Abstract
The inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) by cholinergic agents has been promoted as a potent strategy for treating and managing cognitive decline disorders. A wide range of natural products has long been used as potential sources or formulations of cholinergic inhibitors. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate different Rosmarinus officinalis L. (R. officinalis) extracts for their AChE inhibitory activity using galanthamine as a standard AChE inhibitor. In this study, the ethyl-acetate extract (at a concentration of 250 µg/mL) exhibited the greatest inhibitory effect against AChE with significant inhibition of 75%, comparable to the inhibitor galanthamine with an inhibition of 88%. Kinetic analysis revealed that the extracts could induce a mixed type of inhibition, as observed in the case of galanthamine, with the highest increased Km and decreased Vmax values in the ethyl acetate extract. The antioxidant potential of the three extracts tested was found to be in the order of ethyl-acetate > ethanol > aqueous, with IC50 values of 272 µg/mL, 387 µg/mL, and 534 µg/mL, respectively. Ethyl-acetate was found to have the highest total phenolic content in all extracts. Further, in silico study showed structural binding characterization of rosmarinic acid and carnosic acid with human AChE enzyme. Rosmarinic acid showed strong binding and formed two hydrogen-bonding interactions with Ser-293 and Arg-296. In light of this, the ethyl-acetate extract of the plant may provide some novel potential pharmacological leads for treating and managing cognitive disorders such as Alzheimer’s.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, Rosmarinus officinalis, rosemary, acetylcholinesterase, molecular docking, rosmarinic acid, carnosic acid
1. Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder that causes atrophy and brain cells to die—described as a continuous decline in thinking, behavioral, and social activities [1]. AD primarily affects people older than 65 years of age. Globally, about 55 million people are estimated to have dementia in 2020. This number will almost double over the next 20 years, reaching 78 million in 2030 and 139 million in 2050. The majority of the increase will occur in developing countries. Sixty-one percent of people with dementia live in low- and middle-income countries, but by 2050, that number will increase to seventy-one percent. China, India, South Asia, and the western Pacific are experiencing the fastest growth of AD in the elderly population. The prevalence of AD is estimated to increase by many folds in the coming two decades, with 47 million people currently suffering from it worldwide [2]. AD affects about 4 million people in India and approximately 5.8 million people in the United States [3]. There are approximately 50 million people worldwide with dementia, between 60% and 70% of whom are estimated to have AD [3].
In the current state of research, there is no permanent cure for AD or method to alter the mental process [1]. In addition, as the disease progresses, the brain may suffer from severe complications such as dehydration, malnutrition, or infection that may cause death. To mitigate these symptoms, some medications may temporarily help patients to maintain independence for a limited time [1].
In addition to the protein tau, the accumulation of the protein amyloid plays a significant role in AD development. However, the AD diagnosis is made when a person’s cognitive functioning has declined sufficiently to meet dementia criteria [4]. However, AD is diagnosed when a person has sufficient cognitive decline to meet the criteria for dementia. One of the major reasons for the cognitive decline in AD is the degenerating cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain and the related cholinergic neurotransmission loss in the cerebral cortex and other parts of the brain. Due to sufficient evidence for the deficit cholinergic neurotransmission in AD, the most promising approach promoted for AD treatment includes enhancing acetylcholine (ACh) levels in the brain [5]. Several strategies are used to improve cholinergic neurotransmission [6,7]. Among them, the most successful approach used so far is the cholinergic hypothesis [5]. Cholinergic receptors are stimulated for the enhancement of acetylcholine or to improve ACh’s ability to access the neuronal synaptic cleft by inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) induced ACh hydrolysis through the use of AChE inhibitors (AChEIs) [8,9]. The acetylcholine-hydrolyzing enzyme AChE is located in nerve tissues and is involved in the termination of nerve impulse transmission by catalyzing the hydrolysis of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine [10]. AChEIs have been shown to promote an increased concentration of ACh and enhance the duration of ACh action at the synapse [11]. Therefore, cholinesterase inhibitors are considered one of the effective medications for the symptomatic treatment of AD [12]. In this context, Tacrine, donepezil, and rivastigmine are a few AChE inhibitors approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) [13].
As a result, therapeutic strategies for AD treatment were mainly focused on AChEIs, which led to various synthetic anti-AD drugs such as Galanthamine, Tacrine, Donepezil, etc. However, these drugs were found to have many restrictions due to their shorter half-lives and adverse side effects such as vomiting, nausea, anorexia, and fatigue, with some even exhibiting hepatotoxicity [14,15]. Therefore, scientists worldwide have been exploring alternative strategies to manage this age-related disease, including using herbal medicines as efficient anti-AD drugs or scaffold molecules. [16,17,18]. The probability of decreasing the AD-induced brain degeneration with natural treatments has made this popular and has drawn scientists’ awareness. More importantly, most synthetic anticholinesterase drugs have originated from plant-based molecules, including major bioactive substances such as indole, steroids, alkaloids, glycosides, coumarins, phenylpropanoids, and terpenoids [10].
Rosmarinus officinalis (family Lamiaceae), commonly known as rosemary, is one of the most popular perennial culinary herbs cultivated worldwide [19,20]. Fresh and dried rosemary leaves have been used in food preparation and herbal teas for their characteristic aroma. As a natural antioxidant, rosemary extracts are routinely used as a preservation agent in perishable foods [21,22]. As a natural antioxidant, the European Union has approved rosemary extract (E392) for food preservation. It is also used in traditional medicine in many countries, growing wild even outside its native Mediterranean. Aside from its antibacterial, anticancer, anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory, antinociceptive, antioxidant, and antithrombotic properties, rosemary has been shown to effectively treat cognitive deficiency, reduce thirst, and improve hepatic function [23,24,25,26,27]. R. officinalis oils serve as natural components in perfumes, foods, and pharmaceuticals. Furthermore, at the folklore level, rosemary has been actively used for memory enhancement as well as reducing age-related memory loss in humans [28,29,30]. However, scientific data regarding its ability to inhibit anticholinesterase activity are entirely lacking. Therefore, considering the alarming increase in AD, this perennial culinary herb was evaluated for anticholinesterase activity.
2. Results
2.1. Functional Group Determination and Total Phenolic Content of the R. officinalis Extracts
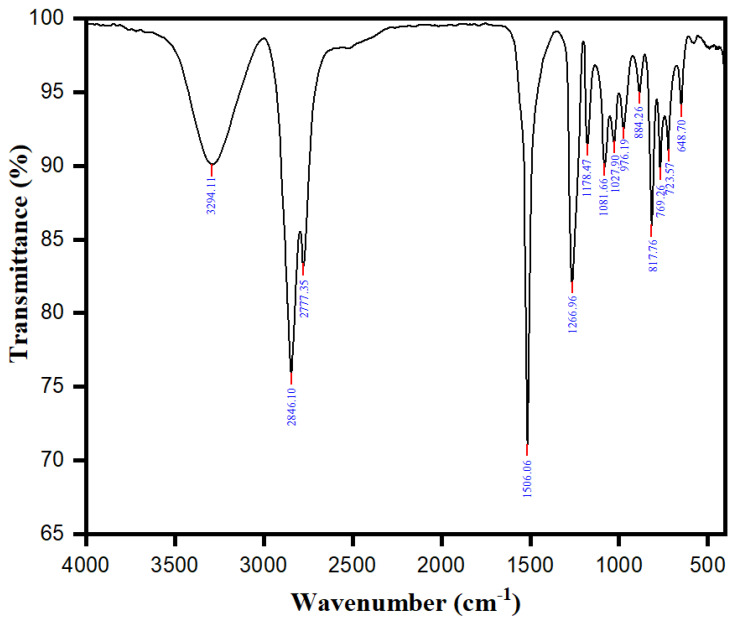
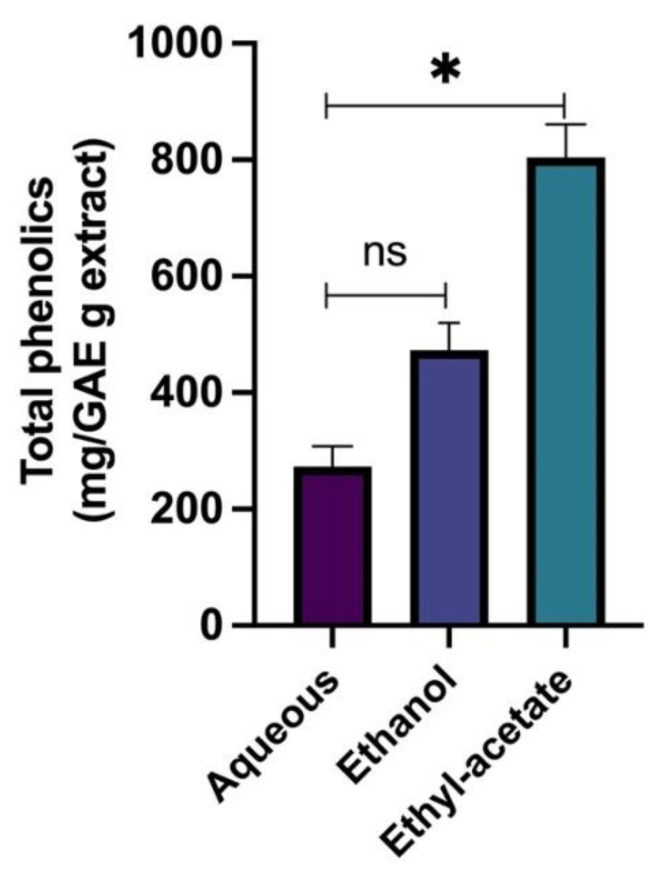
One of the most commonly used techniques for distinguishing functional groups is Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. The FTIR spectra (in the range of 400–4000 cm−1) and the characteristic bands observed in the Rosmarinus officinalis leaf extract are shown in Figure 1 and supplementary Table S1, respectively. The main bands found for the total R. officinalis extracts are assigned to the presence of hydroxyl group (O-H), carboxylic group (COOH), carbonyl group (C=O), (C-H), and (C=C), whose corresponding peak values are presented in supplementary Table S1. All these characteristics correspond to various flavonoids and phenolic compounds present in the R. officinalis extracts (Figure 2). The principal bioactive constituents of rosemary leaves are rosmarinic acid and carnosic acid, which have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic properties. The other major chemical constituents in the R. officinalis extract included flavonoids, terpenoids, and common organic acids (Figure 2). The total phenolic content of various extracts of R. officinalis was estimated by the Folin–Ciocalteu method and was represented as gallic acid equivalents (GAE/g extract). Among them, a significant amount of phenolic content of 804 GAE/g extracts was found in ethyl-acetate extract (EtOAc; p = 0.0149) followed by ethanolic (473 GAE/g) and aqueous (273 GAE/g), as shown in Figure 3. Data are the mean of the results obtained from three separate measurements with their standard deviations as error bars.
Figure 1.
FTIR spectra of R. officinalis extract.
Figure 2.
Major chemical constituents present in the R. officinalis extract.
Figure 3.
Total phenolic content of different extracts of R. officinalis. Data represent the mean of the results obtained from three independent measurements with their standard deviations as error bars. Data were analyzed using t-test and one-way ANOVA. * Indicates significance at p < 0.05 when compared to the aqueous (p value = 0.0149), ns indicates not significant (p value = 0.0606).
2.2. Free Radical Scavenging Potential of the Rosemarinus Officinalis Extracts
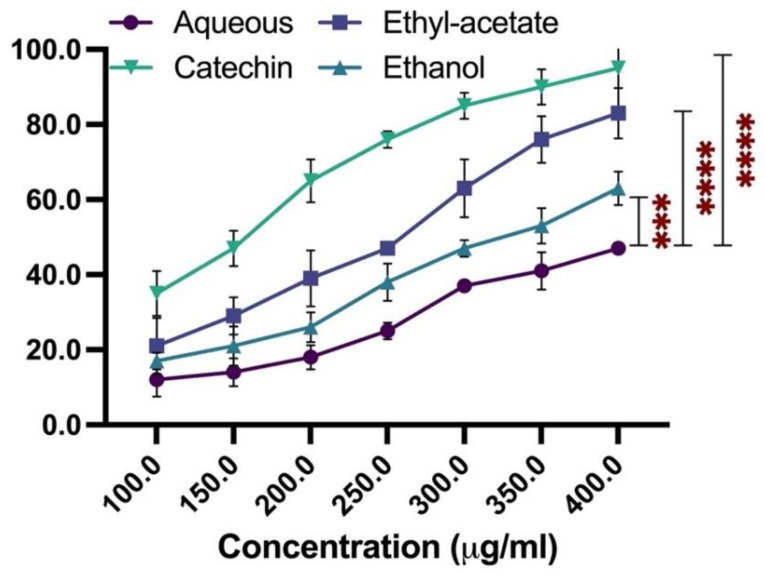
The extracts’ antioxidant activity was determined using DPPH assay in which various concentrations of the R. officinalis extract were added to DPPH. Further, the amount of left out DPPH was estimated at 30 min by measuring absorbance at 520 nm. Next, DPPH scavenging activity was calculated for each plant extract concentration using the absorbance data accumulated and % inhibition of DPPH scavenging. Following this, IC50 values were determined for DPPH free radical scavenging as the plant extract concentration with an ability to bring 50% of the original activity. It was found that the (EtOAc) exhibited the most significant antioxidant activity, with an IC50 value of 272 µg/mL (p = 0.001), followed by ethanolic (p = 0.006) and aqueous extracts (p =0.006) with IC50 values of 387 and 534 µg/mL, respectively. For the standard inhibitor catechin, the IC50 value was found to be 173 µg/mL (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
DPPH radical scavenging activity of the extracts of R. officinalis. Catechin was used as a positive control. The presented data represent the mean of three independent measurements with an average 5–7% error. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA *** and **** indicate significance at p < 0.05 when compared to aqueous with p values 0.006 and 0.001, respectively.
As expected, the observed antioxidant activity of the extracts exhibited a strong correlation with their total phenolic content, as EtOAc, with the highest TPC, showed the most significant antioxidant activity. The cytotoxic effect of ethyl-acetate extract on MCF-7 cells was evaluated using MTT assay and is shown in supplementary Figure S1.
2.3. Inhibition of Acetylcholinesterase by the Extracts
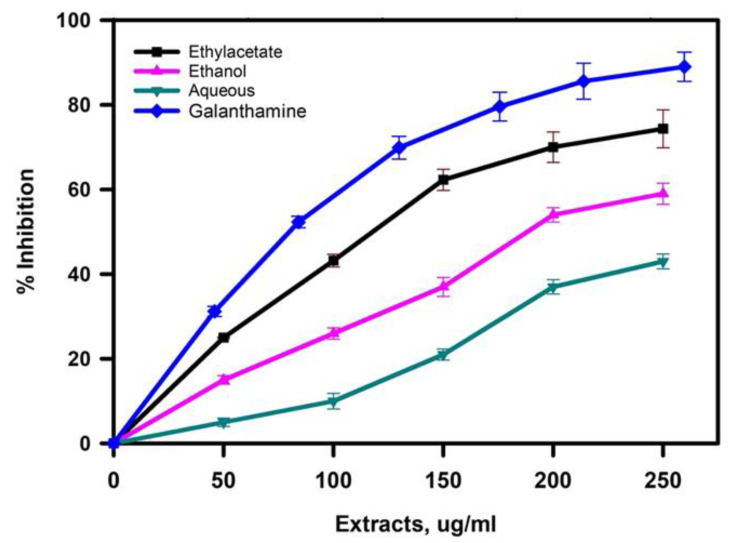
Extracts of R. officinalis were evaluated for AChE inhibitory by using modified Ellman’s method. Figure 5 and Table 1 represent the percentage inhibition of AChE activity by different concentrations of the R. officinalis extracts and each extract’s IC50 values. For the positive control, galanthamine, a standard AChE inhibitor, was used and exhibited an IC50 value of 4.73 ± 0.13 µg/mL. IC50 values were lowest for ethyl-acetate extract followed by ethanolic and aqueous extract with respective values of 101.23, 202.34, and 247 µg/mL. Interestingly, the antioxidant activity of the extracts with their phenolic content was also observed in the same manner. Further, the free radical scavenging ability, i.e., ethyl-acetate’s antioxidant activity, was highest, followed by ethanolic and aqueous extracts, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 5.
Acetylcholinesterase inhibition potential of extracts of R. officinalis. Results presented are the mean of three independent measurements.
Table 1.
IC50 values of DPPH free radical scavenging activity and acetylcholinesterase inhibition by R. officinalis.
| Extract | DPPH Activity (µg/mL) | p Value **** | Anti-Cholinesterase Activity (µg/mL) | p Value **** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catechin | 173 ± 8 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |
| Galanthamine | 0.0001 | 4.73 ± 0.13 | 0.0001 | |
| Ethyl-acetate | 272 ± 7 | 0.0001 | 101.2 ± 5.5 | 0.0001 |
| Ethanol | 387 ± 11 | 0.0001 | 202.3 ± 8.7 | 0.0001 |
| Aqueous | 584 ± 8 | 247 ± 12 |
**** indicate significant when p value <0.05.
2.4. Kinetics of AChE Inhibition Observed by the R. officinalis Extracts
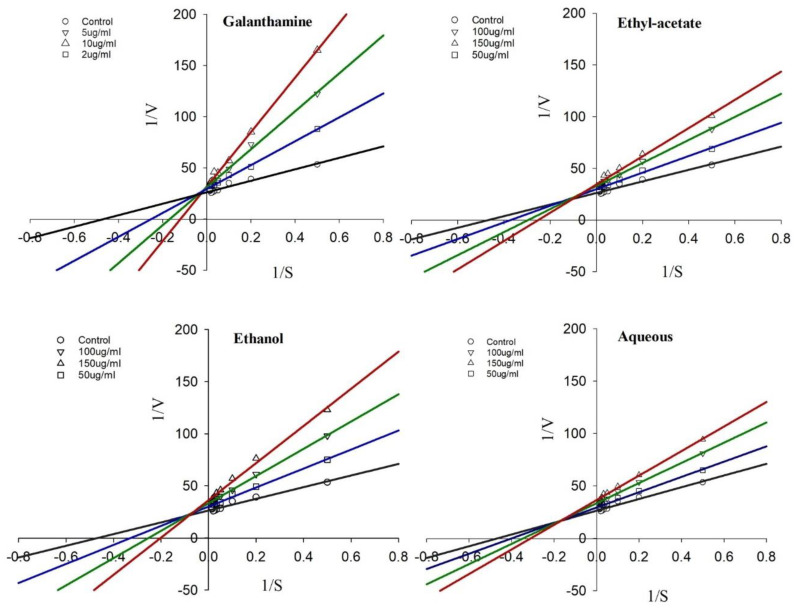
The lack of data on AChE inhibition kinetics by medicinal plant extracts has been observed in traditional therapeutic systems. However, very few studies carried out in this direction have shown that medicinal plant extracts may show enzyme inhibition kinetics close to reported synthetic AChEIs. In this context, AChE enzyme inhibition kinetics of R. officinalis extracts, reported for the first time in this study, were determined from Lineweaver–Burk plots (Figure 6). Kinetic parameters Km and Vmax from the inhibition kinetic curves were determined from the plotted graph’s trend line equations. The kinetic parameter values obtained at each concentration of the extracts have been summarized in Table 2. The extracts exhibited a mixed type of inhibition, as indicated by the intersection of trend lines with each other on the left side above the X-axis of the kinetic plot (Figure 6).
Figure 6.
Kinetics of acetylcholinesterase inhibition by R. officinalis. Lineweaver–Burk plot of inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by different extracts of R. officinalis. Representative data are the average of 3 independent measurements.
Table 2.
Kinetic parameters of acetylcholinesterase inhibition by extracts of R. officinalis.
| Inhibitor | Concentration (µM; µg/mL) |
Km (µM) | V max |
|---|---|---|---|
| Galanthamine | 0 | 2.14 ± 0.13 | 0.38 ± 0.09 |
| 2 | 5.47 ± 0.17 | 0.29 ± 0.06 | |
| 5 | 9.76 ± 0.25 | 0.21 ± 0.07 | |
| 10 | 17.38 ± 0.33 | 0.15 ± 0.05 | |
| Ethyl-acetate | 50 | 4.21 ± 0.28 | 0.32 ± 0.08 |
| 100 | 7.19 ± 0.41 | 0.28 ± 0.10 | |
| 150 | 8.28 ± 0.63 | 0.23 ± 0.08 | |
| Ethanol | 50 | 3.05 ± 0.21 | 0.35 ± 0.05 |
| 100 | 4.65 ± 0.12 | 0.30 ± 0.06 | |
| 150 | 6.24 ± 0.53 | 0.28 ± 0.08 | |
| Aqueous | 50 | 2.50 ± 0.09 | 0.34 ± 0.09 |
| 100 | 3.67 ± 0.11 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | |
| 150 | 4.22 ± 0.29 | 0.27 ± 0.07 |
2.5. Molecular Docking of Rosmarinic Acid and Carnosic Acid with Human AChE
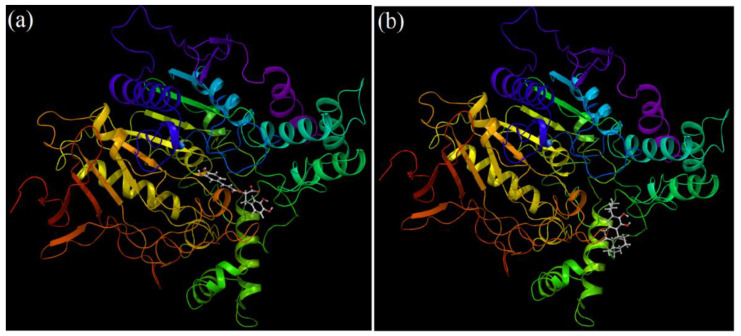
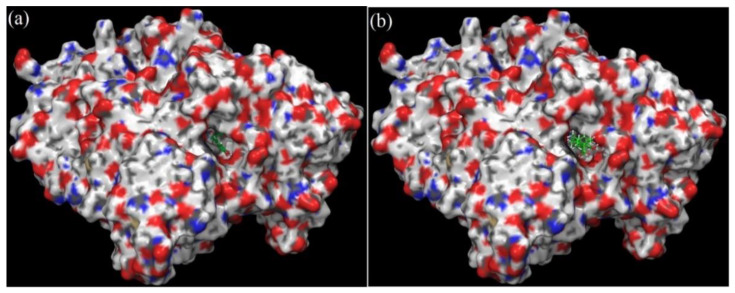
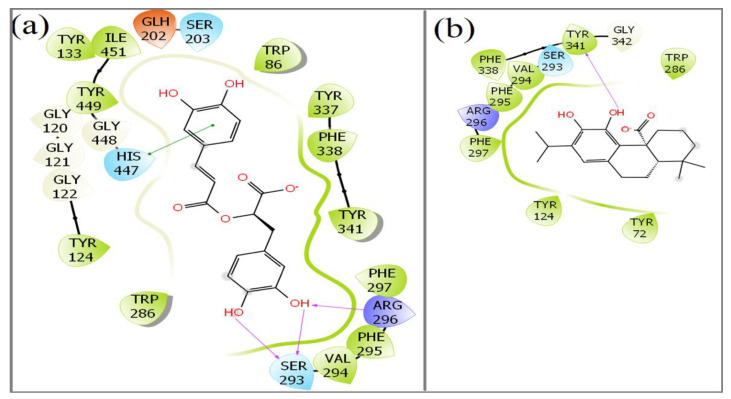
Both the compounds docked stably into the ligand pocket of the human AChE enzyme (Figure 7). The surface representation of docking complexes of both the ligands with AChE is shown in Figure 8. The observed docking scores for rosmarinic acid and carnosic acid are −8.25 and −5.10, respectively. Rosmarinic acid formed two hydrogen-bonding interactions with Ser-293. Moreover, additional hydrogen bond interaction was observed with Arg-296. Furthermore, one π–π interaction was also displayed by His-477 with rosmarinic acid (Figure 9a). On the contrary, carnosic acid showed only one hydrogen interaction with Try-341 (Figure 9b). Rosmarinus officinalis ethyl-acetate leaf extract contains different significant phenolic compounds, including rosmarinic acid and carnosic acid, which were also confirmed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis as shown in Figure S2. The other major components identified were carnosol, methyl carnosate, rosmanol, genkwanin, camphene, borneol acetate, tricyclene, linalool, alpha-terpineol, and bornyl acetate.
Figure 7.
Docking complex of cholinesterase with (a) rosmarinic acid and (b) carnosic acid.
Figure 8.
Surface structure of cholinesterase with (a) rosmarinic acid and (b) carnosic acid.
Figure 9.
Interaction of amino acid residues of acetylcholinesterase with (a) rosmarinic acid and (b) carnosic acid.
3. Discussion
Sufficient shreds of evidence for deficit cholinergic neurotransmission in AD have promoted therapies designed to reverse this cholinergic deficit, mainly based on employing the AChEIs to inhibit AChE. AChEIs are considered one of the most effective medications used for the symptomatic treatment of AD by increasing cholinergic neurotransmission with moderate and short-lived but promising therapeutic effects [31,32]. These have been found to increase the concentration of Ach and prolong the duration of Ach action at the synapse. In addition, these AChE inhibitors exhibit antioxidant activity and modulate amyloid-β plaque formation. The FDA has approved a few AChE inhibitors, such as Tacrine, donepezil, and rivastigmine [33]. However, most of these inhibitors are associated with acute toxicity and low availability. Due to these reasons, there is still a need to explore and identify new AChEIs with reduced toxicity and high availability with enhanced penetrance to the nervous systems. In this context, natural sources, mainly plants, have been investigated to identify new AChEIs, and many plant-derived compounds have been identified as AChEIs with potential for AD treatment [24,34]. Traditional medicinal systems for the treatment of nervous and aging disorders have documented many useful medicinal plants. Further, organic solvent extracts of R. officinalis were prepared and assessed for their antioxidant and anticholinesterase activities.
Previous studies reported that antioxidant activity of different plants is mainly due to the presence of the phenolic compounds [35,36]. Since oxidative stress plays an essential role in AD, these phenolic compounds have been promoted as effective therapeutic agents for this disease. Therefore, our extracts showed higher phenolic content, as expected. The free radical scavenging potential of the R. officinalis extracts results infers that the potent antioxidant potential of the (EtOAc) of R. officinalis may be attributed to the plants’ phenolic compounds, including flavonoids, aromatic compounds, and tannins. Literature studies have shown that polyphenols can inhibit AChE, and most of the AChEIs have been derived from phenolic compounds [37]. However, other non-alkaloid compounds such as terpenoids, sterols, flavonoids, etc. cannot be ruled out, as several non-alkaloid AChEIs have also been reported [38,39]. As reported by other studies, the present results also imply that the R. officinalis extracts’ antioxidant activity could be due to the synergistic effects of different phenolic compounds depending on the concentration and structural chemistry of the phenolic compounds.
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and antioxidant activity studies of R. officinalis strongly indicate that the extract with the most increased antioxidant activity exhibited the highest AChE inhibitory activity. The analysis of results suggests that, probably, higher phenolic content of ethyl-acetate extract might be responsible for its most elevated AChE and antioxidant activity. Further, the kinetics of AChE inhibition in R. officinalis extract showed a mixed type of inhibition. As reported by other studies, the mixed type of inhibition by the extracts may be due to the binding of active molecules present in the extracts to the free enzyme of the enzyme-substrate complex at a site different from that of the substrate-binding site. Probably, this allosteric site has been observed to the peripheral anionic site (PAS). PAS has been reported at the gorge of the active site channel of AChE and has been shown to sequester acetylcholine, the natural substrate of AChE, during cholinergic transmission. Results obtained in our studies conform to other AChE inhibition studies wherein binding of inhibitor ligands has been shown to occur at PAS, which leads to some conformational change in the enzyme at its active site. Some studies have shown that the PAS blockage due to steric hindrances by the binding ligands has also been observed as a major factor responsible for AChE inhibition by the inhibitors. Altogether, as per the results obtained in inhibition kinetics of AChE, it can be expected that the inhibition of AChE by R. officinalis extracts might probably be due to their ability to bind PAS or the steric hindrance phenomenon, as observed in other earlier studies. Either of these two reasons cannot be excluded and may likely involve both mutually. In addition, the concentration-dependent inhibition kinetics of AChE in the presence of R. officinalis extracts is consistent with those observed in pure compound inhibitors [40]. Our results for galanthamine as a mixed inhibitor are uncommon, as it has been normally shown to be a competitive inhibitor. However, some other studies have shown it to be a mixed-type inhibitor [41]. The differences in experimental methodology may be responsible for this unusual behavior of galanthamine. AChE inhibition kinetic results indicated a putative mechanism by which the plant extracts can likely be used as an innovative therapeutic for cognitive decline disorders such as Alzheimer’s. The phytotherapeutic approach’s significant benefits are the vast scope of medicinal properties that each extract exhibits, whereas the inhibitor compounds are usually intended to act on a single target.
The phytochemical profile of R. officinalis extract reported many polyphenolic and flavonoid compounds. Among the polyphenolic compounds, rosmarinic acid and carnosic acid are essential constituents of R. officinalis [42]. Polyphenol compounds from many plant extracts are well known for anticholinesterase activity [43]. Carnosic acid and its major oxidized derivative, carnosol, protect lipids from oxidation in vitro, as determined by high-performance liquid chromatography–ultraviolet and luminescence imaging. Both compounds protected linolenic acid and monogalactosyldiacylglycerol from the effects of singlet oxygen and hydroxyl radicals [44]. Thus, phenolic diterpenes carnosol is one of the significant compounds found in R. officinalis extract and is well-known for its antioxidant properties [45]. Additionally, the R. officinalis extract contains some highly oxidized diterpenes such as rosmanol, isorosmanol, and dimethyl isorosmanol, formed from carnosic acid via enzymatic dehydrogenation and the action of activated oxygen [46]. Rosmarinic acid and carnosic acid were selected for the molecular docking analysis as these compounds are reported for their anticholinesterase activity and anti-neuropathic effects [47,48,49]. Our in silico structural binding studies suggest that both compounds have the potential to inhibit AChE activity with calculated dock scores along with AChE amino acid residue interactions, indicating that the rosmarinic acid seems to have higher inhibiting potential than carnosic acid.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
Acetylcholinesterase, DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl), ascorbic acid, and BHT (Butylated hydroxytoluene) were obtained from Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA. Chemicals used, such as sodium carbonate, hydrochloric acid, etc., were of analytical grade, and organic solvents such as ethanol and ethyl-acetate used for extraction were purchased from Merck Life Sciences, Bengaluru, India.
4.2. Collection of Plant Material and Preparation of Extract
R. officinalis plant was collected from Botanical Garden, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India and was authenticated at the Department of Botany, University of Kashmir. After drying the collected plant material in the shade at a temperature of 30 ± 2 °C, it was crushed in a blender, and the powdered material was filtered by using a sieve of about 0.3 mm aperture size. The powdered material was extracted with the organic solvents ethyl-acetate, ethanol, and water for 48 h by using a Soxhlet extractor. The extracted material was concentrated and was stored at −80 °C for future use.
4.3. Estimation of Total Phenolic Content of the Prepared Rosmarinus Officinalis L. Extracts
For this, the Folin–Ciocalteu method was used, in which an extract sample volume of 1 mL was mixed with 2 mL of Folin–Ciocalteu, and both were kept together at 30 °C for 15–20 min in the dark. Following this, sodium carbonate 5 mL was mixed to the extract solution and incubated for 2 h. Finally, the absorbance was measured with a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 745 nm. For estimation of the content, a standard calibration curve was prepared by using the standard gallic acid in the concentration range of 0.02–0.15 mg/mL, and measurements were recorded as mg gallic acid equivalent (GAE) per gram of the extracted sample.
4.4. Measurement of DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
DPPH scavenging activity was measured by the modified method of Braca et al. [50]. Different concentrations (100–400) of the respective plant extract sample were mixed with DPPH and were vortexed. After proper mixing, the solutions were kept in the dark for 30 min at room temperature, and following this, the absorbance of the solution was measured at 520 nm. BHT was used as a standard (1.5 mg/mL). Percentage inhibition of the antioxidant activity was calculated by using Equation (1), and the values obtained were used for calculation of IC50 value, i.e., required concentration of extract sample for scavenging of 50% DPPH free radicals.
| % inhibition = [(Ac−Ae)/Ac] × 100 | (1) |
where Ac and Ae are absorbances of the solutions without extract sample and in the presence of catechins or the plant extracts, respectively.
4.5. Cell Culture and Cell-Viability Assay
Breast cancer cells (MCF-7) were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (HyClone Laboratories, Logan, UT, USA) and 1% penicillin: streptomycin (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) by incubation at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 in 100 mm plates. The cells were seeded in 96-well plates for the cell viability assay at a density of 5 × 105 cells per well. After the cells had adhered to the plate, the growth medium was replaced with fresh media, and the cells were cultured for 24 h with different concentrations of ethyl-acetate extract ranging from 0 to 250 ug/mL. For the control, PBS was used. Further, the cells were washed with PBS and treated with 50 μL of 5 mg/mL 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) solution and incubated for 3 h at 37 °C to form the formazan crystals. After incubation, the media were removed from the cells. The cells were washed twice with PBS MTT formazan crystals, dissolved in 200 uL of DMSO, and mixed for 10 min to dissolve them completely. After that, absorbance was measured at 570 nm. The average number of live cells was calculated, and the experiments were performed in triplicate. The percentage of viable cells was estimated using the following formula.
| (2) |
4.6. Determination of AChE Enzyme Activity
The AChE enzyme activity was initiated via the modified method of Ellman [51]. In this procedure, 125 μL of AChE enzyme was added to a reaction mixture of 3 mL consisting of 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 7.3, with or without plant extract sample. After thorough mixing, the mixtures were incubated with each other for 15 min at room temperature. For initiating the reaction, 100 μL of 1 mM DTNB and 250 μL of 3.5 mM acetyl-thiocholine iodide were mixed. The reaction mixture was kept for 20 min and, following this, absorbance measurements were carried out at 412 nm in a UV/Vis Spectrophotometer. For control experiments, the enzyme was added after the addition of DTNB in the mixture. For positive control, galanthamine was used. All experiments were carried out in triplicate along with their respective controls. Percentage inhibition of the AChE activity was calculated using Equation (1) and the values obtained for calculating IC50 value.
4.7. Estimation of Inhibition Kinetic Parameters
To check the kind of inhibition exhibited by the plant extracts, the enzyme activity in the presence of extracted samples was measured in different concentrations of the substrate acetyl-thiocholine iodide (1–100 μM). The reaction mixtures were prepared by adding 125 μL of AChE enzyme combined with 0.05 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.3) and plant extract sample (in the concentration range of 50–150 µg/mL). For initiating the reaction, different concentrations of the substrate acetyl-thiocholine iodide with a concentration range of 1 to 100 μM were added, and the reaction was followed for 10 min. The kinetic curve obtained was evaluated for the determination of initial velocity as the slope of the curve. Lineweaver–Burk plots were made from the inhibition assays, and these plots’ Km and Vmax values were determined for each extract concentration [52].
4.8. Induced Fit Docking
Molecular docking of rosmarinic acid and carnosic acid with human AChE was performed. The docking simulation studies of these compounds were performed using Schrodinger 2017-4 suite. The Protein Data Bank (PDB) (http://www.rcsb.org/, access on 20 July 2020) was searched, and the three-dimensional structure of human AChE (PDB code: 6o52), having a resolution of 3.20 Å, was downloaded. The retrieved system was subjected to optimization and energy minimization using Schrodinger’s protein preparation wizard workflow. Further, the missing loops and side chains were also built. Similarly, ligand molecules were also prepared before performing the docking experiment. The two abovementioned ligands’ structures were drawn and converted to a three-dimensional structure using Maestro 11.4 (Maestro, version 11.4, Schrodinger, LLC, New York, NY, USA, 2017). LigPrep, version 3.1 (Schrodinger, LLC, New York, NY, USA, 2017) was applied for ligand preparation. The above-prepared protein and ligand molecules were subjected to Glide S.P. docking. The methodology is reported in detail [53,54].
4.9. Statistical Analysis
The data are presented as the mean and standard error of (S.E.M.) using GraphPad Prism 9.0 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA). The one-way ANOVA technique was used to test whether the mean of the control group and the mean of all samples with one variable were significantly different. Multiple groups with two independent variables were analyzed using two-way ANOVA. An unpaired t-test was used to compare the means of only two groups. A p-value less than 0.05 was regarded as statistically significant.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the anticholinesterase activity of all the extracts, particularly ethyl-acetate, of R. officinalis validate their use in the traditional medicinal system for cognitive disorders such as Alzheimer’s. In addition, the potential anti-Alzheimer activity of the EtOAc of the plant highly warrants its future investigation to identify the active constituent molecules and assess their activity and safety under in vivo models. Further, R. officinalis extract contains many important chemical molecules such as rosemarnic acid and carnosic acid. In silico studies showed rosmarinic acid could interact with AChE amino acid residue and thus possess anticholinesterase activity. Therefore, the results of this study reinforce the potential therapeutic benefits of Rosemarinus officinalis. Further research and clinical trials are necessary to validate these findings and thereby uncover more evidence of its pharmacological effects.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the DSR, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah for technical and financial support.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/plants11040514/s1, Supplementary Figure S1: Cytotoxicity of R. officinalis ethylacetate in MCF-7 cells; Supplementary Figure S2: HPLC high performance liquid chromatography of R. officinalis leaf ethyl acetate showing the peaks of the major components; Supplementary Table S1: FTIR spectra of R. officinalis L extract showing characteristic peaks and corresponding functional groups.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.R.K.; Data curation, M.R.K. and J.S.M.S.; Formal analysis, A.A.M.S., M.R.K. and I.A.R.; Methodology, A.A.M.S. and M.R.K.; Project administration, M.R.K. and J.S.M.S.; Supervision, M.R.K.; Validation, A.A.M.S. and M.R.K., Visualization, J.S.M.S. and M.R.K.; Writing—original draft, M.R.K. and I.A.R.; Writing—review and editing, M.R.K. and I.A.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, under grant No. (D-264-130-1440). The authors, therefore, gratefully acknowledge the DSR technical and financial support.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article and supplementary material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. This research did not involve any animal and/or human participant.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.NIH Alzheimer’s Disease Fact Sheet. [(accessed on 16 October 2021)];2021 July 8; Available online: https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/alzheimers-disease-fact-sheet.
- 2.Prince M., Bryce R., Albanese E., Wimo A., Ribeiro W., Ferri C.P. The global prevalence of dementia: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9:63–75. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2012.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Matthews K.A., Xu W., Gaglioti A.H., Holt J.B., Croft J.B., Mack D., McGuire L.C. Racial and ethnic estimates of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias in the United States (2015–2060) in adults aged ≥65 years. Alzheimers Dement. 2019;1:17–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.06.3063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Howes M.J.R., Perry E. The Role of Phytochemicals in the Treatment and Prevention of Dementia. Drug Aging. 2011;28:439–468. doi: 10.2165/11591310-000000000-00000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yiannopoulou K.G., Papageorgiou S.G. Current and Future Treatments in Alzheimer Disease: An Update. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2020;29:12. doi: 10.1177/1179573520907397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Geula C., Darvesh S. Butyrylcholinesterase, cholinergic neurotransmission and the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Drugs Today. 2004;40:711–721. doi: 10.1358/dot.2004.40.8.850473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Perry E., Walker M., Grace J., Perry R. Acetylcholine in mind: A neurotransmitter correlate of consciousness? Trends Neurosci. 1999;22:273–280. doi: 10.1016/S0166-2236(98)01361-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Schneider L.S. A critical review of cholinesterase inhibitors as a treatment modality in Alzheimer’s disease. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2000;2:111–128. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2000.2.2/lschneider. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Giacobini E. Cholinesterase inhibitors stabilize Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000;920:321–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06942.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mukherjee P.K., Kumar V., Houghton P.J. Screening of Indian medicinal plants for acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity. Phytother. Res. 2007;21:1142–1145. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rollinger J.M., Schuster D., Baier E., Ellmerer E.P., Langer T., Stuppner H. Taspine: Bioactivity-guided isolation and molecular ligand-target insight of a potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor from Magnolia x soulangiana. J. Nat. Prod. 2006;69:1341–1346. doi: 10.1021/np060268p. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Konstantina G.Y., Sokratis G.P. Current and future treatments for Alzheimer’s disease. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2013;61:19–33. doi: 10.1177/1756285612461679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mehta M., Adem A., Sabbagh M. New Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors for Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012;2012:1–8. doi: 10.1155/2012/728983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Akhondzadeh S., Abbasi S.H. Herbal medicine in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Alzheimers Dis. Other Dement. 2006;21:113–118. doi: 10.1177/153331750602100211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mayeux R., Sano M. Treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999;341:1670–1679. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199911253412207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Singh M., Kaur M., Kukreja H., Chugh R., Silakari O., Singh D. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors as Alzheimer therapy: From nerve toxins to neuroprotection. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013;70:165–188. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.09.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tian J., Shi J., Zhang X., Wang Y. Herbal therapy: A new pathway for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2010;2:30. doi: 10.1186/alzrt54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li-Min F., Ju-Tzu L. A Systematic Review of Single Chinese Herbs for Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011;2011:640284. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nep136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.González-Minero F.J., Bravo-Díaz L., Ayala-Gómez A. Rosmarinus officinalis L. (Rosemary): An Ancient Plant with Uses in Personal Healthcare and Cosmetics. Cosmetics. 2020;7:77. doi: 10.3390/cosmetics7040077. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ribeiro-Santos R., Carvalho-Costa D., Cavaleiro C., Costa H.S., Albuquerque T.G., Castilho M.C., Ramos F., Melo N.R., Sanches-Silva A. A novel insight on an ancient aromatic plant: The rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015;45:355–368. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2015.07.015. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Amaral G.P., Mizdal C.R., Stefanello S.T., Mendez A.S.L., Puntel R.L., de Campos M.M.A., Soares F.A.A., Fachinetto R. Antibacterial and antioxidant effects of Rosmarinus officinalis L. extract and its fractions. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2018;9:383–392. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2017.10.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rašković A., Milanović I., Pavlović N., Ćebović T., Vukmirović S., Mikov M. Antioxidant activity of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) essential oil and its hepatoprotective potential. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014;14:225. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wang W., Li N., Luo M., Zu Y., Efferth T. Antibacterial activity and anticancer activity of Rosmarinus officinalis L. essential oil compared to that of its main components. Molecules. 2012;17:2704–2713. doi: 10.3390/molecules17032704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Allegra A., Tonacci A., Pioggia G., Musolino C., Gangemi S. Anticancer Activity of Rosmarinus officinalis L.: Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Potentials. Nutrients. 2020;12:1739. doi: 10.3390/nu12061739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bao T.Q., Li Y., Qu C., Zheng Z.G., Yang H., Li P. Antidiabetic Effects and Mechanisms of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) and its Phenolic Components. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020;48:1353–1368. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X20500664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar M., Amin B., Mehri S., Mirnajafi-Zadeh S.J., Hosseinzadeh H. Anti-inflammatory effects of ethanolic extract of Rosmarinus officinalis L. and rosmarinic acid in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017;86:441–449. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gutiérrez R., Alvarado J.L., Presno M., Pérez-Veyna O., Serrano C.J., Yahuaca P. Oxidative stress modulation by Rosmarinus officinalis in CCl4-induced liver cirrhosis. Phytother. Res. 2010;4:595–601. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Singhal A.K., Naithani V., Bangar O.P. Medicinal plants with a potential to treat Alzheimer and associated symptoms. Int. J. Nutr. Pharmacol. Neurol. Dis. 2012;2:84–91. doi: 10.4103/2231-0738.95927. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Habtemariam S. Natural products in Alzheimer’s disease therapy: Would old therapeutic approaches fix the broken promise of modern medicines? Molecules. 2019;24:1519. doi: 10.3390/molecules24081519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ozarowski M., Mikolajczak P.L., Bogacz A., Gryszczynska A., Kujawska M., Jodynis-Liebert J., Piasecka A., Napieczynska H., Szulc M., Kujawski R., et al. Rosmarinus officinalis L. leaf extract improves memory impairment and affects acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activities in rat brain. Fitoterapia. 2013;91:261–271. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2013.09.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sharma K. Cholinesterase inhibitors as Alzheimer’s therapeutics (Review) Mol. Med. Rep. 2019;20:1479–1487. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lane R.M., Kivipelto M., Greig N.H. Acetylcholinesterase and its inhibition in Alzheimer disease. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2004;27:141–149. doi: 10.1097/00002826-200405000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Guzior N., Wieckowska A., Panek D., Malawska B. Recent development of multifunctional agents as potential drug candidates for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015;22:373–404. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666141106122628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dos Santos T.C., Gomes T.M., Pinto B.A.S., Camara A.L., Paes A.M.A. Naturally Occurring Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors and Their Potential Use for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2018;18:1192. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tungmunnithum D., Thongboonyou A., Pholboon A., Yangsabai A. Flavonoids and Other Phenolic Compounds from Medicinal Plants for Pharmaceutical and Medical Aspects: An Overview. Medicines. 2018;5:93. doi: 10.3390/medicines5030093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tanase C., Coșarcă S., Muntean D.L. A Critical Review of Phenolic Compounds Extracted from the Bark of Woody Vascular Plants and Their Potential Biological Activity. Molecules. 2019;24:1182. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Roseiro L.B., Rauter A.P., Serralheiro M.L.M. Polyphenols as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Structural specificity and impact on human disease. Nutr. Aging. 2012;1:99–111. doi: 10.3233/NUA-2012-0006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Houghton P.J., Ren Y., Howes M.J. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from plants and fungi. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006;23:181–199. doi: 10.1039/b508966m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Orhan I.E., Orhan G., Gurkas E. An overview on natural cholinesterase inhibitors—A multi-targeted drug class—And their mass production. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2011;11:836–842. doi: 10.2174/138955711796575434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rosenfeld C.A., Sultatos L.G. Concentration-dependent kinetics of acetylcholinesterase inhibition by the organophosphate paraoxon. Toxicol. Sci. 2006;90:460–469. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfj094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Rahman A.-U., Khalid A., Sultana N., Nabeel Ghayur M., Ahmed Mesaik M., Khan M.R., Gilani A.H., Choudhary M.I. New natural cholinesterase inhibiting and calcium channel blocking quinoline alkaloids. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2006;21:703–710. doi: 10.1080/14756360600889708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Mena P., Cirlini M., Tassotti M., Herrlinger K.A., Dall’Asta C., del Rio D. Phytochemical Profiling of Flavonoids, Phenolic Acids, Terpenoids, and Volatile Fraction of a Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) Extract. Molecules. 2019;21:1576. doi: 10.3390/molecules21111576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Szwajgier D. Anticholinesterase activity of phenolic acids and their derivatives. Z. Nat. C J. Biosci. 2013;68:125–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Loussouarn M., Krieger-Liszkay A., Svilar L., Bily A., Birtić S., Havaux M. Carnosic Acid and Carnosol, Two Major Antioxidants of Rosemary, Act through Different Mechanisms. Plant Physiol. 2017;175:1381–1394. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.01183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Borrás-Linares I., Pérez-Sánchez A., Lozano-Sánchez J., Barrajón-Catalán E., Arráez-Román D., Cifuentes A., Micol V., Carretero A.S. A bioguided identification of the active compounds that contribute to the antiproliferative/cytotoxic effects of rosemary extract on colon cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015;80:215–222. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2015.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Munné-Bosch S., Schwarz K., Alegre L. Response of Abietane Diterpenes to Stress in Rosmarinus officinalis L.: New Insights into the Function of Diterpenes in Plants. Free Radic. Res. 1999;3:107–112. doi: 10.1080/10715769900301391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Demirezer L.Ö., Gürbüz P., Kelicen Uğur E.P., Bodur E., Özener N., Uz A., Güvenalp Z. Molecular docking and ex vivo and in vitro anticholinesterase activity studies of Salvia sp. and highlighted rosmarinic acid. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2015;45:1141–1148. doi: 10.3906/sag-1404-42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Merad M., Soufi W., Ghalem S., Boukli F., Baig M.H., Ahmad K., Kamal M.A. Molecular interaction of acetylcholinesterase with carnosic acid derivatives: A neuroinformatics study. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets. 2014;13:440–446. doi: 10.2174/18715273113126660157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Mannelli L.d., Micheli L., Maresca M., Cravotto G., Bellumori M., Innocenti M., Mulinacci N., Ghelardini C. Anti-neuropathic effects of Rosmarinus officinalis L. terpenoid fraction: Relevance of nicotinic receptors. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:34832. doi: 10.1038/srep34832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Braca A., De Tommasi N., Di Bari L., Pizza C., Politi M., Morelli I. Antioxidant Principles from Bauhinia t arapotensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2001;64:892–895. doi: 10.1021/np0100845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Albano S.M., Lima A.S., Miguel M.G., Pedro L.G., Barroso J.G., Figueiredo A.C. Antioxidant, anti-5-lipoxygenase and antiacetylcholinesterase activities of essential oils and decoction waters of some aromatic plants. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2012;6:35–48. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Palmer T. Enzymes Biochemistry, Biotechnology, Clinical Chemistry. East-West Press Pvt Ltd.; Delhi, India: 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sheikh I.A. Stereoselectivity and potential endocrine disrupting activity of Bis-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) against human progesterone receptor: A computational perspective. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016;36:741–774. doi: 10.1002/jat.3302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ganaie A.A., Siddiqui H.R., Sheikh I.A. A novel terpenoid class for prevention and treatment of KRAS-driven cancers: Comprehensive analysis using in situ, in vitro and in vivo model systems. Mol. Carcinog. 2020;59:886–896. doi: 10.1002/mc.23200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article and supplementary material.