Abstract
Background
Children with chronic illnesses are at increased risk for reductions in bone strength and subsequent fractures (osteoporosis), either due to the impact of the underlying condition on skeletal development or due to the osteotoxic effect of medications (e.g., glucocorticoids) used to treat the chronic illness. Bisphosphonates are being administered with increasing frequency to children with secondary osteoporosis; however, the efficacy and harm of these agents remains unclear.
Objectives
To examine the efficacy and harm of bisphosphonate therapy in the treatment and prevention of secondary osteoporosis in children and adolescents.
Search methods
We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (Issue 4, 2006), MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL and ISI Web of Science (inception‐December 2006). Further literature was identified through expert contact, key author searches, scanning reference lists of included studies, and contacting bisphosphonate manufacturers.
Selection criteria
Randomized, quasi‐randomized, controlled clinical trials, cohort, and case controls of bisphosphonate(s) in children 0‐18 years of age with at least one low‐trauma fracture event or reductions in bone mineral density in the context of secondary osteoporosis.
Data collection and analysis
Two reviewers independently extracted data and assessed quality. Case series were used for supplemental harms‐related data.
Main results
Six RCTs, two CCTs, and one prospective cohort (n=281 children) were included and classified into osteoporosis due to: 1) neuromuscular conditions (one RCT) and 2) chronic illness (five RCTs, two CCTs, one cohort). Bisphosphonates examined were oral alendronate, clodronate, and intravenous (IV) pamidronate. Study quality varied. Harms data from 23 case series (n=241 children) were used.
Heterogeneity precluded statistically combining the results. Percent change or Z‐score change in lumbar spine areal BMD from baseline were consistently reported. Two studies carried out between‐group analyses; one showed no significant difference (using oral alendronate in anorexia nervosa) while the other demonstrated a treatment effect on lumbar spine with IV pamidronate in burn patients. Frequently reported harms included the acute phase reaction, followed by gastrointestinal complaints, and bone/muscle pain.
Authors' conclusions
The results justify further evaluation of bisphosphonates among children with secondary osteoporosis. However, the evidence does not support bisphosphonates as standard therapy. Short‐term (3 years or less) bisphosphonate use appears to be well‐tolerated. An accepted criterion for osteoporosis in children, a standardized approach to BMD reporting, and examining functional bone health outcomes (e.g., fracture rates) will allow for appropriate comparisons across studies.
Plain language summary
Bisphosphonate therapy for children and adolescents with secondary osteoporosis.
This summary of a Cochrane review presents what we know from research about the effect of bisphosphonates for osteoporosis in children and adolescents. The review shows that bisphosphonates:
‐ may not lead to any difference in bone mineral density (bone thickness and strength).
There was not enough information in the included studies to tell whether bisphosphonates would make a difference to children's bone mineral content (the amount and type of minerals in the bone); the number of broken bones children and adolescents had or the condition of children's vertebrae (for example, new fractures detected on an x‐ray or other scan). We often do not have precise information about side effects and complications. This is particularly true for rare but serious side effects. Possible side effects may include the acute phase reaction (fever, chills, general malaise), low levels of calcium in the body, nausea, abdominal bloating and other digestion problems, damage to the esophagus, bone or muscle pain, dizziness, rash, and memory loss. What is osteoporosis and what are bisphosphonates? Bone is a living, growing part of your body. Throughout your lifetime, new bone cells grow and old bone cells break down to make room for the new, stronger bone. When you have osteoporosis, the old bone breaks down faster than the new bone can replace it. As this happens, the bones lose minerals (such as calcium). This makes bones weaker and more likely to break even after a minor injury, like a little bump or fall. All the bones in your body are weaker if you have osteoporosis but not everyone who has osteoporosis gets a broken bone. To find out whether a person's bones are weaker than normal, a bone mineral density test is done using a special x‐ray, a computed tomography (CT) scan or an ultrasound. In some children with a chronic illness, osteoporosis could be caused by condition they have or because of the medications they take for their condition. This is known as secondary osteoporosis. Bisphosphonates are a type of medication that slows down the cells that break down the old bone. This means the cells that grow new bone have a chance to catch up and strengthen the bone.
Background
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by reductions in bone strength, leading to an increased risk of fractures (NIH Consens 2001). The etiology of osteoporosis varies across the lifespan. It is the most common metabolic bone disorder in adults, typically associated with aging (Genant 1999; Ray 1997; US Dept Health 2004). However, there is increasing awareness that osteoporosis may affect children and adolescents. Osteoporosis among children can be due to an intrinsic skeletal defect (primary osteoporosis), or as a result of systemic diseases or their treatment (secondary osteoporosis) (Ward 2003).
There is a growing list of causes of secondary osteoporosis in children, due in part to improved long‐term outcomes for children with chronic conditions. The more commonly described causes of secondary osteoporosis in childhood include neuromuscular conditions, chronic inflammatory illness, leukemia, endocrine and reproductive disorders, medications (such as glucocorticoids), and inborn errors of metabolism (Ward 2003). The clinical status of children with a chronic illness can be significantly worsened by the effects of secondary osteoporosis, including pain due to fractures and subsequent immobilization (Halton 1996; Kotaniemi 1999; Lettgen 1994; Strauss 2001; Tenbrock 2000). The morbidity associated with osteoporosis due to chronic pediatric illness and the impact to skeletal health later in life highlights the importance of osteoporosis prevention and treatment during childhood.
Bone densitometry is the most common measure of bone mass and density in adults, particularly among post‐menopausal women. Bone mass and mineral density (BMD) are most often assessed by dual energy x‐ray absorptiometry (DXA), producing values for bone mineral content (BMC) and bone area (BA), with a calculation of "areal" BMD by dividing BMC by BA. This is not a true measure of physical density but rather a two‐dimensional measurement that can be affected by bone size. It is well‐known that bone mass/density in adults is a determinant of fracture risk. The evidence for an association between bone mass/density and fracture risk in healthy children is more limited. A recent systematic review based on the analysis of 10 case‐control studies evaluated the association between bone density and fractures in otherwise healthy children (Clark 2006). They concluded that bone mass does appear to contribute to fracture risk in childhood, but that the currently available literature does not permit prediction of fracture risk associated with a given BMD. Since bone mineral accrual proceeds at different rates, at different skeletal sites, the fracture risk associated with a given BMD in children is likely to vary at different ages/pubertal stages and at different skeletal regions. The fracture risk associated with BMD in health and disease at various ages/pubertal stages, in different geo‐ethnic groups and at various skeletal sites remains an important area of study.
The current, practical approach to treat chronic illness osteoporosis in children is first to mitigate the threats to bone health by minimizing osteotoxic medications and providing hormonal replacement for delayed puberty. Conservative interventions to foster bone health have also been suggested, including adequate calcium and vitamin D intake and regular weight‐bearing exercise. In the setting where fractures have already occurred, such measures may not be adequate to rescue patients from the bone fragility state; therefore, alternative agents have been proposed, including bisphosphonates, growth hormone and calcitonin. Of these, bisphosphonates have garnered the greatest attention in the treatment of pediatric osteoporosis based largely on studies of efficacy and safety among children with osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI) (Glorieux 1998; Land 2006a; Land 2006b; Plotkin 2000; Rauch 2002; Rauch 2006a; Rauch 2006b).
As synthetic analogues of pyrophosphate, bisphosphonates increase BMD and reduce fracture rates by inactivating osteoclasts, the cells responsible for the breakdown of existing bone (Fleisch 1998). Pediatric OI studies have shown that the most commonly prescribed bisphosphonate in children, intravenous (IV) cyclical pamidronate, is associated with reduction in pain, improved mobility, increases in BMD, and decreased fracture rates (Glorieux 1998; Plotkin 2000; Rauch 2002). The majority of patients experience an acute phase reaction with the first infusion cycle, characterized by malaise and low‐grade fever (Glorieux 1998), but the reaction is typically mild and self‐limited. Aside from pamidronate, there are limited studies of bisphosphonates, whether first, second or third generation, administered to children (Rosen 1996). In addition to the acute phase reaction, potential side effects from bisphosphonates include hypocalcemia, esophagitis (oral agents), uveitis, as well as other gastrointestinal problems such as diarrhea, respiratory distress and hypersensitivity (Batch 2003; Munns 2004; Shoemaker 1999). Nephrocalcinosis and delayed fracture healing has also been questioned in the use of bisphosphonate therapy (Batch 2003). Osteonecrosis of the jaw has been a concern among adult patients, particularly those receiving chemotherapy for malignancy (Van den Wyn. 2006); however, to date there have been no reported cases in children.
Given the increasing awareness that osteoporosis is a potential cause of significant morbidity among children with chronic illness, and that bisphosphonates are being administered more frequently in children despite a paucity of empirical evidence, it is paramount that the benefits and potential harms of their use be fully elucidated through critical review of the existing literature.
Objectives
To examine the efficacy and harm of bisphosphonate therapy in the treatment and prevention of secondary osteoporosis in children and adolescents.
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
All randomized controlled trials (RCTs), quasi‐randomized, non‐randomized controlled clinical trials (CCTs), cohort, and case control studies that implemented bisphosphonate treatment in children and adolescents were included.
Non‐experimental studies, such as the case series design, allow for a thorough examination of adverse effects, yet can be affected by bias; in particular selection and detection bias (Albrecht 2005). Case studies and case series were not formally included in the review, but were used to provide supplemental data for harm‐related outcomes. Efficacy‐related outcomes were not abstracted from these studies and they were not considered in our conclusions.
Types of participants
Studies that involved children from birth to 18 years of age with secondary osteoporosis were included. Given the lack of specific clinical, radiographic or densitometric criteria for the diagnosis of osteoporosis in the pediatric population at the present time, the following participants were included in the review: children who had at least one low‐trauma fracture and/or reduced bone mineral density.
Data from studies that did not differentiate between participants with OI, idiopathic juvenile osteoporosis (IJO), and participants with osteoporosis due to other conditions were excluded.
Types of interventions
Studies that involved the oral or IV administration of at least one bisphosphonate (e.g. alendronate, pamidronate, etidronate, clodronate, tiludronate, olpadronate, incadronate, risedronate and/or zoledronate) given at any dose were included. For RCTs and CCTs, the comparator arm could be placebo or any other intervention. For observational studies (i.e., cohort and case control), groups were compared on the basis of exposure to bisphosphonates.
Types of outcome measures
Primary outcomes: Efficacy (1) Absolute change in areal and/or volumetric BMD Z‐score or percent change in areal and/or volumetric BMD of the lumbar spine (LS), femoral neck, distal femur, total hip, total body (TB), or proximal and distal forearm, as measured by dual x‐ray absorptiometry (DXA) or computerized tomography (CT); (2) Percent change in lumbar spine and/or TB bone mineral content (BMC), as measured by DXA or CT; (3) Number of children with incident fractures (clinical and/or radiographic) of the appendicular skeleton and of the vertebra, and/or the average number of participants with incident fractures per year; or (4) Change in vertebral morphometry (as determined by alterations in the specific morphometric ratios outlined by Sumnik 2004).
Harms: (5) Adverse events (including acute phase reaction [fever, chills, malaise], hypocalcemia, bone pain, transient iritis and/or uveitis, nephrocalcinosis, delayed fracture healing, death) experienced by the participants; or (6) Total number of participants who left the trial (i.e., withdrawals) due to adverse events as the number of participants.
Secondary outcomes:
(1) Mobility (as reported by the child or child's parent(s)/guardian(s)); (2) Change in bone pain (as reported by the child or child's parent(s)/guardian(s)); (3) Grip strength (as measured by hand‐held dynamometer); (4) Linear Growth; or (5) Change in bone metabolism parameters, such as osteocalcin, alkaline phosphatase, parathyroid hormone, bone specific alkaline phosphatase, anti‐resorptive markers.
Search methods for identification of studies
Five main electronic databases were searched; MEDLINE (1966 to November 2006), EMBASE (1980 to November 2006), The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL, Issue 4, 2006), CINAHL (1982 to December 2006) and ISI Web of Science (1945 to December 2006). The search was not limited by language, year, or study design. The search strategies were developed by an experienced information specialist (Louise Falzon of the Cochrane Musculoskeletal Group) and can be found below. They were performed by one of the reviewers (PNP) and updated by another reviewer (ACT) on January 3, 2007.
Authors of potentially relevant studies and companies that manufacture bisphosphonates were contacted in an attempt to identify unpublished literature. The reviewers initially contacted the manufacturers by e‐mail, and followed‐up shortly thereafter to ensure the acquisition of a response. The authors of a potentially eligible study were contacted to ensure literature saturation and obtain more detailed information whenever study relevance was unclear. In addition, key author searches were conducted, and reference lists of included studies were checked.
The electronic search strategies are available in Appendix 1.
Data collection and analysis
The search strategy was carried out to identify potentially relevant material for the review. Three reviewers (LMW, ACT, PNP) independently completed a broad screening and assessment of article eligibility using the full‐text articles. Differences regarding the inclusion of a study were resolved through discussion.
Details were extracted from the included studies regarding the study design, study population (age, gender, clinical problem), intervention (type of bisphosphonate, route of treatment administration [oral or IV], treatment dose and duration, with and without calcium and vitamin D supplementation) and the primary and secondary outcome measures previously outlined. Two reviewers (ACT, PNP) independently extracted data from each included study, which was verified by another reviewer (NB). Whenever necessary, the authors of the primary studies were contacted to obtain additional information. Adverse events data from case‐series studies were extracted and a summary overview of the number of studies that supported or did not support bisphosphonate efficacy and safety was compiled.
Three reviewers (ACT, PNP, NB) independently assessed study quality, without blinding to authorship or journal (Berlin 1997). The Jadad scale (Jadad 1996) and an assessment of the adequacy of allocation concealment (Schultz 1995) were used to assess quality for all RCTs and CCTs (Higgins 2005) while the Newcastle‐Ottawa Scale (NOS) was used for cohort and case control studies (Higgins 2005; Wells Unpub). Differences in quality appraisal were resolved through discussion.
Data analysis was to be completed using the Cochrane Review Manager 4.2 and SPSS for randomized and non‐randomized studies, respectively. However, after comparing outcomes within disease groups across studies, it was deemed that combining the data statistically would be inappropriate due to heterogeneity between studies in the clinical profile of studied patients, outcome measurement and reporting, and drug regimen. We planned on assessing the effects of publication bias on the results of this systematic review visually using the funnel plot (i.e., a plot of effect estimates against sample size) method (Egger 1997). Statistical heterogeneity of the data was to be measured using the I2 statistic (Higgins 2003). We planned on performing meta‐analyses using a random effects model, based upon intention‐to‐treat data from the individual studies. Since statistical pooling of the data was not conducted, data will be presented descriptively for all included studies.
Evidence was graded based on the system recommended by the Cochrane Musculoskeletal Group, which is described in Evidenced‐based Rheumatology (Tugwell 2004). Whenever studies reported conflicting data, the study with a higher grade was given precedence for inclusion in the review and the data was subsequently extracted. Based on this grading system, a clinical relevance table (Tugwell 2004) was developed. Clinical relevance tables are useful; as they allow readers of Cochrane reviews to understand a review's primary outcome measures in a single, easy‐to‐read format (Tugwell 2004).
Results
Description of studies
The search strategy retrieved 421 records from MEDLINE, 455 from EMBASE, 37 from the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, 55 from CINAHL, and 303 from ISI Web of Science, which reduced to 807 records once duplicates were removed (Figure 1). Of these articles, six RCTs, two CCTs, and one prospective cohort met the inclusion criteria (Table 1: Characteristics of Included Studies). One RCT (Brown 2005) was excluded, because of failure of trial completion due to inadequate enrolment and high attrition (Table 2: Characteristics of Excluded Studies). An additional 23 case‐series studies were identified through the search strategy and contacting the authors of published abstracts. Although we contacted the manufacturers of bisphosphonates (Merck & Co., Inc., Novartis Pharma Canada Inc.), we did not identify any further potentially relevant studies through this way.
1.
There are four ongoing studies awaiting full publication (Table 3: Characteristics of Ongoing Studies): two RCTs (Crabtree and von Scheven), and two case‐series (both by Langman CB). These studies were identified as published abstracts in the literature search.
The nine studies that met the inclusion criteria were divided into two main disease categories, with each group presenting different risk factors for bone health compromise: 1) patients with neuromuscular conditions (NC) and 2) patients with chronic illness (CI).
One RCT (Henderson 2002) was identified in the NC category, examining between‐groups along with within‐groups comparisons for distal femur and LS BMD outcomes, bone biomarkers and adverse events. Henderson 2002 utilized a double‐blind RCT with placebo to examine 6‐matched pairs of quadriplegic children (age range: 6‐15.7 years) with cerebral palsy using IV pamidronate or a saline placebo administered every three months for one year (five dosing sessions, 15 total doses). Pamidronate was administered daily for three days, at a dose of 1 mg/kg/day. All participants also received daily calcium (1000 mg), a pediatric multivitamin, and vitamin D (400 IU) supplementation.
Five RCTs (El‐Husseini 2004, Golden 2005, Kim 2006, Klein 2005, Rudge 2005), two CCTs (Acott 2005; Lepore 1991) and one cohort study (Bianchi 2000) were categorized under the CI group. All studies reported BMD outcomes (LS and/or TB) by DXA in the CI group, with the exception of Lepore 1991 who presented spine BMD by CT scan. BMD outcomes were compared using within‐groups comparisons for all studies, except for Acott 2005, El‐Husseini 2004, Golden 2005, and Klein 2005 who used between‐groups comparisons. El‐Husseini 2004 presented TB BMC using between‐groups comparisons and Rudge 2005 presented LS BMC using within‐groups comparisons. Golden 2005 used oral alendronate to treat osteopenia in adolescent girls with clinical anorexia nervosa, presenting outcome measures of LS and femoral neck BMD and BMC using between‐groups comparisons. Klein 2005 used IV pamidronate to treat children with severe burn injuries, and described results for LS and TB BMC using between‐groups comparisons, as well as adverse events and bone metabolism parameters.
El‐Husseini 2004 randomized 60 recent renal‐transplant patients, mean age 13.4 years (range 9.1‐17.7 years), into four treatment groups (15 patients/group) and examined them for 12 months. These treatment groups were: 1) control group, 2) oral alfacalcidol group (0.25 µg/day), 3) oral alendronate (5 mg/day), and 4) nasal spray calcitonin (200 IU/day). All patients received calcium (500 mg) daily supplementation as well as corticosteroid and cyclosporine, which was part of their immunosuppressive regimen. No differences were detected between the treatment and control groups with respect to the mean cumulative steroid dose at baseline and after treatment.
Rudge 2005 performed a 12‐month, double‐blind placebo RCT using weekly oral alendronate (1‐2 mg/kg in 40 mg tablets) to treat children on long‐term prednisone therapy for underlying chronic illnesses. There were 11 participants in each of the two groups (age range 4.3‐17.2 years), with a steroid treatment history between 0.3 and seven years at time of entry into the study (median 2.1 years). Five of the included participants were treated daily with prednisone (average dose range: 0.1‐2.4 mg/kg) as well.
Kim 2006 performed a three month RCT including 44 children with nephropathy receiving high doses of steroids. The treatment consisted of oral pamidronate (125 mg/day), which was administered only to the treatment group. All children received oral calcium supplements (500 mg/day), as well as steroid pulse therapy, which included IV pulse methylprednisolone for three consecutive days, followed by oral prednisone administration (1 mg/kg/day) for 11 days.
Lepore 1991 used oral clodronate 1200 mg/day with no vitamin D or calcium supplementation for one year to treat seven children affected by active systemic or polyarticular juvenile chronic arthritis. The control group (six participants) was not defined and the authors did not describe how they were assigned to intervention or control groups. We therefore classified this study as a non‐randomized CCT. The age of the participants were not reported.
In Acott 2005, pediatric patients with renal disease and rheumatic conditions who had sustained fragility fractures and had received at least one month of high‐dose steroids were treated. While this study is referred to in the report as a case control design, it is in fact a non‐randomized CCT. In this study, treatment was with IV pamidronate as a single dose once every two months (1 mg/kg/dose) for one year (n=15 participants) or two years (n=2 participants). Participants matched for disease, age, gender and relative steroid exposure (n=17 participants) acted as controls. Participants treated with pamidronate also received calcium supplementation and vitamin D3 therapy. Information on the age of participants was not reported.
In the Bianchi 2000 cohort study, a group of children with osteoporosis with: 1) LS areal BMD less than ‐1.5 SD below the age‐ and gender‐matched mean and a history of fragility fractures or 2) LS areal BMD less than ‐1.5 SD below the mean and continuous glucocorticoid therapy for at least six months, were followed prospectively. Thirty‐eight children receiving care for diffuse connective tissue diseases were treated with daily oral alendronate (5 mg </= 20 kg; 10 mg > 20 kg) for one year (mean age 12.8 +/‐ 3.6 years). An additional thirty‐eight age‐matched children at baseline (mean age 12.2 +/‐ 3.9 years), who had the same diseases but of a lesser severity and therefore did not require corticosteroid therapy and without bone fragility fractures, were identified as the controls and received no intervention.
Golden 2005 conducted a double‐blind RCT with placebo, treating clinically diagnosed anorexia nervosa adolescents with either daily oral alendronate (10 mg/day) for one year (15 participants, mean age 16.9 +/‐ 1.6 years) or placebo (17 participants, mean age 16.9 +/‐ 2.2 years). All participants received daily calcium (1200 mg) and vitamin D (400 IU) supplementation.
Klein 2005 conducted a double‐blinded placebo‐controlled RCT of IV pamidronate to treat children who had suffered from >40 percent TB surface area burns. Children (age range 5‐18 years), were treated with either an IV dose of pamidronate (23 participants) or placebo (20 participants) infused at time of the burn injury and repeated one week later (i.e. two doses, 1.5 mg/kg per dose for pamidronate and placebo). Follow‐up measures were observed at time of discharge from the hospital and at six months after the last dose of treatment.
Twenty‐three case‐series studies were included in the review, each study implementing a bisphosphonate treatment without comparison to a control group. Six case series observed patients with osteoporosis due to neuromuscular (NM) disease (Allington 2005; Bachrach 2006; Hawker 2005; Plotkin 2006; Shaw 1994; Sholas 2005), while 14 observed those with osteoporosis due to chronic illness (Barr 2002, Borzutzky 2006, Cimaz 2002, Falcini 1996, Fernandes 2004, Gandrud 2003, Goldbloom 2005, Lucarelli 2006, Noguera 2003, Samuel 1994, Sekhar 2001, Sellers 1998, Tragiannidis 2006, Wiernikowski 2005). Finally, three case series were classified as "other", as they included a mixture of patients with secondary osteoporosis due to NM disease and chronic illness (Hogler 2004, Kanumakala 2002, Shaw 2000). All 23 studies presented various primary and secondary outcome measures, with adverse events being of greatest interest for the purpose of this review.
Risk of bias in included studies
For RCTs and CCTs, quality was assessed using a validated, five‐point scale (Jadad 1996), which awarded points on the basis of randomization generation (two points), blinding (two points), and a description of withdrawals and dropouts (one point) (Higgins 2005). Higher scores indicate superior quality. Concealment of allocation (Schultz 1995) was also classified for each included controlled study (Higgins 2005), as to whether the study reported a) adequate concealment, b) unclear concealment, c) inadequate concealment or d) lack of allocation concealment. For the cohort study, the Newcastle‐Ottawa Scale (Wells Unpub) was used; it is a nine‐point scale awarding points on the basis of selection of the cohort or cases/controls (four points), comparability of the cohort or cases/controls (two points), and three points awarded on ascertainment of outcome (cohorts) or exposure (cases/controls). The methodological quality scores and classification of concealment of allocation for the individual studies are given in Table 1: Characteristics of Included Studies and detailed scores of each study are described in the text of the results section.
Effects of interventions
The possibility of combining areal BMD measures from two RCTs (El‐Husseini 2004; Rudge 2005) was considered. However, El‐Husseini 2004 reported T‐scores while Rudge 2005 reported Z‐scores, which use different types of standardization and are thus not combinable. Use of standardized mean differences based on T‐ and Z‐scores was considered, however use of the standardized mean difference assumes that the underlying construct is the same. Here it is not, since the T‐score standardizes BMD relative to healthy young adults whereas the Z‐score standardizes BMD relative to an age and gender‐matched population. Typically, the T‐score is reserved for patients who have ceased growing, while the age‐ and gender‐matched Z‐score is preferred for pediatric patients.
Efficacy data from the included studies for each disease category is therefore presented qualitatively for primary outcomes (Additional Table 1) and secondary outcomes (Additional Table 2 ). Data on adverse events from the included studies as well as the case series are also presented qualitatively (Additional Table 3). Furthermore, data are presented in the clinical relevance table (Additional Table 4).
1. Summary of primary outcomes.
| Study ID | BMD | BMC | Incident fractures | Vertebral Morph |
| Henderson 2002 | Between‐Groups Comparisons Distal femur (region 1) BMD raw score percent change from baseline to end of study was significantly different between treatment and placebo groups, P=0.01. Upon reanalysis, the P‐value was found to be essentially unchanged. Distal femur (region 1) BMD mean Z‐score change from baseline to end of study was significantly different between treatment and placebo groups, P=0.01. For the distal portion of the femoral diaphysis (region 3), the authors report that the difference between the placebo group and the bisphosphonate group is not statistically significant (P=0.1). Upon reanalysis, the P‐value remained non‐significant (P=0.2). For the transition region between regions 1 and 3 (region 2), the authors report a statistically significant difference between the placebo group and the bisphosphonate group (P=0.01). Upon reanalysis, the P‐value remained significant although it was slightly larger (P=0.02). LS BMD raw score percent change from baseline to end of study was significantly different between treatment and placebo groups, P=0.01. This was no longer significant when an appropriate (paired) analysis is used (P=0.08). LS BMD mean Z‐score change from baseline to end of study was not significant between treatment and placebo groups, P=0.06 Within‐Groups Comparisons: Distal femur (region 1) BMD raw score increased 89 +/‐ 21%; P=0.009 from baseline to end of study in treatment group compared with 9 +/‐ 6%; P=0.2 in placebo group Distal femur (region 1) BMD mean Z‐score changed 2.1 +/‐ 0.6; P=0.01 from baseline to end of study in the treatment group and did not significantly change in the placebo group, 0.2 +/‐ 0.2; P=0.6 LS BMD raw score increased 33 +/‐ 3 %; P=0.0004 from baseline to end of study in the treatment group and increased 15 +/‐ 5 %; P=0.03 in the placebo group LS BMD mean Z‐Score change from baseline to end of study increased 1.2 +/‐ 0.2; P=0.005 and 0.4 +/‐ 0.3; P=0.2 in the placebo group | N/A | 3/6 control and 0/6 treatment | N/A |
| El‐Husseini 2004 | Between‐Groups Comparisons: A statistical test comparing the mean change in LS BMD T‐score between the control and alendronate groups was calculated (P<0.001 favoring the alendronate group). Within‐Groups Comparisons: L1‐4 BMD T‐score: Group 1 (control) had a significantly lower L2‐4 BMD at the end of treatment than other 3 groups (P < 0.001 ), group 3 (alendronate) had increased L2‐4 aBMD t‐score from pre‐ to post‐treatment (‐2.3 +/‐ 2.1 to ‐1.9 +/‐ 1.8) however, group 2 (alfacalcidol) had the greatest improvement in aBMD t‐score ( ‐2.3 +/‐ 2.1 to ‐0.5 +/‐0.7) pre‐ to post‐treatment. TB BMD t‐score: Group 1 (control) had a significantly lower TB BMD at the end of treatment than other 3 groups (P < 0.001 ), group 3 (alendronate) had increased TB BMD t‐score from pre‐ to post‐treatment (‐1.4 +/‐ 1.4 to ‐0.9 +/‐ 0.7) however, group 2 (alfacalcidol) had the greatest improvement in BMD t‐score ( ‐1.3 +/‐ 1.2 to +0.3 +/‐0.2) pre‐ to post‐treatment | Between‐Groups Comparisons: No significant differences pre‐ and post‐ treatment in total body BMC (g) (exact P‐value not reported however) | 1/15 control and 0/16 treatment | NA |
| Rudge 2005 | Between‐Groups Comparisons: A between‐groups statistical test comparing the mean change in areal bone mineral density Z‐score was calculated and a non‐significant difference was found (P=0.16). Within‐Groups Comparisons: Lumbar spine BMC absolute value change (g) significantly increased in treatment group (P=0.012), compared to the placebo group (P=0.062). | Between‐Groups Comparisons: Not reported Within‐Groups Comparisons: Lumbar spine BMC absolute value change (g) significantly increased in treatment group (P=0.012), compared to the placebo group (P=0.062) | 1/11 control and 0/11 treatment | NA |
| Acott 2005 | Between‐Groups Comparisons: aBMD Z‐score increased significantly relative to baseline [treatment vs control: at 6 months (0.27+/‐0.14 vs ‐0.82 +/‐0.31), 12 months (0.63+/‐ 0.17 vs 0.17 +/‐ 0.27), 18 months (0.55 +/‐ 0.32 vs 0.17 +/‐ 0.27), 24 months (0.15 +/‐ 0.21 vs ‐0.23) +/‐ 0.22, 36 months (0.77 +/‐ 0.71 vs ‐0.68 +/‐ 0.25) with repeated measures ANOVA (P=0.0057). | N/A | 0/17 control and 1/17 treatment | N/A |
| Lepore 1991 | Between‐Groups Comparisons: Not reported Within‐Groups Comparisons: D12, L1‐3 lumbar spine BMD: 8% increase in treatment group and 7% decrease in control group, at 12 months compared with baseline (statistical significance not stated) | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Bianchi 2000 | Between‐Groups Comparisons: Not reported Within‐Groups Comparisons: L2‐4 aBMD (g/cm2) percent change significantly increased in treatment group from baseline to 12 months (14.9+/‐ 9.8%; P<0.002) while the BMD was 2.6 +/‐ 5%; control group when compared with baseline (not a statistically significant difference). | NA | Control not reported, 0/38 treatment | N/A |
| Golden 2005 | Between‐Group Comparisons: L1‐4 aBMD (g/cm2) % change: Increased 3.5 +/‐ 4.6 % in treatment group compared with 2.2 +/‐ 6.1% in the placebo group, P=0.53 (not significant between groups) Femoral neck aBMD (g/cm2) % change: Increased 4.4 +/‐ 6.4 % in treatment group and 2.3 +/‐ 6.9% in the placebo group, P=0.41 (not significant between groups) Femoral neck vBMD (g/cm3) from baseline to follow‐up of the femoral neck was significantly higher in alendronate group compared to the placebo group (0.184+/‐0.005 vs. 0.151 +/‐0.003; P=0.004) Femoral neck vBMD (g/cm3) absolute change was significantly greater in those receiving alendronate (P<0.05). Within‐Group Comparisons: L1‐4 aBMD (g/cm2) increased significantly from baseline to follow‐up in the treatment group (P=0.02) and non‐significantly from baseline to follow‐up in the control group (P=0.18) Femoral neck BMD (g/cm2) increased significantly from baseline to follow‐up in the treatment group (P=0.02) and non‐significantly from baseline to follow‐up in the control group (P=0.22). | Between‐Group Comparisons: No significant differences in absolute value of BMC of the lumbar spine between the treatment and placebo groups | 1/15 control, 2/14 treatment | N/A |
| Klein 2005 | N/A | Between‐Groups Comparisons: At time of discharge from hospital (˜2 months), LS BMC percent change from baseline was significant (P<0.005) between the treatment and placebo groups, however TB BMC was not statistically different between the two groups Significant increase in TB BMC percent change and LS BMC percent change from baseline to 6‐month follow‐up between treatment group and placebo (P<0.005) (Exact percentages not reported) | N/A | N/A |
| Kim 2006 | Between‐Groups Comparisons: Not reported Within‐Groups Comparisons: LS BMD decreased significantly from 0.654+/‐0.069 (g/cm2) to 0.631+/‐0.070 (g/cm2) in the control group (P=0.0017). LS BMD was not reduced in the control group from 0.644+/‐0.189 (g/cm2) to 0.647+/‐0.214 (g/cm2) (P‐value not reported). | N/A | N/A | N/A |
2. Summary of secondary outcomes.
| Ref ID | Mobility | Bone Pain | Grip Strength | Bone Meta/Biomarkers | Linear growth |
| Henderson 2002 | N/A | N/A | N/A | NTx was reduced in treatment group and remained low for 6 months after last dose No change in osteocalcin, bone‐specific alkaline phosphatase | N/A |
| El‐Husseini 2004 | N/A | N/A | N/A | No statistically significant differences, pre‐ and post‐treatment | N/A |
| Rudge 2005 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Mean height velocity was similar in the treatment group (4.2 cm/year, Z‐score ‐1.4) and in the placebo group (4.5 cm/year, Z‐score ‐1.3) |
| Bianchi 2000 | N/A | No bone pain reported in treated group | N/A | uNTx decreased by 27 +/‐ 16.5% in treatment group (not measured in control group) | In pre‐pubertal children (Tanner stages 1 and 2) yearly increase in height was 2.9 +/‐ 1.2 cm during the study, compared with 2.8+/‐ 1.1 cm in the year preceding the study (considered satisfactory by investigators) |
| Acott 2005 | N/A | All patients had a resolution of their bone pain after 48 hours of treatment | N/A | No statistically significant differences, pre‐ and post‐treatment | Annual growth rates of the treated and control groups were not different |
| Lepore 1991 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Golden 2005 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Klein 2005 | N/A | N/A | N/A | No statistically significant differences, pre‐ and post‐treatment | N/A |
| Kim 2006 | N/A | N/A | N/A | No statistically significant changes in serum calcium, BUN, and creatinine level. Serum phosphate level decreased in the control (P<0.05) and treatment groups (P<0.05). The ALP level also decreased in the control (P<0.001) and treatment (P<0.001) groups. Serum PTH level increased in the control (P<0.001) and treatment (P<0.001) groups. Serum osteocalcin levels decreased in control (P<0.001) and treatment (P<0.001) groups. Serum osteocalcin levels decreased in control (P<0.001) and treatment (P<0.001) groups. Urine pyridinoline levels decreased in control (P<0.001) and treatment (P<0.001) groups. | N/A |
3. Harms‐related outcomes.
| Ref ID | Musculo & Min Meta | Gastrointestinal | Non‐spec/Systemic | AE Withdrawals |
| El‐Husseini 2004 | 1 of 15 in alendronate group (hypocalcemia) 1 of 15 in calcitonin group (hypocalcemia) 0 of 15 in alfacalcidol group 0 of 15 in control group | NR | NR | NR |
| Rudge 2005 | NR | NR | NR | 0 withdrawals due to AE |
| Bianchi 2000 | NR | 1 of 39 in treated group (esophageal erosions) 0 of 38 in control group | NR | 1/39 in treatment 0/38 in control |
| Acott 2005 | 0 in treated group 0 in control group | NR | 3 of 17 in treated group (acute phase reaction) 0 of 17 in control group | 0 withdrawals due to AE |
| Lepore 1991 | NR | N/A | NR | 1/7 in treatment (GI side effect) 0/6 in control |
| Henderson 2002 | NR | NR | NR | 0 withdrawals due to AE |
| Golden 2005 | NR | 2 of 15 in treated group (nausea and abdominal bloating) 2 of 17 in control group (nausea and abdominal bloating) | NR | 0/15 in treatment 1/17 from control (dyspepsia) |
| Klein 2005 | NR | NR | NR | 0 withdrawals due to AE |
| Kim 2006 | NR | Some patients in treatment group, number not reported | For patients receiving the drug > 3 months, 3/22 experienced the formation of thin, well‐defined transverse sclerotic lines at the meta‐physeal ends of long bones | NR |
| Barr 2002 | NR | NR | 3 of 10 (fever) | 3/10 |
| Cimaz 2002 | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Falcini 1995 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 0/4 |
| Gandrud 2003 | N/A | N/A | N/A | NR |
| Noguera 2003 | NR | 6 of 10 (non‐specific GI) | 10 of 10 (fever) | 0/10 |
| Wiernikowski 2005 | 2 of 10 (hypocalcemia) | N/A | NR | 0/10 |
| Bachrach 2006 | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Allington 2005 | Reported 0 | Reported 0 | Reported 0 | 0/18 |
| Plotkin 2006 | Reported 0 | Reported 0 | 3/23 rash, unspecified | 0/23 |
| Hawker 2005 | 4 of 24 (bone/muscle pain) | 8 of 24 (non‐specific GI) | 4 of 24 (headache) 2 of 24 (dizziness) 1 of 24 (rash) 1 of 24 (memory loss) | 0/24 |
| Shaw 1994 | Reported 0 | Reported 0 | Reported 0 | 0/3 |
| Hogler 2004 | N/A | N/A | N/A | NR |
| Kanumakala 2002 | 1 of 3 (bone/muscle pain) | NR | 2 of 3 (transient flu‐like) | 0/3 |
| Shaw 2000 | NR | NR | 2 of 4 (acute phase reaction) | 0/4 |
| Sholas 2005 | NR | 1 of 10 Vomiting 1 of 10 Nausea 4 of 10 Diarrhea 1 of 10 Arthralgia 5 of 10 Hematemesis | NR | 1/10 |
| Borzutzky 2006 | Reported 0 | Reported 0 | Reported 0 | 0/5 |
| Fernandes 2004 | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Goldbloom 2005 | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Lucarelli 2006 | NR | NR | 1 of 1 Fever 1 of 1 Headache | 0/1 |
| Samuel 1994 | Reported 0 | Reported 0 | 5/5 experienced band‐like metaphyseal sclerosis appeared on radiography of the long bone | 0/5 |
| Sekhar 2001 | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Sellers 1998 | 0 Reported | 0 Reported | 0 Reported | 0/3 |
| Tragiannidis 2006 | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Presented as Number of children with the adverse events (AE) compared to the number of children treated in that study N/A = Data not available or data not extractable NR = Data not reported Musculoskeletal and Mineral Metabolism = hypocalcemia, bone/muscle pain Gastrointestinal = Esophageal erosions, nausea and abdominal bloating, non‐specific gastrointestinal events Non‐specific / Systemic = Headaches, dizziness, transient flu‐like illness, acute phase reaction, fever, rash memory loss |
4. Clinical relevance table bisphosphonate treatment: BMD Data.
| Outcome (scale) | # pts (# trials) | % change in control | Wt absolute change | Relative % change* | NNT | Statistical sig | Quality of evidence |
| % increase in BMD of Lumbar Spine | 29 (1) | 2.2% | 1.3% 95% CI: ‐2.6, 5.2 | 59.1% 95% CI: ‐118.2, 236.4 (I) | NA | Not statistically significant | Silver |
| % increase in BMD of Femoral Neck | 29 (1) | 2.3% | 2.1% 95% CI: ‐2.7, 6.9 | 91.3% 95% CI: ‐117.4, 300.0 (I) | NA | Not statistically significant | Silver |
| % increase in BMD of Total Hip | 29 (1) | 1.6% | 2.0% 95% CI: ‐4.3, 8.31 | 25% 95% CI: ‐268.8, 518.8 (I) | NA | Not statistically significant | Silver |
| Legend BMD = bone mineral density | CI = confidence interval | I=improvement, CI = confidence interval | NNT/H= Number Needed to Treat to Benefit or Harm |
Patients with neuromuscular disorders: Although the Henderson 2002 study was pair‐randomized, an incorrect (unpaired) analysis was used. However, the primary outcome (i.e., percent change from baseline in BMD at various locations) was reported for each patient, allowing us to re‐analyze the results. Results of our re‐analysis are only reported when they differed from the results reported in the trial report.
The primary focus of the Henderson 2002 study was the BMD of three regions of the distal femur at the end of 12 months. For the metaphyseal region (region 1), a statistically significant difference between the placebo group (9% increase in BMD) and the bisphosphonate group (89%) was reported (P=0.01). For the distal portion of the femoral diaphysis (region 3), the difference between the placebo group and the bisphosphonate group was not statistically significant (P=0.1, 6% versus 33%, respectively). For the transition region between regions 1 and 3 (region 2), a statistically significant difference between the placebo group and the bisphosphonate group was achieved (P=0.01, 9% versus 21%, respectively). Since three regions were tested, and none of them was identified to be of primary interest a priori, a correction for multiple testing is appropriate. Using a conservative Bonferroni correction of the P‐value cutoff for significance (i.e., 0.05/3 = 0.017), only the result for the metaphyseal region (region 1) is statistically significant. A statistically significant difference (P=0.01) between the placebo group (15% increase) and the bisphosphonate group (33% increase) for the LS areal BMD was reported, however, this was no longer significant when we performed the appropriate (paired) analysis (P=0.08).
Serum N‐telopeptides (sNTx) declined in the treatment group and remained low six months after the last dose, indicating that bone resorption decreased as expected, and was persistently low in the short‐term. There were no remarkable changes, however, in change in bone metabolism parameters, such as osteocalcin, alkaline phosphatase, parathyroid hormone, bone specific alkaline phosphatase, anti‐resorptive markers in either treatment or placebo group. Quality was assessed as four using the Jadad scale (an additional point was not awarded for describing the method of randomization) and allocation concealment was unclearly reported.
Patients with chronic illness: Eight controlled studies were classified as belonging in the category for patients with chronic illness.
The El‐Husseini 2004 randomized trial emphasizes within‐group comparisons; however, it was possible to extract sufficient information from the report to perform a statistical test comparing the mean change in LS BMD T‐score between the control and alendronate groups; a significant difference was observed (P<0.05 favouring the alendronate group). There was one new fracture presented in the control group, and no fractures in either of the three treatment groups. No statistically significant differences in bone metabolism parameters were seen between the treated and placebo groups or between baseline and follow‐up within each group. Quality was assessed as one using the Jadad scale (one point was awarded for reporting that the study was randomized) and allocation concealment was unclearly reported.
In the Rudge 2005 randomized trial it was possible to extract sufficient information from the report to perform a between‐groups statistical test comparing the mean change in LS areal BMD Z‐score (non‐significant difference, P=0.16). For within‐groups comparisons, the LS areal BMD Z‐score change was not found to be significant within the treatment (P=0.1) nor the control (0.157) group from baseline to follow‐up. However, LS volumetric BMD increased significantly within the treatment group (P=0.013) but not within the control group (P=0.156). Similarly, when evaluating absolute LS BMC change, a significant increase was seen within the treatment group from baseline to follow‐up (P=0.012), compared to an insignificant change within the placebo arm (P=0.062). One incident fracture was observed in the control group, while there were no new fractures observed in the treatment group. Linear growth rates were similar for both groups. Quality was assessed as four using the Jadad scale (an additional point was not awarded for describing the method of randomization) and the allocation concealment was unclearly reported.
In the Kim 2006 RCT, only within groups comparisons were made. The mean LS BMD decreased significantly in the control group (P=0.0017), however, it did not in the treatment group (P‐value not reported) after the three‐month study. This report received one point using the Jadad scale for reporting that it was a randomized trial and allocation concealment was unclear.
In the Lepore 1991 trial, an 8% increase in the treatment group and a 7% decrease in the control group were observed for LS BMD measures by CT scan (D12, L1‐3) at 1‐year follow‐up compared with baseline. However, except for the mean BMD in the treatment and control groups, no baseline data were reported. No measures of dispersion were reported, rendering it difficult to draw conclusions from this study. One point out of five was awarded for reporting withdrawals on the Jadad instrument and allocation concealment was inadequate.
In the Acott 2005 trial, the children in the intervention group were different from those in the control group at baseline, making comparison of outcome questionable. Within‐groups comparisons demonstrated a statistically significant difference favouring the treatment arm in the change from baseline in LS areal BMD Z‐score at 6, 12, 18, 24 and 36‐months follow‐up (P=0.0057). One participant in the treatment group had a recurrence of a thoracic compression fracture one year following pamidronate cessation. All patients had resolution of their bone pain after the first 48‐hours of treatment. There were no statistically significant differences pre‐ and post‐treatment in bone biomarkers (alkaline phosphatase, bone‐specific alkaline phosphatase, uNTx). Annual linear growth rates of the cases and controls were not different. This report received 0 points using the Jadad index and allocation concealment was inadequate. In the Bianchi 2000 cohort study, LS areal BMD increased significantly within the treatment group from baseline to 12‐months follow‐up (P<0.002), while the LS areal BMD in the control was not statistically different when compared to baseline (P‐value not reported). Neither new fractures nor bone pain were reported in the treatment group during the trial. Urinary N‐telopeptides (uNTx) decreased in the treatment group by end of study over pre‐treatment values. There were no differences in linear growth between the groups. No between‐group analyses were performed.
Using the Newcastle‐Ottawa Scale to assess quality (Wells Unpub), the Bianchi 2000 report received five stars. Stars were awarded for selection representativeness, ascertainment of exposure, selection demonstration that outcome was not present at start of study, assessment of outcome, and adequacy of outcome follow‐up categories. It's important to note that stars were taken away because it lacked a valid control group (i.e., children in the control group had less severe disease than those in the treatment group). Furthermore, the data from the treatment and control groups were juxtaposed in the results section of the report, making it difficult to assess.
In the Golden 2005 double‐blind RCT, LS and femoral neck areal BMD percent change from baseline to 1 year follow‐up were not statistically different between the two groups (P=0.53, P=0.41 respectively). Absolute change in femoral neck volumetric BMD was significantly different from pre‐ to post‐study between the treatment and placebo groups (P<0.05). Within‐group comparisons found LS areal BMD to have differed significantly at follow‐up compared to baseline in the treatment group (P=0.02) but not significantly in the placebo group (P=0.18). Similarly, femoral neck areal BMD at follow‐up increased significantly compared to baseline within the treatment group (P=0.02) but not within the control group (P=0.22). There were no significant differences observed in the absolute value change in LS BMC between the two groups. Three participants sustained incident fractures; one in the placebo group (multiple atraumatic tibia) and two in the treatment group (traumatic humerus, traumatic radius).
Although there was relatively limited loss to follow up, this study may have been underpowered because observed differences were smaller than expected and the standard deviation was larger than anticipated. Quality was assessed as four using the Jadad scale (an additional point was not awarded for describing the method of randomization) and the allocation concealment was adequately reported.
In the Klein 2005 double‐blinded RCT, LS BMC percent change from baseline was significantly different between the treatment and placebo groups approximately two months post‐first infusion (P<0.005). However, there were no statistically significant differences in percent change in TB BMC. At 6 months follow‐up, there was a significant difference in TB BMC percent change between both groups (P<0.005) but not at discharge, in addition to a continued difference in LS BMC (P<0.005). There were no statistically significant differences observed pre‐ and post‐treatment within the groups for bone biomarkers (intact parathyroid hormone, alkaline phosphatase and urine deoxypyridinoline (an anti‐resorptive marker). There was substantial loss to follow‐up: 9/23 (39%) in the pamidronate group; 9/20 (45%) in the placebo group, which weakens the study's results significantly and could bias the treatment effect. Because patients had severe burns, there was a high incidence of sepsis, leading to death in three cases. A total of 10 patients did not return for the six‐month measurements. Quality was assessed as four using the Jadad scale (an additional point was not awarded for describing the method of randomization) and the allocation concealment was unclearly reported.
Case series studies
In studies that used a case‐series design and thereby lacked a control group, the majority showed increases in BMD while receiving bisphosphonate therapy, although it remains unknown whether these changes were the sole and direct result of the bisphosphonate intervention. Within the chronic illness group, all 14 included studies (Barr 2002, Borzutzky 2006, Cimaz 2002, Falcini 1996, Fernandes 2004, Gandrud 2003, Goldbloom 2005, Lucarelli 2006, Noguera 2003, Samuel 1994, Sekhar 2001, Sellers 1998, Tragiannidis 2006, Wiernikowski 2005) reported a positive effect of bisphosphonate use. LS areal BMD, as well as femoral neck BMC was found to have increased in all studies, except for one study, which did not measure BMD, yet observed a decrease in the number of fractures upon bisphosphonate treatment (Samuel 1994). Improvements were also seen in TB BMC, improved motor function, decreased bone resorption, and a decreased incident fracture rate throughout these studies.
Within the NC group, three studies (two pamidronate, one alendronate) reported favourable outcomes including increased LS areal BMD (Allington 2005, Hawker 2005, Shaw 1994). In one study (Plotkin 2006), LS BMD was not significantly different from baseline at 6 months of treatment, however, statistical significance was achieved after one year of treatment (P<0.01). Although there was one new fracture reported in two studies (Plotkin 2006, Sholas 2005), the difference was not statistically significant at the end of follow‐up. There were no new fractures seen in the other studies that monitored incident fractures (Allington 2005, Hawker 2005). Another study (Bachrach 2006) did not conclude whether bisphosphonate use was overall positive or negative, as LS areal BMD and TB BMD was not seen to increase nor decrease during the course of treatment with oral alendronate.
A favourable pattern of bisphosphonate intervention was observed in the "other" group, where three studies noted improvements in LS areal BMD (Kanumakala 2002, Shaw 2000), improved LS BMC (Kanumakala 2002), decreased incident fracture rates (Kanumakala 2002) and decreases in reported pain (Shaw 2000). A study on zoledronate (Hogler 2004) only examined harms, and did not come to a firm conclusion in favour of bisphosphonate intervention, suggesting only continued supervision during treatment.
Overall, 21 of 23 case‐series studies supported the efficacy of bisphosphonates in treating children with secondary osteoporosis. None of the studies discouraged the use of bisphosphonate intervention in this group of children and adolescents.
Harms
Data on harms (number of children with adverse events [AE] and withdrawals due to AE) were extracted for all studies (Table 3). Three main AE categories were identified: musculoskeletal and mineral metabolism, gastrointestinal, and non‐specific or systemic‐related effects. Like the reporting of efficacy data, there were differences in the reporting of harms across studies. For example, data was not available or data was not extractable in five of the 23 case‐series. Furthermore, detailed laboratory and clinical monitoring was inconsistently carried out in the other studies.
Overall, considering all studies, bisphosphonate use was generally well‐tolerated over the short‐term in these patients with underlying chronic illnesses. Only one patient was reported having withdrawn due to an AE (Lepore 1991, clodronate, due to non‐specific GI side effects). However, five deaths were reported in the included studies. In Henderson 2002, 1/6 children died in the placebo group (reason of death not reported) while in Rudge 2005, 1/11 children died in the treatment (alendronate) group due to pulmonary hemorrhage, complicating systemic lupus. In the Klein 2005 trial, 2/18 children in the pamidronate and 1/17 children in the placebo group died from acute sepsis. In all cases, the deaths were reported by the authors as not being attributable to treatment.
Hypocalcemia was reported in three treated patients (El‐Husseini 2004: 1/15, Wiernikowski 2005: 2/10). More frequently reported was a constellation of symptoms known as the "acute phase reaction" (Acott 2005: 3/17 treated patients; 0/17 controls, 19 case‐series patients), followed by gastrointestinal effects (Bianchi 2000: 1/39 patients, esophageal erosions; 26/241 case‐series patients, non‐specific GI effects), bone/muscle pain (five case‐series patients), dizziness (two case‐series patients), rash (four case‐series patient) and memory loss (one case‐series patient). In Golden 2005 RCT, a similar number in the treated and control arms manifested nausea and abdominal bloating. In two studies, 8 children receiving bisphosphonate treatment experienced band‐like metaphyseal sclerosis appeared on radiography of the long bones (Kim 2006, Samuel 1994).
Discussion
While there are numerous examples in the literature of fragility fractures due to osteoporosis in children with chronic illness, this review highlights that to date; there remains a paucity of controlled bisphosphonate intervention trials. The review also makes apparent the lack of agreement on the criteria for initiation of treatment for osteoporosis in children (as evidenced by the observed inconsistent criteria for enrolment in the reviewed studies). The results further highlight the heterogeneity in choice of bisphosphonate agents, dosing regimens, and measurement/reporting of outcomes, all of which precluded the combining of study results. Even among studies where the same agents were used, there were differences in approach to the dosing regimes. For the oral agents, some studies used doses on a per kg basis while others employed higher or lower dose therapy with a weight cut‐off. For IV agents (in this case, pamidronate for controlled studies), the regimes generally offered 1‐1.5 mg/kg/day (3 to 15 mg/kg/year) but the frequency of administration varied (e.g., three consecutive days for three months versus a single infusion two weeks in a row). There was insufficient data to compare the efficacy of IV versus the more convenient oral agents in the chronic illness setting. Overall, the effect of the various bisphosphonates used in these pediatric osteoporosis trials favoured the treatment arm and this, combined with a favourable short‐term safety profile, justifies their further study in the context of clinical trials.
LS areal BMD percent or Z score change from baseline after 1‐2 years of therapy was the most consistently reported outcome parameter, likely because this is the skeletal site where the most comprehensive normative data are available for the commonly used BMD machines in pediatric practice. The exception to this was the study by El‐Husseini 2004, in which the LS areal BMD T‐score was used. The T‐score, which represents the standardized deviation from the healthy adult mean, should be reserved for patients who have ceased growing, while the age‐ and gender‐matched Z‐score is preferred for pediatric patients. In the controlled trials, all but two studies (Bianchi 2000, Kim 2006) showed a significant within‐group increase from baseline in lumbar spine areal BMD following 1‐2 years of oral/intravenous bisphosphonate therapy. Only two studies reported between‐group analyses post‐treatment, one showed no significant difference (using daily oral alendronate in anorexia nervosa and with lumbar spine and femoral neck areal and volumetric BMD outcomes, Golden 2005), and the other demonstrated a treatment effect (using two doses of pamidronate separated by 6 months in burn patients, with lumbar spine and total body BMC outcomes, Klein 2005).
Two studies reported LS or TB BMC percent change following bisphosphonate administration (Klein 2005; Rudge 2005; positive effect) while two others presented the percent change for areal and volumetric spinal and femoral neck BMD from baseline (Golden 2005; Rudge 2005) and another presented percent change for lumbar spine only (Henderson 2002). BMC percent change from baseline to end of study is the most useful outcome measure in children, as it specifically reflects the amount of bone mineral accrued during the study time period. The calculation of volumetric BMD at the spine according to Carter 1992 or Kroger 1992 allows consideration for the impact of bone size on the BMD result, whereas areal BMD may lead to a falsely low result in a child who demonstrates poor linear growth relative to his/her age‐ and gender‐matched peers. Volumetric BMD values at the spine permit evaluation of the evidence for a bone growth effect (or lack thereof) on the serial BMD results. Similar consideration should be given to pubertal stage, where bone mineral accrual may lag due to delayed puberty. Correction of BMD outcomes by using skeletal age (bone age) instead of chronological age is useful in populations for whom delayed puberty is a concern. Ultimately, randomization of sufficient numbers of patients is the optimal manner to account for heterogeneity among patient profiles which may influence the BMD results.
Outcome parameters beyond BMD or BMC were studied either infrequently or not at all in the studies identified through this review. Bone biomarkers are typically assessed in adult osteoporosis trials and have been employed less often in children, due to the lack of standardized normative data and the influence of muscle size on creatinine‐normalized urinary results. In this review, two studies showed a within‐group decrease in resorptive markers in the treated arm while the control groups did not show a within‐group decrease in resorptive markers. Four studies showed no differences in either resorption or formation markers. Therefore, the bone biomarker results did not appear to be in keeping with the positive effects on LS areal BMD that were viewed across the studies in the treatment arms. Clinically relevant (i.e., functional) outcome parameters such as mobility, vertebral morphometry, and pain were either not studied or were assessed inconsistently. Furthermore, there is increased attention to the effect of pharmaceutical interventions on the functional muscle‐bone unit in children, and none of the studies in this review addressed the effect of treatment on muscle parameters (such as lean body mass by DXA), or the relationship between lean body mass changes and bone health outcomes.
All of these trials had small sample sizes (i.e., less than 40 patients per group). Although typical for trials (Chan 2005), this sample size is insufficient to detect evidence for fracture prevention, and so while incident fractures were reported in the controlled studies, no firm conclusions can be drawn. The sample size to detect a difference in vertebral fracture prevention during therapy among adults appears to be more than 200 (Cranney 1999), far in excess of the numbers of patients participating in these pediatric trials.
Bisphosphonate therapy appeared to be generally well‐tolerated in the reviewed studies; all of which were short‐term (one to two years of treatment), although systematic laboratory and clinical monitoring would have improved the quality of the results. Hypocalcemia was reported infrequently compared to patients with OI (Rauch 2003), the reasons for which are unclear. Differences in calcium supplementation or in 25‐hydroxyvitamin D levels at baseline may have played a role in the patients' calcium homeostasis, factors which should be explored more thoroughly in future studies. On the other hand, the acute phase reaction, gastrointestinal side effects and muscle/bone pain emerged as frequent adverse events. There were no reported cases of osteonecrosis of the jaw. In OI, while an absence of a mineralization defect has been observed on trans‐ilial bone biopsies among children receiving two to four years of pamidronate therapy, retention of calcified cartilage (dense tissue) in newly formed trabecular bone has been noted (Rauch 2002), the clinical significance of which is unknown. This observation in pediatric OI patients makes histological monitoring for safety purposes prudent during the course of future bisphosphonate trials among children with secondary osteoporosis.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
Overall, the results of the controlled studies in this review justify further use of bisphosphonates in the context of pediatric clinical trials. While bisphosphonates hold promise for future use in children with secondary osteoporosis, at present there is insufficient evidence for routine use of the drugs in clinical care. On the other hand, the favourable short‐term profile of bisphosphonate agents and preliminary positive effects on BMD and pain reduction may justify their use on compassionate grounds in severe cases where there is clinical evidence for bone fragility that significantly impacts patient quality of life.
Implications for research.
Further research is required in a number of areas of pediatric osteoporosis due to chronic illness. First, natural history studies in children and youth with the various disorders are needed in order to establish the relationship between BMD and bone fragility, and to determine the risk factors for bone morbidity. In this way, criteria for osteoporosis in children can be established and identification of children at risk can be effectively carried out. This will ensure enrollment in clinical trials will be reserved for children with clinical need. An accepted criterion for osteoporosis and a standardized approach to bone health outcomes, such as BMD reporting in children, will allow for appropriate comparisons across studies to be made in future reviews. Such initiatives to foster standardization of outcome reporting in clinical trials have been established in other fields (e.g. OMERACT ‐ Outcome Measures in Rheumatology; Boers 2005).
Further treatment trials are warranted, with attention to controlled studies on a large number of patients so that fracture rates can be evaluated. Optimal dosing for fracture reduction/prevention without over‐suppression of bone turnover merits further study, as does the relative efficacy of IV versus oral agents. Outcome measures in addition to BMD should be considered in future trials, including attention to changes in bone structure/geometry (such as through peripheral quantitative computerized tomography and vertebral morphometry), and evaluation of functional parameters such as fracture rates but also mobility, bone pain and muscle function. Furthermore, the relationship between the intimately linked muscle and bone development in children merits further evaluation in future trials. Bone histomorphometry is an advised evaluative tool in at least a subset of patients undergoing treatment protocols, for the purpose of safety monitoring and to directly document changes in bone architecture and metabolism. Longer‐term evaluation following bisphosphonate therapy is indicated in order to determine the duration of treatment effect and for the purpose of safety monitoring. Finally, since a number of studies in this review have been completed according to authors' reports but are either undergoing preparation for submission or are in peer review, it will be important to update the contents of this review in the near future including this body of research.
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 20 May 2008 | Amended | Converted to new review format. CMSG ID C011‐R |
History
Protocol first published: Issue 2, 2005 Review first published: Issue 4, 2007
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 17 August 2007 | New citation required and conclusions have changed | Substantive amendment |
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Louise Falzon of the Cochrane Musculoskeletal Group for her assistance in developing the search strategy, Isabelle French for her contribution to the development of the protocol, Siobhan O'Donnell for her guidance on data extraction and data presentation, and Margaret Sampson for verifying the literature searches.
Appendices
Appendix 1. Electronic search strategies
MEDLINE was searched using the following terms: 1. exp osteoporosis/ 2. osteoporo$.tw. 3. exp Bone Density/ 4. exp fractures, bone/ 5. (bone$ adj fragil$).tw. 6. bone loss.tw. 7. bmd.tw. 8. bone mineral densit$.tw. 9. or/1‐8 10. exp Diphosphonates/ 11. (diphosphonate$ or bisphosphonate$).tw. 12. etidronic acid.sh. 13. alendronate.sh,tw. 14. pamidronate.sh,tw. 15. etidronate.tw. 16. clodronic acid.sh,tw. 17. clodronate.tw. 18. tiludronate.tw. 19. olpadronate.tw. 20. incadronate.tw. 21. zolendronate.tw. 22. risedronate.tw. 23. exp child/ 24. exp ADOLESCENT/ 25. (child$ or pediatric$ or paediatric$ or teenage$ or adolescen$).tw. 26. or/10‐22 27. or/23‐25 28. and/9,26‐27 29. remove duplicates from 28
EMBASE was searched using the following terms: 1. exp osteoporosis/ 2. osteoporo$.tw. 3. exp Bone Density/ 4. exp fractures/ 5. (bone$ adj fragil$).tw. 6. bone loss.tw. 7. bmd.tw. 8. bone mineral densit$.tw. 9. or/1‐8 10. exp Diphosphonates/ 11. (diphosphonate$ or bisphosphonate$).tw. 12. etidronic acid.sh. 13. alendronate.sh,tw. 14. pamidronate.sh,tw. 15. etidronate.tw. 16. clodronic acid.sh,tw. 17. clodronate.tw. 18. tiludronate.tw. 19. olpadronate.tw. 20. incadronate.tw. 21. zolendronate.tw. 22. risedronate.tw. 23. exp child/ 24. exp ADOLESCENT/ 25. (child$ or pediatric$ or paediatric$ or teenage$ or adolescen$).tw. 26. or/10‐22 27. or/23‐25 28. and/9,26‐27 29. remove duplicates from 28
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials was searched using the following terms: 1. osteoporosis.mp. 2. osteoporo$.tw. 3. Bone Density.mp. 4. fractures.mp. 5. (bone$ adj fragil$).tw. 6. bone loss.tw. 7. bmd.tw. 8. bone mineral densit$.tw. 9. or/1‐8 10. Diphosphonates.mp. 11. (diphosphonate$ or bisphosphonate$).tw. 12. etidronic acid.mp. 13. alendronate.mp. 14. pamidronate.mp. 15. etidronate.mp. 16. clodronic acid.mp. 17. clodronate.mp. 18. tiludronate.mp. 19. olpadronate.mp. 20. incadronate.mp. 21. zolendronate.mp. 22. risedronate.mp. 23. child.mp. 24. ADOLESCENT.mp. 25. (child$ or pediatric$ or paediatric$ or teenage$ or adolescen$).tw. 26. or/10‐22 27. or/23‐25 28. and/9,26‐27
CINAHL was searched using the following terms: 1. exp osteoporosis/ 2. osteoporo$.tw. 3. exp Bone Density/ 4. exp fractures/ 5. (bone$ adj fragil$).tw. 6. bone loss.tw. 7. bmd.tw. 8. bone mineral densit$.tw. 9. or/1‐8 10. exp Diphosphonates/ 11. (diphosphonate$ or bisphosphonate$).tw. 12. etidronic acid.sh. 13. alendronate.sh,tw. 14. pamidronate.sh,tw. 15. etidronate.tw. 16. clodronic acid.sh,tw. 17. clodronate.tw. 18. tiludronate.tw. 19. olpadronate.tw. 20. incadronate.tw. 21. zolendronate.tw. 22. risedronate.tw. 23. exp child/ 24. exp ADOLESCENT/ 25. (child$ or pediatric$ or paediatric$ or teenage$ or adolescen$).tw. 26. or/10‐22 27. or/23‐25 28. and/9,26‐27 29. remove duplicates from 28
ISI Web of Science was searched using the following terms: 1. (osteopor* or bone density or fracture* or bone* adj fragil* or bone loss or bmd or bone mineral densit*) 2. (diphosphonate* or bisphosphonate* or etridronic acid or alendronate or pamidronate or etridronate or clodronic acid or clodronate or tiludronate or olpadronate or incadronate or zolendronate or risedronate) 3. (child* or pediatric* or paediatric* or teenage* or adolescen*) 4. 1 and 2 and 3
Data and analyses
Comparison 1. lumbar spine.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 lumbar spine | 1 | 29 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.30 [‐2.62, 5.22] |
1.1. Analysis.
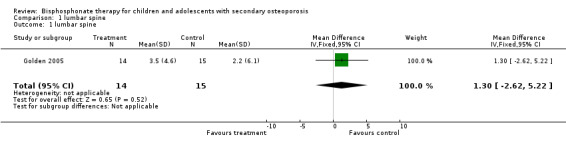
Comparison 1 lumbar spine, Outcome 1 lumbar spine.
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Acott 2005.
| Methods | Controlled Clinical Trial Trial duration: 1‐year |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: pediatric nephrology and rheumatology patients identifying with skeletal fractures. Controls: subjects matched for disease, age, gender and relative steroid exposure. Sample size: 34 (17 cases, 17 controls) Mean age: not reported Female/Male: treatment 8/9, control 8/9 |
|
| Interventions | Cases: Intravenous pamidronate at a dosage of 1 mg/kg/dose (maximum 90 mg) once every 2 months administered over 4 hours for 1‐year (15 subjects), or over 2 years (2 subjects) Calcium and vitamin D supplementation for participants treated with palmidronate: minimum of 500 mg/day of elemental calcium and 400 IU/day of vitamin D for children under 10, mimimum of 1000 mg/day of elemental calcium and 800 IU/day of vitamin D for children over 10 Control: No intervention All patients received atleast one month of high‐dose steroids (60 mg/m2 or 2 mg/kg) before weaning. |
|
| Outcomes | L1‐4 aBMD (Z‐score):
Change in Z‐score Incident Fractures Adverse events: Acute phase reaction, hypocalcemia Bone metabolism parameters: Alkaline phosphatase, Bone specific alkaline phosphatase, anti‐resorptive markers (urinary NTx) Linear Growth |
|
| Notes | Quality Assessment: Jadad Scale = 0/5 (R 0, B 0, W 0) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | D ‐ Not used |
Bianchi 2000.
| Methods | Prospective multicenter cohort 1 subject lost to follow‐up Trial duration: 1‐year |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: Children receiving care for diffuse connective tissue diseases in 5 pediatric departments with:
1) Spine BMD Z‐score <‐1.5 and a history of fragility fractures OR
2) Spine BMD Z‐score <‐1.5 and continuous glucocorticoid therapy for >/= 6 months Exclusion criteria: patients with peptic ulcer disease (but accepted patients with dyspepsia) Sample Size: 76 (38 per group) Mean age baseline +/‐ SD: treatment 12.8 +/‐ 3.6 years, control 12.2 +/‐ 3.9 years Female/Male: treatment 26/12, control not reported |
|
| Interventions | Treatment: Oral alendronate, 5 mg for </= 20kg body weight or 10 mg for > 20 kg body weight, daily for 1‐year Cumulative steroid dose in prednisone equivalents at baseline +/‐ SD: treatment 14 433 +/‐ 1420 mg, control 0 mg Control: No intervention Patients continued with usual therapy (e.g. use of steroids, NSAIDs, methotrexate, cyclosporin, cyclophosphamide, hydroxychloroquine, gold salts, sufasalazine, colchicine) |
|
| Outcomes | L2‐4 aBMD (g/cm2): % change Incident Fractures Adverse events: Acute phase reaction, bone pain Withdrawals due to adverse events Bone metabolism parameters: Anti‐resorptive markers (urinary NTx) Linear Growth |
|
| Notes | Quality Assessment: Newcastle‐Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale (Cohort) = 5 stars / 9 stars
SR 1 star, SS 0 stars, SA 1 star, SD 1 star, C 0 stars, OA 1 star, OF 0 star, OAF 1 star Allocation concealment is not relevant, as this is a cohort study |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | D ‐ Not used |
El‐Husseini 2004.
| Methods | Randomized placebo‐controlled trial with 3 comparators No statement on withdrawals/droputs Trial duration: 1‐year |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: non‐ambulatory children and adolescents with quadriplegic cerebral palsy Pairs matched for age, gender, sex Sample Size 12 subjects (6‐matched pairs), 1 pair lost to follow‐up Mean age: alendronate 14.8 +/‐ 4.2 years, placebo 14.6 +/‐ 4.3 years Female/Male:alendronate 2/13, placebo 4/11 |
|
| Interventions | Oral alendronate (5 mg/day) or placebo administered daily for 1 year Dose: 5 mg alendronate per day All patients received calcium (500 mg) daily supplementation as well as corticosteroid and cyclosporine, which was part of their immunosuppressive regimen |
|
| Outcomes | Lumbar 2‐4 spine BMD: T‐score Whole body BMD: T‐score Bone Metabolism Content: change |
|
| Notes | Quality Assessment: Jadad Scale = 1/5 (R 1, 0 2, W 0) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Golden 2005.
| Methods | Randomized placebo controlled trial Double‐blinded Loss to follow‐up: 3 subjects (1 treatment, 2 placebo) Trial Duration: 1 year |
|
| Participants | Inclusion:
1) Subjects who met Diagnostic and Statistical Manual for Mental Disorders‐IV criteria for anorexia nervosa
2) Primary amenorrhea or secondary amenorrhea of greater than 6‐months duration
3) Lumbar spine BMD Z‐score <‐1.0 Exclusion: 1) Subjects already receiving hormone therapy (steroids or injectable or oral contraceptives) or if they had received such medication within 90 days of enrollment 2) If they had a history of self‐induced vomiting 3) If they had a coexistent medical condition that could contribute to the osteopenia 4) If they had any medical condition that precluded the administration of alendronate 5) Subjects with primary ammenorrhea who had a bone age of less than 13.0 years Sample Size: 32 (15 treatment, 17 placebo) Mean age: treatment 16.9+/‐1.6 years, control 16.9+/‐2.2 years Female/Male: treatment 15/0, control 17/0 |
|
| Interventions | Oral alendronate or oral placebo administered daily at dosage of 10 mg for 1‐year All subjects received daily calcium (1200mg) and vitamin D (400 IU) supplementation |
|
| Outcomes | L1‐4 aBMD (g/cm2): raw/% change L1‐4 aBMD (Z‐score): Z‐score change Femoral neck aBMD (g/cm2) (Z‐score): raw/% change and Z‐score change L1‐4 vBMD (g/cm3): raw/% change L1‐4 vBMD (Z‐score): Z‐score change Femoral neck vBMD (g/cm2) (Z‐score): raw/% change and Z‐score change L1‐4 BMC (g): raw/% change Femoral neck BMC (g): raw/% change Adverse Events: Number of children with AE and withdrawals due to AE |
|
| Notes | Quality Assessment: Jadad Scale = 4/5 (R 1, B 2, W 1) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Low risk | A ‐ Adequate |
Henderson 2002.
| Methods | Randomized placebo controlled trial Stated as double‐blinded Loss to follow‐up: 1 pair (2 subjects) Trial Duration: 1 year |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: non‐ambulatory children and adolescents with quadriplegic cerebral palsy Pairs matched for age, gender, sex Sample Size 12 subjects (6‐matched pairs), 1 pair lost to follow‐up Mean age: pamidronate 9.25 years, placebo 9.31 years Female/Male: pamidronate 3/3, placebo 2/4 |
|
| Interventions | Intravenous pamidronate or saline placebo administered daily for 3 consecutive days, repeated at 3‐month intervals for 1 year (5 dosing sessions, 15 total doses). Dose: 1 mg pamidronate/kg body weight but not <15 mg or >30mg. All subjects received daily calcium (1000mg), pediatric multivitamin, and vitamin D (400 IU) supplementation |
|
| Outcomes | BMD of distal femur ‐ 3 sites (raw/% change, Z‐score change) areal BMD of lumbar spine (raw/%change, Z‐score change) Bone Metabolism Parameters (change) (osteocalcin, serum NTx, Alkaline Phosphatase, bone specifc alkaline phosphatase) Withdrawals due to adverse events |
|
| Notes | Quality Assessment: Jadad Scale = 4/5 (R 1, B 2, W 1) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Kim 2006.
| Methods | Randomized placebo controlled trial Did not report any withdrawals or losses to follow‐up Trial duration: 3 months |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria:
children with nephropathy receiving high doses of steroids with osteoporosis 44 subjects: 22 treatment and 22 in control. Mean age: 8.5+/‐2.39 (control), 8.5+/‐4.49 (treatment). Gender: 11 male/11female (control), 17male/5female (treatment) |
|
| Interventions | Control took oral calcium supplementation (500 mg/day) plus regular steroid therapy and patients in treatment group took oral calcium and oral pamidronate (125 mg) during regular steroid therapy | |
| Outcomes | Mean LS BMD | |
| Notes | Quality Assessment: Jadad Scale = 1/5 (R 1, B 0, W 0) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Klein 2005.
| Methods | Randomized placebo controlled trial Double‐blinded Loss to follow‐up: 18 subjects (42%) in total, which was broken down into treatment 9/23 (39%) and control 9/20 (45%) Trial Duration: 1‐week treatment, 6 months follow‐up |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria:
1) Children between the ages of 5 and 18 that had suffered burns of >40% total body surface area and had been admitted to Shriners Burn Hospital, Galveston, within 1‐week of burn injury. Exclusion criteria: 1) Children with chronic disease 2) Children who developped renal failure following the burn injury were withdrawn from study Sample Size: 43 subjects (23 treatment, 20 placebo) Mean age +/‐ standard deviation: 11.6 +/‐ 3.8 years (range 5 to 18 years) Female/Male: 10/33 Total body surface area burn: 62.4+/‐ 16.5% in treatment, 58.7 +/‐ 13.9% in placebo No significant differences between two groups in baseline parameters (age, gender, burn area, blood biochemistry) |
|
| Interventions | Intravenous pamidronate or placebo , dosage 1.5 mg/kg of body weight to a max of 90 mg and infused over 12 hours. Dose repeated 1‐week later and no further drug was administered. |
|
| Outcomes | Lumbar Spine BMC (g): % change Total Body BMC (g): % change Withdrawals due to adverse events Bone metabolism parameters: intact parathyroid hormone, alkaline phosphatase, anti‐resorptive markers (urine deoxypyridinoline) |
|
| Notes | Quality Assessment: Jadad Scale = 4/5 (R 1, B 2, W 1) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Lepore 1991.
| Methods | Controlled Clinical Trial 1 subject (case) lost to follow‐up Trial duration: 1‐year |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children affected by active systemic or polyarticular juvenile chronic arthritis Cases and control not defined Sample size: 13 (7 cases, 6 controls) Mean age: not reported Female/Male: not reported |
|
| Interventions | Cases: Oral disodium clodronate, 1200 mg daily for 1‐year Controls: No intervention |
|
| Outcomes | D13, L1‐3 Spine BMD by CT scan: % change Withdrawals due to adverse events |
|
| Notes | Quality Assessment: Jadad Scale = 1/5 (R 0, B 0, W 1) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | D ‐ Not used |
Rudge 2005.
| Methods | Randomized placebo controlled trial Double‐blinded 1 subject (9%) lost to follow‐up in treatment, 3 subjects (27%) loss in placebo Compliance to treatment measured Trial Duration: 1‐year |
|
| Participants | Inclusion criteria: children on long‐term prednisone therapy to treat chronic illness (juvenile idiopathic arthritis, systemic lupus, dermatomyositis, inflammatory bowel disease, renal transplantation, autoimmune haemolytic anaemia and allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis with cystic fibrosis) Sample Size: 22 (11 per group) Median age: alendronate 8.7 years, placebo 8 years Female/Male: alendronate 6/5, placebo 7/4 Range of prednisone daily dosage at baseline = 0.1 to 2.4 mg/kg body weight Range of treatment duration at baseline = 0.3 to 7 years |
|
| Interventions | Oral alendronate or oral placebo administered weekly at dosage of 1‐2 mg/kg of body weight for 12 months. Subjects weighing <20kg took one 40 mg tablet fortnightly, subjects weighing 41‐60 kg took 40 mg and 80 mg on alternate weeks, subjects weighing >60 kg took 80 mg weekly. Five subjects were treated daily by prednisone (average dose range: 0.1‐2.4mg/kg) |
|
| Outcomes | L2‐4 aBMD (g/cm2): raw/% change L2‐4 aBMD (Z‐score): % change, Z‐score change L2‐4 vBMD (g/cm3): raw/% change L2‐4 BMC (g): raw/% change Number of Incident Fractures Adverse events: Number of children with AE Withdrawals due to AE Linear Growth |
|
| Notes | Quality Assessment: Jadad Scale = 4/5 (R 1, B 2, W 1) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Allocation concealment? | Unclear risk | B ‐ Unclear |
Notes: A adequate concealment, B unclear concealment, C inadequate concealment, D allocation concealment not used
Abbreviations: R randomization, B blinding, W withdrawals and drop‐outs, SR selection representativeness, SS selection of non‐exposed cohort, SA ascertainment of exposure, SD selection demonstration that outcome was not present at start of study, C comparability of cohorts, OA assessment of outcome, OF follow‐up of outcome, OAF adequacy of outcome follow‐up, AE adverse events
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Brown 2005 | Small sample size that received treatment (after withdrawals, only 5 patients received treatment). Failure to complete trial. |
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
Crabtree.
| Trial name or title | Bone density changes following liver transplantation in children. A RCT of a single dose of intravenous pamidronate |
| Methods | |
| Participants | Children undergoing liver transplantation. Randomized to receive pamidronate, stratified by age groups (A <2 years) (B 2‐9 years) (C >9 years) Sample Size = 32 |
| Interventions | Intravenous Pamidronate , 1 mg/kg, given once, prior to transplantation |
| Outcomes | Lumbar Spine BMD Z‐score Total Body BMD Z‐score Incident FracturesIntravenous Pamidronate , 1 mg/kg, given once, prior to transplantation |
| Starting date | Not reported |
| Contact information | |
| Notes | In submission |
Langman.
| Trial name or title | Bone after cessation of alendronate use in children with fracturing osteoporosis |
| Methods | |
| Participants | Children with fracturing osteoporosis of normal growth for age and pubertal status. Sample Size = 46 |
| Interventions | Oral alendronate, 70 or 35 mg/week depending on body mass (>/= 30kg, or below, respectively). |
| Outcomes | Lumbar Spine BMD Z‐score Incident Fractures Urinary N‐linked Telopeptides Bone specific alkaline phosphatase activity |
| Starting date | 2003 |
| Contact information | |
| Notes | In submission |
Langman CB.
| Trial name or title | Restoration and Maintenance of Bone Density with alendronate in children with osteoporosis or The effects of alendronate in the treatment and follow‐up of osteoporosis in children of normal stature |
| Methods | |
| Participants | Children with osteoporosis (idiopathic osteoporosis (N=61) and corticosteroid‐induced osteoporosis (N=19) ) Sample Size = 129 |
| Interventions | Oral alendronate, varying doses and frequencies |
| Outcomes | Lumbar Spine BMD Z‐score Incident Fractures Oral alendronate, varying doses and frequencies |
| Starting date | Not reported |
| Contact information | |
| Notes | In submission |
von Scheven.
| Trial name or title | Predicting low bone mineral density in childhood inflammatory diseases: Experience from a glaser pediatric research network alendronate trial |
| Methods | |
| Participants | Children with osteoporosis receiving glucocorticoids for inflammatory diseases with a dimished BMD (<‐1.5 SD) 30% lupus, 28% dermatomyositis 13% Crohn's disease 11% vasculitis 7% JIA, 2% MCTD, randomized to receive treatment Sample Size = 61 |
| Interventions | Oral alendronate |
| Outcomes | Lumbar Spine BMD Z‐score |
| Starting date | Not reported |
| Contact information | |
| Notes | Ongoing trial |
Differences between protocol and review
Since the protocol, the primary outcomes were categorized into efficacy and harms. Patients with idiopathic juvenile osteoporosis (IJO) have been excluded from the review, due to the small numbers of retrieved studies. The title of the review was subsequently revised to include only children and adolescents with secondary osteoporosis. Additionally, distal femur changes were added to the first primary outcome, total participants were added to the fifth primary outcome, and linear growth was added to the secondary outcomes. Another reviewer (NB) assisted with quality assessments. Two reviewers were added (ACT, IG).
Contributions of authors
LW ‐ conceptualized the protocol, drafted the initial protocol and supervised all stages of the protocol refinement, drafted the final review ACT, PP ‐ conducted the literature searches, drafted, refined and prepared the protocol for submission, extracted all data, drafted the final review, independently assessed study quality for each trial FR, AC, PT, DM ‐ contributed to the conceptualization and refinement of the protocol, reviewed final manuscript NB ‐ provided expertise on statistical appropriateness of individual trials, and independently assessed study quality for each trial, reviewed final manuscript IG ‐ provided feedback on the clinical relevance table and expertise on statistical issues related to combining the trials
Sources of support
Internal sources
Children's Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute (LMW, PNP), Canada.
External sources
Canadian Institutes for Health Research (LMW, ACT, AC), Canada.
Shriner's of North America (FR), USA.
Canadian Child Health Clinical Scientist Program (LMW), Canada.
University of Ottawa Research Chair (DM), Canada.
Declarations of interest
Leanne Ward and Frank Rauch have been co‐applicants in the past on operating grants from Merck‐Frost & Co to study alendronate, Novartis to study zoledronate and Proctor and Gamble to study risedronate, among patients with OI. Dr. Ward has also been a site investigator on an operating grant from Merck‐Frost & Co to investigate the pharmacokinetics and safety of alendronate among children with steroid‐induced osteoporosis.
Andrea C. Tricco has been a paid consultant for GlaxoSmithKline's non‐bisphosphonate related products.
Phuc‐Nhi Phuong ‐ none declared.
Ann Cranney has been a Consultant on the Merck Osteoporosis Medical Advisory Board and has received research funds from Merck for research to evaluate care gap in the treatment of older adults with fractures.
Nick Barrowman ‐ none declared.
Isabelle Gaboury ‐ none declared.
Peter Tugwell has been a paid consultant for Merck Frost. Please see the CMSG website www.cochranemsk.org for a detailed declaration of interest statement.
David Moher ‐ none declared.
Edited (no change to conclusions)
References
References to studies included in this review
Acott 2005 {published data only}
- Acott PD, Wong JA, Lang BA, Crocker JF. Pamidronate treatment of pediatric fracture patients on chronic steroid therapy. Pediatric Nephrology 2005;20(3):368‐73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bianchi 2000 {published data only}
- Bianchi ML, Cimaz R, Bardare M, Zulian F, Lepore L, Boncompagni A, Galbiati E, Corona F, Luisetto G, Giuntini D, Picco P, Brandi ML, Falcini F. Efficacy and safety of alendronate for the treatment of osteoporosis in diffuse connective tissue diseases in children: a prospective multicenter study. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2000;43(9):1960‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
El‐Husseini 2004 {published data only}
- El‐Husseini AA, El‐Agroudy AE, El‐Sayed MF, Sobh MA, Ghoneim MA. Treatment of osteopenia and osteoporosis in renal transplant children and adolescents. Pediatric Transplant 2004;8(4):357‐61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Golden 2005 {published data only}
- Golden NH, Iglesias EA, Jacobson MS, Carey D, Meyer W, Schebendach J, Hertz S, Shenker IR. Alendronate for the treatment of osteopenia in anorexia nervosa: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2005;90(6):3179‐85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Henderson 2002 {published data only}
- Henderson RC, Lark RK, Kecskemethy HH, Miller F, Harcke HT, Bachrach SJ. Bisphosphonates to treat osteopenia in children with quadriplegic cerebral palsy: A randomized, placebo‐controlled clinical trial. Journal of Pediatrics 2002;141(5):644‐51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kim 2006 {published data only}
- Kim S‐D, Cho B‐S. Pamidronate therapy for preventing steroid‐induced osteoporosis in children with nephropathy. Nephron Clinical Practice 2006;102:c81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Klein 2005 {published data only}
- Klein GL, Wimalawansa SJ, Kulkarni G, Sherrard DJ, Sanford AP, Herndon DN. The efficacy of acute administration of pamidronate on the conservation of bone mass following severe burn injury in children: a double‐blind, randomized, controlled study. Osteoporosis International 2005;16(6):631‐5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lepore 1991 {published data only}
- Lepore L, Pennesi M, Barbi E, Pozzi R. Treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in juvenile chronic arthritis with disodium clodronate. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 1991;9(Suppl 6):33‐5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rudge 2005 {published data only}
- Rudge S, Hailwood S, Horne A, Lucas J, Wu F, Cundy T. Effects of once‐weekly oral alendronate on bone in children on glucocorticoid treatment. Rheumatology 2005;44(6):813‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies excluded from this review
Brown 2005 {published data only}
- Brown JJ, Zacharin MR. Attempted randomized controlled trial of pamidronate versus calcium and calcitriol supplements for management of steroid‐induced osteoporosis in children and adolescents. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2005;41(11):580‐2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to ongoing studies
Crabtree {unpublished data only}
- Bone density changes following liver transplantation in children. A RCT of a single dose of intravenous pamidronate. Ongoing study Not reported.
Langman {unpublished data only}
- Bone after cessation of alendronate use in children with fracturing osteoporosis. Ongoing study 2003.
Langman CB {unpublished data only}
- Restoration and Maintenance of Bone Density with alendronate in children with osteoporosis or The effects of alendronate in the treatment and follow‐up of osteoporosis in children of normal stature. Ongoing study Not reported.
von Scheven {unpublished data only}
- Predicting low bone mineral density in childhood inflammatory diseases: Experience from a glaser pediatric research network alendronate trial. Ongoing study Not reported.
Additional references
Albrecht 2005
- Albrecht J, Meves A, Bigby M. Case reports and case series from Lancet had significant impact on medical literature. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58(12):1227‐32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Allington 2005
- Allington N, Vivegnis D, Gerard P. Cyclic administration of pamidronate to treat osteoporosis in children with cerebral palsy or a neuromuscular disorder: a clinical study. Acta orthopaedica Belgica 2005;71(1):91‐7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bachrach 2006
- Bachrach SJ, Kecskemethy HH, Harcke HT, Lark RK, Miller F, Henderson RC. Pamidronate treatment and posttreatment bone density in children with spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy. Journal of Clinical Densitometry 2006;9(2):167‐74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Barr 2002
- Barr RD, Guo CY, Wiernikowski J, Webber C, Wright M, Atkinson S. Osteopenia in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a pilot study of amelioration with Pamidronate. Medical and Pediatric Oncology 2002;39(1):44‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Batch 2003
- Batch JA, Couper JJ, Rodda C, Cowell CT, Zacharin M. Use of bisphosphonate therapy for osteoporosis in childhood and adolescence. Journal of Pediatrics and Child Health 2003;39(2):88‐92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Berlin 1997
- University of Pennsylvania Meta‐analysis blinding study group. Dose blinding of readers affect the results of meta‐analyses. The Lancet 1997;350:185‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Boers 2005
- Boers M, Brooks P, Simon LS, Strand V, Tugwell P. OMERACT: an international initiative to improve outcome measurement in rheumatology. Clinical and experimental rheumatology 2005;23(5 Suppl 39):S10‐3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Borzutzky 2006
- Borzutzky, A, Reyes, M.L, Figueroa, V, Garcia, C, Cavieres, M. Osteoporosis in children with severe congenital neutropenia: bone mineral density and treatment with bisphosphonates. Journal of pediatric hematology/oncology : official journal of the American Society of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology 2006;28(4):205‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Carter 1992
- Carter DR, Bouxsein ML, Marcus R. New approaches for interpreting projected bone densitometry data. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 1992;7(2):137‐45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chan 2005
- Chan AW, Altman DG. Epidemiology and reporting of randomised trials published in PubMed journals. Lancet 2005;365(9465):1159‐62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cimaz 2002
- Cimaz R, Gattorno M, Sormani MP, Falcini F, Zulian F, Lepore L, Bardare M, Chiesa S, Corona F, Dubini A, Lenhardt A, Martini G, Masi L, Bianchi ML. Changes in markers of bone turnover and inflammatory variables during alendronate therapy in pediatric patients with rheumatic diseases. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29(8):1786‐92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Clark 2006
- Clark EM, Tobias JH, Ness AR. Association between bone density and fractures in children: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Pediatrics 2006;117(2):e291‐7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cranney 1999
- Cranney A, Welch V, Tugwell P, Wells G, Adachi JD, McGowan J, Shea B. Responsiveness of endpoints in osteoporosis clinical trials ‐ an update. Journal of Rheumatology 1999;26(1):222‐8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Egger 1997
- Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta‐analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. British Medical Journal 1997;315(7109):629‐34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Falcini 1996
- Falcini F, Trapani S, Ermini M, Brandi ML. Intravenous administration of alendronate counteracts the in vivo effects of glucocorticoids on bone remodeling. Calcified Tissue International 1996;58(3):166‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Fernandes 2004
- Fernandes JL, Viana SL, Rocha AL, Ribeiro MC, Castro LC. Biphosphonate‐induced radiographic changes in two pediatric patients with rheumatic diseases. Skeletal radiology 2004;33(12):732‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Fleisch 1998
- Fleisch H. Bisphosphonates: mechanism of action. Endocrine Review 1998;19(1):80‐100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gandrud 2003
- Gandrud LM, Cheung JC, Daniels MW, Bachrach LK. Low‐dose intravenous pamidronate reduces fractures in childhood osteoporosis. Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism 2003;16(6):887‐92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Genant 1999
- Genant HK, Cooper C, Poor G, Reid I, Ehrlich G, Kanis J, et al. Interim report and recommendations of the World Health Organization Task‐Force for Osteoporosis. Osteoporosis International 1999;10(4):259‐64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Glorieux 1998
- Glorieux FH, Bishop N, Plotkin H, Chabot G, et al. Cyclic administration of pamidronate in children with severe osteogenesis imperfecta. New England Journal of Medicine 1998;339:947‐52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Goldbloom 2005
- Goldbloom EB, Cummings EA, Yhap M. Osteoporosis at presentation of childhood ALL: management with pamidronate. Pediatric hematology and oncology 2005;22(7):543‐50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Halton 1996
- Halton JM, Atkinson SA, Faher L, Webber C, Gill GJ, Dawson S, Barr RD. Altered mineral metabolism and bone mass in children during treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 1996;11(11):1774‐83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hawker 2005
- Hawker GA, Ridout R, Harris VA, Chase CC, Fielding LJ, Biggar WD. Alendronate in the treatment of low bone mass in steroid‐treated boys with Duchennes muscular dystrophy. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2005;86(2):284‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2003
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta‐analyses. British Medical Journal 2003;327:557‐60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2005
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 4.2.5 [updated May 2005]. The Cochrane Library 2005; Vol. 2005, issue 3.
Hogler 2004
- Hogler W, Yap F, Little D, Ambler G, McQuade M, Cowell CT. Short‐term safety assessment in the use of intravenous zoledronic acid in children. Journal of Pediatrics 2004;145(5):701‐4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jadad 1996
- Jadad A, Moore A, Carrol D, et al. Assessing the quality of randomized trials: Is blinding necessary. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17(1):1‐12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kanumakala 2002
- Kanumakala S, Boneh A, Zacharin M. Pamidronate treatment improves bone mineral density in children with Menkes disease. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease 2002;25(5):391‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kotaniemi 1999
- Kotaniemi A, Savolainen A, Kroger H, Kautiainen H, Isomaki H. Weight‐bearing physical activity, calcium intake, systemic glucocorticoids, chronic inflammation, and body constitution as determinants of lumbar and femoral bone mineral in juvenile chronic arthritis. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 1999;28(1):19‐26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kroger 1992
- Kroger H, Kotaniemi A, Vainio P, Alhava E. Bone densitometry of the spine and femur in children by dual‐energy x‐ray absorptiometry. Bone and Mineral 1992;17(1):75‐85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Land 2006a
- Land C, Rauch F, Munns CF, Sahebjam S, Glorieux FH. Vertebral morphometry in children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta: Effect of intravenous pamidronate treatment. Bone 2006;39:901‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Land 2006b
- Land C, Rauch F, Montpetit K, Ruck‐Gibis J, Glorieux FH. Effect of intravenous pamidronate therapy on functional abilities and level of ambulation in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. Journal of Pediatrics 2006;148:456‐60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lettgen 1994
- Lettgen B, Jeken C, Reiners C. Influence of steroid medication on bone mineral density in children with nephrotic syndrome. Pediatric Nephrology 1994;8(6):667‐70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lucarelli 2006
- Lucarelli S, Borrelli O, Paganelli M, Capocaccia P, Frediani T, Ferri F, Cucchiara S. Vertebral fractures and increased sensitivity to corticosteroids in a child with ulcerative colitis: successful use of pamidronate. Journal of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition 2006;43(4):533‐5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Munns 2004
- Munns CF, Rauch F, Ward L, Glorieux FH. Maternal and fetal outcome after long‐term pamidronate treatment before conception: a report of two cases. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 2004;19(10):1742‐5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
NIH Consens 2001
- Osteoporosis prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. NIH Consensus Statement 2001; Vol. 17, issue 1:1‐45. [PubMed]
Noguera 2003
- Noguera A, Ros JB, Pavia C, Alcover E, Valls C, Villaronga M, Gonzalez E. Bisphosphonates, a new treatment for glucocorticoid‐induced osteoporosis in children. Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism 2003;16(4):529‐36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Plotkin 2000
- Plotkin H, Rauch F, Bishop N, Montpetit K, Ruck‐Gibbis J, Travers R, Glorieux FH. Pamidronate treatment of severe osteogenesis imperfecta in children under three years of age. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2000;85(5):1846‐50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Plotkin 2006
- Plotkin H, Coughlin S, Kreikemeier R, Heldt K, Bruzoni M, Lerner G, Plotkin H, Coughlin S, Kreikemeier R, Heldt K, Bruzoni M, Lerner G. Low doses of pamidronate to treat osteopenia in children with severe cerebral palsy: a pilot study. Developmental medicine and child neurology 2006;48(9):709‐12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rauch 2002
- Rauch F, Travers R, Plotkin H, Glorieux FH. The effects of intravenous pamidronate on the bone tissue of children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2002;110(9):1293‐9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rauch 2003
- Rauch F, Plotkin H, Zeitlin L, Glorieux FH. Bone mass, size, and density in children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta: effect of intravenous pamidronate therapy. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 2003;18(4):610‐4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rauch 2006a
- Rauch F, Munns C, Land C, Glorieux FH. Pamidronate in children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta: effect of treatment discontinuation. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology Metabolism 2006;91:1268‐74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rauch 2006b
- Rauch F, Travers R, Glorieux FH. Pamidronate in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: histomorphometric effects of long‐term therapy. Journal of Clinical Edocrinology Metabolism 2006;91:511‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ray 1997
- Ray NF, Chan JK, Thamer M, Melton LJ III. Medical expenditures for the treatment of osteoporotic fractures in the United States in 1995: report from the National Osteoporosis Foundation. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 1997;12(1):24‐35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rosen 1996
- Rosen CJ, Kessenich CR. Comparative clinical pharmacology and therapeutic use of bisphosphonates in metabolic bone diseases. Drugs 1996;51(4):537‐51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Samuel 1994
- Samuel R, Katz K, Papapoulos SE, Yosipovitch Z, Zaizov R, Liberman UA. Aminohydroxy propylidene bisphosphonate (APD) treatment improves the clinical skeletal manifestations of Gaucher's disease. Pediatrics 1994;94(3):385‐9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schultz 1995
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273(5):408‐12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sekhar 2001
- Sekhar RV, Culbert S, Hoots WK, Klein MJ, Zietz H, Vassilopoulou‐Sellin R. Severe osteopenia in a young boy with Kostmann's congenital neutropenia treated with granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor: suggested therapeutic approach. Pediatrics 2001;108(3):E54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sellers 1998
- Sellers E, Sharma A, Rodd C. The use of pamidronate in three children with renal disease. Pediatric nephrology (Berlin, Germany) 1998;12(9):778‐81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Shaw 1994
- Shaw NJ, White CP, Fraser WD, Rosenbloom L. Osteopenia in cerebral palsy. Archives of Disese in Childhood 1994;71(3):235‐8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Shaw 2000
- Shaw NJ, Boivin CM, Crabtree NJ. Intravenous pamidronate in juvenile osteoporosis. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2000;71(3):143‐5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Shoemaker 1999
- Shoemaker L. Expanding role of bisphosphonate therapy in children. Journal of Pediatrics 1999;134(3):264‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sholas 2005
- Sholas MG, Tann B, Gaebler‐Spira D. Oral bisphosphonates to treat disuse osteopenia in children with disabilities: a case series. Journal of pediatric orthopedics 2005;25(3):326‐31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Strauss 2001
- Strauss AJ, Su JT, Dalton VM, Gelber RD, Sallan SE, Silverman LB. Bone morbidity in children treated for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2001;19(12):3066‐72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sumnik 2004
- Sumnik Z, Land C, Rieger‐Wettengl G, Korber F, Stabrey A, Schoenau E. Effect of pamidronate treatment on vertebral deformity in children with primary osteoporosis. Hormone Research 2004;61:137‐42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tenbrock 2000
- Tenbrock K, Kruppa S, Mokov E, Querfeld U, Michalk D, Schoenau E. Analysis of muscle strength and bone structure in children with renal disease. Pediatric Nephrology 2000;14(7):669‐72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tragiannidis 2006
- Tragiannidis A, Athanassiadou F, Papageorgiou T, Petsatodis G. Severe skeletal complications in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatric hematology and oncology 2006;23(6):523‐5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tugwell 2004
- Tugwell P, Shea B, Boers M, Brooks P, Simon L, Strand V, Wells G (editors). Evidence‐based Rheumatology. London: BMJ Books, 2004. [Google Scholar]
US Dept Health 2004
- US Department of Health and Human Service Public Health Service. Office of the Surgeon General. Bone Health and Osteoporosis: A Report of the Surgeon General. Executive Summary. URL: http://www.surgeongeneral.gov/library/bonehealth/docs/exec_summ.pdf. Rockville, MD, 2004.
Van den Wyn. 2006
- Wyngaert T, Huizing MT, Vermorken JB. Bisphosphonates and osteonecrosis of the jaw: cause and effect or a post hoc fallacy. Annals of Oncology Aug 2006;17(8):1197‐204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ward 2003
- Ward LM, Glorieux FH. The Spectrum of Osteoporosis. In: F.H. Glorieux, H. Juppner, J. Pettifor editor(s). Pediatric Bone Biology and Diseases. 1. Elsevier Science, 2003:401‐42. [Google Scholar]
Wells Unpub
- Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, Tugwell P. The Newcastle‐Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of non‐randomized studies in meta‐analyses. URL: http://www.ohri.ca/.. Ottawa.
Wiernikowski 2005
- Wiernikowski JT, Barr RD, Webber C, Guo CY, Wright M, Atkinson SA. Alendronate for steroid‐induced osteopenia in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia or non‐Hodgkin's lymphoma: results of a pilot study. Journal of Oncology Pharmacy Practice 2005;11(2):51‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


