While optical mapping recordings have been considered technically challenging and expensive, advances in recent years have made the necessary equipment affordable enough (Marina-Breysse et al., 2021) to become a standard technique in many labs. Different methods have been proposed to achieve dual Vm and [Ca2+] optical mapping measurement. Two-camera setups require complex spatial alignment of the cameras and optical elements to split the two fluorescent signals, with only one signal reaching each camera (Holcomb et al., 2009). The complexity of the two-camera setups can be avoided by a single camera for dual Vm and [Ca2+]i signal measurements. The fundamental principle behind single-camera-based methods is to separate the Vm and [Ca2+] fluorescence signals based on differences in excitation and/or emission spectra of the two dyes used. Existing methods (Lee et al., 2011, 2012a,c) are limited to the particular choice of fluorescent dyes, significantly limiting their application. Additionally, there is no established methodology for designing and implementing a single-camera-based dual Vm and [Ca2+]i measurement technique which provides zero-cross talk of the two fluorescence signals. The excitation light band for a Vm dye preferably would not excite a [Ca2+]i dye and vice versa. However, true spectral separation is not possible (with currently available dyes), but illuminating at a wavelength where one or the other dye is not sensitive to the parameter of interest is sufficient. This is essential as the complex bidirectional coupling between Vm and [Ca2+]i (Shiferaw and Karma, 2006) is important when investigating under which HF conditions (Gorski et al., 2015) Vm or [Ca2+]i are responsible for triggering an arrhythmia.
This study presents a theoretical framework to analyze and select the optimal dyes/filters combination to achieve zero-cross talk for dual Vm - [Ca2+] optical mapping applications for simultaneous measurement of Vm and [Ca2+]i signals, using a single sensor. The methodology is based on alternating excitation bands for each fluorescent dye in sync with the camera, recording each signal in alternating frames in order to overcome the challenges of mutual cross-talk of the two signals. Excitation at wavelengths we term semasbestic results in no change of fluorescence of a voltage-sensitive dye as Vm changes, which is suitable to excite a [Ca2+]i dye with no cross-talk. We demonstrate the existence of a family of these excitation wavelengths and the advantage of this methodology experimentally with optical mapping measurements performed in six different animal species, while also showing how previous methods exhibit signal cross-talk. Furthermore, optical-mapping methods using Vm and [Ca+2]i dyes have a broad range of applications, suitable for research of cardiomyocyte cultures (Fast and Ideker, 2000), studying drug effects on heart electrophysiology (Bedut et al., 2016; Streit and Kleinlogel, 2018; Gunawan et al., 2021; Uzelac et al., 2021), gene therapies on Vm and [Ca2+]i dynamics in cardiac tissue and in other organs such as the brain (Baker et al., 2005; Ma et al., 2016; Turrini et al., 2017) as well as in other biological systems driven by Vm and [Ca2+]i dynamics like in C-Elegans (Venkatachalam et al., 2016).
2. Materials and Methods
Previously published methods of simultaneous measurement of Vm-[Ca2+]i with a single sensor (Lee et al., 2011, 2012b,c), have incorrectly used the term isosbestic point of a Vm dye as a suitable excitation wavelength (λExc) for [Ca2+]i dye, expecting no change in measured Vm fluorescence. While isosbestic points (Ahmed and Connor, 1979; Shynkar et al., 2004; Tai et al., 2004; Nič et al., 2009; Bachtel et al., 2011; Uzelac et al., 2019) are defined as the excitation wavelengths at which the total absorbance of a fluorescent dye does not change in response to a change of Vm (Figure 1A; Supplementary Figure 1), it was instead applied as the excitation wavelength at which there is no measurable change in Vm fluorescence signal, expressed as ΔF/F = (F−F0)/F0≈0, where F0 is the fluorescence intensity when the cell's membrane is at the resting membrane potential, and F = F(Vm) is the intensity at any other cell membrane potential.
Isosbestic point is defined as the excitation wavelength at which the absorption spectra for polarized cell membrane and the shifted absorption spectra for maximally depolarized membrane, intersect each other (Bachtel et al., 2011) (Figure 1A). Therefore, when illuminating at an isosbestic point, the absorption coefficient changes minimally (can be approximated to zero), and the integral over the entire emission spectra remains the same. This implies ΔF/F = 0, only if the LPF placed on the camera side passes the entire emission spectra. In practice, this is not possible as cameras have limited dynamic rang, and in common use the LPF on the camera side blocks part of the emission spectra to increase the absolute ΔF/F value (Figure 1A).
In this study, we show that isosbestic points, which are an intrinsic property of fluorescent dyes and as such do not depend on the optical filters transmission properties and sensor spectral response used in many optical mapping setups, are not necessarily the correct wavelengths to use to prevent cross-talk and in fact can give large Vm signal (see top panel Vm signal in Figure 1D obtained with the same optical filter values and the same camera used in Lee et al. (2012b) what authors mistakenly considered to be an isosbestic point excitation). In this study, we establish a methodology to design bi-modal optical-mapping systems with the selection of the correct optical filters, given a choice of Vm and [Ca2+]i dyes. We demonstrate that for a given electrochromic Vm dye, a continuous range of excitation wavelengths exist that result in ΔF/F = 0 (no fractional change of fluorescence) dependable on a given a LPF cut-on wavelength (λLPF) and the spectral response of the camera used. We have termed such a family of wavelengths as semasbestic (self-extinguishable) wavelengths, which are a function of the λLPF for a particular Vm dye. Thus, Vm and [Ca2+]i dyes can be excited with different wavelengths in alternating frames, the Vm with a wavelength outside of a [Ca2+]i dye's absorption spectrum and the [Ca2+]i dye within the absorption spectra of the Vm dye, but using a semasbestic wavelength for the Vm dye, to achieve zero cross-talk for both signals.
The absorption and emission spectra of electrochromic Vm dyes bound to a cardiac cell membrane and shift a few nanometers toward blue as the membrane depolarizes (Loew, 1982) (Figure 1A). The isosbestic point, is the intersection of the absorption curves for the polarized (−80 mV) and fully depolarized (approximately +20 mV) membrane (Figure 1A), typically occurring near the peak of the absorption spectrum (Ahmed and Connor, 1979; Bachtel et al., 2011; Uzelac et al., 2019). Excitation at the isosbestic point results in a leftward shift of the emission curve without changing in amplitude. Therefore, the only case in which no change in Vm signal can be measured (ΔF/F = 0), occurs when using an LPF on the camera side that passes the entire emission spectra for both (polarized/depolarized cell membrane) curves (Figure 1A).
Excitation with wavelengths shorter than the isosbestic (Figure 1A) increases the absorbed light, resulting in an increased amplitude of the shifted emission spectrum. For the emission spectrum range, approximately left of the emission peak, ΔF/F is positive, and for the range right of the peak, ΔF/F is negative. With LPF on the camera side, the actual measured fluorescence signal represents integrated emission spectra from the filter λLPF, and the overall sign of ΔF/F can be positive or negative depending on λLPF. A semasbestic wavelength will be then the excitation wavelength such that integrated intensity over the emission spectra starting from λLPF results in ΔF/F = 0. Therefore, Semasbestic wavelengths depend on the λExc and the λLPF used, resulting in continuous line of ΔF/F = 0 values (Figure 1B).
To demonstrate the existence and usefulness of semasbestic wavelengths, we used the near infra-red electrochromic Vm dye JPW-6003 (Supplementary Figure 1) in isolated Langendorff perfused hearts of six animal species, fish (N = 2), Guinea pigs (N = 2), rabbits (N = 12), cats (N = 6), pigs (N = 7), and sheep (N = 2), totaling 31 experiments, in addition to monolayers cultured from neonatal rat hearts. Details of experimental materials and methods, including heart excision and preparation, cell culture monolayers preparation, excitation light sources, emission optical filters characterization, absorption and emission spectra of the JPW-6003 Vm dye, as well as methods used to obtained ΔF/F = 0 semasbestic points experimentally and their statistical analysis, are provided in the Supplementary Materials.
3. Results
ΔF/F values were measured in isolated heart experiments stained with Vm dye JPW-6003, and excited with a series of different excitation light bands using 10 nm wide bandpass (BP) excitation filters of nominal center wavelengths ranging from 500 to 671 nm. The filters were coupled to either green or red LED collimated light (Figure 1C), and for four different LPFs used on the camera side (Supplementary Figure 2). The excitation light band of each BP filter was modeled with a single effective excitation wavelength (Supplementary Figure 3).
For each LPF-BP filter combination (out of the 60 possible), optical mapping recordings of Vm were obtained for a duration of 2–10 min (depending on the amplitude of ΔF/F signal), acquiring a sequence of images with the Vm across the tissue, at 500 FPS at a resolution of 128 × 128 pixels. For signals of low ΔF/F values close to the semasbestic wavelengths, where signal to noise ratio (SNR) decreases (Figure 1D), the longer recordings (10 min) were used to perform action potential (AP) stacking (ensemble-averaging) (Uzelac and Fenton, 2015) in post-processing. The stacking procedure significantly improved SNR to precisely obtain the small ΔFmax/F magnitude values (Figure 1D; Supplementary Figure 4).
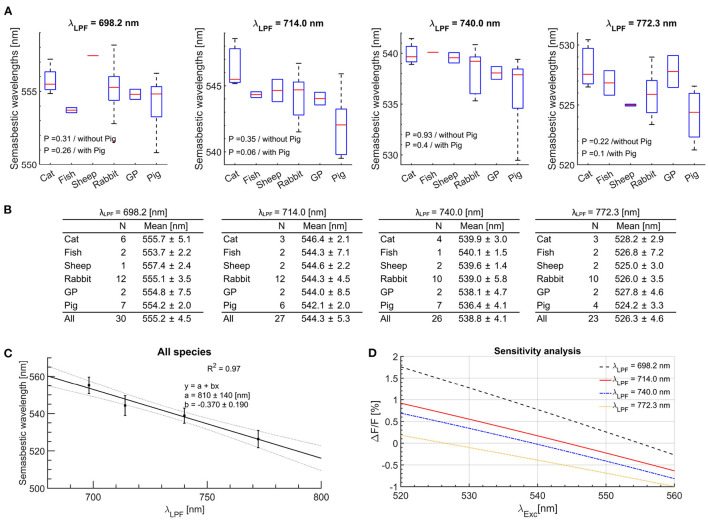
For each isolated experiment and each LPF, semasbestic wavelengths were obtained as zero values of the fit curves of ΔF/F magnitudes obtained for different excitation BP filters. The range of semasbestic wavelength hypothesized theoretically matches well with those obtained experimentally (Figures 1E,F). Among obtained semasbestic wavelengths from the different animal species, no statistically significant difference was observed, with the largest variation found only in pig hearts (Figure 2A). We attribute this difference to the surface fatty tissue layer (that other animals did not have) attenuating non-linearly the emitted fluorescence spectra (van Veen et al., 2004), which resulted in a small leftward shift of the semasbestic wavelengths. One-way ANOVA tests were performed with and without the semasbestic wavelengths obtained in pig hearts, and found that even when including the semasbestic wavelengths of the pig hearts, P-values did not reach statistical significance (P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant). Therefore, semasbestic wavelengths (Figure 2B) appear to be independent of animal species, and a curve can be fitted to relate semasbestic wavelengths as a function of λLPF for Vm JPW-6003 dye, (Figure 2C).
Figure 2.
The semasbestic wavelengths across all experiments for JPW-6003 Vm dye. (A) Box plots are a statistical representation of semasbestic wavelength averaged for each species. The ends of each box are the upper and lower quartiles, with the median marked as a horizontal line inside the box. The whiskers lines represent the upper and lower extremity. The P-values represent results of one-way ANOVA analysis with and without the isosbestic points from isolated pig hearts experiments. (B) The mean values and uncertainties of experimentally obtained semasbestic points across all species for different LFPs used on the camera. (C) A linear curve fit relating the range of semasbestic wavelengths corresponding to different λLPF. (D) Sensitivity analysis near the isosbestic wavelength for different LPFs. Experimentally obtained ΔF/F magnitude values were averaged across all species for the same LPF-BP filter pairs. Excitation wavelengths for up to 10 nm off the semasbestic wavelength result in less than 0.5% in the fractional change of the Vm signal.
Any semasbestic wavelength is suitable to excite a dye. However, in practice using off-the-shelf filters it is expected some mismatch with the filter effective excitation wavelength from the ideal semasbestic wavelength. Any mismatch will result in a cross-talk, the presence of the Vm signal while measuring the fluorescence signal. However, for the excitation wavelengths of up to 10 nm from the ideally suitable semasbestic wavelength, the fractional change of Vm fluorescence is less than 0.5% (Figure 2D). Staining a heart in addition with a dye and assuming the same baseline fluorescence levels of the two dyes, the fractional change of 0.5% will results in ~0.25% fractional change of both fluorescence signals combined, attributed to Vm−Ca cross-talk. In practice for Vm−Ca single-camera measurements, a relative fluorescence change measured in Ca fluorescence channel, of for example 5% means that 0.25% of the measured fluorescence change is attributed to the unwanted Vm signal.
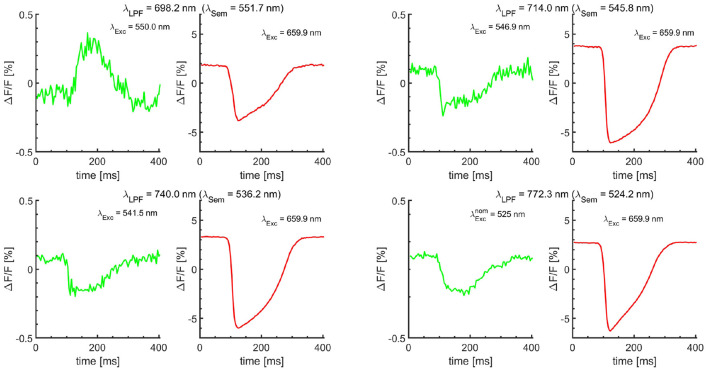
To further demonstrate the proof of concept for Vm−Ca cross-talk minimization for each of the four LPF filters, Vm measurements with JPW-6003 dye only were performed using alternating excitation bands in sync with the camera frame rate (500 Hz at a resolution of 128 × 128 pixels). The sequence of images was recorded with the odd frames corresponding to ideally no change in Vm fluorescence (DFF = 0) and even frames corresponding to the change in Vm signal fluorescence (Figure 3). For odd frames, the off-the-shelf BP excitation filters were used chosen to match as close as possible the ideal semasbestic point corresponding to each of the four different LPFs, and coupled with 525 centered green LED. For even frames, the BP excitation filter of the effective λExc = 660.0 nm wavelength was used. For each of the four validation tests with different LPF, the amount of Vm−Ca cross-talk is around 0.25% except for λLPF = 698.2, which is around 0.4%. The cross-talk is represented as a fractional change in the Vm dye fluorescence. The optical action potential traces corresponding to the same image pixel for even and odd image sequences for direct comparison. As off-the-shelf BP filters were used, the amount of cross-talk depends on the difference between the BP filter effective wavelength from the semasbestic point. Based on the measurement (Figure 3), sensitivity is minimal for = 740.0 nm, using a BP filter of effective excitation wavelength of 5 nm off the semasbestic point and resulting in ΔF/F less than 0.25%.
Figure 3.
Single-camera dual Vm measurements. The Vm dye was excited with alternating excitation bands, using a 660/10 excitation BP filter in even frames. Odd frames were acquired using off-the-shelf excitation BP filters selected to closely match the semasbestic points (λSem) corresponding to the λLPF of the four LPFs. λExc wavelengths are effective excitation wavelengths of the BP filters. Their nominal center wavelengths are listed in Supplementary Figure 3. = 525 nm is the nominal center wavelength of 20 nm wide (OD6) BP filter (Semrock). Shown optical action potential signals are obtained using the stacking procedure from a single pixel, averaging at least 400 periods without any filtering. The stacking resolves small Vm signal changes buried under the noise level, which could be interpreted as no change in Vm signal in the odd frames otherwise. The cross-talk, the presence of Vm signal due to the differences between the filters effective excitation wavelength and corresponding semasbestic points is less than 0.25% for most LPF. The sensitivity to the difference is the lowest for λLPF = 740.0 nm, resulting in ΔF/F amplitude of less than 0.25% using excitation wavelength of more than 5 nm different from the ideal semasbestic point.
4. Discussion
The range of different semasbestic wavelengths of a given Vm dye provides flexibility in the design of an optical mapping system for simultaneous single-camera Vm - Ca recordings, as it is not limited to a single choice of excitation and emission filters, and Vm and Ca fluorescence dyes. The design parameters include the optimal excitation wavelength for a Vm dye (that maximizes ΔF/F), choice of [Ca2+]i dye and its excitation wavelength (semasbestic point), the dual-band pass optical filter on the camera side, and suitable LEDs coupled with excitation filters. Availability of LEDs, optical excitation filters, and the dual-band pass filter of desired spectral properties based on the theoretical design are additional constraints that need to be considered. To begin with the parameters optimization, the first step is to choose a Vm dye.
4.1. Vm Dye Selection
Selection of the Vm dye determines the range of semasbestic wavelengths. For optical mapping method optimization with a chosen Vm dye, the first step is to determine the Vm dye emission spectra to optimize ΔFmax/F. For a chosen JPW-6003 dye its absorption and emission spectra are shown in Supplementary Figure 1. Excitation of the Vm dye with longer wavelengths than the isosbestic point and using longer λLPF on the camera side, increases ΔFmax/F magnitude (Figures 1B–F; Supplementary Figure 5). However, the SNR decreases for longer λLPF due to less fluorescence light reaching the detector. A common practice is to choose λLPF between the Vm dye emission peak and 50% of the peak, the range from 708 to 775 nm for JPW-6003 dye (Supplementary Figure 1). Considering suitable and currently available deep red high-power LEDs, the optimal choice is to use peak emission LEDs around 660 nm.
4.2. [Ca2+]i Dye Selection
Selection of the suitable [Ca2+]i dye is constrained with the range of the semasbestic wavelengths corresponding to the selected range of λLPF values, from 708 to 775 nm. From the equation shown in Figure 2C, the corresponding range of semasbestic wavelengths range from 523 to 548 nm, suitable to excite [Ca2+]i dyes such as Cal-520, Rhod-2, and Rhod-4. In this study, we choose Rhod-2 dye with a peak absorption at 552 nm. However, commercially available LEDs offer peak emission around 525 nm, decreasing emission intensity toward the Rhod-2 absorption peak, making excitation at 540 nm a suitable trade-off. Another important aspect to consider is to avoid overlap of the [Ca2+]i dye absorption spectra with the chosen JPW-6003 Vm dye excitation wavelength of 660 nm. Rhod-2 [Ca2+]i dye absorption spectrum effectively reaches zero above 625 nm, making Rhod-2 dye a suitable choice for [Ca2+]i measurement.
4.3. Dual-Band Pass Filter
A dual-bandpass optical filter is required on the camera to pass the emitted fluorescence from both dyes. With the chosen 540 nm semasbestic wavelength, the Vm dye band is determined from the λExc vs. λLPF curve (Figure 2C) to start at ~730 nm. The first filter band corresponding to the Rhod-2 emission spectra can be from 560 and up to 610 nm. The lower band limit is imposed by excitation BP filter centered at 540 nm so that its transition band effectively reaches zero (<10−4) at 560 nm. The upper limit is determined to avoid overlap with the Vm emission spectra to minimize cross-talk, the presence of Vm signal in the 560–610 nm filter band when the Rhod-2 dye is excited (Supplementary Figures 1, 6).
4.4. Excitation Filters
The LED bell-shaped emission curve results in non-uniform excitation spectra passing through the BP excitation filter. For example, the light intensity passed through the 10 nm wide 540 nm centered BP filter is higher for the wavelength range left of the 540 nm than for the range right of the 540 nm, resulting in different effective (mean) excitation from the nominal 540 nm center wavelength. Since this effective excitation wavelength has to match the semasbestic wavelength, any mismatch will result in a non-zero ΔF/F value. However, the introduced error is small, and the Vm signal change is less than 0.5% using an excitation wavelength in the ±10 nm range around the semasbestic wavelength. The fractional changes were measured only with the Vm dye. Adding the Ca dye, the amount of cross-talk will be even lower, as the fractional change is measured in respect to the summed baseline fluorescence of both dyes (Figure 2D). For the Vm dye excitation, the width and spectral non-uniformity of the passed light are not critical. With a 660 nm centered LED, BP filters with a 660 nm center wavelength of up to 50 nm BP width can be used. The limits are imposed to avoid excitation of the Rhod-2 dye, and a practical limit is due to the LED's bell-shaped emission curve.
4.5. Practical Design With Applications
The optical mapping setup with optimized parameters may come at a high cost requiring the manufacturing of custom filters. However, flexibility in the choice of the semasbestic wavelengths provides leverage in the choice of design parameters while still minimizing the cross-talk for single-camera based simultaneous Vm - Ca measurements to use off the shelf filters. The dual BP filter is the most important for the system design as it determines the semasbestic wavelength. Additionally, any mismatch between the off-the-shelf BP filter effective excitation wavelength and the semasbestic wavelength will result in Vm to Ca cross-talk. However, as outlined above, the amount of cross-talk is less than 0.25% when the difference between the BP filter effective excitation wavelength and the semasbestic point is less than 5 nm (Figures 2D, 3).
For practical realization, we choose an off-the-shelf dual BP filter, of optical density (OD) 6 (Chroma), with the first passband of 560–610 nm, and the second LPF band of the nominal 700 nm wavelength (effective 698.2 nm) (Supplementary Figure 7). Based on the equation (Figure 2C), the corresponding semasbestic wavelength for JPW-6003 Vm dye is 551.7 nm. The closest off-the-shelf 10 nm wide BP filter of 550 nm (nominal wavelength) center wavelength (Edmund Optics) was chosen to be used for Rhod-2 Ca dye excitation (Supplementary Figure 3). An additional OD6 LPF of nominal λLPF = 575 nm (Chroma) was placed over the dual BP filter to avoid overlap between the 550/10 BP excitation filter and the 560–610 nm passband of the dual-band pass filter. This design narrows the Rhod-2 Ca emission spectra range to the 575–610 nm range resulting in reduced Ca fluorescence intensity reaching the camera sensor. However, this was a necessary trade-off using off-the-shelf optical filter filters. For the Vm dye excitation, a 10 nm wide OD4 BP filter of 660 nm nominal center wavelength was used (Edmund Optics). A green LED with 525 nm peak (Luminous Devices) coupled with 550/10 nm BP filter for Rhod-2 Ca dye excitation was used, and a red 660 nm peak LED (LEDEngin) coupled with the 660/10 nm BP for Vm dye excitation (Supplementary Figure 8).
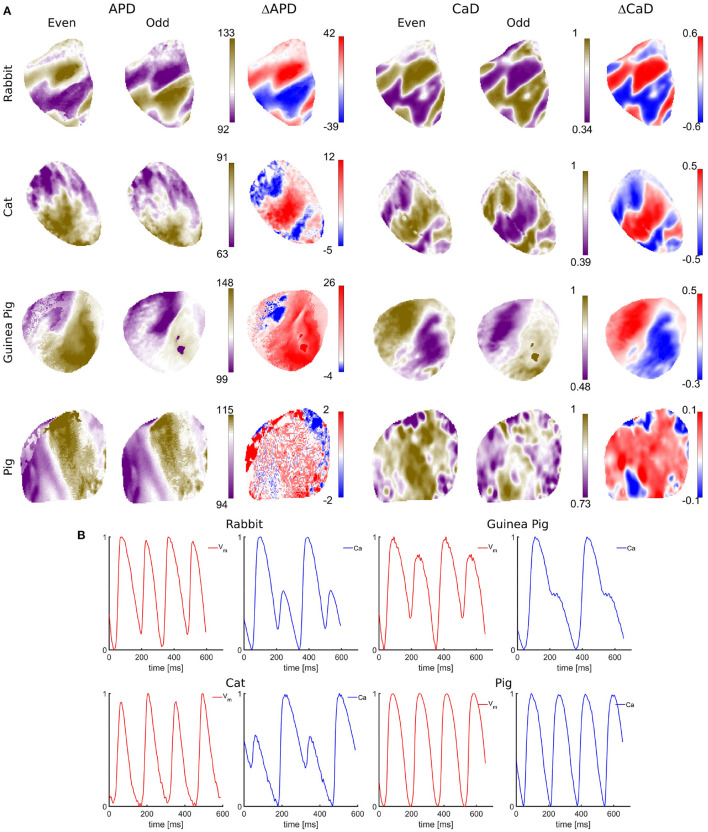
Quantification of spatiotemporal discordant alternans of Vm-[Ca2+]i in cardiac tissue. The optical mapping system with the design parameters described above was used to measure Vm - [Ca2+]i signals with a single-camera in isolated hearts of Rabbit, Cat, Guinea Pig, Pig (Figure 4), and monolayer cell culture of neonatal rats (Figure 5). A restitution protocol was performed for each species, where Vm - Ca signals were recorded at decreasing pacing cycle lengths (PCLs) until a conduction block or ventricular fibrillation (VF) occurs. At shorter PCLs, instabilities in Vm or [Cai] at the cellular level lead to the development of beat to beat alternans in action potential duration (APD) (Pastore et al., 1999), and intracellular calcium duration (CaD) (Uzelac et al., 2017). Through tissue-level coupling, these instabilities lead to complex and irregular spatial dispersion in AP repolarization and in CaD (Figure 4), forming dangerous spatially discordant alternans. Spatially discordant alternans are equivalent to T-wave alternans in clinical ECGs (Pastore et al., 1999; Uzelac et al., 2021), the clinical marker for arrhythmia susceptibility and sudden cardiac death (Walker and Rosenbaum, 2003; Verrier et al., 2009). Among species, the differences in ionic membrane channel densities such as potassium repolarization channels and lack of specific ionic channels create differences in AP morphology. In addition, through Vm - Ca bidirectional coupling, other differences across species exist in terms of handling the intracellular Ca cycling (Figure 4). For rabbit, cat, and guinea pig heart, alternans in Ca seem to drive Vm alternans leading to spatial dispersion of AP repolarization. In contrast, no alternans are observed in Vm nor Ca signals for pig hearts, yet pig hearts develop VF at faster PCLs in the restitution protocols. Understanding these differences across species could lead to a better understanding of different arrhythmia mechanisms modalities and relate them to human heart physiology to more complete understanding arrhythmia in human hearts, devise novel treatments, and help with the global epidemic of HF.
Figure 4.
Single-camera dual Vm−Ca measurements in isolated hearts of different species. (A) Arrhythmic effects under dynamic pacing, shown as spatial dispersion of APD and CaD across tissue for different species for even and odd beats. The spatial dispersion indicates an increased susceptibility to arrhythmia. APD values are obtained from 50% signal rise in amplitude till 50% AP repolarization. Numbers to the right indicate 3rd and 97th percentile APD values expressed in milliseconds. CaD values are obtained as the integral from 50% rise in amplitude till 50% decrease. Blue-red patterns show variations in APD and CaD (ΔAPD, ΔCaD) between even and odd beats (discordant alternans), showing regions alternating out of phase and separated with the nodal lines (white lines). Spatially discordant alternans are the counterpart of T-wave ECG alternans, a well-known marker for arrhythmia susceptibility. Although all species do develop arrhythmia under dynamic pacing, the electrophysiology across species is very different. Spatially discordant alternans are the most pronounced in rabbits, while pig hearts show very little APD and CaD dispersion, with insignificant differences between even and odd beats. (B) Vm and Ca representative AP signals showing temporal alternans for different species.
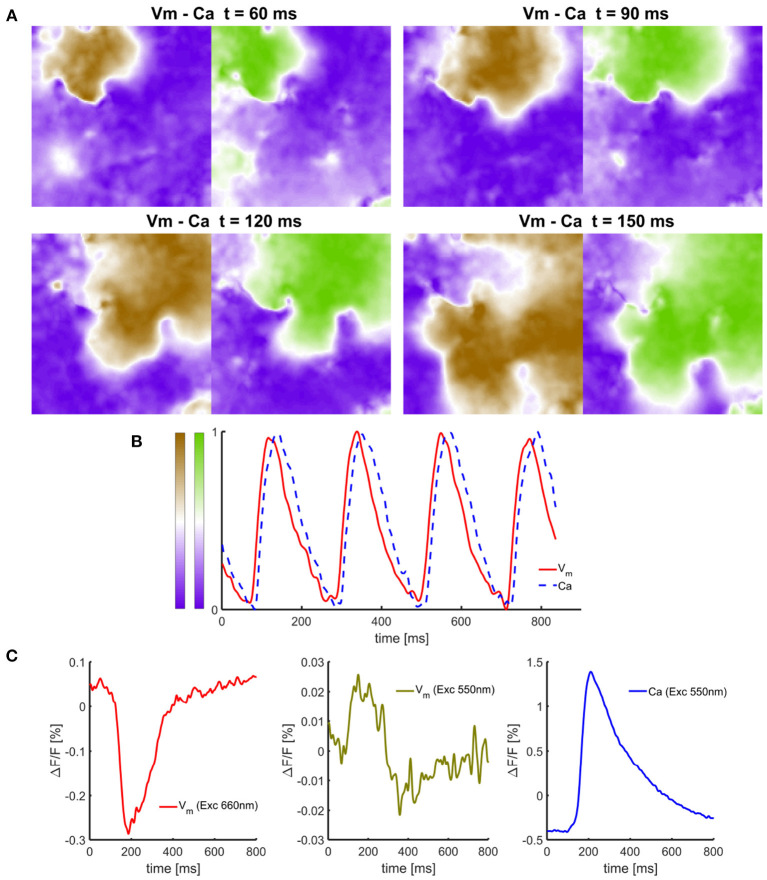
Figure 5.
Simultaneous single-camera-based measurements of Vm and Ca signals in isolated cell culture monolayers of neonatal rats. (A) Time-snapshots of Vm - Ca dynamic at different time points illustrating the presence of anchored spiral wave and spatial loss of correlation between propagating Vm wavefront from Ca dynamics. (B) Normalized Vm and Ca signals obtained from processed raw recordings showing Ca signal lagging in time. (C) Representative unfiltered Vm and Ca signal traces with no filtering expressed as a relative change. In cell culture monolayers, Ca signals have significantly higher SNR than Vm signals originating only from the dye bound to the cell membrane. The amount of cross-talk and the presence of Vm signal in Ca signal with excitation at near the semasbestic point (Exc550) results is a small yet negligible cross-talk compared to the amplitudes of the signals.
5. Conclusions
This study presents a methodology to achieve zero cross-talk (smaller than SNR after stacking) in a single-camera bi-modal optical mapping design based on semasbestic wavelengths. The presented guidelines show how to optimize semasbestic wavelengths to achieve zero cross-talk among Vm and Ca signals, while optimizing signals amplitudes as well. With off-the-shelf bandpass excitation filters of slightly different effective excitation wavelengths than corresponding semasbestic wavelengths (Figure 3) we achieved near zero-cross talk. For a true zero cross-talk, custom manufactured bandpass filters matching the semasbestic point would be needed, and one would need to take into account the LED excitation light spectral profile within the filter passband. The absorption spectra of a given electrochromic Vm dye is spectrally shifted when the dye is bounded within a cell membrane due to a strong interaction between the dye's molecule electric dipole momentum and the cell membrane electric field (Matson et al., 2012). Therefore, contemporary spectroscopy methods to obtain the dye absorption and emission spectra, dissolving the dye in a solvent such as ethanol and using a spectrometer, would result in different semasbestic wavelengths than when performing equivalent measurements on isolated hearts stained with the dye. In this study we conclude that obtained semasbestic wavelengths for a given electrochromic Vm dye, are dependent only on the excitation wavelength λExc and corresponding λLPF of the dye emission band. As validated on isolated hearts of six different species, the semasbestic wavelengths seems to be independent of the species (as validated on six different species and cell culture monolayers).
In the published literature of simultaneous measurement of Vm-[Ca2+]i with a single sensor (Lee et al., 2011, 2012b,c), authors used the same EMCCD camera model and the dual-bandpass filter of 700 nm LPF cut-on wavelength for the JPW-6003 Vm fluorescence showing no visible Vm signal when excited with 540 nm centered band, subsequently used for Rhod-2 Ca dye excitation. However, our findings are different. As shown in Figure 1D, excitation at 540 nm with LPF of 700 nm nominal cut-on wavelength resulted in apparent presence of Vm signal. Therefore, exiting Rhod-2 dye with 540 nm centered bandpass filter and using the dual-band pass filter of 700 nm LPF band for Vm fluorescence results in a cross-talk which can be further minimized with the presented methodology for cross-talk elimination.
While the presented methodology is demonstrated with the semasbestic wavelengths of JPW-6003 Vm dye and using Rhod-2 [Ca2+]i dye, the described methodology does not depend on the choice of the dyes. It applies to any other electrochromic Vm resulting in a different set of semasbestic wavelengths. Therefore, depending on the user's need, we provide a range of semasbestic excitation wavelengths that can be used with JPW-6003 Vm sensitive dye, and a methodology to obtain the same for other Vm sensitive dyes. We followed the common practice in optical mapping to use an LPF to record Vm signal fluorescence. Excitation on the positive-slope side of the excitation spectrum induced an increase in fluorescence during an action potential, which is balanced by recording from the negative-slope side of the emission spectrum. Other classes of semasbestic points may exist with different designs of the emission filter. For example, it is also possible to create a semasbestic wavelength along the negative-slope side of the excitation spectrum and balance this by recording from a band on the positive-slope side of the emission spectrum. However, the close separation between the dye absorption and emission spectra (Supplementary Figure 1) may preclude such an approach for JPW-6003 dye, while it may be feasible for other Vm dyes.
Optical mapping methods using fluorescent dyes are well-established and very important to measure signals from cells and tissue. The use of optical mapping systems is rapidly growing. Nowadays, it is becoming a common tool in many research labs as the equipment is no longer prohibitively expensive (Lee et al., 2017) with novel advances in CMOS sensor technology. The increasing number of research groups are using optical mapping to investigate Vm-[Ca+2]i on biological tissues, and optical mapping methods are even becoming accessible in university classrooms. Simultaneous measurement of Vm and [Ca2+]i enables many studies in the area of electrophysiology related to the Vm and [Ca2+]i dynamic and their bidirectional coupling. For example, cardiac arrhythmia can be caused by AP spatial dispersion driven with Ca alternans at the cellular level (Uzelac et al., 2017) (Supplementary Videos 1, 2). Dual Vm and [Ca2+]i measurements are necessary to understand the underlying mechanism leading to arrhythmia (Groenendaal et al., 2014), and optical mapping studies can be performed even in combination with contractions (Christoph et al., 2018) to study the mechanical stretching effects on cardiac electrophysiology. Time-resolved series of Vm and [Ca2+]i signals at high spatiotemporal resolution are generally applicable to other electrophysiology related studies besides HF. For example, many drugs affect the AP repolarization phase blocking the potassium channels and prolonging the APD, the cellular mechanism of long-QT. Optical mapping provides integrative studies at both the cellular and tissue level to understand how drugs affect the ionic channel currents and intracellular Ca dynamics and to understand the drug's safety profile and associated antiarrhythmic or proarrhythmic at the tissue level (Uzelac et al., 2020, 2021), which would not be possible to understand, studying the drug's effect at the cellular level only. The methodology developed here can also be used to investigate other biological systems with Vm-[Ca+2]i driven dynamics such as the brain (Rad et al., 2017) the pancreas (Yang and Berggren, 2006), smooth (Nelson et al., 1990), and skeletal (Flucher and Tuluc, 2017) muscle among others.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon reasonable request.
Ethics Statement
The animal study was reviewed and approved by the Office of Research and Integrity Assurance at Georgia Institute of Technology and T3 Labs (Translation Testing and Training Laboratories, Inc.), Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) protocols A18012 and A15002.
Author Contributions
IU performed the study design, designed and performed the experiments, and analyzed and interpreted the data. CC contributed to data interpretation, theoretical postulations, and calculations. SI provided critical comments to the study. HC and TK contributed with isolated monolayer cell culture preparation and assisted in related experiments. FF contributed to study design and experiments. All authors worked in writing and reviewing the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by grants NIH 1R01HL143450-01, National Science Foundation 1446675, American Heart Association 15POST25700285, NHLBI R01HL143065, NHLBI R01HL147270, NHLBI R01HL157363, 20TPA35260085, and Department of Defense GRANT12901705 (PR191598).
Conflict of Interest
IU is the owner of Aleksa Tech Inc., a manufacturer of power sources for LED illumination in optical mapping measurements. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Neurophysiology Laboratory, Laboratory for Drug Delivery, and T3 Labs at Georgia Tech for heart donations.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2022.812968/full#supplementary-material
References
- Ahmed Z., Connor J. (1979). Measurement of calcium influx under voltage clamp in molluscan neurones using the metallochromic dye arsenazo III. J. Physiol. 286, 61–82. 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012607 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aistrup G. L., Balke C. W., Wasserstrom J. A. (2011). Arrhythmia triggers in heart failure: the smoking gun of [Ca2+]i dysregulation. Heart Rhythm 8, 1804–1808. 10.1016/j.hrthm.2011.06.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachtel A. D., Gray R. A., Stohlman J. M., Bourgeois E. B., Pollard A. E., Rogers J. M. (2011). A novel approach to dual excitation ratiometric optical mapping of cardiac action potentials with di-4-anepps using pulsed led excitation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 58, 2120–2126. 10.1109/TBME.2011.2148719 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. J., Kosmidis E. K., Vucinic D., Falk C. X., Cohen L. B., Djurisic M., et al. (2005). Imaging brain activity with voltage-and calcium-sensitive dyes. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 25, 245–282. 10.1007/s10571-005-3059-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balijepalli R. C., Kamp T. J. (2008). Caveolae, ion channels and cardiac arrhythmias. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 98, 149–160. 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2009.01.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balijepalli R. C., Kamp T. J. (2011). Cardiomyocyte transverse tubule loss leads the way to heart failure. Future Cardiol. 7, 39–42. 10.2217/fca.10.113 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barone A., Gizzi A., Fenton F., Filippi S., Veneziani A. (2020). Experimental validation of a variational data assimilation procedure for estimating space-dependent cardiac conductivities. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 358, 112615. 10.1016/j.cma.2019.112615 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bedut S., Seminatore-Nole C., Lamamy V., Caignard S., Boutin J. A., Nosjean O., et al. (2016). High-throughput drug profiling with voltage-and calcium-sensitive fluorescent probes in human ipsc-derived cardiomyocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 311, H44–H53. 10.1152/ajpheart.00793.2015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin E. J., Virani S. S., Callaway C. W., Chamberlain A. M., Chang A. R., Cheng S., et al. (2018). Heart disease and stroke statistics-2018 update: a report from the american heart association. Circulation 137, e67–e492. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000573 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry E. M., Fenton F. H. (2008). Visualization of spiral and scroll waves in simulated and experimental cardiac tissue. N. J. Phys. 10, 125016. 10.1088/1367-2630/10/12/125016 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Choi B.-R., Salama G. (2000). Simultaneous maps of optical action potentials and calcium transients in guinea-pig hearts: mechanisms underlying concordant alternans. J. Physiol. 529, 171–188. 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00171.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christoph J., Chebbok M., Richter C., Schröder-Schetelig J., Bittihn P., Stein S., et al. (2018). Electromechanical vortex filaments during cardiac fibrillation. Nature 555, 667–672. 10.1038/nature26001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidenko J. M., Pertsov A. V., Salomonsz R., Baxter W., Jalife J. (1992). Stationary and drifting spiral waves of excitation in isolated cardiac muscle. Nature 355, 349–351. 10.1038/355349a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast V. G., Ideker R. E. (2000). Simultaneous optical mapping of transmembrane potential and intracellular calcium in myocyte cultures. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 11, 547–556. 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2000.tb00008.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flucher B. E., Tuluc P. (2017). How and why are calcium currents curtailed in the skeletal muscle voltage-gated calcium channels? J. Physiol. 595, 1451–1463. 10.1113/JP273423 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gizzi A., Cherry E., Gilmour Jr R. F., Luther S., Filippi S., Fenton F. H. (2013). Effects of pacing site and stimulation history on alternans dynamics and the development of complex spatiotemporal patterns in cardiac tissue. Front. Physiol. 4, 71. 10.3389/fphys.2013.00071 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski P. A., Ceholski D. K., Hajjar R. J. (2015). Altered myocardial calcium cycling and energetics in heart failure–A rational approach for disease treatment. Cell Metab. 21, 183–194. 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.01.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R. A., Pertsov A. M., Jalife J. (1998). Spatial and temporal organization during cardiac fibrillation. Nature 392, 75–78. 10.1038/32164 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groenendaal W., Ortega F. A., Krogh-Madsen T., Christini D. J. (2014). Voltage and calcium dynamics both underlie cellular alternans in cardiac myocytes. Biophys. J. 106, 2222–2232. 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.03.048 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunawan M. G., Sangha S. S., Shafaattalab S., Lin E., Heims-Waldron D. A., Bezzerides V. J., et al. (2021). Drug screening platform using human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived atrial cardiomyocytes and optical mapping. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 10, 68–82. 10.1101/2020.07.14.203232 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herron T. J., Lee P., Jalife J. (2012). Optical imaging of voltage and calcium in cardiac cells & tissues. Circ. Res. 110, 609–623. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.247494 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeker G. S., Katra R. P., Wilson L. D., Plummer B. N., Laurita K. R. (2009). Spontaneous calcium release in tissue from the failing canine heart. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 297, H1235–H1242. 10.1152/ajpheart.01320.2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holcomb M. R., Woods M. C., Uzelac I., Wikswo J. P., Gilligan J. M., Sidorov V. Y. (2009). The potential of dual camera systems for multimodal imaging of cardiac electrophysiology and metabolism. Exp. Biol. Med. 234, 1355–1373. 10.3181/0902-RM-47 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. L., Abate D., Abate K. H., Abay S. M., Abbafati C., Abbasi N., et al. (2018). Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet 392, 1789–1858. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji Y. C., Uzelac I., Otani N., Luther S., Gilmour R. F., Jr., Cherry E. M., et al. (2017). Synchronization as a mechanism for low-energy anti-fibrillation pacing. Heart Rhythm 14, 1254–1262. 10.1016/j.hrthm.2017.05.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly A., Ghouri I. A., Kemi O. J., Bishop M. J., Bernus O., Fenton F. H., et al. (2013). Subepicardial action potential characteristics are a function of depth and activation sequence in isolated rabbit hearts. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 6, 809–817. 10.1161/CIRCEP.113.000334 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurita K. R., Singal A. (2001). Mapping action potentials and calcium transients simultaneously from the intact heart. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 280, H2053–H2060. 10.1152/ajpheart.2001.280.5.H2053 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P., Bollensdorff C., Quinn T. A., Wuskell J. P., Loew L. M., Kohl P. (2011). Single-sensor system for spatially resolved, continuous, and multiparametric optical mapping of cardiac tissue. Heart Rhythm 8, 1482–1491. 10.1016/j.hrthm.2011.03.061 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P., Calvo C. J., Alfonso-Almazán J. M., Quintanilla J. G., Chorro F. J., Yan P., et al. (2017). Low-cost optical mapping systems for panoramic imaging of complex arrhythmias and drug-action in translational heart models. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–14. 10.1038/srep43217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P., Klos M., Bollensdorff C., Hou L., Ewart P., Kamp T. J., et al. (2012a). Simultaneous voltage and calcium mapping of genetically purified human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiac myocyte monolayers. Circ. Res. 110, 1556–1563. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.262535 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P., Taghavi F., Yan P., Ewart P., Ashley E. A., Loew L. M., et al. (2012b). In situ optical mapping of voltage and calcium in the heart. PLoS ONE 7, e42562. 10.1371/journal.pone.0042562 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P., Yan P., Ewart P., Kohl P., Loew L. M., Bollensdorff C. (2012c). Simultaneous measurement and modulation of multiple physiological parameters in the isolated heart using optical techniques. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 464, 403–414. 10.1007/s00424-012-1135-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W., Janardhan A. H., Fedorov V. V., Sha Q., Schuessler R. B., Efimov I. R. (2011). Low-energy multistage atrial defibrillation therapy terminates atrial fibrillation with less energy than a single shock. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 4, 917–925. 10.1161/CIRCEP.111.965830 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loew L. M. (1982). Design and characterization of electrochromic membrane probes. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 6, 243–260. 10.1016/0165-022X(82)90047-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louch W. E., Hake J., Jølle G. F., Mørk H. K., Sjaastad I., Lines G. T., et al. (2010). Control of ca2+ release by action potential configuration in normal and failing murine cardiomyocytes. Biophys. J. 99, 1377–1386. 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.06.055 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Y., Shaik M. A., Kim S. H., Kozberg M. G., Thibodeaux D. N., Zhao H. T., et al. (2016). Wide-field optical mapping of neural activity and brain haemodynamics: considerations and novel approaches. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 371, 20150360. 10.1098/rstb.2015.0360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marina-Breysse M., Garcia-Escolano A., Vila-Garcia J., Reale-Nosei G., Alfonso-Almazán J. M., Yan P., et al. (2021). A complete and low-cost cardiac optical mapping system in translational animal models. Front. Physiol. 12, 696270. 10.3389/fphys.2021.696270 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson M., Carlsson N., Beke-Somfai T., Nordén B. (2012). Spectral properties and orientation of voltage-sensitive dyes in lipid membranes. Langmuir 28, 10808–10817. 10.1021/la301726w [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M., Patlak J., Worley J., Standen N. (1990). Calcium channels, potassium channels, and voltage dependence of arterial smooth muscle tone. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 259, C3–C18. 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.1.C3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nič M., Jirát J., Košata B., Jenkins A., McNaught A. (2009). IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology. IUPAC, Research Triagle Park, NC. [Google Scholar]
- Packer M. (1985). Sudden unexpected death in patients with congestive heart failure: a second frontier. Circulation 72, 681–685. 10.1161/01.CIR.72.4.681 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paredes J., Pollnow S., Dössel O., Salinet J. (2020). “The influence of cardiac ablation on the electrophysiological characterization of rat isolated atrium: preliminary analysis,” in 2020 Computing in Cardiology (Rimini: IEEE; ), 1–4. 10.22489/CinC.2020.265 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pastore J. M., Girouard S. D., Laurita K. R., Akar F. G., Rosenbaum D. S. (1999). Mechanism linking t-wave alternans to the genesis of cardiac fibrillation. Circulation 99, 1385–1394. 10.1161/01.CIR.99.10.1385 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollnow S., Schwaderlapp G., Loewe A., Dössel O. (2020). Monitoring the dynamics of acute radiofrequency ablation lesion formation in thin-walled atria-a simultaneous optical and electrical mapping study. Biomed. Eng. 65, 327–341. 10.1515/bmt-2019-0013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rad M. S., Choi Y., Cohen L. B., Baker B. J., Zhong S., Storace D. A., et al. (2017). Voltage and calcium imaging of brain activity. Biophys. J. 113, 2160–2167. 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.09.040 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scull J. A., McSpadden L. C., Himel H. D., Badie N., Bursac N. (2012). Single-detector simultaneous optical mapping of Vm and [Ca2+]i in cardiac monolayers. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 40, 1006–1017. 10.1007/s10439-011-0478-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiferaw Y., Karma A. (2006). Turing instability mediated by voltage and calcium diffusion in paced cardiac cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 5670–5675. 10.1073/pnas.0511061103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shynkar V. V., Klymchenko A. S., Duportail G., Demchenko A. P., Mély Y. (2004). “Ratiometric fluorescence measurements and imaging of the dipole potential in cell plasma membranes,” in Biophotonics Micro-and Nano-Imaging (Strasbourg: International Society for Optics and Photonics; ), 118–130. 10.1117/12.545768 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sidorov V. Y., Uzelac I., Wikswo J. P. (2011). Regional increase of extracellular potassium leads to electrical instability and reentry occurrence through the spatial heterogeneity of apd restitution. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 301, H209–H220. 10.1152/ajpheart.01141.2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streit J., Kleinlogel S. (2018). Dynamic all-optical drug screening on cardiac voltage-gated ion channels. Sci. Rep. 8, 1–13. 10.1038/s41598-018-19412-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai D. C.-S., Caldwell B. J., LeGrice I. J., Hooks D. A., Pullan A. J., Smaill B. H. (2004). Correction of motion artifact in transmembrane voltage-sensitive fluorescent dye emission in hearts. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 287, H985–H993. 10.1152/ajpheart.00574.2003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomaselli G. F., Zipes D. P. (2004). What causes sudden death in heart failure? Circ. Res. 95, 754–763. 10.1161/01.RES.0000145047.14691.db [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turrini L., Fornetto C., Marchetto G., Müllenbroich M., Tiso N., Vettori A., et al. (2017). Optical mapping of neuronal activity during seizures in zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–12. 10.1038/s41598-017-03087-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzelac I., Crowley C. J., Fenton F. H. (2019). “Isosbestic point in optical mapping theoretical and experimental determination with di-4-anbdqpq transmembrane voltage sensitive dye,” in 2019 Computing in Cardiology Conference (CinC) (Singapore: IEEE; ), 1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzelac I., Fenton F. H. (2015). “Robust framework for quantitative analysis of optical mapping signals without filtering,” in 2015 Computing in Cardiology Conference (CinC) (Nice: IEEE; ), 461–464. 10.1109/CIC.2015.7408686 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Uzelac I., Fenton F. H. (2020). “Personalized low-energy defibrillation through feedback based resynchronization therapy,” in 2020 Computing in Cardiology Conference (CinC) (Rimini: IEEE; ), 1–4. 10.22489/CinC.2020.471 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzelac I., Iravanian S., Ashikaga H., Bhatia N. K., Herndon C., Kaboudian A., et al. (2020). Fatal arrhythmias: Another reason why doctors remain cautious about chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine for treating covid-19. Heart Rhythm. 17, 1445–1451. 10.1016/j.hrthm.2020.05.030 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzelac I., Ji Y. C., Hornung D., Schröder-Scheteling J., Luther S., Gray R. A., et al. (2017). Simultaneous quantification of spatially discordant alternans in voltage and intracellular calcium in langendorff-perfused rabbit hearts and inconsistencies with models of cardiac action potentials and ca transients. Front. Physiol. 8, 819. 10.3389/fphys.2017.00819 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzelac I., Kaboudian A., Iravanian S., Siles-Paredes J. G., Gumbart J. C., Ashikaga H., et al. (2021). Quantifying arrhythmic long qt effects of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin with whole-heart optical mapping and simulations. Heart Rhythm 2, 394–404. 10.1016/j.hroo.2021.06.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Veen R. L., Sterenborg H., Pifferi A., Torricelli A., Cubeddu R. (2004). “Determination of vis-nir absorption coefficients of mammalian fat, with time-and spatially resolved diffuse reflectance and transmission spectroscopy,” in Biomedical Topical Meeting (Miami: Optical Society of America; ), 10.1364/BIO.2004.SF4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam V., Ji N., Wang X., Clark C., Mitchell J. K., Klein M., et al. (2016). Pan-neuronal imaging in roaming caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113, E1082–E1088. 10.1073/pnas.1507109113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrier R. L., Kumar K., Nearing B. D. (2009). Basis for sudden cardiac death prediction by t-wave alternans from an integrative physiology perspective. Heart Rhythm 6, 416–422. 10.1016/j.hrthm.2008.11.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virani S. S., Alonso A., Benjamin E. J., Bittencourt M. S., Callaway C. W., Carson A. P., et al. (2020). Heart disease and stroke statistics-2020 update: a report from the american heart association. Circulation 141, e139–e596. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000757 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. L., Rosenbaum D. S. (2003). Repolarization alternans: implications for the mechanism and prevention of sudden cardiac death. Cardiovasc. Res. 57, 599–614. 10.1016/S0008-6363(02)00737-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M. A., Fenton F. H., Evans S. J., Hastings H. M., Karma A. (2001). Mechanisms for discordant alternans. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 12, 196–206. 10.1046/j.1540-8167.2001.00196.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S.-N., Berggren P.-O. (2006). The role of voltage-gated calcium channels in pancreatic β-cell physiology and pathophysiology. Endocrine Rev. 27, 621–676. 10.1210/er.2005-0888 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon reasonable request.