Abstract
Introduction
Laparoscopic-assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy (LARVH) and abdominal radical hysterectomy (ARH) are commonly used for cervical cancer treatment. However, the clinical application of LARVH versus ARH in treating cervical cancer remains controversial.
Aim
To investigate the efficacy of LARVH versus ARH in treating cervical cancer via comparing several inductors by pooling related studies.
Material and methods
Eligible articles from PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane library were screened using established search terms. Consecutive variables were pooled using weighted mean difference (WMD) and 95% confidence interval (CI). Categorical variables were pooled using odds ratio (OR) and 95% CI.
Results
A total of 13 articles were included in this meta-analysis, comprising 579 patients who underwent LARVH and 810 who underwent ARH. LARVH required a longer operation time (WMD = 50.97, 95% CI: 38.34, 63.59, p < 0.001) than ARH. However, compared to patients who underwent ARH, those who underwent LARVH had less bleeding volume (WMD = −311.21, 95% CI: −482.77, −139.64, p < 0.001), required a shorter hospital stay (WMD = −3.38, 95% CI: −5.00, −1.76, p < 0.001), and had a lower risk of urinary tract infection (OR = 0.34, 95% CI: 0.13, 0.89, p = 0.028). Additionally, patients who underwent LARVH showed a slightly lower recurrence rate (OR = 0.549, 95% CI: 0.302, 0.998, p = 0.049) than patients who underwent ARH. However, subgroup analysis results were not in agreement with the pooled results and indicated an unstable outcome.
Conclusions
Owing to these reasons, LARVH has more application prospects than ARH in treating cervical cancer.
Keywords: meta-analysis, cervical cancer, laparoscopic-assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy, abdominal radical hysterectomy, efficacy comparison
Introduction
Cervical cancer is a common lethal gynaecological malignancy affecting women worldwide. In Asia, over 500,000 new cases are diagnosed annually, with a mortality rate of about 50% [1–3]. Abdominal radical hysterectomy (ARH), first reported in 1900, is widely accepted as the gold standard treatment for patients with early stage cervical cancer [4, 5]. With improvements in laparoscopic techniques, in the late 1980s, laparoscopic-assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy (LARVH) was developed for treating cervical cancer [6, 7]. Owing to the controversial clinical efficacies of LARVH and ARH, determining the better treatment option for cervical cancer is challenging [8, 9].
Several studies have investigated the value of LARVH and ARH to determine the better choice for treating cervical cancer. All comparisons between LARVH and ARH for treating early stage cervical cancers mostly focused on blood loss, hospital stay, recovery, cosmetic results, and oncologic outcomes. However, the clinical application of LARVH versus ARH in treating cervical cancer remains controversial [8, 9]. The application of laparoscopic procedures in oncologic surgery has many advantages, including short hospital stay and less blood loss during the preoperative period [10]. Studies reported that LARVH increased intraoperative complications, such as increased lymphocytes and nerve injury [11, 12]. Recently, a study of meta-analysis investigated the efficacy of ARH and LARVH, and it suggested that attention should be paid to LARVH owing to its lower blood loss and shorter hospital stay [13]. However, significant heterogeneity was observed. Another study reported similar operative time between LARVH and ARH [14]. Thus, further studies that systematically assess the clinical efficacy of LARVH versus ARH are warranted.
Aim
Considering this, a meta-analysis was designed to compare the clinical efficacy of ARH versus LARVH in treating cervical cancer. Subgroup analyses were performed. From the results, we hope to provide some evidence for improving the outcome and prognosis of patients with cervical cancer.
Material and methods
Search strategy
Cervical cancer-associated studies published in English were searched from electronic databases, including PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library. The retrieval period was up to 4 September 2020. Search terms were (LARVH OR (laparoscopic-assisted radical hysterectomy) OR (laparoscopic radical hysterectomy) OR (Laparoscopically Radical Hysterectomy)) AND (Cervical Cancer), and the search was performed by combining subject words with free words. To acquire more eligible studies, paper documents and references of relevant studies were manually searched.
The design was in accordance with PRISMA guidelines. For the research question, the PICO model was accepted.
Selective criteria
Studies involving adult women diagnosed with cervical cancer; those in which the efficacy of LARVH and ARH in treating cervical cancer was compared; those reporting one or more of the following outcomes: operative time, blood loss, hospital stay, or postoperative follow-up data such as recurrence rate, mortality, and complications; and those published in English were included.
Studies in which participants in experimental and control groups were family members or close relatives; reviews, comments, or letters; and duplicate publications were excluded. When the same population data were used for multiple studies, the study with more complete data was chosen.
Data extraction and quality evaluation
Studies were screened according to the above criteria. Subsequently, data such as basic information (first author’s name, year of publication, study type, region and time period, cervical cancer stage, age, gender, and sample size of participants for experimental and control groups) and outcome data (relevant operative data, including operation time, blood loss, and length of stay; postoperative follow-up data, including recurrence rate, mortality, and complications) were retrieved. Additionally, data about FIGO stage, lymph node metastasis, the removed lymph nodes, adjuvant radiotherapy, rate of positive margins, team of operations, and surgery types were also retrieved.
The quality of included randomised control trials was evaluated using the Cochrane collaboration risk-of-bias tool and that of included cohort studies was assessed by the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) [15]. All procedures were independently performed by two investigators; disagreements were resolved by discussion.
Subgroup analysis
Subgroup analyses were performed to explore the impacts of region and study type on outcomes of patients with cervical cancer in the two groups.
Sensitivity analysis and publication bias
Sensitivity analysis was performed using the ‘leave one out’ method to evaluate the stability of pooled data. Egger’s test was applied to assess publication bias. Sensitivity analysis and Egger’s test were performed using Stata 13.0.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables, such as operative time, blood loss, and length of hospital stay, were pooled using weighted mean difference (WMD) and 95% confidence interval (CI); categorical variables, such as recurrence rate, complications, and mortality, were pooled using odds ratio (OR) and 95% CI. Cochran Q statistics and I2 test were used to analyse heterogeneity among studies [16]. If significant heterogeneity was observed (p < 0.05 and/or I2 > 50%), a random effects model was used for pooled analyses; otherwise, a fixed effects model was used. Data were analysed using Stata 13.0.
Results
Study selection
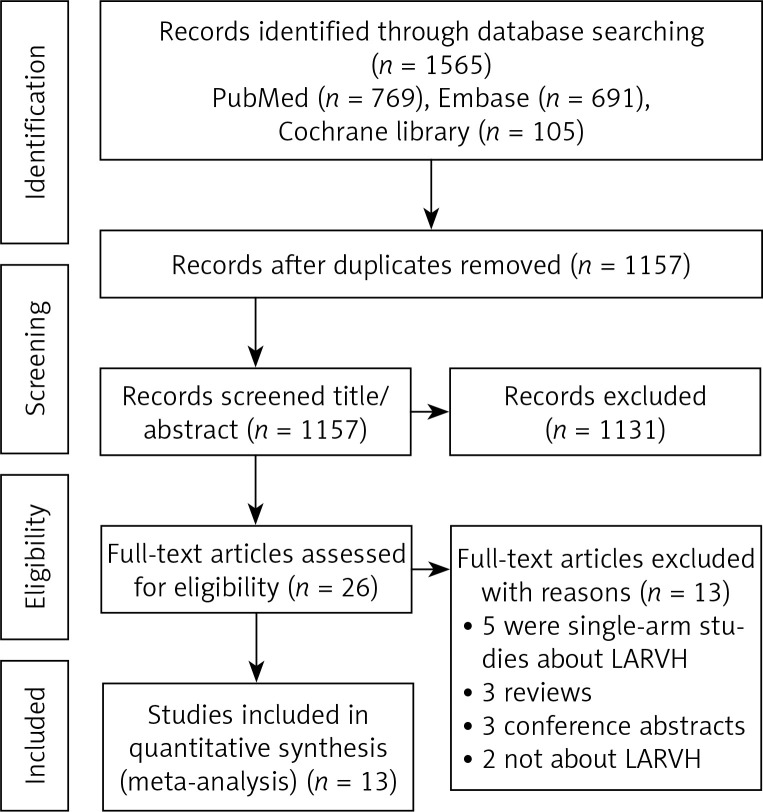
As shown in Figure 1, 1565 studies were selected, including 769 articles from PubMed, 691 from Embase, and 105 from the Cochrane Library. After reviewing the titles, 408 duplicate and 1131 unrelated articles were removed. Then, 26 articles were further reviewed and 13 were removed, including 5 single-arm studies on LARVH, 3 reviews, 3 meeting abstracts and 2 studies unrelated to LARVH. Finally, 13 articles were included [7, 14, 17–27].
Figure 1.
Flow diagram for article selection
Characteristics of included studies
Characteristics of included studies are listed in Table I. Only 1 of the 13 included articles was designed as a randomised controlled trial [22], 5 were prospective studies [17, 19, 22, 23, 26], and 8 were retrospective studies [7, 14, 18–20, 23, 24, 27]. Participants in the included studies came from different countries, including Korea, Bulgaria, China, the UK, Germany, Ireland, Spain, and Canada. All were diagnosed with cervical cancer; cancer stage was classified based on the criteria of the International Federation of Gynaecology and Obstetrics. In total, 1389 patients were included, among which 579 and 810 patients had undergone LARVH and ARH, respectively.
Table I.
Characteristics of the included studies
| Study | Study type | Country | Study period | Type of participants | No. of patients | Age [years] | Quality assessment (NOS) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LARVH | ARH | LARVH | ARH | ||||||
| Choi 2012 | P | Korea | 2004.09–2010.12 | FIGO stage I–IIA | 89 | 99 | 46 (26–74)* | 47 (28–77) | 7 |
| Gortchev 2012 | R | Bulgaria | 2006.01–2010.05 | T1B1 cervical cancer | 46 | 175 | 42.5 ±9.9 | 49.0 ±11.0 | 6 |
| Hou 2011 | P | China | 2009.05–2010.07 | FIGO stage IA–IIB | 33 | 30 | 47.55 (27–63) | 44.94 (27–79) | 5 |
| Jackson 2004 | R | UK | 1993–2003 | FIGO stage 1A2–1B2 | 50 | 50 | 45.7 (27–81) | 45.5 (24–86) | 7 |
| Malur 2001 | R | Germany | 1991.01–1994.03 1994.08–1999.05 |
FIGO stages I to III | 70 | 70 | 47.5 (21–78) | 53.6 (27–78) | 4 |
| Morgan 2007 | R | Ireland | 2000.09–2005.06 | FIGO stage 1a to 1b | 30 | 30 | 38 (20–63) | 35 (25–54) | 7 |
| Naik 2010 | P (RCT) | UK | NA | FIGO stage IB1 | 7 | 6 | 38.5 (33.5–53.5) | 37 (29.5–46) | NA |
| Pahisa 2010 | P | Spain | 1997.01–2007.12 | FIGO stage IA–IIB | 67 | 23 | 51 (29–75) | 48 (31–67) | 7 |
| Papacharalabous 2009 | R | UK | 2003.01–2006.06 | FIGO stage 1A2–1B | 14 | 12 | 38.6 ±3.6 | 43.5 ±12.9 | 5 |
| Sharma 2006 | R | England | 1999–2005 | FIGO stage IA2–IIB | 27 | 28 | 43.4 (28–60) | 42.8 (28–66) | 6 |
| Steed 2004 | P | Canada | 1996.11–2003.12 | FIGO stage IA/IB | 71 | 205 | 43 (30–69) | 44 (24–86) | 6 |
| Yu 2013 | R | China | 2003.12–2008.12 | FIGO stage IA to IIA | 40 | 40 | 44.9 (30–61) | 39.1 (28–57) | 7 |
| Zhang 2017 | R | China | 2008.03–2012.07 | FIGO stage IA2 to IIB | 35 | 42 | 45 (29–64) | 46.6 (27–75) | 6 |
P – prospective, R – retrospective, FIGO – International Federation of Gynaecology and Obstetrics, LARVH – laparoscopic-assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy, ARH – abdominal radical hysterectomy
– mean (range), NOS – Newcastle–Ottawa Scale.
Quality assessment
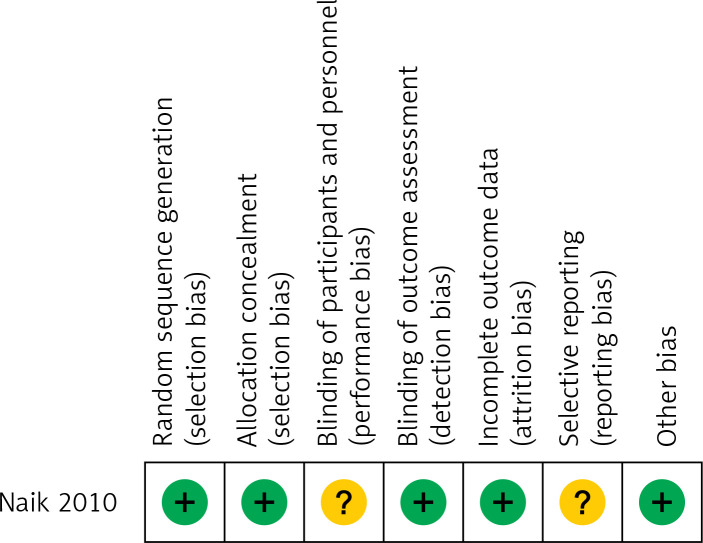
Quality assessment revealed that 12 included studies, except for the study by Naik et al., had an NOS score of more than 4; in addition, most studies had an NOS score of more than 6, suggesting that these studies had high quality (Table I). The quality of the study by Naik et al. was also high, with low risk for most evaluated biases (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Risk-of-bias summary for the randomised control study included in this meta-analysis
“+” – low risk of bias; “?” – unclear risk of bias.
Meta-analysis of perioperative outcome
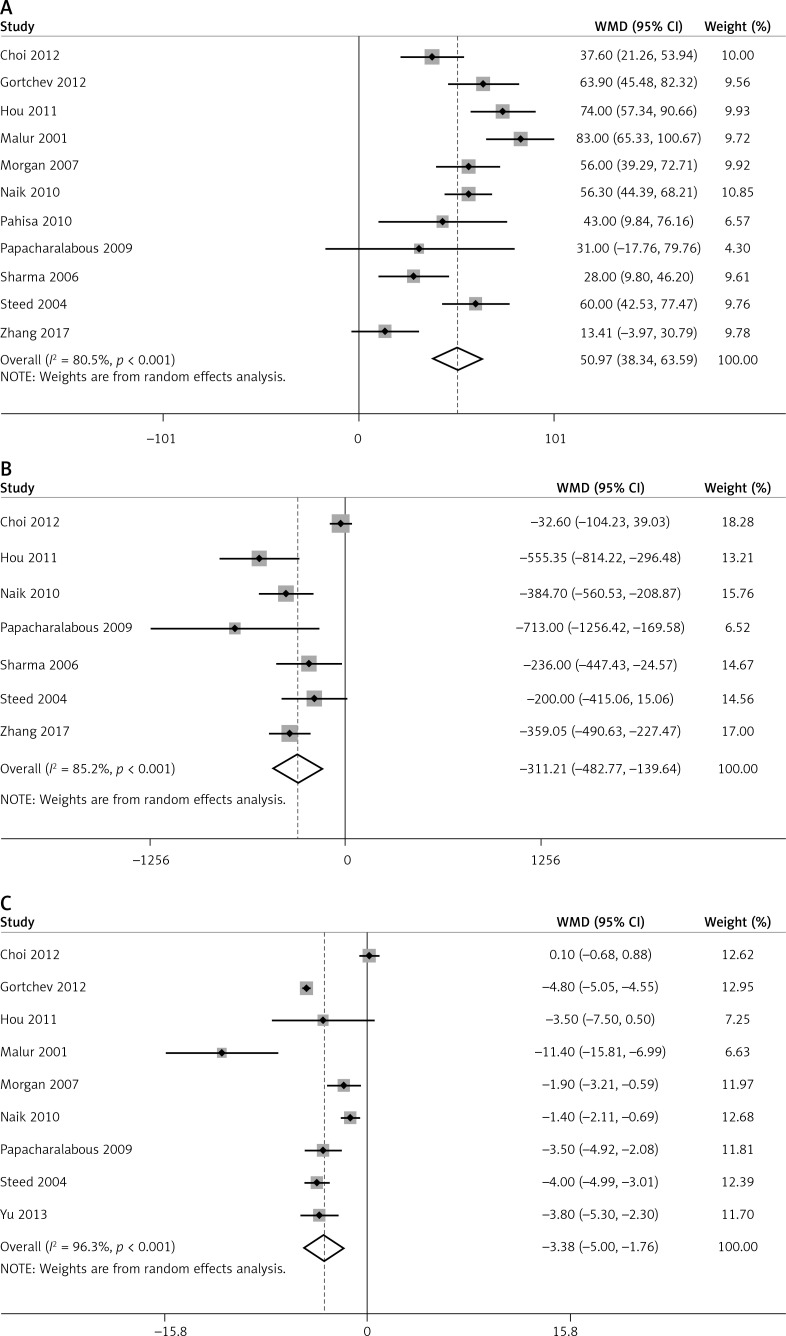
In total, 11, 7, and 9 articles reported operation time, surgical bleeding, and length of hospital stay, respectively. Significant heterogeneity was observed among these studies (p < 0.05, I2 > 50%); thus, pooled analyses of these data were performed using the random effects model.
Compared to ARH, LARVH required a longer operation time (WMD = 50.97, 95% CI: 38.34, 63.59, p < 0.001). However, compared to patients undergoing ARH, those undergoing LARVH had lower bleeding volume (WMD = −311.21, 95% CI: −482.77, −139.64, p < 0.001) and shorter hospital stay (WMD = −3.38, 95% CI: −5.00, −1.76, p < 0.001) (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Pooled perioperative outcome comparisons between patients with cervical cancer who underwent laparoscopic-assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy and those who underwent abdominal radical hysterectomy. A – operation time B – blood loss, C – hospital stay
Subgroup analyses of the study design (prospective vs. retrospective) and region (Asian vs. Western countries) were performed. All results of subgroup analyses were consistent with those of the overall analysis (Table II).
Table II.
Outcomes of subgroup analyses
| Outcomes | No. of studies | Heterogeneity test | Effect value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I 2 | P-value | WMD/OR (95% CI) | P-value | ||
| Operation time (overall): | 11 | 80.5% | < 0.001 | 50.97 (38.34, 63.59) | < 0.001 |
| Study type: | |||||
| Prospective | 5 | 60.6% | 0.038 | 55.46 (43.04, 67.88) | < 0.001 |
| Retrospective | 6 | 87.2% | < 0.001 | 46.99 (24.30, 69.88) | < 0.001 |
| Area: | |||||
| Asia | 3 | 91.9% | < 0.001 | 41.73 (7.57, 75.90) | 0.017 |
| Western | 8 | 65.9% | 0.005 | 55.49 (43.72, 67.25) | < 0.001 |
| Blood loss (overall): | 7 | 85.2% | < 0.001 | –311.21 (–482.77, –139.64) | < 0.001 |
| Study type: | |||||
| Prospective | 4 | 88.4% | < 0.001 | –277.39 (–520.66, –34.11) | 0.025 |
| Retrospective | 3 | 29.1% | 0.244 | –342.29 (–482.77, –139.64) | < 0.001 |
| Area: | |||||
| Asia | 3 | 93.1% | < 0.001 | –297.45 (–596.71, 1.82) | 0.051 |
| Western | 4 | 29.9% | 0.233 | –309.51 (–450.25, –168.76) | < 0.001 |
| Hospital stay (overall): | 9 | 96.3% | < 0.001 | –3.38 (–5.00, –1.76) | < 0.001 |
| Study type: | |||||
| Prospective | 4 | 92.8% | < 0.001 | –1.98 (–3.93, –0.02) | 0.047 |
| Retrospective | 5 | 87.1% | < 0.001 | –4.22 (–5.77, –2.66) | < 0.001 |
| Area: | |||||
| Asia | 3 | 91.1% | < 0.001 | –2.21 (–5.38, 0.97) | 0.173 |
| Western | 6 | 95.2% | < 0.001 | –3.82 (–5.47, –2.16) | < 0.001 |
| Perioperative complications: | 4 | 0.0% | 0.589 | 0.63 (0.35, 1.13) | 0.123 |
| Study type: | |||||
| Prospective | 1 | – | – | 0.40 (0.13, 1.22) | 0.108 |
| Retrospective | 3 | 0.0% | 0.591 | 0.73 (0.37, 1.46) | 0.376 |
| Urinary tract infection: | 3 | 0.0% | 0.479 | 0.34 (0.13, 0.89) | 0.028 |
| Study type: | |||||
| Prospective | 1 | – | – | 0.07 (0.00, 1.67) | 0.100 |
| Retrospective | 2 | 0.0% | 0.582 | 0.42 (0.15, 1.18) | 0.100 |
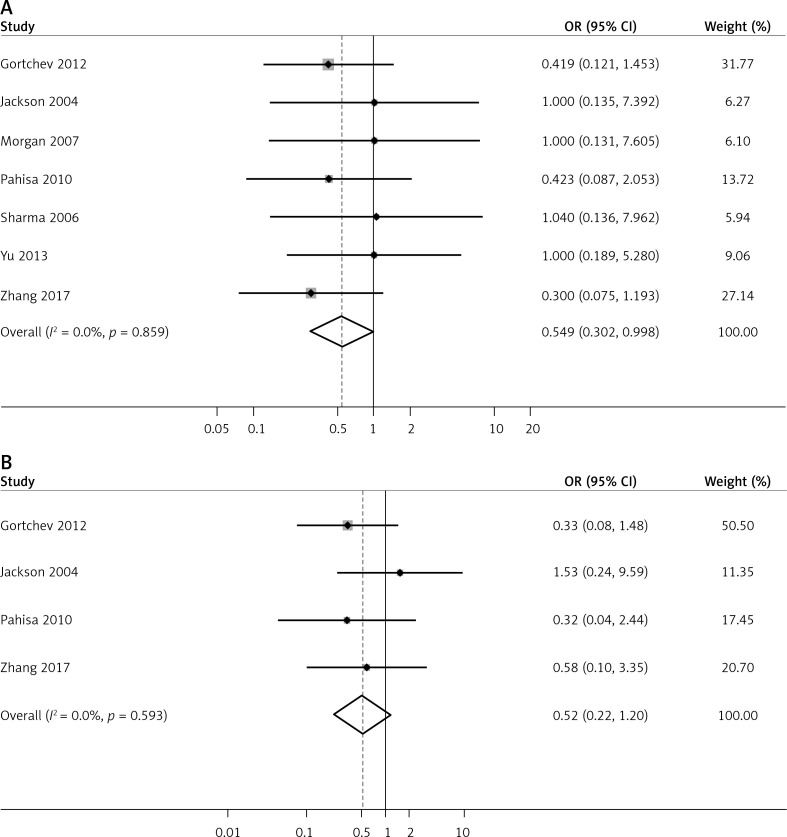
| Recurrence (Overall): | 7 | 0.0% | 0.859 | 0.549 (0.302, 0.998) | 0.049 |
| Study type: | |||||
| Prospective | 1 | – | – | 0.42 (0.09, 2.05) | 0.085 |
| Retrospective | 6 | 0.0% | 0.785 | 0.57 (0.30, 1.08) | 0.286 |
| Area: | |||||
| Asia | 2 | 0.0% | 0.859 | 0.48 (0.17, 1.33) | 0.156 |
| Western | 5 | 0.0% | 0.864 | 0.59 (0.28, 1.23) | 0.160 |
| Death (Overall): | 4 | 0.0% | 0.593 | 0.52 (0.22, 1.20) | 0.124 |
| Study type: | |||||
| Prospective | 1 | – | – | 0.32 (0.04, 2.44) | 0.273 |
| Retrospective | 3 | 0.0% | 0.444 | 0.56 (0.22, 1.39) | 0.211 |
| Area: | |||||
| Asia | 1 | – | – | 0.58 (0.10, 3.35) | 0.539 |
| Western | 3 | 0.0% | 0.388 | 0.50 (0.19, 1.31) | 0.158 |
Egger’s tests identified no significant publication bias in studies that reported regarding operation time (p = 0.620) and hospital stay (p = 0.297). However, there was significant publication bias among studies that reported on blood loss (p = 0.026). Moreover, sensitivity analysis showed that the variation ranges of WMD (95% CI) for operation time (WMD [95% CI] = 47.64 [35.45, 59.84] to 55.45 [44.67, 66.23]), blood loss (WMD [95% CI] = −354.41 [−458.60, −250.22] to −270.72 [−443.23, −98.21]), and hospital stay (WMD [95% CI] = −3.76 [−5.15, −2.36] to −2.81 [−4.45, −1.16]) were not significantly reversed, showing stable outcomes.
Meta-analysis of complications
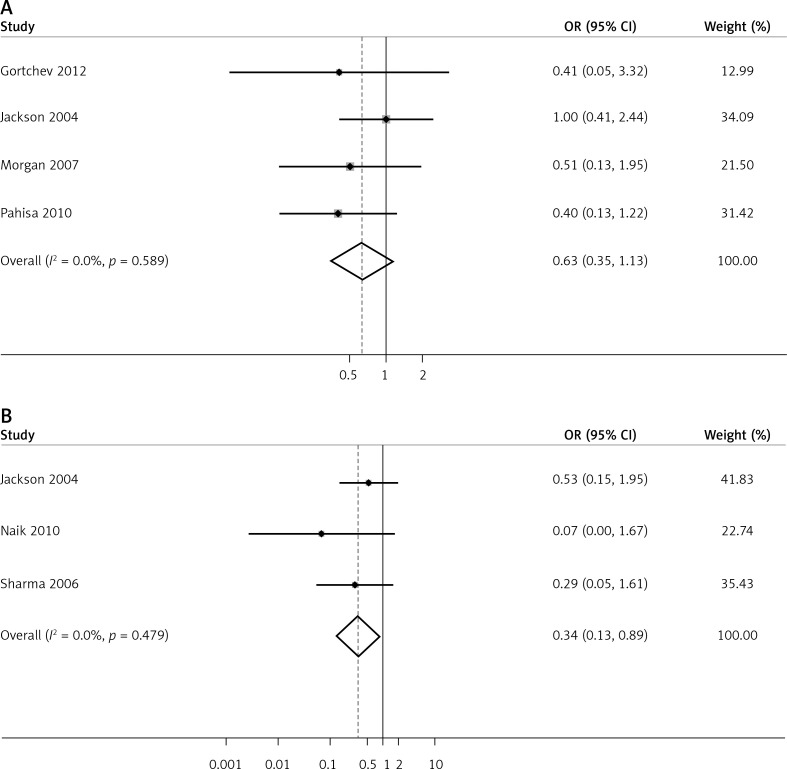
Four articles reported the number of complications in both LARVH and ARH groups (Figure 4 A). No significant heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 0.0%, p = 0.589). Complications between LARVH and ARH were evaluated using the fixed effects model; no significant difference was found between the groups (OR = 0.63, 95% CI: 0.35, 1.13, p = 0.123). Further, subgroup analysis was performed for different types of research (prospective vs. retrospective), and the results were not reversed (Table II). Publication bias among the studies was not significant (Egger’s test; p = 0.359). Higher complication rates were observed in LARVH than in ARH, after removing a study [20], suggesting that the pooled result for overall complication rate analysis was unstable.
Figure 4.
Estimated complications between laparoscopic-assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy and abdominal radical hysterectomy in treating cervical cancer. A – perioperative complications, B – urinary tract infection
Urinary tract infection was the most commonly reported complication in the included studies (n = 3). Pooled data showed that the potential risk for patients developing urinary tract infection was significantly lower in the LARVH group than in the ARH group (OR = 0.34, 95% CI: 0.13, 0.89, p = 0.028; Figure 4 B).
Subgroup analysis of research type showed no significant difference in the rate of urinary tract infection between ARH and LARVH in prospective (OR = 0.07, 95% CI: 0.00, 1.67, p = 0.100) and retrospective studies (OR = 0.42, 95% CI: 0.15, 1.18, p = 0.100; Table II). Sensitivity analysis showed that the outcome was unstable. When a study by Naik et al. [22] or Sharma et al. [25] was removed, no significant difference in the rate of urinary tract infections was found between the ARH and LARVH groups. In addition, Egger’s test demonstrated that publication bias was not significant (p = 0.081).
Meta-analysis of oncologic outcomes
Seven studies reported cancer recurrence in patients after treatment. No significant heterogeneity was observed among them (I2 = 0.0%, p = 0.859); the fixed effects model was used to pool data regarding recurrence in patients after treatment. Pooled results showed that patients who underwent LARVH had lower recurrence rates than patients who underwent ARH (OR = 0.549, 95% CI: 0.302, 0.998, p = 0.049; Figure 5 A). However, subgroup analyses of research type and region identified no significant differences between these groups, which conflicted with the pooled results and indicated an unstable outcome. Similarly, sensitivity analysis showed that the outcome was unstable. After removing the study by Gortchev et al. [18], Pahisa et al. [23], or Zhang et al. [14], cancer recurrence rates no longer significantly differed between patients who underwent LARVH and ARH. Meanwhile, publication bias among these studies was significant (p = 0.017).
Figure 5.
Forest plots of comparison of postoperative outcomes between laparoscopic-assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy and abdominal radical hysterectomy in treating cervical cancer: A – recurrence, B – mortality rate
Four studies reported patient deaths after treatment. No significant heterogeneity was observed (I2 = 0.0%, p = 0.593); thus a fixed effects model was used to pool data on mortality rate. The results indicated no significant difference in postoperative mortality between the groups (OR = 0.52, 95% CI: 0.22, 1.20, p = 0.124, Figure 5 B). Subgroup analyses of research types revealed no significant differences between LARVH and ARH with regard to mortality in prospective (OR = 0.32, 95% CI: 0.04, 2.44, p = 0.273) and retrospective studies (OR = 0.56, 95% CI: 0.22, 1.39, p = 0.211). Moreover, no significant differences were identified with regard to the mortality of patients undergoing LARVH and ARH in Asian (OR = 0.58, 95% CI: 0.10, 3.35, p = 0.539) and Western countries (OR = 0.50, 95% CI: 0.19, 1.31, p = 0.158, Table II). No significant publication bias was observed (p = 0.691). Sensitivity analysis showed that the pooled results of postoperative mortality assessment were stable (OR [95% CI] = 0.39 [0.14, 1.05] to 0.71 [0.24, 2.03]) after removing each study.
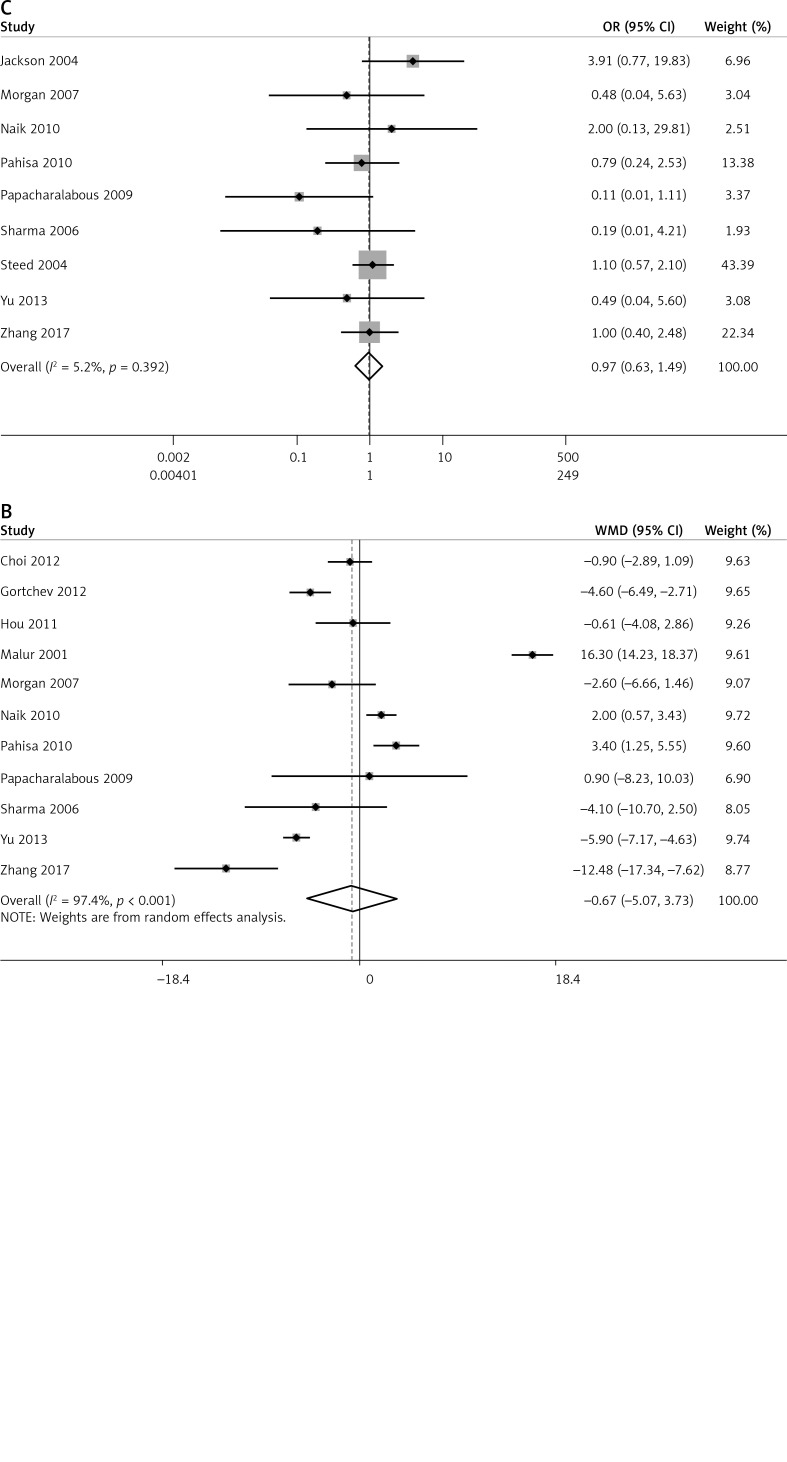
We further compared the number of patients with lymph node metastasis using a fixed effects model (I2 = 0.0%, p = 0.739), and the results revealed a significant difference between the two groups (OR = 0.52, 95% CI: 0.31, 0.87, p = 0.013, Figure 6 A). As for the number of removed lymph nodes, significant heterogeneity was observed among studies (I2 = 97.4%, p < 0.001); therefore a random effects model was used to pool the results. The results indicated no significant difference in the number removed lymph nodes between the groups (OR = –0.67, 95% CI: –5.07, 3.73, p = 0.765, Figure 6 B). Additionally, the percentage of patients requiring adjuvant radiotherapy was analysed based on a fixed effects model (I2 = 5.2%, p = 0.392), and no significant difference was found between the two groups (OR = 0.97, 95% CI: 0.63, 1.49, p = 0.886, Figure 6 C).
Figure 6.
Forest plots of comparison of lymph nodes and patients requiring adjuvant radiotherapy between laparoscopic-assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy and abdominal radical hysterectomy in treating cervical cancer. A – number of patients with lymph node metastasis, B – number of removed lymph nodes C – patients requiring adjuvant radiotherapy
Discussion
This study aimed to compare LARVH with ARH for patients with cervical cancer and to systematically analyse data in published studies. In total, 579 patients who underwent LARVH and 810 who underwent ARH were included. Pooled data showed that although LARVH required a longer operation time than ARH, it was superior to ARH, with lower bleeding volume and shorter hospital stay. No significant difference in total complications was found. The risk of urinary tract infections was significantly lower in patients who underwent LARVH. This study suggested that LARVH might be superior to ARH in treating cervical cancer, with lower bleeding volume, shorter hospital stay, and lower risk of urinary tract infection.
Most published individual studies have supported the longer operating time of LARVH than that of ARH [28, 29]. Although our results were consistent with those of previous studies in terms of the longer operation time of LARVH than of ARH, significant heterogeneity was observed among the included studies that focused on operation time, surgical bleeding, and length of hospital stay. Subsequently, subgroup analysis stratified by study type and region was performed; heterogeneity continued to exist. LARVH requires more skill and experience than ARH [30, 31]. Moreover, vaginal cuff identification requires superior tactile and purely intuitive skills. Thus, with advances in laparoscopy and increasing experience of surgeons, operating time may no longer be a limitation of LARVH. We speculated that heterogeneity is introduced by differences in the degree of skill of surgeons and patient background. Prospective research adjusting patient background and surgeon experience is required to confirm the conclusion of the comparison in operation time, surgical bleeding, and length of hospital stay between LARVH and ARH.
All publications assessing complications between open and laparoscopic surgery supported similar frequency of complications [18, 23]. However, some researchers questioned the clinical efficacy of LARVH compared to that of ARH [32]. LARVH was more suitable in small tumours, as they required less radical resection and owing to the complication that might occur by parametrial removal [22]. The complication rate ranged from 7.8% to 59%, which might be attributed to the different criteria used for defining the complications and the different follow-up periods [33]. Therefore, the extent of parametrial removal and complications should be verified by further studies.
The aim of all treatment strategies is tumour removal with sufficient tumour-free margins, and local control is affected by radical surgery quality. Thus, early surgical treatment and preoperative care are important for patients with cervical cancer [6, 21]. It is important to determine the most successful surgical treatment along with the associated recurrence rate and assessment of postoperative mortality. Our results showed that compared to patients who underwent ARH, those who underwent LARVH had a lower cancer recurrence rate, and no significant difference was found in postoperative mortality. Thus, LARVH had a clinical efficacy equivalent to that of ARH.
This study has some limitations. Firstly, articles published in English and limited electronic databases were searched as the data source; thus, some useful information might have been missed. Secondly, only one study was designed as a randomised control study. Among included studies, five were prospective and eight were retrospective. Retrospective studies might limit the strength of the conclusion. Thirdly, most of the patients in the included studies had cervical cancer at FIGO IA-IB1, but there were also fewer patients with disease at IB2, IIA, IIB, IIIA and IIIB stages (Table III), which might contribute to the heterogeneity in this meta-analysis.
Table III.
Surgical related information
| Study | The Same time period | Group | N | FIGO stage | Lymph node metastasis | Patients treated with adjuvant radiotherapy | Rate of positive margins | Removed lymph nodes | Team of operations | Type of surgery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Choi 2012 | Yes | LARVH | 89 | 3/11/73/2 (IA1/IA2/IB1/IIA) | 4 (4.5%) | 0 | 0 | 19.5 ±6.2 | 1 surgeon (DSB) | 3 II, 86 III |
| ARH | 99 | 1/8/83/7 (IA1/IA2/IB1/IIA) | 7 (7.1%) | 0 | 0 | 20.4 ±7.7 | 1 surgeon (JHL) | 9 II, 90 III | ||
| Gortchev 2012 | Yes | LARVH | 46 | 46 IB1 | 5 (10.9%)/ | NR | NR | 11.3 ±5.2 | 1 surgeon | Type III |
| ARH | 175 | 175 IB1 | 42 (24.0%) | NR | NR | 15.9 ±7.7 | 2 surgeon | |||
| Hou 2011 | Yes | LARVH | 33 | 4/10/15/4 (IA/IB/IIA/IIB) | 0 | NR | NR | 19.74 ±7.43 | The same group of surgeons | NR |
| ARH | 30 | 2/10/14/4 (IA/IB/IIA/IIB) | 0 | NR | NR | 20.35 ±6.62 | ||||
| Jackson 2004 | Yes | LARVH | 50 | 2/47/1 (IA2/IB1/IB2) | 1 (2%) | 7 (14%) | 5 (10%) | Median 15 | The same group of surgeons | NR |
| ARH | 50 | 2/47/1 (IA2/IB1/IB2) | 1 (2%) | 2 (4%) | 1 (2%) | Median 16 | ||||
| Malur 2001 | No | LARVH | 70 | 3/13/41/3/9/1/0 (IA1/IA2/IB/IIA/IIB/IIIA/IIIB) | NR | NR | NR | 27 (10–56)# | Senior registrars | Type II |
| ARH | 70 | 1/1/51/5/11/0/1 (IA1/IA2/IB/IIA/IIB/IIIA/IIIB) | NR | 100% | NR | 10.7 (0–26) | ||||
| Morgan 2007 | Yes | LARVH | 30 | 9/21/0/0 (IA/IB/IIA/IIB) | 0 | 1 (3.3%) | NR | 14.8 (3–37)# | The same group of surgeons | Type III |
| ARH | 30 | 2/24/2/2 (IA/IB/IIA/IIB) | 5 (16.7%) | 2 (6.7%) | NR | 17.4 (6–36) | ||||
| Naik 2010 | Yes | LARVH | 7 | 7 IB1 | 2 (28.57%) | 2 (28.57%) | 1 (14.29%) | 14 (12–19)# | The same group of surgeons | NR |
| ARH | 6 | 6 IB1 | 1 (16.7%) | 1 (16.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 12 (11–14) | ||||
| Pahisa 2010 | No | LARVH | 67 | 3/61/3 (IA2/IB1/IIA) | 7 (10.4%) | 12 (17.9%) | 0 | 15.8 (10–33)# | J.P, S.M–R, or A.T. | NR |
| ARH | 23 | 2/21/0 (IA2/IB1/IIA) | 3 (13.0%) | 5 (21.7%) | 0 | 12.4 (8–27) | ||||
| Papacharalabous 2009 | Yes | LARVH | 14 | 14 (IA2–IB) | 1 (7.7%) | 1 (7.7%) | 0 | 22.4 ±10.6 | S.BM | NR |
| ARH | 12 | 12 (IA2–IB) | 2 (16.7%) | 5 (41.67%) | 0 | 21.5 ±12.8 | A.T or S.BM | |||
| Sharma 2006 | Yes | LARVH | 27 | 27/0 (IB1/IB2) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 | 23.5 (7–62)# | J.BM | NR |
| ARH | 28 | 23/5 (IB1/IB2) | 2 (7.1%) | 2 (7.1%) | 0 | 27.6 (13–57) | J.BM and R.SA | |||
| Steed 2004 | Yes | LARVH | 71 | 14/10/46/1 (IA1/IA2/IB1/IB2) | 5 (7.0%) | 16 (22.5%) | 1 (1.4%) | NR | One surgeon | NR |
| ARH | 205 | 29/11/148/17 (IA1/IA2/IB1/IB2) | 19 (9.3%) | 43 (21.0%) | 6 (2.9%) | NR | Six surgeons | |||
| Yu 2013 | Yes | LARVH | 40 | 12/17/9/2 (IA2/IB1/IB2/IIA) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (2.5%) | 0 | 21.4 (18–28)# | The same group of surgeons | NR |
| ARH | 40 | 6/15/13/6 (IA2/IB1/IB2/IIA) | 5 (12.5%) | 2 (5.0%) | 0 | 27.3 (19–32) | ||||
| Zhang 2017 | Yes | LARVH | 35 | 4/13/10/6/2 (IA2/IB1/IB2/IIA/IIB) | NR | 20 (57.14%) | NR | 23.71 ±9.45 | The same 2 gynaecological oncology surgeons | Type III |
| ARH | 42 | 2/20/8/8/4 (IA2/IB1/IB2/IIA/IIB) | NR | 24 (57.14%) | NR | 36.19 ±12.28 |
NR – not reported, FIGO – International Federation of Gynaecology and Obstetrics
mean (range).
Conclusions
Patients with cervical cancer who undergo LARVH would benefit from lower blood loss and shorter hospital stay. However, owing to the limited sample size and evaluation indicators, the better treatment option between LARVH and ARH should be determined by further clinical evidence.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Olorunfemi G, Ndlovu N, Masukume G, et al. Temporal trends in the epidemiology of cervical cancer in South Africa (1994-2012) Int J Cancer. 2018;143:2238–49. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pedersen K, Fogelberg S, Thamsborg LH, et al. An overview of cervical cancer epidemiology and prevention in Scandinavia. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2018;97:795–807. doi: 10.1111/aogs.13313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Daniyal M, Akhtar N, Ahmad S, et al. Update knowledge on cervical cancer incidence and prevalence in Asia. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16:3617–20. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.9.3617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Calandra D, Curia JD, Skalej E. Wertheim-Schauta operation in the surgical treatment of carcinoma of the cervix uteri. Sem Med. 1963;123:373–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Li X, Li J, Wen H, et al. The survival rate and surgical morbidity of abdominal radical trachelectomy versus abdominal radical hysterectomy for stage IB1 cervical cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23:2953–8. doi: 10.1245/s10434-016-5216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bojahr B, Lober R, Straube W, et al. Gasless laparoscopic-assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy with lymphadenectomy for cervical carcinoma. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 1996;3(4 Suppl):S4–5. doi: 10.1016/s1074-3804(96)80141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Malur S, Possover M, Schneider A. Laparoscopically assisted radical vaginal versus radical abdominal hysterectomy type II in patients with cervical cancer. Surg Endosc. 2001;15:289–92. doi: 10.1007/s004640000306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Stancu B, Grad NO, Mihaileanu VF, et al. Surgical technique of concomitant laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomy and laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Clujul Med. 2017;90:348–52. doi: 10.15386/cjmed-747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tapisiz OL, Dogan AR, Kiykac Altinbas S. Vaginal-assisted laparoscopic sacrohysterocervicopexy with retroperitoneal tunneling. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2018;140:118–9. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.12339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lanowska M, Brink-Spalink V, Mangler M, et al. Vaginal-assisted laparoscopic radical hysterectomy (VALRH) versus laparoscopic-assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy (LARVH) in the treatment of cervical cancer: surgical results and oncologic outcome. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2014;289:1293–300. doi: 10.1007/s00404-013-3121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gallotta V, Conte C, Federico A, et al. Robotic versus laparoscopic radical hysterectomy in early cervical cancer: a case matched control study. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018;44:754–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2018.01.092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Luo C, Liu M, Li X. Efficacy and safety outcomes of robotic radical hysterectomy in Chinese older women with cervical cancer compared with laparoscopic radical hysterectomy. BMC Womens Health. 2018;18:61. doi: 10.1186/s12905-018-0544-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhao Y, Hang B, Xiong GW, et al. Laparoscopic radical hysterectomy in early stage cervical cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2017;27:1132–44. doi: 10.1089/lap.2017.0022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhang S, Ma L, Meng QW, et al. Comparison of laparoscopic-assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy and abdominal radical hysterectomy in patients with early stage cervical cancer: a retrospective study. Medicine. 2017;96:e8005. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lo CK, Mertz D, Loeb M. Newcastle-Ottawa Scale: comparing reviewers’ to authors’ assessments. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;14:45. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-14-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–60. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Choi CH, Lee JW, Lee YY, et al. Comparison of laparoscopic-assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy and laparoscopic radical hysterectomy in the treatment of cervical cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:3839–48. doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2406-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gortchev G, Tomov S, Tantchev L, et al. Robot-assisted radical hysterectomy-perioperative and survival outcomes in patients with cervical cancer compared to laparoscopic and open radical surgery. Gynecol Surg. 2012;9:81–8. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hou CY, Li XL, Jiang F, et al. Comparative evaluation of surgical stress of laparoscopically assisted vaginal radical hysterectomy and lymphadenectomy and laparotomy for early-stage cervical cancer. Oncol Lett. 2011;2:747–52. doi: 10.3892/ol.2011.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jackson KS, Das N, Naik R, et al. Laparoscopically assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy vs. radical abdominal hysterectomy for cervical cancer: a match controlled study. Gynecol Oncol. 2004;95:655–61. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2004.07.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Morgan DJ, Hunter DC, McCracken G, et al. Is laparoscopically assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy for cervical carcinoma safe? A case control study with follow up. BJOG. 2007;114:537–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2007.01291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Naik R, Jackson KS, Lopes A, et al. Laparoscopic assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy versus radical abdominal hysterectomy: a randomised phase II trial: perioperative outcomes and surgicopathological measurements. BJOG. 2010;117:746–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2010.02479.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pahisa J, Martinez-Roman S, Torne A, et al. Comparative study of laparoscopically assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy and open Wertheim-Meigs in patients with early-stage cervical cancer: eleven years of experience. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2010;20:173–8. doi: 10.1111/IGC.0b013e3181bf80ee. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Papacharalabous E, Tailor A, Madhuri T, et al. Early experience of laparoscopically assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy (Coelio-Schauta) versus abdominal radical hysterectomy for early stage cervical cancer. Gynecol Surg. 2009;6:113–7. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sharma R, Bailey J, Anderson R, et al. Laparoscopically assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy (Coelio-Schauta): a comparison with open Wertheim/Meigs hysterectomy. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2006;16:1927–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1438.2006.00661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Steed H, Rosen B, Murphy J, et al. A comparison of laparascopic-assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy and radical abdominal hysterectomy in the treatment of cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2004;93:588–93. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2004.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yu JJ, Yang WX, Wang XM. Laparoscopically-assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy with five years follow-up: a case control study. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2013;34:156–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pergialiotis V, Rodolakis A, Christakis D, et al. Laparoscopically assisted vaginal radical hysterectomy: systematic review of the literature. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2013;20:745–53. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2013.04.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Querleu D. Laparoscopically assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy. Gynecol Oncol. 1993;51:248–54. doi: 10.1006/gyno.1993.1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hertel H, Kohler C, Michels W, et al. Laparoscopic-assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy (LARVH): prospective evaluation of 200 patients with cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2003;90:505–11. doi: 10.1016/s0090-8258(03)00378-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mehra G, Weekes A, Vantrappen P, et al. Laparoscopic assisted radical vaginal hysterectomy for cervical carcinoma: morbidity and long-term follow-up. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2010;36:304–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2009.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hagen B, Shepherd JH, Jacobs IJ. Parametrial resection for invasive cervical cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2000;10:1–6. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1438.2000.00014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Persson J, Reynisson P, Borgfeldt C, et al. Robot assisted laparoscopic radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy with short and long term morbidity data. Gynecol Oncol. 2009;113:185–90. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2009.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]