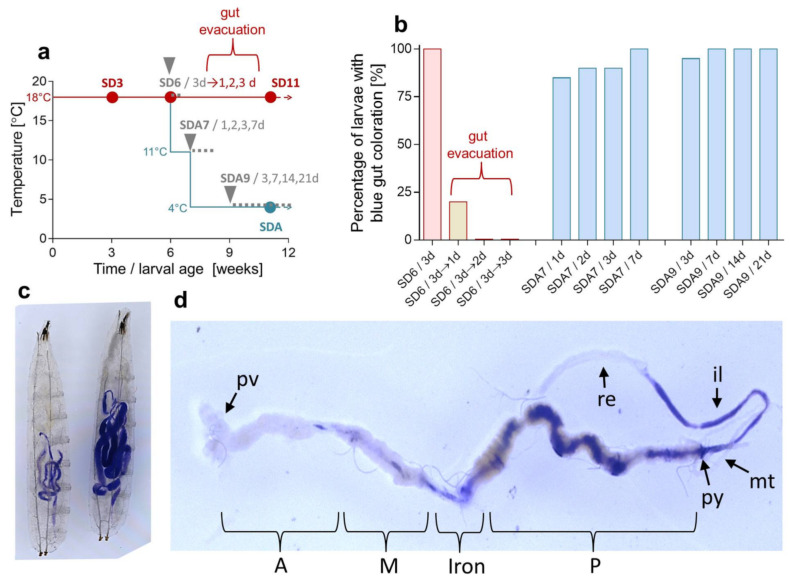
Figure 3.
Diet consumption in diapause, of cold-acclimated larvae of C. costata. (a) shows the times when larvae were transferred to BB-augmented diets (grey triangles) and for how many days (grey font). Each column in (b) shows the percentage of larvae (n = 20 each) with blue gut contents. SD6 larvae exposed to BB diet for 3 d (all guts blue-colored) were returned to a standard diet to show that the blue coloration disappears in 80% of individuals within 1 d, and in all individuals within 2 d (gut evacuation). Most of the diapausing, cold-acclimated larvae (SDA7 and SDA9) exhibit blue guts within a few days of exposure to the BB diet. (c) shows examples of BB diet-fed larvae: left, an SDA9 larva exposed to BB diet for 14 d at 4 °C; right, a non-diapause (LD) larva exposed to BB diet for 1 h at 18 °C. (d) shows a gut dissected from an SDA larva exposed to the BB diet. Gut segments are described according to the gut morphology of D. melanogaster larvae: pv, proventriculus; A, M, P, anterior, middle, and posterior midgut; Iron, iron cells segment; py, pylorus; mt, Malpighian tubules; il, ileum; re, rectum.