An array of distinct, nonspecific stimuli may evoke a prototypic type 2 immune response in the airways. This is achieved through their shared capacity to induce the release of stress signals or “alarmins” from airway sentinels such as airway epithelial cells (AECs), which, in turn, function to initiate and amplify type 2 inflammation by acting primarily upon type 2 innate lymphoid cells and CD4+ (cluster of differentiation 4–positive) T-helper type 2 (Th2) cells (1). IL-33 and HMGB1 (high-mobility group box 1 protein) are two alarmins released from AECs fundamental to establishing a type 2 inflammatory response. Levels of IL-33 and HMGB1 are elevated in patients with asthma, correlating with Th2 inflammation and disease severity, whereas targeting these mediators in animal models ameliorates inflammation and pathology (1–5). Intriguingly, targeting HMGB1 diminishes IL-33–induced type 2 inflammation, suggesting that these mediators coordinate in a feed-forward circuit to amplify Th2 responses (6).
Although the importance of IL-33 and HMGB1 in driving type 2 inflammation is irrefutable, the mechanisms by which diverse stimuli converge to drive their release from AECs is less well defined. Both IL-33 and HMGB1 are constitutively expressed in the nuclei of AECs, and it is proposed that their extracellular availability results from passive release from necrotic or damaged cells or active cell death–independent secretion. Allergen-induced activation of TLR4 or protease-activated receptors and viral-induced necroptosis are all purported mechanisms driving the secretion of these alarmins (7–10). Increasing evidence suggests a signaling cascade whereby AEC exposure to these environmental stimuli elicits extracellular ATP accumulation and autocrine purinergic P2 receptor activation as an intermediary step in driving alarmin release (8, 11, 12); however, the precise receptor subtype responsible remained ambiguous. Genome-wide association studies have highlighted P2Y13-R, a purinergic receptor that is highly sensitive to ADP, as a risk factor for asthma (13). P2Y13-R is upregulated on AECs of allergen-exposed mice, and ADP administration was sufficient to induce IL-33 release and airway eosinophilia (13).
In this issue of the Journal, Werder and colleagues (pp. 300–312) provide compelling evidence implicating P2Y13-R as a key regulator of IL-33 and HMGB1 release (14). An analysis of human lung biopsies showed that the majority of AECs coexpress P2Y13-R, IL-33, and HMGB1. Exposure of AECs to HDM allergen induced the release of the P2Y13-R agonists, ADP and ATP, whereas subsequent pharmacological inhibition of P2Y13-R abrogated cytoplasmic translocation and release of IL-33 and HMGB1 to multiple aeroallergens or rhinovirus. Importantly, the authors showed that these effects were specific to P2Y13-R, as other purinergic receptor antagonists had no effect, whereas AECs from P2Y13-R−/− mice showed reduced allergen-induced alarmin release. Consistent with in vitro findings, IL-33 and HMGB1 release into the airways of acute allergen–exposed mice was preceded by a rapid increase in ADP and/or ATP. Genetic or pharmacological inhibition of P2Y13-R inhibited this allergen-induced alarmin release and downstream inflammation. In an HDM-induced experimental asthma model, P2Y13-R antagonist administration again ameliorated Th2 inflammation and aspects of airway remodeling, but the effect on airway hyperresponsiveness was not assessed, and the benefit was only apparent when antagonist administration preceded allergen exposure, questioning the potential effectiveness of P2Y13-R antagonists in patients with established asthma. However, the authors subsequently demonstrated that therapeutic P2Y13-R antagonism ameliorated airway inflammation and promoted viral clearance in a mouse rhinovirus-induced asthma exacerbation model.
Although the authors demonstrate the importance of the P2Y13-R signaling cascade in dictating the release of IL-33 and HMGB1 from AECs, it would be prudent to determine whether this pathway is conserved in other cell types that produce these alarmins. Targeting P2Y13-R in an in vivo setting clearly impacted extracellular IL-33 and HMGB1, highlighting the physiological relevance of this pathway in specific models. However, P2Y13-R is upregulated on multiple cell types within the mouse lung after allergen challenge (13). Thus, it would be of interest to demonstrate that AECs are indeed the primary target of P2Y13-R–mediated IL-33 and HMGB1 release in these instances and/or whether this signaling network also defines release of alarmins from disparate cell types. Accordingly, the future generation and application of epithelial-specific P2Y13-R floxed mice would be informative. Furthermore, P2 purinergic signaling has been demonstrated to modulate the function of multiple cells, independent of IL-33 and HMGB1 release, and thus it would be helpful to know whether the amelioration of inflammation and pathology observed after inhibition of P2Y13-R in asthma and asthma exacerbation models is entirely attributable to diminished alarmin secretion.
An intriguing aspect of this study is that multiple stimuli all converge on P2Y13-R to mediate IL-33 and HMGB1 release from AECs. It seems probable that allergen or virus trigger ADP and ATP release from AECs and that ensuing autocrine signaling via P2Y13-R is the shared intermediary step in defining the release of these alarmins (Figure 1). However, respiratory syncytial virus can drive HMGB1 release from AECs via necroptosis (10); thus, it will be of interest to elucidate how disparate pathways align and contribute to the release of these alarmins in response to diverse stimuli in distinct physiological settings. Although the authors have convincingly demonstrated the importance of P2Y13-R signaling in governing the release of both IL-33 and HMGB1, it is unclear whether this mechanism is conserved for governance of release of other pro-Th2–inducing alarmins, such as IL-25 and TSLP. There is a level of redundancy in function of these alarmins, and thus determination of the universality of an intermediary ADP/ATP–P2Y13-R signaling step would be important when deciding therapeutic application in distinct settings.
Figure 1.
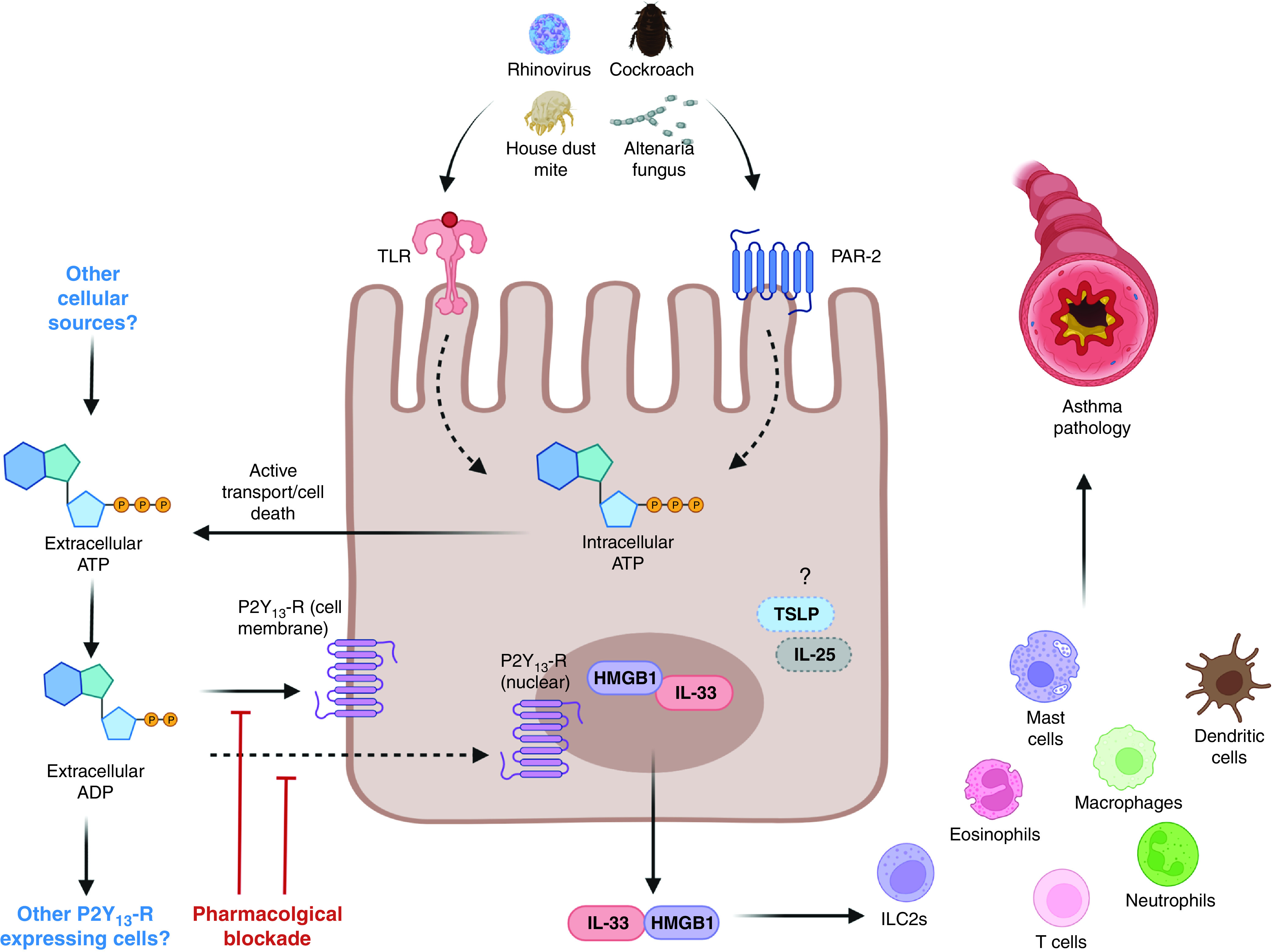
Can targeting purinergic receptors ameliorate asthma and associated exacerbations via regulation of airway epithelial cell alarmin release? Werder and colleagues demonstrate that the exposure of airway epithelial cells to allergens induces the release of the P2Y13-R agonists, ADP and ATP. P2Y13-R activation (transmembrane or nuclear) induces release of the alarmins HMGB1 and IL-33, which, in turn, can drive type 2 immunity and airway mucus secretion. Genetic or pharmacological manipulation of P2Y13-R inhibited alarmin release and downstream inflammation in models of allergen exposure and rhinovrus-driven exacerbation of allergic airway disease. Depicted are opportunities for therapeutic intervention. Questions remain regarding the source of ADP, which triggers AEC P2Y13-R, the cells that respond to these signals (AECs or other P2Y13-R–expressing cells), in addition to the role for other AEC-derived alarmins (e.g., TSLP or IL-25). AEC = airway epithelial cell; HMGB1 = high-mobility group box 1 protein; ILC2 = type 2 innate lymphoid cell; P2Y13-R = purinergic receptor Y13; PAR = protease-activated receptor; TLR = Toll-like receptor; TSLP = thymic stromal lymphopoietin.
Although the authors clearly demonstrate the central role for P2Y13-R in mediating IL-33/HMGB1 release from AECs, it should be noted that no observable difference was apparent between cells derived from healthy subjects or patients with asthma. Epithelial P2Y13-R expression was comparable between healthy donors and patients with asthma, whereas there was equivocal release of ADP/ATP after allergen provocation and of alarmin secretion after stimulation with ADP/ATP. There is clearly, therefore, more scope for exploration of the P2Y13-R pathway in larger cohorts of heterogeneous patients with asthma to infer whether differences in expression or function of this axis are a precipitating factor driving an aberrant Th2 response. There is a suggestion that nuclear expression of P2Y13-R is greater in asthmatic-derived AECs, which is potentially intriguing, but the significance of this observation is currently unclear. Nonetheless, P2Y13-R is seemingly an eminently druggable target in the context of type 2 inflammation and could hold added benefit over current strategies that seek to target IL-33, such as it operating as a common upstream regulator of multiple, partially redundant, pro-Th2 alarmins. Overall, the most promising clinical application for blocking P2Y13-R is likely for the treatment for rhinovirus-induced asthma exacerbations, in which pathological type 2 inflammation has been shown to be IL-33 dependent (15). In this context, the added advantage comes from not only reducing inflammation but also promoting viral clearance by eliminating the IL-33/HMGB1–mediated suppression of host IFNs.
Footnotes
R.J.S. is a Wellcome Trust–funded (209458/Z/17/Z) Senior Research Fellow in Basic Biomedical Sciences. A.J.B. is supported by a Joan Bending, Evelyn Bending, Mervyn Stephens, and Olive Stephens Memorial Fellowship from Asthma UK (AUK-SNF-2017-381).
Originally Published in Press as DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202111-2571ED on December 22, 2021
Author disclosures are available with the text of this article at www.atsjournals.org.
References
- 1. Lloyd CM, Snelgrove RJ. Type 2 immunity: expanding our view. Sci Immunol . 2018;3:eaat1604. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aat1604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Drake LY, Kita H. IL-33: biological properties, functions, and roles in airway disease. Immunol Rev . 2017;278:173–184. doi: 10.1111/imr.12552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Préfontaine D, Nadigel J, Chouiali F, Audusseau S, Semlali A, Chakir J, et al. Increased IL-33 expression by epithelial cells in bronchial asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol . 2010;125:752–754. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.12.935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Shim EJ, Chun E, Lee HS, Bang BR, Kim TW, Cho SH, et al. The role of high-mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) in the pathogenesis of asthma. Clin Exp Allergy . 2012;42:958–965. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2012.03998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Loh Z, Simpson J, Ullah A, Zhang V, Gan WJ, Lynch JP, et al. HMGB1 amplifies ILC2-induced type-2 inflammation and airway smooth muscle remodelling. PLoS Pathog . 2020;16:e1008651. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Oczypok EA, Milutinovic PS, Alcorn JF, Khare A, Crum LT, Manni ML, et al. Pulmonary receptor for advanced glycation end-products promotes asthma pathogenesis through IL-33 and accumulation of group 2 innate lymphoid cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol . 2015;136:747–756.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.03.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Hammad H, Chieppa M, Perros F, Willart MA, Germain RN, Lambrecht BN. House dust mite allergen induces asthma via Toll-like receptor 4 triggering of airway structural cells. Nat Med . 2009;15:410–416. doi: 10.1038/nm.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Snelgrove RJ, Gregory LG, Peiró T, Akthar S, Campbell GA, Walker SA, et al. Alternaria-derived serine protease activity drives IL-33-mediated asthma exacerbations. J Allergy Clin Immunol . 2014;134:583–592.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.02.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Ullah MA, Loh Z, Gan WJ, Zhang V, Yang H, Li JH, et al. Receptor for advanced glycation end products and its ligand high-mobility group box-1 mediate allergic airway sensitization and airway inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol . 2014;134:440–450. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.12.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Simpson J, Loh Z, Ullah MA, Lynch JP, Werder RB, Collinson N, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus infection promotes necroptosis and HMGB1 release by airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2020;201:1358–1371. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201906-1149OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Kouzaki H, Iijima K, Kobayashi T, O’Grady SM, Kita H. The danger signal, extracellular ATP, is a sensor for an airborne allergen and triggers IL-33 release and innate Th2-type responses. J Immunol . 2011;186:4375–4387. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Lynch JP, Werder RB, Simpson J, Loh Z, Zhang V, Haque A, et al. Aeroallergen-induced IL-33 predisposes to respiratory virus-induced asthma by dampening antiviral immunity. J Allergy Clin Immunol . 2016;138:1326–1337. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.02.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Ferreira MAR, Jansen R, Willemsen G, Penninx B, Bain LM, Vicente CT, et al. Australian Asthma Genetics Consortium Collaborators Gene-based analysis of regulatory variants identifies 4 putative novel asthma risk genes related to nucleotide synthesis and signaling. J Allergy Clin Immunol . 2017;139:1148–1157. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.07.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Werder RB, Ullah MA, Rahman MM, Simpson J, Lynch JP, Collinson N, et al. Targeting the P2Y13 receptor suppresses IL-33 and HMGB1 release and ameliorates experimental asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2022;205 doi: 10.1164/rccm.202009-3686OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Jackson DJ, Makrinioti H, Rana BMJ, Shamji BWH, Trujillo-Torralbo MB, Footitt J, et al. IL-33-dependent type 2 inflammation during rhinovirus-induced asthma exacerbations in vivo. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2014;190:1373–1382. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201406-1039OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


