Figure. Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) Compared With Phenome-Wide Association Study (PheWAS).
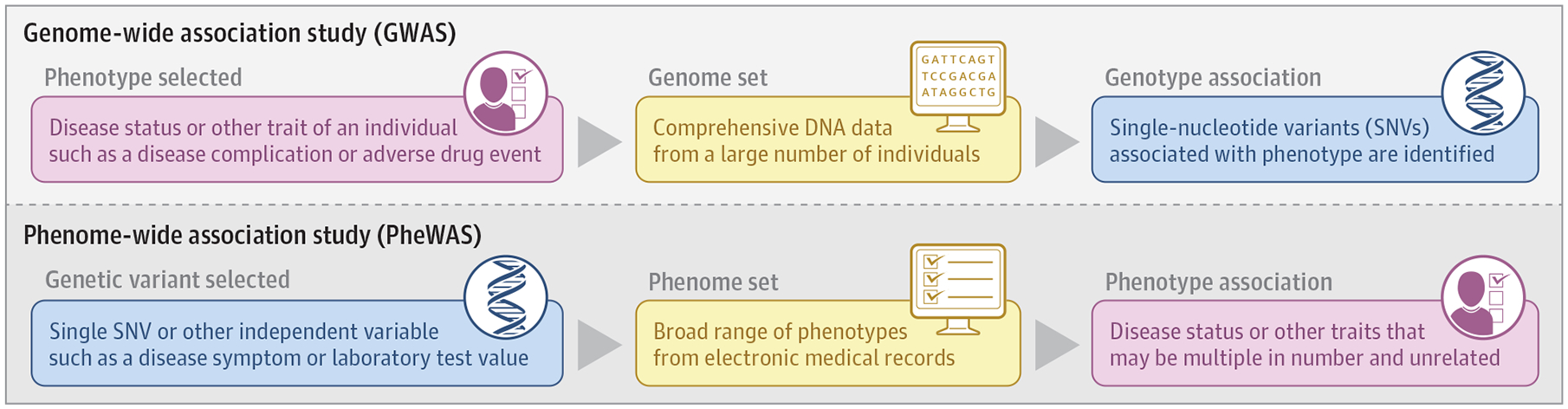
A GWAS (top) contrasted with a PheWAS (bottom). A GWAS starts with families or populations in which individuals have been assigned affected or unaffected status for a disease or other trait, such as a complication of a disease or an adverse outcome during drug treatment, and searches for associated genetic variants. A PheWAS starts with a genetic variant and searches across a set of curated human phenotypes (the “phenome”) to identify associated phenotypes. The “input function” for the PheWAS can be a single genetic variant or sets of variants or other traits.
