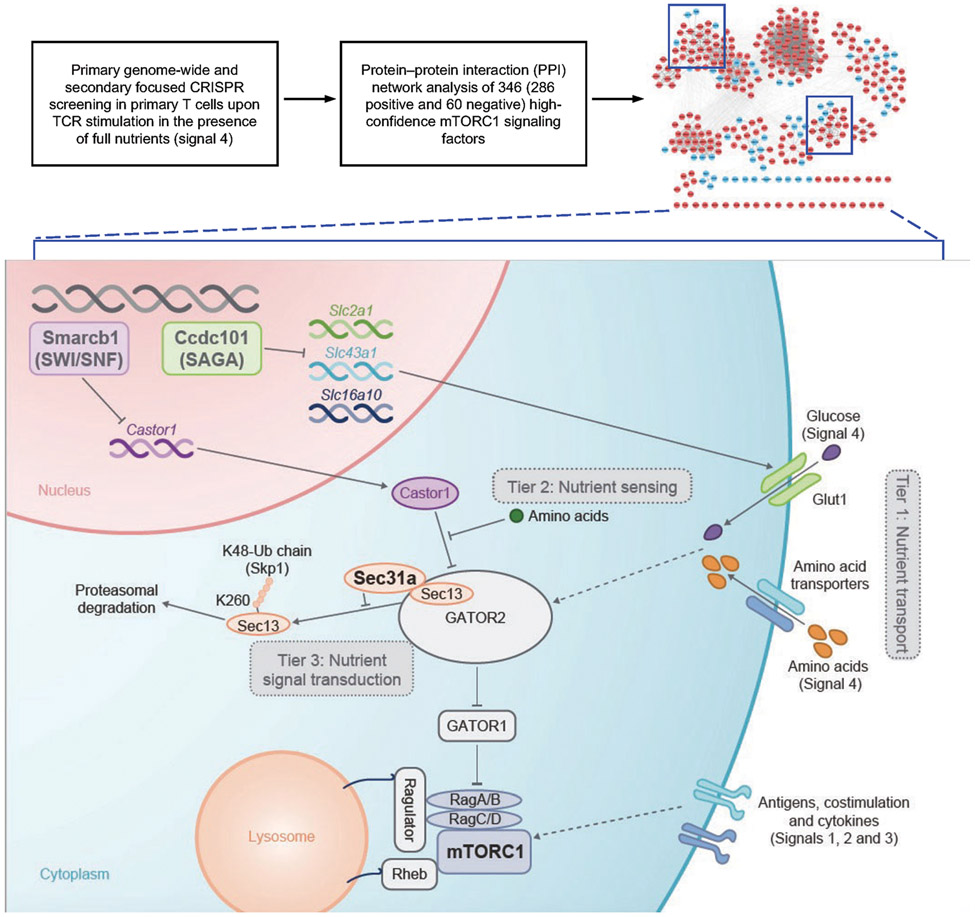
Extended Data Figure 12 (to Figure 5). Schematic of applying CRISPR screening and integrative analyses to dissect nutrient and mTORC1 signaling in primary T cells.
With two rounds of genome-wide and focused CRISPR screenings, we identify 346 high-confidence mTORC1 signaling factors, including many novel activators and inhibitors, as well as known regulators (identified in other systems) that have not been studied in primary T cells. Notably, using analysis of protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks and unbiased functional and proteomic approaches, we further establish the epigenetic and posttranslational mechanisms underpinning the three-tier regulatory modules of nutrient signaling, composed of nutrient transporters (e.g. via affecting expression of Glut1 and other transporters by SAGA complex), sensors (e.g. via epigenetic regulation of Castor1 expression by SWI/SNF complex) and transducers (e.g. via shaping GATOR2 complex stability by Sec31a; regulating Sec13 ubiquitination at lysine 260), which transmit immunological and nutrient cues to mTORC1 signaling for proper regulation of T cell activity in vivo and in vitro.