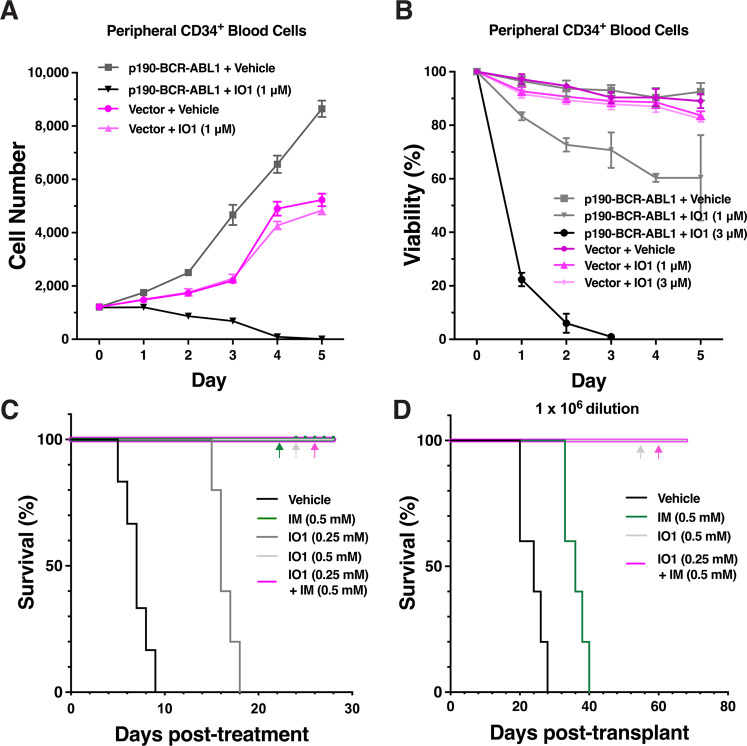
Fig. 1. IODVA1 inhibits the proliferation and survival of BCR-ABL1-driven cells in vitro and in vivo and eradicates leukemia-propagating cells in secondary transplants.
A Cell proliferation of human peripheral CD34+ blood cells transduced with p190-BCR-ABL1 (gray line, squares, and black line, downward triangles) or empty vector (lilac lines, circles, and upward triangles) virus and treated with either vehicle or IODVA1 (IO1, 1 μM). Live cells were counted by flow cytometry (GFP+/7-AAD-). Mean ± SD of a representative experiment done in triplicates. B Cells were transduced and cultured as in (A) but incubated with either vehicle or IODVA1 (IO1, 1 or 3 μM) and viability (%) was determined by trypan blue exclusion. Mean ± SD of a representative experiment done in triplicates. C Kaplan–Meier survival plot of p190-BCR-ABL1 leukemic mice post treatment with vehicle control, IODVA1 (IO1), imatinib (IM), or the combination at the indicated concentrations in the pump. LDBM cells were transduced with p190-BCR-ABL1/EGFP retrovirus and transplanted into recipient mice. After initial assessment of leukemic burden, drugs were delivered for 28 days in subcutaneously implanted osmotic pumps at day 23 post leukemia transplantation. N = 5 mice per group, except for vehicle N = 6. D Kaplan–Meier survival plot of secondary mice transplants with the 106-cell dilution. Bone marrow cells from mice treated with vehicle, IM, IODVA1 (IO1), or the combination at the indicated concentrations were transplanted into secondary recipients. N = 5 mice per group. Colored arrows indicate overlapping corresponding curves.