Abstract
Background:
Urban neighborhood greenness is associated with greater cardiovascular health in the general population, and with better pregnancy and neonatal outcomes. Hypertension in pregnancy is a leading cause of maternal mortality and long-term cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in women. We sought to examine the association between greenness and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.
Study Design:
This study is a secondary analysis of a prospective cohort study of 1943 women who received prenatal care from December 2013 through December 2016 at a single, urban, tertiary academic medical center in Philadelphia, PA. Greenness measure was quantified via residential tree canopy cover within circumferential buffers of 100m and 500m radii around participants’ homes. Associations between greenness and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (defined as gestational hypertension or preeclampsia) were estimated using multilevel logistic regression accounting for maternal sociodemographic information (race-ethnicity, insurance status, age) medical history (diabetes, body mass index, smoking history, parity), neighborhood deprivation index, and including 1,225 Philadelphia residents for whom key exposure and outcome data were available.
Results:
At baseline, the participants’ mean (SD) age was 27.5 (5.9) years, (range 14–44 years). The majority of participants were non-Hispanic Black (857, 70.2%). Participants with less tree canopy cover within 100m and 500m buffers were significantly more likely to have hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. The multivariable-adjusted odds ratio of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy among participants with less than 10% compared to those with greater than 30% tree canopy cover was 2.14 (95% CI 1.11–4.15) within 100m buffer and 2.77 (95% CI 1.23–6.24) within 500m buffer.
Conclusion:
In our cohort, greenness was associated with lower hypertensive disorders of pregnancy odds. Our findings add to evidence that greenness may confer health benefits and warrant further investigations in identifying whether there is a causal pathway through which greenness may be protective against hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.
Keywords: gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, tree canopy cover, greenness, maternal morbidity, environmental exposures, health disparities, environmental racism, urban health
Introduction
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP), which include gestational hypertension and preeclampsia, are a leading cause of maternal morbidity and mortality in the United States (U.S.) and worldwide.1 Preeclampsia occurs in about 3% of pregnancies, and HDP affect 5 to 10% of pregnancies.2 HDP often lead to, and are associated with severe maternal morbidity as defined by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (unexpected outcomes of labor and delivery that result in significant short- or long-term consequences to a woman’s health).3 HDP are also associated with increased long-term cardiovascular morbidity and mortality for women.4–7 In addition to overall morbidity, HDP and other cardiovascular complications of pregnancy contribute to a significantly higher proportion of maternal mortality in the U.S. among non-Hispanic Black women compared to non-Hispanic White women.8
The role of neighborhood environments in shaping health generally, and pregnancy outcomes specifically, is well-documented. Neighborhood greenness, especially tree canopy cover, is an aspect of the environment which may confer protective health effects. Noise pollution, air quality, and temperature, all of which are influenced by tree canopy, have been associated with increased risk of developing HDP, as well as preterm birth, low birth weight and stillbirth.9–12 In the general population, greenness has previously been associated with lower risks of a range of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases including hyperlipidemia, myocardial infarction, ischemic heart disease, heart failure and chronic hypertension.13–15 Exposure to greenspace is also thought to impact cardiovascular health through the strengthening of social connections, which is well documented to have a positive impact on health.16 Furthermore, exposure to greenness is also associated with immediate physiologic cardiovascular benefits including reductions in heart rate and blood pressure.17–19 Finally, greenspace is theorized to convey immunologic benefits that may also underlie potential cardiovascular benefits of nature.20
Differential exposure to environmental factors by race21 may contribute to observed racial disparities in pregnancy outcomes,22,23 but whether greater neighborhood greenness may attenuate disparities in HDP is unknown. Our study, therefore, had two objectives. First, we sought to quantify associations between greenness and odds of HDP in a cohort of pregnant women living in Philadelphia. Second, we sought to evaluate if the relationship between greenness and HDP differed between non-Hispanic Black and non-Hispanic White women. Greenness, if associated with lower HDP odds, may represent an attractive place-based intervention for policy-makers seeking to address maternal morbidity and mortality in the US.
Methods
Study Cohort
We performed a retrospective study from a prospective cohort of women who were recruited during the course of prenatal care in a tertiary hospital in Philadelphia. The parent study, Motherhood & Microbiome (M&M),24,25 enrolled 2000 pregnant participants from 2013–2017. This analysis includes just the women who lived in Philadelphia with the fine-scale greenspace layer. There were three study visits during pregnancy which were at 16–20 weeks; 20–24 weeks; and 24–28 weeks of gestation. Cervicovaginal swabs were obtained at each visit since the primary goal of the study was to understand associations between the microbial/immune state and spontaneous preterm birth. There were multiple psychosocial questionnaires administered including instruments for perceived stress, anxiety, and depression. There were no additional study visits. However, permission to obtain clinical data and demographic data throughout pregnancy was included as part of the consent process. Women were excluded from the cohort study if they met any of the following criteria: (1) major fetal anomaly, (2) HIV positive status, (3) history of organ transplant, and (4) chronic steroid use (>20 mg per day for more than 30 days at the time of first study visit).
For our analysis, inclusion criteria were the following: a geocodable home address within Philadelphia and gestational age at delivery 20 weeks or greater. Women with spontaneous preterm birth were excluded from the primary analysis, as this is a competing outcome, which may occur before women develop either gestational hypertension or preeclampsia. Women with a history of chronic hypertension were also excluded, as they cannot be diagnosed with gestational hypertension (Figure 1). Participants missing exposure or outcome data were excluded from the analysis. The University of Pennsylvania institutional review board approved this study (ID #818914). We followed the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) reporting guideline.26
Figure 1:
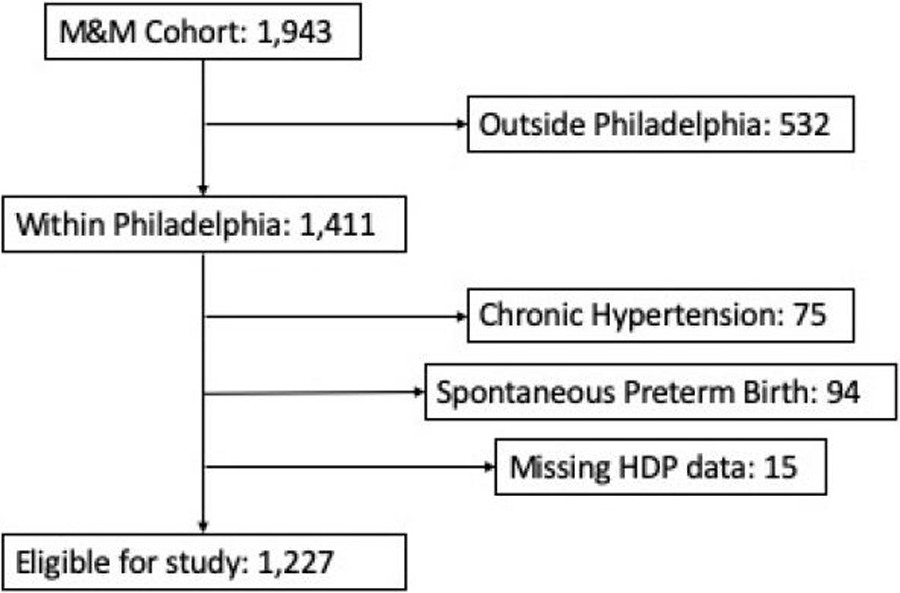
flowchart of Motherhood and Microbiome Cohort Participants eligible for analysis
Exposure Assessment
Neighborhood greenness was measured by tree canopy cover. Data were acquired from the Philadelphia’s Parks and Recreation open access database on tree canopy. Tree canopy data is a collection of tree canopy outlines generated by Intergraph Government Solutions (IGS) for trees greater than 6’ diameter from 2015 LiDAR data capture.27 While the exposure was independently assessed over halfway through our study period, evidence shows neighborhood characteristics such as tree canopy cover change relatively slowly,28 and the Philadelphia Tree Canopy assessment shows minimal changes in the areas most inhabited by our sample population between 2008 and 2018.29
For each participant’s home address, we used ArcGis Pro 10.0 (Esri, Redlands, California) to create buffers at 100m and 500m radii (see figure 2a for example), which approximately encompass respectively one, and four city blocks. Buffer radii were selected based upon prior studies reporting health benefits associated with greenness.30,31 This setting of buffer size is typically based on the assumption that this range represents the neighborhood environment where people spend their time sitting, walking or interacting with neighbors. Buffers were then spatially joined to the tree canopy dataset. We then calculated the amount of tree canopy within each buffer as a percentage of total land area. For analysis, participants were classified into four groups based on examples from prior similar studies (tree canopy cover 0–10%, 10–20%, 20–30% and >30%).30 See Figure 2b for tree canopy cover distribution in Philadelphia.
Figure 2a:

Example of Philadelphia home with 50m, 100m, 500m buffers
Figure 2b:
Tree Canopy Distribution in Philadelphia, PA by Neighborhood.
Outcome
HDP was defined as either gestational hypertension or preeclampsia. Cases of HDP were confirmed with manual review of electronic medical records during the primary study. Gestational hypertension and preeclampsia diagnoses were given by patients’ clinical providers, following the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ guidelines. 32
Covariates
Individual-level covariates included self-identified race/ethnicity, health insurance status, age at delivery, parity, diabetes history, smoking history and pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI) as a continuous variable. These variables were selected because they are associated with, or known risk factors for HDP. To account for neighborhood-level socioeconomic status, we used census tract-level neighborhood deprivation data from the Nationwide Community Deprivation Index.33 The index from 0–1 (national average is 0.4) with lower numbers reflecting higher neighborhood socioeconomic status. Variables included in the index are poverty rate, median household income, education, rates of health insurance cover, the fraction of households receiving public assistance, and fraction of houses that are vacant. We also accounted for seasonality, since some health benefits of trees such as shade and decreased temperature are only present during leaf-growing time periods. We defined leaf-growing season as March 21st to September 21st given that deciduous trees begin to lose their leaves in the fall, then regrow them in the spring. We then determined if each participant’s last menstrual period (LMP) took place in or out of leaf-growing season based on estimated LMP, given existing evidence suggesting that environmental exposures surrounding placentation contribute to risk of preeclampsia.11,34
Statistical Analysis
We used descriptive statistics to compare women with and without HDP. We used multilevel logistic regressions accounting for clustering of participants within census tracts to examine the association between neighborhood greenness and the odds developing HDP. The main model assessed HDP in relation to each greenness buffer at the individual level, adjusting for race/ethnicity, age, parity and history of pre-gestational or gestational diabetes, insurance status, smoking history, pre-pregnancy BMI and seasonality (leafgrowing vs not-leafgrowing) of LMP at the individual level, and neighborhood deprivation index at the census tract level. We chose the neighborhood deprivation index at the census tract level because recent evidence showed that in the U.S., overall, 70.4% of total geographic variations in life expectancy is attributable to census-tract level differences.35 In other words, adjusting for census tract-level socioeconomic variables allows us to address spatial correlation and significantly accounts for social determinants of health that may otherwise be responsible for observed disparities, including in our cohort.
Given the history of residential racial segregation in US cities and its impact on the built environment greenness distributions vary by race/ethnicity, we conducted subgroup analyses of non-Hispanic Black and non-Hispanic White participants to assess whether associations of greenness and HDP were similar across racial groups.36 We did not conduct the subgroup analysis for Hispanic participants and those in the Other category because of the small sample sizes. Finally, to address potential selection bias because we excluded women with chronic hypertension and women with spontaneous preterm birth from the primary analysis, we performed a sensitivity analysis using a multinomial, multilevel logistic regression model of associations of tree canopy cover with four possible outcomes: 1) Term delivery without HDP; 2) preeclampsia (regardless of delivery timing, and including participants with a history of chronic hypertension) 3) gestational hypertension (regardless of delivery timing); and 4) spontaneous preterm birth without HDP. Statistical analyses were performed using STATA (Version 16, StataCorp, College Station, Texas). Statistical tests were 2-tailed, and P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
A total of 1,225 women were included in the final analysis (see flowchart in Figure 1). Supplemental table 1 compares included and excluded participants. A total of 281 participants had HDP (22.9%): 253 participants had gestational hypertension, of which 48 progressed to preeclampsia. Twenty-eight participants developed preeclampsia without prior diagnosis of gestational hypertension. Characteristics according to HDP status are presented in Table 1. Women with HDP were more likely to be non-Hispanic Black, older, nulliparous and have a higher BMI. Mean (SD) tree canopy cover within 100m radius buffers was 16.6% (9.3%), and within 500m radius buffers, 17.1% (7.4%). Participants who developed HDP had lower exposure to tree canopy cover (Table 2).
Table 1.
Study participant characteristics among women with and without hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP), Motherhood and Microbiome cohort, n=1,1225 (2 excluded due to missing data)
| no HDP (n=944) | HDP (n=281) | |
|---|---|---|
| Race/Ethnicity (%) | ||
| Non-Hispanic White | 198 (21.0%) | 37 (13.2%) |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 638 (67.5%) | 219 (78.0%) |
| Hispanic | 46 (4.9%) | 12 (4.3%) |
| Other | 62 (6.6%) | 13 (4.5%) |
| Age (%) | ||
| <20 | 78 (8.3%) | 32 (11.4%) |
| 20–34 | 734 (77.7%) | 205 (72.95%) |
| 35+ | 132 (14%) | 44 (15.66%) |
| Heath insurance (%) | ||
| Employer-based | 379 (40.1%) | 105 (37.37%) |
| Medicaid/uninsured | 565 (59.9%) | 176 (62.63%) |
| Education | ||
| < High school | 86 (9.1%) | 37 (13.2%) |
| High school /Some College | 479 (50.7%) | 157 (55.9%) |
| Graduated college | 151 (16.0%) | 46 (16.4%) |
| Graduate/Professional | 161 (17.1%) | 30 (10.9%) |
| Other | 67 (7.10) | 11 (3.9%) |
| prenatal BMI (SD) | 27.57 (6.89) | 31.03 (8.6%) |
| Smoking during pregnancy | 77 (8.1%) | 17 (6.0%) |
| Parity (%) | ||
| Multiparous | 539 (57.1%) | 127 (45.2%) |
| Nulliparous | 405 (42.9%) | 154 (54.8%) |
| Diabetes (%) | ||
| No diabetes | 901 (95.4%) | 244 (86.8%) |
| Gestational diabetes | 31 (3.3%) | 27 (9.6%) |
| Pre-gestational diabetes | 12 (1.27%) | 9 (3.20%) |
| LMP Seasonality (%) | ||
| Not-leaf growing | 500 (53.0%) | 161 (57.3%) |
| Leaf-growing season | 444 (47.0%) | 120 (42.7%) |
| Neighborhood deprivation index (SD) | 0.5 (0.11) | 0.53 (0.12) |
Data presented as n (%) unless otherwise specified. 2 participants excluded due to missing BMI and Deprivation index data.
Table 2.
Associations between tree canopy cover & hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP), n=1,225 *Adjusted for age, prenatal body-mass index, smoking history, parity, history of diabetes, health insurance, last menstrual period seasonality, and deprivation index by census tract)
| no HDP n (%) | HDP n (%) | OR (95% CI) n = 1225 | P-Value | Adjusted* OR (95% CI) n= 1225 | P-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer size | Tree canopy cover | ||||||
| 100m |
>30% | 98 (10.4%) | 14 (4.0%) | 1 (ref) | - | 1 (ref) | - |
| 20–30% | 189 (20.0%) | 57 (20.3%) | 2.11 (1.12–3.98) | 0.047 | 2.00 (1.02–3.93) | 0.05 | |
| 10–20% | 421 (44.6%) | 140 (49.8%) | 2.33 (1.29–4.21) | 0.057 | 1.98 (1.05–3.73) | 0.04 | |
| <10% | 236 (25.0%) | 70 (24.9%) | 2.08 (1.12–3.86) | 0.023 | 2.14 (1.11–4.16) | 0.02 | |
At the 100m buffer level in unadjusted analysis, participants with less than 10% tree canopy cover had increased odds of having HDP compared to those with greater than 30% tree canopy cover (OR 2.08, 95% CI 1.12 – 3.86). The association persisted after adjusting for individual- and neighborhood-level covariates including race/ethnicity, age, health insurance status, parity, history of diabetes, pregnancy BMI, LMP seasonality, and neighborhood deprivation index by census tract. Participants with less than 10% tree canopy cover had more than twice the odds of HDP compared to those with greater than 30% (aOR 2.14, 95% CI 1.11 – 4.15). We conducted the same analysis using tree canopy cover as a continuous variable, and the unadjusted analysis showed that for each standard deviation increase in tree canopy cover within 100m buffers, there was a 13% (95% CI 1%−25%, P=0.047) decrease in HDP odds. The results were similar in the adjusted multilevel logistic model, showing a 14% (95% CI 1%−26%, P=0.05) decrease of HDP odds per standard deviation increase in tree canopy cover. The 500m sensitivity analysis showed similar results (see supplemental table 2). Notably, for each standard deviation in tree canopy cover increase, there was a 19% (95% CI 5%−31%, P=0.01) decrease in HDP odds.
In this cohort, non-Hispanic Black women were more likely than non-Hispanic White women to be younger, obese, have Medicaid insurance or no insurance, and to have HDP (Supplemental Table 3). Non-Hispanic Black participants were also disproportionately exposed to low levels of tree canopy cover. In the subgroup analyses analysis at the 100m buffer level, non-Hispanic Black women exposed to <10% tree canopy cover had higher adjusted odds of HDP compared to non-Hispanic Black women with >30% (OR 3.29, 95% CI 1.24 – 8.70) (see table 3). results were even more pronounced at the 500m level (See supplemental table 2). Among non-Hispanic White participants, we did not detect significant associations between tree canopy cover and HDP (see supplemental table 4).
Table 3.
Association between tree canopy cover and hypertensive disorder of pregnancy (HDP) among Non-Hispanic Black participants, n = 857 (* adjusted for prenatal BMI, parity, history of diabetes, age, insurance, seasonality of last menstrual period and deprivation index by census tract)
| buffer size | Tree canopy cover | no HDP | HDP | OR (95% CI) | P-Value | Adjusted* OR (95% CI) | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 m | >30% | 49 (7.7%) | 6 (2.7%) | 1 (ref) | - | 1 (ref) | - |
| 20–30% | 142 (22.3%) | 49 (22.4%) | 2.82 (1.14–6.99) | 0.025 | 3.23 (1.23–8.50) | 0.017 | |
| 10–20% | 314 (49.2%) | 118 (53.9%) | 3.07 (1.28–7.35) | 0.012 | 3.13 (1.23–7.95) | 0.016 | |
| <10% | 133 (20.8%) | 46 (21.00%) | 2.82 (1.14–7.03) | 0.026 | 3.29 (1.24–8.70) | 0.017 |
Because we were concerned that the exclusion of women with spontaneous preterm birth and chronic hypertension could cause selection bias, we performed a sensitivity analysis which included these women. We performed a multinomial multilevel logistic regression model in which women could have one of 4 outcomes: Term delivery without HDP (base outcome), gestational hypertension (regardless of delivery timing), preeclampsia (regardless of delivery timing, and including participants with chronic hypertension), or preterm birth without HDP. In this breakdown, lesser tree canopy cover was associated with significantly increased odds of gestational hypertension only. At 100m, participants with less than 10% tree canopy cover had nearly 3 times the odds of developing gestational hypertension compared to those with greater than 30% (aOR 2.56, 95% CI 1.18 to 5.55). (Supplemental Table 5). There were no significant associations of tree canopy cover with preterm birth without HDP or with preeclampsia.
Discussion
Principal Findings & Results
This study demonstrates that lower levels of neighborhood tree canopy cover were associated with higher odds of HDP after adjusting for individual sociodemographic variables, medical covariates previously associated with HDP and neighborhood-level deprivation, a holistic indicator of overall socioeconomic status. Noting significant racial disparities in HDP, our results suggest that less greenness is particularly strongly associated with higher odds of HDP among non-Hispanic Black women. We did not detect a significant association among non-Hispanic White participants; however due to small sample size and wide confidence intervals, we cannot rule out an association. In our sensitivity analysis, while there was an association between tree canopy cover and gestational hypertension odds, this association was not significant for preeclampsia, which may be due to the smaller sample size of participants who developed preeclampsia.
This study adds to evidence demonstrating the importance of neighborhood environment in adverse pregnancy outcomes. Greenness has been associated with improved neonatal outcomes, including lower risk of preterm birth and low birth weight.37 A single study evaluating greenness found associations with neonatal outcomes, but found no association between greenness and preeclampsia, however it did not investigate gestational hypertension.38 In terms of cardiovascular health, a 2019 community-based study showed that increases in neighborhood greenness were associated with lower blood pressure and hypertension prevalence, and the associations were stronger among women than men.15
Clinical Implications
There are several mechanisms that may explain the association between higher tree canopy cover and lower odds of HDP, including improved air quality, reduced urban heat island effect, and lower stress.16,20 For instance, trees remove fine particles from the atmosphere and consequently improve air quality,39 while air pollution from road traffic is associated with increased risk of preeclampsia.10,40 A previous study found lower levels of personal exposure to air pollution among pregnant women residing in greener areas, based on normalized difference vegetation index within 100 m buffers.41 Trees also provide shade and reduce ambient temperature,42 and higher ambient temperatures and humidity surrounding conception are also associated with preeclampsia.11 Additionally, proximity to green spaces is associated with lower noise annoyance.43 One study showed that prevalence of preeclampsia was higher among pregnant patients exposed to greater levels of noise pollution, especially early onset and severe preeclampsia.9 Furthermore, the increased amount of shade from tree canopy cover may increase levels of physical activity and a perceived sense of community cohesion associated with lower odds of cardiovascular disease in the general population.44–46 Recent experimental evidence demonstrated that exposure to greenness led to a positive physiological response and increased community cohesion in a Philadelphia neighborhood walking trial, and being in view of greened vacant neighborhood lots decreased participants’ heartrate significantly more than did being in view of non-greened vacant lots or not in view of any vacant lots. 19 Other covariates associated with increased risk of HDP, such as pre-pregnancy BMI, are also affected by environmental exposures, including tree canopy cover. Studies have found associations between residential tree canopy cover and physical activity, as well as obesity. In other words, pre-pregnancy BMI may mediate the effect of tree canopy cover on HDP risk.47
The cumulative experience of stress from a variety of sources – including environmental, discrimination, and poverty – may make the presence of green space, a known buffer to stress, particularly important in Black neighborhoods.48 These results are also in line with prior research demonstrating the importance of sociodemographic context in evaluating risk factors for pregnancy outcomes. For example, a recent study of green spaces, health inequality and pregnancy outcomes in Spain, found beneficial effects of green spaces only among pregnant participants of lower socioeconomic position.49
The larger effect size of the impact of greenness on HDP among Black women may be due to environmental racism. Environmental racism is a concept from the environmental justice movement that illustrates the fact that Black, Indigenous and other people of color are more likely to live near polluters and more likely to be exposed to a higher magnitude of pollution compared to White people, as a result of state-sanctioned policies.50,51 For example, historical government-sanctioned housing segregation on the basis of race (redlining), and subsequent decades of White flight and neighborhood disinvestment52 are linked to present day differences in neighborhood social and physical environment, including crime, air quality, and temperature. Studies have identified racial disparities in distribution of green spaces, with census tracts with a higher proportion of racial and ethnic minorities having less greenness, as well as losing more greenness overtime compared the those with a higher proportion of White residents.28 This was true in our study sample with disproportionate exposure to low tree canopy cover among Black women. Other environmental factors associated with greenness follow a similar pattern. A recent study on intra-urban heat showed that nationally, formerly redlined neighborhoods are on average 2.6° C warmer than non-redlined neighborhoods, and the difference can be as high as 7°C.53 Similarly, disparities in neighborhood air quality fall along racial lines and redlining status.21,54 The protective effect of trees may thus be most tangible among women facing a disproportionately high level of toxic environmental exposures.
In addition to its association with maternal mortality, HDP is associated with long-term cardiovascular morbidity in women,7,55,56 as well as elevated blood pressures in their children.57 If validated as a potential intervention, increased exposure and access to greenness may serve as a tool to address racial disparities in maternal morbidity and mortality, as well as disparities in post-partum and long-term complications, and chronic illness associated with HDP.58 This hypothesis is supported by a recent study of tree canopy cover in Philadelphia, which showed that achieving city-wide tree canopy cover of at least 30% by 2025 could prevent 403 premature deaths annually, 244 of which in areas of lower socioeconomic status.59 For these reasons, our findings support the idea that neighborhood greening may be a non-pharmacological strategy for policy makers and health systems to reduce maternal morbidity and mortality associated with HDP, as well as to address racial disparities in pregnancy outcomes.
Research Implications
The association between low tree canopy cover and odds of developing HDP during pregnancy found in our study is non-experimental, and does not address whether the identified association infers causality, and if so, by which pathway this might occur. This therefore warrants further studies evaluating the interaction between greenness and other environmental exposures such as air and noise pollution, ambient temperatures, and HDP risk, as well as the impact of environmental changes on HDP incidence. Furthermore, additional research on associations between greenness and HDP in suburban settings is warranted.
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths of our study include prospective enrollment before the outcome of HDP was assessed. We had a large sample of non-Hispanic Black women who are particularly at-risk for HDP. However, this study is based out of a single-center, tertiary care center in an urban setting; participants included in this analysis (Philadelphians) were more likely to be non-Hispanic Black, more likely to have Medicaid insurance or be uninsured than those who resided outside of Philadelphia and thus not included (Supplemental Table 1). Notably, the HDP incidence was 23%, which is greater than the incidence of HDP in the general population. Therefore, our findings may not be generalizable to other settings or populations. Tree canopy cover is a static measure that does not necessarily reflect participants’ engagement and activity related to green spaces such as frequency or time spent outdoors, and there may be unmeasured confounders we were not able to adjust for. Our study is observational, therefore the associations identified cannot be determined to be causal. Lastly, we did not account for spatial autocorrelation between potentially overlapping buffers, however, we accounted for autocorrelation at the census tract level by adjusting for the census-tract neighborhood deprivation index.
Conclusion
In our cohort, low-level tree canopy cover was independently associated with elevated odds of HDP, especially among non-Hispanic Black participants. Prior studies of neighborhood greenness in pregnancy are limited by not assessing gestational hypertension, whereas ours addresses this gap. Our findings warrant further investigations to examine the interactions between greenness, environmental factors such as air quality, noise pollution and temperature, and their impact on the incidence of HDP in pregnancy. Additionally, this contributes to a framework for policy-makers for planning and designing urban environments that incorporate place-based initiatives such as tree-planting and upkeep to address health inequities, especially in more socioeconomically deprived neighborhoods.
Supplementary Material
Key Points:
Why was the study conducted?
To identify whether urban neighborhood greenness, measured as tree canopy cover, is associated with lower risk of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.
What are the key findings?
In this prospective cohort study of 1,225 women, those with less than 10% residential tree canopy cover (within 100m and 500m radius buffers) had more than twice the odds of developing hypertensive disorders of pregnancy compared to women with greater than 30% residential tree canopy cover.
What does this study add to what is already known?
Increasing neighborhood greenness should be studied experimentally as an intervention to reduce the burden of, and disparities in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. In addition to other pregnancy outcomes such as preterm birth and low birthweight, low greenness is associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy in a single-center urban cohort.
Acknowledgements:
The authors would like to thank David Buckler (University of Pennsylvania) for his assistance in statistical review of the analysis of this study.
Funding: NIH R01NR014784 (PI Elovitz), March of Dimes Prematurity Research Center (PI Driscoll)
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest: None
References
- 1.Ghulmiyyah L, Sibai B. Maternal Mortality From Preeclampsia/Eclampsia. Semin Perinatol 2012;36(1):56–59. doi: 10.1053/j.semperi.2011.09.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bateman BT, Shaw KM, Kuklina E V, Callaghan WM, Seely EW. Hypertension in Women of Reproductive Age in the United States: NHANES 1999–2008. PLoS One 2012;7(4):36171. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036171 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.How Does CDC Identify Severe Maternal Morbidity? | CDC https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/maternalinfanthealth/smm/severe-morbidity-ICD.htm. Accessed June 12, 2020.
- 4.Tooher J, Thornton C, Makris A, Ogle R, Korda A, Hennessy A. All Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy Increase the Risk of Future Cardiovascular Disease. Hypertension 2017;70(4):798–803. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.09246 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Maffei S, Guiducci L, Cugusi L, et al. Women-specific predictors of cardiovascular disease risk - new paradigms. Int J Cardiol 2019;286:190–197. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.02.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Riise HKR, Sulo G, Tell GS, et al. Association Between Gestational Hypertension and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease Among 617 589 Norwegian Women. J Am Heart Assoc 2018;7(10). doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.008337 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Haas DM, Parker CB, Marsh DJ, et al. Association of Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes With Hypertension 2 to 7 Years Postpartum. J Am Heart Assoc 2019;8(19):e013092. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.013092 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Petersen EE, Davis NL, Goodman D, et al. Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Pregnancy-Related Deaths — United States, 2007–2016. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2019;68(35):762–765. https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/maternalinfanthealth/pqc.htm. Accessed April 15, 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Auger N, Duplaix M, Bilodeau-Bertrand M, Lo E, Smargiassi A. Environmental noise pollution and risk of preeclampsia. Environ Pollut 2018;239:599–606. doi: 10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2018.04.060 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wu J, Ren C, Delfino RJ, Chung J, Wilhelm M, Ritz B. Association between local traffic-generated air pollution and preeclampsia and preterm delivery in the South Coast Air Basin of california. Environ Health Perspect 2009;117(11):1773–1779. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0800334 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tam WH, Sahota DS, Lau TK, Li CY, Fung TY. Seasonal variation in pre-eclamptic rate and its association with the ambient temperature and humidity in early pregnancy. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2008;66(1):22–26. doi: 10.1159/000114252 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bekkar B, Pacheco S, Basu R, DeNicola N. Association of Air Pollution and Heat Exposure With Preterm Birth, Low Birth Weight, and Stillbirth in the US: A Systematic Review. JAMA Netw open 2020;3(6):e208243. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.8243 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wang K, Lombard J, Rundek T, et al. Relationship of Neighborhood Greenness to Heart Disease in 249 405 US Medicare Beneficiaries. J Am Heart Assoc 2019;8(6). doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.010258 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kim HJ, Min JY, Kim HJ, Min KB. Parks and green areas are associated with decreased risk for hyperlipidemia. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2016;13(12). doi: 10.3390/ijerph13121205 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yang BY, Markevych I, Bloom MS, et al. Community greenness, blood pressure, and hypertension in urban dwellers: The 33 Communities Chinese Health Study. Environ Int 2019;126:727–734. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.02.068 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hartig T, Mitchell R, de Vries S, Frumkin H. Nature and Health. Annu Rev Public Health 2014;35(1):207–228. doi: 10.1146/annurev-publhealth-032013-182443 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sung J, Woo J-M, Kim W, Lim S-K, Chung E-J. The Effect of Cognitive Behavior Therapy-Based “Forest Therapy” Program on Blood Pressure, Salivary Cortisol Level, and Quality of Life in Elderly Hypertensive Patients. Clin Exp Hypertens 2012;34(1):1–7. doi: 10.3109/10641963.2011.618195 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kondo MC, Jacoby SF, South EC. Does spending time outdoors reduce stress? A review of real-time stress response to outdoor environments. Health Place 2018;51:136–150. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2018.03.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.South EC, Kondo MC, Cheney RA, Branas CC. Neighborhood blight, stress, and health: a walking trial of urban greening and ambulatory heart rate. Am J Public Health 2015;105(5):909–913. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2014.302526 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kuo M. How might contact with nature promote human health? Promising mechanisms and a possible central pathway. Front Psychol 2015;6:1093. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01093 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tessum CW, Apte JS, Goodkind AL, et al. Inequity in consumption of goods and services adds to racial-ethnic disparities in air pollution exposure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019;116(13):6001–6006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1818859116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Burris HH, Lorch SA, Kirpalani H, Pursley DWM, Elovitz MA, Clougherty JE. Racial disparities in preterm birth in USA: A biosensor of physical and social environmental exposures. Arch Dis Child 2019;104(10):931–935. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2018-316486 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Burris HH, Hacker MR. Birth outcome racial disparities: A result of intersecting social and environmental factors. Semin Perinatol 2017;41(6):360–366. doi: 10.1053/j.semperi.2017.07.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Elovitz MA, Gajer P, Riis V, et al. Cervicovaginal microbiota and local immune response modulate the risk of spontaneous preterm delivery. Nat Commun 2019;10(1):1305. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09285-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gerson KD, McCarthy C, Elovitz MA, Ravel J, Sammel MD, Burris HH. Cervicovaginal microbial communities deficient in Lactobacillus species are associated with second trimester short cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2020;222(5):491.e1–491.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.11.1283 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Ann Intern Med 2007;147(8):573–577. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-147-8-200710160-00010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.PPR Tree Canopy Outlines (2015). City of Philadelphia | Metadata Catalog https://metadata.phila.gov/#home/datasetdetails/5c49d8cb63a2aa28893742e6/representationdetails/5c49d8cc63a2aa28893742eb/. Accessed April 15, 2020.
- 28.Casey JA, James P, Cushing L, Jesdale BM, Morello-Frosch R. Race, ethnicity, income concentration and 10-year change in urban greenness in the United States. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2017;14(12). doi: 10.3390/ijerph14121546 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.O’Neil-Dunne J. Tree Canopy Assessment: Philadelphia, PA.; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Astell-Burt T, Feng X. Does sleep grow on trees? A longitudinal study to investigate potential prevention of insufficient sleep with different types of urban green space. SSM - Popul Heal 2020;10. doi: 10.1016/j.ssmph.2019.100497 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zhang L, Tan P. Associations between Urban Green Spaces and Health are Dependent on the Analytical Scale and How Urban Green Spaces are Measured. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2019;16(4):578. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16040578 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.American College ofObstetricians and Gynecologists’ Committee on Practice Bulletins—Obstetrics. Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol 2019;133(1):e1–e25. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Brokamp C, Beck AF, Goyal NK, Ryan P, Greenberg JM, Hall ES. Material community deprivation and hospital utilization during the first year of life: an urban population–based cohort study. Ann Epidemiol 2019;30:37–43. doi: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2018.11.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kaufmann P, Black S, Huppertz B. Endovascular Trophoblast Invasion: Implications for the Pathogenesis of Intrauterine Growth Retardation and Preeclampsia. Biol Reprod 2003;69(1):1–7. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.102.014977 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Boing AFAC, Boing AFAC, Cordes J, Kim R, Subramanian SV. Quantifying and explaining variation in life expectancy at census tract, county, and state levels in the United States 2020;117(30). https://www.pnas.org/content/117/30/17688. Accessed August 10, 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Duncan DT, Kawachi I, White K, Williams DR. The geography of recreational open space: Influence of neighborhood racial composition and neighborhood poverty. J Urban Heal 2013;90(4):618–631. doi: 10.1007/s11524-012-9770-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Abelt K, McLafferty S. Green streets: Urban green and birth outcomes. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2017;14(7). doi: 10.3390/ijerph14070771 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Laurent O, Wu J, Li L, Milesi C. Green spaces and pregnancy outcomes in Southern California. Heal Place 2013;24:190–195. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2013.09.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nowak DJ, Hirabayashi S, Bodine A, Hoehn R. Modeled PM2.5 removal by trees in ten U.S. cities and associated health effects. Environ Pollut 2013;178:395–402. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.03.050 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Malmqvist E, Jakobsson K, Tinnerberg H, Rignell-Hydbom A, Rylander L. Gestational Diabetes and Preeclampsia in Association with Air Pollution at Levels below Current Air Quality Guidelines. Environ Health Perspect 2013;121(4):488–493. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1205736 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Dadvand P, de Nazelle A, Triguero-Mas M, et al. Surrounding Greenness and Exposure to Air Pollution During Pregnancy: An Analysis of Personal Monitoring Data. Environ Health Perspect 2012;120(9):1286–1290. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1104609 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schinasi LH, Benmarhnia T, De Roos AJ. Modification of the association between high ambient temperature and health by urban microclimate indicators: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Res 2018;161:168–180. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2017.11.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dzhambov AM, Dimitrova DD. Green spaces and environmental noise perception. Urban For Urban Green 2015;14(4):1000–1008. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2015.09.006 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Li J, Siegrist J. Physical activity and risk of cardiovascular disease-a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2012. doi: 10.3390/ijerph9020391 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Shanahan DF, Bush R, Gaston KJ, et al. Health Benefits from Nature Experiences Depend on Dose. Sci Rep 2016;6(1):28551. doi: 10.1038/srep28551 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Barth J, Schneider S, Von Känel R. Lack of social support in the etiology and the prognosis of coronary heart disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychosom Med 2010. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0b013e3181d01611 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Huang WZ, Yang BY, Yu HY, et al. Association between community greenness and obesity in urban-dwelling Chinese adults. Sci Total Environ 2020;702:135040. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135040 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wolch JR, Byrne J, Newell JP. Urban green space, public health, and environmental justice: The challenge of making cities “just green enough.” Landsc Urban Plan 2014;125:234–244. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2014.01.017 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Dadvand P, de Nazelle A, Figueras F, et al. Green space, health inequality and pregnancy. Environ Int 2012;40(1):110–115. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2011.07.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Corburn J. Concepts for Studying Urban Environmental Justice. Curr Environ Heal reports 2017;4(1):61–67. doi: 10.1007/s40572-017-0123-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Bravo MA, Anthopolos R, Bell ML, Miranda ML. Racial isolation and exposure to airborne particulate matter and ozone in understudied US populations: Environmental justice applications of downscaled numerical model output. Environ Int 2016;92–93:247–255. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2016.04.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Boustan LP. Was Postwar Suburbanization “White Flight”? Evidence from the Black Migration Vol 125.; 2010. doi: 10.1162/qjec.2010.125.1.417 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hoffman JS, Shandas V, Pendleton N. The effects of historical housing policies on resident exposure to intra-urban heat: A study of 108 US urban areas. Climate 2020;8(1):12. doi: 10.3390/cli8010012 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Houston D, Wu J, Ong P, Winer A. Structural disparities of urban traffic in Southern California: Implications for vehicle-related air pollution exposure in minority and high-poverty neighborhoods. J Urban Aff 2004;26(5):565–592. doi: 10.1111/j.0735-2166.2004.00215.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Brown MC, Best KE, Pearce MS, Waugh J, Robson SC, Bell R. Cardiovascular disease risk in women with pre-eclampsia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Epidemiol 2013;28(1):1–19. doi: 10.1007/s10654-013-9762-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Drost JT, Arpaci G, Ottervanger JP, et al. Cardiovascular risk factors in women 10 years post early preeclampsia: the Preeclampsia Risk EValuation in FEMales study (PREVFEM). Eur J Prev Cardiol 2012;19(5):1138–1144. doi: 10.1177/1741826711421079 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Tenhola S, Rahiala E, Halonen P, Vanninen E, Voutilainen R. Maternal Preeclampsia Predicts Elevated Blood Pressure in 12-Year-Old Children: Evaluation by Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring. Pediatr Res 2006;59(2):320–324. doi: 10.1203/01.pdr.0000196734.54473.e3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Williams RA. Cardiovascular disease in African American women: A health care disparities issue. J Natl Med Assoc 2009;101(6):536–540. doi: 10.1016/S0027-9684(15)30938-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kondo MC, Mueller N, Locke DH, et al. Health impact assessment of Philadelphia’s 2025 tree canopy cover goals. Lancet Planet Heal 2020;4(4):e149–e157. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(20)30058-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


